Parathyroid chief cell on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Parathyroid chief cells (also called parathyroid principal cells or simply parathyroid cells, C-cells, or parafollicular cells) are one of the two cell types of the parathyroid glands, along with oxyphil cells. The chief cells are much more prevalent in the parathyroid gland than the oxyphil cells. It is perceived that oxyphil cells may be derived from chief cells at puberty, as they are not present at birth like chief cells.
Most individuals display four parathyroid glands adjacent to the
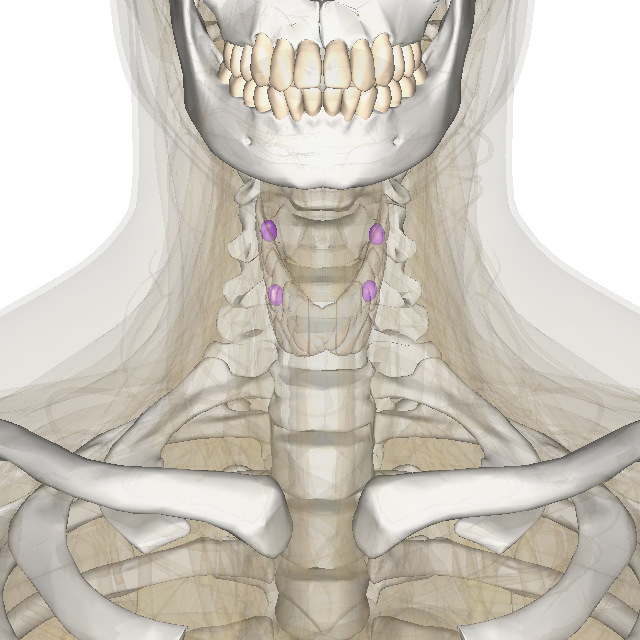 The chief cells of the parathyroid glands sense the amount of calcium in the blood, and release the calcium-increasing hormone
The chief cells of the parathyroid glands sense the amount of calcium in the blood, and release the calcium-increasing hormone
 Because the formation of PTH regulates the calcium level in the blood, it can affect all areas of the body. The overactivity of a parathyroid gland is known as hyperparathyroidism. It is unknown what directly causes hyperparathyroidism. However there are many factors that can cause over-secretion of PTH. The further consequence of this disorder can be osteopenia, or even
Because the formation of PTH regulates the calcium level in the blood, it can affect all areas of the body. The overactivity of a parathyroid gland is known as hyperparathyroidism. It is unknown what directly causes hyperparathyroidism. However there are many factors that can cause over-secretion of PTH. The further consequence of this disorder can be osteopenia, or even
thyroid gland
The thyroid, or thyroid gland, is an endocrine gland in vertebrates. In humans it is in the neck and consists of two connected lobes. The lower two thirds of the lobes are connected by a thin band of tissue called the thyroid isthmus. The thy ...
anterior in the neck.
Histology
The chief cells are organized as dense cords surrounding the capillaries in the parathyroid. Chief cells appear as a dark purple in an H&E stain, with the oxyphil cells staining as a lighter pink. They are polygonal in shape with a round nucleus. Chief cells spend most time inactive due to normal calcium level conditions. These inactive cells are classified as cuboidal. They have low levels of secretory granules, as opposed to active chief cells. These granules can containacid phosphatase
Acid phosphatase (EC 3.1.3.2, acid phosphomonoesterase', phosphomonoesterase, glycerophosphatase, acid monophosphatase, acid phosphohydrolase, acid phosphomonoester hydrolase, uteroferrin, acid nucleoside diphosphate phosphatase, orthophosphoric-m ...
. Acid phosphatase is only found in larger secretory granules, 400 to 900 nm in diameter, and is less prevalent in smaller granules. This acid phosphatase is also present in the Golgi apparatus of the chief cell. However, the Golgi apparatus areas associated with parathyroid hormone packaging contained little or no acid phosphatase. The chief cells become active in response to low calcium in the blood. The low level is sensed by the calcium- sensing receptor. These active cells have a greater electron density than the inactive chief cells. The electron density is caused by the secretory granules. The chief cell is thought to have a clear cytoplasm.
Function
 The chief cells of the parathyroid glands sense the amount of calcium in the blood, and release the calcium-increasing hormone
The chief cells of the parathyroid glands sense the amount of calcium in the blood, and release the calcium-increasing hormone parathyroid hormone
Parathyroid hormone (PTH), also called parathormone or parathyrin, is a peptide hormone secreted by the parathyroid glands that regulates the serum calcium concentration through its effects on bone, kidney, and intestine.
PTH influences bone ...
(PTH) accordingly to correct or maintain normal blood calcium levels. It therefore regulates calcium metabolism
Calcium metabolism is the movement and regulation of calcium ions (Ca2+) ''in'' (via the gut) and ''out'' (via the gut and kidneys) of the body, and ''between'' body compartments: the blood plasma, the extracellular and intracellular fluids, and ...
as part of the endocrine system. PTH raises calcium levels by releasing calcium from bone storage, as well as retaining calcium from the urine, and alerts the intestines to absorb more calcium from ingested nutrients. Too much of either hormone can be an indicator of disease.
Calcium-sensing receptor (CaR)
The secretion ofparathyroid hormone
Parathyroid hormone (PTH), also called parathormone or parathyrin, is a peptide hormone secreted by the parathyroid glands that regulates the serum calcium concentration through its effects on bone, kidney, and intestine.
PTH influences bone ...
(PTH) is regulated by the interaction of the calcium-sensing receptor with calcium in the blood. The calcium-sensing receptor is present on the plasma membrane of the chief cells. The CaR is a G protein-coupled receptor
G protein-coupled receptors (GPCRs), also known as seven-(pass)-transmembrane domain receptors, 7TM receptors, heptahelical receptors, serpentine receptors, and G protein-linked receptors (GPLR), form a large group of evolutionarily-related p ...
, as part of the C family. The CaR is divided into three general domains. These include an NH2- terminal extracellular end, a COOH-terminal intracellular end, and seven transmembrane domains. The CaR interacts positively with phospholipase C
Phospholipase C (PLC) is a class of membrane-associated enzymes that cleave phospholipids just before the phosphate group (see figure). It is most commonly taken to be synonymous with the human forms of this enzyme, which play an important role ...
(PLC) and adenylyl cyclase
Adenylate cyclase (EC 4.6.1.1, also commonly known as adenyl cyclase and adenylyl cyclase, abbreviated AC) is an enzyme with systematic name ATP diphosphate-lyase (cyclizing; 3′,5′-cyclic-AMP-forming). It catalyzes the following reaction:
:A ...
. The CaR includes phosphorylation sites for protein kinase C (PKC) and protein kinase A (PKA). The phosphorylation of the PLC is seen to inhibit the secretion of PTH due to high calcium levels in the blood. The function of the PKA sites is currently unknown.
Clinical significance
Hyperparathyroidism
 Because the formation of PTH regulates the calcium level in the blood, it can affect all areas of the body. The overactivity of a parathyroid gland is known as hyperparathyroidism. It is unknown what directly causes hyperparathyroidism. However there are many factors that can cause over-secretion of PTH. The further consequence of this disorder can be osteopenia, or even
Because the formation of PTH regulates the calcium level in the blood, it can affect all areas of the body. The overactivity of a parathyroid gland is known as hyperparathyroidism. It is unknown what directly causes hyperparathyroidism. However there are many factors that can cause over-secretion of PTH. The further consequence of this disorder can be osteopenia, or even osteoporosis
Osteoporosis is a systemic skeletal disorder characterized by low bone mass, micro-architectural deterioration of bone tissue leading to bone fragility, and consequent increase in fracture risk. It is the most common reason for a broken bone a ...
, which is the loss of bone density. This leaves bones more porous, fragile, and likely to experience fracture. This can be detected by usage of dual-energy X-ray absorptiometry (DEXA
Dual-energy X-ray absorptiometry (DXA, or DEXA) is a means of measuring bone mineral density (BMD) using spectral imaging. Two X-ray beams, with different energy levels, are aimed at the patient's bones. When soft tissue absorption is subtracted ...
). Interesting enough, a derivative of synthetic PTH is often given to patients with osteoporosis to combat the disease.
Vitamin D deficiency
Vitamin D
Vitamin D is a group of Lipophilicity, fat-soluble secosteroids responsible for increasing intestinal absorption of calcium, magnesium, and phosphate, and many other biological effects. In humans, the most important compounds in this group ar ...
in the kidney assists in the absorption of calcium in the blood. Some individuals may be vitamin D deficient, which prevents them from retaining calcium. While their parathyroid gland is functional, it senses a very low level of calcium in the blood and constantly secretes hormone, increasing PTH levels.
Medications
There are many drugs that can affect calcium level in the blood, and therefore PTH secretion. For example, many individuals may take a calcium carbonate supplement, which increases the calcium level in the blood. PTH is decreased. Many medications may also increase urination, furthering loss of calcium.Parathyroid adenoma
Aparathyroid adenoma
A parathyroid adenoma is a benign tumor of the parathyroid gland. It generally causes hyperparathyroidism; there are very few reports of parathyroid adenomas that were not associated with hyperparathyroidism.
A human being usually has four parath ...
is the most common cause of hyperparathyroidism. They are more commonly found in women than in men. In this form, the chief cells mutate to exhibit multiple nuclei. Chief cells in parathyroid adenomas also display acid phosphatase activity. It is a benign tumor of the gland that requires surgical removal. These benign adenomas are typically affect only one or two of the parathyroid glands, known respectively as a single adenoma or double adenoma. Typically, no disease is linked to the cause. A primary adenoma can only develop as a primary cause.
Chief cell hyperplasia
In many way, chief cell hyperplasia is similar to parathyroid adenoma. The hyperplasia is seen as an enlargement of all four of the parathyroid glands, as opposed to a parathyroid adenoma is viewed as an enlargement of one gland. Chief cell hyperplasia is a common disorder in individuals with other endocrine abnormalities, though it may still occur sporadically. A chief cell hyperplasia can develop from either a primary or secondary cause.Parathyroid carcinoma
In extremely rare cases, a malignant tumor may develop within the parathyroid gland. They can be detected intraoperatively, imaging, or through blood testing. A thick fibrous capsule is usually present around the gland, as opposed to the thin capsule present in benign adenomas. Parathyroid hormone level is often greater in carcinomas than in benign disorders.Hypoparathyroidism
There are very few cases of hypoparathyroidism. Most often, it is related with surgical removal of the parathyroid glands. It can also be due to a head or neck injury and further loss of function of the glands. Hypoparathyroidism can also be linked to a low serum magnesium level in the blood. Serum magnesium is necessary for full secretion of PTH. Without the parathyroid glands, there is no trigger to release calcium into the blood. Another consequence of hypoparathyroidism is the lack of calcium in the blood to trigger muscle contraction. Without calcium present, muscles innervation is unable to take place. This is especially crucial in the function of the most important muscle of the body – the heart.See also
* Oxyphil cell (parathyroid) *List of human cell types derived from the germ layers
This is a list of cells in humans derived from the three embryonic germ layers – ectoderm, mesoderm, and endoderm.
Cells derived from ectoderm
Surface ectoderm Skin
* Trichocyte
* Keratinocyte
Anterior pituitary
* Gonadotrope
* Corti ...
References
External links
* {{Authority control Peptide hormone secreting cells Human cells Parathyroid