Pavel Cherenkov on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Pavel Alekseyevich Cherenkov (russian: Па́вел Алексе́евич Черенко́в ; July 28, 1904 – January 6, 1990) was a
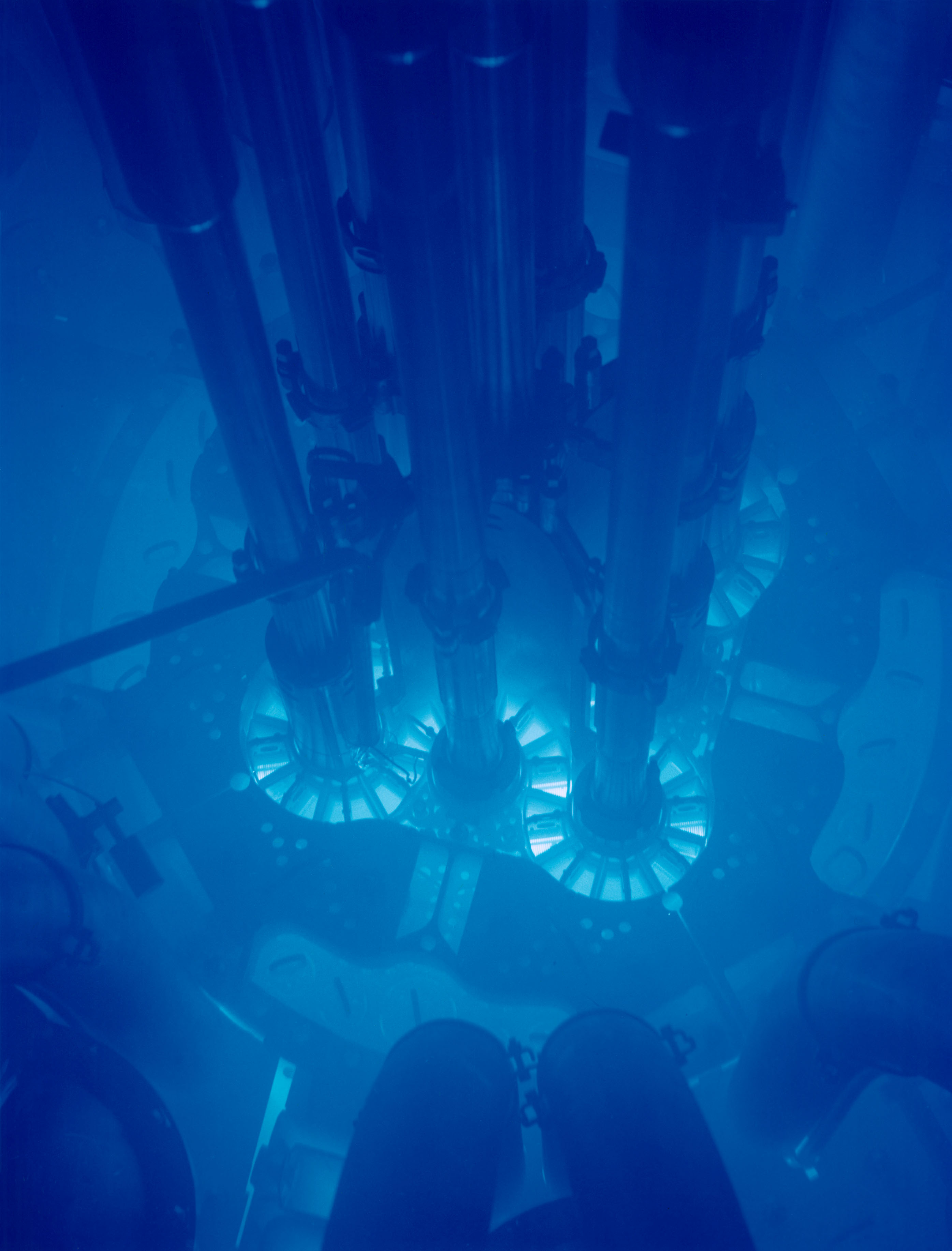 In 1934, while working under S. I. Vavilov, Cherenkov observed the emission of blue light from a bottle of water subjected to radioactive bombardment. This phenomenon, associated with charged
In 1934, while working under S. I. Vavilov, Cherenkov observed the emission of blue light from a bottle of water subjected to radioactive bombardment. This phenomenon, associated with charged
Cherenkov's photo
– from the
Soviet
The Soviet Union,. officially the Union of Soviet Socialist Republics. (USSR),. was a List of former transcontinental countries#Since 1700, transcontinental country that spanned much of Eurasia from 1922 to 1991. A flagship communist state, ...
physicist who shared the Nobel Prize
The Nobel Prizes ( ; sv, Nobelpriset ; no, Nobelprisen ) are five separate prizes that, according to Alfred Nobel's will of 1895, are awarded to "those who, during the preceding year, have conferred the greatest benefit to humankind." Alfr ...
in physics
Physics is the natural science that studies matter, its fundamental constituents, its motion and behavior through space and time, and the related entities of energy and force. "Physical science is that department of knowledge which ...
in 1958 with Ilya Frank
Ilya Mikhailovich Frank (russian: Илья́ Миха́йлович Франк; 23 October 1908 – 22 June 1990) was a Soviet winner of the Nobel Prize for Physics in 1958 jointly with Pavel Alekseyevich Cherenkov and Igor Y. Tamm, also of the ...
and Igor Tamm
Igor Yevgenyevich Tamm ( rus, И́горь Евге́ньевич Тамм , p=ˈiɡərʲ jɪvˈɡʲenʲjɪvitɕ ˈtam , a=Ru-Igor Yevgenyevich Tamm.ogg; 8 July 1895 – 12 April 1971) was a Soviet physicist who received the 1958 Nobel Prize in ...
for the discovery of Cherenkov radiation, made in 1934.
Biography
Cherenkov was born in 1904 to Alexey Cherenkov and Mariya Cherenkova in the small village of Novaya Chigla. This town is in present-dayVoronezh Oblast
Voronezh Oblast (russian: Воронежская область, Voronezhskaya oblast) is a federal subject of Russia (an oblast). Its administrative center is the city of Voronezh. Its population was 2,308,792 as of the 2021 Census.
Geograph ...
, Russia
Russia (, , ), or the Russian Federation, is a transcontinental country spanning Eastern Europe and Northern Asia. It is the largest country in the world, with its internationally recognised territory covering , and encompassing one-ei ...
.
In 1928, he graduated from the Department of Physics and Mathematics of Voronezh State University. In 1930, he took a post as a senior researcher in the Lebedev Physical Institute
The Lebedev Physical Institute of the Russian Academy of Sciences (LPI RAS or just LPI) (in russian: Физи́ческий институ́т имени П.Н.Ле́бедева Российской академии наук (ФИАН)), situated ...
. That same year he married Maria Putintseva, daughter of A.M. Putintsev, a Professor of Russian Literature
Russian literature refers to the literature of Russia and its émigrés and to Russian-language literature. The roots of Russian literature can be traced to the Middle Ages, when epics and chronicles in Old East Slavic were composed. By the ...
. They had a son, Alexey, and a daughter, Yelena.
Cherenkov was promoted to section leader, and in 1940 was awarded the degree of Doctor of Physico-Mathematical Sciences. In 1953, he was confirmed as Professor of Experimental Physics. Starting in 1959, he headed the institute's photo-meson processes laboratory. He remained a professor for fourteen years. In 1970, he became an Academician of the USSR Academy of Sciences
The Academy of Sciences of the Soviet Union was the highest scientific institution of the Soviet Union from 1925 to 1991, uniting the country's leading scientists, subordinated directly to the Council of Ministers of the Soviet Union (until 1946 ...
.
Cherenkov died in Moscow
Moscow ( , US chiefly ; rus, links=no, Москва, r=Moskva, p=mɐskˈva, a=Москва.ogg) is the capital and largest city of Russia. The city stands on the Moskva River in Central Russia, with a population estimated at 13.0 million ...
on January 6, 1990, and was buried in Novodevichy Cemetery
Novodevichy Cemetery ( rus, Новоде́вичье кла́дбище, Novodevichye kladbishche) is a cemetery in Moscow. It lies next to the southern wall of the 16th-century Novodevichy Convent, which is the city's third most popular touris ...
.
Discoveries in physics
 In 1934, while working under S. I. Vavilov, Cherenkov observed the emission of blue light from a bottle of water subjected to radioactive bombardment. This phenomenon, associated with charged
In 1934, while working under S. I. Vavilov, Cherenkov observed the emission of blue light from a bottle of water subjected to radioactive bombardment. This phenomenon, associated with charged subatomic particle
In physical sciences, a subatomic particle is a particle that composes an atom. According to the Standard Model of particle physics, a subatomic particle can be either a composite particle, which is composed of other particles (for example, a p ...
s moving at velocities greater than the phase velocity
The phase velocity of a wave is the rate at which the wave propagates in any medium. This is the velocity at which the phase of any one frequency component of the wave travels. For such a component, any given phase of the wave (for example, ...
of light, proved to be of great importance in subsequent experimental work in nuclear physics
Nuclear physics is the field of physics that studies atomic nuclei and their constituents and interactions, in addition to the study of other forms of nuclear matter.
Nuclear physics should not be confused with atomic physics, which studies t ...
, and for the study of cosmic ray
Cosmic rays are high-energy particles or clusters of particles (primarily represented by protons or atomic nuclei) that move through space at nearly the speed of light. They originate from the Sun, from outside of the Solar System in our own ...
s. Eponymously, it was dubbed the Cherenkov effect, as was the Cherenkov detector
A Cherenkov detector (pronunciation: /tʃɛrɛnˈkɔv/; Russian: Черенко́в) is a particle detector using the speed threshold for light production, the speed-dependent light output or the speed-dependent light direction of Cherenkov rad ...
, which has become a standard piece of equipment in particle-physics research for observing the existence and velocity of high-speed particles. The device was installed in Sputnik 3
Sputnik 3 (russian: Спутник-3, Satellite 3) was a Soviet satellite launched on 15 May 1958 from Baikonur Cosmodrome by a modified R-7/SS-6 ICBM. The scientific satellite carried a large array of instruments for geophysical research of ...
.
Pavel Cherenkov also shared in the development and construction of electron accelerators and in the investigation of photo-nuclear and photo-meson reactions.
Awards and honours
Cherenkov was awarded twoStalin Prize Stalin Prize may refer to:
* The State Stalin Prize in science and engineering and in arts, awarded 1941 to 1954, later known as the USSR State Prize
The USSR State Prize (russian: links=no, Государственная премия СССР, ...
s, the first in 1946, sharing the honor with Vavilov, Frank and Tamm
Tamm is a '' Stadt'' (town) in the district of Ludwigsburg, Baden-Württemberg, Germany. It is situated 6 km northwest of Ludwigsburg, 4 km south of Bietigheim-Bissingen, and approx. 17 km north of Stuttgart's city center. As of ...
, and another in 1952. He was also awarded the USSR State Prize
The USSR State Prize (russian: links=no, Государственная премия СССР, Gosudarstvennaya premiya SSSR) was the Soviet Union's state honor. It was established on 9 September 1966. After the dissolution of the Soviet Union, t ...
in 1977. In 1958, he was awarded the Nobel Prize in Physics
)
, image = Nobel Prize.png
, alt = A golden medallion with an embossed image of a bearded man facing left in profile. To the left of the man is the text "ALFR•" then "NOBEL", and on the right, the text (smaller) "NAT•" then " ...
for the discovery of the Cherenkov effect. He was also awarded the Soviet Union's Hero of Socialist Labour
The Hero of Socialist Labour (russian: links=no, Герой Социалистического Труда, Geroy Sotsialisticheskogo Truda) was an honorific title in the Soviet Union and other Warsaw Pact countries from 1938 to 1991. It repre ...
title in 1984. Cherenkov was a member of the Communist Party of the Soviet Union
" Hymn of the Bolshevik Party"
, headquarters = 4 Staraya Square, Moscow
, general_secretary = Vladimir Lenin (first) Mikhail Gorbachev (last)
, founded =
, banned =
, founder = Vladimir Lenin
, newspape ...
.
In popular culture
The novel '' Ghost Fleet'' makes the claim that many believe the ''Star Trek
''Star Trek'' is an American science fiction media franchise created by Gene Roddenberry, which began with the eponymous 1960s television series and quickly became a worldwide pop-culture phenomenon. The franchise has expanded into vari ...
'' character Pavel Chekov
Pavel Andreievich Chekov (russian: Павел Андреевич Чехов) is a fictional character in the ''Star Trek'' universe.
Walter Koenig portrayed Chekov in the second and third seasons of the original ''Star Trek'' series and the ...
is named after Pavel Cherenkov.
In ''Starship Troopers
''Starship Troopers'' is a military science fiction novel by American writer Robert A. Heinlein. Written in a few weeks in reaction to the US suspending nuclear tests, the story was first published as a two-part serial in ''The Magazine of F ...
'' spaceships travel faster than light using Cherenkov Drive.
References
External links
*Cherenkov's photo
– from the
Russian Academy of Sciences
The Russian Academy of Sciences (RAS; russian: Росси́йская акаде́мия нау́к (РАН) ''Rossíyskaya akadémiya naúk'') consists of the national academy of Russia; a network of scientific research institutes from across t ...
*
* including his Nobel Lecture, December 11, 1958 ''Radiation of Particles Moving at a Velocity Exceeding That of Light, and Some of the Possibilities for Their Use in Experimental Physics''
{{DEFAULTSORT:Cherenkov, Pavel Alekseyevich
1904 births
1990 deaths
Burials at Novodevichy Cemetery
Experimental physicists
Heroes of Socialist Labour
Recipients of the USSR State Prize
Full Members of the USSR Academy of Sciences
Nobel laureates in Physics
Particle physicists
Soviet inventors
Soviet Nobel laureates
Soviet physicists
Stalin Prize winners
Communist Party of the Soviet Union members
Voronezh State University alumni
Moscow Power Engineering Institute faculty
Foreign associates of the National Academy of Sciences