Peruvian general election, 2016 on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
General elections were held in Peru on 10 April 2016 to determine the President of Peru, president, vice-presidents, composition of the Congress of the Republic of Peru and the Peruvian representatives of the Andean Parliament.
In the race for the presidency, incumbent President Ollanta Humala was ineligible for re-election due to constitutional term limits. Popular Force candidate Keiko Fujimori, daughter of former President Alberto Fujimori, was the leading candidate in the first round with almost 40 per cent of the vote, but fell short of the 50 per cent majority required to avoid a second round. Peruvians for Change candidate Pedro Pablo Kuczynski narrowly beat Broad Front (Peru), Broad Front candidate Verónika Mendoza to finish in second and earn a place in the second round. The run-off was held on 5 June 2016. With support from those opposing Fujimori, Kuczynski won by a narrow margin of less than half a percentage point. He was sworn in as President on 28 July.
In the Congressional elections, Popular Force won in a landslide, receiving more than a third of the vote and winning an absolute majority of 73 out of 130 seats. Broad Front (Peru), Broad Front with 20 seats and Peruvians for Change with 18 seats emerged as the main opposition blocs.
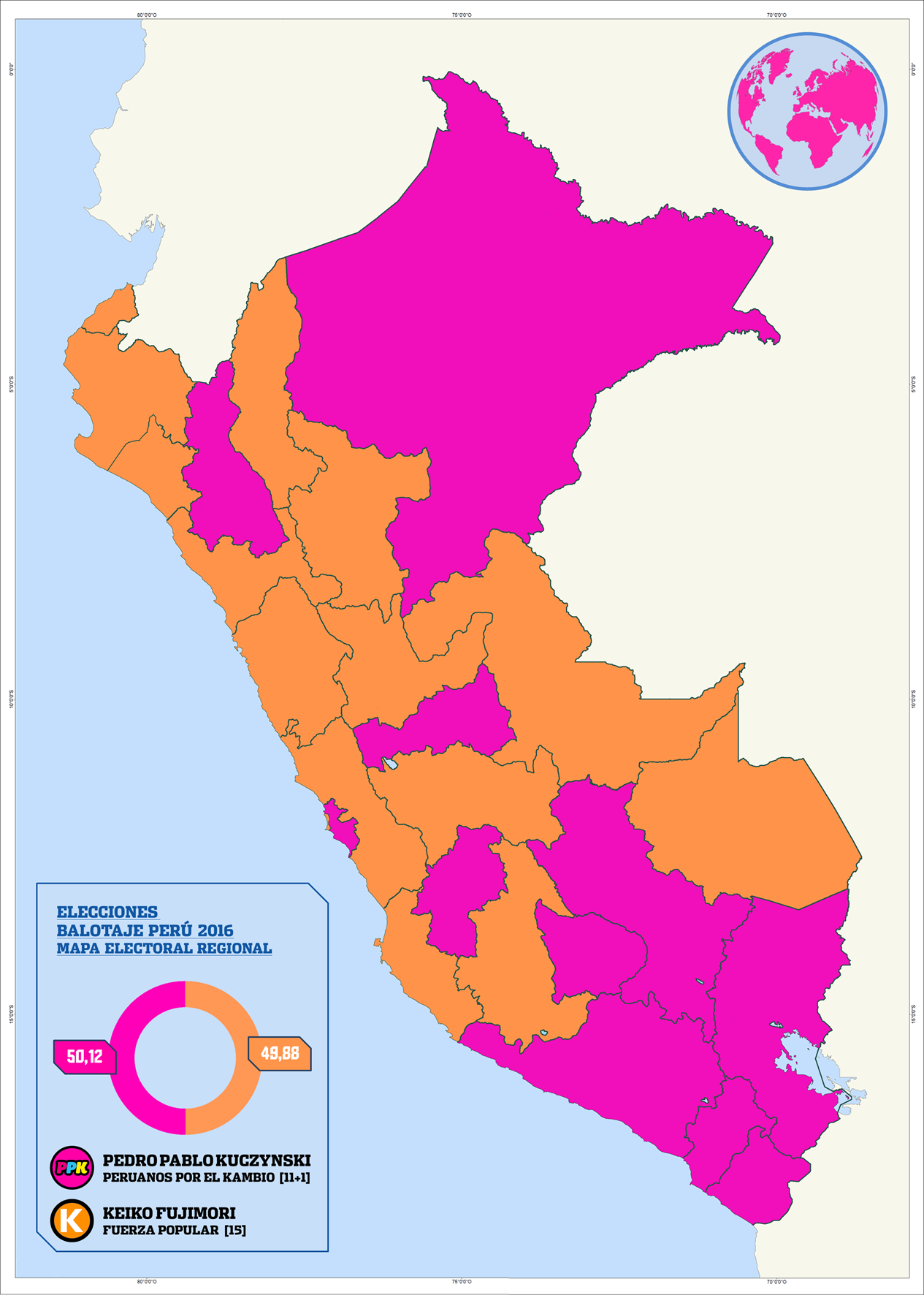
 The first round was held on 10 April. Exit polls indicated that Keiko Fujimori placed first in the first round of voting with approximately 40% of the vote, with Pedro Pablo Kuczynski and Veronika Mendoza each receiving approximately 20%.
The second round was held on 5 June. Exit polls indicated that Pedro Pablo Kuczynski held a slight lead over Keiko Fujimori. As counting continued, the gap narrowed significantly. Preliminary results gave Kuczynski a 0.25 per cent advantage over Fujimori, with less than 50,000 votes between them. Approximately 50,000 votes were challenged during the count. Fujimori conceded the election to Kuczynski on 10 June.
The first round was held on 10 April. Exit polls indicated that Keiko Fujimori placed first in the first round of voting with approximately 40% of the vote, with Pedro Pablo Kuczynski and Veronika Mendoza each receiving approximately 20%.
The second round was held on 5 June. Exit polls indicated that Pedro Pablo Kuczynski held a slight lead over Keiko Fujimori. As counting continued, the gap narrowed significantly. Preliminary results gave Kuczynski a 0.25 per cent advantage over Fujimori, with less than 50,000 votes between them. Approximately 50,000 votes were challenged during the count. Fujimori conceded the election to Kuczynski on 10 June.
Background
On 13 November 2015, incumbent President Ollanta Humala called for a general election to be held on 10 April 2016. He said that he would respect the Constitution of Peru, constitutional term limit restrictions and would not run again.Electoral system
The President of Peru, President was elected using the two-round system. The 130 members of the Congress of the Republic of Peru, Congress of the Republic were elected in 25 multi-member constituencies using open list proportional representation.Presidential nominees
Campaign highlights
The presidential tickets were to be filed with the National Office of Electoral Processes (ONPE) by 10 January 2016. Congressional lists were to be filed with the ONPE by 10 February 2016. In March 2016, presidential candidates Julio Guzmán from All for Peru and César Acuña Peralta from Alliance for Progress (Peru), Alliance for Progress were barred from the elections; Guzmán due to a violation of party rules in the party's internal election and Acuña Peralta due to monetary giveaways during a campaign rally, a violation of an electoral law enacted by Congress in November 2015. Keiko Fujimori was a highly polarizing figure during the election. The daughter of the controversial former president Alberto Fujimori, who was serving time in prison at the time, she was popular among the poor and loyalists who credit her father with the defeat of Shining Path. This popularity allowed her to win in the first round of the presidential elections. She was viewed unfavorably by a number of people who oppose Fujimori for human rights abuses and corrupt practices, and who feared that her victory would mark a return of ''Fujimorismo''. Mendoza, who placed third and could not stand in the runoff election, gave her full endorsement to Kuczynski, in order to prevent Fujimori's victory.Main presidential nominees
* Alfredo Barnechea is Popular Action (Peru), Popular Action's nominee. A renowned journalist in the 1980s, his first stint in politics occurred in 1983, as he ran for mayor of Lima with the Peruvian Aprista Party, APRA, losing to Alfonso Barrantes. Elected to the lower house Congress of the Republic of Peru, Peruvian Congress in 1985 Peruvian general election, 1985, he quit the party and remained in opposition to Alan García. Participating in the 1990 Democratic Front (Peru), Democratic Front campaign, he subsequently attained a master's degree in public administration from Harvard Kennedy School. A member of Popular Action (Peru), Popular Action since 2013, ideologically he considers himself a Social democracy, social democrat. * Keiko Fujimori, is the nominee and leader of the conservative Popular Force. She is the daughter of former President Alberto Fujimori, who serves in prison for a series of crimes and human rights violations during his presidency. A graduate of Columbia Business School, she served in the Congress of the Republic of Peru, Peruvian Congress from 2006 to 2011, and made it to the run-off with Ollanta Humala in the 2011 Peruvian general election, 2011 election, losing by a small margin. Her nomination remained a highly polarizing one throughout the election. * Alan García, is the leader of the Social democracy, social democrat American Popular Revolutionary Alliance, APRA and Popular Alliance (Peru), Popular Alliance's nominee. One of the two former presidents running in the election, this was his fourth and final run before his suicide in 2019. His first presidency from 1985 to 1990 is considered by historians a failure due to the country's period of instability caused by terrorism and a severe economic crisis, in contrast to his second presidency, which is regarded a success based on the steady economy experienced and poverty reduction, although marred by corruption accusations. In this election, he ran under an electoral coalition with the Christian People's Party (Peru), Christian People's Party and Go Peru, with former presidential nominee Lourdes Flores as his first running mate. Academically, he holds a law degree from the National University of San Marcos, and a master's in sociology at the University of Paris 1 Pantheon-Sorbonne. * Pedro Pablo Kuczynski, is the nominee and leader of the Liberal conservatism, liberal conservative Peruvians for Change. A prominent economist from the University of Oxford and Princeton University, this was his second presidential run following his third place in 2011 Peruvian general election, 2011. He served in Alejandro Toledo's presidency as Prime Minister of Peru, Prime Minister and Ministry of Economy and Finance (Peru), Minister of Economy and Finance, in addition to serving as Ministry of Energy and Mines (Peru), Minister of Energy and Mines in the second presidency of Fernando Belaúnde. * Verónika Mendoza, is Broad Front (Peru), Broad Front's nominee, a Socialism, socialist coalition. A psychology major from the Paris Diderot University, she served in the Congress of the Republic of Peru, Peruvian Congress from 2011 to 2016, representing the constituency of Cuzco, elected under the Peru Wins coalition of ex-president Ollanta Humala, but later left it. Throughout the campaign, she received much criticism for her left-wing policies, and for previous refusing to call Venezuela "a dictatorship" under Hugo Chávez and Nicolás Maduro.Minor presidential nominees
* Alejandro Toledo, former President of Peru (2001–2006) – Possible Peru * Gregorio Santos, Governor of Cajamarca Region (2011–2014) – Direct Democracy (Peru), Direct Democracy * Antero Flores Aráoz, former Ministry of Defense (Peru), Minister of Defense (2007–2009) – Order (Peru), Order * Miguel Hilario – Peru Progressing * Fernando Olivera (politician), Fernando Olivera, former Minister of Justice (2001–2002) – Hope Front (Peru), Hope FrontWithdrawn nominees
Disqualified nominees
*Opinion polls
Results
President

 The first round was held on 10 April. Exit polls indicated that Keiko Fujimori placed first in the first round of voting with approximately 40% of the vote, with Pedro Pablo Kuczynski and Veronika Mendoza each receiving approximately 20%.
The second round was held on 5 June. Exit polls indicated that Pedro Pablo Kuczynski held a slight lead over Keiko Fujimori. As counting continued, the gap narrowed significantly. Preliminary results gave Kuczynski a 0.25 per cent advantage over Fujimori, with less than 50,000 votes between them. Approximately 50,000 votes were challenged during the count. Fujimori conceded the election to Kuczynski on 10 June.
The first round was held on 10 April. Exit polls indicated that Keiko Fujimori placed first in the first round of voting with approximately 40% of the vote, with Pedro Pablo Kuczynski and Veronika Mendoza each receiving approximately 20%.
The second round was held on 5 June. Exit polls indicated that Pedro Pablo Kuczynski held a slight lead over Keiko Fujimori. As counting continued, the gap narrowed significantly. Preliminary results gave Kuczynski a 0.25 per cent advantage over Fujimori, with less than 50,000 votes between them. Approximately 50,000 votes were challenged during the count. Fujimori conceded the election to Kuczynski on 10 June.
Congress
Popular Force won in a landslide, taking more than a third of the vote and an absolute majority of 73 out of 130 seats. Behind them in opposition, Peruvians for Change with 18 seats and Broad Front (Peru), Broad Front with 20 seats. Other parties which gained representation in Congress include Alliance for the Progress of Peru (9 seats), Popular Alliance (Peru), Popular Alliance (5 seats) and Popular Action (Peru), Popular Action (5 seats).Andean Parliament
Only the three main parties obtained representation in the Andean Parliament, with Popular Force obtaining 3 seats (plus six substitutes) each, and Broad Front and Peruvians for Change obtaining only one seat (and two substitutes). Popular Force got the most votes, with 38.1% of the valid ballots. Former congressman Rolando Sousa of Popular Force obtained the most individual votes, with 407,811.Notes
References
{{Peruvian elections Elections in Peru 2016 elections in South America, Peru 2016 in Peru Presidential elections in Peru April 2016 events in South America June 2016 events in South America