Pashtun tribes on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
The Pashtun tribes ( ps, پښتانه قبايل), historically also known as Afghan tribes, are the tribes of the
 The Bettani speak various
The Bettani speak various
Pashtun people
Pashtuns (, , ; ps, پښتانه, ), also known as Pakhtuns or Pathans, are an Iranian ethnic group who are native to the geographic region of Pashtunistan in the present-day countries of Afghanistan and Pakistan. They were historically r ...
, a large Eastern Iranian
The Eastern Iranian languages are a subgroup of the Iranian languages emerging in Middle Iranian times (from c. the 4th century BC). The Avestan language is often classified as early Eastern Iranian. As opposed to the Middle Western Iranian diale ...
ethnic group who use the Pashto language
Pashto (,; , ) is an Eastern Iranian language in the Indo-European language family. It is known in historical Persian literature as Afghani ().
Spoken as a native language mostly by ethnic Pashtuns, it is one of the two official langua ...
and follow Pashtunwali
Pashtunwali or Pakhtunwali ( ps, پښتونولي) is the traditional lifestyle and is best described as a code of honor of the Pashtun people, by which they live. Scholars widely have interpreted it as being "the way of the Afghans" or "the code ...
code of conduct. They are found primarily in Afghanistan
Afghanistan, officially the Islamic Emirate of Afghanistan,; prs, امارت اسلامی افغانستان is a landlocked country located at the crossroads of Central Asia and South Asia. Referred to as the Heart of Asia, it is borde ...
and Pakistan
Pakistan ( ur, ), officially the Islamic Republic of Pakistan ( ur, , label=none), is a country in South Asia. It is the world's List of countries and dependencies by population, fifth-most populous country, with a population of almost 24 ...
and form the world's largest tribal society
A society is a group of individuals involved in persistent social interaction, or a large social group sharing the same spatial or social territory, typically subject to the same political authority and dominant cultural expectations. Soc ...
, comprising over 49 million people and between 350 and 400 tribes and clans. They are traditionally divided into four tribal confederacies: the Sarbani (), the Bettani
The Bettani ( ps, بېټني), also spelled Baittani or Bhittani, is a Pashtun tribe located mostly in Afghanistan and Pakistan. The Bettani are named after ''Shaykh Beṭ'', their legendary ancestor who is said to be the second son of Qais Abd ...
(), the Gharghashti () and the Karlani ().
Folkloric genealogies trace the descendants of the Pashtuns to Qais Abdur Rashid and his three sons ''Saṛban'' (), ''Bēṭ'' (), and ''Gharghax̌t'' () as well as an adopted son, not directly adopted by Qais Abdul Rashid, therefore, the identity of Karlan himself and the man who adopted him, according to some books written on the history of the Pashtuns, is either unclear or controversial, the Karlani confederacy Ormur Baraki, who became the progenitor of the Karlani.
There are several levels of organisation of Pashtun tribes. The "tribe" is subdivided into kinship groups, each of which is a ''khel'' and ''zai''. A ''khel'' or ''zai'' is further divided into ''plarina'', each of which consists of several extended families. A large tribe often has dozens of subtribes whose members may see themselves as belonging to each, some or all of the sub-tribes in their family tree depending upon the social situation: co-operative, competitive or confrontational.
Etymologies
''Tarbur'' refers to a "tribe" split into two or more clans. ''Tarbur'' means "cousin" in Pashto, so tarbur could be an enemy as well in the Pashtun culture that they can occupy your land or property. Every Pashtun tribe is then divide into subtribes, also called ''khel'' or ''zai''. ''Zai'' in Pashto means "descendant". William Crooke has said that ''khel'' is from anArabic
Arabic (, ' ; , ' or ) is a Semitic language spoken primarily across the Arab world.Semitic languages: an international handbook / edited by Stefan Weninger; in collaboration with Geoffrey Khan, Michael P. Streck, Janet C. E.Watson; Walter ...
word meaning "association" or "company".
A ''khel'' is often based in a single village, but it may also be based on a larger area including several villages, or part of a town.
''Plarina'' is related to the Bactrian term ''plār'', which derives from Old Iranian ''piðar'' (in Bactrian and Pashto
Pashto (,; , ) is an Eastern Iranian language in the Indo-European language family. It is known in historical Persian literature as Afghani ().
Spoken as a native language mostly by ethnic Pashtuns, it is one of the two official langua ...
, Old Iranian /ð/ usually yields /l/), and is related to Sanskrit
Sanskrit (; attributively , ; nominally , , ) is a classical language belonging to the Indo-Aryan languages, Indo-Aryan branch of the Indo-European languages. It arose in South Asia after its predecessor languages had Trans-cultural diffusion ...
''pitar'' and English "father". The plural form of ''plār'' is ''plārina''. A ''plārina'' is considered only when the 7th generation is born, meaning the father of multiple families (''kahol''). Usually, the 7th forefather is assumed to take from one-and-a-half century to two centuries. ''Kul'' (plural ''kahol'') is the smallest unit in Pashtun tribal system, named after an ancestor of 1. ''Zāmon'' ("children"), 2. ''Lmasay / Nwasay'' ("grandchildren"), 3. ''Kaṛwasay'' ("great-grandchildren"), and 4. ''Kaoday'' ("great-great-grandchildren"). Once the fourth generation is born, it would be labelled a "family" or ''kūl''.
Dialects
 The Bettani speak various
The Bettani speak various Pashto dialects
Pashto dialects ( ps, د پښتو ژبګوټي də Pəx̌tó žәbgóṭi) can be divided into two large varieties: Northern Pashto and Southern Pashto. Each of the two varieties of Pashto is further divided into a number of dialects. Norther ...
. The Ghilji or (Gharzai) of the central region around Paktika
Paktika (Pashto/Dari: ) is one of the 34 provinces of Afghanistan, located in the eastern part of the country. Forming part of the larger Loya Paktia region, Paktika has a population of about 789,000, mostly ethnic Pashtuns. The town of Sharana ...
speak Central Pashto
Central Pashto ( ps, منځنۍ پښتو) () are the middle dialects: Dzadrāṇi, Banusi and Waziri. These dialects are affected by what Ibrahim Khan terms as "the Great Karlāṇ Vowel Shift".
Here is a comparison of Middle Dialects with So ...
, a dialect with unique phonetic features, transitional between the southern and the northern dialects of Pashto. The Lohani (Rohani, Nohani) Marwat, as well as some other minor Lodi tribes and the Bettani proper, speak the Marwat Lodi Bettani dialect, which is a southern Pashto variety, however, its phonetics are different from the southern Kandahari Pashto. The Sheerani tribe of the Bettani confederacy speaks another southern dialect. The northern Bettani clans speak the northern or "hard" Pashto variety. Some of the Bettani lineages, including some (but not all) clans of the Niazi, have abandoned Pashto. Today they speak other languages, like Urdu
Urdu (;"Urdu"
'' Hindko, Saraiki,
 The origin of Pashtuns is unclear but historians have come across references to various ancient peoples called ''
The origin of Pashtuns is unclear but historians have come across references to various ancient peoples called ''
BĒṬANĪ
Originally published on 15 December 1989. In the 15th century, the Bettani are known to have mainly inhabited the Logar, Zurmat, and Ghazni regions. Subsequently, many of their lineages settled to the northeast, spreading up to the Damaan Valley, Mianwali, and parts of the present-day Hazara Division of
/ref> Ahmad Shah is now regarded as the founder of the modern state of Afghanistan. He controlled areas from
Pashtun Tribe, Clan, & Ethnic Genealogies
US Naval Postgraduate School (on the Wayback Machine) *Sungur, Z.T. (2013)
Articulation of Tribalism into Modernity: the Case of Pashtuns in Afghanistan
(Master's Thesis). Middle East Technical University, Ankara. {{DEFAULTSORT:Pashtun Tribes Demographics of Pakistan Social groups of Pakistan Social groups of Afghanistan Pashtun people Lists of modern Indo-European tribes and clans
'' Hindko, Saraiki,
Punjabi
Punjabi, or Panjabi, most often refers to:
* Something of, from, or related to Punjab, a region in India and Pakistan
* Punjabi language
* Punjabi people
* Punjabi dialects and languages
Punjabi may also refer to:
* Punjabi (horse), a British Th ...
, Dari
Dari (, , ), also known as Dari Persian (, ), is the variety of the Persian language spoken in Afghanistan. Dari is the term officially recognised and promoted since 1964 by the Afghan government for the Persian language,Lazard, G.Darī ...
.
The Gharghashti Kakar Naghar
Naghar is a small village located in the Bageshwar district in the Indian state of Uttarakhand. It is about from its district headquarters and is located on the bank of the Pungar River in the Pungar Valley (or Dugpatti).
The population is ...
Panni Mandokhel
The Mandokhel ( ps, مندو خیل ) is a PashtunTalebi, Abdul Latif Yaad. Pashtanay Qabeelay. 2nd ed.: Danish, 2007. Print. p.256-257 tribe primarily found in northern regions of Balochistan Province, Pakistan and southern Afghanistan. Most of t ...
and Musakhel and other minor settled in the region around Quetta
Quetta (; ur, ; ; ps, کوټه) is the tenth most populous city in Pakistan with a population of over 1.1 million. It is situated in south-west of the country close to the International border with Afghanistan. It is the capital of th ...
Zhob and Loralai speak dialect, which is a "soft" Pashto dialect very similar to Kandahari Pashto. The Safi, some of the Jaduns, and some other minor northern Gharghashti tribes speak the northern or "hard" Pashto variety. The Jaduns
The Jadoon (also Gadoon) (Hindko/ ur, جدون; ps, جدون ,ګدون) is a Pashtun Afghan tribe in Pakistan, partly in Gadoon in Swabi, and partly in Abbottabad and Haripur districts of Khyber Pakhtunkhwa province. Across the Durand line, some ...
, living on the Mahabun mountain slopes around Swabi speak Pashto, while those living in Hazara speak Pashto and Hindko. Some clans of the Safi tribe speak the Pashayi languages but are mostly bilingual in Pashto.
The Karlani speak some of the most distinctive Pashto dialects which are lexically different from standard Pashto varieties, and phonetically very varied. Furthermore, the Karlani dialects have a tendency towards a change in the pronunciation of vowels. Depending on the particular dialect, the standard Pashto � may change into � �/å/o �/ȫ/e respectively. In the Karlani dialects of Waziristan, Bannu, Tani (southern Khost),also, Mangal, which follow the vowel shift to the greatest extent, these four vowels normally change into � respectively. Much of the Ormur tribe settled in some villages of Waziristan and Logar, who give their name to Ormur the folkloric ancestor of the Karlani, speak the Ormuri language which is distinct from Pashto. However, in general the Ormur are bilingual in Pashto, particularly in the Karlani dialect of Wazirwola
Waziristāní ( ps, وزیرستانۍ), also known as Wazirwóla ( ps, وزیرواله, meaning "of the Wazirs") and Wazirí, is a central Pashto dialect spoken in North Waziristan and South Waziristan. Waziristani differs in pronunciation an ...
.
The southwestern Sarbani tribes, most notably the Durrani, speak (Kandahari Pashto) a "soft" dialect of Pashto; while northwestern Sarbani tribes such as Gigyani tribe
Gigyani is a tribe of Pakhtuns
Pashtuns (, , ; ps, پښتانه, ), also known as Pakhtuns or Pathans, are an Iranian ethnic group who are native to the geographic region of Pashtunistan in the present-day countries of Afghanistan and ...
, Yousafzai Khalil and Mohmand tribes etc., most notably they speak (Peshawari Pashto) Pashto a "hard" dialect of Pashto. Both of them are considered upper class dialects. In addition, a small section of the Tarin clan of the Sarbani living east of Quetta
Quetta (; ur, ; ; ps, کوټه) is the tenth most populous city in Pakistan with a population of over 1.1 million. It is situated in south-west of the country close to the International border with Afghanistan. It is the capital of th ...
speak the distinctive Wanetsi (Tareeno) dialect, which is considered by some modern scholars to be distinctive enough to be classified as its own language.
History
 The origin of Pashtuns is unclear but historians have come across references to various ancient peoples called ''
The origin of Pashtuns is unclear but historians have come across references to various ancient peoples called ''Pakthas
This is a list of ancient Indo-Aryan peoples and tribes that are mentioned in the literature of Indic religions.
From the second or first millennium BCE, ancient Indo-Aryan peoples and tribes turned into most of the population in the northern ...
'' (''Pactyans'') between the 2nd and the 1st millennium, who may be their early ancestors. Often characterised as a warrior and martial race, their history is mostly spread among various countries of South and Central Asia
Central Asia, also known as Middle Asia, is a region of Asia that stretches from the Caspian Sea in the west to western China and Mongolia in the east, and from Afghanistan and Iran in the south to Russia in the north. It includes the fo ...
, centered on their traditional seat of power in medieval Afghanistan. One theory suggests that the modern Ghilji lineages descended from the medieval Khalaj or Khilji tribe. Some Bettani lineages, however, are said to have descended in part from the medieval Ghorid people. The Bettani are named after their folkloric leader or ancestor, ''Shaikh Bet Baba'' (claimed to be among the first Pashto-language poets
Pashto (,; , ) is an Eastern Iranian language in the Indo-European language family. It is known in historical Persian literature as Afghani ().
Spoken as a native language mostly by ethnic Pashtuns, it is one of the two official languag ...
), who lived in the Altamur range, located between the Logar and Zurmat valleys. He is reported to have been buried in Ghazni
Ghazni ( prs, غزنی, ps, غزني), historically known as Ghaznain () or Ghazna (), also transliterated as Ghuznee, and anciently known as Alexandria in Opiana ( gr, Αλεξάνδρεια Ωπιανή), is a city in southeastern Afghanistan ...
.Balland, Daniel. ''Encyclopaedia Iranica''BĒṬANĪ
Originally published on 15 December 1989. In the 15th century, the Bettani are known to have mainly inhabited the Logar, Zurmat, and Ghazni regions. Subsequently, many of their lineages settled to the northeast, spreading up to the Damaan Valley, Mianwali, and parts of the present-day Hazara Division of
Khyber Pakhtunkhwa
Khyber Pakhtunkhwa (; ps, خېبر پښتونخوا; Urdu, Hindko: خیبر پختونخوا) commonly abbreviated as KP or KPK, is one of the four provinces of Pakistan. Located in the northwestern region of the country, Khyber Pakhtunkhwa ...
, Pakistan, in the east, and parts of Kunduz Afghanistan in the north. In the 19th century, the traditional way of life of the Bettani combined small-scale irrigated
Irrigation (also referred to as watering) is the practice of applying controlled amounts of water to land to help grow crops, landscape plants, and lawns. Irrigation has been a key aspect of agriculture for over 5,000 years and has been develo ...
agriculture with seasonal nomad
A nomad is a member of a community without fixed habitation who regularly moves to and from the same areas. Such groups include hunter-gatherers, pastoral nomads (owning livestock), tinkers and trader nomads. In the twentieth century, the po ...
ism or seminomadism. They engaged in pastoral migrations, along the mountain slopes in summers, and inversely, towards the Indus plains in winters. From the 13th century, various Khilji dynasties and ruling entities took control in the Bengal
Bengal ( ; bn, বাংলা/বঙ্গ, translit=Bānglā/Bôngô, ) is a geopolitical, cultural and historical region in South Asia, specifically in the eastern part of the Indian subcontinent at the apex of the Bay of Bengal, predom ...
and Delhi Sultanates of the Indian subcontinent
The Indian subcontinent is a physiographical region in Southern Asia. It is situated on the Indian Plate, projecting southwards into the Indian Ocean from the Himalayas. Geopolitically, it includes the countries of Bangladesh, Bhutan, In ...
.
In the 15th century, the Lodi tribe founded the Lodi dynasty, the last dynasty to rule the Delhi Sultanate. In the 16th century, the Sur Empire with its capital at Delhi
Delhi, officially the National Capital Territory (NCT) of Delhi, is a city and a union territory of India containing New Delhi, the capital of India. Straddling the Yamuna river, primarily its western or right bank, Delhi shares borders w ...
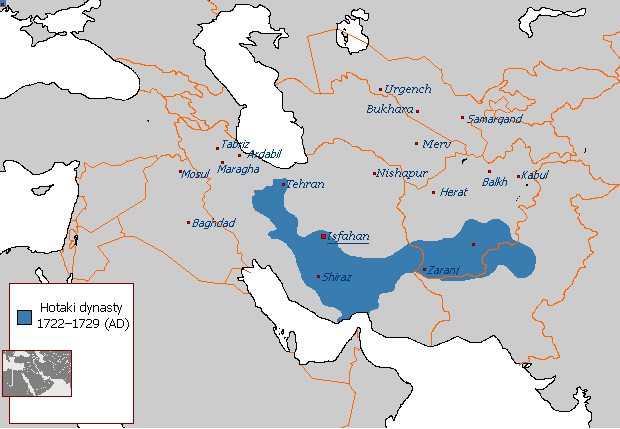
was founded by Sher Shah Suri, a member of the Sur clan of the Bettani confederacy. Between 1709 and 1738, the Hotak clan of the Ghilji tribe ruled the Hotak Empire based first in Kandahar, Afghanistan and later very briefly in Isfahan, Persia.
In the 16th century, Taj Khan Karrani of the Karlani tribe founded the Karrani dynasty, the last dynasty to rule the Bengal Sultanate. Several Karlani clans served in the Mughal army
The Army of the Mughal Empire was the force by which the Mughal emperors established their empire in the 15th century and expanded it to its greatest extent at the beginning of the 18th century. Although its origins, like the Mughals themselves, ...
. The Bhopal State
Bhopal State (pronounced ) was an Islamic principality founded in the beginning of 18th-century India by the Afghan Mughal noble Dost Muhammad Khan. It was a tributary state during 18th century, a princely salute state with 19-gun salute ...
, in the present-day Madhya Pradesh
Madhya Pradesh (, ; meaning 'central province') is a state in central India. Its capital is Bhopal, and the largest city is Indore, with Jabalpur, Ujjain, Gwalior, Sagar, and Rewa being the other major cities. Madhya Pradesh is the second ...
state of Central India, was founded in 1723 by Dost Mohammad Khan Mirazikhel. He was from the Orakzai clan of the Karlani tribe, and was a mercenary in the Mughal army. After his death in 1728, his descendants, the Nawabs of Bhopal, continued ruling the state until Hamidullah Khan, the last sovereign nawab of the dynasty, officially acceded the state to India
India, officially the Republic of India (Hindi: ), is a country in South Asia. It is the List of countries and dependencies by area, seventh-largest country by area, the List of countries and dependencies by population, second-most populous ...
in 1949.
Ahmad Shah Durrani of the Sadozai clan of the ''Abdali'' tribe (now known as "Durrani" after him) established the Durrani Empire in 1747 with its capital at Kandahar. Ahmad Shah adopted the title ''Durr-e Durrānī'' ("pearl of pearls" or "pearl of the age"), and the name of his tribe ''Abdali'' was changed to "Durrani" after him.The Hephthalites: Archaeological and Historical Analysis, Aydogdu Kurbanov, Berlin, 2010, page 242./ref> Ahmad Shah is now regarded as the founder of the modern state of Afghanistan. He controlled areas from
Khorasan
Khorasan may refer to:
* Greater Khorasan, a historical region which lies mostly in modern-day northern/northwestern Afghanistan, northeastern Iran, southern Turkmenistan, Tajikistan, and Uzbekistan
* Khorasan Province, a pre-2004 province of Ira ...
in the west up to Kashmir and Delhi
Delhi, officially the National Capital Territory (NCT) of Delhi, is a city and a union territory of India containing New Delhi, the capital of India. Straddling the Yamuna river, primarily its western or right bank, Delhi shares borders w ...
in the east, and from the Amu Darya
The Amu Darya, tk, Amyderýa/ uz, Amudaryo// tg, Амударё, Amudaryo ps, , tr, Ceyhun / Amu Derya grc, Ὦξος, Ôxos (also called the Amu, Amo River and historically known by its Latin name or Greek ) is a major river in Central Asi ...
in the north up to the Arabian Sea
The Arabian Sea ( ar, اَلْبَحرْ ٱلْعَرَبِيُّ, Al-Bahr al-ˁArabī) is a region of the northern Indian Ocean bounded on the north by Pakistan, Iran and the Gulf of Oman, on the west by the Gulf of Aden, Guardafui Channe ...
in the south. It was the second-greatest Muslim empire in the second half of the 18th century, surpassed in size only by the Ottoman Empire
The Ottoman Empire, * ; is an archaic version. The definite article forms and were synonymous * and el, Оθωμανική Αυτοκρατορία, Othōmanikē Avtokratoria, label=none * info page on book at Martin Luther University ...
.
In 1826, Dost Mohammad Khan
Dost Mohammad Khan Barakzai (Pashto/ Persian: ; 23 December 17929 June 1863), nicknamed the Amir-i Kabir, Also titled Amir al-Mu'minin, was a member of the Barakzai dynasty and one of the prominent rulers of the Emirate of Afghanistan. His 37-ye ...
, of the Barakzai clan of the Durrani tribe, founded the Barakzai dynasty
The two branches of the Barakzai dynasty (, "sons of Barak") ruled modern day Afghanistan from 1823 to 1973 when the monarchy ended under Musahiban Mohammed Zahir Shah. The Barakzai dynasty was established by Dost Mohammad Khan after the Durr ...
centered at Kabul. The Barakzai dynasty ruled present-day Afghanistan until 1973 when Mohammed Zahir Shah, the last Barakzai king, was overthrown in a bloodless coup by his own cousin Mohammed Daoud Khan
Mohammed Daoud Khan ( ps, ), also romanized as Daud Khan or Dawood Khan (18 July 1909 – 28 April 1978), was an Afghan politician and general who served as prime minister of Afghanistan from 1953 to 1963 and, as leader of the 1973 Afghan cou ...
. The coup ended the Barakzai kingdom and established the Republic of Afghanistan (1973—1978). The current heir apparent
An heir apparent, often shortened to heir, is a person who is first in an order of succession and cannot be displaced from inheriting by the birth of another person; a person who is first in the order of succession but can be displaced by the b ...
and crown prince of the Barakzai kingdom (23 July 2007 – present) is Ahmad Shah Khan.
During the Delhi Sultanate era, the Pashtun Lodi dynasty replaced the Turkic rulers in North India. Some ruled from the Bengal Sultanate. Majority Pashtuns fought the Safavids and Mughals before obtaining an independent
Independent or Independents may refer to:
Arts, entertainment, and media Artist groups
* Independents (artist group), a group of modernist painters based in the New Hope, Pennsylvania, area of the United States during the early 1930s
* Independe ...
state in the early 18th century, which began with a successful revolution by Mirwais Hotak
Mir Ways ibn Shah 'Alam, also known as Mirwais Khan Hotak ( Pashto/ Dari: ) (1673–1715) was an Afghan ruler from the Ghilji tribe of Kandahar, Afghanistan, and the founder of the Hotak dynasty.
In 1709, after overthrowing and assassinating ...
followed by conquests of Ahmad Shah Durrani. During the 19th and early 20th century, the Barakzai dynasty
The two branches of the Barakzai dynasty (, "sons of Barak") ruled modern day Afghanistan from 1823 to 1973 when the monarchy ended under Musahiban Mohammed Zahir Shah. The Barakzai dynasty was established by Dost Mohammad Khan after the Durr ...
found itself involved perforce between an Anglo- Russian military and diplomatic confrontation known as the " Great Game". Pashtuns are the largest dominion ethnic group in Afghanistan and ruled as the dominant ethno-linguistic group for over 300 years.
See also
* Ethnic groups in Pakistan *Ethnic groups in Afghanistan
Afghanistan is a multiethnic and mostly tribal society. The population of the country consists of numerous ethnolinguistic groups: Pashtun, Tajik, Hazara, Uzbek, Aimaq, Turkmen, Baloch, Pashai, Nuristani, Kurds, Gujjar, Arab, Brahui, ...
*Iranian peoples
The Iranian peoples or Iranic peoples are a diverse grouping of Indo-European peoples who are identified by their usage of the Iranian languages and other cultural similarities.
The Proto-Iranians are believed to have emerged as a separate ...
* List of ancient Iranian peoples
* Pashtunistan
*Pashtunwali
Pashtunwali or Pakhtunwali ( ps, پښتونولي) is the traditional lifestyle and is best described as a code of honor of the Pashtun people, by which they live. Scholars widely have interpreted it as being "the way of the Afghans" or "the code ...
References
External links
Pashtun Tribe, Clan, & Ethnic Genealogies
US Naval Postgraduate School (on the Wayback Machine) *Sungur, Z.T. (2013)
Articulation of Tribalism into Modernity: the Case of Pashtuns in Afghanistan
(Master's Thesis). Middle East Technical University, Ankara. {{DEFAULTSORT:Pashtun Tribes Demographics of Pakistan Social groups of Pakistan Social groups of Afghanistan Pashtun people Lists of modern Indo-European tribes and clans