Pea galaxy on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]

 A Pea galaxy, also referred to as a Pea or Green Pea, might be a type of luminous blue compact galaxy that is undergoing very high rates of star formation. Pea galaxies are so-named because of their small size and greenish appearance in the images taken by the Sloan Digital Sky Survey (SDSS).
"Pea" galaxies were first discovered in 2007 by the volunteer citizen scientists within the forum section of the online
A Pea galaxy, also referred to as a Pea or Green Pea, might be a type of luminous blue compact galaxy that is undergoing very high rates of star formation. Pea galaxies are so-named because of their small size and greenish appearance in the images taken by the Sloan Digital Sky Survey (SDSS).
"Pea" galaxies were first discovered in 2007 by the volunteer citizen scientists within the forum section of the online
 In January 2016, a study was published in the journal
In January 2016, a study was published in the journal
 In a presentation to the American Astronomical Society Meeting #229 in January 2017, Matt Brorby and Philip Kaaret describe the observations of two GPs and their x-ray emission. Using both space telescope programs
In a presentation to the American Astronomical Society Meeting #229 in January 2017, Matt Brorby and Philip Kaaret describe the observations of two GPs and their x-ray emission. Using both space telescope programs
 In May 2015, authors Alaina Henry, Claudia Scarlata, Crystal Martin, and Dawn Erb published a paper titled: "Lyα Emission from Green Peas: The Role of Circumgalactic Gas Density, Covering, and Kinematics". The motivation of this work was to understand why some galaxies have Lyα emission, while others don't. A host of physical conditions in galaxies regulate the output of this spectral feature; hence, understanding its emission is fundamentally important for understanding how galaxies form and how they impact their intergalactic surroundings.
Henry et al. hypothesized that, since the GPs seem more like galaxies at redshift=z>2, and Lyα is common at these redshifts, that Lyα would be common in the GPs as well. Observations with the HST using the COS, as in 'Description', proved this to be true for a sample of 10 GPs. The spectra, shown here to the right, indicate resonant scattering of Lyα photons that are emitted near zero velocity. The wealth of data existing on the GPs, combined with the COS spectra, allowed Henry et al. to explore the physical mechanisms that regulate the Lyα output. These authors concluded that variations in the amount of neutral hydrogen gas, which scatters Lyα photons, are the cause of a factor of 10 difference in Lyα output in their sample.
The spectrum of GP_J1219 (an image of which is in 'Description') shows its very strong flux measurements when compared to other 9 GPs. Indeed, only GP_J1214 has a value approaching that of J1219. Note also the double peaks in some GPs and the velocity values of the emissions, indicating the inflow and outflow of matter in the GPs.
In May 2015, authors Alaina Henry, Claudia Scarlata, Crystal Martin, and Dawn Erb published a paper titled: "Lyα Emission from Green Peas: The Role of Circumgalactic Gas Density, Covering, and Kinematics". The motivation of this work was to understand why some galaxies have Lyα emission, while others don't. A host of physical conditions in galaxies regulate the output of this spectral feature; hence, understanding its emission is fundamentally important for understanding how galaxies form and how they impact their intergalactic surroundings.
Henry et al. hypothesized that, since the GPs seem more like galaxies at redshift=z>2, and Lyα is common at these redshifts, that Lyα would be common in the GPs as well. Observations with the HST using the COS, as in 'Description', proved this to be true for a sample of 10 GPs. The spectra, shown here to the right, indicate resonant scattering of Lyα photons that are emitted near zero velocity. The wealth of data existing on the GPs, combined with the COS spectra, allowed Henry et al. to explore the physical mechanisms that regulate the Lyα output. These authors concluded that variations in the amount of neutral hydrogen gas, which scatters Lyα photons, are the cause of a factor of 10 difference in Lyα output in their sample.
The spectrum of GP_J1219 (an image of which is in 'Description') shows its very strong flux measurements when compared to other 9 GPs. Indeed, only GP_J1214 has a value approaching that of J1219. Note also the double peaks in some GPs and the velocity values of the emissions, indicating the inflow and outflow of matter in the GPs.
 At the time this paper was published, only five Green Peas (GPs) had been imaged by the
At the time this paper was published, only five Green Peas (GPs) had been imaged by the 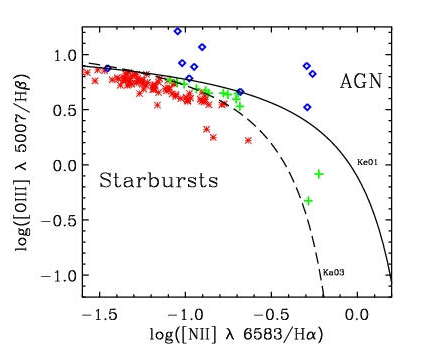 GPs are rare. Of the one million objects that make up GZ's image bank, only 251 GPs were found. After having to discard 148 of these 251 because of atmospheric contamination of their
GPs are rare. Of the one million objects that make up GZ's image bank, only 251 GPs were found. After having to discard 148 of these 251 because of atmospheric contamination of their 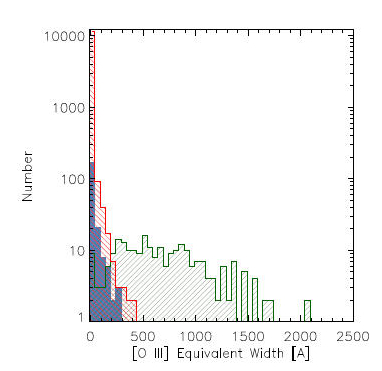 GPs have a strong IIIemission line when compared to the rest of their spectral continuum. In a SDSS spectrum, this shows up as a large peak with IIIat the top. The wavelength of III(500.7 nm) was chosen to determine the luminosities of the GPs using
GPs have a strong IIIemission line when compared to the rest of their spectral continuum. In a SDSS spectrum, this shows up as a large peak with IIIat the top. The wavelength of III(500.7 nm) was chosen to determine the luminosities of the GPs using 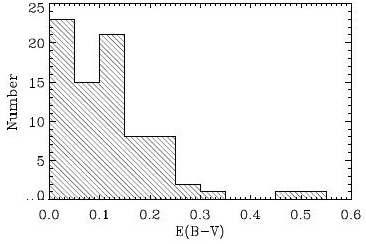 GPs have low
GPs have low  As well as the optical images from the SDSS, measurements from the GALEX survey were used to determine the ultraviolet values. This survey is well matched in depth and area, and 139 of the sampled 251 GPs are found in GALEX Release 4 (G.R.4). For the 56 of the 80 star-forming GPs with GALEX detections, the median luminosity is ~30,000 million (~30,000 million solar luminosities).
When compiling the Cardamone paper, spectral classification was made using Gas And Absorption Line Fitting (GANDALF). This sophisticated computer software was programmed by Marc Sarzi, who helped analyze the SDSS spectra.
As well as the optical images from the SDSS, measurements from the GALEX survey were used to determine the ultraviolet values. This survey is well matched in depth and area, and 139 of the sampled 251 GPs are found in GALEX Release 4 (G.R.4). For the 56 of the 80 star-forming GPs with GALEX detections, the median luminosity is ~30,000 million (~30,000 million solar luminosities).
When compiling the Cardamone paper, spectral classification was made using Gas And Absorption Line Fitting (GANDALF). This sophisticated computer software was programmed by Marc Sarzi, who helped analyze the SDSS spectra.
 Color selection was by using the difference in the levels of three
Color selection was by using the difference in the levels of three
 Amorin et al. find that the amount of metals, including the abundance of nitrogen, are different from normal values and that GPs are not consistent with the mass-metallicity relation, as concluded by Cardamone et al. This analysis indicates that GPs can be considered as genuine metal-poor galaxies. They then argue that this oxygen under-abundance is due to a recent interaction-induced inflow of gas, possibly coupled with a selective metal-rich gas loss driven by supernovae winds and that this can explain their findings. This further suggests that GPs are likely very short-lived as the intense star formation in them would quickly enrich the gas.
Amorin et al. find that the amount of metals, including the abundance of nitrogen, are different from normal values and that GPs are not consistent with the mass-metallicity relation, as concluded by Cardamone et al. This analysis indicates that GPs can be considered as genuine metal-poor galaxies. They then argue that this oxygen under-abundance is due to a recent interaction-induced inflow of gas, possibly coupled with a selective metal-rich gas loss driven by supernovae winds and that this can explain their findings. This further suggests that GPs are likely very short-lived as the intense star formation in them would quickly enrich the gas.
 In May 2011, R.Amorin, J.M.Vilchez and E.Perez-Montero published a conference proceeding paper titled "Unveiling the Nature of the "Green Pea" galaxies". In it they review recent scientific results and announcing a forthcoming paper on their recent observations at the
In May 2011, R.Amorin, J.M.Vilchez and E.Perez-Montero published a conference proceeding paper titled "Unveiling the Nature of the "Green Pea" galaxies". In it they review recent scientific results and announcing a forthcoming paper on their recent observations at the  The second graph (on the right; fig.2 in paper) plots O/H vs. stellar mass. The 2D histogram of SDSS SFGs is shown in logarithmic scale and their best likelihood fit is shown by a black solid line. The subset of 62 GPs are indicated by circles and their best linear fit is shown by a dashed line. For comparison we also show the quadratic fit presented in Amorin ''et al.'' 2010 for the full sample of 80 GPs. SFGs at z ≥ 2 by Erb et al. are also shown by asterisks for comparison.
The second graph (on the right; fig.2 in paper) plots O/H vs. stellar mass. The 2D histogram of SDSS SFGs is shown in logarithmic scale and their best likelihood fit is shown by a black solid line. The subset of 62 GPs are indicated by circles and their best linear fit is shown by a dashed line. For comparison we also show the quadratic fit presented in Amorin ''et al.'' 2010 for the full sample of 80 GPs. SFGs at z ≥ 2 by Erb et al. are also shown by asterisks for comparison.
 The third graph (on the left; fig.3 in paper) plots N/O vs. stellar mass. Symbols as in fig.1.
The third graph (on the left; fig.3 in paper) plots N/O vs. stellar mass. Symbols as in fig.1.
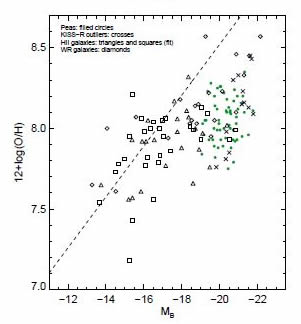
 The fourth graph (on the right; fig.4 in paper) plots O/H vs. B-band (rest-frame) absolute magnitude. The meaning of symbols is indicated. Distances used in computing (extinction corrected) absolute magnitudes were, in all cases, calculated using spectroscopic redshifts and the same cosmological parameters. The dashed line indicates the fit to the HII galaxies in the Luminosity-Metallicity Relationship (MZR) given by Lee et al. 2004.
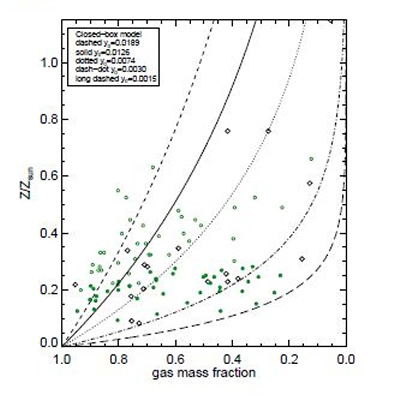
The fifth graph (on the left; fig.5 in paper) plots gas mass fraction vs. metallicity. Different lines correspond to closed-box models at different yields, as indicated in the legend. Open and filled circles are GPs which are above and below the fit to their MZR. Diamonds are values for the same Wolf-Rayet galaxies as in Fig. 4.
The fourth graph (on the right; fig.4 in paper) plots O/H vs. B-band (rest-frame) absolute magnitude. The meaning of symbols is indicated. Distances used in computing (extinction corrected) absolute magnitudes were, in all cases, calculated using spectroscopic redshifts and the same cosmological parameters. The dashed line indicates the fit to the HII galaxies in the Luminosity-Metallicity Relationship (MZR) given by Lee et al. 2004.
The fifth graph (on the left; fig.5 in paper) plots gas mass fraction vs. metallicity. Different lines correspond to closed-box models at different yields, as indicated in the legend. Open and filled circles are GPs which are above and below the fit to their MZR. Diamonds are values for the same Wolf-Rayet galaxies as in Fig. 4.

 A Pea galaxy, also referred to as a Pea or Green Pea, might be a type of luminous blue compact galaxy that is undergoing very high rates of star formation. Pea galaxies are so-named because of their small size and greenish appearance in the images taken by the Sloan Digital Sky Survey (SDSS).
"Pea" galaxies were first discovered in 2007 by the volunteer citizen scientists within the forum section of the online
A Pea galaxy, also referred to as a Pea or Green Pea, might be a type of luminous blue compact galaxy that is undergoing very high rates of star formation. Pea galaxies are so-named because of their small size and greenish appearance in the images taken by the Sloan Digital Sky Survey (SDSS).
"Pea" galaxies were first discovered in 2007 by the volunteer citizen scientists within the forum section of the online astronomy
Astronomy () is a natural science that studies celestial objects and phenomena. It uses mathematics, physics, and chemistry in order to explain their origin and evolution. Objects of interest include planets, moons, stars, nebulae, g ...
project Galaxy Zoo
Galaxy Zoo is a crowdsourced astronomy project which invites people to assist in the morphological classification of large numbers of galaxies. It is an example of citizen science as it enlists the help of members of the public to help in scien ...
(GZ), part of the Zooniverse
Zooniverse is a citizen science web portal owned and operated by the Citizen Science Alliance. It is home to some of the Internet's largest, most popular and most successful citizen science projects. The organization grew from the original Gal ...
web portal
A web portal is a specially designed website that brings information from diverse sources, like emails, online forums and search engines, together in a uniform way. Usually, each information source gets its dedicated area on the page for displayi ...
.
Description
The Pea galaxies, also known as Green Peas (GPs), are compact oxygen-rich emission line galaxies that were discovered at redshift between ''z'' = 0.112 and 0.360. These low-mass galaxies have an upper size limit generally no bigger than across, and typically they reside in environments less than two-thirds the density of normal galaxy environments. An average GP has a redshift of ''z'' = 0.258, a mass of ~3,200 million (~3,200 million solar masses), a star formation rate of /yr (~10 solar masses a year), an IIIequivalent width
The equivalent width of a spectral line is a measure of the area of the line on a plot of intensity versus wavelength in relation to underlying continuum level. It is found by forming a rectangle with a height equal to that of continuum emission ...
of 69.4 nm and a low metallicity. A GP is purely star-forming, rather than having an active galactic nucleus
An active galactic nucleus (AGN) is a compact region at the center of a galaxy that has a much-higher-than-normal luminosity over at least some portion of the electromagnetic spectrum with characteristics indicating that the luminosity is not prod ...
. They have a strong emission line at the IIIwavelength
In physics, the wavelength is the spatial period of a periodic wave—the distance over which the wave's shape repeats.
It is the distance between consecutive corresponding points of the same phase on the wave, such as two adjacent crests, t ...
of 500.7 nm. III O++ or doubly ionized oxygen
In astronomy and atomic physics, doubly ionized oxygen is the ion O2+ (O III in spectroscopic notation). Its emission forbidden lines in the visible spectrum fall primarily at the wavelength 500.7 nm, and secondarily at 495.9 nm. Befor ...
, is a forbidden mechanism
In spectroscopy, a forbidden mechanism (forbidden transition or forbidden line) is a spectral line associated with absorption or emission of photons by atomic nuclei, atoms, or molecules which undergo a transition that is not allowed by a particul ...
of the visible spectrum
The visible spectrum is the portion of the electromagnetic spectrum that is visible to the human eye. Electromagnetic radiation in this range of wavelengths is called ''visible light'' or simply light. A typical human eye will respond to wa ...
and is only possible at very low density
Density (volumetric mass density or specific mass) is the substance's mass per unit of volume. The symbol most often used for density is ''ρ'' (the lower case Greek letter rho), although the Latin letter ''D'' can also be used. Mathematical ...
. When the entire photometric SDSS catalogue was searched, 40,222 objects were returned, which leads to the conclusion the GPs are rare objects.
GPs are the least massive and most actively star-forming galaxies in the local universe. "These galaxies would have been normal in the early Universe, but we just don’t see such active galaxies
An active galactic nucleus (AGN) is a compact region at the center of a galaxy that has a much-higher-than-normal luminosity over at least some portion of the electromagnetic spectrum with characteristics indicating that the luminosity is not pr ...
today", said Kevin Schawinski. "Understanding the Green Peas may tell us something about how stars were formed in the early Universe and how galaxies evolve".
GPs exist at a time when the universe
The universe is all of space and time and their contents, including planets, stars, galaxies, and all other forms of matter and energy. The Big Bang theory is the prevailing cosmological description of the development of the universe. ...
was three-quarters of its present age and so are clues as to how galaxy formation and evolution
The study of galaxy formation and evolution is concerned with the processes that formed a heterogeneous universe from a homogeneous beginning, the formation of the first galaxies, the way galaxies change over time, and the processes that have gen ...
took place in the early universe. With the publication of Amorin's GTC paper in February 2012, it is now thought that GPs might be old galaxies having formed most of their stellar mass several billion years ago. Old stars have been spectroscopically confirmed in one of the three galaxies in the study by the presence of magnesium
Magnesium is a chemical element with the symbol Mg and atomic number 12. It is a shiny gray metal having a low density, low melting point and high chemical reactivity. Like the other alkaline earth metals (group 2 of the periodic ta ...
.
 In January 2016, a study was published in the journal
In January 2016, a study was published in the journal Nature
Nature, in the broadest sense, is the physical world or universe. "Nature" can refer to the phenomena of the physical world, and also to life in general. The study of nature is a large, if not the only, part of science. Although humans are ...
identifying J0925+1403 as a Lyman continuum photons (LyC) 'leaker' with an escape fraction of ~8% (see section below). A follow-up study using the same Hubble Space Telescope
The Hubble Space Telescope (often referred to as HST or Hubble) is a space telescope that was launched into low Earth orbit in 1990 and remains in operation. It was not the first space telescope, but it is one of the largest and most vers ...
(HST) data identifies four more LyC leakers, described as GPs. In 2014–15, two separate sources identified two other GPs to be likely LyC leaking candidates (J1219 and J0815), suggesting that these two GPs are also low-redshift analogs of high-redshift Lyman-alpha and LyC leakers. Finding local LyC leakers is crucial to theories about the early universe and reionization
In the fields of Big Bang theory and cosmology, reionization is the process that caused matter in the universe to reionize after the lapse of the " dark ages".
Reionization is the second of two major phase transitions of gas in the universe (t ...
. More details here: Izotov et al. 2016
The image to the right shows Pea galaxy GP_J1219. This was observed in 2014 by a HST team whose principal investigator was Alaina Henry, using the Cosmic Origins Spectrograph
The Cosmic Origins Spectrograph (COS) is a science instrument that was installed on the Hubble Space Telescope during Servicing Mission 4 ( STS-125) in May 2009. It is designed for ultraviolet (90–320 nm) spectroscopy of faint point sources ...
and the Near Ultraviolet channel. The scale bar in the image shows 1 arc second
A minute of arc, arcminute (arcmin), arc minute, or minute arc, denoted by the symbol , is a unit of angular measurement equal to of one degree. Since one degree is of a turn (or complete rotation), one minute of arc is of a turn. The n ...
(1"), which corresponds to ~10,750 light years at the distance of 2.69 billion light years for GP_J1219. When using the COS Multi-Anode Micro-channel Array, in NUV imaging mode, the detector plate scale is ~40 pixels per arcsecond (0.0235 arcseconds per pixel).
GPs feature significantly within the Zoogems project, which uses the Hubble Space Telescope to examine interesting images from the citizen science website Galaxy Zoo, collected since 2007. Among the ~300 possible candidates for the Zoogems observations are 75 GPs. The original GP classifications used SDSS images, which are not as good quality as HST. These new HST images have produced one study in 2021 which challenges theories that GPs are similar to the first galaxies in the re-ionisation epoch, in that the stellar population in GPs may be older than any early galaxies that might have existed. Quoting from the abstract: "A substantial presence of old stars would indicate that the mechanisms allowing large escape fractions in these local galaxies may be different from those at play during the reionization epoch."
History of discovery
Years 2007 to 2010
Galaxy Zoo
Galaxy Zoo is a crowdsourced astronomy project which invites people to assist in the morphological classification of large numbers of galaxies. It is an example of citizen science as it enlists the help of members of the public to help in scien ...
(GZ) is a project online since July 2007 which seeks to classify up to one million galaxies. On July 28, 2007, two days after the start of the Galaxy Zoo Internet forum
An Internet forum, or message board, is an online discussion site where people can hold conversations in the form of posted messages. They differ from chat rooms in that messages are often longer than one line of text, and are at least temporar ...
, citizen scientist 'Nightblizzard' posted two green objects thought to be galaxies. A discussion, or thread, was started on this forum by Hanny Van Arkel (cf. Hanny's Voorwerp) on the 12th of August 2007 called "Give peas a chance" in which various green objects were posted. This thread started humorously, as the name is a word play
Word play or wordplay (also: play-on-words) is a literary technique and a form of wit in which words used become the main subject of the work, primarily for the purpose of intended effect or amusement. Examples of word play include puns, pho ...
of the title of the John Lennon
John Winston Ono Lennon (born John Winston Lennon; 9 October 19408 December 1980) was an English singer, songwriter, musician and peace activist who achieved worldwide fame as founder, co-songwriter, co-lead vocalist and rhythm guitarist of ...
song "Give Peace a Chance
"Give Peace a Chance" is an anti-war song written by John Lennon (originally credited to Lennon–McCartney), and recorded with the participation of a small group of friends in a performance with Yoko Ono in a hotel room in Montreal, Quebec, C ...
", but by December 2007, it had become clear that some of these unusual objects were a distinct group of galaxies. These "Pea galaxies" appear in the SDSS as unresolved green images. This is because the Peas have a very bright, or powerful, Spectral line
A spectral line is a dark or bright line in an otherwise uniform and continuous spectrum, resulting from emission or absorption of light in a narrow frequency range, compared with the nearby frequencies. Spectral lines are often used to iden ...
in their spectra for highly-ionized
Ionization, or Ionisation is the process by which an atom or a molecule acquires a negative or positive charge by gaining or losing electrons, often in conjunction with other chemical changes. The resulting electrically charged atom or molecule ...
oxygen
Oxygen is the chemical element with the symbol O and atomic number 8. It is a member of the chalcogen group in the periodic table, a highly reactive nonmetal, and an oxidizing agent that readily forms oxides with most elements as ...
, which in SDSS color composites increases the luminosity, or brightness, of the "r" color band with respect to the two other color bands "g" and "i". The "r" color band shows as green in SDSS images. Enthusiasts, calling themselves the "Peas Corps" (another humorous play on the Peace Corps
The Peace Corps is an independent agency and program of the United States government that trains and deploys volunteers to provide international development assistance. It was established in March 1961 by an executive order of President John F ...
), collected over a hundred of these Peas, which were eventually placed together into a dedicated discussion thread started by Carolin Cardamone in July 2008. The collection, once refined, provided values that could be used in a systematic computer search of the GZ database of one million objects, which eventually resulted in a sample of 251 Pea galaxies, also known as Green Peas (GPs).
In November 2009, authors C. Cardamone, Kevin Schawinski, M. Sarzi, S. Bamford, N. Bennert, C. Urry, Chris Lintott
Christopher John Lintott (born 26 November 1980) is a British astrophysicist, author and broadcaster. He is a Professor of Astrophysics in the Department of Physics at the University of Oxford. Lintott is involved in a number of popular scie ...
, W. Keel and 9 others published a paper in the Monthly Notices of the Royal Astronomical Society
''Monthly Notices of the Royal Astronomical Society'' (MNRAS) is a peer-reviewed scientific journal covering research in astronomy and astrophysics. It has been in continuous existence since 1827 and publishes letters and papers reporting orig ...
titled "Galaxy Zoo Green Peas: Discovery of A Class of Compact Extremely Star-Forming Galaxies". Within this paper, 10 Galaxy Zoo volunteers are acknowledged as having made a particularly significant contribution. They are: Elisabeth Baeten, Gemma Coughlin, Dan Goldstein, Brian Legg, Mark McCallum, Christian Manteuffel, Richard Nowell, Richard Proctor, Alice Sheppard and Hanny Van Arkel. They are thanked for "giving Peas a chance". Citations for 2009MNRAS.399.1191C are available from the SAO/NASA Astrophysics Data System. More details here: Cardamone 2009 Physics
It would be wrong to assume that the 80 GPs were all new discoveries. Out of the 80 original, 46 GPs have previous citations dated before November 2009 in the NASA/IPAC Extragalactic Database The NASA/IPAC Extragalactic Database (NED) is an online astronomical database for astronomers that collates and cross-correlates astronomical information on extragalactic objects (galaxies, quasars, radio, x-ray and infrared sources, etc.). NED was ...
. The original 80 GPs were part of a sample from SDSS data-release 7 (DR7), but did not include galaxies from other sources. Some of these other sources did include objects that might well have been classed as GPs if they were in the SDSS sample. One example of a paper that demonstrates this is: In April 2009, authors J. J. Salzer, A. L. Williams and C. Gronwall published a paper in the Astrophysical Journal
''The Astrophysical Journal'', often abbreviated ''ApJ'' (pronounced "ap jay") in references and speech, is a peer-reviewed scientific journal of astrophysics and astronomy, established in 1895 by American astronomers George Ellery Hale and ...
Letters titled "A Population of Metal-Poor Galaxies with ~L* Luminosities at Intermediate Redshifts". In this paper, "new spectroscopy and metallicity estimates for a sample of 15 star-forming galaxies with redshifts in the range 0.29 – 0.42" were presented. These objects were selected using the KPNO International Spectroscopic Survey (KISS). Certainly 3 of these 15 when viewed as objects in SDSS are green (KISSR 1516, KISSR 2042 and KISSRx 467). Indeed, quoting from Salzer et al. 2009, section 4.1, it reads "A New Class of Galaxy? Given the large number of studies of metal abundances in galaxies with intermediate and high redshift mentioned in the Introduction, it may seem odd that systems similar to those described here have not been recognized previously."
In June 2010, authors R. Amorin, E. Perez-Montero and J. Vilchez published a paper in The Astrophysical Journal
''The Astrophysical Journal'', often abbreviated ''ApJ'' (pronounced "ap jay") in references and speech, is a peer-reviewed scientific journal of astrophysics and astronomy, established in 1895 by American astronomers George Ellery Hale and ...
Letters titled "On the oxygen and nitrogen chemical abundances and the evolution of the "green pea" galaxies". In it they explore issues concerning the metallicity of 79 GPs, disputing the original findings in Cardamone et al. They conclude, "arguing that recent interaction-induced inflow of gas, possibly coupled with a selective metal-rich gas loss drive by supernova winds may explain our findings and the known galaxy properties". More details here: Two papers by Amorin
2011
In February 2011, authors Y. Izotov, N. Guseva and T. Thuan published a paper in the Astrophysical Journal titled "Green Pea Galaxies and Cohorts: Luminous Compact Emission-line Galaxies in the Sloan Digital Sky Survey". They find that the 80 GPs are not a rare class of galaxies on their own, but rather a subset of a class known as 'Luminous Compact Galaxies' (LCGs), of which there are 803. More details here: Luminous Compact Galaxies In November 2011, authors Y. Izotov, N. Guseva, K. Fricke and C. Henkel published a paper in Astronomy and Astrophysics titled 'Star-forming galaxies with hot dust emission in the SDSS discovered by theWide-field Infrared Survey Explorer
Wide-field Infrared Survey Explorer (WISE, observatory code C51, Explorer 92 and SMEX-6) is a NASA infrared astronomy space telescope in the Explorers Program. It was launched in December 2009, and placed in hibernation mode in February 201 ...
(WISE)'. In this paper, they find four galaxies that have very red colours in the wavelength range 3.4 micrometres (W1) and 4.6 micrometres (W2). This implies that the dust in these galaxies is at temperatures up to 1000K. These four galaxies are GPs and more than double the number of known galaxies with these characteristics.
2012
In January 2012, authors R. Amorin, R. Perez-Montero and J.Vilchez published a 'Conference proceeding' titled "Unveiling the Nature of the "Green Pea" galaxies". In this publication, they announce that they have conducted a set of observations using theOptical System for Imaging and low Resolution Integrated Spectroscopy The Optical System for Imaging and low Resolution Integrated Spectroscopy (OSIRIS) is an optical spectrometer at the Gran Telescopio Canarias (GTC) in Spain. It was the first instrument in operation at the GTC. OSIRIS's key scientific project is ...
(OSIRIS) at the Gran Telescopio Canarias
The Gran Telescopio Canarias (GranTeCan or GTC) is a reflecting telescope located at the Roque de los Muchachos Observatory on the island of La Palma, in the Canaries, Spain. It is the world's largest single-aperture optical telescope.
Constr ...
, and that there is a forthcoming paper about their research. These observations "will provide new insights on the evolutionary state of the Green Peas. In particular, we will be able to see whether the Green Peas show an extended, old stellar population underlying the young starbursts, like those typically dominant in terms of stellar mass in most Blue Compact Galaxies". More details here: Two papers by Amorin
In January 2012, authors L. Pilyugin, J. Vilchez, L. Mattsson and T. Thuan published a paper in the MNRAS
''Monthly Notices of the Royal Astronomical Society'' (MNRAS) is a peer-reviewed scientific journal covering research in astronomy and astrophysics. It has been in continuous existence since 1827 and publishes letters and papers reporting origina ...
titled: "Abundance determination from global emission-line SDSS spectra: exploring objects with high N/O ratios". In it they compare the oxygen and nitrogen abundances derived from global emission-line SDSS spectra of galaxies using (1) the electron temperature method and (2) two recent strong line calibrations: the O/N and N/S calibrations. Three sets of objects were compared: composite hydrogen-rich nebula, 281 SDSS galaxies and a sample of GPs with detectable III4363 auroral lines. Among the questions surrounding the GPs are how much nebulae influence their spectra and results. Through comparisons of the three objects using proven methodology
In its most common sense, methodology is the study of research methods. However, the term can also refer to the methods themselves or to the philosophical discussion of associated background assumptions. A method is a structured procedure for br ...
and analysis of metallicity, they conclude that "the high nitrogen-to-oxygen ratios derived in some Green Pea galaxies may be caused by the fact that their SDSS spectra are spectra of composite nebulae made up of several components with different physical properties (such as metallicity). However, for the hottest Green Pea galaxies, which appear to be dwarf galaxies, this explanation does not seem to be plausible."
In January 2012, author S. Hawley published a paper in the Publications of the Astronomical Society of the Pacific
''Publications of the Astronomical Society of the Pacific'' (often abbreviated as ''PASP'' in references and literature) is a monthly peer-reviewed scientific journal managed by the Astronomical Society of the Pacific. It publishes research and ...
titled "Abundances in "Green Pea" Star-forming Galaxies". In this paper, former NASA astronaut Steven Hawley
Steven Alan Hawley (born December 12, 1951) is a former NASA astronaut who flew on five U.S. Space Shuttle flights. He is professor of physics and astronomy and director of engineering physics at the University of Kansas.
Early life
Hawley w ...
compares the results from previous GP papers regarding their metallicities. Hawley compares different ways of calibrating and interpreting the various results, mainly from Cardamone et al. and Amorin et al. but some from Izotov et al., and suggests why the various discrepancies between these papers' findings might be. He also considers such details as the contribution of Wolf–Rayet star
Wolf–Rayet stars, often abbreviated as WR stars, are a rare heterogeneous set of stars with unusual spectra showing prominent broad emission lines of ionised helium and highly ionised nitrogen or carbon. The spectra indicate very high surface ...
s to the gas ionization, and which sets of emission lines give the most accurate results for these galaxies. He ends by writing: "The calibrations derived from the Green Peas differ from those commonly utilized and would be useful if star-forming galaxies like the Green Peas with extremely hot ionizing sources are found to be more common."
In February 2012, authors S. Chakraborti, N. Yadav, C. Cardamone and A. Ray published a paper in The Astrophysical Journal Letters titled 'Radio Detection of Green Peas: Implications for Magnetic Fields in Young Galaxies'. In this paper, magnetism studies using new data from the Giant Metrewave Radio Telescope describe various observations based around the GPs. They show that the three "very young" starburst galaxies that were studied have magnetic fields larger than the Milky Way. This is at odds with the current understanding that galaxies build up their magnetic properties over time. More details here: Radio detection
In April 2012, authors R. Amorin, E. Perez-Montero, J. Vilchez and P. Papaderos published a paper in the Astrophysical Journal titled "The Star Formation History and Metal Content of the 'Green Peas'. New Detailed GTC-OSIRIS spectrophotometry of Three Galaxies". They give the results for the deep broad-band imaging and long-slit spectroscopy for 3 GPs that had been observed using the OSIRIS
Osiris (, from Egyptian ''wsjr'', cop, ⲟⲩⲥⲓⲣⲉ , ; Phoenician: 𐤀𐤎𐤓, romanized: ʾsr) is the god of fertility, agriculture, the afterlife, the dead, resurrection, life, and vegetation in ancient Egyptian religion. He wa ...
instrument, mounted on the 10.4m Gran Telescopio Canarias
The Gran Telescopio Canarias (GranTeCan or GTC) is a reflecting telescope located at the Roque de los Muchachos Observatory on the island of La Palma, in the Canaries, Spain. It is the world's largest single-aperture optical telescope.
Constr ...
at the Roque de los Muchachos Observatory
Roque de los Muchachos Observatory ( es, Observatorio del Roque de los Muchachos, ORM) is an astronomical observatory located in the municipality of Garafía on the island of La Palma in the Canary Islands, Spain. The observatory site is operated b ...
. More details here: GTC-OSIRIS
In August 2012, authors R. Amorín, J. Vílchez, G. Hägele, V. Firpo, E. Pérez-Montero and P. Papaderos published a paper in the Astrophysical Journal Letters titled "Complex gas kinematics in compact, rapidly assembling star-forming galaxies". Using the ISIS spectrograph on the William Herschel Telescope
The William Herschel Telescope (WHT) is a optical/near-infrared reflecting telescope located at the Roque de los Muchachos Observatory on the island of La Palma in the Canary Islands, Spain. The telescope, which is named after William Hersc ...
, they publish results of the high-quality spectra that they took of six galaxies, five of which are GPs. After studying the hydrogen alpha emission lines (ELs) in the spectra of all six, it is shown that these ELs are made up of multiple lines, meaning that the GPs have several chunks of gas and stars moving at large velocities relative to each other. These ELs also show that the GPs are effectively a 'turbulent mess', with parts (or clumps) moving at speeds of over 500 km/s (five hundred km/s) relative to each other.
2013
In January 2013, authors S. Parnovsky, I. Izotova and Y. Izotov published a paper inAstrophysics and Space Science
''Astrophysics and Space Science'' is a bimonthly peer-reviewed scientific journal covering astronomy, astrophysics, and space science and astrophysical aspects of astrobiology. It was established in 1968 and is published by Springer Science+ ...
titled "H alpha and UV luminosities and star formation rates in a large sample of luminous compact galaxies". In it, they present a statistical study of the star formation rates (SFR) derived from the GALEX observations in the Ultraviolet continuum and in the H alpha emission line for a sample of ~800 luminous compact galaxies (LCGs). Within the larger set of LCGs, including the GPs, SFR of up to /yr (~110 solar masses a year) are found, as well as estimates of the ages of the starbursts.
In April 2013, authors A. Jaskot and M. Oey published a paper in the Astrophysical Journal titled "The Origin and Optical Depth of Ionizing Radiation in the "Green Pea" Galaxies". Six "extreme" GPs are studied. Using these, the authors endeavour to narrow down the list of possibilities about what is producing the radiation and the substantial amounts of high-energy photon
A photon () is an elementary particle that is a quantum of the electromagnetic field, including electromagnetic radiation such as light and radio waves, and the force carrier for the electromagnetic force. Photons are massless, so they a ...
that might be escaping from the GPs. Following on from this paper, observations on the Hubble Space Telescope, totalling 24 orbits, were taken in December 2013. The Cosmic Origins Spectrograph and the Advanced Camera for Surveys were used on four of the "extreme" GPs. More details here: Two papers by Jaskot and Oey
2014
In January 2014, authors Y. Izotov, N. Guseva, K. Fricke and C. Henkel published a paper in Astronomy & Astrophysics entitled "Multi-wavelength study of 14000 star-forming galaxies from the Sloan Digital Sky Survey". In it, they use a variety of sources to demonstrate: "that the emission emerging from young star-forming regions is the dominant dust-heating source for temperatures to several hundred degrees in the sample star-forming galaxies". The first source of data is SDSS from which 14,610 spectra with strong emission lines are selected. These 14,610 spectra were then cross-identified with sources from photometric sky surveys in other wavelength ranges. Those are: 1) GALEX for the ultraviolet; 2)the2MASS
The Two Micron All-Sky Survey, or 2MASS, was an astronomical survey of the whole sky in infrared light. It took place between 1997 and 2001, in two different locations: at the U.S. Fred Lawrence Whipple Observatory on Mount Hopkins, Arizona, and ...
survey for the near-infrared; 3)the Wide-field Infrared Survey Explorer
Wide-field Infrared Survey Explorer (WISE, observatory code C51, Explorer 92 and SMEX-6) is a NASA infrared astronomy space telescope in the Explorers Program. It was launched in December 2009, and placed in hibernation mode in February 201 ...
All-Sky Source Catalog for infrared at differing wavelengths; 4)the IRAS
The Infrared Astronomical Satellite (Dutch: ''Infrarood Astronomische Satelliet'') (IRAS) was the first space telescope to perform a survey of the entire night sky at infrared wavelengths. Launched on 25 January 1983, its mission lasted ten mo ...
survey for the far-infrared and the 5) NVSS Survey at radio-wavelengths. Only a small fraction of the SDSS objects were detected in the last two surveys. Among the results is a list of twenty galaxies with the highest magnitudes which have hot dust of several hundred degrees. Of these twenty, all could be classified as GPs and/or LCGs. Also among the results, the luminosity is obtained in the sample galaxies in a wide wavelength range. At the highest luminosities, the sample galaxies had luminosites approaching those of high-redshift Lyman-break galaxy Lyman-break galaxies are star-forming galaxies at high redshift that are selected using the differing appearance of the galaxy in several imaging filters due to the position of the Lyman limit. The technique has primarily been used to select gal ...
.
In January 2014, authors A. Jaskot, M. Oey, J. Salzer, A. Van Sistine and M. Haynes gave a presentation titled "Neutral Gas and Low-Redshift Starbursts: From Infall to Ionization" to the American Astronomical Society at their meeting #223. The presentation included data from The Arecibo Observatory Legacy Fast ALFA Survey (ALFALFA). The authors analyzed the optical spectra of the GPs and concluded "While the ALFALFA survey demonstrates the role of external processes in triggering starbursts, the Green Peas show that starbursts' radiation can escape to affect their external environment", finding "that the Peas are likely optically thin to Lyman continuum (LyC) radiation."
In June 2014, authors A. Jaskot and M. Oey published a conference report titled "The Origin and Optical Depth of Ionizing Photons in the Green Pea Galaxies". This appears in "Massive Young Star Clusters Near and Far: From the Milky Way to Reionization", based on the 2013 Guillermo Haro Conference. More details here: Two papers by Jaskot and Oey
2015
In May 2015, authors A. Henry, C. Scarlata, C. L. Martin and D. Erb published a paper in the Astrophysical Journal entitled, "Lyα Emission from Green Peas: The Role of Circumgalactic Gas Density, Covering, and Kinematics". In this paper, ten Green Peas were studied in the ultraviolet, using high resolution spectroscopy with the Hubble Space Telescope using the Cosmic Origins Spectrograph. This study showed, for the first time, that Green Peas have strong Lyα emission much like distant, high-redshift galaxies observed in a younger universe. Henry et al. explored the physical mechanisms that determine how Lyα escapes from the Green Peas, and concluded that variations in the neutral hydrogen column density were the most important factor. More details here: Lyman Alpha Emission from Green Peas.2016
In May 2016, author Miranda C. P. Straub published a research paper in theopen access journal
Open access (OA) is a set of principles and a range of practices through which research outputs are distributed online, free of access charges or other barriers. With open access strictly defined (according to the 2001 definition), or libre op ...
Citizen Science: Theory and Practice called 'Giving Citizen Scientists a Chance: A Study of Volunteer-led Scientific Discovery'. The abstract states: "The discovery of a class of galaxies called Green Peas provides an example of scientific work done by volunteers. This unique situation arose out of a science crowdsourcing website called Galaxy Zoo."
In April 2016, Yang et al. published "Green Pea Galaxies Reveal Secrets of Lyα Escape." Archival Lyman-alpha spectra of 12 GPs that have been observed with the HST/COS were analysed and modelled with radiative transfer models. The dependence of Lyman-alpha (LyA) escape fractions on various properties were explored. All 12 GPs show LyA lines in emission, with a LyA equivalent width distribution similar to high-redshift emitters. Among the findings are that the LyA escape fraction depends strongly on metallicity and moderately on dust extinction. The papers results suggest that low H1 column density and low metallicity are essential for LyA escape. "In conclusion, GPs provide an unmatched opportunity to study LyA escape in LyA Emitters."
2017
 In a presentation to the American Astronomical Society Meeting #229 in January 2017, Matt Brorby and Philip Kaaret describe the observations of two GPs and their x-ray emission. Using both space telescope programs
In a presentation to the American Astronomical Society Meeting #229 in January 2017, Matt Brorby and Philip Kaaret describe the observations of two GPs and their x-ray emission. Using both space telescope programs Chandra
Chandra ( sa, चन्द्र, Candra, shining' or 'moon), also known as Soma ( sa, सोम), is the Hindu god of the Moon, and is associated with the night, plants and vegetation. He is one of the Navagraha (nine planets of Hinduism) a ...
GO: 16400764 and Hubble GO: 13940, they examine Luminous Compact Galaxies, both GPs, J0842+1150 and SHOC 486. They conclude: 1) These are the first x-ray observations of GPs. 2) The two GPs studied are the first test of Lx-SFR-Z planar relation and that they are consistent with this. 3) Low metallicity galaxies exhibit enhanced x-ray emission relative to normal metallicity starforming galaxies. 4) GPs are useful for predictions of X-ray output in the early universe.
In March 2017, Yang et al. published a paper in the Astrophysical Journal
''The Astrophysical Journal'', often abbreviated ''ApJ'' (pronounced "ap jay") in references and speech, is a peer-reviewed scientific journal of astrophysics and astronomy, established in 1895 by American astronomers George Ellery Hale and ...
called: "Lyα and UV Sizes of Green Pea Galaxies". The authors studied the Lyman-alpha (LyA) escape in a statistical sample of 43 GPs with HST/COS LyA spectra, taken from 6 HST programs. Their conclusions include: 1) Using GPs that cover the whole ranges of dust extinction and metallicity, they find about two-thirds are strong LyA emitters. This confirms that GPs generally are "the best analogs of high-z (redshift) Lyman-alpha Emitters (LAEs) in the nearby universe." The LyA escape fractions show anti-correlations with a few LyA kinematic features. 3) The authors find many correlations regarding the dependence of LyA escape on galactic properties, such as dust extinction and metallicity.) The single shell radiative transfer model can reproduce most LyA profiles of GPs.) An empirical linear relation between the LyA escape fraction, dust extinction and the LyA red peak velocity.
In August 2017, Yang et al. published a study in the Astrophysical Journal called: "Lyα profile, dust, and prediction of Lyα escape fraction in Green Pea Galaxies". The authors state that GPs are nearby analogues of high redshift Lyman-alpha (LyA)- emitting galaxies. Using spectral data from the HST-COS MAST archive, 24 GPs were studied for their LyA escape and the spatial profiles of LyA and UV continuum emissions. Results include: 1) Having compared LyA and UV sizes from the 2D spectra and 1D spatial profiles, it is found that most GPs show more extended LyA emission than the UV continuum. 2) 8 GPs had their spatial profiles of LyA photons at blueshifted and redshifted velocities compared. 3) The LyA escape fraction was compared with the size ration of LyA to UV. It was found that GPs that have LyA escape fractions greater than 10% "tend to have more compact LyA morphology".
In October 2017, Lofthouse et al. published a study in the Monthly Notices of the Royal Astronomical Society
''Monthly Notices of the Royal Astronomical Society'' (MNRAS) is a peer-reviewed scientific journal covering research in astronomy and astrophysics. It has been in continuous existence since 1827 and publishes letters and papers reporting orig ...
named: The authors used integral field spectroscopy, from the SWIFT and Palm 3K instruments, to perform a spatially-resolved spectroscopic analysis of four GPs, numbered 1,2,4 and 5. Among the results are that GPs 1 & 2 are rotationally-supported (they have a rotating centre), while GPs 4 & 5 are dispersion-dominated systems. GPs 1 & 2 show morphologies indicative of ongoing or mergers. However, GPs 4 & 5 show no signs of recent interactions and have similar star-forming rates. This indicates mergers are not "a necessary requirement for driving the high star formation in these types of galaxies".
In December 2017, authors Jaskot, Oey, Scarlata and Dowd published a paper in the Astrophysical Journal Letters titled:"Kinematics and Optical Depth in the Green Peas: Suppressed Superwinds in Candidate LyC Emitters". Within the paper, they say that current thinking describes how superwinds clear neutral gas away from young starburst galaxies, which in turn regulates the escape of Lyman Continuum photons from star-forming galaxies. Models predict however that in the most extreme compact starbursts, those superwinds may not launch. The authors explore the role of outflows in generating low optical depth in GPs, using observations from the Hubble Space Telescope. They compare the kinematics of ultraviolet absorption and with Lyman alpha escape fraction, Lyman alpha peak separation or low-ionisation absorption. The most extreme GPs show the slowest velocities, which "are consistent with models for suppressed superwinds, which suggests that outflows may not be the only cause of LyC escape from galaxies."
J0925+1403 and LyC leakage
In January 2016, a letter was published in the journalNature
Nature, in the broadest sense, is the physical world or universe. "Nature" can refer to the phenomena of the physical world, and also to life in general. The study of nature is a large, if not the only, part of science. Although humans are ...
called: "Eight per cent leakage of Lyman continuum photons from a compact, star-forming dwarf galaxy" by authors: Y.I. Izotov, I. Orlitová, D. Schaerer, T.X. Thuan, A. Verhamme, N.G. Guseva & G. Worseck. The abstract states: "One of the key questions in observational cosmology is the identification of the sources responsible for ionisation of the Universe after the cosmic Dark Ages". It also states: "Here we present far-ultraviolet observations of a nearby low-mass star-forming galaxy, J0925+1403, selected for its compactness and high excitation... The galaxy is 'leaking' ionising radiation, with an escape fraction of 7.8%." These levels of radiation are thought to be similar to those of the first galaxies in the universe, which emerged in a time known as reionization
In the fields of Big Bang theory and cosmology, reionization is the process that caused matter in the universe to reionize after the lapse of the " dark ages".
Reionization is the second of two major phase transitions of gas in the universe (t ...
. These findings have led the research team to conclude that J0925 can ionise intergalactic material up to 40 times its own stellar mass. The study was a result of observations carried out using the Cosmic Origins Spectrograph aboard the Hubble Space Telescope.
GP J0925 is thought to be similar to the most distant, and thus earliest, galaxies in the universe and has been shown to 'leak' LyC. It is about 3 billion light years away (redshift z=0.301), or approximately 75% of the current age of the universe. Co-author Trinh Thuan said in a statement: "The finding is significant because it gives us a good place to look for probing the reionization phenomenon, which took place early in the formation of the universe that became the universe we have today". He also stated: "As we make additional observations using Hubble, we expect to gain a much better understanding of the way photons are ejected from this type of galaxy, and the specific galaxy types driving cosmic reionization." He concludes: "These are crucial observations in the process of stepping back in time to the early universe."
LyC detection in J1152+3400, J1333+6246, J1442-0209, J1503+3644
In October 2016, a study was published in theMNRAS
''Monthly Notices of the Royal Astronomical Society'' (MNRAS) is a peer-reviewed scientific journal covering research in astronomy and astrophysics. It has been in continuous existence since 1827 and publishes letters and papers reporting origina ...
entitled: "Detection of high Lyman continuum leakage from four low-redshift compact star-forming galaxies". Its authors are Y. I. Izotov, D. Schaerer, T. X. Thuan, G. Worseck, N. G. Guseva, I. Orlitova, A. Verhamme. The abstract states: "Following our first detection reported in Izotov et al. (2016) s above we present the detection of Lyman continuum (LyC) radiation of four other compact star-forming galaxies observed with the Cosmic Origins Spectrograph (COS) onboard the Hubble Space Telescope (HST)".
This study contains the methods and findings from Izotov et al. 2016 (a) which concentrated on one galaxy, whereas the above paper, Izotov et al. 2016 (b) has findings for four galaxies, all of which have LyC leakage. When compared with other known local galaxies that leak LyC, as listed in this article, Izotov et al. 2016 (a & b) doubles the numbers of known leakers.
Lyman alpha emission
 In May 2015, authors Alaina Henry, Claudia Scarlata, Crystal Martin, and Dawn Erb published a paper titled: "Lyα Emission from Green Peas: The Role of Circumgalactic Gas Density, Covering, and Kinematics". The motivation of this work was to understand why some galaxies have Lyα emission, while others don't. A host of physical conditions in galaxies regulate the output of this spectral feature; hence, understanding its emission is fundamentally important for understanding how galaxies form and how they impact their intergalactic surroundings.
Henry et al. hypothesized that, since the GPs seem more like galaxies at redshift=z>2, and Lyα is common at these redshifts, that Lyα would be common in the GPs as well. Observations with the HST using the COS, as in 'Description', proved this to be true for a sample of 10 GPs. The spectra, shown here to the right, indicate resonant scattering of Lyα photons that are emitted near zero velocity. The wealth of data existing on the GPs, combined with the COS spectra, allowed Henry et al. to explore the physical mechanisms that regulate the Lyα output. These authors concluded that variations in the amount of neutral hydrogen gas, which scatters Lyα photons, are the cause of a factor of 10 difference in Lyα output in their sample.
The spectrum of GP_J1219 (an image of which is in 'Description') shows its very strong flux measurements when compared to other 9 GPs. Indeed, only GP_J1214 has a value approaching that of J1219. Note also the double peaks in some GPs and the velocity values of the emissions, indicating the inflow and outflow of matter in the GPs.
In May 2015, authors Alaina Henry, Claudia Scarlata, Crystal Martin, and Dawn Erb published a paper titled: "Lyα Emission from Green Peas: The Role of Circumgalactic Gas Density, Covering, and Kinematics". The motivation of this work was to understand why some galaxies have Lyα emission, while others don't. A host of physical conditions in galaxies regulate the output of this spectral feature; hence, understanding its emission is fundamentally important for understanding how galaxies form and how they impact their intergalactic surroundings.
Henry et al. hypothesized that, since the GPs seem more like galaxies at redshift=z>2, and Lyα is common at these redshifts, that Lyα would be common in the GPs as well. Observations with the HST using the COS, as in 'Description', proved this to be true for a sample of 10 GPs. The spectra, shown here to the right, indicate resonant scattering of Lyα photons that are emitted near zero velocity. The wealth of data existing on the GPs, combined with the COS spectra, allowed Henry et al. to explore the physical mechanisms that regulate the Lyα output. These authors concluded that variations in the amount of neutral hydrogen gas, which scatters Lyα photons, are the cause of a factor of 10 difference in Lyα output in their sample.
The spectrum of GP_J1219 (an image of which is in 'Description') shows its very strong flux measurements when compared to other 9 GPs. Indeed, only GP_J1214 has a value approaching that of J1219. Note also the double peaks in some GPs and the velocity values of the emissions, indicating the inflow and outflow of matter in the GPs.
Papers by A. Jaskot and M.S. Oey
In April 2013, authors A. Jaskot and M. Oey published a paper inThe Astrophysical Journal
''The Astrophysical Journal'', often abbreviated ''ApJ'' (pronounced "ap jay") in references and speech, is a peer-reviewed scientific journal of astrophysics and astronomy, established in 1895 by American astronomers George Ellery Hale and ...
titled "The Origin and Optical Depth of Ionizing Radiation in the "Green Pea" Galaxies". Six "extreme" GPs are studied. Using these, they endeavour to narrow down the list of possibilities about what is producing the UV-radiation and the substantial amounts of high-energy photon
A photon () is an elementary particle that is a quantum of the electromagnetic field, including electromagnetic radiation such as light and radio waves, and the force carrier for the electromagnetic force. Photons are massless, so they a ...
that might be escaping from the GPs. Through trying to observe these photons in nearby galaxies such as the GPs, our understanding of how galaxies behaved in the early Universe might well be revolutionised. It is reported that the GPs are exciting candidates to help astronomers understand a major milestone in the development of the cosmos 13 billion years ago, during the epoch of reionization
In the fields of Big Bang theory and cosmology, reionization is the process that caused matter in the universe to reionize after the lapse of the " dark ages".
Reionization is the second of two major phase transitions of gas in the universe (t ...
.
In February 2014, authors A. Jaskot and M. Oey published a conference report titled "The Origin and Optical Depth of Ionizing Photons in the Green Pea Galaxies". This will appear in "Massive Young Star Clusters Near and Far: From the Milky Way to Reionization", based on the 2013 Guillermo Haro Conference. In the publication, Jaskot and Oey write: "We are currently analyzing observations from IMACS and MagE on the Magellan Telescopes
The Magellan Telescopes are a pair of optical telescopes located at Las Campanas Observatory in Chile. The two telescopes are named after the astronomer Walter Baade and the philanthropist Landon T. Clay. First light for the telescopes was on ...
and COS and ACS on Hubble Space Telescope
The Hubble Space Telescope (often referred to as HST or Hubble) is a space telescope that was launched into low Earth orbit in 1990 and remains in operation. It was not the first space telescope, but it is one of the largest and most vers ...
(HST) to distinguish between WR ( Wolf-Rayet star) and the shock ionization scenarios and confirm the GPs’ optical depth
In physics, optical depth or optical thickness is the natural logarithm of the ratio of incident to ''transmitted'' radiant power through a material.
Thus, the larger the optical depth, the smaller the amount of transmitted radiant power throu ...
s. The absence of WR features in the deeper IMACS spectra tentatively supports the shock scenario, although the detection limits do not yet definitively rule out the WR photoionization
Photoionization is the physical process in which an ion is formed from the interaction of a photon with an atom or molecule.
Cross section
Not every interaction between a photon and an atom, or molecule, will result in photoionization. The prob ...
hypothesis."
Physics from the Cardamone 2009 paper
 At the time this paper was published, only five Green Peas (GPs) had been imaged by the
At the time this paper was published, only five Green Peas (GPs) had been imaged by the Hubble Space Telescope
The Hubble Space Telescope (often referred to as HST or Hubble) is a space telescope that was launched into low Earth orbit in 1990 and remains in operation. It was not the first space telescope, but it is one of the largest and most vers ...
(HST). Three of these images reveal GPs to be made up of bright clumps of star formation and low surface density features indicative of recent or ongoing galaxy merger
Galaxy mergers can occur when two (or more) galaxies collide. They are the most violent type of galaxy interaction. The gravitational interactions between galaxies and the friction between the gas and dust have major effects on the galaxies ...
s. These three HST images were imaged as part of a study of local ultraviolet
Ultraviolet (UV) is a form of electromagnetic radiation with wavelength from 10 nm (with a corresponding frequency around 30 PHz) to 400 nm (750 THz), shorter than that of visible light, but longer than X-rays. UV radiation ...
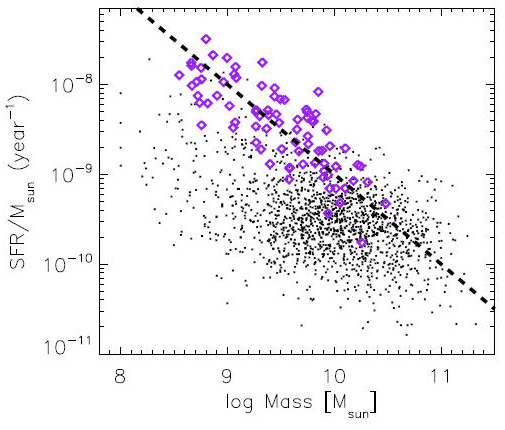
(UV-luminous) galaxies in 2005. Major mergers are frequently sites of active star-formation and to the right a graph is shown that plots specific star formation rate (SFR / Galaxy Mass) against galaxy mass. In this graph, the GPs are compared to the 3003 mergers from the Galaxy Zoo Merger Sample (GZMS). It shows that the GPs have low masses typical of dwarf galaxy
A dwarf galaxy is a small galaxy composed of about 1000 up to several billion stars, as compared to the Milky Way's 200–400 billion stars. The Large Magellanic Cloud, which closely orbits the Milky Way and contains over 30 billion stars, is so ...
and much higher star-forming rates (SFR) when compared to the GZMS. The black, dashed line shows a constant SFR of /yr (~10 solar masses). Most GPs have a SFR between 3 and /yr (between ~3 and ~30 solar masses).
 GPs are rare. Of the one million objects that make up GZ's image bank, only 251 GPs were found. After having to discard 148 of these 251 because of atmospheric contamination of their
GPs are rare. Of the one million objects that make up GZ's image bank, only 251 GPs were found. After having to discard 148 of these 251 because of atmospheric contamination of their Stellar spectra
Astronomical spectroscopy is the study of astronomy using the techniques of spectroscopy to measure the spectrum of electromagnetic radiation, including visible light, ultraviolet, X-ray, infrared and radio waves that radiate from stars and othe ...
, the 103 that were left, with the highest signal-to-noise ratio, were analyzed further using the classic emission line diagnostic
Diagnosis is the identification of the nature and cause of a certain phenomenon. Diagnosis is used in many different disciplines, with variations in the use of logic, analytics, and experience, to determine " cause and effect". In systems engin ...
by Baldwin, Phillips and Terlevich which separates starbursts and active galactic nuclei
An active galactic nucleus (AGN) is a compact region at the center of a galaxy that has a much-higher-than-normal luminosity over at least some portion of the electromagnetic spectrum with characteristics indicating that the luminosity is not prod ...
. 80 were found to be starburst galaxies. The graph to the left classifies 103 narrow-line GPs (all with SNR ≥ 3 in the emission lines) as 10 active galactic nuclei
An active galactic nucleus (AGN) is a compact region at the center of a galaxy that has a much-higher-than-normal luminosity over at least some portion of the electromagnetic spectrum with characteristics indicating that the luminosity is not prod ...
(blue diamonds), 13 transition objects (green crosses) and 80 starbursts (red stars). The solid line is: Kewley et al. (2001) maximal starburst contribution (labelled Ke01). The dashed line is: Kauffmann et al. (2003) separating purely star-forming objects from AGN (labelled Ka03).
 GPs have a strong IIIemission line when compared to the rest of their spectral continuum. In a SDSS spectrum, this shows up as a large peak with IIIat the top. The wavelength of III(500.7 nm) was chosen to determine the luminosities of the GPs using
GPs have a strong IIIemission line when compared to the rest of their spectral continuum. In a SDSS spectrum, this shows up as a large peak with IIIat the top. The wavelength of III(500.7 nm) was chosen to determine the luminosities of the GPs using Equivalent width
The equivalent width of a spectral line is a measure of the area of the line on a plot of intensity versus wavelength in relation to underlying continuum level. It is found by forming a rectangle with a height equal to that of continuum emission ...
(Eq.Wth.). The histogram on the right shows on the horizontal scale the Eq.Wth. of a comparison of 10,000 normal galaxies (marked red), UV-luminous Galaxies (marked blue) and GPs (marked green). As can be seen from the histogram, the Eq.Wth. of the GPs is much larger than normal for even prolific starburst galaxies such as UV-luminous Galaxies.
Within the Cardamone et al. paper, comparisons are made with other compact galaxies, namely Blue Compact Dwarfs Galaxies and UV-luminous Galaxies, at local and much higher distances. The findings show that GPs form a different class of galaxies than Ultra Blue Compact Dwarfs, but may be similar to the most luminous members of the Blue Compact Dwarf Galaxy category. The GPs are also similar to UV-luminous high redshift galaxies such as Lyman-break Galaxies and Lyman-alpha emitter
A Lyman-alpha emitter (LAE) is a type of distant galaxy that emits Lyman-alpha radiation from neutral hydrogen.
Most known LAEs are extremely distant, and because of the finite travel time of light they provide glimpses into the history of the un ...
s. It is concluded that if the underlying processes occurring in the GPs are similar to that found in the UV-luminous high redshift galaxies, the GPs may be the last remnants of a mode of star formation common in the early Universe.
 GPs have low
GPs have low interstellar reddening
In astronomy, extinction is the absorption and scattering of electromagnetic radiation by dust and gas between an emitting astronomical object and the observer. Interstellar extinction was first documented as such in 1930 by Robert Julius Trumple ...
values, as shown in the histogram on the right, with nearly all GPs having ''E''(''B''-''V'') ≤ 0.25. The distribution shown indicates that the line-emitting regions of star-forming GPs are not highly reddened, particularly when compared to more typical star-forming or starburst galaxies. This low reddening combined with very high UV luminosity is rare in galaxies in the local Universe and is more typically found in galaxies at higher redshifts.
Cardamone et al. describe GPs as having a low metallicity, but that the oxygen present is highly ionized. The average GP has a metallicity of log /H12~8.69, which is solar ''or'' sub-solar, depending on which set of standard values is used. Although the GPs are in general consistent with the mass-metallicity relation, they depart from it at the highest mass end and thus do not follow the trend. GPs have a range of masses, but a more uniform metallicity than the sample compared against. These metallicities are common in low mass galaxies such as Peas.
 As well as the optical images from the SDSS, measurements from the GALEX survey were used to determine the ultraviolet values. This survey is well matched in depth and area, and 139 of the sampled 251 GPs are found in GALEX Release 4 (G.R.4). For the 56 of the 80 star-forming GPs with GALEX detections, the median luminosity is ~30,000 million (~30,000 million solar luminosities).
When compiling the Cardamone paper, spectral classification was made using Gas And Absorption Line Fitting (GANDALF). This sophisticated computer software was programmed by Marc Sarzi, who helped analyze the SDSS spectra.
As well as the optical images from the SDSS, measurements from the GALEX survey were used to determine the ultraviolet values. This survey is well matched in depth and area, and 139 of the sampled 251 GPs are found in GALEX Release 4 (G.R.4). For the 56 of the 80 star-forming GPs with GALEX detections, the median luminosity is ~30,000 million (~30,000 million solar luminosities).
When compiling the Cardamone paper, spectral classification was made using Gas And Absorption Line Fitting (GANDALF). This sophisticated computer software was programmed by Marc Sarzi, who helped analyze the SDSS spectra.
Analysis of the Cardamone 2009 paper
These values are from Table 4, pages 16–17 of Cardamone 2009 et al., which shows the 80 GPs that have been analysed here. The long 18-digit numbers are the SDSS DR7 reference numbers. Color selection was by using the difference in the levels of three
Color selection was by using the difference in the levels of three Optical filter
An optical filter is a device that selectively transmits light of different wavelengths, usually implemented as a glass plane or plastic device in the optical path, which are either dyed in the bulk or have interference coatings. The optical ...
s, in order to capture these color limits: u-r ≤ 2.5 (1), r-i ≤ -0.2 (2), r-z ≤ 0.5 (3), g-r ≥ r-i + 0.5 (4), u-r ≥ 2.5 (r-z) (5). If the diagram on the right (one of two in the paper) is looked at, the effectiveness of this color selection can be seen. The Color-color diagram shows ~100 GPs (green crosses), 10,000 comparison galaxies (red points) and 9,500 comparison quasar (purple stars) at similar redshifts to the GPs. The black lines show how these figures are on the diagram.
Comparing a GP to the Milky Way
The Milky Way is the galaxy that includes our Solar System, with the name describing the galaxy's appearance from Earth: a hazy band of light seen in the night sky formed from stars that cannot be individually distinguished by the naked eye. ...
can be useful when trying to visualize these star-forming rates. An average GP has a mass of ~3,200 million (~3,200 million solar masses). The Milky Way (MW) is a spiral galaxy and has a mass of ~1,125,000, million (~1,125,000 million solar masses). So the MW has the mass of ~390 GPs.
Research has shown that the MW converts /yr (~2 solar masses per year) worth of interstellar medium into stars. An average GP converts /yr (~10 solar masses) of interstellar gas into stars, which is ~5 times the rate of the MW.
One of the original ways of recognizing GPs, before SQL programming was involved, was because of a discrepancy about how the SDSS labels them within Skyserver. Out of the 251 of the original GP sample that were identified by the SDSS spectroscopic pipeline as having galaxy spectra, only 7 were targeted by the SDSS spectral fibre allocation as galaxies i.e. 244 were not.
Papers by R. Amorin, J.M. Vilchez and E. Perez-Montero
In June 2010, authors R. Amorín, E. Pérez-Montero and J.M. Vílchez published a paper inThe Astrophysical Journal
''The Astrophysical Journal'', often abbreviated ''ApJ'' (pronounced "ap jay") in references and speech, is a peer-reviewed scientific journal of astrophysics and astronomy, established in 1895 by American astronomers George Ellery Hale and ...
letters titled "On the Oxygen and Nitrogen Chemical Abundances and the Evolution of the "Green Pea" Galaxies", which disputes the metallicities calculated in the original Cardamone et al. GPs paper Amorin et al. use a different methodology from Cardamone et al. to produce metallicity values more than one fifth (20%) of the previous values (about 20% solar or one fifth solar) for the 80 'starburst' GPs. These mean values are log /H12~8.05, which shows a clear offset of 0.65dex between the two papers' values. For these 80 GPs, Amorin et al., using a direct method, rather than strong-line methods as used in Cardamone et al., calculate physical properties, as well as oxygen
Oxygen is the chemical element with the symbol O and atomic number 8. It is a member of the chalcogen group in the periodic table, a highly reactive nonmetal, and an oxidizing agent that readily forms oxides with most elements as ...
and nitrogen
Nitrogen is the chemical element with the symbol N and atomic number 7. Nitrogen is a nonmetal and the lightest member of group 15 of the periodic table, often called the pnictogens. It is a common element in the universe, estimated at se ...
ionic abundances. These metals pollute hydrogen and helium, which make up the majority of the substances present in galaxies. As these metals are produced in supernovae, the more recent a galaxy is, the fewer metals it would have. As GPs are in the nearby, or recent, Universe, they should have more metals than galaxies at an earlier time.
 Amorin et al. find that the amount of metals, including the abundance of nitrogen, are different from normal values and that GPs are not consistent with the mass-metallicity relation, as concluded by Cardamone et al. This analysis indicates that GPs can be considered as genuine metal-poor galaxies. They then argue that this oxygen under-abundance is due to a recent interaction-induced inflow of gas, possibly coupled with a selective metal-rich gas loss driven by supernovae winds and that this can explain their findings. This further suggests that GPs are likely very short-lived as the intense star formation in them would quickly enrich the gas.
Amorin et al. find that the amount of metals, including the abundance of nitrogen, are different from normal values and that GPs are not consistent with the mass-metallicity relation, as concluded by Cardamone et al. This analysis indicates that GPs can be considered as genuine metal-poor galaxies. They then argue that this oxygen under-abundance is due to a recent interaction-induced inflow of gas, possibly coupled with a selective metal-rich gas loss driven by supernovae winds and that this can explain their findings. This further suggests that GPs are likely very short-lived as the intense star formation in them would quickly enrich the gas.
 In May 2011, R.Amorin, J.M.Vilchez and E.Perez-Montero published a conference proceeding paper titled "Unveiling the Nature of the "Green Pea" galaxies". In it they review recent scientific results and announcing a forthcoming paper on their recent observations at the
In May 2011, R.Amorin, J.M.Vilchez and E.Perez-Montero published a conference proceeding paper titled "Unveiling the Nature of the "Green Pea" galaxies". In it they review recent scientific results and announcing a forthcoming paper on their recent observations at the Gran Telescopio Canarias
The Gran Telescopio Canarias (GranTeCan or GTC) is a reflecting telescope located at the Roque de los Muchachos Observatory on the island of La Palma, in the Canaries, Spain. It is the world's largest single-aperture optical telescope.
Constr ...
. This paper is also a modified report of a presentation at the Joint European and National Astronomy Meeting (JENAM) 2010. They conclude that GPs are a genuine population of metal-poor, luminous and very compact starburst galaxies. Amongst the data, five graphs illustrate the findings they have made. Amorin et al. use masses calculated by Izotov, rather than by Cardamone. The metallicities that Amorin et al. use agree with Izotov's findings, or vice versa, rather than Cardamone's.
The first graph (on the left; fig.1 in paper) plots the nitrogen/oxygen vs. oxygen/hydrogen abundance ratio. The 2D histogram of SDSS star forming galaxies is shown in logarithmic scale while the GPs are indicated by circles. This shows that GPs are metal-poor.
 The second graph (on the right; fig.2 in paper) plots O/H vs. stellar mass. The 2D histogram of SDSS SFGs is shown in logarithmic scale and their best likelihood fit is shown by a black solid line. The subset of 62 GPs are indicated by circles and their best linear fit is shown by a dashed line. For comparison we also show the quadratic fit presented in Amorin ''et al.'' 2010 for the full sample of 80 GPs. SFGs at z ≥ 2 by Erb et al. are also shown by asterisks for comparison.
The second graph (on the right; fig.2 in paper) plots O/H vs. stellar mass. The 2D histogram of SDSS SFGs is shown in logarithmic scale and their best likelihood fit is shown by a black solid line. The subset of 62 GPs are indicated by circles and their best linear fit is shown by a dashed line. For comparison we also show the quadratic fit presented in Amorin ''et al.'' 2010 for the full sample of 80 GPs. SFGs at z ≥ 2 by Erb et al. are also shown by asterisks for comparison.
 The third graph (on the left; fig.3 in paper) plots N/O vs. stellar mass. Symbols as in fig.1.
The third graph (on the left; fig.3 in paper) plots N/O vs. stellar mass. Symbols as in fig.1.
 The fourth graph (on the right; fig.4 in paper) plots O/H vs. B-band (rest-frame) absolute magnitude. The meaning of symbols is indicated. Distances used in computing (extinction corrected) absolute magnitudes were, in all cases, calculated using spectroscopic redshifts and the same cosmological parameters. The dashed line indicates the fit to the HII galaxies in the Luminosity-Metallicity Relationship (MZR) given by Lee et al. 2004.
The fifth graph (on the left; fig.5 in paper) plots gas mass fraction vs. metallicity. Different lines correspond to closed-box models at different yields, as indicated in the legend. Open and filled circles are GPs which are above and below the fit to their MZR. Diamonds are values for the same Wolf-Rayet galaxies as in Fig. 4.
The fourth graph (on the right; fig.4 in paper) plots O/H vs. B-band (rest-frame) absolute magnitude. The meaning of symbols is indicated. Distances used in computing (extinction corrected) absolute magnitudes were, in all cases, calculated using spectroscopic redshifts and the same cosmological parameters. The dashed line indicates the fit to the HII galaxies in the Luminosity-Metallicity Relationship (MZR) given by Lee et al. 2004.
The fifth graph (on the left; fig.5 in paper) plots gas mass fraction vs. metallicity. Different lines correspond to closed-box models at different yields, as indicated in the legend. Open and filled circles are GPs which are above and below the fit to their MZR. Diamonds are values for the same Wolf-Rayet galaxies as in Fig. 4.
GTC-OSIRIS spectrophotometry
In February 2012, authors R. Amorin, E. Perez-Montero, J. Vilchez and P. Papaderos published a paper titled "The star formation history and metal content of the "Green Peas". New detailed GTC-OSIRIS spectrophotometry of three galaxies" in which they presented the findings of observations carried out using theGran Telescopio Canarias
The Gran Telescopio Canarias (GranTeCan or GTC) is a reflecting telescope located at the Roque de los Muchachos Observatory on the island of La Palma, in the Canaries, Spain. It is the world's largest single-aperture optical telescope.
Constr ...
at the Roque de los Muchachos Observatory
Roque de los Muchachos Observatory ( es, Observatorio del Roque de los Muchachos, ORM) is an astronomical observatory located in the municipality of Garafía on the island of La Palma in the Canary Islands, Spain. The observatory site is operated b ...
. They gather deep broad-band imaging and long-slit spectroscopy of 3 GPs using high precision equipment.
Their findings show that the three GPs display relatively low extinction
Extinction is the termination of a kind of organism or of a group of kinds (taxon), usually a species. The moment of extinction is generally considered to be the death of the last individual of the species, although the capacity to breed and ...
, low oxygen abundances and high nitrogen-to-oxygen ratios. Also reported are the clear signatures of Wolf–Rayet star
Wolf–Rayet stars, often abbreviated as WR stars, are a rare heterogeneous set of stars with unusual spectra showing prominent broad emission lines of ionised helium and highly ionised nitrogen or carbon. The spectra indicate very high surface ...
s, of which a population are found (between ~800 and ~1200). A combination of population and evolutionary synthesis models strongly suggest a formation history dominated by starbursts. These models show that these three GPs currently undergo a major starburst producing between ~4% and ~20% of their stellar mass. However, as these models imply, they are old galaxies having formed most of their stellar mass several billion
Billion is a word for a large number, and it has two distinct definitions:
*1,000,000,000, i.e. one thousand million, or (ten to the ninth power), as defined on the short scale. This is its only current meaning in English.
* 1,000,000,000,000, i. ...
years ago. The presence of old stars has been spectroscopically verified in one of the three galaxies by the detection of Magnesium
Magnesium is a chemical element with the symbol Mg and atomic number 12. It is a shiny gray metal having a low density, low melting point and high chemical reactivity. Like the other alkaline earth metals (group 2 of the periodic ta ...
. Surface photometry, using data from the Hubble Space Telescope archive, indicates that the three GPs possess an exponential low surface brightness envelope (see Low-surface-brightness galaxy). This suggests that GPs are identifiable with major episodes in the assembly history of local Blue Compact Dwarf galaxies.
The three galaxies are (using SDSS references):
*587724199349387411
*587729155743875234
*587731187273892048
Comparison to luminous compact galaxies
In February 2011, Yuri Izotov, Natalia Guseva and Trinh Thuan published a paper titled "Green Pea Galaxies and Cohorts: Luminous Compact Emission-line Galaxies in the Sloan Digital Sky Survey", examining the GPs and comparing these to a larger set of 803 Luminous Compact Galaxies (LCGs). They use a different set of selection criteria from Cardamone et al. These are: a) a high extinction-corrected luminosity > 3x10^40Erg
The erg is a unit of energy equal to 10−7joules (100 nJ). It originated in the Centimetre–gram–second system of units (CGS). It has the symbol ''erg''. The erg is not an SI unit. Its name is derived from (), a Greek word meaning 'work' o ...
s s^-1 of the hydrogen beta emission line; (see hydrogen spectral series
The emission spectrum of atomic hydrogen has been divided into a number of spectral series, with wavelengths given by the Rydberg formula. These observed spectral lines are due to the electron making transitions between two energy levels in an ...
) b) a high equivalent width greater than 5 nm; c) a strong IIIwavelength at the 436.3 nm emission line allowing accurate abundance determination; d) a compact structure on SDSS images; and e) an absence of obvious active galactic nuclei
An active galactic nucleus (AGN) is a compact region at the center of a galaxy that has a much-higher-than-normal luminosity over at least some portion of the electromagnetic spectrum with characteristics indicating that the luminosity is not prod ...
spectroscopic features.
Its conclusions (shortened) are:
# The selected galaxies have redshifts between 0.02 and 0.63, a range equal or greater than a factor of 2 when compared to the GPs. They find the properties of LCGs and GPs are similar to Blue Compact Dwarf galaxies. Explaining how the colours of emission-line galaxies change with distance using SDSS, they conclude that GPs are just subsamples within a narrow redshift range of their larger LCG sample.
# Although there were no upper limits on the hydrogen beta luminosities, it was found that there was a 'self-regulating' mechanism which bound the LCGs to a limit of ~3x10^42 Erg
The erg is a unit of energy equal to 10−7joules (100 nJ). It originated in the Centimetre–gram–second system of units (CGS). It has the symbol ''erg''. The erg is not an SI unit. Its name is derived from (), a Greek word meaning 'work' o ...
s s^-1.
# In the IIIwavelength 500.7 nm ratio to hydrogen beta vs. IIwavelength 658.3 nm ratio to hydrogen alpha, LCGs occupy the region, in the diagnostic diagram, of star-forming galaxies with the highest excitation. However, some active galactic nuclei
An active galactic nucleus (AGN) is a compact region at the center of a galaxy that has a much-higher-than-normal luminosity over at least some portion of the electromagnetic spectrum with characteristics indicating that the luminosity is not prod ...
also lie in this region in the diagnostic diagram.
# The oxygen abundances 12 + log O/H in LCGs are in the range 7.6–8.4 with a median value of ~8.11, confirming Amorin et al.'s analysis of a subset of GPs. This range of oxygen abundances is typical of nearby lower-luminosity Blue Compact Dwarfs. These results show that the original Cardamone et al. median oxygen abundance of 12 + log O/H = ~8.7 is overestimated, as a different, empirical method was originally used, rather than the direct method by Amorin et al. and Izotov et al. There is no dependence of oxygen abundance on redshift.
# In the luminosity-metallicity diagram (fig. 8 in paper), LCGs are shifted by ~2 magnitudes brighter when compared to nearby emission-line galaxies. LCGs form a common luminosity-metallicity relation, as for the most actively star-forming galaxies. Some LCGs have oxygen abundances and luminosities similar to Lyman-break galaxies (LBGs), despite much lower redshifts, thus enabling the study of LBGs through LCGs.
Radio detection
In February 2012, authors Sayan Chakraborti, Naveen Yadav, Alak Ray and Carolin Cardamone published a paper titled "Radio Detection of Green Peas: Implications for Magnetic Fields in Young Galaxies" which deals with the magnetic properties of the GPs. In it, they describe observations which have produced some unexpected results raising puzzling questions about the origin and evolution of magnetism in young galaxies. The ages are estimated from looking at the star formation that the GPs currently have ongoing and then estimating the age of the most recent starburst. GPs are very young galaxies, with models of the observed stellar populations indicating that they are around 10^8 (one hundred million) years old (1/100th the age of theMilky Way
The Milky Way is the galaxy that includes our Solar System, with the name describing the galaxy's appearance from Earth: a hazy band of light seen in the night sky formed from stars that cannot be individually distinguished by the naked eye. ...
). There is some question as to whether the GPs all started from the same starburst or if multiple starbursts went on (much older stellar populations are hidden as we can't see the light from these).
Using data from the Giant Metrewave Radio Telescope (GMRT) and archive observations from the Karl G. Jansky Very Large Array
The Karl G. Jansky Very Large Array (VLA) is a centimeter-wavelength radio astronomy observatory located in central New Mexico on the Plains of San Agustin, between the towns of Magdalena and Datil, ~ west of Socorro. The VLA comprises twent ...
(VLA), Chakraborti et al. produced a set of results which are based around the VLA FIRST detection of stacked flux from 32 GPs and three 3-hour low frequency observations from the GMRT which targeted the three most promising candidates which had expected fluxes at the milli-Jansky
The jansky (symbol Jy, plural ''janskys'') is a non- SI unit of spectral flux density, or spectral irradiance, used especially in radio astronomy. It is equivalent to 10−26 watts per square metre per hertz.
The ''flux density'' or ''monoch ...
(mJy) level.
Chakraborti et al. find that the three GPs observed by the GMRT have a magnetic field of B~39 μ G, and more generally a figure of greater than B~30μG for all the GPs. This is compared to a figure of B~5μG for the Milky Way
The Milky Way is the galaxy that includes our Solar System, with the name describing the galaxy's appearance from Earth: a hazy band of light seen in the night sky formed from stars that cannot be individually distinguished by the naked eye. ...
. The present understanding is of magnetic field growth based on the amplification of seed fields by dynamo theory
In physics, the dynamo theory proposes a mechanism by which a celestial body such as Earth or a star generates a magnetic field. The dynamo theory describes the process through which a rotating, convecting, and electrically conducting fluid can ...
and its action over a galaxy's lifetime. The observations of GPs challenge that thinking.
Given the high star-forming rates of GPs generally, they are expected to host a large number of supernovae. Supernovae accelerate electrons to high energies, near to the speed of light, which may then emit synchrotron radiation in radio spectrum
The radio spectrum is the part of the electromagnetic spectrum with frequencies from 0 Hz to 3,000 GHz (3 THz). Electromagnetic waves in this frequency range, called radio waves, are widely used in modern technology, particula ...
frequencies.
In 2021, Kanekar et al. reported the first detection of HI 21 cm line emission in 19 GPs using the Green Bank Telescope
The Robert C. Byrd Green Bank Telescope (GBT) in Green Bank, West Virginia, US is the world's largest fully steerable radio telescope, surpassing the Effelsberg 100-m Radio Telescope in Germany. The Green Bank site was part of the National Radi ...
and Arecibo Observatory. Their results give the first estimates of atomic gas mass in Green Pea galaxies.
See also
* * * * * – One of nine galaxies shown to leak Lyman Continuum photons. * * * – One of nine galaxies shown to 'leak' Lyman continuum photons. *References
{{Portal bar, Stars, Spaceflight, Outer space, Solar System Galaxies Crowdsourcing Citizen science 2007 in science