Perak Malay on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Perak Malay (
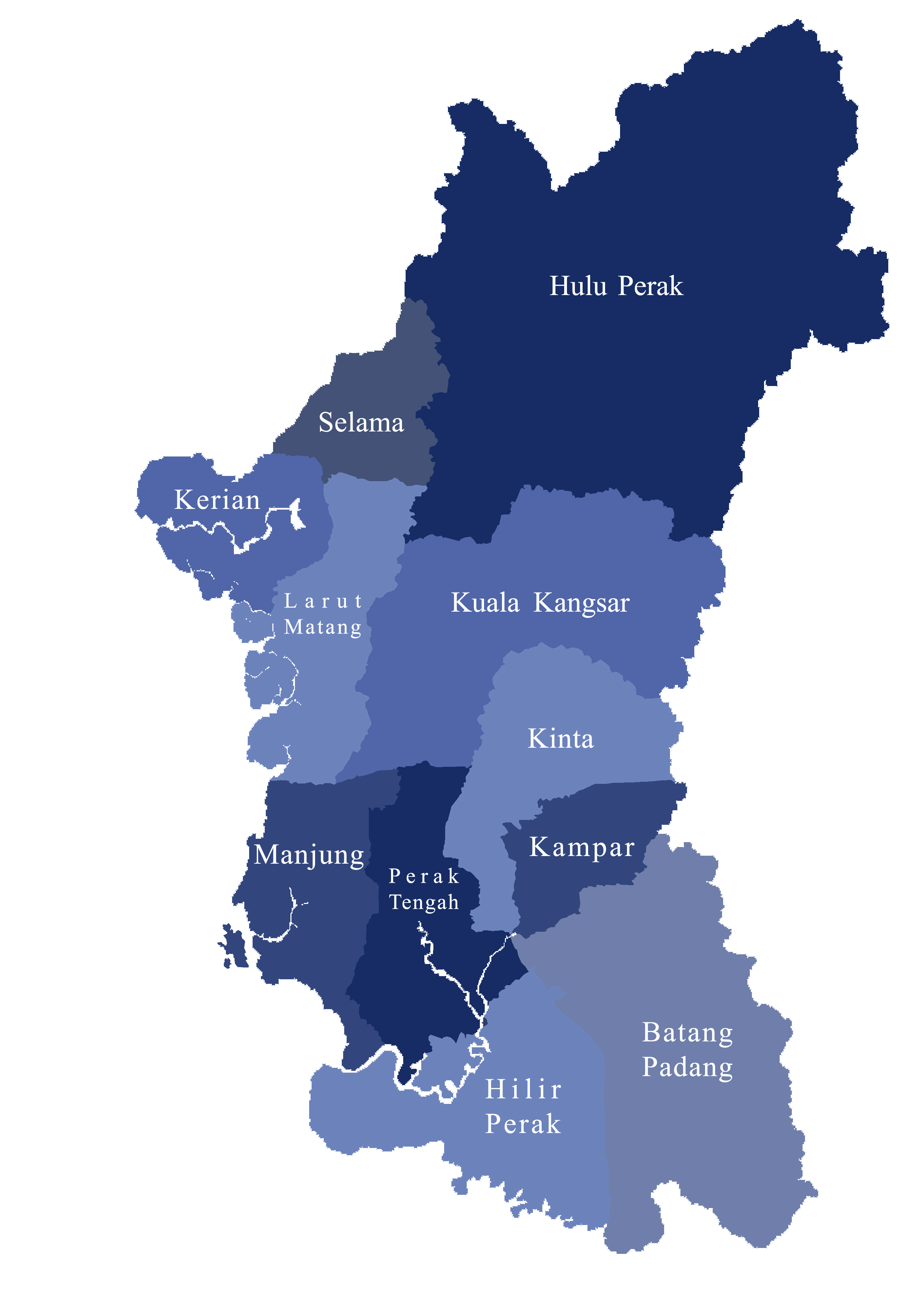 Perak Malay is spoken throughout the whole state except in the northwestern parts of Perak (
Perak Malay is spoken throughout the whole state except in the northwestern parts of Perak (
''* Kuala Kangsar variant''
''** Influence of the northern dialect''
Standard Malay
Malaysian Malay ( ms, Bahasa Melayu Malaysia), also known as Standard Malay (Malay: ''Bahasa Melayu Standard''), ( English translation: Malaysian language), or simply Malay, is a standardized form of the Malay language used in Malaysia (as o ...
: ''bahasa Melayu Perak''; Jawi script
Jawi (; ace, Jawoë; Kelantan-Pattani Malay, Kelantan-Pattani: ''Yawi''; ) is a writing system used for writing several languages of Southeast Asia, such as Acehnese language, Acehnese, Banjar language, Banjarese, Kerinci language, Kerinci, ...
: ž©┘枦ž│ ┘ģ┘䞦┘Ŗ┘ł ┌ż┘Ŗž▒ž¦┘é) is one of the Malay
Malay may refer to:
Languages
* Malay language or Bahasa Melayu, a major Austronesian language spoken in Indonesia, Malaysia, Brunei and Singapore
** History of the Malay language, the Malay language from the 4th to the 14th century
** Indonesi ...
dialects
The term dialect (from Latin , , from the Ancient Greek word , 'discourse', from , 'through' and , 'I speak') can refer to either of two distinctly different types of linguistic phenomena:
One usage refers to a variety of a language that is a ...
spoken within the state of Perak
Perak () is a state of Malaysia on the west coast of the Malay Peninsula. Perak has land borders with the Malaysian states of Kedah to the north, Penang to the northwest, Kelantan and Pahang to the east, and Selangor to the south. Thailand's ...
, Malaysia
Malaysia ( ; ) is a country in Southeast Asia. The federation, federal constitutional monarchy consists of States and federal territories of Malaysia, thirteen states and three federal territories, separated by the South China Sea into two r ...
. Although it is neither the official language nor the standard dialect in the whole state of Perak, its existence which co-exists with other major dialects in the state of Perak still plays an important role in maintaining the identity of Perak. In spite of the fact that there are five main dialects traditionally spoken in Perak, only one of which is intended by the name "Perak Malay". There are subtle phonetic
Phonetics is a branch of linguistics that studies how humans produce and perceive sounds, or in the case of sign languages, the equivalent aspects of sign. Linguists who specialize in studying the physical properties of speech are phoneticians. ...
, syntactic
In linguistics, syntax () is the study of how words and morphemes combine to form larger units such as phrases and sentences. Central concerns of syntax include word order, grammatical relations, hierarchical sentence structure (constituency), ...
and lexical
Lexical may refer to:
Linguistics
* Lexical corpus or lexis, a complete set of all words in a language
* Lexical item, a basic unit of lexicographical classification
* Lexicon, the vocabulary of a person, language, or branch of knowledge
* Lex ...
distinctions from other major Malay dialects. Perak Malay can be divided into two sub-dialects, Kuala Kangsar
The Kuala Kangsar (Perak Malay: ''Kole Kangso'') is the royal town of Perak, Malaysia. It is located at the downstream of Kangsar River where it joins the Perak River, approximately northwest of Ipoh, Perak's capital, and southeast of ...
and Perak Tengah
Perak Tengah District (Central Perak) is a district in Perak, Malaysia. It is administered by the Perak Tengah District Council, which is based at the town of Seri Iskandar; Parit is however the largest settlement in the area.
Administrative d ...
, named after the '' daerah'' (districts) where they are predominantly spoken.
Classification
Linguistically, the Malay dialects spoken in the state of Perak are diverse. In fact, there is still no definite classification of the type of Malay dialects used in Perak. Ismail Hussein (1973) classified the Malay dialects in Perak into five types segregated into five different areas. While Harun Mat Piah (1983) categorized them into six. Although Asmah Haji Omar (1985) divided the Malay dialects in Perak into five types, the specifications of the division did not coincide with that of Ismail's.Distribution
 Perak Malay is spoken throughout the whole state except in the northwestern parts of Perak (
Perak Malay is spoken throughout the whole state except in the northwestern parts of Perak (Kerian
The Kerian District (alternately Krian) is an administrative district in Perak, Malaysia. It covers the northwestern corner of Perak, bordering the states of Penang and Kedah to the north; the main town of Parit Buntar is located a mere southeast ...
, Larut, Matang and Selama
The Larut, Matang and Selama District is a district of Perak, Malaysia. Taiping is the capital town of this district. Larut, Matang and Selama used to be three small different districts and they merged into one larger district later. Larut, M ...
), and a few parts of Manjung
The Manjung District, formerly Dindings, is a district in the southwestern part of the state of Perak, Malaysia. The district is well known for Pangkor Island, an attraction in Perak and the home of the Royal Malaysian Navy (TLDM), Lumut Naval Ba ...
district including Pangkor Island
Pangkor Island ( ms, Pulau Pangkor) is an island in Manjung District, Perak, Malaysia. It has a population of approximately 25,000. Nearby islands include Pangkor Laut Island, Giam Island, Mentagor Island, Simpan Island, and Tukun Terindak Islan ...
where the northern dialect is predominantly spoken.
In the northeastern part of Perak (Hulu Perak
Hulu Perak District (Upper Perak) is a district in Perak, Malaysia. As the largest district in Perak, there are border to the east of the district is the state of Kelantan, to the west is Kedah, to the south is the district of Kuala Kangsar whil ...
) and some parts of Selama and Kerian, the Malay people natively speak a distinct variant of Malay language which is most closely related to Kelantan-Pattani Malay
Kelantan-Pattani Malay (; ; in Pattani; in Kelantan) is an Austronesian language of the Malayic subfamily spoken in the Malaysian state of Kelantan and the neighbouring southernmost provinces of Thailand. It is the primary spoken language of ...
and the Malay dialects of southern Thailand
Southern Thailand, Southern Siam or Tambralinga is a southernmost cultural region of Thailand, separated from Central Thailand region by the Kra Isthmus.
Geography
Southern Thailand is on the Malay Peninsula, with an area of around , bounded ...
due to geographical borders and historical assimilation. This variant is occasionally classified as a sub-dialect of Yawi. The district of Hulu Perak once was ruled by the Kingdom of Reman
The Kingdom of Reman or Kingdom of Rahman ( ms, Kerajaan Reman; Jawi: ┘āž▒ž¦ž¼žŻ┘å ž▒┘ģž¦┘å; ; ) was a landlocked semi-independent Malay kingdom established in northern Malay Peninsula.
It was one of seven regions of Pattani Kingdom, an aut ...
. Reman was historically a part of Greater Pattani (which is now a province
A province is almost always an administrative division within a country or sovereign state, state. The term derives from the ancient Roman ''Roman province, provincia'', which was the major territorial and administrative unit of the Roman Empire ...
of Thailand
Thailand ( ), historically known as Siam () and officially the Kingdom of Thailand, is a country in Southeast Asia, located at the centre of the Indochinese Peninsula, spanning , with a population of almost 70 million. The country is bo ...
) before gaining independence in 1810 from the Pattani Kingdom
Patani, or the Sultanate of Patani ( Jawi: ┘āž│┘äžĘž¦┘å┘å ┌żžĘž¦┘å┘Ŗ) was a Malay sultanate in the historical Pattani Region. It covered approximately the area of the modern Thai provinces of Pattani, Yala, Narathiwat and part of the norther ...
via a rebellion by the Royal Family.
In the southern parts of Perak (Hilir Perak
Hilir Perak District (Lower Perak) is a district in Perak, Malaysia. The district is governed by Teluk Intan Municipal Council which is based in the town of Teluk Intan. The District council was known as Hilir Perak District Council until 4 April ...
and Batang Padang
The Batang Padang District ( ms, Daerah Batang Padang) is a district in Perak, Malaysia. This district is administered by a local council, namely, the Tapah District Council, based in Tapah. The major towns of Batang Padang are Bidor, Tapah and ...
) and also in the districts of Kampar and Kinta and several parts of Manjung, the dialect is heavily influenced by southern Malay dialects of the peninsula such as Selangor
Selangor (; ), also known by its Arabic language, Arabic honorific Darul Ehsan, or "Abode of Sincerity", is one of the 13 Malaysian states. It is on the west coast of Peninsular Malaysia and is bordered by Perak to the north, Pahang to the east ...
, Malacca
Malacca ( ms, Melaka) is a state in Malaysia located in the southern region of the Malay Peninsula, next to the Strait of Malacca. Its capital is Malacca City, dubbed the Historic City, which has been listed as a UNESCO World Heritage Site si ...
and Johore-Riau Malay and various languages of Indonesian archipelago namely Javanese, Banjar, Rawa
The Revolutionary Association of the Women of Afghanistan (RAWA) (Persian:ž¼┘ģž╣█īž¬ ž¦┘å┘é┘䞦ž©█ī ž▓┘垦┘å ž¦┘üž║ž¦┘åž│ž¬ž¦┘å, ''Jami╩┐at-e Enqel─übi-ye Zan─ün-e Afgh─ünest─ün'', Pashto:ž» ž¦┘üž║ž¦┘åž│ž¬ž¦┘å ž» ┌Ü┌ģ┘ł ž¦┘å┘é┘䞦ž©█ī ž¼┘ģž╣█īž¬) ...
, Mandailing
The Mandailing is an ethnic group in Sumatera, Indonesia that is commonly associated with the Batak people. They are found mainly in the northern section of the island of Sumatra in Indonesia. They came under the influence of the Kaum Padri who ...
and Buginese as a result of historical immigration, civil war
A civil war or intrastate war is a war between organized groups within the same state (or country).
The aim of one side may be to take control of the country or a region, to achieve independence for a region, or to change government policies ...
such as Klang War
The Klang War or Selangor Civil War was a series of conflicts that lasted from 1867 to 1874 in the Malay state of Selangor in the Malay Peninsula (modern-day Malaysia).
It was initially fought between Raja Abdullah bin Raja Jaafar, the admini ...
and other inevitable factors.
Whilst there are many Malay dialects significantly found in Perak, all Malay dialectologist Dialectology (from Greek , ''dialektos'', "talk, dialect"; and , ''-logia'') is the scientific study of linguistic dialect, a sub-field of sociolinguistics. It studies variations in language based primarily on geographic distribution and their assoc ...
s basically agreed that Perak Malay is spoken by the native Malay people
Malays ( ms, Orang Melayu, Jawi: žŻ┘łž▒┌Ā ┘ģ┘䞦┘Ŗ┘ł) are an Austronesian ethnic group native to eastern Sumatra, the Malay Peninsula and coastal Borneo, as well as the smaller islands that lie between these locations ŌĆö areas that are ...
who traditionally have long been subsisting along the riverine system of Perak which comprises Perak River
The Perak River ( ms, Sungai Perak; ) is the second longest river in Peninsular Malaysia after Pahang River in Pahang, Malaysia. A number of towns are on the banks of the river including the royal town of Kuala Kangsar. Most of the settlements in ...
valley and its vicinity except those at the upper stream. Historically, it was a tradition for the Malay peasant
A peasant is a pre-industrial agricultural laborer or a farmer with limited land-ownership, especially one living in the Middle Ages under feudalism and paying rent, tax, fees, or services to a landlord. In Europe, three classes of peasants ...
s in Perak to settle along the Perak River. Royal residences also were built at various sites along the river basin
A drainage basin is an area of land where all flowing surface water converges to a single point, such as a river mouth, or flows into another body of water, such as a lake or ocean. A basin is separated from adjacent basins by a perimeter, the ...
, and there was never any attempt to move to another tributary.
Characteristics
Phonology
Open final syllables
It has been said that in general, the Malay people in Malaya distinguish the dialect of Perak by the final vowel inStandard Malay
Malaysian Malay ( ms, Bahasa Melayu Malaysia), also known as Standard Malay (Malay: ''Bahasa Melayu Standard''), ( English translation: Malaysian language), or simply Malay, is a standardized form of the Malay language used in Malaysia (as o ...
substituted into strong 'e': , in contrast to , , and in the other Malay dialects, similar to inland Terengganu dialect. So as for the word (eye) which is shown by the phonemes in Standard Malay, is pronounced as in Perak Malay notably in central Perak region. It appears that Perak Malay has a vowel raising rule which changes word final vowel of Standard Malay to .
Exception of this rule occurs for some words as shown in the table below. This exception is regarded as common amongst most Malay dialects in the peninsula.
As the prevalence of Perak Malay, the diphthongs presented by the graphemes and are often articulated as varied forms of monophthongs
A monophthong ( ; , ) is a pure vowel sound, one whose articulation at both beginning and end is relatively fixed, and which does not glide up or down towards a new position of articulation. The monophthongs can be contrasted with diphthongs, wh ...
. Still and all, diphthongization of monophthongs occurs in certain conditions instead. For instance, the final vowels sound /-i/ and /-u/ are articulated to some extent as diphthongs iyand uwrespectively. The monophthongization
Monophthongization is a sound change by which a diphthong becomes a monophthong, a type of vowel shift. It is also known as ungliding, as diphthongs are also known as gliding vowels. In languages that have undergone monophthongization, digraphs ...
patterns phonetically vary by the sub-dialects.
The pattern /-ai̯/ transformed to aːis particularly restricted to some areas within the district of Perak Tengah. Typically in most villages in Parit
Parit ( Jawi: ┌żž¦ž▒┘Ŗž¬; ) is a main town of Perak Tengah District, Perak, Malaysia.
List of Schools in Parit:-
Primary schools:
# Sekolah Rendah Kebangsaan Parit (SRKP).
# Sekolah Rendah Kebangsaan Iskandar Shah (SRKIS).
# Sekolah Jenis Keb ...
and southward to Bota
Bota ( Jawi: ž©┘łž¬ž¦; ) is a mukim in Perak Tengah District, Perak, Malaysia. It comprises two geographical areas: Bota Kiri and Bota Kanan (Left Bota and Right Bota, respectively) as it is divided by the Perak River. There is a river terra ...
, this pattern is applied. While in the sub-districts of Kampung Gajah and northward to Lambor, the speakers tend to utter in the similar form as in Kuala Kangsar sub-dialect.
Closed final syllables
There is a phonological rule in Perak Malay that neutralizes the finalnasals
In phonetics, a nasal, also called a nasal occlusive or nasal stop in contrast with an oral stop or nasalized consonant, is an occlusive consonant produced with a lowered velum, allowing air to escape freely through the nose. The vast majorit ...
to alveolar nasal
The voiced alveolar nasal is a type of consonantal sound used in numerous spoken languages. The symbol in the International Phonetic Alphabet that represents dental, alveolar, and postalveolar nasals is , and the equivalent X-SAMPA symbol is ...
. The final nasals and phonetically exist in certain environments. In other circumstances, the nasals are neutralized to . This neutralizing rule operates only if the final nasals are directly preceded by or . In addition, the and are allophones
In phonology, an allophone (; from the Greek , , 'other' and , , 'voice, sound') is a set of multiple possible spoken soundsor ''phones''or signs used to pronounce a single phoneme in a particular language. For example, in English, (as in ''s ...
of and in closed final syllables in general Malaysian
Malaysian may refer to:
* Something from or related to Malaysia, a country in Southeast Asia
* Malaysian Malay, a dialect of Malay language spoken mainly in Malaysia
* Malaysian people, people who are identified with the country of Malaysia regard ...
phonology
Phonology is the branch of linguistics that studies how languages or dialects systematically organize their sounds or, for sign languages, their constituent parts of signs. The term can also refer specifically to the sound or sign system of a ...
.
Rhoticity
Most of Malay dialects particularly in Malaysia arenon-rhotic
Rhoticity in English is the pronunciation of the historical rhotic consonant by English speakers. The presence or absence of rhoticity is one of the most prominent distinctions by which varieties of English can be classified. In rhotic variet ...
. Perak Malay is one of non-rhotic variants of Malay language and the 'r' is guttural. In Perak Malay, if the 'r' appears in the initial and middle position of a word, it will be pronounced as French 'r' specifically voiced uvular fricative
The voiced uvular fricative is a type of consonantal sound, used in some spoken languages. The symbol in the International Phonetic Alphabet that represents this sound is , an inverted small uppercase letter , or in broad transcription if rhot ...
, übut if it comes in the final position of a word and in a postvocalic setting, it will be dropped or deleted and then substituted into an open vowel; usually 'o' by affecting the open vowel preceding it.
Vocabulary
Personal pronouns
Perak Malay differs lexically from Standard Malay for some personal pronouns. The suffix'' '-me' ''indicates plural pronoun. Possibly'' '-me' ''is derived from the word that means 'all' in Malay. ''Notes:''''* Kuala Kangsar variant''
''** Influence of the northern dialect''
Intensifiers
Instead of using '' or '' as intensifier for an adjective, Perak Malay speakers also use specific intensifiers for some adjectives.Animals
Perak Malay also differs phonetically and lexically from Standard Malay for some animals.Fruits and plants
Perak Malay has distinct names for specific fruits and plants. Some differ in pronunciation from Standard Malay.References
Bibliography
* * * * * * * * * * * * {{Austronesian languages Agglutinative languages Malay dialects Malay language Languages of Malaysia Perak Malayic languages