Pointing machine on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]



 A pointing machine is a
A pointing machine is a
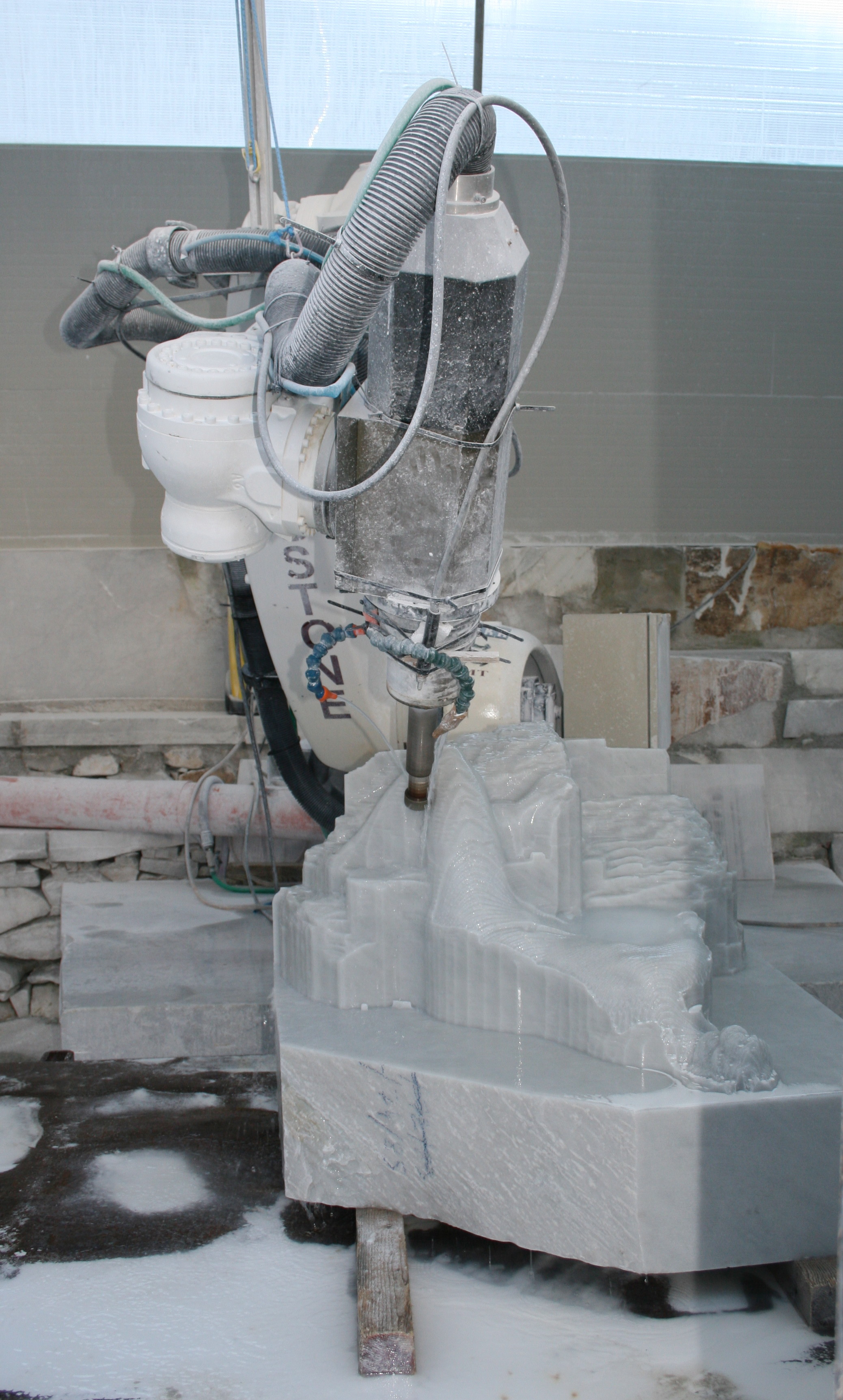
An example of a sculpture being computer carved in marble
/ref>
Video on the use of the pointing machine
Carving in marble with the aid of a pointing machine
{{Commons category, Pointing machine Visual arts materials Tools Woodcarving Sculpture techniques Copying




 A pointing machine is a
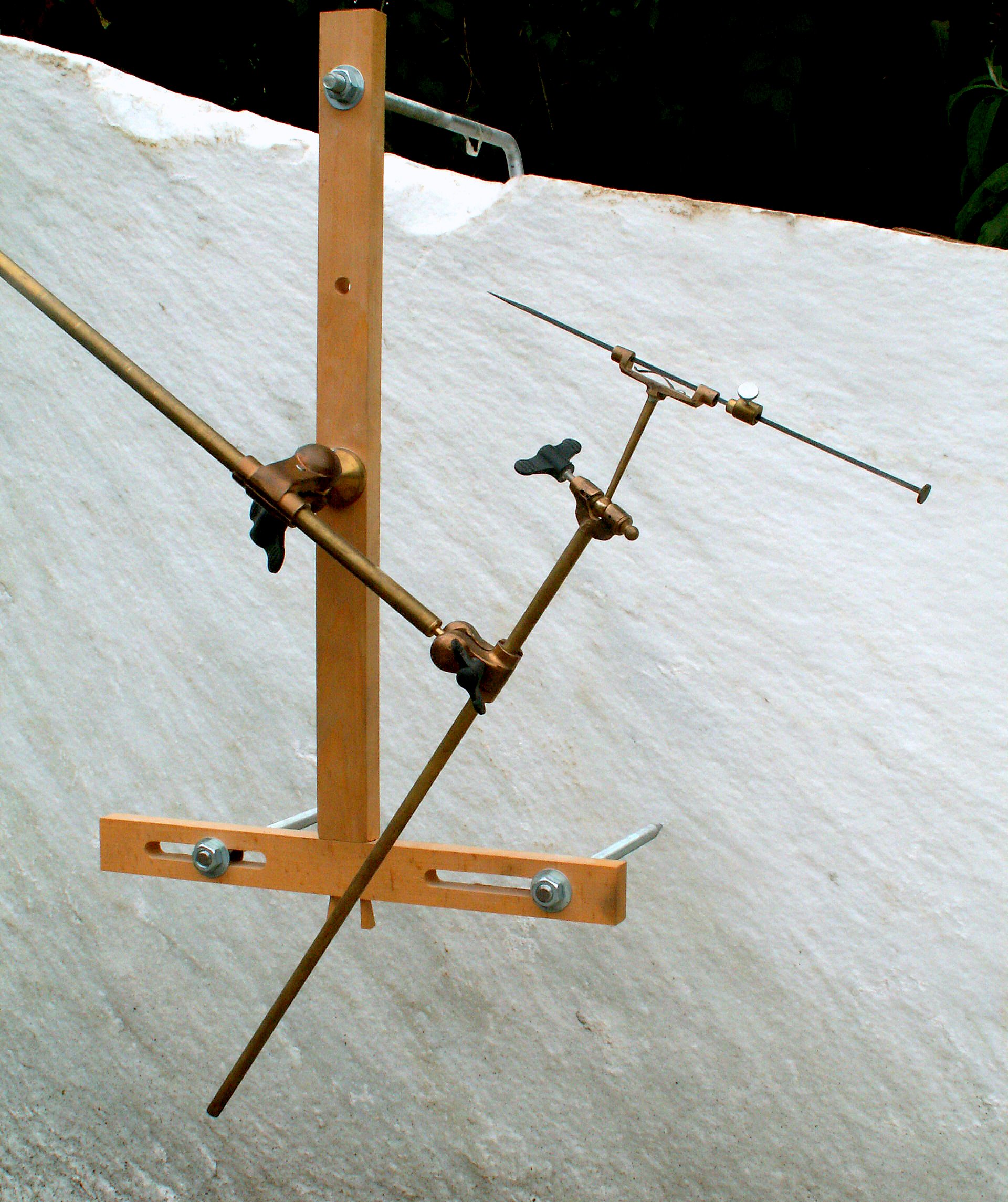
A pointing machine is a measuring tool
A measuring instrument is a device to measure a physical quantity. In the physical sciences, quality assurance, and engineering, measurement is the activity of obtaining and comparing physical quantities of real-world objects and events. Establ ...
used by stone sculptors and woodcarvers to accurately copy plaster
Plaster is a building material used for the protective or decorative coating of walls and ceilings and for moulding and casting decorative elements. In English, "plaster" usually means a material used for the interiors of buildings, while "re ...
, clay
Clay is a type of fine-grained natural soil material containing clay minerals (hydrous aluminium phyllosilicates, e.g. kaolin, Al2 Si2 O5( OH)4).
Clays develop plasticity when wet, due to a molecular film of water surrounding the clay pa ...
or wax sculpture
Sculpture is the branch of the visual arts that operates in three dimensions. Sculpture is the three-dimensional art work which is physically presented in the dimensions of height, width and depth. It is one of the plastic arts. Durable ...
models
A model is an informative representation of an object, person or system. The term originally denoted the plans of a building in late 16th-century English, and derived via French and Italian ultimately from Latin ''modulus'', a measure.
Models c ...
into wood
Wood is a porous and fibrous structural tissue found in the stems and roots of trees and other woody plants. It is an organic materiala natural composite of cellulose fibers that are strong in tension and embedded in a matrix of lignin ...
or stone
In geology, rock (or stone) is any naturally occurring solid mass or aggregate of minerals or mineraloid matter. It is categorized by the minerals included, its Chemical compound, chemical composition, and the way in which it is formed. Rocks ...
.
In essence the device is a pointing needle that can be set to any position and then fixed. It further consists of brass
Brass is an alloy of copper (Cu) and zinc (Zn), in proportions which can be varied to achieve different mechanical, electrical, and chemical properties. It is a substitutional alloy: atoms of the two constituents may replace each other wi ...
or stainless steel
Stainless steel is an alloy of iron that is resistant to rusting and corrosion. It contains at least 11% chromium and may contain elements such as carbon, other nonmetals and metals to obtain other desired properties. Stainless steel's r ...
rods and joints
A joint or articulation (or articular surface) is the connection made between bones, ossicles, or other hard structures in the body which link an animal's skeletal system into a functional whole.Saladin, Ken. Anatomy & Physiology. 7th ed. McGraw- ...
which can be placed into any position and then tightened. It is not actually a machine
A machine is a physical system using power to apply forces and control movement to perform an action. The term is commonly applied to artificial devices, such as those employing engines or motors, but also to natural biological macromolecul ...
; its name is derived from the Italian ''macchinetta di punta''.
The invention of the tool has been ascribed to both the French sculptor
Sculpture is the branch of the visual arts that operates in three dimensions. Sculpture is the three-dimensional art work which is physically presented in the dimensions of height, width and depth. It is one of the plastic arts. Durable sc ...
and medallist
A medalist (or medallist) is an artist who designs medals, plaquettes, badges, metal medallions, coins and similar small works in relief in metal. Historically, medalists were typically also involved in producing their designs, and were usually ...
Nicolas-Marie Gatteaux (1751–1832) and to the British sculptor John Bacon (1740–1799). It was later perfected by Canova
Antonio Canova (; 1 November 1757 – 13 October 1822) was an Italian Neoclassical sculptor, famous for his marble sculptures. Often regarded as the greatest of the Neoclassical artists,. his sculpture was inspired by the Baroque and the cl ...
. However, similar devices were used in ancient times, when the copying of Greek sculptures for the Roman market was a large industry.
Use
The pointing machine is used for making one-to-one copies of existing sculptures and to reproduce models made of plaster, modeling clay or modeling wax in materials like stone or wood. It is not possible to use a pointing machine to produce enlarged or reduced copies; the traditional instruments for this are a set of calipers or a three-dimensional version of thepantograph
A pantograph (, from their original use for copying writing) is a mechanical linkage connected in a manner based on parallelograms so that the movement of one pen, in tracing an image, produces identical movements in a second pen. If a line dr ...
. However, there is also a special version of the pointing machine that was used for mirroring, enlargements or reduced carving.
To better control the end result of the finished sculpture, sculptors have increasingly taken to making a detailed model and then reproducing it, on the same scale or enlarged, in stone. Particularly in the 19th century, sculptors would follow a specific procedure: first a wax or clay model was made, of which a plaster cast was taken, which in its turn served as the model to be copied in stone with the use of calipers or a pointing machine. This is called the indirect method of carving.
The advantages of this method are that the end result is very controllable and that the chance of making irreparable mistakes is reduced drastically. In addition, the process is much faster when carving difficult sculptures, because the search for the right shape is done during the modelling process instead of during the carving itself, thus making it much easier to adjust it or make changes. Finally, using this method, much or all of the work can be done by assistant sculptors, increasing productivity. The disadvantages of using the pointing machine are a great loss of directness and the risk of loss of expression.
Famous sculptors increasingly tended to use assistants. Sometimes a sculptor would run a large workshop with dozens of assistants and pupils. Art academies were formed where the skills of sculpture were taught in detail. The consequence of this development was the generation of 'academy art', from which some sculptors wanted to distance themselves. Sculptors eventually returned to more direct forms of expression, by means of for example the 'direct carving
This page describe terms and jargon related to sculpture and sculpting.
__NOTOC__
A
armature
:An armature is an internal frame or skeleton which supports a modelled sculpture. A typical armature for a small sculpture is made of heavy gau ...
method', impressionism
Impressionism was a 19th-century art movement characterized by relatively small, thin, yet visible brush strokes, open composition, emphasis on accurate depiction of light in its changing qualities (often accentuating the effects of the passa ...
and expressionism
Expressionism is a modernist movement, initially in poetry and painting, originating in Northern Europe around the beginning of the 20th century. Its typical trait is to present the world solely from a subjective perspective, distorting it ra ...
. This was sometimes influenced by the indigenous art of Africa
Africa is the world's second-largest and second-most populous continent, after Asia in both cases. At about 30.3 million km2 (11.7 million square miles) including adjacent islands, it covers 6% of Earth's total surface area ...
and Oceania
Oceania (, , ) is a geographical region that includes Australasia, Melanesia, Micronesia, and Polynesia. Spanning the Eastern and Western hemispheres, Oceania is estimated to have a land area of and a population of around 44.5 million ...
, which brought about a shock because of its directness and raw expression. The pointing machine's popularity waned as a result, reflecting the diminishing knowledge and skills of carving in wood and stone during the 20th century.
Technique
To transfer measuring points from a model to a block of stone or wood, the sculptor usually takes three reference points on both model and block. By using these points a sculpture can be measured accurately, for the three directions of measuring – width, height and depth – are thus defined. These three measuring points are traditionally used by sculptors to copy a sculpture withcaliper
A caliper (British spelling also calliper, or in plurale tantum sense a pair of calipers) is a device used to measure the dimensions of an object.
Many types of calipers permit reading out a measurement on a ruled scale, a dial, or a digital d ...
s, but this was simplified significantly with the invention of the pointing machine.
In using the pointing machine, the sculptor mounts or glues three metal rivets, that correspond to each other, on both model and block of stone or wood. To these basic points, a (usually wooden) T-shaped support is hooked up, the ''cross''. On this crosswood, the actual pointing device is attached. The sculptor sets the device by moving the arms of the tool so that the point of the needle just touches the point to be measured on the model (for instance, the nose of a bust
Bust commonly refers to:
* A woman's breasts
* Bust (sculpture), of head and shoulders
* An arrest
Bust may also refer to:
Places
* Bust, Bas-Rhin, a city in France
*Lashkargah, Afghanistan, known as Bust historically
Media
* ''Bust'' (magazin ...
). The needle is set at a right angle to the surface that is measured and the stop is tightened.
The sculptor then takes the whole cross, pointing machine and all, to the block of stone or wood and sets it up on the identical, corresponding basic points.
The needle that defines the measuring point can slide. By subsequently carving or drilling carefully until the needle touches the stop, the sculptor can place their measuring point exactly in the block.
By thus copying several dozens or hundreds of points, an accurate copy can be carved. The quality of the copy will still depend on the skill of the sculptor, however, because these points are only the basis for the final sculpture.
The real advantage is the need to measure each point only once, instead of three times with callipers (once each for height, width and depth). Also there is no need to read scales
Scale or scales may refer to:
Mathematics
* Scale (descriptive set theory), an object defined on a set of points
* Scale (ratio), the ratio of a linear dimension of a model to the corresponding dimension of the original
* Scale factor, a number w ...
in inch
Measuring tape with inches
The inch (symbol: in or ″) is a unit of length in the British imperial and the United States customary systems of measurement. It is equal to yard or of a foot. Derived from the Roman uncia ("twelfth ...
es or centimetre
330px, Different lengths as in respect to the Electromagnetic spectrum, measured by the Metre and its deriveds scales. The Microwave are in-between 1 meter to 1 millimeter.
A centimetre (international spelling) or centimeter (American spellin ...
s, and consequently there is less room for error.
Usually, the sculptor will make their own crosswood for the statue
A statue is a free-standing sculpture in which the realistic, full-length figures of persons or animals are carved or cast in a durable material such as wood, metal or stone. Typical statues are life-sized or close to life-size; a sculpture t ...
, as a small statue needs a much smaller crosswood than a life-size statue does.
History and future
Before the invention of the pointing machine by Gatteaux, sculptors used several methods to measure and copy sculpture, such asgrids
AIDS is caused by a human immunodeficiency virus (HIV), which originated in non-human primates
in Central and West Africa. While various sub-groups of the virus acquired human infectivity at different times, the present pandemic had its origins i ...
, which were already in use in early Egyptian sculpture, plumb-bob
A plumb bob, plumb bob level, or plummet, is a weight, usually with a pointed tip on the bottom, suspended from a string and used as a vertical reference line, or plumb-line. It is a precursor to the spirit level and used to establish a vertic ...
s, measuring sticks and calipers. The main technique was to measure the model from three fixed points with calipers.
Nowadays laser
A laser is a device that emits light through a process of optical amplification based on the stimulated emission of electromagnetic radiation. The word "laser" is an acronym for "light amplification by stimulated emission of radiation". The ...
pointing machines are available. These have the advantages that the needle does not hinder carving and that the sculptor is given an audible warning when the right depth is reached.
The latest developments are computer guided router systems that scan
Scan may refer to:
Acronyms
* Schedules for Clinical Assessment in Neuropsychiatry (SCAN), a psychiatric diagnostic tool developed by WHO
* Shared Check Authorization Network (SCAN), a database of bad check writers and collection agency for ba ...
a model
A model is an informative representation of an object, person or system. The term originally denoted the plans of a building in late 16th-century English, and derived via French and Italian ultimately from Latin ''modulus'', a measure.
Models c ...
and can reproduce it in a variety of materials and in any desired size./ref>
References
External links
Video on the use of the pointing machine
Carving in marble with the aid of a pointing machine
{{Commons category, Pointing machine Visual arts materials Tools Woodcarving Sculpture techniques Copying