The following
outline
Outline or outlining may refer to:
* Outline (list), a document summary, in hierarchical list format
* Code folding, a method of hiding or collapsing code or text to see content in outline form
* Outline drawing, a sketch depicting the outer edge ...
is provided as an overview of and topical guide to the Byzantine Empire:
Byzantine Empire
The Byzantine Empire, also referred to as the Eastern Roman Empire or Byzantium, was the continuation of the Roman Empire primarily in its eastern provinces during Late Antiquity and the Middle Ages, when its capital city was Constantinopl ...
(or Byzantium) – the
Constantinople
la, Constantinopolis ota, قسطنطينيه
, alternate_name = Byzantion (earlier Greek name), Nova Roma ("New Rome"), Miklagard/Miklagarth (Old Norse), Tsargrad ( Slavic), Qustantiniya ( Arabic), Basileuousa ("Queen of Cities"), Megalopolis ( ...
-centred
Roman Empire
The Roman Empire ( la, Imperium Romanum ; grc-gre, Βασιλεία τῶν Ῥωμαίων, Basileía tôn Rhōmaíōn) was the post- Republican period of ancient Rome. As a polity, it included large territorial holdings around the Mediter ...
of the
Middle Ages
In the history of Europe, the Middle Ages or medieval period lasted approximately from the late 5th to the late 15th centuries, similar to the post-classical period of global history. It began with the fall of the Western Roman Empire ...
. It is also referred to as the Eastern Roman Empire, primarily in the context of
Late Antiquity
Late antiquity is the time of transition from classical antiquity to the Middle Ages, generally spanning the 3rd–7th century in Europe and adjacent areas bordering the Mediterranean Basin. The popularization of this periodization in English ha ...
, while the Roman Empire was still administered with separate eastern and
western
Western may refer to:
Places
*Western, Nebraska, a village in the US
*Western, New York, a town in the US
*Western Creek, Tasmania, a locality in Australia
*Western Junction, Tasmania, a locality in Australia
*Western world, countries that id ...
political centres. In its own time, there was no such thing as "the Byzantine Empire," there was just the ongoing Roman Empire; "Byzantine Empire" is a scholarly term of convenience to differentiate the empire from its earlier existence during
classical antiquity
Classical antiquity (also the classical era, classical period or classical age) is the period of cultural history between the 8th century BC and the 5th century AD centred on the Mediterranean Sea, comprising the interlocking civilizations of ...
before the western half collapsed ''(see
decline of the Roman Empire)''. Its citizens continued to refer to their empire as the Roman Empire ( grc-gre, Βασιλεία Ῥωμαίων, ''Basileia Rhōmaiōn'';
[.] la, Imperium Romanum) or Romania (). After the Western Roman Empire
fragmented and collapsed in the 5th century, the eastern half continued to thrive, existing for an additional thousand years until it fell to the
Ottoman Turks in 1453. During much of its existence, the empire was the most powerful economic, cultural, and military force in Europe.
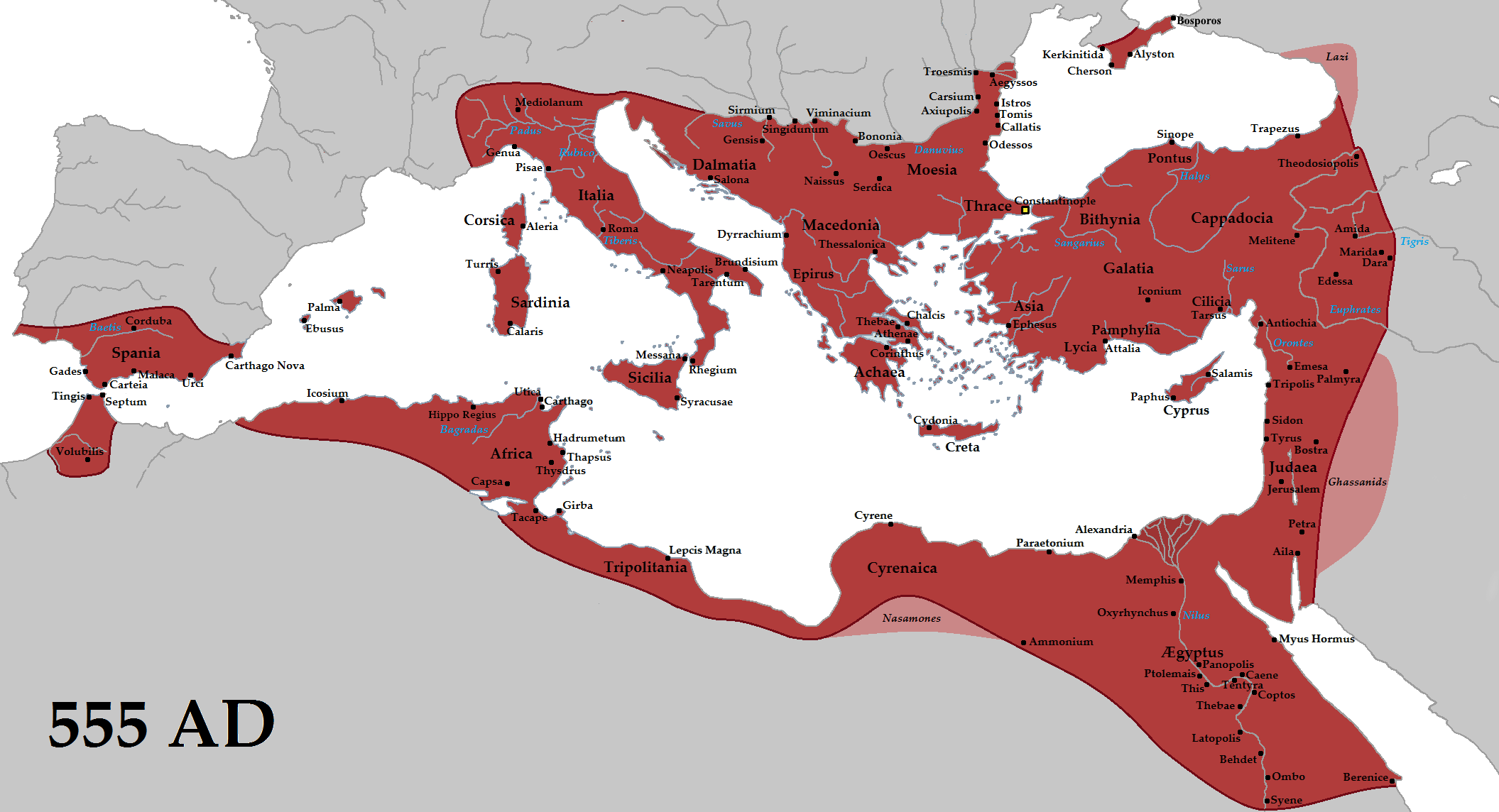
Geography of the Byzantine Empire
Regions of the Byzantine Empire
*
Albania under the Byzantine Empire In 395, the Roman Empire was permanently divided and the area that now constitutes modern Albania became part of the Byzantine Empire.
Antiquity
After the region fell to the Romans in 168 BC, it became part of the province of Macedonia. The centr ...
*
Byzantine Armenia
Byzantine Armenia, sometimes known as Western Armenia, is the name given to the parts of Kingdom of Armenia that became part of the Byzantine Empire. The size of the territory varied over time, depending on the degree of control the Byzantine ...
*
Byzantine Crete
The island of Crete came under the rule of the Byzantine Empire in two periods: the first extends from the late antique period (3rd century) to the conquest of the island by Andalusian exiles in the late 820s, and the second from the island's rec ...
*
Byzantine Egypt
, conventional_long_name = Roman Egypt
, common_name = Egypt
, subdivision = Province
, nation = the Roman Empire
, era = Late antiquity
, capital = Alexandria
, title_leader = Praefectus Augustalis
, image_map = Roman E ...
*
Byzantine Greece
Byzantine Greece has a history that mainly coincides with that of the Byzantine Empire itself.
Background: Roman Greece
The Greek peninsula became a Roman protectorate in 146 BC, and the Aegean islands were added to this territory in 133 BC. ...
Administrative divisions of the Byzantine Empire
*
Subdivisions of the Byzantine Empire Subdivisions of the Byzantine Empire were administrative units of the Eastern Roman or Byzantine Empire (330–1453). The Empire had a developed administrative system, which can be divided into three major periods: the late Roman/early Byzantine, w ...
= Provinces of the Byzantine Empire
=
*
Bithynia
*
Byzacena
Byzacena (or Byzacium) ( grc, Βυζάκιον, ''Byzakion'') was a Late Roman province in the central part of Roman North Africa, which is now roughly Tunisia, split off from Africa Proconsularis.
History
At the end of the 3rd century AD, t ...
*
Byzantine Crete
The island of Crete came under the rule of the Byzantine Empire in two periods: the first extends from the late antique period (3rd century) to the conquest of the island by Andalusian exiles in the late 820s, and the second from the island's rec ...
*
Catepanate of Italy
The Catepanate (or Catapanate) of Italy ( el, ''Katepaníkion Italías'') was a province of the Byzantine Empire from 965 until 1071. At its greatest extent, it comprised mainland Italy south of a line drawn from Monte Gargano to the Gulf of S ...
*
Catepanate of Serbia
*
Drougoubiteia
*
Duchy of Perugia
*
Duchy of Rome
The Duchy of Rome ( la, Ducatus Romanus) was a state within the Byzantine Exarchate of Ravenna. Like other Byzantine states in Italy, it was ruled by an imperial functionary with the title ''dux''. The duchy often came into conflict with the Papa ...
*
Duchy of the Pentapolis
In the Byzantine Empire, the Duchy of the Pentapolis was a duchy (Latin: ''ducatus''), a territory ruled by a duke (''dux'') appointed by and under the Exarch of Ravenna. The Pentapolis (from the Greek term ''πεντάπολις'', "five cities") ...
*
Duchy of Venetia
The Republic of Venice ( vec, Repùblega de Venèsia) or Venetian Republic ( vec, Repùblega Vèneta, links=no), traditionally known as La Serenissima ( en, Most Serene Republic of Venice, italics=yes; vec, Serenìsima Repùblega de Venèsia, ...
*
Egypt (Roman province)
*
Europa (Roman province)
Europa was a Roman province within the Diocese of Thrace.
History
Established by Roman Emperor Diocletian (284–305), the province largely corresponds to what is modern day European Turkey. The province's capital was initially Arcadiopolis ...
*
Duchy of Gaeta
The Duchy of Gaeta was an early medieval state centered on the coastal South Italian city of Gaeta. It began in the early ninth century as the local community began to grow autonomous as Byzantine power lagged in the Mediterranean and the penin ...
*
Galatia (Roman province)
Galatia () was the name of a province of the Roman Empire in Anatolia (modern central Turkey). It was established by the first emperor, Augustus (sole rule 30 BC – 14 AD), in 25 BC, covering most of formerly independent Celtic Galatia, with it ...
*
Haemimontus
Haemimontus ( el, ) was a Late Antiquity, late Roman Empire, Roman and early Byzantine Roman province, province, situated in northeastern Thrace. It was subordinate to the Diocese of Thrace and to the praetorian prefecture of the East. Its capita ...
*
Helenopontus
Pontus or Pontos (; el, Πόντος, translit=Póntos, "Sea") is a region on the southern coast of the Black Sea, located in the modern-day eastern Black Sea Region of Turkey. The name was applied to the coastal region and its mountainous hi ...
*
Honorias
Honorias ( el, ) was a late Roman province encompassing parts of Bithynia and Paphlagonia in Asia Minor (modern Asian Turkey).
Its capital was Claudiopolis (modern Bolu), and its governor held the modest rank of ''praeses''.
History
The pr ...
*
Isauria
*
Mauretania Caesariensis
*
Mauretania Tingitana
Mauretania Tingitana (Latin for "Tangerine Mauretania") was a Roman province, coinciding roughly with the northern part of present-day Morocco. The territory stretched from the northern peninsula opposite Gibraltar, to Sala Colonia (or Chella ...
*
Mesopotamia (Roman province)
Mesopotamia was the name of a Roman province, initially a short-lived creation of the Roman emperor Trajan in 116–117 and then re-established by Emperor Septimius Severus in c. 198. Control of the province was subsequently fought over betwe ...
*
Moesia Secunda
Moesia (; Latin: ''Moesia''; el, Μοισία, Moisía) was an ancient region and later Roman province situated in the Balkans south of the Danube River, which included most of the territory of modern eastern Serbia, Kosovo, north-eastern Alban ...
*
Duchy of Naples
*
Palaestina Prima
Palaestina Prima or Palaestina I was a Byzantine province that existed from the late 4th century until the Muslim conquest of the Levant in the 630s, in the region of Palestine. It was temporarily lost to the Sassanid Empire (Persian Empire) in ...
*
Paphlagonia
Paphlagonia (; el, Παφλαγονία, Paphlagonía, modern translit. ''Paflagonía''; tr, Paflagonya) was an ancient region on the Black Sea coast of north-central Anatolia, situated between Bithynia to the west and Pontus (region), Pontus t ...
*
Paristrion
*
Phrygia Pacatiana
In classical antiquity, Phrygia ( ; grc, Φρυγία, ''Phrygía'' ) was a kingdom in the west central part of Anatolia, in what is now Asian Turkey, centered on the Sangarios River. After its conquest, it became a region of the great empires ...
*
Phrygia Salutaris
In classical antiquity, Phrygia ( ; grc, Φρυγία, ''Phrygía'' ) was a kingdom in the west central part of Anatolia, in what is now Asian Turkey, centered on the Sangarios River. After its conquest, it became a region of the great empire ...
*
Pontus Polemoniacus
Pontus or Pontos may refer to:
* Short Latin name for the Pontus Euxinus, the Greek name for the Black Sea (aka the Euxine sea)
* Pontus (mythology), a sea god in Greek mythology
* Pontus (region), on the southern coast of the Black Sea, in modern ...
*
Rhodope (Roman province)
*
Scythia Minor
Scythia Minor or Lesser Scythia (Greek: , ) was a Roman province in late antiquity, corresponding to the lands between the Danube and the Black Sea, today's Dobruja divided between Romania and Bulgaria. It was detached from Moesia Inferior by th ...
*
Spania
Spania ( la, Provincia Spaniae) was a province of the Eastern Roman Empire from 552 until 624 in the south of the Iberian Peninsula and the Balearic Islands. It was established by the Emperor Justinian I in an effort to restore the western prov ...
*
Theodorias (province)
Theodorias ( el, Θεοδωριάς) was a Byzantine province created in 528 by Emperor Justinian I and named in honour of his wife, the Empress Theodora.
History
It comprised a small coastal territory taken from the earlier provinces of Syr ...
*
Thessaly
Thessaly ( el, Θεσσαλία, translit=Thessalía, ; ancient Thessalian: , ) is a traditional geographic and modern administrative region of Greece, comprising most of the ancient region of the same name. Before the Greek Dark Ages, The ...
= Themes of the Byzantine Empire
=
*
Theme (Byzantine district)
The themes or ( el, θέματα, , singular: , ) were the main military/administrative divisions of the middle Byzantine Empire. They were established in the mid-7th century in the aftermath of the Slavic invasion of the Balkans and Muslim co ...
= Cities of the Byzantine Empire
=
*
Constantinople
la, Constantinopolis ota, قسطنطينيه
, alternate_name = Byzantion (earlier Greek name), Nova Roma ("New Rome"), Miklagard/Miklagarth (Old Norse), Tsargrad ( Slavic), Qustantiniya ( Arabic), Basileuousa ("Queen of Cities"), Megalopolis ( ...
(capital)
*
Thessalonika
Thessaloniki (; el, Θεσσαλονίκη, , also known as Thessalonica (), Saloniki, or Salonica (), is the second-largest city in Greece, with over one million inhabitants in its metropolitan area, and the capital of the geographic region of ...
Affiliated polities
*
Republic of Venice
The Republic of Venice ( vec, Repùblega de Venèsia) or Venetian Republic ( vec, Repùblega Vèneta, links=no), traditionally known as La Serenissima ( en, Most Serene Republic of Venice, italics=yes; vec, Serenìsima Repùblega de Venèsia, ...
*
Frankokratia
*
Despotate of Epirus
*
Empire of Trebizond
*
Bulgarian Empire
*
Serbian Empire
The Serbian Empire ( sr, / , ) was a medieval Serbian state that emerged from the Kingdom of Serbia. It was established in 1346 by Dušan the Mighty, who significantly expanded the state.
Under Dušan's rule, Serbia was the major power in the ...
Demography of the Byzantine Empire
*
Population of the Byzantine Empire
The population of the Byzantine Empire encompassed all ethnic and tribal groups living there, mainly Byzantine Greeks, but also Khazars, Bulgars, Turks, Armenians, Slavs, Goths, Arabs, Illyrians, Thracians, Assyrians, Tzans and other groups. It ...
Government and politics of the Byzantine Empire
*
Byzantine emperors
This is a list of the Byzantine emperors from the foundation of Constantinople in 330 AD, which marks the conventional start of the Eastern Roman Empire, to its fall to the Ottoman Empire in 1453 AD. Only the emperors who were recognized as ...
**
Byzantine emperors family tree
This is a family tree of all the Byzantine emperors, Eastern Roman Emperors who ruled in Constantinople. Most of the Eastern emperors were related in some form to their predecessors, sometimes by direct descent or by marriage. From the Doukid dynas ...
*
Byzantine bureaucracy
Through the 5th century Hellenistic political systems, philosophies
Philosophical schools of thought and philosophical movements.
A
Absurdism -
Action, philosophy of -
Actual idealism -
Actualism -
Advaita Vedanta -
Aesthetic Re ...
**
Byzantinism
*
Byzantine diplomacy
Political institutions of the Byzantine Empire
Political institutions of the Byzantine Empire
*
Byzantine Senate
Byzantine law
Byzantine law
Byzantine law was essentially a continuation of Roman law with increased Orthodox Christian and Hellenistic influence. Most sources define ''Byzantine law'' as the Roman legal traditions starting after the reign of Justinian I in the 6th century ...
Military of the Byzantine Empire
Military of the Byzantine Empire
*
Byzantine battle tactics
The Byzantine army evolved from that of the late Roman period taking as leading models and shaping itself on the late Hellenistic armies, but it became considerably more sophisticated in strategy, tactics and organization. The language of the ...
*
Byzantine military manuals
This article lists and briefly discusses the most important of many treatises on military science produced in the Byzantine Empire.
Background
The Eastern Roman Empire was, for much of its history, one of the major powers of the medieval world ...
Byzantine armed forces
*
Byzantine army
*
Navy
A navy, naval force, or maritime force is the branch of a nation's armed forces principally designated for naval and amphibious warfare; namely, lake-borne, riverine, littoral, or ocean-borne combat operations and related functions. It in ...
Military conflicts
*
Byzantine wars
General history of the Byzantine Empire
History of the Byzantine Empire
This history of the Byzantine Empire covers the history of the Eastern Roman Empire from late antiquity until the Fall of Constantinople in 1453 AD. Several events from the 4th to 6th centuries mark the transitional period during which the Roman ...
*
Byzantine civilisation in the twelfth century
*
Byzantine Empire under the Amorian dynasty
*
Byzantine Empire under the Angelos dynasty
*
Byzantine Empire under the Doukas dynasty
The Byzantine Empire was ruled by emperors of the Doukas dynasty between 1059 and 1081. There are six emperors and co-emperors of this period: the dynasty's founder, Emperor Constantine X Doukas (r. 1059–1067), his brother John Doukas, ''k ...
*
Byzantine Empire under the Heraclian dynasty
The Byzantine Empire was ruled by emperors of the dynasty of Heraclius between 610 and 711. The Heraclians presided over a period of cataclysmic events that were a watershed in the history of the Empire and the world.
Heraclius, the founder of ...
*
Byzantine Empire under the Isaurian dynasty
The Byzantine Empire was ruled by the Isaurian or Syrian dynasty from 717 to 802. The Isaurian emperors were successful in defending and consolidating the Empire against the Caliphate after the onslaught of the early Muslim conquests, but were ...
*
Byzantine Empire under the Komnenos dynasty
The Byzantine Empire was ruled by emperors of the Komnenos dynasty for a period of 104 years, from 1081 to about 1185. The ''Komnenian'' (also spelled ''Comnenian'') period comprises the reigns of five emperors, Alexios I, John II, Manuel I, A ...
*
Byzantine Empire under the Leonid dynasty
The Eastern Roman Empire was ruled by the House of Leo from AD 457, the accession of Leo I, to 518, the death of Anastasius I. The rule of the Leonid dynasty coincided with the rapid decline, collapse and eventual fall of the Western Roman Empir ...
*
Byzantine Empire under the Macedonian dynasty
The Byzantine Empire underwent a revival during the reign of the Macedonian emperors of the late 9th, 10th, and early 11th centuries, when it gained control over the Adriatic Sea, Southern Italy, and all of the territory of the Tsar Samuil of Bul ...
*
Byzantine Empire under the Nikephorian dynasty
Following the deposition of the Byzantine empress Irene of Athens, the throne of the Byzantine Empire passed to a relatively short-lived dynasty, the Nikephorian dynasty, named after its founder, Nikephoros I. The empire was in a weaker and more ...
*
Byzantine Empire under the Palaiologos dynasty
*
Byzantine Empire under the Theodosian dynasty
The Eastern Roman empire, Eastern Roman Empire was ruled by the Theodosian dynasty from 379, the accession of Theodosius I, to 457, the death of Marcian. The rule of the Theodosian dynasty saw the final East-West division of the Roman Empire, betw ...
*
Byzantine Iconoclasm
The Byzantine Iconoclasm ( gr, Εικονομαχία, Eikonomachía, lit=image struggle', 'war on icons) were two periods in the history of the Byzantine Empire when the use of religious images or icons was opposed by religious and imperial a ...
*
History of Lebanon under Byzantine rule
*
History of the Jews in the Byzantine Empire
The history of the Jews in the Byzantine Empire has been well recorded and preserved.
Background and legal standing
After the decline of the Greek-speaking Hellenistic Judaism in ancient times, the use of the Greek language and the integration o ...
*
Decline of the Byzantine Empire
The Byzantine Empire experienced several cycles of growth and decay over the course of nearly a thousand years, including major losses during the Early Muslim conquests of the 7th century. However, modern historians generally agree that the star ...
**
Fall of Constantinople
Military history of the Byzantine Empire
*
List of Byzantine wars
A ''list'' is any set of items in a row. List or lists may also refer to:
People
* List (surname)
Organizations
* List College, an undergraduate division of the Jewish Theological Seminary of America
* SC Germania List, German rugby union ...
*
List of sieges of Constantinople
The following is a list of sieges of Constantinople, a historic city located in an area which is today part of Istanbul, Turkey. The city was built on the land that links Europe to Asia through Bosporus and connects the Sea of Marmara and the Bl ...
*
Byzantine–Sassanid Wars
**
Byzantine–Sassanid War of 602–628
*
Byzantine–Arab Wars
**
Byzantine–Arab Wars (780–1180)
Between 780–1180, the Byzantine Empire and the Abbasid & Fatimid caliphates in the regions of Iraq, Palestine, Syria, Anatolia and Southern Italy fought a series of wars for supremacy in the Eastern Mediterranean. After a period of indecisive a ...
***
Sack of Amorium
The Sack of Amorium by the Abbasid Caliphate in mid-August 838 was one of the major events in the long history of the Arab–Byzantine Wars. The Abbasid campaign was led personally by the Caliph al-Mu'tasim (), in retaliation to a virtually unop ...
(838)
*
Rus'–Byzantine Treaty
**
Rus'–Byzantine Treaty (907)
**
Rus'–Byzantine Treaty (911)
**
Rus'–Byzantine Treaty (945)
*
Rus'–Byzantine War
**
Rus'–Byzantine War (860)
The siege of Constantinople of 860 was the only major military expedition of the Rus' Khaganate (Byzantine Greek: Ῥῶς) that probably never happened. It is recorded only in Russian chronicles, and reproduced by Catherine the Great in 1786, ...
**
Rus'–Byzantine War (907)
**
Rus'–Byzantine War (941)
**
Rus'–Byzantine War (1024)
The Battle of Lemnos in 1024 was the culmination of a raid by Kievan Rus' troops through the Dardanelles and into the Aegean Sea. It was the penultimate conflict between the Byzantine Empire and the Rus'.
The only source for the conflict is the h ...
**
Rus'–Byzantine War (1043)
*
Byzantine–Venetian Treaty of 1082
*
Byzantine–Venetian War (1294–1302)
*
Byzantine civil war of 1321–1328
*
Byzantine civil war of 1341–1347
The Byzantine civil war of 1341–1347, sometimes referred to as the Second Palaiologan Civil War, was a conflict that broke out in the Byzantine Empire after the death of Andronikos III Palaiologos over the guardianship of his nine-year-old so ...
*
Byzantine civil war of 1373–1379
The Byzantine civil war of 1373–1379 was a military conflict fought in the Byzantine Empire between Byzantine Emperor John V Palaiologos and his son, Andronikos IV Palaiologos, also growing into an Ottoman civil war as well, when Savcı Bey, th ...
*
Byzantine–Genoese War (1348–1349)
*
Byzantine–Bulgarian Wars
The Byzantine–Bulgarian wars were a series of conflicts fought between the Byzantines and Bulgarians which began when the Bulgars first settled in the Balkan peninsula in the 5th century, and intensified with the expansion of the Bulgarian Em ...
**
Byzantine conquest of Bulgaria
From ca. 970 until 1018, a series of conflicts between the Bulgarian Empire and the Byzantine Empire led to the gradual reconquest of Bulgaria by the Byzantines, who thus re-established their control over the entire Balkan peninsula for the firs ...
*
Byzantine–Norman wars
Wars between the Normans and the Byzantine Empire were fought from 1040 until 1185, when the last Norman invasion of the Byzantine Empire was defeated. At the end of the conflict, neither the Normans nor the Byzantines could boast much power, as ...
*
Byzantine–Seljuq Wars
*
Byzantine–Georgian wars
The Byzantine–Georgian wars ( ka, ბიზანტიურ-ქართული ომები, tr) were a series of conflicts fought during the 11th-13th centuries over several strategic districts in the Byzantine-Georgian marchlands.
Ba ...
*
Byzantine–Mongol alliance
*
Byzantine–Ottoman Wars
Byzantine historiography
*
Byzantine studies
Byzantine studies is an interdisciplinary branch of the humanities that addresses the history, culture, demography, dress, religion/theology, art, literature/epigraphy, music, science, economy, coinage and politics of the Eastern Roman Empire. T ...
Works on Byzantine history
Culture of the Byzantine Empire
Byzantine culture
The Byzantine Empire, also referred to as the Eastern Roman Empire or Byzantium, was the continuation of the Roman Empire primarily in its eastern provinces during Late Antiquity and the Middle Ages, when its capital city was Constantinopl ...
*
Byzantine architecture
*
Byzantine art
Byzantine art comprises the body of Christian Greek artistic products of the Eastern Roman Empire, as well as the nations and states that inherited culturally from the empire. Though the empire itself emerged from the decline of Rome and lasted u ...
**
Macedonian art Macedonian art may refer to:
* Macedonian art (Byzantine), the period of Byzantine art, during the reign of Macedonian dynasty
- in terms of ethnicity:
* Art of Ancient Macedonians, the art of Ancient Macedonians, during the period of classical ...
**
Byzantine dance
**
Byzantine literature
Byzantine literature is the Greek literature of the Middle Ages, whether written in the territory of the Byzantine Empire or outside its borders.Encyclopædia Britannica - "Greek literature: Byzantine literature" It forms the second period in th ...
***
Acritic songs
The Acritic songs ( "frontiersmen songs") are the epic poems that emerged in the Byzantine Empire probably around the ninth century. The songs celebrated the exploits of the Akritai, the frontier guards defending the eastern borders of the Byzant ...
***
Byzantine novel
Byzantine romance represents a revival of the ancient Greek romance of Roman times. Works in this category were written by Byzantine Greeks of the Eastern Roman Empire during the 12th century.
History
Under the Comnenian dynasty, Byzantine writ ...
**
Byzantine music
*
Byzantine calendar
The Byzantine calendar, also called the Roman calendar, the Creation Era of Constantinople or the Era of the World ( grc, Ἔτη Γενέσεως Κόσμου κατὰ Ῥωμαίους, also or , abbreviated as ε.Κ.; literal translation of ...
*
Byzantine cuisine
*
Byzantine dress
Byzantine dress changed considerably over the thousand years of the Empire, but was essentially conservative. Popularly, Byzantine dress remained attached to its classical Greek roots with most changes and different styles being evidenced in the ...
*
Byzantine gardens
*
Byzantine Greeks
The Byzantine Greeks were the Greek-speaking Eastern Romans of Orthodox Christianity throughout Late Antiquity and the Middle Ages. They were the main inhabitants of the lands of the Byzantine Empire (Eastern Roman Empire), of Constantinople ...
*
Byzantine philosophy
Religion in the Byzantine Empire
*
History of late ancient Christianity
**
State church of the Roman Empire
***
Byzantine Papacy
The Byzantine Papacy was a period of Byzantine domination of the Roman papacy from 537 to 752, when popes required the approval of the Byzantine Emperor for episcopal consecration, and many popes were chosen from the '' apocrisiarii'' (liaisons ...
*
Eastern Orthodox Church
The Eastern Orthodox Church, also called the Orthodox Church, is the second-largest Christian church, with approximately 220 million baptized members. It operates as a communion of autocephalous churches, each governed by its bishops vi ...
**
Byzantine Rite
**
Icons
An icon () is a religious work of art, most commonly a painting, in the cultures of the Eastern Orthodox, Oriental Orthodox, and Catholic churches. They are not simply artworks; "an icon is a sacred image used in religious devotion". The most c ...
***
Byzantine Iconoclasm
The Byzantine Iconoclasm ( gr, Εικονομαχία, Eikonomachía, lit=image struggle', 'war on icons) were two periods in the history of the Byzantine Empire when the use of religious images or icons was opposed by religious and imperial a ...
**
Degrees of Orthodox monasticism
The degrees of Eastern Orthodox and Eastern Catholic monasticism are the stages an Eastern Orthodox monk or nun passes through in their religious vocation.
In the Eastern Orthodox Church, the process of becoming a monk or nun is intentionally slo ...
***
Mount Athos
***
Saint Catherine's Monastery
Saint Catherine's Monastery ( ar, دير القدّيسة كاترين; grc-gre, Μονὴ τῆς Ἁγίας Αἰκατερίνης), officially the Sacred Autonomous Royal Monastery of Saint Katherine of the Holy and God-Trodden Mount Sinai, ...
*
Paulicianism
Paulicianism (Classical Armenian: Պաւղիկեաններ, ; grc, Παυλικιανοί, "The followers of Paul"; Arab sources: ''Baylakānī'', ''al Bayāliqa'' )Nersessian, Vrej (1998). The Tondrakian Movement: Religious Movements in the ...
Byzantine language
*
Medieval Greek
Medieval Greek (also known as Middle Greek, Byzantine Greek, or Romaic) is the stage of the Greek language between the end of classical antiquity in the 5th–6th centuries and the end of the Middle Ages, conventionally dated to the Fall of Co ...
Byzantine economy
*
Byzantine economy
The Byzantine economy was among the most robust economies in the Mediterranean for many centuries. Constantinople was a prime hub in a trading network that at various times extended across nearly all of Eurasia and North Africa. Some scholars arg ...
*
Byzantine agriculture
The Byzantine economy was among the most robust economies in the Mediterranean for many centuries. Constantinople was a prime hub in a trading network that at various times extended across nearly all of Eurasia and North Africa. Some scholars arg ...
*
Byzantine currency
Byzantine currency, money used in the Eastern Roman Empire after the fall of the West, consisted of mainly two types of coins: the gold solidus and a variety of clearly valued bronze coins. By the end of the empire the currency was issued only ...
*
Byzantine coinage
Byzantine currency, money used in the Eastern Roman Empire after the fall of the West, consisted of mainly two types of coins: the gold solidus and a variety of clearly valued bronze coins. By the end of the empire the currency was issued only in ...
*
Byzantine mints
*
Byzantine silk
Byzantine silk is silk woven in the Byzantine Empire (Byzantium) from about the fourth century until the Fall of Constantinople in 1453.
The Byzantine capital of Constantinople was the first significant silk-weaving center in Europe. Silk was on ...
*
Slavery in the Byzantine Empire
Byzantine education
*
Byzantine university
**
University of Constantinople
The Imperial University of Constantinople, sometimes known as the University of the Palace Hall of Magnaura ( el, Πανδιδακτήριον τῆς Μαγναύρας), was an Eastern Roman educational institution that could trace its corporat ...
*
Byzantine rhetoric Byzantine rhetoric refers to rhetorical theorizing and production during the time of the Byzantine Empire. Byzantine rhetoric is significant in part because of the sheer volume of rhetorical works produced during this period. Rhetoric was the most ...
Byzantine science and technology
*
Byzantine science
Byzantine science played an important role in the transmission of classical knowledge to the Islamic world and to Renaissance Italy, and also in the transmission of Islamic science to Renaissance Italy. Its rich historiographical tradition preser ...
*
Byzantine medicine
Byzantine medicine encompasses the common medical practices of the Byzantine Empire from c. 400 AD to 1453 AD. Byzantine medicine was notable for building upon the knowledge base developed by its Greco-Roman predecessors. In preserving medical pr ...
*
List of Byzantine inventions
See also
*
Outline of classical studies
*
Agnes of France, Byzantine Empress
*
Albanian Greek Catholic Church
The Albanian Greek Catholic Church ( la, Ecclesiae Graecae Catholico Albanica; sq, Kisha Katolike Bizantine Shqiptare), also known as the Albanian Byzantine Catholic Church, is an autonomous ('' sui iuris'' in Latin) Byzantine Rite particular ...
*
Alexander (Byzantine emperor)
Alexander Porphyrogenitus ( gr, Αλέξανδρος, ''Alexandros'', 23 November 8706 June 913) was briefly Byzantine emperor from 912 to 913, and the third emperor of the Macedonian dynasty.
Life
Alexander was the third son of Emperor Basil ...
*
Argyros (Byzantine family)
Argyros (, derived from , "silver"), feminine Argyre (), Latinized as Argyrus and Argyra, was the name of a prominent aristocratic family of Roman Emperors of the Byzantine Empire active from the middle of the 9th century until the very end of t ...
*
Bandon (Byzantine Empire)
The ''bandon'' ( el, βάνδον) was the basic military unit and administrative territorial entity of the middle Byzantine Empire. Its name, like the Latin and ("ensign, banner"), had a Germanic origin. It derived from the Gothic , which is p ...
*
Book of Job in Byzantine illuminated manuscripts
There are fourteen known Byzantine manuscripts of the Book of Job dating from the 9th to 14th centuries, as well as a post-Byzantine codex illuminated with cycle of miniatures. The quantity of Job illustrations survived in the fifteen manuscript ...
*
Bristol Byzantine
Bristol Byzantine is a variety of Byzantine Revival architecture that was popular in the city of Bristol from about 1850 to 1880.
Many buildings in the style have been destroyed or demolished, but notable surviving examples include the Colston ...
*
Byzantine & Christian Museum
The Byzantine and Christian Museum ( el, Βυζαντινό και Χριστιανικό Μουσείο, links=no) is situated at Vassilissis Sofias Avenue in Athens, Greece. It was founded in 1914, and houses more than 25,000 exhibits with rare ...
*
Byzantine Catholic World
*
Byzantine Chain
*
Byzantine Church, Lin
The Byzantine Church ( sq, Rrënojat e Kishës Bizantine) is a ruined church in Lin, Korçë County, Albania. It is a Cultural Monument of Albania. The church has been included within the possible UNESCO site of the Natural and Cultural Heritag ...
*
Byzantine Discalced Carmelites
*
Byzantine Fresco Chapel
The Byzantine Fresco Chapel is a part of the Menil Collection in Houston, Texas, near the University of St. Thomas. From February 1997 to February 2012, it displayed the only intact Byzantine frescoes of this size and importance in the entire we ...
*
Byzantine Institute of America
*
Byzantine Master of the Crucifix of Pisa
The Crucifix of Pisa is a painting of the crucifixion painted on wood panel, dating to sometime around 1230 and currently in the Museo nazionale di San Matteo, Pisa, Italy. Its anonymous author is referred to as the Byzantine Master of the Crucifix ...
*
Byzantine Museum of Antivouniotissa
The Antivouniotissa Museum (Greek language, Greek: Βυζαντινό Μουσείο Αντιβουνιώτισσας) is a museum of post-Byzantine art, Byzantine icon, religious art of the Cretan School, Cretan and early Heptanese School (painti ...
*
Byzantine Museum of Ioannina
*
Byzantine Museum of Kastoria
*
Byzantine Revival architecture
Neo-Byzantine architecture (also referred to as Byzantine Revival) was a revival movement, most frequently seen in religious, institutional and public buildings. It incorporates elements of the Byzantine style associated with Eastern and Or ...
*
Byzantine Rite Christianity in Canada
Byzantine Rite Christianity in Canada refers to all Eastern Orthodox, Eastern Catholic, and independent groups in Canada who use the Byzantine Rite.
History
It is unclear when Eastern Christians first settled in Canada. Russian Orthodox missiona ...
*
Byzantine Rite Lutheranism
Eastern Lutheranism (also known as Byzantine Lutheranism or Byzantine Rite Lutheranism) refers to Lutheran churches, such as those of Ukraine and Slovenia, that use a form of the Byzantine Rite as their liturgy. It is unique in that it is based o ...
*
Byzantine and Modern Greek Studies
''Byzantine and Modern Greek Studies'' or BMGS is a peer reviewed British journal which contains articles that pertain to both Byzantine Studies and Modern Greek studies, i.e. the language, literature, history and archaeology of the post-classica ...
*
Byzantine and Post-Byzantine Collection of Chania
*
Byzantine commonwealth
The term Byzantine commonwealth was coined by 20th-century historians to refer to the area where Byzantine general influence ( Byzantine liturgical and cultural tradition) was spread during the Middle Ages by the Byzantine Empire and its missiona ...
*
Byzantine fault tolerance
*
Byzantine heraldry
*
Byzantine lyra
The Byzantine lyra or lira ( gr, λύρα) was a medieval bowed string musical instrument in the Byzantine (Eastern Roman) Empire. In its popular form, the lyra was a pear-shaped instrument with three to five strings, held upright and played by ...
*
Byzantine text-type
In the textual criticism of the New Testament, the Byzantine text-type (also called Majority Text, Traditional Text, Ecclesiastical Text, Constantinopolitan Text, Antiocheian Text, or Syrian Text) is one of the main text types. It is the form fo ...
*
Cathedral of St. Mary Byzantine Catholic Church
*
Chios Byzantine Museum
*
Constantine III (Byzantine emperor)
Heraclius Constantine ( la, Heraclius novus Constantinus; grc-gre, Ἡράκλειος Κωνσταντῖνος, Herakleios Konstantinos; 3 May 612 – 25 May 641), often enumerated as Constantine III, was one of the shortest reigning Byzantine ...
*
Cours (Byzantine general)
*
Early Byzantine mosaics in the Middle East
Early Byzantine mosaics in the Middle East are a group of Christian mosaics created between the 4th and the 8th centuries in ancient Syria, Palestine and Egypt when the area belonged to the Byzantine Empire. The eastern provinces of the Eastern ...
*
Eastern (Byzantine) Catholic Martyrology for February
*
Eastern (Byzantine) Catholic Martyrology for January
*
Georgian Byzantine-Rite Catholics Georgian Byzantine Rite Catholics, or members of the Georgian Greek Catholic Church, are Catholics from the Georgian people who practice the Byzantine Rite in Old Georgian, which is also the liturgical language of the Georgian Orthodox Church.
Hist ...
*
Greek Byzantine Catholic Church
The Greek Byzantine Catholic Church ( el, Ελληνική Βυζαντινή Καθολική Εκκλησία, ''Ellinikí Vizantiní Katholikí Ekklisía;'') or the Greek Catholic Church is a ''sui iuris'' Eastern Catholic particular church of ...
*
Holy Ghost Byzantine Catholic Church (Pittsburgh)
Holy Ghost Byzantine Catholic Church is an Eastern Catholic church in Pittsburgh, Pennsylvania, United States. It is located in the city's North Side neighborhood at 1437 Superior Avenue. Today it is best known as the church from which the funeral ...
*
Immortals (Byzantine)
The Immortals ( el, Ἀθάνατοι, ''Athanatoi'') were one of the elite ''Tagma (military), tagmata'' military units of the Byzantine Empire, first raised during the late 10th century. The name derives from alpha privativum, ''a-'' ("without") ...
*
Index of Byzantine Empire-related articles
*
Irene Palaiologina (Byzantine empress)
Irene Palaiologina (died after 1356) was the empress consort of Matthew Kantakouzenos.
Family
Irene was a daughter of '' despotēs'' Demetrios Palaiologos and his wife, possibly Theodora Komnene. Irene's paternal grandparents were Andronikos II ...
*
John the Deacon (Byzantine writer)
*
Julian Byzantine
*
Kephale (Byzantine Empire) In the late Byzantine Empire, the term ''kephale'' ( gr, κεφαλή, kephalē, head) was used to denote local and provincial governors.
It entered use in the second half of the 13th century, and was derived from the colloquial language. Consequen ...
*
Kleisoura (Byzantine district)
*
Komnenian Byzantine army
The Byzantine army of the Komnenian era or Komnenian army was the force established by Byzantine emperor Alexios I Komnenos during the late 11th/early 12th century, and perfected by his successors John II Komnenos and Manuel I Komnenos during t ...
*
List of Byzantine foreign treaties
*
List of Byzantine monuments in Istanbul
A ''list'' is any set of items in a row. List or lists may also refer to:
People
* List (surname)
Organizations
* List College, an undergraduate division of the Jewish Theological Seminary of America
* SC Germania List, German rugby union ...
*
List of Byzantine revolts and civil wars
This is a list of civil wars or other internal civil conflicts fought during the history of the Eastern Roman or Byzantine Empire (330–1453). The definition of organized civil unrest is any conflict that was fought within the borders of the By ...
*
List of Byzantine scholars
This is a list of Byzantine scientists and other scholars.
Before the 9th century
Most important scholars known before the Macedonian Renaissance were active under the Justinian dynasty.
* Pappus of Alexandria (290–350), mathematician
* Theon ...
*
List of Byzantine usurpers
The following is a list of usurpers in the Eastern Roman Empire or Byzantine Empire, from the start of the reign of Arcadius in 395 to the fall of Constantinople in 1453.
Usurper emperors
The following is a listing of Byzantine emperors who ro ...
*
List of Roman and Byzantine Empresses
This is a list of Roman and Byzantine empresses. A Roman empress was a woman who was the wife of a Roman emperor, the ruler of the Roman Empire.
The Romans had no single term for the position: Latin and Greek titles such as '' augusta'' (Greek ...
*
List of exiled and pretending Byzantine Empresses
*
List of leaders during the Byzantine Papacy
*
*
Museum of Byzantine Culture
The Museum of Byzantine Culture ( el, Μουσείο Βυζαντινού Πολιτισμού) is a museum in Thessaloniki, Central Macedonia, Greece, which opened in 1994.
History
To design the museum, a nationwide architectural competition was ...
*
Neo-Byzantine architecture in the Russian Empire
Russian-Byzantine architecture (Russo-Byzantine architecture, russian: русско-византийский стиль) is a revivalist direction in Russian architecture and decorative and applied arts, based on the interpretation of the forms ...
*
Norman-Arab-Byzantine culture
*
Palaiologan Byzantine army
The Palaiologan army refers to Byzantine army, the military forces of the Byzantine Empire under the Byzantine Empire under the Palaiologoi, rule of the Palaiologos dynasty, from the late 13th century to its final collapse in the mid-15th century. ...
*
Pannonia, Byzantine Empire
Pannonia was a Byzantine province, which existed in present-day Syrmia region of Serbia in the 6th century. Its capital was Sirmium (modern-day Sremska Mitrovica).
It differed significantly in its area from the Roman province of Pannonia, and i ...
*
Papias (Byzantine office)
*
Phokas (Byzantine family) Phokas ( grc-gre, Φωκᾶς, ''Phōkâs'') or Phocas (from Latin), feminine form Phokaina or Phocaina (, ''Phṓkaina''), was the name of a Byzantine aristocratic clan from Cappadocia, which in the 9th and 10th centuries provided a series of high- ...
*
Political mutilation in Byzantine culture
Mutilation was a common method of punishment for criminals in the Byzantine Empire, but it also had a role in the empire's political life. By blinding a rival, one would not only restrict his mobility but also make it almost impossible for hi ...
*
Prosopography of the Byzantine World
The Prosopography of the Byzantine World (PBW) is a project to create a prosopographical database of individuals named in textual sources in the Byzantine Empire and surrounding areas in the period from 642 to 1265. The project is a collaboration b ...
*
Quantum Byzantine agreement
*
Raoul (Byzantine family) The Raoul ( el, ) was a Byzantine aristocratic family of Norman origin, prominent during the Palaiologan period. From the 14th century on, they were also known as Ral s (). The feminine form of the name was Raoulaina (). Origin
The exact origin o ...
*
Saint Anne Catholic Church of the Byzantine Rite
*
Serbo-Byzantine architecture
The Serbo-Byzantine architectural style or Vardar architectural school (or "style"), is an ecclesiastical architectural style that flourished in the Serbia in the Middle Ages#Late Middle Ages, Serbian Late Middle Ages (ca. 1300–1389), during the ...
*
St. John Chrysostom Byzantine Catholic Church (Pittsburgh)
*
St. John the Baptist Byzantine Catholic Cathedral (Pittsburgh)
St. John the Baptist Byzantine Catholic Cathedral is the mother church of Byzantine Catholic Metropolitan Church of Pittsburgh, the United States, American branch of the Ruthenian Greek Catholic Church, Ruthenian Catholic Church. It is located a ...
*
St. John the Baptist Byzantine Catholic Cemetery
St. John the Baptist Byzantine Catholic Cemetery is an Eastern Catholic cemetery in Bethel Park, Pennsylvania, Bethel Park, Pennsylvania, United States, a suburb approximately south of downtown Pittsburgh. It is situated on a hillside in the so ...
*
St. Michael Byzantine Catholic Church Toledo
St. Michael parish is a Ruthenian Greek Catholic Church, which uses the Divine Liturgy of the Byzantine Rite. Accordingly, St. Michael is in full communion with the Bishop of Rome (more commonly referred to as the Pope of Rome) and is a parish wit ...
*
St. Nicholas Byzantine Catholic Church
St. Nicholas Byzantine Catholic Church, also known as St. Nicholas Greek Catholic Church, is a historic Catholic Church Church (building), church at 504 S. Liberty Street in Perryopolis, Pennsylvania, Perryopolis, Fayette County, Pennsylvania. I ...
References
External links
; Byzantine studies, resources and bibliography
* Adena, L.
The Enduring Legacy of Byzantium", ''Clio History Journal'', 2008.
* Ciesniewski, C.
The Byzantine Achievement, ''Clio History Journal'', 2006.
* Fox, Clinton R
* [https://web.archive.org/web/20101127205009/http://www.third-millennium-library.com/MedievalHistory/Cambridge/IV/Eastern-Door.html The Cambridge Medieval History (IV) The Eastern Roman Empire (717–1453)].
Byzantine studies homepageat
Dumbarton Oaks
Dumbarton Oaks, formally the Dumbarton Oaks Research Library and Collection, is a historic estate in the Georgetown neighborhood of Washington, D.C. It was the residence and garden of wealthy U.S. diplomat Robert Woods Bliss and his wife, ...
. Includes links to numerous electronic texts.
Byzantium: Byzantine studies on the Internet Links to various online resources.
Online sourcebook.
De Re Militari Resources for medieval history, including numerous translated sources on the Byzantine wars.
Numerous primary sources on Byzantine history.
Bibliography on Byzantine Material Culture and Daily Life Hosted by the
University of Vienna
The University of Vienna (german: Universität Wien) is a public research university located in Vienna, Austria. It was founded by Duke Rudolph IV in 1365 and is the oldest university in the German-speaking world. With its long and rich hist ...
; in English.
Constantinople Home Page Links to texts, images and videos on Byzantium.
Byzantium in Crimea: Political History, Art and Culture
Institute for Byzantine Studies of the Austrian Academy of Sciences (with further resources and a repository with papers on various aspects of the Byzantine Empire)
; Miscellaneous
*
De Imperatoribus Romanis Scholarly biographies of many Byzantine emperors.
A film explaining the political and economical reasons for the fall of the Empire, filmed by the Russian Orthodox Church.
12 Byzantine Rulersby Lars Brownworth of
The Stony Brook School
The Stony Brook School is a 7–12 private, Christian, co-educational, college-preparatory boarding and day school in Stony Brook, New York, United States. It was established in 1922 by John Fleming Carson and fellow members of the Stony ...
; audio lectures
NYTimes review
(Maps of the Roman/Byzantine Empire throughout its lifetime)
{{DEFAULTSORT:Byzantine Empire
1
Outlines of geography and places
Wikipedia outlines
 The following
The following