Pentaceratops on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
''Pentaceratops'' ("five-horned face") is a
 The first specimens were collected by
The first specimens were collected by  Sometimes the identification of a specimen as ''Pentaceratops'' has proven to be highly contentious. In 1998 Thomas Lehman described OMNH 10165, a very large skull and its associated
Sometimes the identification of a specimen as ''Pentaceratops'' has proven to be highly contentious. In 1998 Thomas Lehman described OMNH 10165, a very large skull and its associated
 ''Pentaceratops'' was a large
''Pentaceratops'' was a large
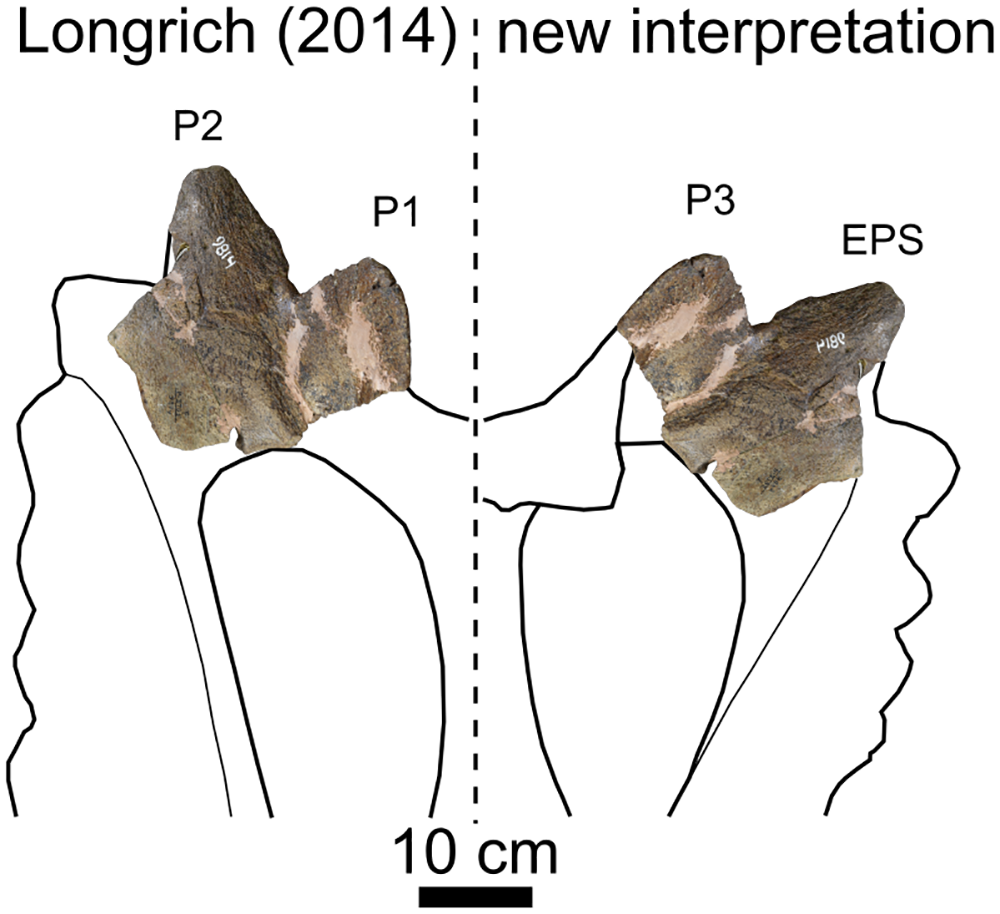
 Longrich stated that the holotype and referred specimen of ''P. aquilonius'' fall within the diagnosis of ''Pentaceratops'', and were recovered very close to the type species in the phylogeny. He noted that the placement of ''Utahceratops'' does not make the genus
Longrich stated that the holotype and referred specimen of ''P. aquilonius'' fall within the diagnosis of ''Pentaceratops'', and were recovered very close to the type species in the phylogeny. He noted that the placement of ''Utahceratops'' does not make the genus
The Kirtlandian land-vertebrate "age" – faunal composition, temporal position and biostratigraphic correlation in the nonmarine Upper Cretaceous of western North America
" New Mexico Museum of Natural History and Science, Bulletin 35:7-29. * * Lucas, S.G., Sullivan, R.M., Hunt, A.P., 2006, Re-evaluation of ''Pentaceratops'' and ''Chasmosaurus'' (Ornithischia, Ceratopsidae) in the Upper Cretaceous of the Western Interior: New Mexico Museum of Natural History and Science, Bulletin 35
genus
Genus ( plural genera ) is a taxonomic rank used in the biological classification of living and fossil organisms as well as viruses. In the hierarchy of biological classification, genus comes above species and below family. In binomial nom ...
of herbivorous ceratopsid
Ceratopsidae (sometimes spelled Ceratopidae) is a family of ceratopsian dinosaurs including ''Triceratops'', ''Centrosaurus'', and ''Styracosaurus''. All known species were quadrupedal herbivores from the Upper Cretaceous. All but one species are ...
dinosaur
Dinosaurs are a diverse group of reptiles of the clade Dinosauria. They first appeared during the Triassic period, between 243 and 233.23 million years ago (mya), although the exact origin and timing of the evolution of dinosaurs is t ...
from the late Cretaceous
The Cretaceous ( ) is a geological period that lasted from about 145 to 66 million years ago (Mya). It is the third and final period of the Mesozoic Era, as well as the longest. At around 79 million years, it is the longest geological period of ...
Period of what is now North America
North America is a continent in the Northern Hemisphere and almost entirely within the Western Hemisphere. It is bordered to the north by the Arctic Ocean, to the east by the Atlantic Ocean, to the southeast by South America and th ...
. Fossils of this animal were first discovered in 1921, but the genus was named in 1923 when its type species
In zoological nomenclature, a type species (''species typica'') is the species name with which the name of a genus or subgenus is considered to be permanently taxonomically associated, i.e., the species that contains the biological type specim ...
, ''Pentaceratops sternbergii'', was described. ''Pentaceratops'' lived around 76–73 million years ago
The abbreviation Myr, "million years", is a unit of a quantity of (i.e. ) years, or 31.556926 teraseconds.
Usage
Myr (million years) is in common use in fields such as Earth science and cosmology. Myr is also used with Mya (million years ago ...
, its remains having been mostly found in the Kirtland Formation
The Kirtland Formation (originally the Kirtland Shale) is a sedimentary geological formation.
Description
The Kirtland Formation is the product of alluvial muds and overbank sand deposits from the many channels draining the coastal plain th ...
in the San Juan Basin in New Mexico
)
, population_demonym = New Mexican ( es, Neomexicano, Neomejicano, Nuevo Mexicano)
, seat = Santa Fe, New Mexico, Santa Fe
, LargestCity = Albuquerque, New Mexico, Albuquerque
, LargestMetro = Albuquerque metropolitan area, Tiguex
, Offi ...
. About a dozen skulls and skeletons have been uncovered, so anatomical understanding of ''Pentaceratops'' is fairly complete. One exceptionally large specimen later became its own genus, '' Titanoceratops'', due to its more derived morphology, similarities to ''Triceratops
''Triceratops'' ( ; ) is a genus of herbivorous chasmosaurine ceratopsid dinosaur that first appeared during the late Maastrichtian stage of the Late Cretaceous period, about 68 million years ago in what is now North America. It is one ...
,'' and lack of unique characteristics shared with ''Pentaceratops''.
''Pentaceratops'' was about 6 meters (20 feet) long, and has been estimated to have weighed around . It had a short nose horn, two long brow horns, and long horns on the jugal bone
The jugal is a skull bone found in most reptiles, amphibians and birds. In mammals, the jugal is often called the malar or zygomatic. It is connected to the quadratojugal and maxilla, as well as other bones, which may vary by species.
Ana ...
s. Its skull had a very long frill with triangular hornlets on the edge.
Discoveries and species
 The first specimens were collected by
The first specimens were collected by Charles Hazelius Sternberg
Charles Hazelius Sternberg (June 15, 1850 – July 20, 1943) was an American fossil collector and paleontologist. He was active in both fields from 1876 to 1928, and collected fossils for Edward Drinker Cope and Othniel C. Marsh, and for the ...
in the San Juan Basin in New Mexico
)
, population_demonym = New Mexican ( es, Neomexicano, Neomejicano, Nuevo Mexicano)
, seat = Santa Fe, New Mexico, Santa Fe
, LargestCity = Albuquerque, New Mexico, Albuquerque
, LargestMetro = Albuquerque metropolitan area, Tiguex
, Offi ...
. Sternberg worked in commission for the Swedish Uppsala University
Uppsala University ( sv, Uppsala universitet) is a public research university in Uppsala, Sweden. Founded in 1477, it is the oldest university in Sweden and the Nordic countries still in operation.
The university rose to significance during ...
. In 1921 he recovered a skull and a rump, specimens PMU R.200 and PMU R.286, at the Meyers Creek near the Kimbetoh Wash in a layer of the Kirtland Formation
The Kirtland Formation (originally the Kirtland Shale) is a sedimentary geological formation.
Description
The Kirtland Formation is the product of alluvial muds and overbank sand deposits from the many channels draining the coastal plain th ...
. He sent these fossils to paleontologist Carl Wiman. In 1922 Sternberg decided to work independently and began a dig north of Tsaya Trading Post, in the Fossil Forest of San Juan County. Here he discovered a complete skeleton, which he sold to the American Museum of Natural History
The American Museum of Natural History (abbreviated as AMNH) is a natural history museum on the Upper West Side of Manhattan in New York City. In Theodore Roosevelt Park, across the street from Central Park, the museum complex comprises 26 int ...
. The museum then sent out a team headed by Charles Mook and Peter Kaisen to assist Sternberg in securing this specimen; subsequent digging by Sternberg in 1923 brought the total of AMNH specimens to four. The rump of the main specimen was discarded by the museum because it had insufficient value as a display.
The species was named and described by Henry Fairfield Osborn in 1923, as ''Pentaceratops sternbergii''. The generic name means "five-horned face", derived from the Greek
Greek may refer to:
Greece
Anything of, from, or related to Greece, a country in Southern Europe:
*Greeks, an ethnic group.
*Greek language, a branch of the Indo-European language family.
**Proto-Greek language, the assumed last common ancestor ...
''penta'' (πέντα, meaning five), ''keras'' (κέρας, horn) and ''-ops'' (ὤψ, face), in reference to its two long epijugal bones, spikes which protrude out sidewards from under its eyes, in addition to the three more obvious horns as with ''Triceratops
''Triceratops'' ( ; ) is a genus of herbivorous chasmosaurine ceratopsid dinosaur that first appeared during the late Maastrichtian stage of the Late Cretaceous period, about 68 million years ago in what is now North America. It is one ...
''. Osborn obligingly gave it the specific name ''sternbergii'' to honor its discoverer.H.F. Osborn, 1923, "A new genus and species of Ceratopsia from New Mexico, ''Pentaceratops sternbergii'', ''American Museum Novitates'' 93: 1-3 The name had been suggested to Osborn by William Diller Matthew
William Diller Matthew FRS (February 19, 1871 – September 24, 1930) was a vertebrate paleontologist who worked primarily on mammal fossils, although he also published a few early papers on mineralogy, petrological geology, one on botany, one on ...
; the specific epithet served as a consolation to the almost bankrupt Sternberg whose 1923 fossils were initially not acquired by the museum that had to use its 1923/1924 budget to process the finds of the great Asian expeditions by Roy Chapman Andrews
Roy Chapman Andrews (January 26, 1884 – March 11, 1960) was an American explorer, adventurer and naturalist who became the director of the American Museum of Natural History. He led a series of expeditions through the politically disturbed ...
.
The holotype
A holotype is a single physical example (or illustration) of an organism, known to have been used when the species (or lower-ranked taxon) was formally described. It is either the single such physical example (or illustration) or one of seve ...
was the skull discovered by Sternberg in 1922, specimen AMNH 6325. It was found in a layer of the Fruitland Formation, dating from the Campanian
The Campanian is the fifth of six ages of the Late Cretaceous Epoch on the geologic timescale of the International Commission on Stratigraphy (ICS). In chronostratigraphy, it is the fifth of six stages in the Upper Cretaceous Series. Campani ...
, about seventy-five million years old. The other three AMNH specimens were AMNH 1624, a smaller skull; AMNH 1622, a pair of brow horns; and AMNH 1625, a piece of skull frill.
In 1930, Wiman named a second species of ''Pentaceratops'': ''P. fenestratus''. It was based on Sternberg's 1921 specimens and the specific name referred to a hole in the left squamosal The squamosal is a skull bone found in most reptiles, amphibians, and birds. In fishes, it is also called the pterotic bone.
In most tetrapods, the squamosal and quadratojugal bones form the cheek series of the skull. The bone forms an ancestral co ...
.C. Wiman, 1930, "Über Ceratopsia aus der Oberen Kreide in New Mexico", ''Nova Acta Regiae Societatis Scientiarum Upsaliensis, Series 4'' 7(2): 1-19 This was later considered to be the same species as ''Pentaceratops sternbergii'' and thus a junior synonym
The Botanical and Zoological Codes of nomenclature treat the concept of synonymy differently.
* In botanical nomenclature, a synonym is a scientific name that applies to a taxon that (now) goes by a different scientific name. For example, Linn ...
, the hole being the likely effect of an injury.
In 1929 Sternberg's son, George Fryer Sternberg
George Fryer Sternberg (1883–1969) was a paleontologist best known for his discovery in Gove County, Kansas of the "fish-within-a-fish" of ''Xiphactinus audax'' with a recently eaten ''Gillicus arcuatus'' within its stomach. Sternberg was bor ...
, discovered specimen USNM V12002, a right squamosal. ''Pentaceratops'' proved to be a quite common fossil in the Fruitland and Kirtland formations. It has even been used as a guide fossil
Biostratigraphy is the branch of stratigraphy which focuses on correlating and assigning relative ages of rock strata by using the fossil assemblages contained within them.Hine, Robert. “Biostratigraphy.” ''Oxford Reference: Dictionary of ...
: the appearance of ''Pentaceratops sternbergii'' in the fossil record marks the end of the Judithian
The Judithian was a North American faunal stage lasting from 83.5 to 70.6 million years ago. It overlaps with the Campanian global stage.
Fauna
Dinosaur faunas of the Judithian age may represent the peak of dinosaur evolution in North America. H ...
land vertebrate age and the start of the Kirtlandian. Subsequent finds include specimens MNA Pl. 1668, MNA Pl. 1747, NMMNH P-27468 and USNM 2416, partial skeletons with skull; YPM 1229, a skeleton lacking the skull; UALP 13342 and UKVP 16100, skulls; UNM B-1701, USNM 12741, USNM 12743, USNM 8604, SMP VP-1596, SMP VP-1488, SMP VP-1500 and SMP VP-1712, fragmentary skulls. Apart from the San Juan Basin finds, a juvenile specimen of ''Pentaceratops'', SDMNH 43470, was found in the Williams Fork Formation of Colorado
Colorado (, other variants) is a state in the Mountain West subregion of the Western United States. It encompasses most of the Southern Rocky Mountains, as well as the northeastern portion of the Colorado Plateau and the western edge of the ...
in 2006.
 Sometimes the identification of a specimen as ''Pentaceratops'' has proven to be highly contentious. In 1998 Thomas Lehman described OMNH 10165, a very large skull and its associated
Sometimes the identification of a specimen as ''Pentaceratops'' has proven to be highly contentious. In 1998 Thomas Lehman described OMNH 10165, a very large skull and its associated skeleton
A skeleton is the structural frame that supports the body of an animal. There are several types of skeletons, including the exoskeleton, which is the stable outer shell of an organism, the endoskeleton, which forms the support structure inside ...
found in New Mexico in 1941. The skull is presently on display at the Sam Noble Oklahoma Museum of Natural History, and is the largest ''Pentaceratops'' exemplar known, with the distinction of having produced the largest known skull
The skull is a bone protective cavity for the brain. The skull is composed of four types of bone i.e., cranial bones, facial bones, ear ossicles and hyoid bone. However two parts are more prominent: the cranium and the mandible. In humans, th ...
of any land vertebrate
Vertebrates () comprise all animal taxa within the subphylum Vertebrata () ( chordates with backbones), including all mammals, birds, reptiles, amphibians, and fish. Vertebrates represent the overwhelming majority of the phylum Chordata, with ...
.Lehman, T.M., 1998, "A gigantic skull and skeleton of the horned dinosaur ''Pentaceratops sternbergi'' from New Mexico: Journal of Paleontology, 72(5): 894-906 However, in 2011, the skeleton was renamed as a separate genus, '' Titanoceratops'', due to its more derived morphology, similarities to ''Triceratops
''Triceratops'' ( ; ) is a genus of herbivorous chasmosaurine ceratopsid dinosaur that first appeared during the late Maastrichtian stage of the Late Cretaceous period, about 68 million years ago in what is now North America. It is one ...
,'' and lack of unique characteristics shared with ''Pentaceratops''.
In 2014 Nicholas Longrich
Nicholas is a male given name and a surname.
The Eastern Orthodox Church, the Roman Catholic Church, and the Anglican Churches celebrate Saint Nicholas every year on December 6, which is the name day for "Nicholas". In Greece, the name and i ...
named a new species: ''Pentaceratops aquilonius'', "the northern one," based on fragmentary fossils discovered during the 1930s near Manyberries in Alberta
Alberta ( ) is one of the thirteen provinces and territories of Canada. It is part of Western Canada and is one of the three prairie provinces. Alberta is bordered by British Columbia to the west, Saskatchewan to the east, the Northwest T ...
, Canada
Canada is a country in North America. Its ten provinces and three territories extend from the Atlantic Ocean to the Pacific Ocean and northward into the Arctic Ocean, covering over , making it the world's second-largest country by to ...
. The species has been described as having a first epiparietal pointing upwards instead of forwards. In 2016, Mallon ''et al.'' found ''P. aquilonius'' to be morphologically similar to ''Spiclypeus shipporum
''Spiclypeus'' (meaning "spike shield") is an extinct genus of chasmosaurine ceratopsian dinosaur known from the Late Cretaceous Judith River Formation (late Campanian stage) of Montana, United States.
Discovery
In 2000, Bill D. Shipp, a nuclea ...
'', with it possibly being the same species, and considered ''P. aquilonius'' a ''nomen dubium
In binomial nomenclature, a ''nomen dubium'' (Latin for "doubtful name", plural ''nomina dubia'') is a scientific name that is of unknown or doubtful application.
Zoology
In case of a ''nomen dubium'' it may be impossible to determine whether a s ...
''.
Description
 ''Pentaceratops'' was a large
''Pentaceratops'' was a large ceratopsid
Ceratopsidae (sometimes spelled Ceratopidae) is a family of ceratopsian dinosaurs including ''Triceratops'', ''Centrosaurus'', and ''Styracosaurus''. All known species were quadrupedal herbivores from the Upper Cretaceous. All but one species are ...
; Dodson estimated the body length at . The skull length of AMNH 1624 is while PMU R.200 has a length of . In 2016 Paul estimated its length at 5.5 meters (18 ft) and its weight at 2.5 metric tons (2.75 short tons). The nose horn of ''Pentaceratops'' is small and pointing upward and backward. The brow horns are very long and curving strongly forward. The somewhat upward tilted frill of ''Pentaceratops'' is considerably longer than that of ''Triceratops
''Triceratops'' ( ; ) is a genus of herbivorous chasmosaurine ceratopsid dinosaur that first appeared during the late Maastrichtian stage of the Late Cretaceous period, about 68 million years ago in what is now North America. It is one ...
'', with two large holes (parietal fenestrae
A fenestra (fenestration; plural fenestrae or fenestrations) is any small opening or pore, commonly used as a term in the biological sciences. It is the Latin word for "window", and is used in various fields to describe a pore in an anatomical st ...
) in it. It is rectangular, adorned by large triangular osteoderm
Osteoderms are bony deposits forming scales, plates, or other structures based in the dermis. Osteoderms are found in many groups of extant and extinct reptiles and amphibians, including lizards, crocodilians, frogs, temnospondyls (extinct amp ...
s: up to twelve episquamosals at the squamosal The squamosal is a skull bone found in most reptiles, amphibians, and birds. In fishes, it is also called the pterotic bone.
In most tetrapods, the squamosal and quadratojugal bones form the cheek series of the skull. The bone forms an ancestral co ...
and three epiparietals at the parietal bone
The parietal bones () are two bones in the skull which, when joined at a fibrous joint, form the sides and roof of the cranium. In humans, each bone is roughly quadrilateral in form, and has two surfaces, four borders, and four angles. It is n ...
. These are largest at the rear corners of the frill, and are separated by a large U-shaped notch at the midline, a feature not recognized until 1981 when specimen UKVP 16100 was described.Rowe, T., Colbert, E.H. and Nations, J.D., 1981, "The occurrence of ''Pentaceratops'' with a description of its frill", In: Lucas, S.G., Rigby, J.K. and Kues, B.S. (eds.) ''Advances in San Juan Basin Paleontology'', University of New Mexico Press, Alburquerque p. 29-48 Within the notch the first epiparietals point forwards. The very thick jugal and the squamosal do not touch each other, a possible autapomorphy
In phylogenetics, an autapomorphy is a distinctive feature, known as a derived trait, that is unique to a given taxon. That is, it is found only in one taxon, but not found in any others or outgroup taxa, not even those most closely related to ...
.
The torso of ''Pentaceratops'' is tall and wide. The rear dorsal vertebrae bear long spines from which ligaments possibly ran to the front, to balance the high frill. The prepubis is long. The ischium
The ischium () form ...
is long and strongly curves forward. In smaller specimens the thigh bone bows outwards.Paul, G.S., 2010, ''The Princeton Field Guide to Dinosaurs'', Princeton University Press p. 272
Classification
Osborn originally assigned ''Pentaceratops'' toCeratopsia
Ceratopsia or Ceratopia ( or ; Greek: "horned faces") is a group of herbivorous, beaked dinosaurs that thrived in what are now North America, Europe, and Asia, during the Cretaceous Period, although ancestral forms lived earlier, in the Jurass ...
. Within this group ''Pentaceratops'' belonged to the Ceratopsinae or Chasmosaurinae
Chasmosaurinae is a subfamily of ceratopsid dinosaurs. They were one of the most successful groups of herbivores of their time. Chasmosaurines appeared in the early Campanian, and became extinct, along with all other non-avian dinosaurs, durin ...
. It appears to be most closely related to '' Utahceratops''. Their clade
A clade (), also known as a monophyletic group or natural group, is a group of organisms that are monophyletic – that is, composed of a common ancestor and all its lineal descendants – on a phylogenetic tree. Rather than the English ter ...
was perhaps more derived than the earlier genus '' Chasmosaurus'' but more basal than ''Anchiceratops
''Anchiceratops'' ( ) is an extinct genus of chasmosaurine ceratopsid dinosaur that lived approximately 72 to 71 million years ago during the latter part of the Cretaceous Period in what is now Alberta, Canada.
''Anchiceratops'' was a medium-siz ...
'', the latter representing a line of which ''Triceratops'' was a member, which lived a few million years later, right at the end of the Cretaceous period, when all ceratopsians died out.
The cladogram
A cladogram (from Greek ''clados'' "branch" and ''gramma'' "character") is a diagram used in cladistics to show relations among organisms. A cladogram is not, however, an evolutionary tree because it does not show how ancestors are related to ...
of the phylogeny
A phylogenetic tree (also phylogeny or evolutionary tree Felsenstein J. (2004). ''Inferring Phylogenies'' Sinauer Associates: Sunderland, MA.) is a branching diagram or a tree showing the evolutionary relationships among various biological s ...
of ''Pentaceratops'' according to a study by Scott Sampson
Scott Donald Sampson (born April 22, 1961) is a Canadian paleontologist and science communicator. Sampson is currently the Executive Director of California Academy of Sciences in San Francisco, California. He was previously Vice President of Res ...
''et al.'' in 2010 found that the genus was most closely related to ''Utahceratops'', from a similar age and region. The below cladogram follows Longrich (2014), who named a new species of ''Pentaceratops'', and included nearly all chasmosaurine species.
paraphyletic
In taxonomy, a group is paraphyletic if it consists of the group's last common ancestor and most of its descendants, excluding a few monophyletic subgroups. The group is said to be paraphyletic ''with respect to'' the excluded subgroups. In ...
, as there is no requirement that genera are monophyletic
In cladistics for a group of organisms, monophyly is the condition of being a clade—that is, a group of taxa composed only of a common ancestor (or more precisely an ancestral population) and all of its lineal descendants. Monophyletic gr ...
. The Williams Fork chasmosaur differs from the ''Pentaceratops'' and ''Utahceratops'' species, and might require a new specific or generic name.
Paleobiology
''Pentaceratops'', like all ceratopsians, was anherbivore
A herbivore is an animal anatomically and physiologically adapted to eating plant material, for example foliage or marine algae, for the main component of its diet. As a result of their plant diet, herbivorous animals typically have mouthpar ...
. During the Cretaceous, flowering plants were "geographically limited on the landscape" and so it is likely that this dinosaur fed on the predominant plants of the era: fern
A fern (Polypodiopsida or Polypodiophyta ) is a member of a group of vascular plants (plants with xylem and phloem) that reproduce via spores and have neither seeds nor flowers. The polypodiophytes include all living pteridophytes exce ...
s, cycads
Cycads are seed plants that typically have a stout and woody ( ligneous) trunk with a crown of large, hard, stiff, evergreen and (usually) pinnate leaves. The species are dioecious, that is, individual plants of a species are either male or ...
and conifers
Conifers are a group of cone-bearing seed plants, a subset of gymnosperms. Scientifically, they make up the division Pinophyta (), also known as Coniferophyta () or Coniferae. The division contains a single extant class, Pinopsida. All ext ...
. It would have used its sharp ceratopsian beak to bite off the branches which were then shredded - leaves, needles and all - by the tooth batteries, providing a self-sharpening continuous cutting edge in both upper and lower jaws. Ultimately the plant material was digested by the large gut.
Paleoecology
''Pentaceratops'' lived around 76–73million years ago
The abbreviation Myr, "million years", is a unit of a quantity of (i.e. ) years, or 31.556926 teraseconds.
Usage
Myr (million years) is in common use in fields such as Earth science and cosmology. Myr is also used with Mya (million years ago ...
, its remains having been mostly found in the Kirtland Formation
The Kirtland Formation (originally the Kirtland Shale) is a sedimentary geological formation.
Description
The Kirtland Formation is the product of alluvial muds and overbank sand deposits from the many channels draining the coastal plain th ...
in the San Juan Basin in New Mexico
)
, population_demonym = New Mexican ( es, Neomexicano, Neomejicano, Nuevo Mexicano)
, seat = Santa Fe, New Mexico, Santa Fe
, LargestCity = Albuquerque, New Mexico, Albuquerque
, LargestMetro = Albuquerque metropolitan area, Tiguex
, Offi ...
. Other dinosaurs that shared its habitat
In ecology, the term habitat summarises the array of resources, physical and biotic factors that are present in an area, such as to support the survival and reproduction of a particular species. A species habitat can be seen as the physical ...
include '' Parasaurolophus cyrtocristatus'', the pachycephalosaur '' Sphaerotholus'', the armored dinosaur ''Nodocephalosaurus
''Nodocephalosaurus'' (meaning "knob headed lizard") is a monospecific genus of ankylosaurid dinosaur from New Mexico that lived during the Late Cretaceous (late Campanian to early Maastrichtian stage, 73.49 to 73.04 Ma) in what is now the De-n ...
'' and the tyrannosauroid ''Bistahieversor
''Bistahieversor'' (meaning "Bistahi destroyer"), also known as the "Bisti Beast", is a genus of eutyrannosaurian tyrannosauroid dinosaur; the genus contains only a single known species, ''B. sealeyi'', described in 2010, from the Late Cretaceo ...
''.
See also
* Timeline of ceratopsian research * Ah-Shi-Sle-Pah Wilderness Study Area, the type locality for ''Pentaceratops fenestratus''References
Sources
* * * Lehman, T. M., 2001, Late Cretaceous dinosaur provinciality: In: Mesozoic Vertebrate Life, edited by Tanke, D. H., and Carpenter, K., Indiana University Press, pp. 310–328. * * Sullivan, R.M., and Lucas, S.G. 2006.The Kirtlandian land-vertebrate "age" – faunal composition, temporal position and biostratigraphic correlation in the nonmarine Upper Cretaceous of western North America
" New Mexico Museum of Natural History and Science, Bulletin 35:7-29. * * Lucas, S.G., Sullivan, R.M., Hunt, A.P., 2006, Re-evaluation of ''Pentaceratops'' and ''Chasmosaurus'' (Ornithischia, Ceratopsidae) in the Upper Cretaceous of the Western Interior: New Mexico Museum of Natural History and Science, Bulletin 35
External links
* * * {{Taxonbar, from=Q131253 Chasmosaurines Late Cretaceous dinosaurs of North America Fossil taxa described in 1923 Taxa named by Henry Fairfield Osborn Kirtland fauna Paleontology in New Mexico Campanian genus first appearances Campanian genus extinctions Ornithischian genera