Phase-shift oscillator on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
A phase-shift oscillator is a

linear
Linearity is the property of a mathematical relationship (''function'') that can be graphically represented as a straight line. Linearity is closely related to '' proportionality''. Examples in physics include rectilinear motion, the linear r ...
electronic oscillator
An electronic oscillator is an electronic circuit that produces a periodic, oscillation, oscillating electronic signal, often a sine wave or a square wave or a triangle wave. Oscillation, Oscillators convert direct current (DC) from a power supp ...
circuit that produces a sine wave
A sine wave, sinusoidal wave, or just sinusoid is a curve, mathematical curve defined in terms of the ''sine'' trigonometric function, of which it is the graph of a function, graph. It is a type of continuous wave and also a Smoothness, smooth p ...
output. It consists of an inverting amplifier
This article illustrates some typical operational amplifier applications. A non-ideal operational amplifier's equivalent circuit has a finite input impedance, a non-zero output impedance, and a finite gain. A real op-amp has a number of non-ideal f ...
element such as a transistor
upright=1.4, gate (G), body (B), source (S) and drain (D) terminals. The gate is separated from the body by an insulating layer (pink).
A transistor is a semiconductor device used to Electronic amplifier, amplify or electronic switch, switch e ...
or op amp
An operational amplifier (often op amp or opamp) is a DC-coupled high- gain electronic voltage amplifier with a differential input and, usually, a single-ended output. In this configuration, an op amp produces an output potential (relative to ...
with its output fed back to its input through a phase-shift network consisting of resistor
A resistor is a passive two-terminal electrical component that implements electrical resistance as a circuit element. In electronic circuits, resistors are used to reduce current flow, adjust signal levels, to divide voltages, bias active el ...
s and capacitor
A capacitor is a device that stores electrical energy in an electric field by virtue of accumulating electric charges on two close surfaces insulated from each other. It is a passive electronic component with two terminals.
The effect of ...
s in a ladder network
Electronic filter topology defines electronic filter circuits without taking note of the values of the components used but only the manner in which those components are connected.
Filter design characterises filter circuits primarily by their ...
. The feedback network 'shifts' the phase
Phase or phases may refer to:
Science
*State of matter, or phase, one of the distinct forms in which matter can exist
*Phase (matter), a region of space throughout which all physical properties are essentially uniform
* Phase space, a mathematic ...
of the amplifier output by 180 degrees at the oscillation frequency to give positive feedback
Positive feedback (exacerbating feedback, self-reinforcing feedback) is a process that occurs in a feedback loop which exacerbates the effects of a small disturbance. That is, the effects of a perturbation on a system include an increase in the ...
. Phase-shift oscillators are often used at audio frequency
An audio frequency or audible frequency (AF) is a periodic vibration whose frequency is audible to the average human. The SI unit of frequency is the hertz (Hz). It is the property of sound that most determines pitch.
The generally accepted ...
as audio oscillator
An electronic oscillator is an electronic circuit that produces a periodic, oscillation, oscillating electronic signal, often a sine wave or a square wave or a triangle wave. Oscillation, Oscillators convert direct current (DC) from a power supp ...
s.
The filter produces a phase shift that increases with frequency
Frequency is the number of occurrences of a repeating event per unit of time. It is also occasionally referred to as ''temporal frequency'' for clarity, and is distinct from ''angular frequency''. Frequency is measured in hertz (Hz) which is eq ...
. It must have a maximum phase shift of more than 180 degrees at high frequencies so the phase shift at the desired oscillation frequency can be 180 degrees. The most common phase-shift network cascades three identical resistor-capacitor stages that produce a phase shift of zero at low frequencies and 270° at high frequencies.
The first integrated circuit was a phase shift oscillator invented by Jack Kilby in 1958.
Implementations

Bipolar implementation
This schematic drawing shows the oscillator using acommon-emitter
In electronics, a common-emitter amplifier is one of three basic single-stage bipolar-junction-transistor (BJT) amplifier topologies, typically used as a voltage amplifier. It offers high current gain (typically 200), medium input resistance a ...
connected bipolar transistor
A bipolar junction transistor (BJT) is a type of transistor that uses both electrons and electron holes as charge carriers. In contrast, a unipolar transistor, such as a field-effect transistor, uses only one kind of charge carrier. A bipolar t ...
as amplifier. The two resistors ''R'' and three capacitors ''C'' form the RC phase-shift network which provides feedback from collector to base of the transistor. Resistor ''R''b provides base bias current. Resistor ''R''c is the collector load resistor for the collector current. Resistor ''R''s isolates the circuit from the external load.

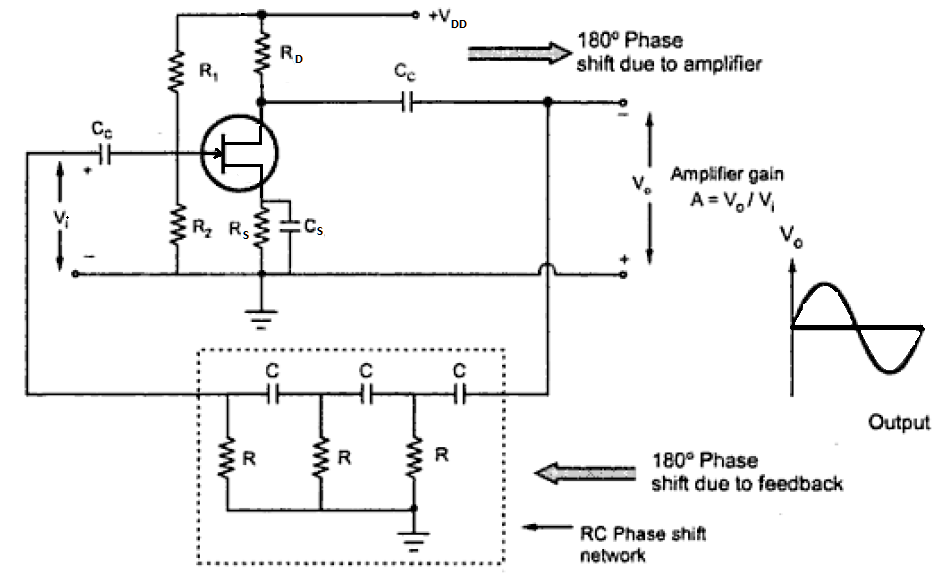
FET implementation
This circuit implements the oscillator with aFET
The field-effect transistor (FET) is a type of transistor that uses an electric field to control the flow of current in a semiconductor. FETs (JFETs or MOSFETs) are devices with three terminals: ''source'', ''gate'', and ''drain''. FETs contr ...
. ''R''1, ''R''2, ''R''s, and ''C''s provide bias
Bias is a disproportionate weight ''in favor of'' or ''against'' an idea or thing, usually in a way that is closed-minded, prejudicial, or unfair. Biases can be innate or learned. People may develop biases for or against an individual, a group, ...
for the transistor. Note that the topology used for positive feedback is voltage series feedback.
Op-amp implementation
The implementation of the phase-shift oscillator shown in the diagram uses anoperational amplifier
An operational amplifier (often op amp or opamp) is a DC-coupled high-gain electronic voltage amplifier with a differential input and, usually, a single-ended output. In this configuration, an op amp produces an output potential (relative to c ...
(op-amp), three capacitor
A capacitor is a device that stores electrical energy in an electric field by virtue of accumulating electric charges on two close surfaces insulated from each other. It is a passive electronic component with two terminals.
The effect of ...
s and four resistor
A resistor is a passive two-terminal electrical component that implements electrical resistance as a circuit element. In electronic circuits, resistors are used to reduce current flow, adjust signal levels, to divide voltages, bias active el ...
s.
The circuit's modeling equations for the oscillation frequency and oscillation criterion are complicated because each RC stage loads the preceding ones. Assuming an ideal amplifier, with very low output impedance and very high input impedance, the oscillation frequency is:
:
The feedback resistor required to just sustain oscillation is:
:
The equations are simpler when all the resistors (except the negative feedback
Negative feedback (or balancing feedback) occurs when some function (Mathematics), function of the output of a system, process, or mechanism is feedback, fed back in a manner that tends to reduce the fluctuations in the output, whether caused by ...
resistor) have the same value and all the capacitors have the same value. In the diagram, if and , then:
:
and the oscillation criterion is:
:
As with other feedback oscillators, when the power is applied to the circuit, thermal electrical noise
In electronics, noise is an unwanted disturbance in an electrical signal.
Noise generated by electronic devices varies greatly as it is produced by several different effects.
In particular, noise is inherent in physics, and central to the ...
in the circuit or the turn-on transient
ECHELON, originally a secret government code name, is a surveillance program ( signals intelligence/SIGINT collection and analysis network) operated by the five signatory states to the UKUSA Security Agreement:Given the 5 dialects that ...
provides an initial signal to start oscillation. In practice, the feedback resistor must be a little bit larger so the oscillation will grow in amplitude rather than remain the same (small) amplitude. If the amplifier were ideal, then amplitude would increase without limit, but in practice amplifiers are nonlinear and their instantaneous gain varies. As the amplitude increases, amplifier saturation will decrease the amplifier's average gain. Consequently, the oscillation amplitude will keep increasing until the average loop gain
In electronics and control system theory, loop gain is the sum of the gain, expressed as a ratio or in decibels, around a feedback loop. Feedback loops are widely used in electronics in amplifiers and oscillators, and more generally in both elec ...
of the circuit falls to unity; at that point, the amplitude will stabilize.
When the oscillation frequency is high enough to be near the amplifier's cutoff frequency
In physics and electrical engineering, a cutoff frequency, corner frequency, or break frequency is a boundary in a system's frequency response at which energy flowing through the system begins to be reduced ( attenuated or reflected) rather than ...
, the amplifier will contribute significant phase shift itself, which will add to the phase shift of the feedback network. Therefore, the circuit will oscillate at a frequency at which the phase shift of the feedback filter is less than 180 degrees.
The single op-amp circuit needs a relatively high gain (about 30) to maintain the oscillation due to the RC sections loading each other. If each RC segment did not affect the others, a gain of about 8 to 10 would be sufficient for oscillation. An isolated version of the oscillator can be made by inserting an op-amp buffer between each RC stage (this also simplifies the modeling equations).
References
External links
* {{DEFAULTSORT:Phase-Shift Oscillator Electronic oscillators de:Phasenschieber#Phasenschiebergenerator