Polynesian dog on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 The Polynesian Dog refers to a few
The Polynesian Dog refers to a few
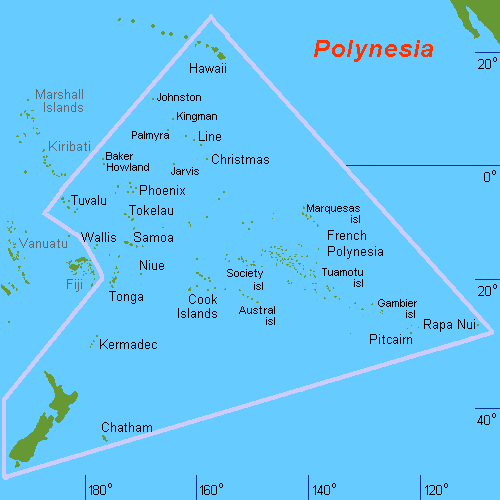
 The distribution of Polynesian dogs on other islands was somewhat patchy. Islands like
The distribution of Polynesian dogs on other islands was somewhat patchy. Islands like
 DNA evidence indicates that Polynesian dogs descended from the domesticated dogs of
DNA evidence indicates that Polynesian dogs descended from the domesticated dogs of
extinct
Extinction is the termination of a kind of organism or of a group of kinds (taxon), usually a species. The moment of extinction is generally considered to be the death of the last individual of the species, although the capacity to breed and ...
varieties of domesticated dogs
The dog (''Canis familiaris'' or ''Canis lupus familiaris'') is a domesticated descendant of the wolf. Also called the domestic dog, it is derived from the extinct Pleistocene wolf, and the modern wolf is the dog's nearest living relative. ...
from the islands of Polynesia
Polynesia () "many" and νῆσος () "island"), to, Polinisia; mi, Porinihia; haw, Polenekia; fj, Polinisia; sm, Polenisia; rar, Porinetia; ty, Pōrīnetia; tvl, Polenisia; tkl, Polenihia (, ) is a subregion of Oceania, made up of ...
. These dogs were used for both companionship and food and were introduced alongside poultry and pigs to various islands. They became extinct as a result of the crossbreeding that occurred after European breeds of dogs were introduced. Modern studies done on the DNA of the Polynesian dogs indicate that they descended from the domesticated dogs of Southeast Asia
Southeast Asia, also spelled South East Asia and South-East Asia, and also known as Southeastern Asia, South-eastern Asia or SEA, is the geographical south-eastern region of Asia, consisting of the regions that are situated south of mainland ...
and may have shared a remote ancestor with the dingo
The dingo (''Canis familiaris'', ''Canis familiaris dingo'', ''Canis dingo'', or ''Canis lupus dingo'') is an ancient ( basal) lineage of dog found in Australia. Its taxonomic classification is debated as indicated by the variety of scienti ...
.
Taxonomy
In 1839, the British naturalist Charles Hamilton Smith gave this dog thescientific name
In taxonomy, binomial nomenclature ("two-term naming system"), also called nomenclature ("two-name naming system") or binary nomenclature, is a formal system of naming species of living things by giving each a name composed of two parts, bo ...
of ''Canis pacificus'' in his 1840 book ''The Natural History of Dogs: Canidae Or Genus Canis of Authors; Including Also the Genera Hyaena and Proteles''. In the third edition of ''Mammal Species of the World
''Mammal Species of the World: A Taxonomic and Geographic Reference'' is a standard reference work in mammalogy giving descriptions and bibliographic data for the known species of mammals. It is now in its third edition, published in late 2005, ...
'' published in 2005, the mammalogist W. Christopher Wozencraft listed under the wolf ''Canis lupus'' the taxon "''familiaris'' Linneaus, 1758 omestic dog. Wozencraft then listed ''Canis pacificus'' C. E. H. Smith, 1839 as junior taxonomic synonym for the domestic dog.
History and distribution
These dogs were introduced by the ancestors of the Polynesian people during their settlement of the far-flung islands, with a few majorarchipelago
An archipelago ( ), sometimes called an island group or island chain, is a chain, cluster, or collection of islands, or sometimes a sea containing a small number of scattered islands.
Examples of archipelagos include: the Indonesian Arch ...
s developing isolated breeds.
Notable breeds include:
*Hawaiian Poi Dog
The Hawaiian Poi Dog ( haw, ʻīlio or ''ʻīlio mākuʻe'') is an extinct breed of pariah dog from Hawaiʻi which was used by Native Hawaiians as a spiritual protector of children and as a source of food.
History
The original Hawaiian p ...
– introduced to the Hawaiian Islands
The Hawaiian Islands ( haw, Nā Mokupuni o Hawai‘i) are an archipelago of eight major islands, several atolls, and numerous smaller islets in the North Pacific Ocean, extending some from the island of Hawaii in the south to northernmost ...
*Kurī
Kurī is the Māori name for the extinct Polynesian dog. It was introduced to New Zealand by the Polynesian ancestors of the Māori during their migration from East Polynesia in the 13th century AD. According to Māori tradition, the demigod ...
– introduced to New Zealand
New Zealand ( mi, Aotearoa ) is an island country in the southwestern Pacific Ocean. It consists of two main landmasses—the North Island () and the South Island ()—and over 700 smaller islands. It is the sixth-largest island coun ...
*Marquesan Dog
The Marquesan Dog or Marquesas Islands Dog is an extinct breed of dog from the Marquesas Islands. Similar to other strains of Polynesian dogs, it was introduced to the Marquesas by the ancestors of the Polynesian people during their migrations ...
– introduced to the Marquesas Islands
The Marquesas Islands (; french: Îles Marquises or ' or '; Marquesan: ' (North Marquesan) and ' ( South Marquesan), both meaning "the land of men") are a group of volcanic islands in French Polynesia, an overseas collectivity of France in ...
* Tahitian Dog – introduced to the Society Islands
The Society Islands (french: Îles de la Société, officially ''Archipel de la Société;'' ty, Tōtaiete mā) are an archipelago located in the South Pacific Ocean. Politically, they are part of French Polynesia, an overseas country of the F ...
** Tuamotuan Dog – introduced to the Tuamotus
The Tuamotu Archipelago or the Tuamotu Islands (french: Îles Tuamotu, officially ) are a French Polynesian chain of just under 80 islands and atolls in the southern Pacific Ocean. They constitute the largest chain of atolls in the world, extendin ...
, this may have been a longer-haired version of the Tahitian Dog. Described by British naturalist Georg Forster
Johann George Adam Forster, also known as Georg Forster (, 27 November 1754 – 10 January 1794), was a German naturalist, ethnologist, travel writer, journalist and revolutionary. At an early age, he accompanied his father, Johann Reinhold ...
.
 The distribution of Polynesian dogs on other islands was somewhat patchy. Islands like
The distribution of Polynesian dogs on other islands was somewhat patchy. Islands like Mangareva
Mangareva is the central and largest island of the Gambier Islands in French Polynesia. It is surrounded by smaller islands: Taravai in the southwest, Aukena and Akamaru in the southeast, and islands in the north. Mangareva has a permanent p ...
, Tokelau
Tokelau (; ; known previously as the Union Islands, and, until 1976, known officially as the Tokelau Islands) is a dependent territory of New Zealand in the southern Pacific Ocean. It consists of three tropical coral atolls: Atafu, Nukunonu, a ...
and the Marquesas possessed domesticated dog populations after initial settlement that went extinct before the arrival of European explorers. On Easter Island
Easter Island ( rap, Rapa Nui; es, Isla de Pascua) is an island and special territory of Chile in the southeastern Pacific Ocean, at the southeasternmost point of the Polynesian Triangle in Oceania. The island is most famous for its nearl ...
, no evidence or traces of dogs have been found in middens around the island or in the oral tradition of the Rapa Nui people
The Rapa Nui (Rapa Nui: , Spanish: ) are the Polynesian peoples indigenous to Easter Island. The easternmost Polynesian culture, the descendants of the original people of Easter Island make up about 60% of the current Easter Island population a ...
. They were virtually absent from Western Polynesia (i.e., Samoa
Samoa, officially the Independent State of Samoa; sm, Sāmoa, and until 1997 known as Western Samoa, is a Polynesian island country consisting of two main islands ( Savai'i and Upolu); two smaller, inhabited islands ( Manono and Apolima); ...
and Tonga
Tonga (, ; ), officially the Kingdom of Tonga ( to, Puleʻanga Fakatuʻi ʻo Tonga), is a Polynesian country and archipelago. The country has 171 islands – of which 45 are inhabited. Its total surface area is about , scattered over in ...
) by the time Europeans arrived. However, dogs brought on European ships were recognized by the natives when they were introduced as items of trade, indicating a universal cultural recognition of dogs across the islands. While Māori
Māori or Maori can refer to:
Relating to the Māori people
* Māori people of New Zealand, or members of that group
* Māori language, the language of the Māori people of New Zealand
* Māori culture
* Cook Islanders, the Māori people of the Co ...
brought dogs to New Zealand, the Moriori
The Moriori are the native Polynesian people of the Chatham Islands (''Rēkohu'' in Moriori; ' in Māori), New Zealand. Moriori originated from Māori settlers from the New Zealand mainland around 1500 CE. This was near the time of th ...
had no dogs in the Chatham Islands
The Chatham Islands ( ) (Moriori: ''Rēkohu'', 'Misty Sun'; mi, Wharekauri) are an archipelago in the Pacific Ocean about east of New Zealand's South Island. They are administered as part of New Zealand. The archipelago consists of about t ...
at the time of European discovery.
Relationship to humans
The Polynesians raised dogs for companionship and food. Along with domesticated pigs and chickens,dog meat
Dog meat is the flesh and other edible parts derived from dogs. Historically, human consumption of dog meat has been recorded in many parts of the world. During the 19th century westward movement in the United States, ''mountainmen'', native ...
was an important animal protein source for the human populations of Polynesia. For the most part, they were fed a vegetarian diet of either breadfruit
Breadfruit (''Artocarpus altilis'') is a species of flowering tree in the mulberry and jackfruit family ( Moraceae) believed to be a domesticated descendant of '' Artocarpus camansi'' originating in New Guinea, the Maluku Islands, and the Phil ...
s, coconut
The coconut tree (''Cocos nucifera'') is a member of the palm tree family (Arecaceae) and the only living species of the genus ''Cocos''. The term "coconut" (or the archaic "cocoanut") can refer to the whole coconut palm, the seed, or the f ...
s, yams or poi made from taro
Taro () (''Colocasia esculenta)'' is a root vegetable. It is the most widely cultivated species of several plants in the family Araceae that are used as vegetables for their corms, leaves, and petioles. Taro corms are a food staple in Afri ...
, while the larger Kurī predominantly subsisted on a diet of fish.
They never became feral
A feral () animal or plant is one that lives in the wild but is descended from domesticated individuals. As with an introduced species, the introduction of feral animals or plants to non-native regions may disrupt ecosystems and has, in some ...
because of the scarcity of food in the native forests. The diet and environment of the islands resulted in a dog with small stature and a docile disposition, and European explorers described them as lazy. They were said to rarely bark, but would howl occasionally.
The distinct breeds of the Polynesian Dog became extinct between the 19th and early 20th centuries due to interbreeding
In biology, a hybrid is the offspring resulting from combining the qualities of two organisms of different breeds, varieties, species or genera through sexual reproduction. Hybrids are not always intermediates between their parents (such as in ...
with introduced European dog breeds; the declining consumption of dog meat was another contributing factor.
In mythology
Dogs were an important part of thePolynesian narrative
The Polynesian narrative or Polynesian mythology encompasses the oral traditions of the people of Polynesia (a grouping of Central and South Pacific Ocean island archipelagos in the Polynesian Triangle) together with those of the scattered cul ...
. They are often associated with the legendary exploits of the demigod Māui. According to Māori narrative, Māui transformed his brother-in-law Irawaru
In Māori mythology, Irawaru is the origin of the dog. He is the husband of Hinauri, the sister of Māui. Māui becomes annoyed with Irawaru and stretches out his limbs, turning him into a dog. When Hinauri asks Māui if he has seen her husband, ...
, husband of Hina, into the first dog, which was used to explain the human characteristics of dogs. In the Tongan narrative
Tongan narrative (or Tongan mythology) is a variant of a more general Polynesian narrative in Tonga.
Creation myth
In the beginning there was just the sea and the spirit world, Pulotu, and between them was a rock called Touiao Futuna. On the rock ...
, Maui-Atalaga and his son/brother Maui-Kijikiji attempted to hunt down Fulububuta, an enormous man-eating dog, larger than a horse, living in a cave on the Fijian island of Moturiki
Moturiki is an island belonging to Fiji's Lomaiviti Archipelago. Covering an area of 10.4 square kilometers, it is situated at 17.45° South and 178.44° East.
In the proto-polynesian language, 'Motu' means 'island' and Riki' means 'small' hence ...
. However, Atalaga is killed and dragged into a cave by the monster, which is later slain by Maui-Kijikiji, who wastes away mourning his dead father.
Genetic studies
 DNA evidence indicates that Polynesian dogs descended from the domesticated dogs of
DNA evidence indicates that Polynesian dogs descended from the domesticated dogs of Southeast Asia
Southeast Asia, also spelled South East Asia and South-East Asia, and also known as Southeastern Asia, South-eastern Asia or SEA, is the geographical south-eastern region of Asia, consisting of the regions that are situated south of mainland ...
and may have shared a remote ancestor with the dingo
The dingo (''Canis familiaris'', ''Canis familiaris dingo'', ''Canis dingo'', or ''Canis lupus dingo'') is an ancient ( basal) lineage of dog found in Australia. Its taxonomic classification is debated as indicated by the variety of scienti ...
. The study of mtDNA show they carried two haplotype
A haplotype ( haploid genotype) is a group of alleles in an organism that are inherited together from a single parent.
Many organisms contain genetic material ( DNA) which is inherited from two parents. Normally these organisms have their DNA o ...
s: Arc1 and Arc2.
In 2011, the mDNA of dogs from the Malay Peninsula
The Malay Peninsula ( Malay: ''Semenanjung Tanah Melayu'') is a peninsula in Mainland Southeast Asia. The landmass runs approximately north–south, and at its terminus, it is the southernmost point of the Asian continental mainland. The ar ...
found that the two most common dog haplotypes of the Indonesian region, in particular Bali
Bali () is a province of Indonesia and the westernmost of the Lesser Sunda Islands. East of Java and west of Lombok, the province includes the island of Bali and a few smaller neighbouring islands, notably Nusa Penida, Nusa Lembongan, and ...
and Kalimantan
Kalimantan () is the Indonesian portion of the island of Borneo. It constitutes 73% of the island's area. The non-Indonesian parts of Borneo are Brunei and East Malaysia. In Indonesia, "Kalimantan" refers to the whole island of Borneo.
In 2019, ...
, were mDNA haplotype A75 (40%) and "the dingo founder haplotype" A29 (8%). Also present were haplotypes A120 and A145. All 4 haplotypes fall within the a2 mDNA sub-haplogroup. The study also looked at archaeological specimens of ancient Polynesian dogs from which only a "short-haplotype" (a short sequence) could be derived. This short haplotype was named Arc2 and corresponds to mDNA haplotypes A75 and A120, and it could be found in 70% of samples found as far away as Hawaii and New Zealand. No dogs from Taiwan nor the Philippines carried the dingo or Polynesian haplotypes, which indicates that dogs did not enter the Pacific from a northeastern route.
In 2015, a study looked at the mDNA sequences taken from ancient New Zealand Kurī dog samples discovered at an archaeological site at Wairau Bar and found they correspond to the a2 mDNA sub-haplogroup. The dog samples all carried the mDNA haplotype A192, which has only been reported in some modern village dogs from Bali, Indonesia. When compared with the two ancient Polynesian haplotypes Arc1 and Arc2, all of the Wairau Bar dogs matched Arc2. Dogs from Wairau Bar likely represent part of the initial population of dogs introduced to New Zealand, having arrived with people around the beginning of the fourteenth century.
All of these dogs carry haplotypes that fall under the mDNA a2 sub-haplogroup and are therefore descendants of a dog/Chinese wolf hybrid ancestor. In 2015, the most comprehensive study of mDNA haplotypes to date found that the a2 sub-haplogroup represents 3% of all dogs in Southeast Asia, 22% in the Indian subcontinent and 16% in East Asia.
Dogs enter Oceania from southern China
In 2020, an mDNA study of ancient dog fossils from theYellow River
The Yellow River or Huang He (Chinese: , Mandarin: ''Huáng hé'' ) is the second-longest river in China, after the Yangtze River, and the sixth-longest river system in the world at the estimated length of . Originating in the Bayan Ha ...
and Yangtze River
The Yangtze or Yangzi ( or ; ) is the longest river in Asia, the third-longest in the world, and the longest in the world to flow entirely within one country. It rises at Jari Hill in the Tanggula Mountains (Tibetan Plateau) and flows ...
basins of southern China
South China () is a geographical and cultural region that covers the southernmost part of China. Its precise meaning varies with context. A notable feature of South China in comparison to the rest of China is that most of its citizens are not n ...
showed that most of the ancient dogs fell within mDNA haplogroup A1b, as do the Australian dingoes and the pre-colonial dogs of the Pacific, but in low frequency in China today. The specimen from the Tianluoshan archaeological site, Zhejiang
Zhejiang ( or , ; , also romanized as Chekiang) is an eastern, coastal province of the People's Republic of China. Its capital and largest city is Hangzhou, and other notable cities include Ningbo and Wenzhou. Zhejiang is bordered by Ji ...
province dates to 7,000 YBP and is basal to the entire lineage. The dogs belonging to this haplogroup were once widely distributed in southern China, then dispersed through Southeast Asia into New Guinea and Oceania
Oceania (, , ) is a geographical region that includes Australasia, Melanesia, Micronesia, and Polynesia. Spanning the Eastern and Western hemispheres, Oceania is estimated to have a land area of and a population of around 44.5 million ...
, but were replaced in China 2,000 YBP by dogs of other lineages.
See also
*Hawaiian Poi Dog
The Hawaiian Poi Dog ( haw, ʻīlio or ''ʻīlio mākuʻe'') is an extinct breed of pariah dog from Hawaiʻi which was used by Native Hawaiians as a spiritual protector of children and as a source of food.
History
The original Hawaiian p ...
, an extinct breed of pariah dog from Hawaiʻi
References
Bibliography
* * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * *Further reading
* * * * {{Extinct breeds of dog Dog meat Extinct dog breeds Extinct animals of Oceania