Pentium II on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
The Pentium II brand refers to Intel's sixth-generation microarchitecture (" P6") and
The Intel Pentium II ('Klamath') CPU
Tom's Hardware, March 1, 1997.Lal Shimpi, Anand
Intel Pentium II
Anandtech, May 30, 1997. Intel improved 16-bit code execution performance on the Pentium II, an area in which the Pentium Pro was at a notable handicap, by adding segment register caches. Most consumer software of the day was still using at least some 16-bit code, because of a variety of factors. The issues with partial registers was also addressed by adding an internal flag to skip pipeline flushes whenever possible. To compensate for the slower L2 cache, the Pentium II featured 32 KB of L1 cache, double that of the Pentium Pro, as well as 4 write buffers (vs. 2 on the Pentium Pro); these can also be used by either pipeline, instead of each one being fixed to one pipeline. The Pentium II was also the first P6-based CPU to implement the Intel MMX integer
, SandPile.org, accessed May 5, 2007. The 300 MHz version, however, only became available in large quantities later in 1997. These CPUs had a 66 MHz
 The Pentium II Xeon was a high-end version of Deschutes core intended for use on workstations and servers. Principally, it used a different type of slot ( Slot 2), case, board design, and more expensive full-speed custom L2 cache, which was off-die. Versions were produced with 512 KB, 1 MB or 2 MB L2 caches by varying the number of 512 KB chips incorporated on the board.
The Pentium II Xeon was a high-end version of Deschutes core intended for use on workstations and servers. Principally, it used a different type of slot ( Slot 2), case, board design, and more expensive full-speed custom L2 cache, which was off-die. Versions were produced with 512 KB, 1 MB or 2 MB L2 caches by varying the number of 512 KB chips incorporated on the board.
 In Intel's "Family/Model/Stepping" scheme, Deschutes CPUs are family 6, model 5 and have the part number 80523.
In Intel's "Family/Model/Stepping" scheme, Deschutes CPUs are family 6, model 5 and have the part number 80523.
Specification Update for the Pentium II Processor
 Later, in 1999, the 0.25; 0.18 (400
Later, in 1999, the 0.25; 0.18 (400


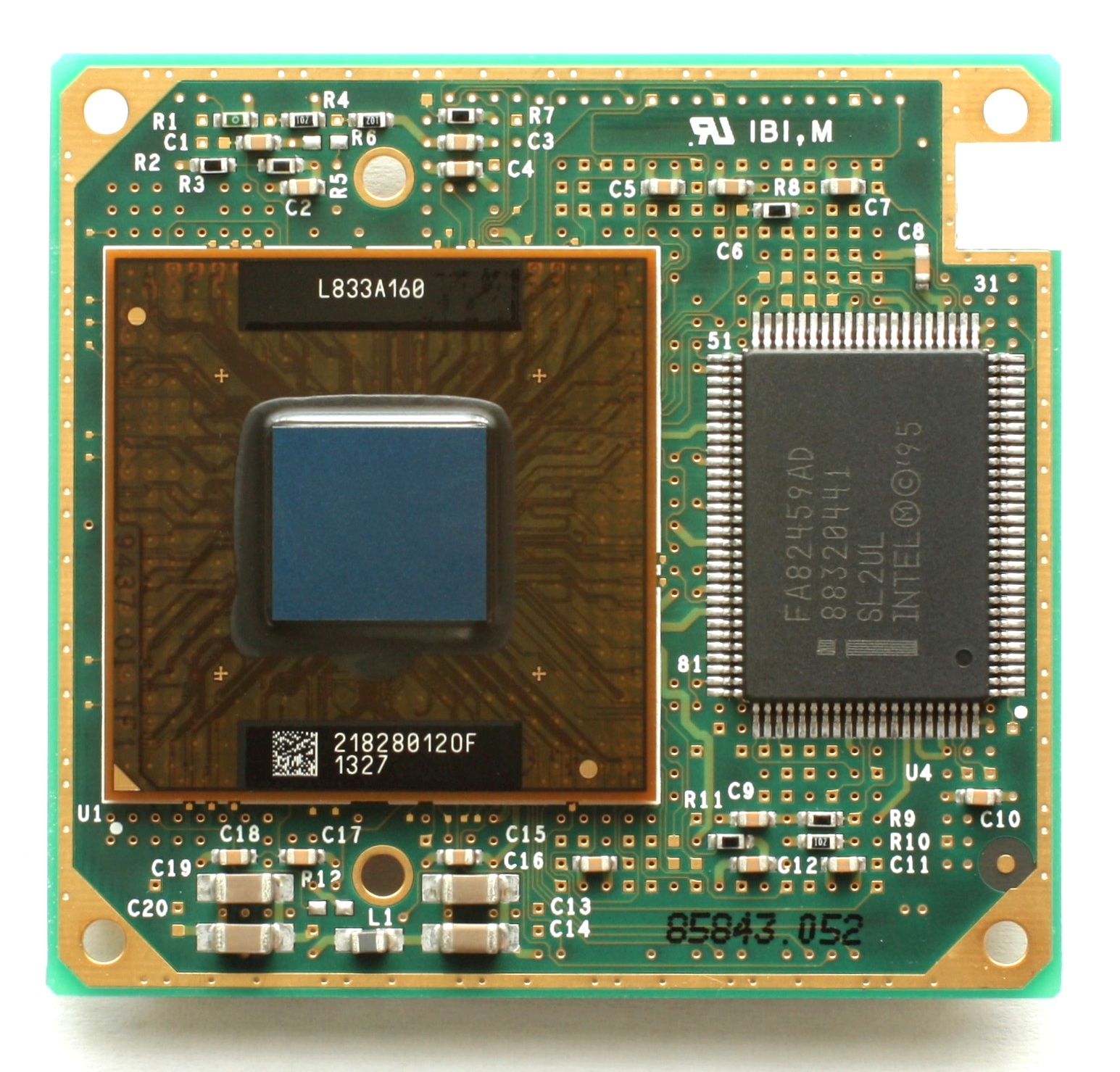 Mobile Pentium II
* L1 cache: 16 + 16 KB (Data + Instructions)
* L2 cache: 512 KB, as external chips on the CPU module clocked at half the CPU frequency.
* Package:
Mobile Pentium II
* L1 cache: 16 + 16 KB (Data + Instructions)
* L2 cache: 512 KB, as external chips on the CPU module clocked at half the CPU frequency.
* Package:
 Mobile Pentium II PE ("Performance Enhanced")
* L1 cache: 16 + 16 KB (Data + Instructions)
* L2 cache: 256 KB, on-die, full speed.
* Package:
Mobile Pentium II PE ("Performance Enhanced")
* L1 cache: 16 + 16 KB (Data + Instructions)
* L2 cache: 256 KB, on-die, full speed.
* Package:
Listing of various PII, PIII, and Celeron alphanumeric model designations
CPU-INFO: Intel Pentium II, indepth processor history
Construction Analysis: Intel 266MHz 32-Bit Pentium II (Klamath) Processor
Integrated Circuit Engineering Corporation Intel datasheets
Pentium II (Klamath)
Pentium II (Deschutes)
Mobile Pentium II (Tonga)
Mobile Pentium II in Micro-PGA and BGA packages (Dixon)
{{DEFAULTSORT:Pentium Ii Computer-related introductions in 1997 Pentium 2 Superscalar microprocessors 32-bit microprocessors
x86
x86 (also known as 80x86 or the 8086 family) is a family of complex instruction set computer (CISC) instruction set architectures initially developed by Intel based on the Intel 8086 microprocessor and its 8088 variant. The 8086 was intr ...
-compatible microprocessor
A microprocessor is a computer processor where the data processing logic and control is included on a single integrated circuit, or a small number of integrated circuits. The microprocessor contains the arithmetic, logic, and control circ ...
s introduced on May 7, 1997. Containing 7.5 million transistor
upright=1.4, gate (G), body (B), source (S) and drain (D) terminals. The gate is separated from the body by an insulating layer (pink).
A transistor is a semiconductor device used to Electronic amplifier, amplify or electronic switch, switch ...
s (27.4 million in the case of the mobile Dixon with 256 KB L2 cache
A CPU cache is a hardware cache used by the central processing unit (CPU) of a computer to reduce the average cost (time or energy) to access data from the main memory. A cache is a smaller, faster memory, located closer to a processor core, whic ...
), the Pentium II featured an improved version of the first ''P6''-generation core of the Pentium Pro
The Pentium Pro is a sixth-generation x86 microprocessor developed and manufactured by Intel and introduced on November 1, 1995. It introduced the P6 microarchitecture (sometimes termed i686) and was originally intended to replace the original ...
, which contained 5.5 million transistors. However, its L2 cache subsystem was a downgrade when compared to the Pentium Pros. It is a single-core microprocessor.
In 1998, Intel stratified the Pentium II family by releasing the Pentium II-based Celeron line of processors for low-end workstations and the Pentium II Xeon line for servers and high-end workstations. The Celeron was characterized by a reduced or omitted (in some cases present but disabled) on-die full-speed L2 cache and a 66 MT/s FSB. The Xeon was characterized by a range of full-speed L2 cache (from 512 KB to 2048 KB), a 100 MT/s FSB, a different physical interface ( Slot 2), and support for symmetric multiprocessing.
In February 1999, the Pentium II was replaced by the nearly identical Pentium III, which only added the then-new SSE instruction set. However, the older family would continue to be produced until June 2001 for desktop units, September 2001 for mobile units, and the end of 2003 for embedded devices.
Overview
The Pentium II microprocessor was largely based upon the microarchitecture of its predecessor, thePentium Pro
The Pentium Pro is a sixth-generation x86 microprocessor developed and manufactured by Intel and introduced on November 1, 1995. It introduced the P6 microarchitecture (sometimes termed i686) and was originally intended to replace the original ...
, but with some significant improvements.
Unlike previous Pentium and Pentium Pro processors, the Pentium II CPU was packaged in a slot-based module rather than a CPU socket. The processor and associated components were carried on a daughterboard similar to a typical expansion board within a plastic cartridge. A fixed or removable heatsink was carried on one side, sometimes using its own fan.
This larger package was a compromise allowing Intel to separate the secondary cache
Cache, caching, or caché may refer to:
Places United States
* Cache, Idaho, an unincorporated community
* Cache, Illinois, an unincorporated community
* Cache, Oklahoma, a city in Comanche County
* Cache, Utah, Cache County, Utah
* Cache County ...
from the processor while still keeping it on a closely coupled back-side bus. The L2 cache ran at half the processor's clock frequency, unlike the Pentium Pro, whose off die L2 cache ran at the same frequency as the processor. However, its associativity was increased to 16-way (compared to 4-way on the Pentium Pro) and its size was always 512 KB, twice of the smallest option of 256 KB on the Pentium Pro. Off-package cache solved the Pentium Pro's low yield issues, allowing Intel to introduce the Pentium II at a mainstream price level.Pabst, ThomasThe Intel Pentium II ('Klamath') CPU
Tom's Hardware, March 1, 1997.Lal Shimpi, Anand
Intel Pentium II
Anandtech, May 30, 1997. Intel improved 16-bit code execution performance on the Pentium II, an area in which the Pentium Pro was at a notable handicap, by adding segment register caches. Most consumer software of the day was still using at least some 16-bit code, because of a variety of factors. The issues with partial registers was also addressed by adding an internal flag to skip pipeline flushes whenever possible. To compensate for the slower L2 cache, the Pentium II featured 32 KB of L1 cache, double that of the Pentium Pro, as well as 4 write buffers (vs. 2 on the Pentium Pro); these can also be used by either pipeline, instead of each one being fixed to one pipeline. The Pentium II was also the first P6-based CPU to implement the Intel MMX integer
SIMD
Single instruction, multiple data (SIMD) is a type of parallel processing in Flynn's taxonomy. SIMD can be internal (part of the hardware design) and it can be directly accessible through an instruction set architecture (ISA), but it shoul ...
instruction set which had already been introduced on the Pentium MMX.
The Pentium II was basically a more consumer-oriented version of the Pentium Pro. It was cheaper to manufacture because of the separate, slower L2 cache memory. The improved 16-bit performance and MMX support made it a better choice for consumer-level operating systems, such as Windows 9x, and multimedia applications. The slower and cheaper L2 cache's performance penalty was mitigated by the doubled L1 cache and architectural improvements for legacy code. General processor performance was increased while costs were cut.
All ''Klamath'' and some early ''Deschutes'' Pentium IIs use a combined L2 cache controller / tag RAM chip that only allows for 512 MB to be cached; while more RAM could be installed in theory, this would result in very slow performance. While this limit was practically irrelevant for the average home user at the time, it was a concern for some workstation or server users. Presumably, Intel put this limitation deliberately in place to distinguish the Pentium II from the more upmarket Pentium Pro line, which has a full 4 GB cacheable area. The '82459AD' revision of the chip on some 333 MHz and all 350 MHz and faster Pentium IIs lifted this restriction and also offered a full 4 GB cacheable area.
Variants
Klamath
The original ''Klamath'' Pentium II microprocessor (Intel product code 80522) ran at 233, 266, and 300MHz
The hertz (symbol: Hz) is the unit of frequency in the International System of Units (SI), equivalent to one event (or cycle) per second. The hertz is an SI derived unit whose expression in terms of SI base units is s−1, meaning that one he ...
and was produced in a 0.35 μm process.IA-32 implementation Intel P2 (incl. Celeron and Xeon), SandPile.org, accessed May 5, 2007. The 300 MHz version, however, only became available in large quantities later in 1997. These CPUs had a 66 MHz
front-side bus
A front-side bus (FSB) is a computer communication interface (bus) that was often used in Intel-chip-based computers during the 1990s and 2000s. The EV6 bus served the same function for competing AMD CPUs. Both typically carry data between the ...
and were initially used on motherboards equipped with the aging Intel 440FX ''Natoma'' chipset designed for the Pentium Pro. Pentium II-based systems using the Intel 440LX ''Balboa'' chipset widely popularized SDRAM (which was to replace EDO RAM and was already introduced with 430VX), and the AGP graphics bus.
On July 14, 1997, Intel announced a version of the Pentium II ''Klamath'' with 2× 72-bit ECC L2 cache for entry-level servers, as opposed to the 2× 64-bit non-ECC L2 cache on regular models. The extra bits give it error-correction capability built into hardware, without impacting performance. The variant can be determined through the CPU part number.
In Intel's "Family/Model/Stepping" scheme, Klamath CPUs are family 6, model 3.
Deschutes
The ''Deschutes'' core Pentium II (80523), which debuted at 333 MHz in January 1998, was produced with a 0.25 μm process and has a significantly lower power draw. The die size is 113 mm2. The 333 MHz variant was the final Pentium II CPU that used the older 66 MHzfront-side bus
A front-side bus (FSB) is a computer communication interface (bus) that was often used in Intel-chip-based computers during the 1990s and 2000s. The EV6 bus served the same function for competing AMD CPUs. Both typically carry data between the ...
; all subsequent Deschutes-core models used a 100 MHz FSB. Later in 1998, Pentium IIs running at 266, 300, 350, 400, and 450 MHz were also released. The ''Deschutes'' core introduced FXSAVE and FXRSTOR instructions for fast FPU context save and restore. Towards the end of its design life, Deschutes chips capable of 500 MHz within Intel cooling and design specifications were produced. However, these were not marketed. Rather than destroy already multiplier-locked units, those Deschutes units that had been tested and locked with a multiplier of 5 were sold as being 333 MHz. This was accomplished by disabling the 100 MHz bus option. Overclockers, upon learning of this, purchased the units in question and ran them well over 500 MHz; most notably, when overclocking, the final batch of "333 MHz" CPUs were capable of speeds much higher than CPUs sold at 350, 400, or 450 MHz.
Concurrent with the release of Deschutes cores supporting a 100 MHz front-side bus was Intel's release of the 440BX ''Seattle'' chipset and its derivatives, the 440MX, 450NX, and 440ZX chipsets. Replacing the aged 66 MHz FSB, which had been on the market since 1993, the 100 MHz FSB resulted in solid performance improvements for the Pentium II lineup. Pentium II chips starting with 350 MHz were released in both SECC and SECC2 form factors. Late Pentium IIs also marked the switch to flip-chip
Flip chip, also known as controlled collapse chip connection or its abbreviation, C4, is a method for interconnecting dies such as semiconductor devices, IC chips, integrated passive devices and microelectromechanical systems (MEMS), to externa ...
based packaging with direct heatsink contact to the die, as opposed to traditional bonding.
While ''Klamath'' features 4 cache chips and simulates dual-porting through interleaving (2x 64-bit) for a slight performance improvement on concurrent accesses, ''Deschutes'' only sports 2 cache chips and offers slightly lower L2 cache performance at the same clockspeed. Furthermore, ''Deschutes'' always features ECC-enabled L2 cache.
 The Pentium II Xeon was a high-end version of Deschutes core intended for use on workstations and servers. Principally, it used a different type of slot ( Slot 2), case, board design, and more expensive full-speed custom L2 cache, which was off-die. Versions were produced with 512 KB, 1 MB or 2 MB L2 caches by varying the number of 512 KB chips incorporated on the board.
The Pentium II Xeon was a high-end version of Deschutes core intended for use on workstations and servers. Principally, it used a different type of slot ( Slot 2), case, board design, and more expensive full-speed custom L2 cache, which was off-die. Versions were produced with 512 KB, 1 MB or 2 MB L2 caches by varying the number of 512 KB chips incorporated on the board.
 In Intel's "Family/Model/Stepping" scheme, Deschutes CPUs are family 6, model 5 and have the part number 80523.
In Intel's "Family/Model/Stepping" scheme, Deschutes CPUs are family 6, model 5 and have the part number 80523.
Pentium II OverDrive
In 1998, the 0.25 μm Deschutes core was utilized in the creation of thePentium II Overdrive The Pentium OverDrive was a microprocessor marketing brand name used by Intel, to cover a variety of consumer upgrade products sold in the mid-1990s. It was originally released for 486 motherboards, and later some Pentium sockets. Intel dropped the ...
processor, which was aimed at allowing corporate Pentium Pro
The Pentium Pro is a sixth-generation x86 microprocessor developed and manufactured by Intel and introduced on November 1, 1995. It introduced the P6 microarchitecture (sometimes termed i686) and was originally intended to replace the original ...
users to upgrade their aging servers. Combining the Deschutes core in a flip-chip
Flip chip, also known as controlled collapse chip connection or its abbreviation, C4, is a method for interconnecting dies such as semiconductor devices, IC chips, integrated passive devices and microelectromechanical systems (MEMS), to externa ...
package with a 512 KB full-speed L2 cache chip from the Pentium II Xeon into a Socket 8-compatible module resulted in a 300 or 333 MHz processor that could run on a 60 or 66 MHz front-side bus. This combination brought together some of the more attractive aspects of the Pentium II and the Pentium II Xeon: MMX support/improved 16-bit performance and full-speed L2 cache, respectively. The later "Dixon" mobile Pentium II would emulate this combination with 256 KB of full-speed cache.
In Intel's "Family/Model/Stepping" scheme, the Pentium II OverDrive CPU identifies itself as family 6, model 3, though this is misleading, as it is not based on the family 6/model 3 Klamath core. As mentioned in the Pentium II Processor update documentation from Intel, "although this processor has a CPUID of 163xh, it uses a Pentium II processor CPUID 065xh processor core."Tonga
The 0.25 μm ''Tonga'' core was the first mobile Pentium II and had all of the features of the desktop models. In Intel's "Family/Model/Stepping" scheme, Tonga CPUs are family 6, model 5.Dixon
 Later, in 1999, the 0.25; 0.18 (400
Later, in 1999, the 0.25; 0.18 (400 MHz
The hertz (symbol: Hz) is the unit of frequency in the International System of Units (SI), equivalent to one event (or cycle) per second. The hertz is an SI derived unit whose expression in terms of SI base units is s−1, meaning that one he ...
) μm ''Dixon'' core with 256 KB of on-die full speed cache was produced for the mobile market. Reviews showed that the Dixon core was the fastest type of Pentium II produced.
In Intel's "Family/Model/Stepping" scheme, Dixon CPUs are family 6, model 6 and their Intel product code is 80524. These identifiers are shared with the ''Mendocino'' Celeron processors.
Core specifications
Desktop


Klamath (80522)
* L1 cache: 16 + 16 KB (Data + Instructions) * L2 cache: 512 KB, as external chips on the CPU module clocked at half the CPU frequency. * Packaging: Slot 1 module * MMX *Front-side bus
A front-side bus (FSB) is a computer communication interface (bus) that was often used in Intel-chip-based computers during the 1990s and 2000s. The EV6 bus served the same function for competing AMD CPUs. Both typically carry data between the ...
: 66 MHz, GTL+
* VCore: 2.8 V
* Process: 0.35 μm CMOS
* First release: May 7, 1997
* Clockrate: 233, 266, 300 MHz
Deschutes (80523)
* L1 cache: 16 + 16 KB (Data + Instructions) * L2 cache: 512 KB, as external chips on the CPU module clocked at half the CPU frequency. * Packaging: Slot 1 module * MMX *Front-side bus
A front-side bus (FSB) is a computer communication interface (bus) that was often used in Intel-chip-based computers during the 1990s and 2000s. The EV6 bus served the same function for competing AMD CPUs. Both typically carry data between the ...
: 66, 100 MHz, GTL+
* VCore: 2.0 V
* Process: 0.25 μm CMOS
* First release: January 26, 1998
* Clockrate: 266–450 MHz
** 66 MHz FSB : 266, 300, 333 MHz
** 100 MHz FSB: 350, 400, 450 MHz
Deschutes (Pentium II Overdrive)
* L1 cache: 16 + 16 KB (Data + Instructions) * L2 cache: 512 KB external chip on CPU module running at 100% of CPU speed * Socket: Socket 8 *Front-side bus
A front-side bus (FSB) is a computer communication interface (bus) that was often used in Intel-chip-based computers during the 1990s and 2000s. The EV6 bus served the same function for competing AMD CPUs. Both typically carry data between the ...
: 60 or 66 MHz, GTL+
* VCore: 3.1–3.3 V (Has on-board voltage regulator)
* Fabrication: 0.25 μm
* Based on the Deschutes-generation Pentium II
* First release: 1998
* Supports MMX technology
* The sSpec number SL2KE denotes a Pentium II Overdrive sold with an integrated heatsink/fan combination for Socket 8. ote that the sSpec number SL2EA denotes a Pentium II Overdrive sold with an integrated heatsink but no fan for Slot 1.Mobile
Tonga (80523)
 Mobile Pentium II
* L1 cache: 16 + 16 KB (Data + Instructions)
* L2 cache: 512 KB, as external chips on the CPU module clocked at half the CPU frequency.
* Package:
Mobile Pentium II
* L1 cache: 16 + 16 KB (Data + Instructions)
* L2 cache: 512 KB, as external chips on the CPU module clocked at half the CPU frequency.
* Package: MMC-1
Mobile Module Connector 1 (MMC-1) is a 280-pin microprocessor cartridge developed by Intel for used by their mobile Pentium, Pentium MMX, Pentium II and Celeron processors. It contains the microprocessor and its associated L2 cache
A CPU cache ...
, MMC-2
Mobile Module Connector 2 (MMC-2) is Intel's 400-pin processor cartridge used with Pentium II, Celeron and Pentium III mobile processors. It contains CPU, 443BX (Pentium II) Northbridge, off-die L2 cache (early Pentium II only) and voltage regu ...
, Mini-Cartridge
* MMX
* Front-side bus
A front-side bus (FSB) is a computer communication interface (bus) that was often used in Intel-chip-based computers during the 1990s and 2000s. The EV6 bus served the same function for competing AMD CPUs. Both typically carry data between the ...
: 66 MHz, GTL+
* VCore: 1.6 V
* Process: 0.25 μm CMOS
* First release: April 2, 1998
* Clockrate: 233, 266, 300 MHz
Dixon (80524)
 Mobile Pentium II PE ("Performance Enhanced")
* L1 cache: 16 + 16 KB (Data + Instructions)
* L2 cache: 256 KB, on-die, full speed.
* Package:
Mobile Pentium II PE ("Performance Enhanced")
* L1 cache: 16 + 16 KB (Data + Instructions)
* L2 cache: 256 KB, on-die, full speed.
* Package: BGA1
A ball grid array (BGA) is a type of surface-mount packaging (a chip carrier) used for integrated circuits. BGA packages are used to permanently mount devices such as microprocessors. A BGA can provide more interconnection pins than can be put ...
, MMC-1
Mobile Module Connector 1 (MMC-1) is a 280-pin microprocessor cartridge developed by Intel for used by their mobile Pentium, Pentium MMX, Pentium II and Celeron processors. It contains the microprocessor and its associated L2 cache
A CPU cache ...
, MMC-2
Mobile Module Connector 2 (MMC-2) is Intel's 400-pin processor cartridge used with Pentium II, Celeron and Pentium III mobile processors. It contains CPU, 443BX (Pentium II) Northbridge, off-die L2 cache (early Pentium II only) and voltage regu ...
, μPGA1 PPGA-B615
* MMX
* Front-side bus
A front-side bus (FSB) is a computer communication interface (bus) that was often used in Intel-chip-based computers during the 1990s and 2000s. The EV6 bus served the same function for competing AMD CPUs. Both typically carry data between the ...
: 66, 100 MHz, GTL+
* VCore: 1.5, 1.55, 1.6, 2.0 V
* Process: 0.25; 0.18 (400 MHz
The hertz (symbol: Hz) is the unit of frequency in the International System of Units (SI), equivalent to one event (or cycle) per second. The hertz is an SI derived unit whose expression in terms of SI base units is s−1, meaning that one he ...
) μm CMOS
* First release: January 25, 1999
* Clockrate: 266, 300, 333, 366, 400 MHz
* Containing 27.4 million transistor
upright=1.4, gate (G), body (B), source (S) and drain (D) terminals. The gate is separated from the body by an insulating layer (pink).
A transistor is a semiconductor device used to Electronic amplifier, amplify or electronic switch, switch ...
s
* Die size (semiconductor
A semiconductor is a material which has an electrical conductivity value falling between that of a conductor, such as copper, and an insulator, such as glass. Its resistivity falls as its temperature rises; metals behave in the opposite way. ...
chip) is 10.36 mm x 17.36 mm = 179.8496 mm2
See also
* List of Intel Pentium II microprocessors *Intel Celeron
Celeron is Intel's brand name for low-end IA-32 and x86-64 computer microprocessor models targeted at low-cost personal computers.
Celeron processors are compatible with IA-32 software. They typically offer less performance per clock speed comp ...
References
External links
Listing of various PII, PIII, and Celeron alphanumeric model designations
CPU-INFO: Intel Pentium II, indepth processor history
Construction Analysis: Intel 266MHz 32-Bit Pentium II (Klamath) Processor
Integrated Circuit Engineering Corporation Intel datasheets
Pentium II (Klamath)
Pentium II (Deschutes)
Mobile Pentium II (Tonga)
Mobile Pentium II in Micro-PGA and BGA packages (Dixon)
{{DEFAULTSORT:Pentium Ii Computer-related introductions in 1997 Pentium 2 Superscalar microprocessors 32-bit microprocessors