Placental abruption on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Placental abruption is when the
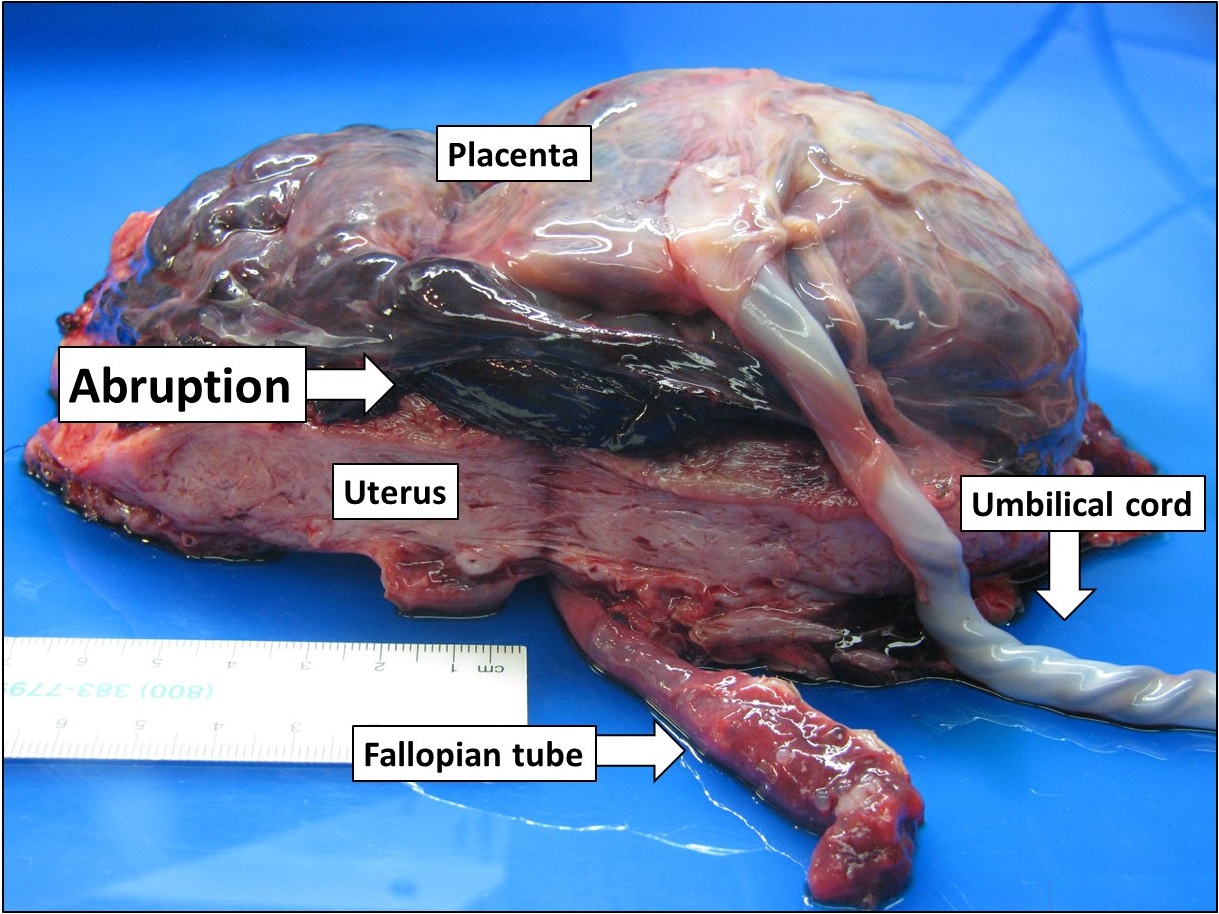 In the vast majority of cases, placental abruption is caused by the maternal vessels tearing away from the decidua basalis, not the fetal vessels. The underlying cause is often unknown. A small number of abruptions are caused by trauma that stretches the uterus. Because the placenta is less elastic than the uterus, it tears away when the uterine tissue stretches suddenly. When anatomical risk factors are present, the placenta does not attach in a place that provides adequate support, and it may not develop appropriately or be separated as it grows. Cocaine use during the third trimester has a 10% chance of causing abruption. Though the exact mechanism is not known, cocaine and tobacco cause systemic vasoconstriction, which can severely restrict the placental blood supply (hypoperfusion and ischemia), or otherwise disrupt the vasculature of the placenta, causing tissue necrosis, bleeding, and therefore abruption.
In most cases, placental disease and abnormalities of the
In the vast majority of cases, placental abruption is caused by the maternal vessels tearing away from the decidua basalis, not the fetal vessels. The underlying cause is often unknown. A small number of abruptions are caused by trauma that stretches the uterus. Because the placenta is less elastic than the uterus, it tears away when the uterine tissue stretches suddenly. When anatomical risk factors are present, the placenta does not attach in a place that provides adequate support, and it may not develop appropriately or be separated as it grows. Cocaine use during the third trimester has a 10% chance of causing abruption. Though the exact mechanism is not known, cocaine and tobacco cause systemic vasoconstriction, which can severely restrict the placental blood supply (hypoperfusion and ischemia), or otherwise disrupt the vasculature of the placenta, causing tissue necrosis, bleeding, and therefore abruption.
In most cases, placental disease and abnormalities of the
placenta
The placenta is a temporary embryonic and later fetal organ that begins developing from the blastocyst shortly after implantation. It plays critical roles in facilitating nutrient, gas and waste exchange between the physically separate mate ...
separates early from the uterus
The uterus (from Latin ''uterus'', plural ''uteri'') or womb () is the organ in the reproductive system of most female mammals, including humans that accommodates the embryonic and fetal development of one or more embryos until birth. The ...
, in other words separates before childbirth
Childbirth, also known as labour and delivery, is the ending of pregnancy where one or more babies exits the internal environment of the mother via vaginal delivery or caesarean section. In 2019, there were about 140.11 million births glob ...
. It occurs most commonly around 25 weeks of pregnancy. Symptoms may include vaginal bleeding
Vaginal bleeding is any expulsion of blood from the vagina. This bleeding may originate from the uterus, vaginal wall, or cervix. Generally, it is either part of a normal menstrual cycle or is caused by hormonal or other problems of the reproductiv ...
, lower abdominal pain
Abdominal pain, also known as a stomach ache, is a symptom associated with both non-serious and serious medical issues.
Common causes of pain in the abdomen include gastroenteritis and irritable bowel syndrome. About 15% of people have a m ...
, and dangerously low blood pressure. Complications for the mother can include disseminated intravascular coagulopathy
Disseminated intravascular coagulation (DIC) is a condition in which blood clots form throughout the body, blocking small blood vessels. Symptoms may include chest pain, shortness of breath, leg pain, problems speaking, or problems moving parts ...
and kidney failure
Kidney failure, also known as end-stage kidney disease, is a medical condition in which the kidneys can no longer adequately filter waste products from the blood, functioning at less than 15% of normal levels. Kidney failure is classified as eit ...
. Complications for the baby can include fetal distress Fetal distress, also known as non-reassuring fetal status, is a condition during pregnancy or labor in which the fetus shows signs of inadequate oxygenation. Due to its imprecision, the term "fetal distress" has fallen out of use in American obstetr ...
, low birthweight, preterm delivery, and stillbirth.
The cause of placental abruption is not entirely clear. Risk factors include smoking, pre-eclampsia, prior abruption (most important and predictive risk factor), trauma
Trauma most often refers to:
* Major trauma, in physical medicine, severe physical injury caused by an external source
* Psychological trauma, a type of damage to the psyche that occurs as a result of a severely distressing event
*Traumatic i ...
during pregnancy, cocaine
Cocaine (from , from , ultimately from Quechua: ''kúka'') is a central nervous system (CNS) stimulant mainly used recreationally for its euphoric effects. It is primarily obtained from the leaves of two Coca species native to South Ameri ...
use, and previous cesarean section
Caesarean section, also known as C-section or caesarean delivery, is the surgical procedure by which one or more babies are delivered through an incision in the mother's abdomen, often performed because vaginal delivery would put the baby or ...
. Diagnosis is based on symptoms and supported by ultrasound
Ultrasound is sound waves with frequencies higher than the upper audible limit of human hearing. Ultrasound is not different from "normal" (audible) sound in its physical properties, except that humans cannot hear it. This limit varies ...
. It is classified as a complication of pregnancy.
For small abruption, bed rest
Bed rest, also referred to as the rest-cure, is a medical treatment in which a person lies in bed for most of the time to try to cure an illness. Bed rest refers to voluntarily lying in bed as a treatment and not being confined to bed because of ...
may be recommended, while for more significant abruptions or those that occur near term, delivery may be recommended. If everything is stable, vaginal delivery
A vaginal delivery is the birth of offspring in mammals (baby, babies in humans) through the vagina (also called the "birth canal"). It is the most common method of childbirth worldwide. It is considered the preferred method of delivery, with l ...
may be tried, otherwise cesarean section
Caesarean section, also known as C-section or caesarean delivery, is the surgical procedure by which one or more babies are delivered through an incision in the mother's abdomen, often performed because vaginal delivery would put the baby or ...
is recommended. In those less than 36 weeks pregnant, corticosteroids may be given to speed development of the baby's lungs. Treatment may require blood transfusion
Blood transfusion is the process of transferring blood products into a person's circulation intravenously. Transfusions are used for various medical conditions to replace lost components of the blood. Early transfusions used whole blood, but mo ...
or emergency hysterectomy.
Placental abruption occurs in about 1 in 200 pregnancies. Along with placenta previa
Placenta praevia is when the placenta attaches inside the uterus but in a position near or over the cervical opening. Symptoms include vaginal bleeding in the second half of pregnancy. The bleeding is bright red and tends not to be associated wi ...
and uterine rupture
Uterine rupture is when the muscular wall of the uterus tears during pregnancy or childbirth. Symptoms, while classically including increased pain, vaginal bleeding, or a change in contractions, are not always present. Disability or death of the ...
it is one of the most common causes of vaginal bleeding in the later part of pregnancy. Placental abruption is the reason for about 15% of infant deaths around the time of birth. The condition was described at least as early as 1664.
Signs and symptoms
In the early stages of placental abruption, there may be no symptoms. When symptoms develop, they tend to develop suddenly. Common symptoms include: * sudden-onset abdominal pain * contractions that seem continuous and do not stop * vaginal bleeding * enlarged uterus (disproportionate to the gestational age of the fetus) * decreased fetal movement * decreased fetal heart rate.Vaginal bleeding
Vaginal bleeding is any expulsion of blood from the vagina. This bleeding may originate from the uterus, vaginal wall, or cervix. Generally, it is either part of a normal menstrual cycle or is caused by hormonal or other problems of the reproductiv ...
, if it occurs, may be bright red or dark.
A placental abruption caused by arterial bleeding at the center of the placenta leads to sudden development of severe symptoms and life-threatening conditions including fetal heart rate abnormalities, severe maternal hemorrhage, and disseminated intravascular coagulation (DIC). Those abruptions caused by venous bleeding at the periphery of the placenta develop more slowly and cause small amounts of bleeding, intrauterine growth restriction
Intrauterine growth restriction (IUGR), or fetal growth restriction, refers to poor growth of a fetus while in the womb during pregnancy. IUGR is defined by clinical features of malnutrition and evidence of reduced growth regardless of an infant's ...
, and oligohydramnios (low levels of amniotic fluid).
Risk factors
* Pre-eclampsia * Chronic hypertension * Shortumbilical cord
In placental mammals, the umbilical cord (also called the navel string, birth cord or ''funiculus umbilicalis'') is a conduit between the developing embryo or fetus and the placenta. During prenatal development, the umbilical cord is physiologi ...
* Premature rupture of membranes
* Prolonged rupture of membranes (>24 hours).
* Thrombophilia
* Polyhydramnios
* Multiparity
* Multiple pregnancy
* Maternal age: pregnant women who are younger than 20 or older than 35 are at greater risk
Risk factors for placental abruption include disease, trauma, history, anatomy, and exposure to substances. The risk of placental abruption increases sixfold after severe maternal trauma. Anatomical risk factors include uncommon uterine anatomy (e.g. bicornuate uterus
A bicornuate uterus or bicornate uterus (from the Latin ''cornū'', meaning "horn"), is a type of mullerian anomaly in the human uterus, where there is a deep indentation at the fundus (top) of the uterus.
Pathophysiology
A bicornuate uterus ...
), uterine synechiae
Asherman's syndrome (AS) is an acquired uterine condition that occurs when scar tissue (adhesions) forms inside the uterus and/or the cervix. It is characterized by variable scarring inside the uterine cavity, where in many cases the front and bac ...
, and leiomyoma. Substances that increase risk of placental abruption include cocaine and tobacco when consumed during pregnancy, especially the third trimester. History of placental abruption or previous Caesarian section increases the risk by a factor of 2.3.
Pathophysiology
 In the vast majority of cases, placental abruption is caused by the maternal vessels tearing away from the decidua basalis, not the fetal vessels. The underlying cause is often unknown. A small number of abruptions are caused by trauma that stretches the uterus. Because the placenta is less elastic than the uterus, it tears away when the uterine tissue stretches suddenly. When anatomical risk factors are present, the placenta does not attach in a place that provides adequate support, and it may not develop appropriately or be separated as it grows. Cocaine use during the third trimester has a 10% chance of causing abruption. Though the exact mechanism is not known, cocaine and tobacco cause systemic vasoconstriction, which can severely restrict the placental blood supply (hypoperfusion and ischemia), or otherwise disrupt the vasculature of the placenta, causing tissue necrosis, bleeding, and therefore abruption.
In most cases, placental disease and abnormalities of the
In the vast majority of cases, placental abruption is caused by the maternal vessels tearing away from the decidua basalis, not the fetal vessels. The underlying cause is often unknown. A small number of abruptions are caused by trauma that stretches the uterus. Because the placenta is less elastic than the uterus, it tears away when the uterine tissue stretches suddenly. When anatomical risk factors are present, the placenta does not attach in a place that provides adequate support, and it may not develop appropriately or be separated as it grows. Cocaine use during the third trimester has a 10% chance of causing abruption. Though the exact mechanism is not known, cocaine and tobacco cause systemic vasoconstriction, which can severely restrict the placental blood supply (hypoperfusion and ischemia), or otherwise disrupt the vasculature of the placenta, causing tissue necrosis, bleeding, and therefore abruption.
In most cases, placental disease and abnormalities of the spiral arteries
Spiral arteries are small arteries which temporarily supply blood to the endometrium of the uterus during the luteal phase of the menstrual cycle.
In histology, identifying the presence of these arteries is one of the most useful techniques in i ...
develop throughout the pregnancy and lead to necrosis, inflammation, vascular problems, and ultimately, abruption. Because of this, most abruptions are caused by bleeding from the arterial supply, not the venous supply. Production of thrombin
Thrombin (, ''fibrinogenase'', ''thrombase'', ''thrombofort'', ''topical'', ''thrombin-C'', ''tropostasin'', ''activated blood-coagulation factor II'', ''blood-coagulation factor IIa'', ''factor IIa'', ''E thrombin'', ''beta-thrombin'', ''gamma- ...
via massive bleeding causes the uterus to contract and leads to DIC.
The accumulating blood pushes between the layers of the decidua, pushing the uterine wall and placenta apart. When the placenta is separated, it is unable to exchange waste, nutrients, and oxygen, a necessary function for the fetus's survival. The fetus dies when it no longer receives enough oxygen and nutrients to survive.
Diagnosis
Placental abruption is suspected when a pregnant mother has sudden localized abdominal pain with or without bleeding. The fundus may be monitored because a rising fundus can indicate bleeding. Anultrasound
Ultrasound is sound waves with frequencies higher than the upper audible limit of human hearing. Ultrasound is not different from "normal" (audible) sound in its physical properties, except that humans cannot hear it. This limit varies ...
may be used to rule out placenta praevia
Placenta praevia is when the placenta attaches inside the uterus but in a position near or over the cervical opening. Symptoms include vaginal bleeding in the second half of pregnancy. The bleeding is bright red and tends not to be associated ...
but is not diagnostic for abruption. The diagnosis is one of exclusion, meaning other possible sources of vaginal bleeding or abdominal pain have to be ruled out in order to diagnose placental abruption. Of note, use of magnetic resonance imaging has been found to be highly sensitive in depicting placental abruption, and may be considered if no ultrasound evidence of placental abruption is present, especially if the diagnosis of placental abruption would change management.
Classification
Based on severity: * Class 0: Asymptomatic. Diagnosis is made retrospectively by finding an organized blood clot or a depressed area on a delivered placenta. * Class 1: Mild and represents approximately 48% of all cases. Characteristics include the following: ** No vaginal bleeding to mild vaginal bleeding ** Slightly tender uterus ** Normal maternal blood pressure and heart rate ** No coagulopathy ** Nofetal distress Fetal distress, also known as non-reassuring fetal status, is a condition during pregnancy or labor in which the fetus shows signs of inadequate oxygenation. Due to its imprecision, the term "fetal distress" has fallen out of use in American obstetr ...
* Class 2: Moderate and represents approximately 27% of all cases. Characteristics include the following:
** No vaginal bleeding to moderate vaginal bleeding
** Moderate-to-severe uterine tenderness with possible tetanic contractions
** Maternal tachycardia with orthostatic changes in blood pressure and heart rate
** Fetal distress
** Hypofibrinogenemia (i.e., 50–250 mg/dL)
* Class 3: Severe and represents approximately 24% of all cases. Characteristics include the following:
** No vaginal bleeding to heavy vaginal bleeding
** Very painful tetanic uterus
** Maternal shock
** Hypofibrinogenemia (i.e., <150 mg/dL)
** Coagulopathy
** Fetal death
Prevention
Although the risk of placental abruption cannot be eliminated, it can be reduced. Avoiding tobacco, alcohol and cocaine during pregnancy decreases the risk. Staying away from activities which have a high risk of physical trauma is also important. Women who have high blood pressure or who have had a previous placental abruption and want to conceive must be closely supervised by a doctor. The risk of placental abruption can be reduced by maintaining a gooddiet
Diet may refer to:
Food
* Diet (nutrition), the sum of the food consumed by an organism or group
* Dieting, the deliberate selection of food to control body weight or nutrient intake
** Diet food, foods that aid in creating a diet for weight loss ...
including taking folate
Folate, also known as vitamin B9 and folacin, is one of the B vitamins. Manufactured folic acid, which is converted into folate by the body, is used as a dietary supplement and in food fortification as it is more stable during processing an ...
, regular sleep
Sleep is a sedentary state of mind and body. It is characterized by altered consciousness, relatively inhibited sensory activity, reduced muscle activity and reduced interactions with surroundings. It is distinguished from wakefulness by a de ...
patterns and correction of pregnancy-induced hypertension.
Use of aspirin
Aspirin, also known as acetylsalicylic acid (ASA), is a nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug (NSAID) used to reduce pain, fever, and/or inflammation, and as an antithrombotic. Specific inflammatory conditions which aspirin is used to treat inc ...
before 16 weeks of pregnancy to prevent pre-eclampsia also appears effective at preventing placental abruption.
Management
Treatment depends on the amount of blood loss and the status of the fetus. If the fetus is less than 36 weeks, and neither mother or fetus are in any distress, then they may simply be monitored in hospital until a change in condition or fetal maturity whichever comes first. Immediate delivery of the fetus may be indicated if the fetus is mature or if the fetus or mother is in distress. Blood volume replacement to maintain blood pressure andblood plasma
Blood plasma is a light amber-colored liquid component of blood in which blood cells are absent, but contains proteins and other constituents of whole blood in suspension. It makes up about 55% of the body's total blood volume. It is the intr ...
replacement to maintain fibrinogen
Fibrinogen (factor I) is a glycoprotein complex, produced in the liver, that circulates in the blood of all vertebrates. During tissue and vascular injury, it is converted enzymatically by thrombin to fibrin and then to a fibrin-based blood cl ...
levels may be needed. Vaginal birth is usually preferred over Caesarean section unless there is fetal distress. Caesarean section carries an increased risk in cases of disseminated intravascular coagulation. The mother should be monitored for 7 days for postpartum hemorrhage
Postpartum bleeding or postpartum hemorrhage (PPH) is often defined as the loss of more than 500 ml or 1,000 ml of blood following childbirth. Some have added the requirement that there also be signs or symptoms of low blood volume fo ...
. Excessive bleeding from uterus may necessitate hysterectomy. The mother may be given Rhogam if she is Rh negative.
Prognosis
The prognosis of this complication depends on whether treatment is received by the patient, on the quality of treatment, and on the severity of the abruption. Outcomes for the baby also depend on the gestational age. In the Western world, maternal deaths due to placental abruption are rare. The fetal prognosis is worse than the maternal prognosis; approximately 12% of fetuses affected by placental abruption die. 77% of fetuses that die from placental abruption die before birth; the remainder die due to complications of preterm birth. Without any form of medical intervention, as often happens in many parts of the world, placental abruption has a high maternal mortality rate.Mother
* A large loss of blood may require ablood transfusion
Blood transfusion is the process of transferring blood products into a person's circulation intravenously. Transfusions are used for various medical conditions to replace lost components of the blood. Early transfusions used whole blood, but mo ...
.
* If the mother's blood loss cannot be controlled, an emergency hysterectomy may become necessary.
* The uterus may not contract properly after delivery so the mother may need medication to help her uterus contract.
* The mother may develop a blood clotting disorder, disseminated intravascular coagulation.
* A severe case of shock may affect other organs, such as the liver, kidney, and pituitary gland. Diffuse cortical necrosis in the kidney is a serious and often fatal complication.
* Placental abruption may cause bleeding through the uterine muscle and into the mother's abdominal cavity, a condition called Couvelaire uterus.
* Maternal death.
Baby
* The baby may be born at a low birthweight. * Preterm delivery (prior to 37 weeks gestation). * The baby may be deprived of oxygen and thus develop asphyxia. * Placental abruption may also result in death of the baby, or stillbirth. * The newborn infant may have learning issues at later development stages, often requiring professional pedagogical aid.Epidemiology
Placental abruption occurs in approximately 0.2–1% of all pregnancies. Though different causes change when abruption is most likely to occur, the majority of placental abruptions occur before 37 weeks gestation, and 12–14% occur before 32 weeks gestation.References
{{Pathology of pregnancy, childbirth and the puerperium Health issues in pregnancy Wikipedia medicine articles ready to translate