Paiján culture on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 The Paiján culture was an archaeological culture that emerged on the northern coast of
The Paiján culture was an archaeological culture that emerged on the northern coast of
/ref> * Intermediate: have a "maximum width that may be at the base of the convex-sided body or convexity may be so poor that attribution is dubious". * Miscellaneous: have "stemmed points that do not fall within the other three classes".
 The Paiján culture was an archaeological culture that emerged on the northern coast of
The Paiján culture was an archaeological culture that emerged on the northern coast of Peru
, image_flag = Flag of Peru.svg
, image_coat = Escudo nacional del Perú.svg
, other_symbol = Great Seal of the State
, other_symbol_type = National seal
, national_motto = "Firm and Happy f ...
between 13,000 and 10,000 cal BP (11,000-8,000 BCE
Common Era (CE) and Before the Common Era (BCE) are year notations for the Gregorian calendar (and its predecessor, the Julian calendar), the world's most widely used calendar era. Common Era and Before the Common Era are alternatives to the or ...
). It was first described by Peruvian archaeologist Rafael Larco Hoyle
Rafael Larco Hoyle (18 May 1901 in Chicama Valley, Peru – 23 October 1966, Lima), raised at Chiclin, his family's estate, was sent to school in Maryland, United States, at the age of twelve. He later entered Cornell University to study agric ...
in the 1940s from the Pampa de los Fósiles site. Later research, mainly by French archaeologist Claude Chauchat, identified dozens of open air sites, which include camps, workshops and quarries.
Chivateros is a notable prehistoric stone tool quarry in the Ventanilla District of Peru associated with Paijan culture.
Generally, this culture would belong to the Lithic stage
In the sequence of cultural stages first proposed for the archaeology of the Americas by Gordon Willey and Philip Phillips in 1958, the Lithic stage was the earliest period of human occupation in the Americas, as post-glacial hunter gatherers s ...
of cultural development.
Geography
Most findings are concentrated along the valleys of the rivers Jequetepeque, Cupisnique, Chicama and Moche in the northern coast of Peru; more limited evidences of Paiján presence have been found in the central and south coasts of Peru as well as in the highland site of El Inga in Ecuador.Environment
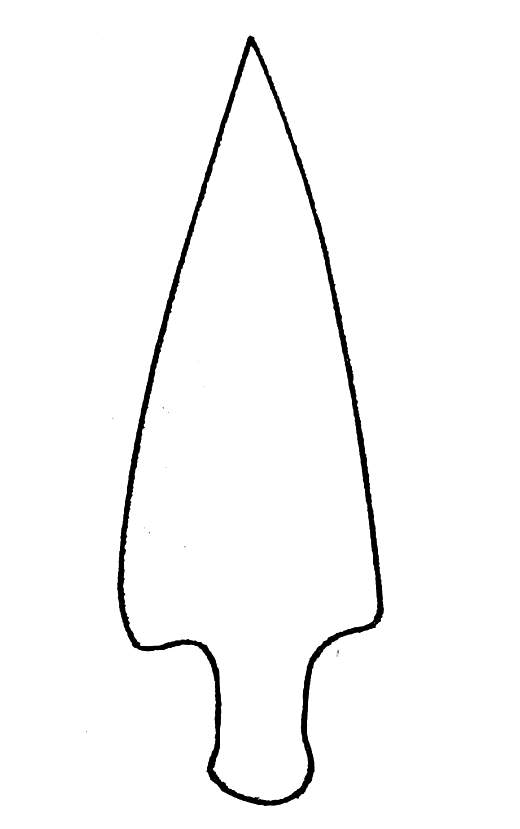
The Paiján environment was arid with sparse vegetation and small animals such as rodents, lizards and snails; further resources were provided by the sea which at the time was located 15 kilometers farther than today due to a lower sea level. To adapt to this environment, the Paiján developed long needle–likeprojectile point
In North American archaeological terminology, a projectile point is an object that was hafted to a weapon that was capable of being thrown or projected, such as a javelin, dart, or arrow. They are thus different from weapons presumed to have ...
s which were mounted on hollow shafts of cane or reed and be used as harpoons to catch fish; they also collected snails, hunted small animals such as vizcachas and used grinding stones to process plants.
Paijan projectile points
Paijan stemmed points are separated into several classes when being classified as they are found on sites. These classes include: lanceolate, triangular, intermediate, and miscellaneous. * Lanceolate: have convex-sided bodies with a "maximum width that is different from the base; the tip is very long, thin and sharp". * Triangular: have "straight sides with a maximum width that is located at the base of the body".“The Paijan Complex, Pampa De Cupisnique, Peru”/ref> * Intermediate: have a "maximum width that may be at the base of the convex-sided body or convexity may be so poor that attribution is dubious". * Miscellaneous: have "stemmed points that do not fall within the other three classes".
Common tools
Common Paijan tools used included single and double sidescrapers, unifaces – pieces or tabular blocks retouched on one face only all around the edge to give them an ovate shape, borers – rare small jasper blocks that have 3 points, and most abundantly - denticulates which have thick, steep edges. Bifaces are another common artifact found on Paiján sites.Time period
Based on the evidence as of 2015, the Paiján complex has been dated to ca. 13,000-10,000 cal BP. Early Paiján sites indicate large bands that moved seasonally between the coastal plains and the western slopes of the Andes. Late Paiján subphase sites feature three types of projectile points, Talambo, Contracting Narrow stem, and Contracting Broad stem types. They are now dated between 11,200 and 9,600 cal BP. These sites evidence smaller groups of decreased mobility. According to anthropologistTom Dillehay
Tom Dillehay is an American anthropologist who is the Rebecca Webb Wilson University Distinguished Professor of Anthropology, Religion, and Culture and Professor of Anthropology at Vanderbilt University. In addition to Vanderbilt, Dillehay has tau ...
, a possible explanation for this change is that an amelioration of the climate increased the availability of wild plants and animals; thus, Paiján people required less movement to meet their requirements while still relying on hunting-gathering
A traditional hunter-gatherer or forager is a human living an ancestrally derived lifestyle in which most or all food is obtained by foraging, that is, by gathering food from local sources, especially edible wild plants but also insects, fungi, ...
.Tom Dillehay, "Profiles in Holocene History", p. 38.
Oldest human remains
In 1975, at La Pampa de los Fósiles, Claude Chauchat discovered skeletal remains of a teenager about 12–13 years old, and of a young woman of about 25 years old, buried in a layer of ash. Radiocarbon studies gave an age of 10,200 ± 180 before present. They are therefore considered as the oldest human remains in Peru.See also
* Paiján * Amotape complex * Lauricocha cultureNotes
References
* * Dillehay, Tom. "Profiles in Holocene History". In Helaine Silverman and William H. Isbell (eds.), ''Handbook of South American archaeology''. New York: Springer, 2008, pp. 29–43. * Dillehay, Tom. ''The Settlement of the Americas: a new prehistory''. New York: Basic Books, 2000. * Dillehay, Tom, Duccio Bonavia and Peter Kaulicke. "The first settlers". In Helaine Silverman (ed.), ''Andean archaeology''. Malden, MA: Blackwell, 2004, pp. 16–34. * Lavallée, Danièle. ''The first South Americans: the peopling of a continent from the earliest evidence to high culture''. Salt Lake City: University of Utah Press, 2000. * Moseley, Michael. ''The Incas and their ancestors: the archaeology of Peru''. London: Thames and Hudson, 2004. {{DEFAULTSORT:Paijan Culture Andean civilizations Prehistory of Peru Pre-Columbian cultures Andean preceramic Oldest human remains in the Americas Pre-Columbian projectile points