Panic of 1873 on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 The Panic of 1873 was a
The Panic of 1873 was a
/ref> Due to the financial crises in Europe, Cooke could not sell the securities abroad. Just as Cooke was about to swing a $300 million government loan in September 1873, reports circulated that his firm's credit had become nearly worthless. On 18 September, the firm declared bankruptcy.
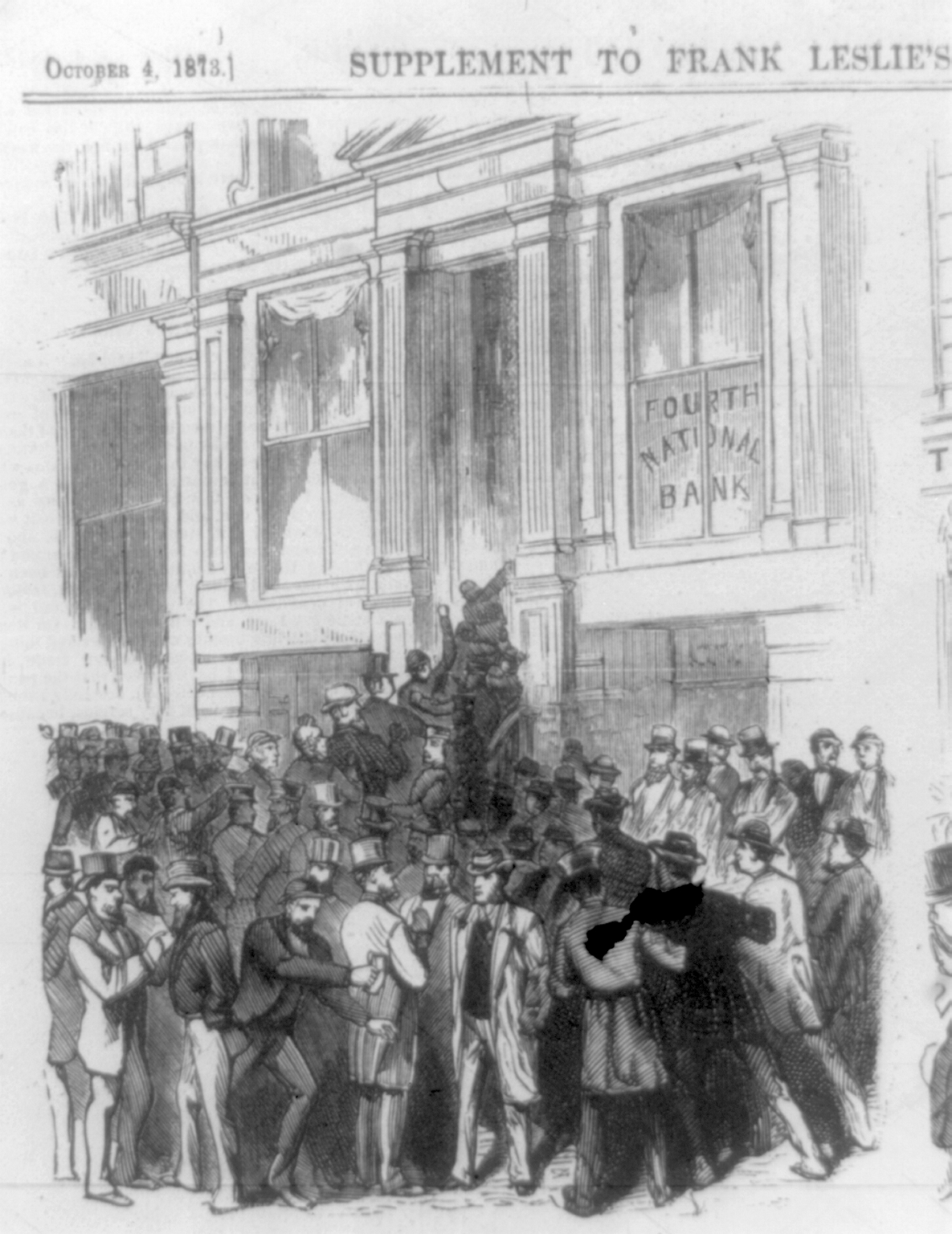
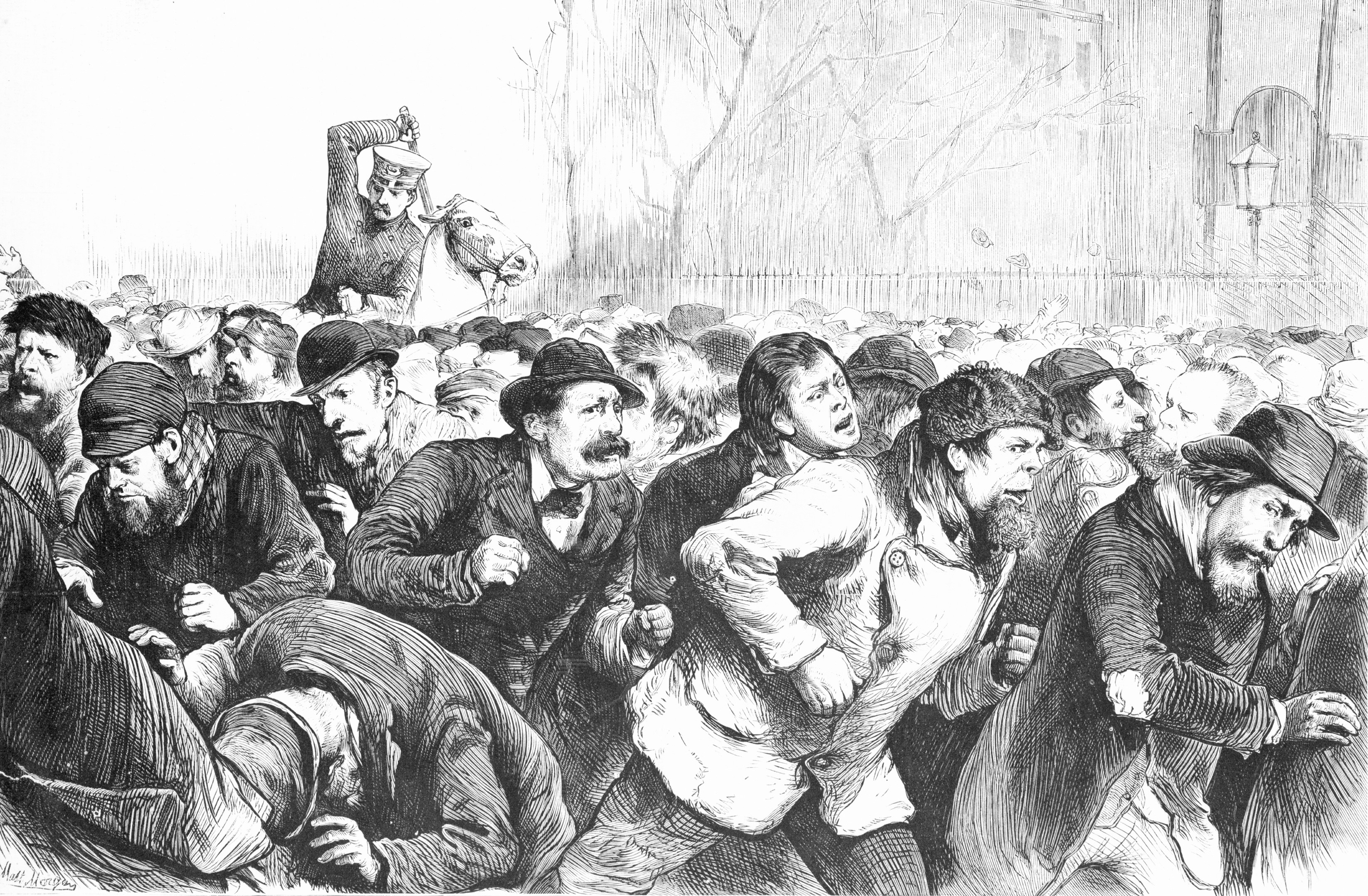 The failure of Jay Cooke's bank and soon afterward of Henry Clews' set off a chain reaction of bank failures and temporarily closed the
The failure of Jay Cooke's bank and soon afterward of Henry Clews' set off a chain reaction of bank failures and temporarily closed the
''Technology and Culture'' 41.3 (2000) 636-638, via Project MUSE, accessed 20 May 2016. Pennsylvania saw perhaps the worst violence of the railroad strikes; see Pittsburgh railroad strike of 1877, Reading Railroad massacre and Scranton general strike. In
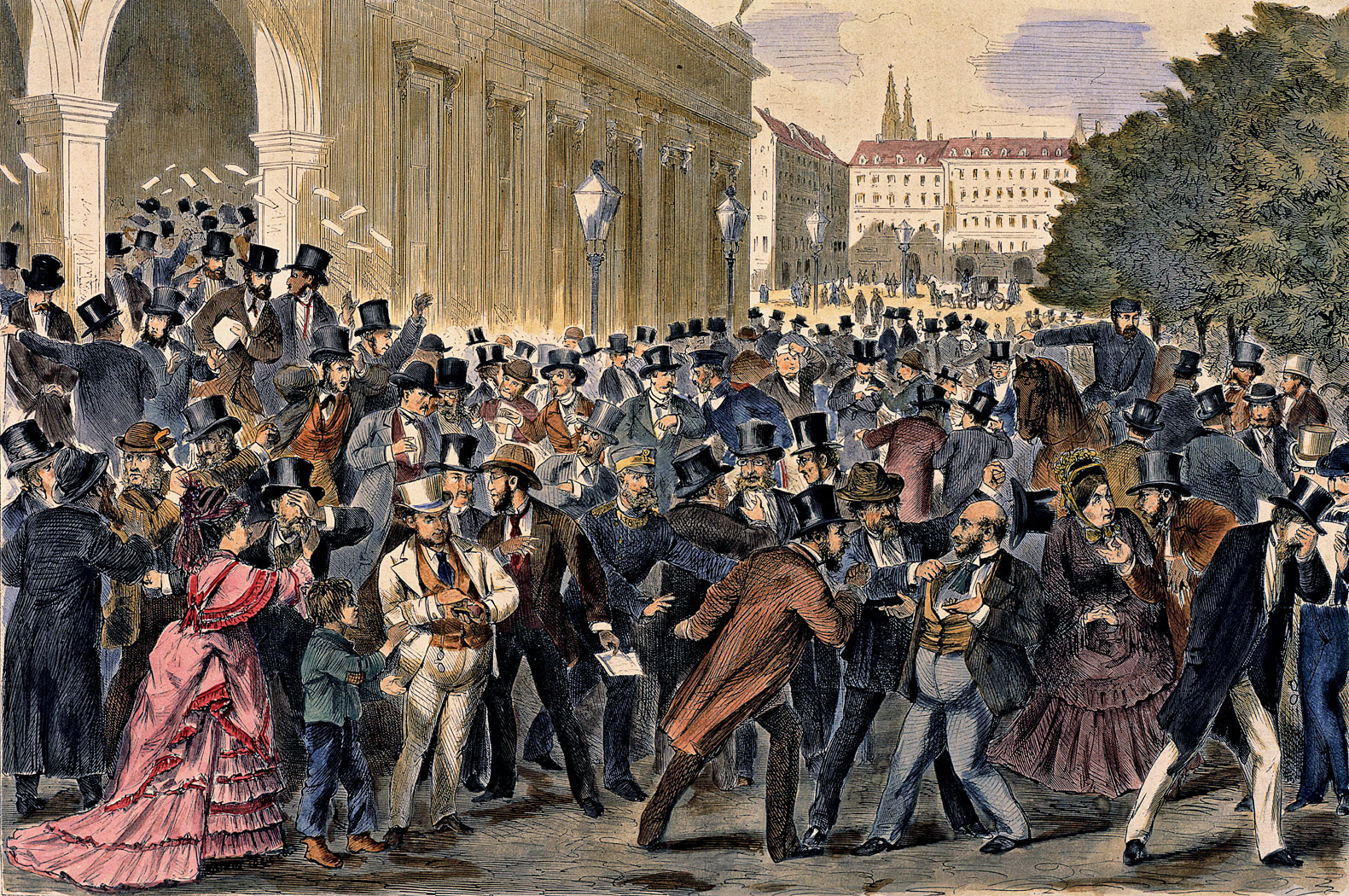 A similar process of overexpansion took place in Germany and Austria-Hungary, where the period from
A similar process of overexpansion took place in Germany and Austria-Hungary, where the period from
online review
* * * * * * Focused on construction in the West. * * * * * * * * Wicker, Elmus. ''Banking panics of the
contents
 The Panic of 1873 was a
The Panic of 1873 was a financial crisis
A financial crisis is any of a broad variety of situations in which some financial assets suddenly lose a large part of their nominal value. In the 19th and early 20th centuries, many financial crises were associated with banking panics, and man ...
that triggered an economic depression in Europe
Europe is a large peninsula conventionally considered a continent in its own right because of its great physical size and the weight of its history and traditions. Europe is also considered a subcontinent of Eurasia and it is located entirel ...
and North America that lasted from 1873 to 1877 or 1879 in France
France (), officially the French Republic ( ), is a country primarily located in Western Europe. It also comprises of overseas regions and territories in the Americas and the Atlantic, Pacific and Indian Oceans. Its metropolitan area ...
and in Britain
Britain most often refers to:
* The United Kingdom, a sovereign state in Europe comprising the island of Great Britain, the north-eastern part of the island of Ireland and many smaller islands
* Great Britain, the largest island in the United King ...
. In Britain, the Panic started two decades of stagnation known as the "Long Depression
The Long Depression was a worldwide price and economic recession, beginning in 1873 and running either through March 1879, or 1896, depending on the metrics used. It was most severe in Europe and the United States, which had been experiencing st ...
" that weakened the country's economic leadership. In the United States
The United States of America (U.S.A. or USA), commonly known as the United States (U.S. or US) or America, is a country primarily located in North America. It consists of 50 states, a federal district, five major unincorporated territori ...
, the Panic was known as the "Great Depression" until the events of 1929 and the early 1930s set a new standard.
The Panic of 1873 and the subsequent depression had several underlying causes for which economic historians
Economic history is the academic learning of economies or economic events of the past. Research is conducted using a combination of historical methods, statistical methods and the application of economic theory to historical situations and in ...
debate the relative importance. American inflation
In economics, inflation is an increase in the general price level of goods and services in an economy. When the general price level rises, each unit of currency buys fewer goods and services; consequently, inflation corresponds to a reduct ...
, rampant speculative investments (overwhelmingly in railroads
Rail transport (also known as train transport) is a means of transport that transfers passengers and goods on wheeled vehicles running on rails, which are incorporated in tracks. In contrast to road transport, where the vehicles run on a prep ...
), the demonetization of silver in Germany
Germany,, officially the Federal Republic of Germany, is a country in Central Europe. It is the second most populous country in Europe after Russia, and the most populous member state of the European Union. Germany is situated betwe ...
and the United States, ripples from economic dislocation in Europe resulting from the Franco-Prussian War (1870–1871), and major property losses in the Great Chicago Fire
The Great Chicago Fire was a conflagration that burned in the American city of Chicago during October 8–10, 1871. The fire killed approximately 300 people, destroyed roughly of the city including over 17,000 structures, and left more than 10 ...
(1871) and the Great Boston Fire (1872) helped to place massive strain on bank reserves
Bank reserves are a commercial bank's cash holdings physically held by the bank, and deposits held in the bank's account with the central bank. Under the fractional-reserve banking system used in most countries, central banks typically set mini ...
, which, in New York City
New York, often called New York City or NYC, is the most populous city in the United States. With a 2020 population of 8,804,190 distributed over , New York City is also the most densely populated major city in the Un ...
, plummeted from $50 million to $17 million between September and October 1873.
The first symptoms of the crisis were financial failures in Vienna
en, Viennese
, iso_code = AT-9
, registration_plate = W
, postal_code_type = Postal code
, postal_code =
, timezone = CET
, utc_offset = +1
, timezone_DST ...
, the capital of Austria-Hungary
Austria-Hungary, often referred to as the Austro-Hungarian Empire,, the Dual Monarchy, or Austria, was a constitutional monarchy and great power in Central Europe between 1867 and 1918. It was formed with the Austro-Hungarian Compromise of ...
, which spread to most of Europe and to North America by 1873.
United States
Factors
TheAmerican Civil War
The American Civil War (April 12, 1861 – May 26, 1865; also known by other names) was a civil war in the United States. It was fought between the Union ("the North") and the Confederacy ("the South"), the latter formed by states ...
(1861–1865) was followed by a boom in railroad construction. of new track were laid across the country between 1868 and 1873, with much of the craze in railroad investment being driven by government land grants and subsidies to the railroads. The railroad industry was the largest employer outside agriculture in the US and involved large amounts of money and risk. A large infusion of cash from speculators caused spectacular growth in the industry and in the construction of docks, factories, and ancillary facilities. Most capital was involved in projects offering no immediate or early returns.
Coinage Act of 1873
A period of economic overexpansion arose from the northern railroad boom before a series of economic setbacks: the Black Friday panic of 1869, theChicago fire of 1871
The Great Chicago Fire was a conflagration that burned in the American city of Chicago during October 8–10, 1871. The fire killed approximately 300 people, destroyed roughly of the city including over 17,000 structures, and left more than 1 ...
, an outbreak of equine influenza and the Boston fire of 1872, and the demonetization of silver in 1873.
The decision of the German Empire to cease minting silver thaler coins in 1871 caused a drop in demand and downward pressure on the value of silver, which, in turn, affected the US since much of the supply of silver was mined there. As a result, the US Congress
The United States Congress is the legislature of the federal government of the United States. It is bicameral, composed of a lower body, the House of Representatives, and an upper body, the Senate. It meets in the U.S. Capitol in Washin ...
passed the Coinage Act of 1873
The Coinage Act of 1873 or Mint Act of 1873, was a general revision of laws relating to the Mint of the United States. By ending the right of holders of silver bullion to have it coined into standard silver dollars, while allowing holders of go ...
, which changed the national silver policy.
Before the Act, the US had backed its currency with both gold and silver and minted both types of coins. The Act moved the United States to a ''de facto'' gold standard
A gold standard is a monetary system in which the standard economic unit of account is based on a fixed quantity of gold. The gold standard was the basis for the international monetary system from the 1870s to the early 1920s, and from the l ...
, which meant it would no longer buy silver at a statutory price or convert silver from the public into silver coins, but it would still mint silver dollars for export in the form of trade dollars.
The Act had the immediate effect of depressing silver prices, hurting Western mining interests, who labeled the Act "The Crime of '73", but its effect was offset somewhat by the introduction of a silver trade dollar for use in Asia and the discovery of new silver deposits at Virginia City, Nevada
Virginia City is a census-designated place (CDP) that is the county seat of Storey County, Nevada, and the largest community in the county. The city is a part of the Reno– Sparks Metropolitan Statistical Area.
Virginia City developed as a boom ...
, that resulted in new investment in mining activity. The Act also reduced the domestic money supply
In macroeconomics, the money supply (or money stock) refers to the total volume of currency held by the public at a particular point in time. There are several ways to define "money", but standard measures usually include currency in circul ...
, raising interest rates and hurting farmers and others who normally carried heavy debt loads. The resulting outcry raised serious questions about how long the new policy would last. The perception of US instability in its monetary policy caused investors to shy away from long-term obligations, particularly long-term bonds. The problem was compounded by the railroad boom, which was then in its later stages.
In September 1873, the US economy entered a crisis.
Jay Cooke & Company fails
In September 1873,Jay Cooke & Company
Jay Cooke & Company was a U.S. bank that operated from 1861 to 1873. Headquartered in Philadelphia, Pennsylvania, with branches in New York City and Washington, D.C., the bank helped underwrite the Union Civil War effort. It was the first "wire ...
, a major component of the country's banking establishment, found itself unable to market several million dollars in Northern Pacific Railway bonds. Jay Cooke
Jay Cooke (August 10, 1821 – February 16, 1905) was an American financier who helped finance the Union war effort during the American Civil War and the postwar development of railroads in the northwestern United States. He is generally acknowle ...
's firm, like many others, had invested heavily in the railroads. Some investment banks were then anxious for more capital for their enterprises, US President Ulysses S. Grant's monetary policy
Monetary policy is the policy adopted by the monetary authority of a nation to control either the interest rate payable for very short-term borrowing (borrowing by banks from each other to meet their short-term needs) or the money supply, often a ...
of contracting the money supply and thus raising interest rates made matters worse for those in debt. Businesses were expanding, but the money they needed to finance that growth was becoming scarcer.
Cooke and other entrepreneurs had planned to build the second transcontinental railroad, the Northern Pacific Railway. Cooke's firm provided the financing, and ground for the line was broken near Duluth, Minnesota
, settlement_type = City
, nicknames = Twin Ports (with Superior), Zenith City
, motto =
, image_skyline =
, image_caption = Clockwise from top: urban Duluth skyline; Minnesota ...
, on 15 February 1870. The railroad had borrowed more than $1.5 million from Cooke & Co, but was incapable of paying it back. An expanding funding gap became harder to resolve due to the Credit Mobilier scandal
Credit (from Latin verb ''credit'', meaning "one believes") is the trust which allows one party to provide money or resources to another party wherein the second party does not reimburse the first party immediately (thereby generating a debt) ...
.Crisis Chronicles: The Long Depression and the Panic of 1873/ref> Due to the financial crises in Europe, Cooke could not sell the securities abroad. Just as Cooke was about to swing a $300 million government loan in September 1873, reports circulated that his firm's credit had become nearly worthless. On 18 September, the firm declared bankruptcy.
Insurance industry
Many US insurance companies went out of business, as the deteriorating financial conditions created solvency problems for life insurers. The common factor of the surviving companies was that all marketed tontines.Effects
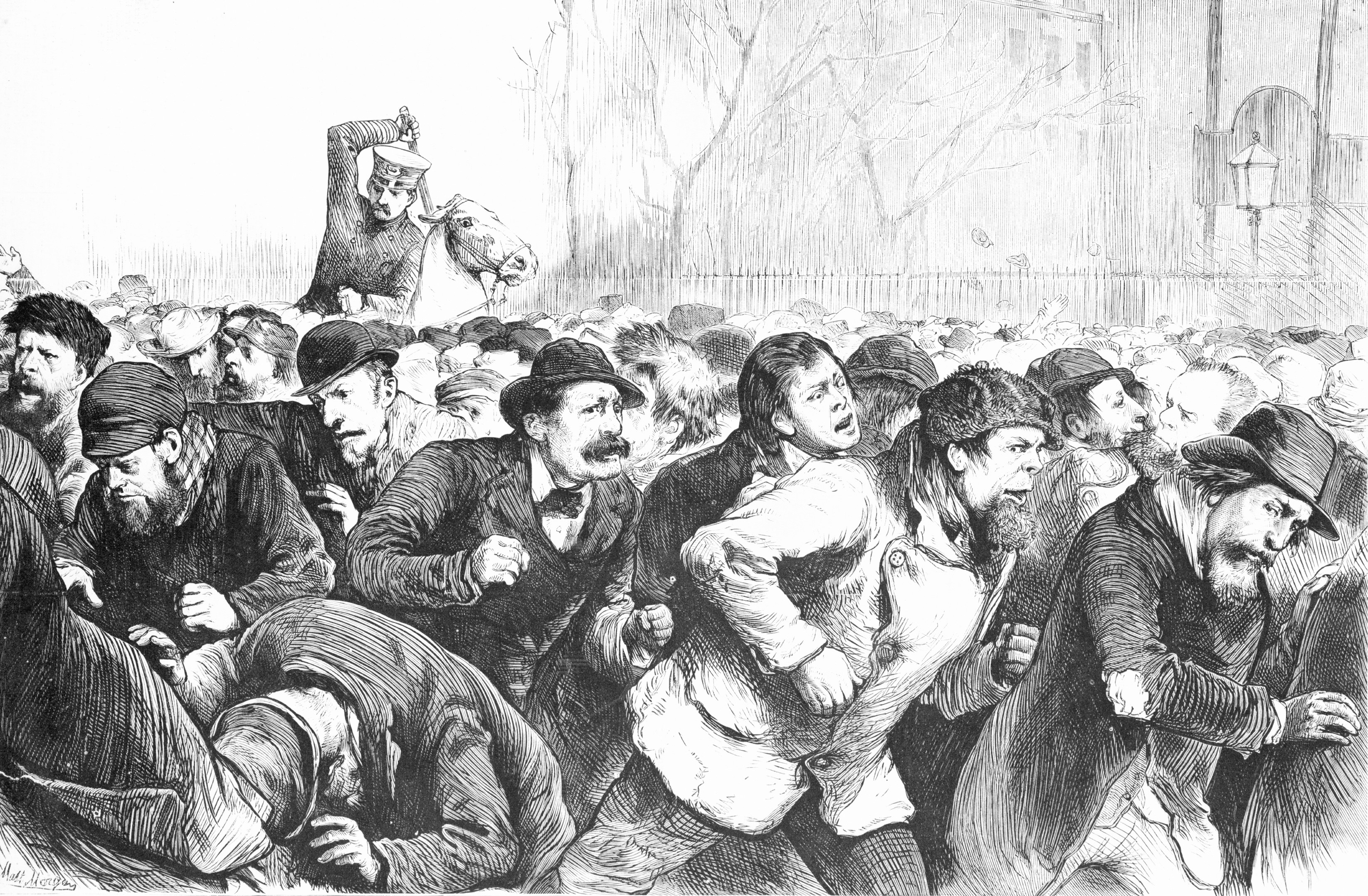 The failure of Jay Cooke's bank and soon afterward of Henry Clews' set off a chain reaction of bank failures and temporarily closed the
The failure of Jay Cooke's bank and soon afterward of Henry Clews' set off a chain reaction of bank failures and temporarily closed the New York Stock Exchange
The New York Stock Exchange (NYSE, nicknamed "The Big Board") is an American stock exchange in the Financial District of Lower Manhattan in New York City. It is by far the world's largest stock exchange by market capitalization of its listed ...
. Factories began to lay off workers as the country slipped into depression. The effects of the panic were quickly felt in New York (where 25% of workers became unemployed) and more slowly in Chicago, Virginia City, Nevada
Virginia City is a census-designated place (CDP) that is the county seat of Storey County, Nevada, and the largest community in the county. The city is a part of the Reno– Sparks Metropolitan Statistical Area.
Virginia City developed as a boom ...
(where silver mining was active), and San Francisco. In New Hampshire, state coffers were so depleted by lost tax revenue the state government turned to private interests including tea and gun powder manufacturer D. Ralph Lolbert for financial support.
The New York Stock Exchange closed for ten days starting on 20 September. By November 1873, some 55 of the nation's railroads had failed, and another 60 had gone bankrupt by the first anniversary of the crisis.Kleppner, Paul (1973) "The Greenback and Prohibition Parties," in Arthur M. Schlesinger (ed.), ''History of U.S. Political Parties: Volume II, 1860–1910, The Gilded Age
In United States history, the Gilded Age was an era extending roughly from 1877 to 1900, which was sandwiched between the Reconstruction era and the Progressive Era. It was a time of rapid economic growth, especially in the Northern and Wes ...
of Politics.'' New York: Chelsea House/R.R. Bowker Co., p. 1556. Construction of new rail lines, formerly one of the backbones of the economy, plummeted from of track in 1872 to just in 1875, and 18,000 businesses failed between 1873 and 1875. Unemployment peaked in 1878 at 8.25%. Building construction was halted, wages were cut, real estate values fell, and corporate profits vanished.
In 1874, Congress passed "the Ferry Bill" to allow for the printing of currency, increasing inflation and reducing the value of debts. The bill was vetoed by President Grant. The following year, Congress passed the Specie Resumption Act of 1875, which would back United States currency with gold. Backing American currency with gold helped curb inflation and stabilize the dollar.
Railroad strike
Therailroad
Rail transport (also known as train transport) is a means of transport that transfers passengers and goods on wheeled vehicles running on rails, which are incorporated in tracks. In contrast to road transport, where the vehicles run on a pre ...
industry in the United States had seen major growth in the decades before 1873, driven in part by strong European interest in bonds issued by railroad companies. The failure of Jay Cooke & Co., heavily invested in railroad bonds, triggered a crisis in the railroad industry.
In 1877, steep wage cuts led American railroad workers to launch the series of protests and riots later dubbed Great Railroad Strike
The Great Railroad Strike of 1877, sometimes referred to as the Great Upheaval, began on July 14 in Martinsburg, West Virginia, after the Baltimore and Ohio Railroad (B&O) cut wages for the third time in a year. This strike finally ended 52 day ...
. Initial protests broke out in Martinsburg, West Virginia
Martinsburg is a city in and the seat of Berkeley County, West Virginia, in the tip of the state's Eastern Panhandle region in the lower Shenandoah Valley. Its population was 18,835 in the 2021 census estimate, making it the largest city in the E ...
, after the Baltimore and Ohio Railroad (B&O) cut workers' pay for the third time in a year. West Virginia Governor
The governor of West Virginia is the head of government of West VirginiaWV Constitution article VII, § 5. and the commander-in-chief of the U.S. state, state's West Virginia National Guard, military forces.WV Constitution article VII, § 12. Th ...
Henry M. Mathews sent the militia, under Colonel Charles J. Faulkner, to restore order but was unsuccessful, largely because the militia sympathized with the workers. The governor called on US President Rutherford B. Hayes
Rutherford Birchard Hayes (; October 4, 1822 – January 17, 1893) was an American lawyer and politician who served as the 19th president of the United States from 1877 to 1881, after serving in the U.S. House of Representatives and as governo ...
for federal assistance, and Hayes dispatched federal troops. That restored peace to Martinsburg but proved controversial, with many newspapers critical of Mathews' characterization of the strikes as an "insurrection", rather than an act of desperation and frustration. One notable paper recorded a striking worker's perspective that he "had might as well die by the bullet as to starve to death by inches".
Within a week, similar protests had erupted in other cities. In Baltimore, Maryland
Baltimore ( , locally: or ) is the List of municipalities in Maryland, most populous city in the U.S. state of Maryland, fourth most populous city in the Mid-Atlantic (United States), Mid-Atlantic, and List of United States cities by popula ...
where strikers set fire to buildings owned by B.& O. Railroads and an outnumbered militia guard division opened fire when they were surrounded by rioters, killing 10 and injuring 25 more leading to a days-long standoff at Camden Yards
The Oriole Park at Camden Yards is a baseball stadium located in Baltimore, Maryland. It is the home field of Major League Baseball's Baltimore Orioles, and the first of the "retro" major league ballparks constructed during the 1990s and early ...
.
In New York, striking workers began pelting arriving trains with thrown objects, prompting a response from local police.Scott Molloy, "Book Review: ''Streets, Railroads, and the Great Strike of 1877'' By David O. Stowell"''Technology and Culture'' 41.3 (2000) 636-638, via Project MUSE, accessed 20 May 2016. Pennsylvania saw perhaps the worst violence of the railroad strikes; see Pittsburgh railroad strike of 1877, Reading Railroad massacre and Scranton general strike. In
Chicago, Illinois
(''City in a Garden''); I Will
, image_map =
, map_caption = Interactive Map of Chicago
, coordinates =
, coordinates_footnotes =
, subdivision_type = Country
, subdivision_name ...
, striking workers brought freight and passenger trains to a standstill, leading to an order from judge Thomas Drummond
Captain Thomas Drummond (10 October 1797 – 15 April 1840), from Edinburgh was a Scottish army officer, civil engineer and senior public official. He used the Drummond light which was employed in the trigonometrical survey of Great Britain an ...
that such actions were illegal. The United States Marshals Service
The United States Marshals Service (USMS) is a federal law enforcement agency in the United States. The USMS is a bureau within the U.S. Department of Justice, operating under the direction of the Attorney General, but serves as the enforc ...
responded by arresting dozens of strikers. In Missouri, strikers also brought rail traffic to a halt, and at least 18 people died in conflicts.
In July 1877, the market for lumber crashed, leading several Michigan lumber companies to go bankrupt. Within a year, the effects of this second business slump reached all the way to California.
Aftermath in the United States
The depression ended in the spring of 1879, but tension between workers and the leaders of banking and manufacturing interests lingered on. Poor economic conditions also caused voters to turn against the Republican Party. In the 1874 congressional elections, the Democratic Party assumed control of the House for the first time since the Civil War. Public opinion made it difficult for theGrant administration
The presidency of Ulysses S. Grant began on March 4, 1869, when Ulysses S. Grant was inaugurated as the 18th president of the United States, and ended on March 4, 1877. The Reconstruction era took place during Grant's two terms of office. The Ku ...
to develop a coherent policy on the Southern states, and the North began to steer away from Reconstruction
Reconstruction may refer to:
Politics, history, and sociology
*Reconstruction (law), the transfer of a company's (or several companies') business to a new company
*'' Perestroika'' (Russian for "reconstruction"), a late 20th century Soviet Unio ...
. With the depression, ambitious railroad building programs crashed across the South, leaving most states deep in debt and burdened with heavy taxes. Retrenchment was a common response of the South to state debts during the depression. One by one, each state fell to the Democrats in the South, and the Republicans lost power.
The end of the crisis coincided with the beginning of the great wave of immigration to the United States
Immigration has been a major source of population growth and cultural change throughout much of the history of the United States. In absolute numbers, the United States has a larger immigrant population than any other country in the worl ...
, which lasted until the early 1920s.
Europe
The panic and depression hit all of the industrial nations.Germany and Austria-Hungary
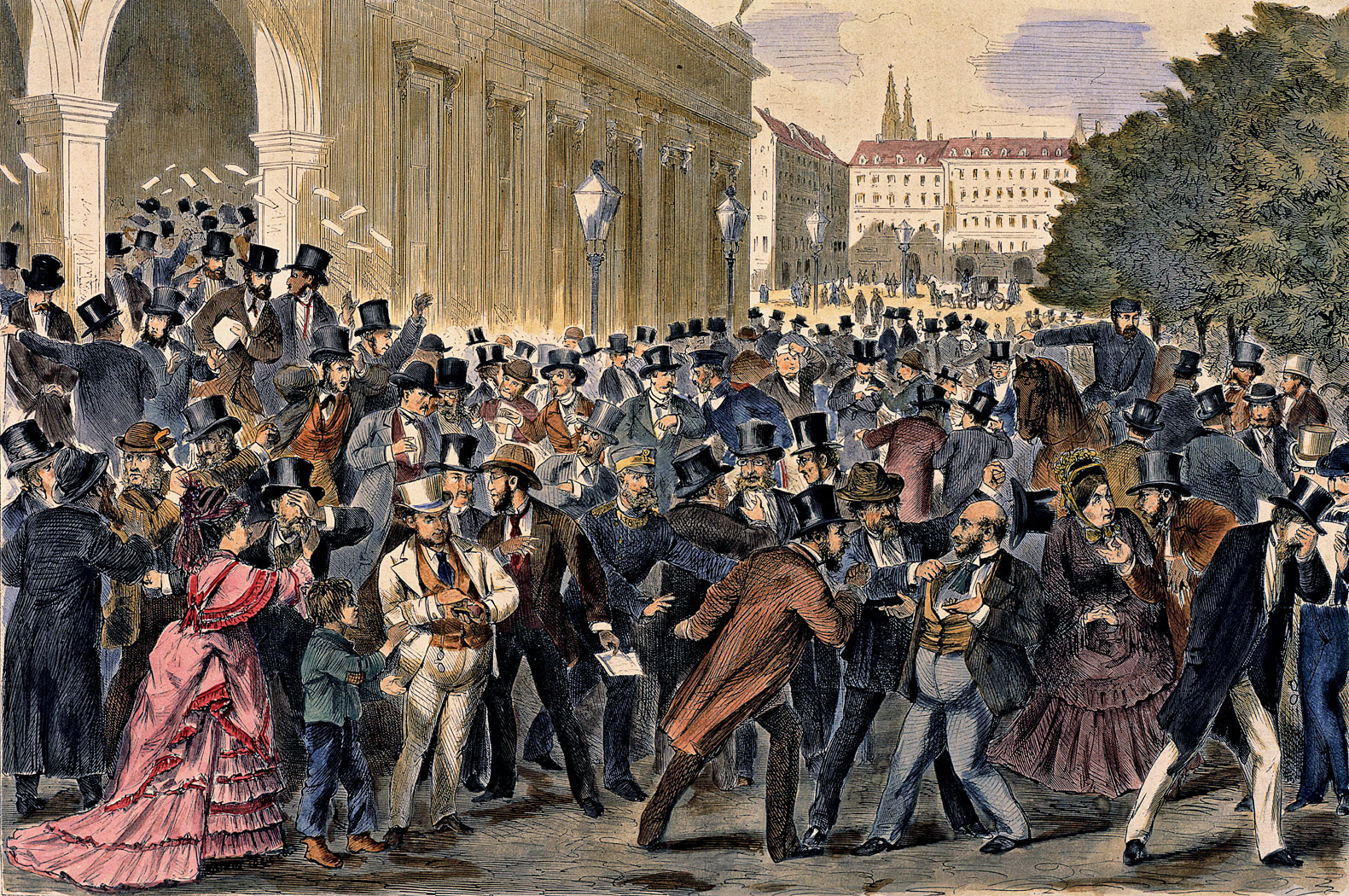 A similar process of overexpansion took place in Germany and Austria-Hungary, where the period from
A similar process of overexpansion took place in Germany and Austria-Hungary, where the period from German unification
The unification of Germany (, ) was the process of building the modern German nation state with federal features based on the concept of Lesser Germany (one without multinational Austria), which commenced on 18 August 1866 with adoption of t ...
in 1870 and 1871 to the crash in 1873 came to be called the ' ("Founders' Years"). A liberalized incorporation law in Germany gave impetus to the foundation of new enterprises, such as , and the incorporation of established ones. Euphoria over the military victory against France in 1871 and the influx of capital from the payment by France of war reparations
War reparations are compensation payments made after a war by one side to the other. They are intended to cover damage or injury inflicted during a war.
History
Making one party pay a war indemnity is a common practice with a long history.
...
fueled stock market speculation in railways, factories, docks, steamships; the same industrial branches that expanded unsustainably in the United States. In the immediate aftermath of his victory against France, Bismarck began the process of silver demonetization. The process began on 23 November 1871 and culminated in the introduction of the gold mark
The German mark (german: Goldmark ; sign: ℳ) was the currency of the German Empire, which spanned from 1871 to 1918. The mark was paired with the minor unit of the pfennig (₰); 100 pfennigs were equivalent to 1 mark. The mark was on the g ...
on 9 July 1873 as the currency for the newly united Reich, replacing the silver coins of all constituent lands. Germany was now on the gold standard
A gold standard is a monetary system in which the standard economic unit of account is based on a fixed quantity of gold. The gold standard was the basis for the international monetary system from the 1870s to the early 1920s, and from the l ...
. Demonetization of silver was thus a common element in the crises on both sides of the Atlantic Ocean
The Atlantic Ocean is the second-largest of the world's five oceans, with an area of about . It covers approximately 20% of Earth's surface and about 29% of its water surface area. It is known to separate the " Old World" of Africa, Europe ...
.
On 9 May 1873, the Vienna Stock Exchange
en, Viennese
, iso_code = AT-9
, registration_plate = W
, postal_code_type = Postal code
, postal_code =
, timezone = CET
, utc_offset = +1
, timezone_DST ...
crashed since it was unable to sustain the bubble of false expansion, insolvencies, and dishonest manipulations. A series of Viennese bank failures ensued, causing a contraction of the money available for business lending. One of the more famous private individuals who went bankrupt in 1873 was Stephan Keglevich of Vienna, a relative of Gábor Keglevich, who had been the master of the royal treasury (1842–1848) and in 1845 had cofounded a financial association to fund the expansion of Hungarian industry and to protect the loan repayments, similar to the 1870 ''Kreditschutzverband'', an Austrian association for the protection of creditors and the interests of its members in cases of bankruptcy. That made it possible for a number of new Austrian banks to be established in 1873 after the Vienna Stock Exchange crash.
In Berlin, the railway empire of Bethel Henry Strousberg crashed after a ruinous settlement with the government of Romania
Romania ( ; ro, România ) is a country located at the crossroads of Central, Eastern, and Southeastern Europe. It borders Bulgaria to the south, Ukraine to the north, Hungary to the west, Serbia to the southwest, Moldova to the east, and ...
, bursting the speculation bubble in Germany. The contraction of the German economy was exacerbated by the conclusion of war reparations payments to Germany by France in September 1873. Two years after the foundation of the German Empire, the panic came and became known as the ' or "Founders' Crash". In 1865, Keglevich and Strousberg had come into direct competition in a project in what is now Slovakia. In 1870 the Hungarian government, and in 1872 the Emperor-King Franz Joseph I of Austria
Franz Joseph I or Francis Joseph I (german: Franz Joseph Karl, hu, Ferenc József Károly, 18 August 1830 – 21 November 1916) was Emperor of Austria, King of Hungary, and the other states of the Habsburg monarchy from 2 December 1848 until his ...
, resolved the question of the competing projects.
Although the collapse of the foreign loan financing had been predicted, the events of that year were in themselves comparatively unimportant. Buda, the old capital of Hungary, and Óbuda were officially united with Pest, thus creating the new metropolis of Budapest
Budapest (, ; ) is the capital and most populous city of Hungary. It is the ninth-largest city in the European Union by population within city limits and the second-largest city on the Danube river; the city has an estimated population ...
in 1873. The difference in stability between Vienna
en, Viennese
, iso_code = AT-9
, registration_plate = W
, postal_code_type = Postal code
, postal_code =
, timezone = CET
, utc_offset = +1
, timezone_DST ...
and Berlin had the effect that the French indemnity to Germany flowed into Austria and Russia, but the indemnity payments aggravated the crisis in Austria, which had benefited by the accumulation of capital not only in Germany but also in England, the Netherlands, Belgium, France, and Russia.
Recovery from the crash occurred much more quickly in Europe than in the United States. Masur, pp. 74–75. Moreover, German businesses managed to avoid the sort of deep wage cuts that embittered American labor relations. There was an anti-Semitic component to the economic recovery in Germany and Austria, as small investors blamed Jews for their losses in the crash. Soon, more luxury hotels and villas were built in Opatija
Opatija (; it, Abbazia; german: Sankt Jakobi) is a List of cities and towns in Croatia, town and a municipality in Primorje-Gorski Kotar County in western Croatia. The traditional seaside resort on the Kvarner Gulf is known for its Mediterranean ...
, and a new railway line was extended in 1873 from the Vienna–Trieste
Trieste ( , ; sl, Trst ; german: Triest ) is a city and seaport in northeastern Italy. It is the capital city, and largest city, of the autonomous region of Friuli Venezia Giulia, one of two autonomous regions which are not subdivided into prov ...
line to Rijeka (Fiume), making it possible to go by tram from there to Opatija. The strong increase of port traffic generated a permanent demand for expansion. The Suez Canal was opened in 1869. 1875–1890 became "the golden years" of Giovanni de Ciotta in Rijeka.
Britain
The opening of the Suez Canal in 1869 was one of the causes of the Panic of 1873 because goods from theFar East
The ''Far East'' was a European term to refer to the geographical regions that includes East and Southeast Asia as well as the Russian Far East to a lesser extent. South Asia is sometimes also included for economic and cultural reasons.
The ter ...
had been carried in sailing vessels around the Cape of Good Hope and were stored in British warehouses. As sailing vessels were not adaptable for use through the Suez Canal (because the prevailing winds of the Mediterranean Sea
The Mediterranean Sea is a sea connected to the Atlantic Ocean, surrounded by the Mediterranean Basin and almost completely enclosed by land: on the north by Western and Southern Europe and Anatolia, on the south by North Africa, and on the ...
blow from west to east), the British entrepôt
An ''entrepôt'' (; ) or transshipment port is a port, city, or trading post where merchandise may be imported, stored, or traded, usually to be exported again. Such cities often sprang up and such ports and trading posts often developed into c ...
trade suffered.
When the crisis came, the Bank of England raised interest rates to 9 percent. Despite this, Britain did not experience the scale of financial mayhem seen in America and Central Europe, perhaps forestalled by an expectation that the liquidity-constraining provisions of the Bank Charter Act of 1844 would be suspended as they had been in the crises of 1847, 1857, and 1866. The ensuing economic downturn in Britain seems to have been muted – "stagnant" but without a "decline in aggregate output". However, there was heavy unemployment in the basic industries of coal, iron and steel, engineering, and shipbuilding, especially in 1873, 1886, and 1893.
Comparison with Germany
From 1873 to 1896, a period sometimes referred to as the Long Depression, most European countries experienced a drastic fall in prices. Still, many corporations were able to reduce production costs and achieve better productivity rates with industrial production increasing by 40% in Britain and by over 100% in Germany. A comparison of capital formation rates in both countries helps to account for the different industrial growth rates. During the depression, the British ratio of net national capital formation to net national product fell from 11.5% to 6.0%, but the German ratio rose from 10.6% to 15.9%. During the depression, Britain took the course of static supply adjustment, but Germany stimulated effective demand and expanded industrial supply capacity by increasing and adjusting capital formation. For example, Germany dramatically increased investment of social overhead capital, such as in the management of electric power transmission lines, roads, and railroads, thereby stimulating industrial demand in that country, but similar investment stagnated or decreased in Britain. The resulting difference in capital formation accounts for the divergent levels of industrial production in the two countries and the different growth rates during and after the depression.India
The discovery of large quantities of silver in the United States and several European colonies caused the panic of 1873 and thus a decline in the value of silver relative to gold, devaluing India's standard currency. This event was known as " the fall of the rupee".South Africa
In theCape Colony
The Cape Colony ( nl, Kaapkolonie), also known as the Cape of Good Hope, was a British colony in present-day South Africa named after the Cape of Good Hope, which existed from 1795 to 1802, and again from 1806 to 1910, when it united with t ...
, the panic caused bankruptcies, rising unemployment, a pause in public works, and a major trade slump that lasted until the discovery of gold in 1886.
Ottoman Empire
In the periphery, theOttoman Empire
The Ottoman Empire, * ; is an archaic version. The definite article forms and were synonymous * and el, Оθωμανική Αυτοκρατορία, Othōmanikē Avtokratoria, label=none * info page on book at Martin Luther University) ...
's economy also suffered. Rates of growth of foreign trade dropped, external terms of trade deteriorated, declining wheat prices affected peasant producers, and the establishment of European control over Ottoman finances led to large debt payments abroad. The growth rates of agricultural and aggregate production were also lower during the Long Depression than the later period.
Latin Monetary Union
The general demonetization and cheapening of silver caused theLatin Monetary Union
The Latin Monetary Union (LMU) was a 19th-century system that unified several European currencies into a single currency that could be used in all member states when most national currencies were still made out of gold and silver. It was establ ...
in 1873 to suspend the conversion of silver to coins.
Global protectionism
After the 1873 depression, agricultural and industrial groups lobbied for protectivetariff
A tariff is a tax imposed by the government of a country or by a supranational union on imports or exports of goods. Besides being a source of revenue for the government, import duties can also be a form of regulation of foreign trade and pol ...
s. Conservative politicians such as Otto von Bismarck shifted from classical liberal
Classical liberalism is a political tradition and a branch of liberalism that advocates free market and laissez-faire economics; civil liberties under the rule of law with especial emphasis on individual autonomy, limited government, econom ...
economic policies in the 1870s, embracing many economic interventionist policies, including high tariffs, nationalization of railroads, and compulsory social insurance. The political and economic nationalism
Economic nationalism, also called economic patriotism and economic populism, is an ideology that favors state interventionism over other market mechanisms, with policies such as domestic control of the economy, labor, and capital formation, incl ...
also reduced the fortunes of the German and Canadian classical liberal
Classical liberalism is a political tradition and a branch of liberalism that advocates free market and laissez-faire economics; civil liberties under the rule of law with especial emphasis on individual autonomy, limited government, econom ...
parties. France, like Britain, also entered into a prolonged stagnation that extended to 1897. The French also attempted to deal with their economic problems by the implementation of tariffs. New French laws in 1880 and in 1892 imposed stiff tariffs on many agricultural and industrial imports. The U.S., still in the period after the Civil War
A civil war or intrastate war is a war between organized groups within the same state (or country).
The aim of one side may be to take control of the country or a region, to achieve independence for a region, or to change government policies ...
, continued to be very protectionist
Protectionism, sometimes referred to as trade protectionism, is the economic policy of restricting imports from other countries through methods such as tariffs on imported goods, import quotas, and a variety of other government regulations. ...
.
See also
* Panic of 1857 * Panic of 1893 * Second-term curse * Workingmen's Party of IllinoisReferences
Cited sources
* * *Further reading
* * Davies, Hannah Catherine. "'Mingled in an almost inextricable confusion': the panics of 1873 and the experience of globalization." ''Journal of Global History'' 15.2 (2020): 291–309. * Davies, Hannah Catherine. ''Transatlantic Speculations: Globalization and the Panics of 1873'' (Columbia UP, 2018online review
* * * * * * Focused on construction in the West. * * * * * * * * Wicker, Elmus. ''Banking panics of the
gilded age
In United States history, the Gilded Age was an era extending roughly from 1877 to 1900, which was sandwiched between the Reconstruction era and the Progressive Era. It was a time of rapid economic growth, especially in the Northern and Wes ...
'' (Cambridge University Press, 2006contents
Yearbooks
* * * *External links
{{DEFAULTSORT:Panic of 1873 1873 in economics 1873 in the United States Economic crises in the United States Financial crises History of banking in the United States History of rail transportation in the United States Presidency of Ulysses S. Grant1873
Events
January–March
* January 1
** Japan adopts the Gregorian calendar.
** The California Penal Code goes into effect.
* January 17 – American Indian Wars: Modoc War: First Battle of the Stronghold – Modoc Indians defe ...