

The following
outline is provided as an overview of, and topical guide to,
India
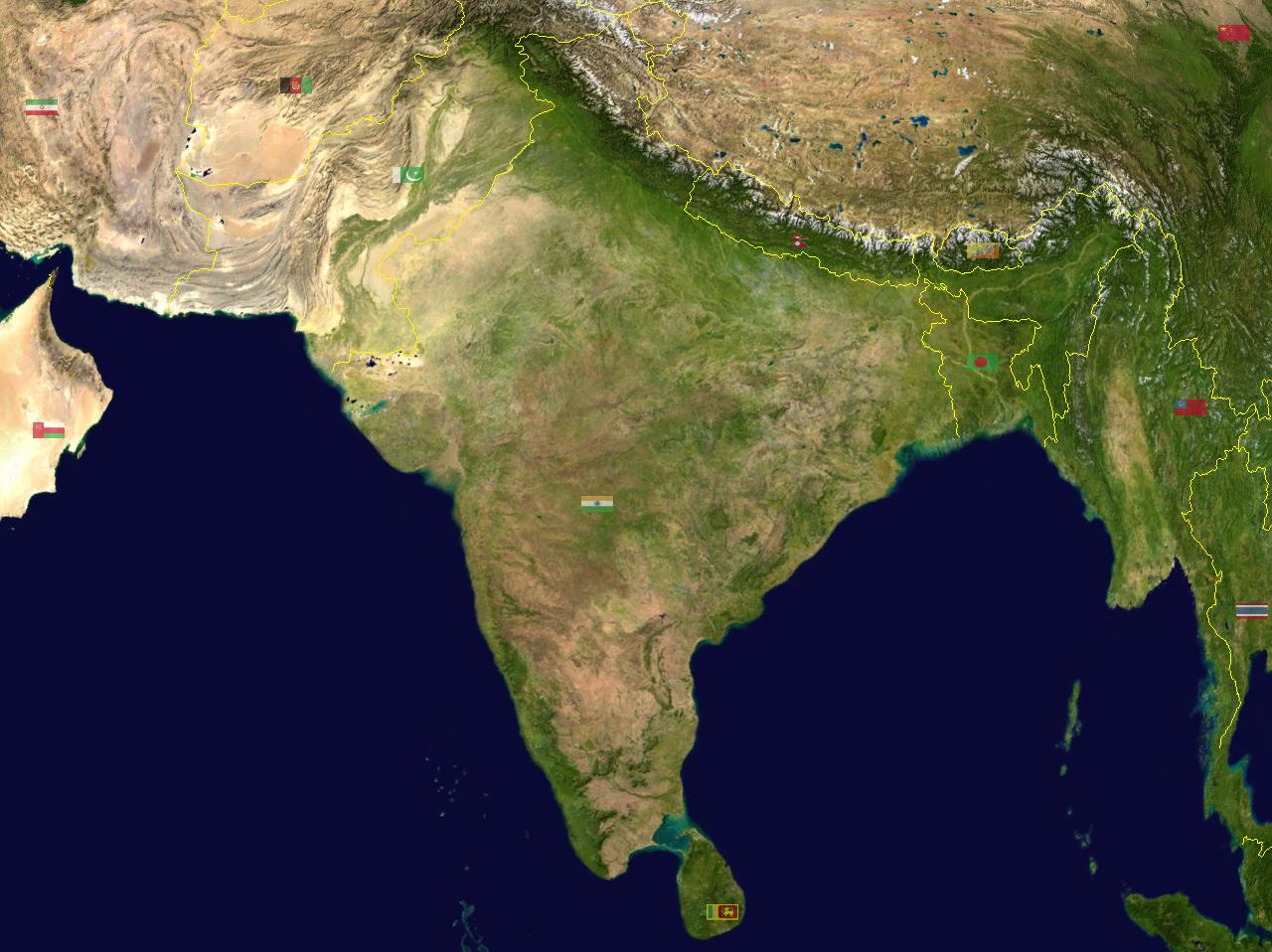
India, officially the Republic of India (Hindi: ), is a country in South Asia. It is the List of countries and dependencies by area, seventh-largest country by area, the List of countries and dependencies by population, second-most populous ...
:
The
seventh-largest country by area, India is located on the
Indian subcontinent
The Indian subcontinent is a physiographical region in Southern Asia. It is situated on the Indian Plate, projecting southwards into the Indian Ocean from the Himalayas. Geopolitically, it includes the countries of Bangladesh, Bhutan, In ...
in
South Asia
South Asia is the southern subregion of Asia, which is defined in both geographical and ethno-cultural terms. The region consists of the countries of Afghanistan, Bangladesh, Bhutan, India, Maldives, Nepal, Pakistan, and Sri Lanka.;;;;; ...
. India was home to the ancient
Indus Valley civilisation
The Indus Valley Civilisation (IVC), also known as the Indus Civilisation was a Bronze Age civilisation in the northwestern regions of South Asia, lasting from 3300 BCE to 1300 BCE, and in its mature form 2600 BCE to 1900& ...
, and is the birthplace of four world religions:
Hinduism
Hinduism () is an Indian religion or '' dharma'', a religious and universal order or way of life by which followers abide. As a religion, it is the world's third-largest, with over 1.2–1.35 billion followers, or 15–16% of the global p ...
,
Sikhism
Sikhism (), also known as Sikhi ( pa, ਸਿੱਖੀ ', , from pa, ਸਿੱਖ, lit=disciple', 'seeker', or 'learner, translit=Sikh, label=none),''Sikhism'' (commonly known as ''Sikhī'') originated from the word ''Sikh'', which comes fro ...
,
Buddhism
Buddhism ( , ), also known as Buddha Dharma and Dharmavinaya (), is an Indian religion or philosophical tradition based on teachings attributed to the Buddha. It originated in northern India as a -movement in the 5th century BCE, and ...
,
Jainism
Jainism ( ), also known as Jain Dharma, is an Indian religion. Jainism traces its spiritual ideas and history through the succession of twenty-four tirthankaras (supreme preachers of ''Dharma''), with the first in the current time cycle bein ...
. India endured
colonisation
Colonization, or colonisation, constitutes large-scale population movements wherein migrants maintain strong links with their, or their ancestors', former country – by such links, gain advantage over other inhabitants of the territory. When ...
, eventually being
administered by the United Kingdom from the mid-19th century to the mid-20th century. India became an independent nation in 1947 after a
struggle for independence that was mainly
non-violent resistance, led by influential figures like Mahatma Gandhi, and underwent a violent
partition. India is the
second most populous country with
over 1.4 billion people, and is also the most populous
democracy
Democracy (From grc, δημοκρατία, dēmokratía, ''dēmos'' 'people' and ''kratos'' 'rule') is a form of government in which the people have the authority to deliberate and decide legislation (" direct democracy"), or to choose g ...
in the world.
General reference

* Pronunciation:
* Common English country name:
India
India, officially the Republic of India (Hindi: ), is a country in South Asia. It is the List of countries and dependencies by area, seventh-largest country by area, the List of countries and dependencies by population, second-most populous ...
* Official English country name:
The Republic of India
* Common endonym(s):
Bharat,
Hindustan
''Hindūstān'' ( , from '' Hindū'' and ''-stān''), also sometimes spelt as Hindōstān ( ''Indo-land''), along with its shortened form ''Hind'' (), is the Persian-language name for the Indian subcontinent that later became commonly used b ...
* Official endonym(s):
Bharat Ganarajya
*
Adjectival(s):
Indian
Indian or Indians may refer to:
Peoples South Asia
* Indian people, people of Indian nationality, or people who have an Indian ancestor
** Non-resident Indian, a citizen of India who has temporarily emigrated to another country
* South Asia ...
*
Demonym
A demonym (; ) or gentilic () is a word that identifies a group of people (inhabitants, residents, natives) in relation to a particular place. Demonyms are usually derived from the name of the place (hamlet, village, town, city, region, province, ...
(s):
Indian
Indian or Indians may refer to:
Peoples South Asia
* Indian people, people of Indian nationality, or people who have an Indian ancestor
** Non-resident Indian, a citizen of India who has temporarily emigrated to another country
* South Asia ...
*
Etymology
Etymology () The New Oxford Dictionary of English (1998) – p. 633 "Etymology /ˌɛtɪˈmɒlədʒi/ the study of the class in words and the way their meanings have changed throughout time". is the study of the history of the form of words ...
:
Names of India
*
International rankings of India
*
ISO country codes
ISO 3166-1 (''Codes for the representation of names of countries and their subdivisions – Part 1: Country codes'') is a standard defining codes for the names of countries, dependent territories, and special areas of geographical interest. It ...
:IN, IND, 356
*
ISO region codes
ISO 3166-2 is part of the ISO 3166 standard published by the International Organization for Standardization (ISO), and defines codes for identifying the principal subdivisions (e.g., provinces or states) of all countries coded in ISO 3166-1. The ...
:See
ISO 3166-2:IN
*
Internet
The Internet (or internet) is the global system of interconnected computer networks that uses the Internet protocol suite (TCP/IP) to communicate between networks and devices. It is a '' network of networks'' that consists of private, p ...
country code top-level domain
A country code top-level domain (ccTLD) is an Internet top-level domain generally used or reserved for a country, sovereign state, or dependent territory identified with a country code. All ASCII ccTLD identifiers are two letters long, and all ...
:
.in
.in (india) is the Internet country code top-level domain ( ccTLD) for India. It was made available in 1989, four years after original generic top-level domains such as .com, .net and the country code like .us. It is currently administe ...
Geography of India
* India is:
** a
subcontinent
A continent is any of several large landmasses. Generally identified by convention rather than any strict criteria, up to seven geographical regions are commonly regarded as continents. Ordered from largest in area to smallest, these seven ...
** a
country
A country is a distinct part of the world, such as a state, nation, or other political entity. It may be a sovereign state or make up one part of a larger state. For example, the country of Japan is an independent, sovereign state, whi ...
*** a
megadiverse country
* Location:
**
Eastern Hemisphere
The Eastern Hemisphere is the half of the planet Earth which is east of the prime meridian (which crosses Greenwich, London, United Kingdom) and west of the antimeridian (which crosses the Pacific Ocean and relatively little land from pole ...
**
Northern Hemisphere
The Northern Hemisphere is the half of Earth that is north of the Equator. For other planets in the Solar System, north is defined as being in the same celestial hemisphere relative to the invariable plane of the solar system as Earth's Nort ...
***
Eurasia
Eurasia (, ) is the largest continental area on Earth, comprising all of Europe and Asia. Primarily in the Northern and Eastern Hemispheres, it spans from the British Isles and the Iberian Peninsula in the west to the Japanese archipelag ...
****
Asia
Asia (, ) is one of the world's most notable geographical regions, which is either considered a continent in its own right or a subcontinent of Eurasia, which shares the continental landmass of Afro-Eurasia with Africa. Asia covers an are ...
*****
South Asia
South Asia is the southern subregion of Asia, which is defined in both geographical and ethno-cultural terms. The region consists of the countries of Afghanistan, Bangladesh, Bhutan, India, Maldives, Nepal, Pakistan, and Sri Lanka.;;;;; ...
******
Greater India
Greater India, or the Indian cultural sphere, is an area composed of many countries and regions in South and Southeast Asia that were historically influenced by Indian culture, which itself formed from the various distinct indigenous cultures ...
******
Indian subcontinent
The Indian subcontinent is a physiographical region in Southern Asia. It is situated on the Indian Plate, projecting southwards into the Indian Ocean from the Himalayas. Geopolitically, it includes the countries of Bangladesh, Bhutan, In ...
**
Time zone
A time zone is an area which observes a uniform standard time for legal, commercial and social purposes. Time zones tend to follow the boundaries between countries and their subdivisions instead of strictly following longitude, because it ...
:
Indian Standard Time
Indian Standard Time (IST), sometimes also called India Standard Time, is the time zone observed throughout India, with a time offset of UTC+05:30. India does not observe daylight saving time or other seasonal adjustments. In military and ...
(
UTC+05:30)
**
Extreme points of India
The extreme points of India include the coordinates that are further north, south, east or west than any other location in India; and the highest and the lowest altitudes in the country. The northernmost point claimed by India is in territory disp ...

*** High:
Kangchenjunga
Kangchenjunga, also spelled Kanchenjunga, Kanchanjanghā (), and Khangchendzonga, is the third highest mountain in the world. Its summit lies at in a section of the Himalayas, the ''Kangchenjunga Himal'', which is bounded in the west by the ...
– third highest peak on
Earth
Earth is the third planet from the Sun and the only astronomical object known to harbor life. While large volumes of water can be found throughout the Solar System, only Earth sustains liquid surface water. About 71% of Earth's sur ...
*** Low:
Kuttanad
Kuttanad ( ml, കുട്ടനാട്) is a region covering the Alappuzha, Kottayam and Pathanamthitta Districts, in the state of Kerala, India, well known for its vast paddy fields and geographical peculiarities. The region has the lo ...
** Land boundaries: 14,103 km
:: 4,053 km
:: 3,380 km including the territorial disputes along its border; ''
McMahon Line
The McMahon Line is the boundary between Tibet and British India as agreed in the maps and notes exchanged by the respective plenipotentiaries on 24–25 March 1914 at Delhi, as part of the 1914 Simla Convention.
The line delimited the r ...
''
:: including the
Line of Control
The Line of Control (LoC) is a military control line between the Indian and Pakistanicontrolled parts of the former princely state of Jammu and Kashmir—a line which does not constitute a legally recognized international boundary, but serv ...
2,912 km
:: 1,690 km
:: 1,463 km
:: 605 km
:: 106 km
:* Coastline: 7,000 km
::
Indian Ocean
The Indian Ocean is the third-largest of the world's five oceanic divisions, covering or ~19.8% of the water on Earth's surface. It is bounded by Asia to the north, Africa to the west and Australia to the east. To the south it is bounded by ...
::
Arabian Sea
The Arabian Sea ( ar, اَلْبَحرْ ٱلْعَرَبِيُّ, Al-Bahr al-ˁArabī) is a region of the northern Indian Ocean bounded on the north by Pakistan, Iran and the Gulf of Oman, on the west by the Gulf of Aden, Guardafui Channe ...
::
Bay of Bengal
The Bay of Bengal is the northeastern part of the Indian Ocean, bounded on the west and northwest by India, on the north by Bangladesh, and on the east by Myanmar and the Andaman and Nicobar Islands of India. Its southern limit is a line bet ...
*
Population of India
Population typically refers to the number of people in a single area, whether it be a city or town, region, country, continent, or the world. Governments typically quantify the size of the resident population within their jurisdiction us ...
: 1,210,193,422 people (2011 census) –
2nd most populous country
**
Census of India
The decennial Census of India has been conducted 16 times, as of 2021. While it has been undertaken every 10 years, beginning in 1872 under British Viceroy Lord Mayo, the first complete census was taken in 1881. Post 1949, it has been conducted by ...
*
Area of India: –
7th largest country
*
Atlas of India
*
Subcontinent
A continent is any of several large landmasses. Generally identified by convention rather than any strict criteria, up to seven geographical regions are commonly regarded as continents. Ordered from largest in area to smallest, these seven ...
(
Indian subcontinent
The Indian subcontinent is a physiographical region in Southern Asia. It is situated on the Indian Plate, projecting southwards into the Indian Ocean from the Himalayas. Geopolitically, it includes the countries of Bangladesh, Bhutan, In ...
)
Environment of India
*
Climate of India
The climate of India consists of a wide range of weather conditions across a vast geographic scale and varied topography. Based on the Köppen system, India hosts six major climatic sub types, ranging from arid deserts in the west, alpine t ...
**
Climate change in India
*
Environmental issues in India
There are multiple environmental issues in India. Air pollution, water pollution, garbage, domestically prohibited goods and pollution of the natural environment are all challenges for India. Nature is also causing some drastic effects on I ...
**
Ecoregions of India
Ecoregions of the world, spanning all land area (terrestrial) of the planet, were first defined and mapped in 2001 and subsequently revised in 2017. Later, freshwater ecoregions and Marine ecoregion, marine ecoregions of the world were identified. ...
*
Renewable energy in India
**
Solar power in India
Solar power in India is a fast developing industry.
The country's solar installed capacity was 61.966 GWAC as of 30 November 2022.
Solar power generation in India ranks fourth globally in 2021.
The Indian Government had an initial tar ...
**
Wind power in India
*
Geology of India
The geology of India is diverse. Different regions of India contain rocks belonging to different geologic periods, dating as far back as the Eoarchean Era. Some of the rocks are very deformed and altered. Other deposits include recently d ...
*
National parks of India
National parks in India are IUCN (International Union of Conservation of Nature) category II protected areas. India's first national park was established in 1936, now known as Jim Corbett National Park, in Uttarakhand. By 1970, India only had ...
*
List of mountains in India
Highest major summits in India
Other significant mountains
* Agastyamalai
* Anamudi
* Anginda
* Apharwat Peak
* Bamba Dhura
* Bandarpunch
* Betlingchhip
* Blue Mountain
* Brammah
* Burphu Dhura
* Chandrashila
* Changuch
* Chaudhara
* ...
/Orography of India
*
Protected areas of India
There are four categories of protected areas in India, constituted under the Wildlife Protection Act, 1972. Tiger reserves consist of areas under national parks and wildlife sanctuaries. There are 52 tiger reserves in India. the protected area ...
*
Wildlife of India
India is home to a large variety of wildlife. It is a biodiversity hotspot with its various ecosystems ranging from the Himalayas in the north to the evergreen rain forests in the south, the sands of the west to the marshy mangroves of the ea ...
**
Flora of India
The flora of India is one of the richest in the world due to the wide range of climate, topology and habitat in the country. There are estimated to be over 18,000 species of flowering plants in India, which constitute some 6-7 percent of the to ...
**
Fauna of India
India is the world's 8th most biodiverse region with a 0.46 BioD score on diversity index, 102,718 species of fauna and 23.39% of the nation's geographical area under forest and tree cover in 2020. India encompasses a wide range ...
***
Birds of India
This is a list of the bird species of India and includes extant and recently extinct species recorded within the political limits of the Republic of India as defined by the Indian government are known to have 1364 species as of 2021, of which 81 ...
***
Mammals of India
This list of mammals of India comprises all the mammal species alive in India today. Some of them are common to the point of being considered vermin while others are exceedingly rare. Many species are known from just a few zoological specimens ...
Geographic features of India

*
North India
North India is a loosely defined region consisting of the northern part of India. The dominant geographical features of North India are the Indo-Gangetic Plain and the Himalayas, which demarcate the region from the Tibetan Plateau and Cen ...
*
East India
East India is a region of India consisting of the Indian states of Bihar, Jharkhand, Odisha
and West Bengal and also the union territory of the Andaman and Nicobar Islands. The region roughly corresponds to the historical region of Magad ...
*
South India
South India, also known as Dakshina Bharata or Peninsular India, consists of the peninsular southern part of India. It encompasses the Indian states of Andhra Pradesh, Karnataka, Kerala, Tamil Nadu, and Telangana, as well as the union terr ...
*
West India
Western India is a loosely defined region of India consisting of its western part. The Ministry of Home Affairs in its Western Zonal Council Administrative division includes the states of Goa, Gujarat, and Maharashtra along with the Unio ...
*
Central India
Central India is a loosely defined geographical region of India. There is no clear official definition and various ones may be used. One common definition consists of the states of Chhattisgarh and Madhya Pradesh, which are included in al ...
*
Northeast India
, native_name_lang = mni
, settlement_type =
, image_skyline =
, image_alt =
, image_caption =
, motto =
, image_map = Northeast india.png
, ...
*
Extreme points of India
The extreme points of India include the coordinates that are further north, south, east or west than any other location in India; and the highest and the lowest altitudes in the country. The northernmost point claimed by India is in territory disp ...
*
Beaches of India
*
Glaciers of India
*
Islands of India
*
Lakes of India
This is a list of notable lakes in India.
Andhra Pradesh
* Kolleru Lake
* Kondakarla Ava
* Kaniairi Lake
* Cumbum
* Pulicat Lake
Assam
* Dora Beel
*Urpad Beel
* Samaguri Beel
*Morikalang Beel
* Haflong Lak ...
*
Mountains of India
**
Volcanoes of India
*
Rivers of India
The rivers in India play an important role in the lives of its people. They provide potable water, cheap transportation, electricity, and the livelihood for many people nationwide. This easily explains why nearly all the major cities of India are l ...
**
Waterfalls of India
*
Valleys of India
A valley is an elongated low area often running between hills or mountains, which will typically contain a river or stream running from one end to the other. Most valleys are formed by erosion of the land surface by rivers or streams over ...
*
List of World Heritage Sites in India
The UNESCO, United Nations Educational, Scientific and Cultural Organization (UNESCO) designates World Heritage Sites of outstanding universal value to cultural heritage, cultural or natural heritage which have been nominated by countries which ...
Physical divisions of India
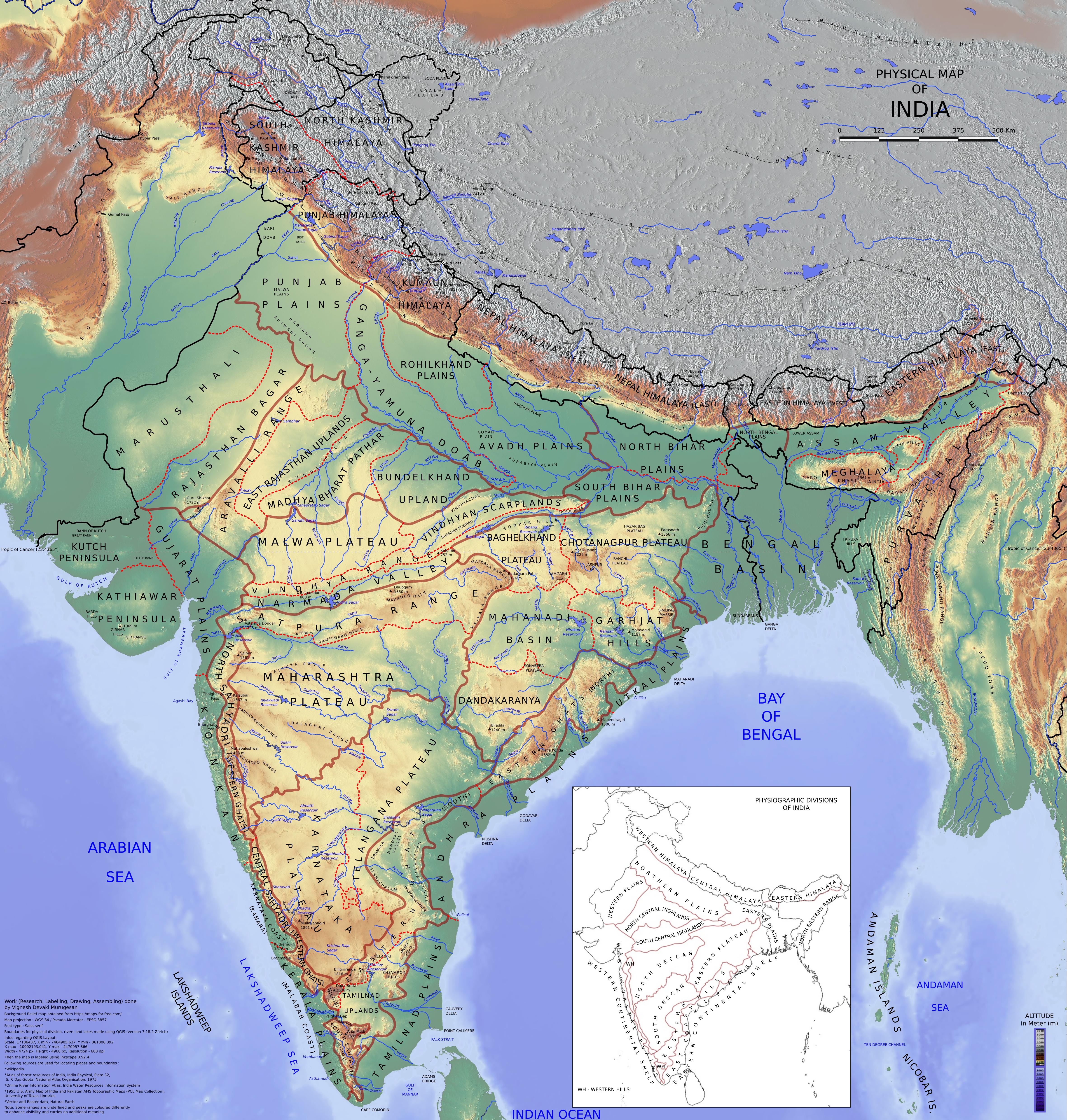
* The northern mountains including the
Himalaya
The Himalayas, or Himalaya (; ; ), is a mountain range in Asia, separating the plains of the Indian subcontinent from the Tibetan Plateau. The range has some of the planet's highest peaks, including the very highest, Mount Everest. Over 10 ...
s, which includes the
Karakoram
The Karakoram is a mountain range in Kashmir region spanning the borders of Pakistan, China, and India, with the northwest extremity of the range extending to Afghanistan and Tajikistan. Most of the Karakoram mountain range falls under the ...
ranges and the northeast mountain ranges.
*
Indo-Gangetic plains
The Indo-Gangetic Plain, also known as the North Indian River Plain, is a fertile plain encompassing northern regions of the Indian subcontinent, including most of northern and eastern India, around half of Pakistan, virtually all of Bangla ...
*
Thar Desert
The Thar Desert, also known as the Great Indian Desert, is an arid region in the north-western part of the Subcontinent that covers an area of and forms a natural boundary between India and Pakistan. It is the world's 20th-largest desert, ...
* Central Highlands and
Deccan Plateau
The large Deccan Plateau in southern India is located between the Western Ghats and the Eastern Ghats, and is loosely defined as the peninsular region between these ranges that is south of the Narmada river. To the north, it is bounded by th ...
*
Eastern coastal plains
The Eastern Coastal Plains is a wide stretch of landmass of India, lying between the Eastern Ghats and the Bay of Bengal. It is wider and leveled than the Western Coastal Plains and stretches from Tamil Nadu in the south to West Bengal in the n ...
*
Western coastal plains
The Western Coastal Plains is a strip of coastal plain 50 kilometres (31 mi) in width between the west coast of India and the Western Ghats hills, which starts near the south of the Tapi River. The plains are located between the Western Ghats ...
* Bordering seas and
islands
An island (or isle) is an isolated piece of habitat that is surrounded by a dramatically different habitat, such as water. Very small islands such as emergent land features on atolls can be called islets, skerries, cays or keys. An island ...
Administrative divisions of India
Administrative divisions of India
The administrative divisions of India are subnational administrative units of India; they are composed of a nested hierarchy of administrative divisions.
Indian states and territories frequently use different local titles for the same level ...
= Administrative divisional structure of India
=
= States and union territories of India
=
States and union territories of India
India is a federal union comprising 28 states and 8 union territories, with a total of 36 entities. The states and union territories are further subdivided into districts and smaller administrative divisions.
History
Pre-indep ...
*
Autonomous regions of India
The Sixth Schedule of the Constitution of India allows for the formation of autonomous administrative divisions which have been given autonomy within their respective states. Most of these autonomous district councils are located in North E ...
*
Emblems of Indian states
India is a country in South Asia. It is made up of 28 states and 8 union territories. Most of the states and union territories of India have their own state emblem, seal or coat of arms which are used as official governmental symbol, while five st ...
*
States and union territories of India
India is a federal union comprising 28 states and 8 union territories, with a total of 36 entities. The states and union territories are further subdivided into districts and smaller administrative divisions.
History
Pre-indep ...
** By name
*** States by name
****
Andhra Pradesh
Andhra Pradesh (, abbr. AP) is a state in the south-eastern coastal region of India. It is the seventh-largest state by area covering an area of and tenth-most populous state with 49,386,799 inhabitants. It is bordered by Telangana to the ...
(outline)
****
Arunachal Pradesh
Arunachal Pradesh (, ) is a state in Northeastern India. It was formed from the erstwhile North-East Frontier Agency (NEFA) region, and became a state on 20 February 1987. It borders the states of Assam and Nagaland to the south. It shares ...
(outline)
****
Assam
Assam (; ) is a state in northeastern India, south of the eastern Himalayas along the Brahmaputra and Barak River valleys. Assam covers an area of . The state is bordered by Bhutan and Arunachal Pradesh to the north; Nagaland and Manipur ...
(outline)
****
Bihar
Bihar (; ) is a state in eastern India. It is the 2nd largest state by population in 2019, 12th largest by area of , and 14th largest by GDP in 2021. Bihar borders Uttar Pradesh to its west, Nepal to the north, the northern part of West ...
(outline)
****
Chhattisgarh
Chhattisgarh (, ) is a landlocked state in Central India. It is the ninth largest state by area, and with a population of roughly 30 million, the seventeenth most populous. It borders seven states – Uttar Pradesh to the north, Madhya Prad ...
(outline)
****
Goa (outline)
****
Gujarat
Gujarat (, ) is a state along the western coast of India. Its coastline of about is the longest in the country, most of which lies on the Kathiawar peninsula. Gujarat is the fifth-largest Indian state by area, covering some ; and the ninth ...
(outline)
****
Haryana
Haryana (; ) is an Indian state located in the northern part of the country. It was carved out of the former state of East Punjab on 1 Nov 1966 on a linguistic basis. It is ranked 21st in terms of area, with less than 1.4% () of India's land ...
(outline)
****
Himachal Pradesh
Himachal Pradesh (; ; "Snow-laden Mountain Province") is a state in the northern part of India. Situated in the Western Himalayas, it is one of the thirteen mountain states and is characterized by an extreme landscape featuring several pea ...
(outline)
****
Jharkhand
Jharkhand (; ; ) is a state in eastern India. The state shares its border with the states of West Bengal to the east, Chhattisgarh to the west, Uttar Pradesh to the northwest, Bihar to the north and Odisha to the south. It has an area of . I ...
(outline)
****
Karnataka
Karnataka (; ISO 15919, ISO: , , also known as Karunāḍu) is a States and union territories of India, state in the southwestern region of India. It was Unification of Karnataka, formed on 1 November 1956, with the passage of the States Reor ...
(
outline)
****
Kerala
Kerala ( ; ) is a state on the Malabar Coast of India. It was formed on 1 November 1956, following the passage of the States Reorganisation Act, by combining Malayalam-speaking regions of the erstwhile regions of Cochin, Malabar, South Ca ...
(
outline)
****
Madhya Pradesh
Madhya Pradesh (, ; meaning 'central province') is a state in central India. Its capital is Bhopal, and the largest city is Indore, with Jabalpur, Ujjain, Gwalior, Sagar, and Rewa being the other major cities. Madhya Pradesh is the second ...
(outline)
****
Maharashtra
Maharashtra (; , abbr. MH or Maha) is a state in the western peninsular region of India occupying a substantial portion of the Deccan Plateau. Maharashtra is the second-most populous state in India and the second-most populous country subdi ...
(
outline)
****
Manipur
Manipur () ( mni, Kangleipak) is a state in Northeast India, with the city of Imphal as its capital. It is bounded by the Indian states of Nagaland to the north, Mizoram to the south and Assam to the west. It also borders two regions of ...
(outline)
****
Meghalaya
Meghalaya (, or , meaning "abode of clouds"; from Sanskrit , "cloud" + , "abode") is a state in northeastern India. Meghalaya was formed on 21 January 1972 by carving out two districts from the state of Assam: (a) the United Khasi Hills and J ...
(outline)
****
Mizoram
Mizoram () is a state in Northeast India, with Aizawl as its seat of government and capital city. The name of the state is derived from "Mizo", the self-described name of the native inhabitants, and "Ram", which in the Mizo language means "lan ...
(outline)
****
Nagaland
Nagaland () is a landlocked state in the northeastern region of India. It is bordered by the Indian states of Arunachal Pradesh to the north, Assam to the west, Manipur to the south and the Sagaing Region of Myanmar to the east. Its capital cit ...
(outline)
****
Odisha
Odisha (English: , ), formerly Orissa ( the official name until 2011), is an Indian state located in Eastern India. It is the 8th largest state by area, and the 11th largest by population. The state has the third largest population of ...
(
outline)
****
Punjab
Punjab (; Punjabi Language, Punjabi: پنجاب ; ਪੰਜਾਬ ; ; also Romanization, romanised as ''Panjāb'' or ''Panj-Āb'') is a geopolitical, cultural, and historical region in South Asia, specifically in the northern part of the I ...
(outline)
****
Rajasthan
Rajasthan (; lit. 'Land of Kings') is a state in northern India. It covers or 10.4 per cent of India's total geographical area. It is the largest Indian state by area and the seventh largest by population. It is on India's northwestern ...
(
outline)
****
Sikkim
Sikkim (; ) is a state in Northeastern India. It borders the Tibet Autonomous Region of China in the north and northeast, Bhutan in the east, Province No. 1 of Nepal in the west and West Bengal in the south. Sikkim is also close to the Sil ...
(
outline)
****
Tamil Nadu
Tamil Nadu (; , TN) is a state in southern India. It is the tenth largest Indian state by area and the sixth largest by population. Its capital and largest city is Chennai. Tamil Nadu is the home of the Tamil people, whose Tamil language ...
(
outline)
****
Telangana
Telangana (; , ) is a state in India situated on the south-central stretch of the Indian peninsula on the high Deccan Plateau. It is the eleventh-largest state and the twelfth-most populated state in India with a geographical area of and 35 ...
(
outline)
****
Tripura
Tripura (, Bengali: ) is a state in Northeast India. The third-smallest state in the country, it covers ; and the seventh-least populous state with a population of 36.71 lakh ( 3.67 million). It is bordered by Assam and Mizoram to the ea ...
(outline)
****
Uttar Pradesh
Uttar Pradesh (; , 'Northern Province') is a state in northern India. With over 200 million inhabitants, it is the most populated state in India as well as the most populous country subdivision in the world. It was established in 195 ...
(
outline)
****
Uttarakhand
Uttarakhand ( , or ; , ), also known as Uttaranchal ( ; the official name until 2007), is a state in the northern part of India. It is often referred to as the "Devbhumi" (literally 'Land of the Gods') due to its religious significance and ...
(outline)
****
West Bengal
West Bengal (, Bengali: ''Poshchim Bongo'', , abbr. WB) is a state in the eastern portion of India. It is situated along the Bay of Bengal, along with a population of over 91 million inhabitants within an area of . West Bengal is the fou ...
(
outline)
*** Union territories by name
****
Andaman and Nicobar Islands
The Andaman and Nicobar Islands is a union territory of India consisting of 572 islands, of which 37 are inhabited, at the junction of the Bay of Bengal and the Andaman Sea. The territory is about north of Aceh in Indonesia and separated f ...
****
Chandigarh
Chandigarh () is a planned city in India. Chandigarh is bordered by the state of Punjab to the west and the south, and by the state of Haryana to the east. It constitutes the bulk of the Chandigarh Capital Region or Greater Chandigarh, which al ...
****
Dadra and Nagar Haveli and Daman and Diu
Dadra and Nagar Haveli and Daman and Diu is a union territory in India. The territory was constituted through the merger of the former territories of Dadra and Nagar Haveli and Daman and Diu. Plans for the proposed merger were announced by t ...
****
Delhi
Delhi, officially the National Capital Territory (NCT) of Delhi, is a city and a union territory of India containing New Delhi, the capital of India. Straddling the Yamuna river, primarily its western or right bank, Delhi shares borders w ...
****
Jammu and Kashmir Jammu and Kashmir may refer to:
* Kashmir, the northernmost geographical region of the Indian subcontinent
* Jammu and Kashmir (union territory), a region administered by India as a union territory
* Jammu and Kashmir (state), a region administered ...
****
Ladakh
Ladakh () is a region administered by India as a union territory which constitutes a part of the larger Kashmir region and has been the subject of dispute between India, Pakistan, and China since 1947. (subscription required) Quote: "Jammu a ...
****
Lakshadweep
Lakshadweep (), also known as Laccadives (), is a union territory of India. It is an archipelago of 36 islands in the Arabian sea, located off the Malabar Coast.
The name ''Lakshadweep'' means "one lakh islands" in Sanskrit, though the Lac ...
****
Puducherry Puducherry or Pondicherry may refer to:
* Puducherry (union territory), a union territory of India
** Pondicherry, capital of the union territory of Puducherry
** Puducherry district, a district of the union territory of Puducherry
** Puducherry t ...
** By rank
***
By economic rank
***
By various rankings
**
By population
**
By population density
**
By size
**
By state code
*
State and territory capitals
= Divisions of India
=
= Municipalities of India
=

Municipalities of India
A municipality is usually a single administrative division having corporate status and powers of self-government or jurisdiction as granted by national and regional laws to which it is subordinate.
The term ''municipality'' may also mean the g ...
*
Cities in India
The following tables are the list of cities in India by population. Often cities are bifurcated into multiple regions (municipalities) which results in creation of cities within cities which may figure in the list. The entire work of this article ...
**
National Capital of India:
New Delhi
New Delhi (, , ''Naī Dillī'') is the capital of India and a part of the National Capital Territory of Delhi (NCT). New Delhi is the seat of all three branches of the government of India, hosting the Rashtrapati Bhavan, Parliament Hous ...
** Financial Capital of India:
Mumbai
Mumbai (, ; also known as Bombay — the official name until 1995) is the capital city of the Indian state of Maharashtra and the ''de facto'' financial centre of India. According to the United Nations, as of 2018, Mumbai is the secon ...
** Cultural Capital of India:
Kolkata
Kolkata (, or , ; also known as Calcutta , the official name until 2001) is the capital of the Indian state of West Bengal, on the eastern bank of the Hooghly River west of the border with Bangladesh. It is the primary business, comme ...
** Banking Capital of India:
Chennai
Chennai (, ), formerly known as Madras ( the official name until 1996), is the capital city of Tamil Nadu, the southernmost Indian state. The largest city of the state in area and population, Chennai is located on the Coromandel Coast of th ...
** Silicon Valley of India:
Bangalore
Bangalore (), officially Bengaluru (), is the capital and largest city of the Indian state of Karnataka. It has a population of more than and a metropolitan population of around , making it the third most populous city and fifth most ...
**
Big cities in North East India
**
Million-plus cities in India
**
Most populous cities in India
Geography of states and territories
Demography of India
Demographics of India
India is the second most populated country in the world with a sixth of the world's population. According to official estimates, India's population stood at 1.38 billion.
Between 1975 and 2010, the population doubled to 1.2 billio ...
*
Ethnic groups of India
*
Racial groups of India
*
Religion of India
Demographics of states and territories
Government and politics of India

*
Form of government
A government is the system or group of people governing an organized community, generally a state.
In the case of its broad associative definition, government normally consists of legislature, executive, and judiciary. Government is ...
:
Sovereign
''Sovereign'' is a title which can be applied to the highest leader in various categories. The word is borrowed from Old French , which is ultimately derived from the Latin , meaning 'above'.
The roles of a sovereign vary from monarch, ruler or ...
socialist
Socialism is a left-wing economic philosophy and movement encompassing a range of economic systems characterized by the dominance of social ownership of the means of production as opposed to private ownership. As a term, it describes the ...
secular
Secularity, also the secular or secularness (from Latin ''saeculum'', "worldly" or "of a generation"), is the state of being unrelated or neutral in regards to religion. Anything that does not have an explicit reference to religion, either negativ ...
federal parliamentary
A parliamentary system, or parliamentarian democracy, is a system of democratic governance of a state (or subordinate entity) where the executive derives its democratic legitimacy from its ability to command the support ("confidence") of the ...
multi-party
In political science, a multi-party system is a political system in which multiple political parties across the political spectrum run for national elections, and all have the capacity to gain control of government offices, separately or in coa ...
representative democratic republic
A republic () is a " state in which power rests with the people or their representatives; specifically a state without a monarchy" and also a "government, or system of government, of such a state." Previously, especially in the 17th and 18th ...
.
**
Sovereign
''Sovereign'' is a title which can be applied to the highest leader in various categories. The word is borrowed from Old French , which is ultimately derived from the Latin , meaning 'above'.
The roles of a sovereign vary from monarch, ruler or ...
– this means an independent nation.
**
Socialist
Socialism is a left-wing economic philosophy and movement encompassing a range of economic systems characterized by the dominance of social ownership of the means of production as opposed to private ownership. As a term, it describes the ...
– this implies social and economic equality for all Indian citizens. This guarantees equal opportunity and equal social status. The government attempts to reduce economic inequality by reducing concentration of wealth.
**
Secular
Secularity, also the secular or secularness (from Latin ''saeculum'', "worldly" or "of a generation"), is the state of being unrelated or neutral in regards to religion. Anything that does not have an explicit reference to religion, either negativ ...
– practices separation of religion and state. This implies freedom to choose one's religion. The state gives every citizen the right to practice and propagate a religion of his choice, and also right to reject all religions. The state treats all religions as equal and there is no official state religion.
**
Democratic – this means the government is democratically elected, and the head of the government (prime minister) is elected by the people.
**
Republic
A republic () is a " state in which power rests with the people or their representatives; specifically a state without a monarchy" and also a "government, or system of government, of such a state." Previously, especially in the 17th and 18th ...
– this means the head of the state (president) is not a hereditary
monarch
A monarch is a head of stateWebster's II New College DictionarMonarch Houghton Mifflin. Boston. 2001. p. 707. Life tenure, for life or until abdication, and therefore the head of state of a monarchy. A monarch may exercise the highest authority ...
but indirectly elected by the people.
*
Capital
Capital may refer to:
Common uses
* Capital city, a municipality of primary status
** List of national capital cities
* Capital letter, an upper-case letter Economics and social sciences
* Capital (economics), the durable produced goods used fo ...
of India:
New Delhi
New Delhi (, , ''Naī Dillī'') is the capital of India and a part of the National Capital Territory of Delhi (NCT). New Delhi is the seat of all three branches of the government of India, hosting the Rashtrapati Bhavan, Parliament Hous ...
*
Elections in India
India has a parliamentary system as defined by its constitution, with power distributed between the central government and the states.
The President of India is the ceremonial head of state of the country and supreme commander-in-chief for a ...
**
1951
Events
January
* January 4 – Korean War: Third Battle of Seoul – Chinese and North Korean forces capture Seoul for the second time (having lost the Second Battle of Seoul in September 1950).
* January 9 – The Government of the United ...
1957
1957 ( MCMLVII) was a common year starting on Tuesday of the Gregorian calendar, the 1957th year of the Common Era (CE) and ''Anno Domini'' (AD) designations, the 957th year of the 2nd millennium, the 57th year of the 20th century, and the 8th year ...
1962
Events January
* January 1 – Western Samoa becomes independent from New Zealand.
* January 3 – Pope John XXIII excommunicates Fidel Castro for preaching communism.
* January 8 – Harmelen train disaster: 93 die in the wor ...
1967
Events
January
* January 1 – Canada begins a year-long celebration of the 100th anniversary of Confederation, featuring the Expo 67 World's Fair.
* January 5
** Spain and Romania sign an agreement in Paris, establishing full consular and ...
1971 *
The year 1971 had three partial solar eclipses ( February 25, July 22 and August 20) and two total lunar eclipses ( February 10, and August 6).
The world population increased by 2.1% this year, the highest increase in history.
Events
J ...
1977
Events January
* January 8 – Three bombs explode in Moscow within 37 minutes, killing seven. The bombings are attributed to an Armenian separatist group.
* January 10 – Mount Nyiragongo erupts in eastern Zaire (now the Democrat ...
1980
Events January
* January 4 – U.S. President Jimmy Carter proclaims a grain embargo against the USSR with the support of the European Commission.
* January 6 – Global Positioning System time epoch begins at 00:00 UTC.
* January 9 ...
1984
Events
January
* January 1 – The Bornean Sultanate of Brunei gains full independence from the United Kingdom, having become a British protectorate in 1888.
* January 7 – Brunei becomes the sixth member of the Association of Southeas ...
1989
File:1989 Events Collage.png, From left, clockwise: The Cypress Street Viaduct, Cypress structure collapses as a result of the 1989 Loma Prieta earthquake, killing motorists below; The proposal document for the World Wide Web is submitted; The Exxo ...
1991
File:1991 Events Collage.png, From left, clockwise: Boris Yeltsin, elected as Russia's first president, waves the new flag of Russia after the 1991 Soviet coup d'état attempt, orchestrated by Soviet hardliners; Mount Pinatubo erupts in the Phi ...
1996
File:1996 Events Collage.png, From left, clockwise: A bomb explodes at Centennial Olympic Park in Atlanta, set off by a radical anti-abortionist; The center fuel tank explodes on TWA Flight 800, causing the plane to crash and killing everyone o ...
1998
1998 was designated as the ''International Year of the Ocean''.
Events January
* January 6 – The ''Lunar Prospector'' spacecraft is launched into orbit around the Moon, and later finds evidence for frozen water, in soil in permanently s ...
1999
File:1999 Events Collage.png, From left, clockwise: The funeral procession of King Hussein of Jordan in Amman; the 1999 İzmit earthquake kills over 17,000 people in Turkey; the Columbine High School massacre, one of the first major school shoot ...
2004
2004 was designated as an International Year of Rice by the United Nations, and the International Year to Commemorate the Struggle Against Slavery and its Abolition (by UNESCO).
Events January
* January 3 – Flash Airlines Flight ...
2009
File:2009 Events Collage V2.png, From top left, clockwise: The vertical stabilizer of Air France Flight 447 is pulled out from the Atlantic Ocean; Barack Obama becomes the first African American to become President of the United States; Protests ...
2014
File:2014 Events Collage.png, From top left, clockwise: Stocking up supplies and personal protective equipment (PPE) for the Western African Ebola virus epidemic; Citizens examining the ruins after the Chibok schoolgirls kidnapping; Bundles of wa ...
,
2019
File:2019 collage v1.png, From top left, clockwise: Hong Kong protests turn to widespread riots and civil disobedience; House of Representatives votes to adopt articles of impeachment against Donald Trump; CRISPR gene editing first used to experim ...
*
Political parties in India
India has a multi-party system. The Election Commission of India (ECI) accords recognition to the national level and the state level political parties based upon objective criteria. A recognised political party enjoys privileges like a reserve ...
**
Aam Aadmi Party
The Aam Aadmi Party (; AAP) is a List of political parties in India, political party in India, as one of the national political parties. The AAP was founded in November 2012 by Arvind Kejriwal and his then-companions following the 2011 Indian ...

**
All India Trinamool Congress
The All India Trinamool Congress (English: All India Grassroots Congress; AITC), colloquially the Trinamool Congress ( TMC) is an Indian political party which is predominantly active in West Bengal. The party is led by Mamata Banerjee, the cur ...
**
Bahujan Samaj Party
The Bahujan Samaj Party (BSP) is a national level political party in India that was formed to represent Bahujans (literally means "community in majority"), referring to Scheduled Castes, Scheduled Tribes, and Other Backward Classes (OBC), al ...
**
Bharatiya Janata Party
The Bharatiya Janata Party (BJP; ; ) is a political party in India, and one of the two major List of political parties in India, Indian political parties alongside the Indian National Congress. Since 2014, it has been the List of ruling p ...
**
Communist Party of India
Communist Party of India (CPI) is the oldest Marxist–Leninist communist party in India and one of the nine national parties in the country. The CPI was founded in modern-day Kanpur (formerly known as Cawnpore) on 26 December 1925.
H ...
**
Communist Party of India (Marxist)
The Communist Party of India (Marxist) (abbreviated as CPI(M)/CPIM/CPM) is a Marxist–Leninist communist political party in India. It is the largest communist party of India in terms of membership and electoral seats and one of the na ...
**
Dravidian parties
Dravidian parties include an array of regional political parties in the state of Tamil Nadu, India, which trace their origins and ideologies either directly or indirectly to the Justice Party and the Dravidian movement of C. Natesanar and Per ...
***
Dravida Munnetra Kazhagam
The Dravida Munnetra Kazhagam (; DMK) is a political party based in the state of Tamil Nadu where it is currently the ruling party having a comfortable majority without coalition support and the union territory of Puducherry where it is curre ...
***
All India Anna Dravida Munnetra Kazhagam
The All India Anna Dravida Munnetra Kazhagam (; AIADMK) is an Indian regional political party with great influence in the state of Tamil Nadu and the union territory of Puducherry. It is a Dravidian party founded by the former chief mi ...
***
Pattali Makkal Katchi
Paattali Makkal Katchi (; PMK) is a political party in Tamil Nadu, India, founded by S. Ramadoss in 1989 for the Vanniyars, a caste in northern Tamil Nadu. It is currently part of the BJP led National Democratic Alliance (NDA). It contests ...
***
Marumalarchi Dravida Munnetra Kazhagam
***
Naam Tamilar Katchi
Naam Tamilar Katchi (We Tamils Party; NTK) is a Tamil nationalism, Tamil nationalist party in the Indian state of Tamil Nadu and the States and union territories of India, union territory of Puducherry (union territory), Puducherry. The party is ...

***
Desiya Murpokku Dravida Kazhagam
The Desiya Murpokku Dravida Kazhagam (; DMDK) is an Indian regional political party in the state of Tamil Nadu. It is a Dravidian party founded by the former leader of the opposition in the Tamil Nadu Legislative Assembly Vijayakant (Ca ...
**
Indian National Congress
The Indian National Congress (INC), colloquially the Congress Party but often simply the Congress, is a political party in India with widespread roots. Founded in 1885, it was the first modern nationalist movement to emerge in the British E ...
**
Janata Dal (United)
**
Maharashtra Navnirman Sena
The Maharashtra Navnirman Sena (translation: Maharashtra Reformation Army; MNS) is a Regionalist far-right Indian political party based in the state of Maharashtra and operates on the ideology of "Hindutva" and " Marathi" Manus. It was found ...
**
Nationalist Congress Party
The Nationalist Congress Party ( NCP) is one of the nine national parties in India. The party generally supports Indian nationalism and Gandhian secularism. It is the largest opposition party in Maharashtra and is also a significant party i ...
**
Samajwadi Party
The Samajwadi Party ( SP; translation: ''Socialist Party'', founded 4 October 1992) is a socialist political party in India, headquartered in New Delhi but mainly based in Uttar Pradesh, with significant presence in other states as well. With a ...
**
Shiromani Akali Dal
**
Shivsena
Shiv Sena (IAST: ''Śiva Sēnā'') () was a right-wing to far-right Marathi regionalist and Hindu ultranationalist political party in India founded in 1966 by cartoonist Bal Thackeray. Originally emerging from nativist movements in Bo ...

**
Rashtriya Janata Dal
The Rashtriya Janata Dal ( RJD; translation: ''National People's Party'') is an Indian political party, based in the states of Bihar, Jharkhand and Kerala. The party was founded in 1997 by Lalu Prasad Yadav.
The party's support base has tradit ...
**
Telugu Desam Party
The Telugu Desam Party (; TDP) is an Indian regional political party operating in Andhra Pradesh and Telangana at the state and central level. Since its founding by N. T. Rama Rao (often referred to as NTR) on 29 March 1982, the party has foc ...
**
Telangana Rashtra Samithi
Bharat Rashtra Samithi ( ; BRS), formerly known as Telangana Rashtra Samithi ( TRS), is an Indian political party which is predominantly active in the state of Telangana. It was founded on 27 April 2001 as by K. Chandrashekar Rao, with a sing ...
**
Yuvajana Sramika Rythu Congress Party YSRCP
*
Political scandals in India
The following is a ''list of proven scandals in India'' since independence, including political, financial and corporate scandals. The year, or decade, is when the scandal was first reported.
1940s
* 1947 - INA treasure chest disappearance
* ...
*
Taxation in India
Socio-economic issues in India
*
Religious violence in India
Religious violence in India includes acts of violence by followers of one religious group against followers and institutions of another religious group, often in the form of rioting. Religious violence in India has generally involved Hindus an ...
*
Katchatheevu Issue
*
Religious tolerance in India
*
Terrorism in India
Terrorism in India, according to the Home Ministry, poses a significant threat to the people of India. Compared to other countries, India faces a wide range of terror groups. Terrorism found in India includes Islamic terrorism, separatist ...
*
Naxalism
*
Caste system in India
The caste system in India is the paradigmatic ethnographic example of classification of castes. It has its origins in ancient India, and was transformed by various ruling elites in medieval, early-modern, and modern India, especially the Mug ...
**
Caste politics in India
In India, a caste is a (usually endogamous) social group where membership is decided by birth. Castes often have related political preferences. Broadly, Indian castes are divided into the Forward Castes, Other Backward Classes, Scheduled Ca ...
**
Caste-related violence in India
Caste-related violence in India has occurred and continues to occur in various forms.
According to a report by Human Rights Watch: Discriminatory and cruel, inhuman, and degrading treatment of over 165 million people in India has been justified ...
**
Reservation in India
Reservation is a system of affirmative action in India that provides historically disadvantaged groups representation in education, employment, government schemes, scholarships and politics. Based on provisions in the Indian Constitution, it ...
*
Human rights in India
Human rights in India is an issue complicated by the country's large size and population as well as its diverse culture, despite its status as the world's largest sovereign, secular, democratic republic. The Constitution of India provides for Fun ...
**
LGBT rights in India
; ne, हिजडा; Marathi: हिजडा). In Telugu, they are referred to as ( నపుంసకుడు) or (హిజ్రా), in Urdu as ( ہیجڑا), in Gujarati as (પાવૈયા) or ( હીજડા), in Tamil ...
**
Freedom of religion in India
Branches of the government of India
Executive of the government of India
*
Head of state
A head of state (or chief of state) is the public persona who officially embodies a state Foakes, pp. 110–11 " he head of statebeing an embodiment of the State itself or representatitve of its international persona." in its unity and ...
:
President of India
The president of India ( IAST: ) is the head of state of the Republic of India. The president is the nominal head of the executive, the first citizen of the country, as well as the commander-in-chief of the Indian Armed Forces. Droupadi Murm ...
*
Vice-President of India
The vice president of India (IAST: ) is the deputy to the head of state of the Republic of India, i.e. the president of India. The office of vice president is the second-highest constitutional office after the president and ranks second in the ...
*
The Cabinet
*
Head of government
The head of government is the highest or the second-highest official in the executive branch of a sovereign state, a federated state, or a self-governing colony, autonomous region, or other government who often presides over a cabinet, a ...
:
Prime Minister of India
The prime minister of India (IAST: ) is the head of government of the Republic of India. Executive authority is vested in the prime minister and their chosen Council of Ministers, despite the president of India being the nominal head of the ...
* Head of the
civil services
The civil service is a collective term for a sector of government composed mainly of career civil servants hired on professional merit rather than appointed or elected, whose institutional tenure typically survives transitions of political leaders ...
:
Cabinet Secretary of India
The Cabinet Secretary is the top-most executive official and senior-most civil servant of the Government of India. The Cabinet Secretary is the ''ex-officio'' head of the Civil Services Board, the Cabinet Secretariat, the Indian Administrativ ...
Legislature of the government of India
*
Parliament of India
The Parliament of India ( IAST: ) is the supreme legislative body of the Republic of India. It is a bicameral legislature composed of the president of India and two houses: the Rajya Sabha (Council of States) and the Lok Sabha (House of ...
**
Rajya Sabha
The Rajya Sabha, constitutionally the Council of States, is the upper house of the bicameral Parliament of India. , it has a maximum membership of 245, of which 233 are elected by the legislatures of the states and union territories using si ...
''(Council of States)'' –
upper house
An upper house is one of two chambers of a bicameral legislature, the other chamber being the lower house.''Bicameralism'' (1997) by George Tsebelis The house formally designated as the upper house is usually smaller and often has more restric ...
of the parliament (
Vice-President of India
The vice president of India (IAST: ) is the deputy to the head of state of the Republic of India, i.e. the president of India. The office of vice president is the second-highest constitutional office after the president and ranks second in the ...
serves as the Chairman of the Rajya Sabha)
**
Lok Sabha
The Lok Sabha, constitutionally the House of the People, is the lower house of India's bicameral Parliament, with the upper house being the Rajya Sabha. Members of the Lok Sabha are elected by an adult universal suffrage and a first-p ...
''(House of the People)'' –
lower house
A lower house is one of two Debate chamber, chambers of a Bicameralism, bicameral legislature, the other chamber being the upper house. Despite its official position "below" the upper house, in many legislatures worldwide, the lower house has co ...
of the parliament (
Speaker
Speaker may refer to:
Society and politics
* Speaker (politics), the presiding officer in a legislative assembly
* Public speaker, one who gives a speech or lecture
* A person producing speech: the producer of a given utterance, especially:
** In ...
)
Judiciary of the government of India
*
Supreme Court of India
The Supreme Court of India ( IAST: ) is the supreme judicial authority of India and is the highest court of the Republic of India under the constitution. It is the most senior constitutional court, has the final decision in all legal matters ...
(
Chief Justice of India
The chief justice of India ( IAST: ) is the chief judge of the Supreme Court of India as well as the highest-ranking officer of the Indian Judiciary. The Constitution of India grants power to the president of India to appoint, in consultation ...
)
*
List of high courts in India
The high courts of India are the highest courts of appellate jurisdiction in each state and union territory of India. However, a high court exercises its original civil and criminal jurisdiction only if the subordinate courts are not authorize ...
*
District Courts of India
The district courts of India are the district courts of the state governments in India for every district or for one or more districts together taking into account of the number of cases, population distribution in the district. They administe ...
Foreign relations of India
International organisation membership
The Republic of India is a member of:
Law and order in India
*
Cannabis in India
Cannabis in India has been known to be used at least as early as 2000 BCE. In Indian society, common terms for cannabis preparations include charas (resin), ganja (flower), and bhang (seeds and leaves), with Indian drinks such as bhang lassi ...
*
Capital punishment in India
Capital punishment in India is a legal penalty for some crimes under the country's main substantive penal legislation, the Indian Penal Code, as well as other laws. Executions are carried out by hanging as the primary method of execution as gi ...
*
Company Law in India
*
Indian Contract Act, 1872
The Indian Contract Act, 1872 prescribes the law relating to contracts in India and is the key act regulating Indian contract law. The Act is based on the principles of English Common Law. It is applicable to all the states of India. It determi ...
*
Constitution of India
The Constitution of India ( IAST: ) is the supreme law of India. The document lays down the framework that demarcates fundamental political code, structure, procedures, powers, and duties of government institutions and sets out fundamental ...
**
Basic Structure
**
Directive Principles
The Directive Principles of State Policy of India are the guidelines to be followed by the government of India for the governance of the country. They are not enforceable by any court, but the principles laid down there in are considered 'Fund ...
**
Fundamental Rights
Fundamental rights are a group of rights that have been recognized by a high degree of protection from encroachment. These rights are specifically identified in a constitution, or have been found under due process of law. The United Nations' Susta ...
**
Fundamental Duties
*
Criminal Law in India
**
Indian Penal Code
The Indian Penal Code (IPC) is the official criminal code of India. It is a comprehensive code intended to cover all substantive aspects of criminal law. The code was drafted on the recommendations of first law commission of India established ...
**
Code of Criminal Procedure (India)
The Code of Criminal Procedure commonly called Criminal Procedure Code (CrPC) is the main legislation on procedure for administration of substantive criminal law in India. It was enacted in 1973 and came into force on 1 April 1974. It provide ...
*
Indian tort law
Tort law in India is primarily governed by judicial precedent as in other common law jurisdictions, supplemented by statutes governing damages, civil procedure, and codifying common law torts. As in other common law jurisdictions, a tort is b ...
*
Property Law in India
Property is a system of rights that gives people legal control of valuable things, and also refers to the valuable things themselves. Depending on the nature of the property, an owner of property may have the right to consume, alter, share, ...
*
Crime in India
Crime in India has been recorded since the British Raj, with comprehensive statistics now compiled annually by the National Crime Records Bureau (NCRB), under the Ministry of Home Affairs (India) (MHA).
In 2021, a total of 60,96,310 crimes, co ...
**
Bride burning
Bride burning is a form of domestic violence practiced in countries located on or around the Indian subcontinent. A category of dowry death, bride-burning occurs when a young woman is murdered by her husband or his family for her family's ref ...
**
Organised crime in India
Organised crime in India refers to organised crime elements originating in India and active in many parts of the world. The purpose of organised crime in India, as elsewhere in the world, is monetary gain. Its virulent form in modern times is d ...
**
Eve teasing
Eve (; ; ar, حَوَّاء, Ḥawwāʾ; el, Εὕα, Heúa; la, Eva, Heva; Syriac: romanized: ) is a figure in the Book of Genesis in the Hebrew Bible. According to the origin story, "Creation myths are symbolic stories describing how the ...
**
Female foeticide in India Female foeticide in India ( hi, text= भ्रूण हत्या, translit=bhrūṇ-hatyā, translation=foeticide) is the abortion of a female foetus outside of legal methods. A research by Pew Research Center based on Union government data in ...
**
Rape in India
Rape is the fourth most common crime against women in India. According to the 2021 annual report of the National Crime Records Bureau (NCRB), 31,677 rape cases were registered across the country, or an average of 86 cases daily, a rise from 2 ...
***
2012 Delhi gang rape case
The 2012 Delhi gang rape and murder, commonly known as the Nirbhaya case, involved a rape and fatal assault that occurred on 16 December 2012 in Munirka, a neighbourhood in South West Delhi. The incident took place when Jyoti Singh, a 22-year ...
*
Directive Principles in India
*
Dowry law in India
The dowry system in India refers to the durable goods, cash, and real or movable property that the bride's family gives to the groom, his parents and his relatives as a condition of the marriage. Dowry is referred to dahez in Hindi and as ''jahez ...
*
Fundamental Rights in India
The Fundamental Rights in India enshrined in the III (Article 12-32) of the Constitution of India guarantee civil liberties such that all Indians can lead their lives in peace and harmony as citizens of India. These rights are known as "fun ...
*
History of Indian law
*
Law enforcement in India
Indian law is enforced by a number of agencies. Unlike many federal nations, the constitution of India delegates the maintenance of law and order primarily to the states and territories.
At the federal level, some of India's paramilitar ...
*
Nationality Law in India
*
Labour Law in India
*
List of prisons in India
As of 31 December 2020, there are 1,306 functioning jails in India, having 4,88,511 prisoners and actual capacity to house 4,14,033 prisoners. The 1,306 prisons in the country consist of 145 Central Jails, 413 District Jails, 565 Sub Jails, 88 Ope ...
*
Prisons in India
Prisons, and their administration, is a state subject covered by item 4 under the State List in the Seventh Schedule of the Constitution of India. The management and administration of prisons falls exclusively in the domain of the State governme ...
National law enforcement agencies
*
Ministry of Home Affairs
An interior ministry (sometimes called a ministry of internal affairs or ministry of home affairs) is a government department that is responsible for internal affairs.
Lists of current ministries of internal affairs
Named "ministry"
* Ministry ...
(
Minister of Home Affairs
An interior minister (sometimes called a minister of internal affairs or minister of home affairs) is a cabinet official position that is responsible for internal affairs, such as public security, civil registration and identification, emergency ...
•
Home Secretary
The secretary of state for the Home Department, otherwise known as the home secretary, is a senior minister of the Crown in the Government of the United Kingdom. The home secretary leads the Home Office, and is responsible for all nationa ...
)
All India Service
The All India Services (AIS) comprises the Indian Administrative Service, Indian Police Service and Indian Forest Service. A unique feature of the All India Services is that the members of these services are recruited by the centre (Union gover ...
for policing —
Indian Police Service
The Indian Police Service ( IPS) is a civil service under the All India Services. It replaced the Indian Imperial Police in 1948, a year after India became independent from the British Raj.
Along with the Indian Administrative Service ( ...
:*
Border Security Force
The Border Security Force (BSF) is India's border guarding organisation on its border with Pakistan and Bangladesh. It is one of the seven Central Armed Police Forces (CAPF) of India, and was raised in the wake of the 1965 war on 1 December 1 ...
:*
Central Bureau of Investigation
The Central Bureau of Investigation (CBI) is the premier investigating agency of India. It operates under the jurisdiction of the Ministry of Personnel, Public Grievances and Pensions. Originally set up to investigate bribery and government ...
:*
Central Industrial Security Force
The Central Industrial Security Force (CISF) is a federal police organisation in India under the Ministry of Home Affairs. It is one among the Central Armed Police Forces (CAPF). CISF provides security to over 356 industrial units (including ...
:*
Central Reserve Police Force
:*
Defence Security Corps
The Defence Security Corps (DSC), is a corps of the Indian Army responsible for providing security cover to the defence installations of the three services (Army, Navy, Air Force) and other sensitive installations. The DSC troops are sanctioned ...
:*
Directorate of Revenue Intelligence
:*
Indian Coast Guard
The Indian Coast Guard (ICG) is a maritime law enforcement and search and rescue agency of India with jurisdiction over its territorial waters including its contiguous zone and exclusive economic zone. The Indian Coast Guard was formally es ...
:*
Indo-Tibetan Border Police
The Indo-Tibetan Border Police (ITBP) is a border patrol organization of India deployed along its borders with Tibet Autonomous Region. It is one of the seven Central Armed Police Forces, established in 1962 in the aftermath of the Sino-Indi ...
:*
National Security Guards
The National Security Guard (NSG), commonly known as Black Cats, is a counter-terrorism unit of India under the Ministry of Home Affairs. It was founded on 16 October 1984, following Operation Blue Star, for combating terrorist activities and p ...
:*
Railway Protection Force
Railway Protection Force is a security force under the ownership of Indian Railways, Ministry of Railways, Government of India established by the Railway Protection Force Act, 1957; enacted by the Indian Parliament for "the better protection ...
:*
Special Protection Group
The Special Protection Group (SPG) is an agency of the Government of India whose sole responsibility is protecting the Prime Minister of India and in some cases, his or her family. It was formed in 1988 by an Act of the Parliament of India. T ...
:*
Narcotics Control Bureau
The Narcotics Control Bureau ( NCB) is an Indian central law enforcement and intelligence agency under the Ministry of Home Affairs, Government of India. The agency is tasked with combating drug trafficking and the use of illegal substanc ...
State police forces

= Police commissionerates
=
*
Vijayawada City Police
The Vijayawada City Police'' ,is the local law enforcement agency for the city of Vijayawada, Andhra Pradesh and is headed by the city police commissioner.
Organizational structure
The Vijayawada Police Commissionerate is headed by Commissioner ...
*
Hyderabad City Police
Hyderabad City Police is the local law enforcement agency for the city of Hyderabad, Telangana and is headed by the Commissioner of Police. The city police traces its origins to 1847 under Hyderabad State.
History
1847–1948
The Nizam of Hyder ...
*
Visakhapatnam City Police
The Visakhapatnam City Police is the local law enforcement agency for the city of Visakhapatnam, Andhra Pradesh
Andhra Pradesh (, abbr. AP) is a state in the south-eastern coastal region of India. It is the seventh-largest state by are ...
*
Bangalore City Police
The Bangalore City Police (BCP) is the law-enforcement agency of the South Indian city of Bangalore. The BCP works under the Karnataka State Police jurisdiction and is headed by the Commissioner of Police, Bangalore City, currently Pratap Red ...
*
Greater Chennai Police
The Greater Chennai Police, a division of the Tamil Nadu Police, is the law enforcement agency for the city of Chennai in India and the surrounding area. The city police force is headed by a Commissioner of Police and the administrative contr ...
*
Delhi Police
The Delhi Police (DP) is the law enforcement agency for the National Capital Territory of Delhi (NCT). Delhi Police comes under the jurisdiction of the Ministry of Home Affairs (MHA), Government of India. In 2015, sanctioned strength of Delhi ...
*
Kolkata Police
*
Mumbai Police
The Mumbai Police ( Marathi: मुंबई पोलीस, IAST: ''Mumbaī Pulīs'', formerly ''Bombay Police'') is the police department of the city of Mumbai, Maharashtra. It is a part of Maharashtra Police and has the primary responsibilit ...
*
Nagpur Police
The division was established during the 1861 police re-organization; however, the city's policing history began before that time.
History
Nagpur was ruled by Gond kings, then later by Maratha Bhonsale before the British East India Company took ov ...
Armed forces of India


* Command
**
Commander-in-chief:
President of India
The president of India ( IAST: ) is the head of state of the Republic of India. The president is the nominal head of the executive, the first citizen of the country, as well as the commander-in-chief of the Indian Armed Forces. Droupadi Murm ...
***
Ministry of Defence of India
****
Minister of Defence
A defence minister or minister of defence is a cabinet official position in charge of a ministry of defense, which regulates the armed forces in sovereign states. The role of a defence minister varies considerably from country to country; in som ...
*****
Defence Secretary
A defence minister or minister of defence is a cabinet official position in charge of a ministry of defense, which regulates the armed forces in sovereign states. The role of a defence minister varies considerably from country to country; in so ...
*****
Strategic Nuclear Command
The Strategic Forces Command (SFC), sometimes called Strategic Nuclear Command, forms part of India's Nuclear Command Authority (NCA). It is responsible for the management and administration of the country's tactical and strategic nuclear weap ...
*****
Strategic Forces Command
The Strategic Forces Command (SFC), sometimes called Strategic Nuclear Command, forms part of India's Nuclear Command Authority (NCA). It is responsible for the management and administration of the country's tactical and strategic nuclear wea ...
*****
Chief of Army Staff of the Indian Army
The Chief of the Army Staff (COAS) (unofficially known as the Army Chief) is a statutory position in the Indian Army held usually by a four star general. As the highest ranking officer to serve solely in the Indian Army, the chief is the profess ...
*****
Chief of Naval Staff of the Indian Navy
The Chief of the Naval Staff (India), also known as the Navy Chief, abbreviated to CNS, is a statutory position in the Indian Navy held by a four star admiral. As the highest ranking officer to serve solely in the Indian Navy, the chief is th ...
*****
Chief of Air Staff of the Indian Air Force
* Forces
**
Army
An army (from Old French ''armee'', itself derived from the Latin verb ''armāre'', meaning "to arm", and related to the Latin noun ''arma'', meaning "arms" or "weapons"), ground force or land force is a fighting force that fights primarily on ...
:
Indian Army
The Indian Army is the Land warfare, land-based branch and the largest component of the Indian Armed Forces. The President of India is the Commander-in-Chief, Supreme Commander of the Indian Army, and its professional head is the Chief of Arm ...
***
Army ranks and insignia of India
Indian Army Ranks can be broadly classified into three categories: Commissioned Officers, Junior Commissioned Officers and Other Ranks.
These ranks generally correspond with those of the British Indian Army. Traditional names for ranks are sti ...
**
Navy
A navy, naval force, or maritime force is the branch of a nation's armed forces principally designated for naval and amphibious warfare; namely, lake-borne, riverine, littoral, or ocean-borne combat operations and related functions. It in ...
:
Indian Navy
The Indian Navy is the maritime branch of the Indian Armed Forces. The President of India is the Supreme Commander of the Indian Navy. The Chief of Naval Staff, a four-star admiral, commands the navy. As a blue-water navy, it operates si ...
***
Naval ranks and insignia of India
***
Indian Ocean Naval Symposiumwebsite
**
Air Force
An air force – in the broadest sense – is the national military branch that primarily conducts aerial warfare. More specifically, it is the branch of a nation's armed services that is responsible for aerial warfare as distinct from an ...
:
Indian Air Force
The Indian Air Force (IAF) is the air force, air arm of the Indian Armed Forces. Its complement of personnel and aircraft assets ranks third amongst the air forces of the world. Its primary mission is to secure Indian airspace and to conduct ...
***
Air Force ranks and insignia of India
**
Indian Coast Guard
The Indian Coast Guard (ICG) is a maritime law enforcement and search and rescue agency of India with jurisdiction over its territorial waters including its contiguous zone and exclusive economic zone. The Indian Coast Guard was formally es ...
**
Special forces
Special forces and special operations forces (SOF) are military units trained to conduct special operations. NATO has defined special operations as "military activities conducted by specially designated, organized, selected, trained and equi ...
:
Special Forces of India
**
Indian Peace Keeping Force
Indian Peace Keeping Force (IPKF) was the Indian military contingent performing a peacekeeping operation in Sri Lanka between 1987 and 1990. It was formed under the mandate of the 1987 Indo-Sri Lankan Accord that aimed to end the Sri Lank ...
**
Paramilitary forces of India
India maintains 10 paramilitary forces.
List of Paramilitary forces
From 1986 to 2011 the Central Armed Police Forces were considered as Central Police Forces (CPF). However, as per their respective acts they all are Armed Police Forces.
R ...
**
National Security Guard
The National Security Guard (NSG), commonly known as Black Cats, is a counter-terrorism unit of India under the Ministry of Home Affairs. It was founded on 16 October 1984, following Operation Blue Star, for combating terrorist activities and ...
**
Special Protection Group
The Special Protection Group (SPG) is an agency of the Government of India whose sole responsibility is protecting the Prime Minister of India and in some cases, his or her family. It was formed in 1988 by an Act of the Parliament of India. T ...
*
Military academies in India
The Indian Defence services have established numerous academies and staff colleges across India for the purpose of training professional soldiers in military sciences, warfare command and strategy, and associated technologies.
Education and traini ...
*
India and weapons of mass destruction
India possesses nuclear weapons and previously developed chemical weapons. Although India has not released any official statements about the size of its nuclear arsenal, recent estimates suggest that India has 160 nuclear weapons and has prod ...
**
Integrated Guided Missile Development Program
The Integrated Guided Missile Development Programme (IGMDP) was an Indian Ministry of Defence programme for the research and development of the comprehensive range of missiles. The programme was managed by the Defence Research and Development O ...
Government of states
*
Governor
A governor is an administrative leader and head of a polity or political region, ranking under the head of state and in some cases, such as governors-general, as the head of state's official representative. Depending on the type of political ...
*
Chief minister
*
Chief secretary
*
Vidhan Sabha
The State Legislative Assembly, or Vidhan Sabha, or also Saasana Sabha, is a legislative body in the states and union territories of India. In the 28 states and 3 union territories with a unicameral state legislature, it is the sole legislati ...
*
Vidhan Parishad
The State Legislative Council, or Vidhan Parishad, or Saasana Mandali is the upper house in those states of India that have a bicameral state legislature; the lower house being the State Legislative Assembly. Its establishment is defined in Ar ...
*
Zilla Parishad
*
Panchayati Raj
The Panchayat raj is a political system, originating from the Indian subcontinent, found mainly in India, Pakistan, Bangladesh, Sri Lanka, and Nepal. It is the oldest system of local government in the Indian subcontinent, and historical ment ...
Politics by states and territories
History of India
History of India by period
*
Prehistoric India
According to consensus in modern genetics, anatomically modern humans first arrived on the Indian subcontinent from Africa between 73,000 and 55,000 years ago. Quote: "Y-Chromosome and Mt-DNA data support the colonization of South Asia by m ...
**
Riwatian people (1,900,000 BC)
**
Soanian people (500,000 BC)
**
South Asian Stone Age
The South Asian Stone Age covers the Palaeolithic, Mesolithic and Neolithic periods in South Asia. Evidence for the most ancient ''Homo sapiens'' in South Asia has been found in the cave sites of Cudappah of India, Batadombalena and Belilena in ...
(70,000–3300 BCE)
*
Ancient India
According to consensus in modern genetics, anatomically modern humans first arrived on the Indian subcontinent from Africa between 73,000 and 55,000 years ago. Quote: "Y-Chromosome and Mt-DNA data support the colonization of South Asia by ...
**
Ancient Indian cities
Ancient history is a time period from the beginning of writing and recorded human history to as far as late antiquity. The span of recorded history is roughly 5,000 years, beginning with the Sumerian cuneiform script. Ancient history cov ...
**
Indus Valley civilization
The Indus Valley Civilisation (IVC), also known as the Indus Civilisation was a Bronze Age civilisation in the northwestern regions of South Asia, lasting from 3300 BCE to 1300 BCE, and in its mature form 2600 BCE to 1900& ...
(3300–1700 BCE)
**
Late Harappan culture (1700–1300 BCE)
**
Vedic period
The Vedic period, or the Vedic age (), is the period in the late Bronze Age and early Iron Age of the history of India when the Vedic literature, including the Vedas (ca. 1300–900 BCE), was composed in the northern Indian subcontinent, betwe ...
(1700–500 BCE)
**
Iron Age
The Iron Age is the final epoch of the three-age division of the prehistory and protohistory of humanity. It was preceded by the Stone Age ( Paleolithic, Mesolithic, Neolithic) and the Bronze Age ( Chalcolithic). The concept has been mostly ...
(1200–300 BCE)
***
Mahajanapadas
The Mahājanapadas ( sa, great realm, from ''maha'', "great", and ''janapada'' "foothold of a people") were sixteen kingdoms or oligarchic republics that existed in ancient India from the sixth to fourth centuries BCE during the second urba ...
(700–300 BCE)
***
Magadha Empire
****
Haryanka dynasty
The Haryanka dynasty was the third ruling dynasty of Magadha, an empire of ancient India, which succeeded the Pradyota dynasty and Barhadratha dynasty. Initially, the capital was Rajagriha. Later, it was shifted to Pataliputra, near the pr ...
(684–413 BCE)
****
Shishunaga dynasty
The Shaishunaga dynasty (IAST: Śaiśunāga, literally "of Shishunaga") is the fourth ruling dynasty of Magadha, an empire of ancient India. According to the Hindu ''Puranas'', this dynasty was the second ruling dynasty of Magadha, succeeding ...
(413–345 BCE)
****
Nanda dynasty
The Nanda dynasty ruled in the northern part of the Indian subcontinent during the fourth century BCE, and possibly during the fifth century BCE. The Nandas overthrew the Shaishunaga dynasty in the Magadha region of eastern India, and expanded ...
(424–321 BCE)
***
Maurya Empire
The Maurya Empire, or the Mauryan Empire, was a geographically extensive Iron Age historical power in the Indian subcontinent based in Magadha, having been founded by Chandragupta Maurya in 322 BCE, and existing in loose-knit fashion until ...
(322- 185 BCE)
**
Middle kingdoms of India
The middle kingdoms of India were the political entities in the Indian subcontinent from 200 BCE to 1200 CE. The period begins after the decline of the Maurya Empire and the corresponding rise of the Satavahana dynasty, starting with Simuka, ...
(250 BCE–1279 CE)
***
Chola Empire
The Chola dynasty was a Tamil thalassocratic empire of southern India and one of the longest-ruling dynasties in the history of the world. The earliest datable references to the Chola are from inscriptions dated to the 3rd century BCE d ...
(250 BCE–1070 CE)
***
Satavahana
The Satavahanas (''Sādavāhana'' or ''Sātavāhana'', IAST: ), also referred to as the Andhras in the Puranas, were an ancient Indian dynasty based in the Deccan region. Most modern scholars believe that the Satavahana rule began in the l ...
(230 BCE–220 CE)
***
Shunga Empire
The Shunga Empire (IAST: ') was an ancient Indian dynasty from Magadha that controlled areas of the most of the northern Indian subcontinent from around 185 to 73 BCE. The dynasty was established by Pushyamitra, after taking the throne of the ...
(185–75 BCE)
***
Kushan Empire
The Kushan Empire ( grc, Βασιλεία Κοσσανῶν; xbc, Κυϸανο, ; sa, कुषाण वंश; Brahmi: , '; BHS: ; xpr, 𐭊𐭅𐭔𐭍 𐭇𐭔𐭕𐭓, ; zh, 貴霜 ) was a syncretic empire, formed by the Yuezhi, ...
(60–240 CE)
***
Gupta Empire
The Gupta Empire was an ancient Indian empire which existed from the early 4th century CE to late 6th century CE. At its zenith, from approximately 319 to 467 CE, it covered much of the Indian subcontinent. This period is considered as the Gold ...
(280–550 CE)
***
Pala Empire
The Pāla Empire (r. 750-1161 CE) was an imperial power during the post-classical period in the Indian subcontinent, which originated in the region of Bengal. It is named after its ruling dynasty, whose rulers bore names ending with the suffi ...
(750–1174 CE)
***
Rashtrakuta
Rashtrakuta ( IAST: ') (r. 753-982 CE) was a royal Indian dynasty ruling large parts of the Indian subcontinent between the sixth and 10th centuries. The earliest known Rashtrakuta inscription is a 7th-century copper plate grant detailing the ...
(753–982 CE)
*
Islamic empires in India
Muslim period in the Indian subcontinent is conventionally said to start in 712, after the conquest of Sindh and Multan by the Umayyad caliphate. It began in the Indian subcontinent in the course of a gradual conquest. The perfunctory rule by t ...
(1206–1596)
**
Delhi Sultanate
The Delhi Sultanate was an Islamic empire based in Delhi that stretched over large parts of the Indian subcontinent for 320 years (1206–1526). (1206–1596)
**
Deccan Sultanates
The Deccan sultanates were five Islamic late-medieval Indian kingdoms—on the Deccan Plateau between the Krishna River and the Vindhya Range—that were ruled by Muslim dynasties: namely Ahmadnagar, Berar, Bidar, Bijapur, and Golconda. ...
(1490–1596)
*
Hoysala Empire
The Hoysala Empire was a Kannadiga power originating from the Indian subcontinent that ruled most of what is now Karnataka between the 10th and the 14th centuries. The capital of the Hoysalas was initially located at Belur, but was later moved ...
(1040–1346)
*
Ahom Kingdom (1228–1826)
*
Vijayanagara Empire
The Vijayanagara Empire, also called the Karnata Kingdom, was a Hindu empire based in the region of South India, which consisted the modern states of Karnataka, Andhra Pradesh, Tamil Nadu, Kerala, Goa and some parts of Telangana and Mahar ...
(1336–1646)
*
Mughal Empire
The Mughal Empire was an early-modern empire that controlled much of South Asia between the 16th and 19th centuries. Quote: "Although the first two Timurid emperors and many of their noblemen were recent migrants to the subcontinent, the d ...
(1526–1858)
*
Maratha Empire
The Maratha Empire, also referred to as the Maratha Confederacy, was an early modern Indian confederation that came to dominate much of the Indian subcontinent in the 18th century. Maratha rule formally began in 1674 with the coronation of Sh ...
(1674–1818)
*
Colonial India
Colonial India was the part of the Indian subcontinent that was occupied by European colonial powers during the Age of Discovery. European power was exerted both by conquest and trade, especially in spices.
The search for the wealth and prospe ...
(1858–1947)
**
British Raj
The British Raj (; from Hindi ''rāj'': kingdom, realm, state, or empire) was the rule of the British Crown on the Indian subcontinent;
*
* it is also called Crown rule in India,
*
*
*
*
or Direct rule in India,
* Quote: "Mill, who was him ...
**
Princely state
A princely state (also called native state or Indian state) was a nominally sovereign entity of the British Indian Empire that was not directly governed by the British, but rather by an Indian ruler under a form of indirect rule, subject to ...
s
*
Indian independence movement
The Indian independence movement was a series of historic events with the ultimate aim of ending British rule in India. It lasted from 1857 to 1947.
The first nationalistic revolutionary movement for Indian independence emerged from Bengal ...
**
Quit India Movement
The Quit India Movement, also known as the August Kranti Movement, was a movement launched at the Bombay session of the All India Congress Committee by Mahatma Gandhi on 8th August 1942, during World War II, demanding an end to British rule in ...
**
Partition of India
The Partition of British India in 1947 was the change of political borders and the division of other assets that accompanied the dissolution of the British Raj in South Asia and the creation of two independent dominions: India and Pakistan. T ...
(1947)
*
History of Republic of India
History (derived ) is the systematic study and the documentation of the human activity. The time period of event before the invention of writing systems is considered prehistory. "History" is an umbrella term comprising past events as well ...
(1947–present)
History of India by region
History of India by subject
*
Economic history of India
India was the one of the largest economies in the world, for about two and a half millennia starting around the end of 1st millennium BC and ending around the beginning of British rule in India.
Around 500 BC, the Mahajanapadas minted punch-m ...
*
Economy of India under the British Raj
*
History of Buddhism in India
Buddhism is an ancient Indian religion, which arose in and around the ancient Kingdom of Magadha (now in Bihar, India), and is based on the teachings of Gautama Buddha who was deemed a "Buddha" ("Awakened One"), although Buddhist doctrine ...
*
History of clothing in India
*
History of education in the Indian subcontinent
*
History of Hinduism
The history of Hinduism covers a wide variety of related religious traditions native to the Indian subcontinent. It overlaps or coincides with the development of religion in the Indian subcontinent since the Iron Age, with some of its tradition ...
*
History of Indian archaeology
*
History of Indian football
The history of football in India is a long and detailed one, as it was the national sport at one time. The impetus for this was to unify the Indian Army. There is evidence for refereed between a team of football games being played in the Indian ...
**
History of the India national football team
The history of the India national football team dates back to the 1920s. They have never played in the World Cup although they qualified in 1950. They have had no entries in the tournament from 1950 onwards. India has never won the final of the A ...
*
History of Indian influence on Southeast Asia
Southeast Asia was in the Indian sphere of cultural influence from 290 BCE to the 15th century CE, when Hindu-Buddhist influences were incorporated into local political systems. Kingdoms in the southeast coast of the Indian Subcontinent had esta ...
*
History of Indian Institutes of Technology
*
History of railways in India
*
History of sex in India
*
History of the Indian cricket team
*
History of the rupee
The history of the rupee traces back to ancient Indian subcontinent. The mention of ''rūpya'' by Pāṇini is seemingly the earliest reference in a text about coins. The term in Indian subcontinent was used for referring to a coin.
The word "r ...
*
Indian maritime history
Indian maritime history begins during the 3rd millennium BCE when inhabitants of the Indus Valley initiated maritime trading contact with Mesopotamia. As per Vedic records, Indian traders and merchants traded with the far east and Arabia. Du ...
*
Indian natural history
Natural history in the Indian subcontinent has a long heritage with a recorded history going back to the Vedic era. Natural history research in early times included the broad fields of palaeontology, zoology and botany. These studies would today b ...
*
LGBT history in India
The LGBTQ community has a long recorded history in Ancient India due to the prevalence of the accepting Hindu spiritual traditions and cultures across the subcontinent, with a turbulent period following Islamic Turkic rule and Christian European co ...
*
Linguistic history of India
Since the Iron Age in India, the native languages of the Indian subcontinent are divided into various language families, of which the Indo-Aryan and the Dravidian are the most widely spoken. There are also many languages belonging to unre ...
*
List of massacres in India
A massacre is the deliberate slaughter of members of one group by one or more members of another more powerful group. A massacre may be indiscriminate or highly methodical in application. A massacre is a single event, though it may occur durin ...
*
Military history of India
The predecessors to the contemporary Army of India were many: the sepoy regiments, native cavalry, irregular horse and Indian sapper and miner companies raised by the three British presidencies. The Army of India was raised under the British R ...
**
History of the Indian Air Force
The Indian Air Force was established on 8 October 1932 independently of the army and navy and in a similar format to the British Royal Air Force. It had been a recommendation of the Skeen Committee, which had been tasked to look into demands fo ...
*
Peopling of India
The peopling of India refers to the migration of ''Homo sapiens'' into the Indian subcontinent. Anatomically modern humans settled India in multiple waves of early migrations, over tens of millennia. The first migrants came with the Coastal M ...
*
Science and technology in ancient India
The history of science and technology in the Indian subcontinent begins with the prehistoric human activity of the Indus Valley Civilization to the early Indian states and empires.
Prehistory
By 5500 BCE a number of sites similar to Mehrgarh ...
*
Slavery in India
The early history of slavery in the Indian subcontinent is contested because it depends on the translations of terms such as ''dasa'' and ''dasyu''. Greek writer Megasthenes in his work Indika, while describing the Maurya Empire states that sla ...
*
Timeline of major famines in India during British rule
The timeline of major famines in India during British rule covers major famines on the Indian subcontinent from 1765 to 1947. The famines included here occurred both in the princely states (regions administered by Indian rulers), British India ...
*
History of Dravidian people
Culture of India


*
Caste system in India
The caste system in India is the paradigmatic ethnographic example of classification of castes. It has its origins in ancient India, and was transformed by various ruling elites in medieval, early-modern, and modern India, especially the Mug ...
*
Indian dress
*
Festivals in India
This is a partial listing of festivals in India.
Related lists
By type
* List of literary festivals in India
* List of Indian classical music festivals
By region
* List of festivals of West Bengal
** Festivals in Kolkata
* List of fairs and ...
*
Humour in India
*
Media in India
The Indian media consists of several different types of communications of mass media: television, radio, cinema, newspapers, magazines, and Internet-based Websites/portals. Indian media was active since the late 18th century. The print media st ...
*
National symbols of India
The Republic of India has several official national symbols including a historical document, a flag, an emblem, an anthem, a memorial tower as well as several national heroes. The design of the national flag was officially adopted by the Cons ...
**
Coat of arms of India
**
Flag of India
The national flag of India, colloquially called the tricolour, is a horizontal rectangular tricolour flag of India saffron, white and India green; with the ', a 24-spoke wheel, in navy blue at its centre. It was adopted in its present fo ...
**
National anthem of India
"" (Sanskrit: जन गण मन) is the national anthem of the Republic of India. It was originally composed as '' Bharoto Bhagyo Bidhata'' in Bengali by polymath Rabindranath Tagore. The first stanza of the song ''Bharoto Bhagyo Bidhata ...
*
Public holidays in India
Public Holidays in India, also known as Statutory Holidays, or colloquially Government Holidays, consist of a variety of cultural, nationalistic, and religious holidays that are legislated in India at the union or state levels. While many of t ...
*
Religion in India
Religion in India is characterised by a diversity of religious beliefs and practices. The Indian subcontinent is the birthplace of four of the world's major religions; namely Hinduism, Buddhism, Jainism, and Sikhism. The preamble of Indian co ...
**
Hinduism in India
Hinduism is the largest religion in India. According to the 2011 Census of India, 966.3 million people identify as Hindu, representing 79.8% of the country's population. India contains 94% of the global Hindu population. The Indian sub ...
**
Dravidian in india
**
Islam in India
Islam is India's second-largest religion, with 14.2% of the country's population, approximately 172.2 million people identifying as adherents of Islam in 2011 Census. India is also the country with the second or third largest number of Musli ...
**
Buddhism in India
Buddhism ( , ), also known as Buddha Dharma and Dharmavinaya (), is an Indian religion or philosophical tradition based on teachings attributed to the Buddha. It originated in northern India as a -movement in the 5th century BCE, and gr ...
**
Christianity in India
Christianity is India's third-largest religion with about 27.8 million adherents, making up 2.3 percent of the population as of the 2011 census. The written records of the Saint Thomas Christians state that Christianity was introduced to th ...
**
**
Jainism in India
Jainism is India's sixth-largest religion and is practiced throughout India.
Per the 2011 census, there are 4,451,753 Jains in the 1.35 billion population of India, the majority living in Maharashtra, Rajasthan, Gujarat and Madhya Pradesh, Ka ...
**
Sikhism in India
Indian Sikhs number over 20 million people and account for 1.7% of India's population as of 2011, forming the country's fourth-largest religious group. The majority of the nation's Sikhs live in the northern state of Punjab, which is the onl ...
**
Zoroastrianism in India
Zoroastrianism in India has significant history within the country. Zoroastrians have lived in the Indian subcontinent since the Sasanian period. The Zoroastrians also moved to India in successive migrations during the Islamic period. The init ...
**
Baháʼí Faith in India
*
World Heritage Sites in India
Cuisine of India
*
Main dishes
*
Sweets and desserts
*
Drinks
A drink or beverage is a liquid intended for human consumption. In addition to their basic function of satisfying thirst, drinks play important roles in human culture. Common types of drinks include plain drinking water, milk, juice, smoothies a ...
*
Snacks
A snack is a small portion of food generally eaten between meals. Snacks come in a variety of forms including packaged snack foods and other processed foods, as well as items made from fresh ingredients at home.
Traditionally, snacks are ...
*
Spices
A spice is a seed, fruit, root, bark, or other plant substance primarily used for flavoring or coloring food. Spices are distinguished from herbs, which are the leaves, flowers, or stems of plants used for flavoring or as a garnish. Spices are ...
*
Condiments
A condiment is a preparation that is added to food, typically after cooking, to impart a specific flavor, to enhance the flavor, or to complement the dish. A table condiment or table sauce is more specifically a condiment that is served separat ...
*
History
History (derived ) is the systematic study and the documentation of the human activity. The time period of event before the invention of writing systems is considered prehistory. "History" is an umbrella term comprising past events as well ...
*
Supermarket chains in India
*
Fast food
Fast food is a type of mass-produced food designed for commercial resale, with a strong priority placed on speed of service. It is a commercial term, limited to food sold in a restaurant or store with frozen, preheated or precooked ingredie ...
Cuisine by regions
*
East Indian cuisine
**
Assamese
**
Bengali
Bengali or Bengalee, or Bengalese may refer to:
*something of, from, or related to Bengal, a large region in South Asia
* Bengalis, an ethnic and linguistic group of the region
* Bengali language, the language they speak
** Bengali alphabet, the w ...
**
Bihari
**
Odiya
Odia, also spelled Oriya or Odiya, may refer to:
* Odia people in Odisha, India
* Odia language, an Indian language, belonging to the Indo-Aryan branch of the Indo-European language family
* Odia alphabet, a writing system used for the Odia languag ...
**
Sikkimese
**
Assamese
**
Tripuri
Tripuri refer to:
*Tripuri people, an ethnic group in India and Bangladesh, also known as Tipra people
**Tripuri language
**Tripuri nationalism
**Tripuri calendar
**Tripuri culture
**Tripuri cuisine
**Tripuri dances
**Tripuri dress
**Tripuri games ...
**
Naga
Naga or NAGA may refer to:
Mythology
* Nāga, a serpentine deity or race in Hindu, Buddhist and Jain traditions
* Naga Kingdom, in the epic ''Mahabharata''
* Phaya Naga, mythical creatures believed to live in the Laotian stretch of the Mekong Ri ...
*
North Indian cuisine
North Indian cuisine is collectively the cuisine of Northern India, which includes the cuisines of Jammu and Kashmir, Punjab, Haryana, Himachal Pradesh, Rajasthan, Uttarakhand, Delhi, Uttar Pradesh and adjoining western Bihar.
Sub-types of Nor ...
**
Punjabi
Punjabi, or Panjabi, most often refers to:
* Something of, from, or related to Punjab, a region in India and Pakistan
* Punjabi language
* Punjabi people
* Punjabi dialects and languages
Punjabi may also refer to:
* Punjabi (horse), a British Th ...
**
Uttar Pradeshi
**
Rajasthani
**
Mughlai
**
Pahadi
**
Bhojpuri
Bhojpuri (;[Bhojpuri entry, Oxford Dictionaries](_blank)
, Oxford U ...
**
Benarasi
**
Kashmiri Kashmiri may refer to:
* People or things related to the Kashmir Valley or the broader region of Kashmir
* Kashmiris, an ethnic group native to the Kashmir Valley
* Kashmiri language, their language
People with the name
* Kashmiri Saikia Baruah ...
**
Sindhi
Sindhi may refer to:
*something from, or related to Sindh, a province of Pakistan
* Sindhi people, an ethnic group from the Sindh region
* Sindhi language, the Indo-Aryan language spoken by them
People with the name
* Sarkash Sindhi (1940–2012 ...
**
Awadhi
Awadhi (; ), also known as Audhi (), is an Indo-Aryan language spoken in northern India and Nepal. It is primarily spoken in the Awadh region of present-day Uttar Pradesh, India. The name ''Awadh'' is connected to Ayodhya, the ancient city ...
**
Haryanvi
Haryanvi ( ' or '), also known as Bangru, is an Indo-Aryan language spoken in the state of Haryana in India, and to a lesser extent in Delhi. Haryanvi is considered to be part of the dialect group of Western Hindi, which also includes Kharib ...
*
South Indian cuisine
South Indian cuisine includes the cuisines of the five southern states of India—Andhra Pradesh, Karnataka, Kerala, Tamil Nadu and Telangana—and the union territories of Lakshadweep, Pondicherry, and the Andaman and Nicobar Islands ...
**
Malabar
**
Kerala
Kerala ( ; ) is a state on the Malabar Coast of India. It was formed on 1 November 1956, following the passage of the States Reorganisation Act, by combining Malayalam-speaking regions of the erstwhile regions of Cochin, Malabar, South Ca ...
**
Tamil
Tamil may refer to:
* Tamils, an ethnic group native to India and some other parts of Asia
** Sri Lankan Tamils, Tamil people native to Sri Lanka also called ilankai tamils
**Tamil Malaysians, Tamil people native to Malaysia
* Tamil language, na ...
**
Andhra
Andhra Pradesh (, abbr. AP) is a state in the south-eastern coastal region of India. It is the seventh-largest state by area covering an area of and tenth-most populous state with 49,386,799 inhabitants. It is bordered by Telangana to the ...
**
Karnataka
Karnataka (; ISO 15919, ISO: , , also known as Karunāḍu) is a States and union territories of India, state in the southwestern region of India. It was Unification of Karnataka, formed on 1 November 1956, with the passage of the States Reor ...
**
Telangana
Telangana (; , ) is a state in India situated on the south-central stretch of the Indian peninsula on the high Deccan Plateau. It is the eleventh-largest state and the twelfth-most populated state in India with a geographical area of and 35 ...
**
Hyderabadi
Hyderabad ( ; , ) is the capital and largest city of the Indian state of Telangana and the ''de jure'' capital of Andhra Pradesh. It occupies on the Deccan Plateau along the banks of the Musi River, in the northern part of Southern India. ...
**
Mangalorean
**
Chettinad
Chettinad (also known as Chettinadu) is a region located mainly in the Sivaganga district historically ruled by Ramnad kingdom of Pandya Nadu and has a small portion extending into the Pudukottai District in Tamil Nadu, India..Karaikudi and ...
**
Udupi
Udupi (alternate spelling Udipi; also known as Odipu) is a city in the Indian state of Karnataka. Udupi is situated about north of the educational, commercial and industrial hub of Mangalore and about west of state capital Bangalore by road.
...
**
Coorg
Kodagu (also known by its former name Coorg) is an administrative district in the Karnataka state of India. Before 1956, it was an administratively separate Coorg State, at which point it was merged into an enlarged Mysore State.
It occupies ...
**
Rayalseema cuisine
*
West Indian cuisine
**
Goan
Goans ( kok, गोंयकार, Romi Konkani: , pt, Goeses) is the demonym used to describe the people native to Goa, India, who form an ethno-linguistic group resulting from the assimilation of Indo-Aryan, Dravidian, Indo-Portuguese, and ...
**
Gujarati
Gujarati may refer to:
* something of, from, or related to Gujarat, a state of India
* Gujarati people, the major ethnic group of Gujarat
* Gujarati language, the Indo-Aryan language spoken by them
* Gujarati languages, the Western Indo-Aryan sub- ...
**
Maharashtrian/Marathi
**
Malvani/Konkani
**
Parsi
Parsis () or Parsees are an ethnoreligious group of the Indian subcontinent adhering to Zoroastrianism. They are descended from Persians who migrated to Medieval India during and after the Arab conquest of Iran (part of the early Muslim conq ...
The arts in India
*
Art in India
*
Comics in India
**
Webcomics in India
*
Television in India
The television industry in India is very diverse and produces thousands of programs in many of the Indian languages. More than half of all Indian households own a television. As of 2016, the country had over 857 channels of which 184 were pay ...
*
Theatre in India
Theatre of India is one of the most ancient forms of theatre and it features a detailed textual, sculptural, and dramatic effects which emerged in mid first millennium BC. Like in the areas of music and dance, the Indian theatre is also defin ...
*
Indian classical dance
**
Dance forms of Andhra Pradesh
The dance forms of Andhra Pradesh take on a wide variety of colors, costumes, and types; and involve different settings and musical instruments.
Vilasini Natyam
Vilasini Natyam is a dance tradition of devadasis in Andhra Pradesh. It faced nea ...
Architecture of India

*
Hindu temple architecture
Hindu temple architecture as the main form of Hindu architecture has many varieties of style, though the basic nature of the Hindu temple remains the same, with the essential feature an inner sanctum, the '' garbha griha'' or womb-chamber, whe ...
*
Buddhist architecture
Buddhist religious architecture developed in the Indian subcontinent. Three types of structures are associated with the religious architecture of early Buddhism: monasteries ( viharas), places to venerate relics ( stupas), and shrines or prayer ...
*
Indian rock-cut architecture
Indian rock-cut architecture is more various and found in greater abundance in that country than any other form of rock-cut architecture around the world. Rock-cut architecture is the practice of creating a structure by carving it out of solid n ...
*
Indian vernacular architecture
Indian vernacular architecture the informal, functional architecture of structures, often in rural areas of India, built of local materials and designed to meet the needs of the local people. The builders of these structures are unschooled in f ...
*
Dravidian Architecture
Dravidian architecture, or the South Indian temple style, is an architectural idiom in Hindu temple architecture that emerged from South India, reaching its final form by the sixteenth century. It is seen in Hindu temples, and the most distinc ...
*
Hemadpanthi
Hemadpanti Sculpture (also spelled as Hemadpanthi) is an architectural style, named after its founder, the prime minister Hemadpant (1259-1274 CE) of the court of Seuna Yadavas of Devagiri.
Architectural elements
This building style was formed d ...
*
Western Chalukya Architecture
*
Badami Chalukya Architecture
*
Rajasthani architecture
The architecture of the Indian state of Rajasthan has usually been a regional variant of the style of Indian architecture prevailing in north India at the time. Rajasthan is especially notable for the forts and palaces of the many Rajput ruler ...
*
Architecture of Karnataka
The antiquity of architecture of Karnataka () can be traced to its southern Neolithic and early Iron Age, Having witnessed the architectural ideological and utilitarian transformation from shelter- ritual- religion. Here the nomenclature 'Archite ...
*
Architecture of Bengal
The architecture of Bengal, which comprises the modern country of Bangladesh and the Indian states of West Bengal, Tripura and Assam's Barak Valley, has a long and rich history, blending indigenous elements from the Indian subcontinent, with in ...
*
Hoysala architecture
Hoysala architecture is the building style in Hindu temple architecture developed under the rule of the Hoysala Empire between the 11th and 14th centuries, in the region known today as Karnataka, a state of India. Hoysala influence was at its pe ...
*
Vijayanagara architecture
Vijayanagara architecture of 1336–1565 CE was a notable building idiom that developed during the rule of the imperial Hindu Vijayanagara Empire. The empire ruled South India, from their regal capital at Vijayanagara, on the banks of the Tung ...
*
Kalinga Architecture
*
Mughal architecture
*
Indo-Islamic architecture
*
Indo-Saracenic Revival architecture
Indo-Saracenic architecture (also known as Indo-Gothic, Mughal-Gothic, Neo-Mughal, or Hindoo style) was a revivalist architectural style mostly used by British architects in India in the later 19th century, especially in public and government ...
*
Chandigarh
Chandigarh () is a planned city in India. Chandigarh is bordered by the state of Punjab to the west and the south, and by the state of Haryana to the east. It constitutes the bulk of the Chandigarh Capital Region or Greater Chandigarh, which al ...
*
List of Indian architects
The following is a list of notable architects.
17th &18th century architects
19th century
* Henry Irwin
* Samuel Swinton Jacob
* Frederick William Stevens
* Charles Wyatt
* Edwin Lutyens
* Herbert Baker
20th and 21st centuries
* Laurie B ...
Cinema of India

*
Lists of Indian films
The Cinema of India consists of motion pictures produced in India, which had a large effect on world cinema since the late 20th century. Major centers of film production across the country include Mumbai, Chennai, Hyderabad, Visakhapatnam, Ko ...
*
List of Indian documentary films
*
List of highest-grossing Bollywood films
*
List of Bhojpuri films
A ''list'' is any set of items in a row. List or lists may also refer to:
People
* List (surname)
Organizations
* List College, an undergraduate division of the Jewish Theological Seminary of America
* SC Germania List, German rugby unio ...
*
List of Marathi films
This is the list of films produced in the Marathi language in India. The Marathi film industry is the oldest of all Indian film industries.
''Raja'' ''Harishchandra'', the first silent film of India was directed by Dadasaheb Phalke with t ...
* List of Assamese films
* List of Tamil-language films
* List of Telugu-language films
* List of Malayalam films
* List of Kannada films
* List of Bengali films
* List of Indian film actresses
* List of Indian film actors
* List of Indian film directors
* List of Indian film choreographers
* Indian cinematographers, List of Indian film cinematographers
* List of Indian film score composers
* List of film festivals in Asia#India, List of film festivals in India
* List of Indian film producers
* List of Indian film screenwriters
= Film Awards
=
* National Film Awards
* Filmfare Awards
* Stardust Awards
* Star Screen Awards
* Bollywood Movie Awards
* Global Indian Film Awards
* IIFA Awards
* Zee Cine Awards
* Nandi Awards
* Karnataka State Film Awards
= Cinema by region
=
Music of India


* Indian classical music
** Hindustani classical music
** Carnatic classical music
* Indian folk music
** Bhavageete
** Bhangra (music)
** Lavani
** Dandiya
** Baul music
* Qawwali
* Indian pop
* Indian hip hop
* Filmi
* Indian rock
* Sangeet Natak Akademi
* Thyagaraja Aradhana
* Cleveland Thyagaraja Aradhana
* Chembai sangeetha utsavam
* List of Indian playback singers
* Indian musical instruments
= Music by states and territories
=
Literature of India
* List of Indian poets
* List of Indian authors
* Indian epic poetry
* Jnanpith award
* Sahitya Akademi Award
* Indian Literature (journal)
* Indian folklore
= Literature by language
=
Languages in India
Sports in India
* India at the Olympics
* India at the Commonwealth Games
* India at the Asian Games
* India at the Lusofonia Games
* Traditional sports of India
* Wrestling in India
* Field hockey in India
* Cricket in India
* Football in India
* Kabaddi
* Indian Rugby Team, Rugby in India
* Indian martial art
* Sports in Delhi
Major Sports Leagues
* Hockey India League (Hockey)
* Indian Premier League (Cricket)
* I-League (Football)
* Indian Super League (Football)
* Indian Badminton League (IBL) (Badminton)
* Pro Kabaddi (Kabaddi)
* Ultimate Table Tennis (Table Tennis
* World Divyang T10 (Physically challenged Cricket)
* Ultimate Kho Kho (Kho-Kho)
Culture by region
Economy and infrastructure of India
* List of countries by GDP (nominal), Economic rank, by nominal GDP (2011): 9th (twelfth)
* Agriculture in India
** Animal husbandry in India
** Fishing industry in India
** Forestry in India
* Banking in India
** List of banks#India, Banks in India
** Reserve Bank of India
* Bombay Stock Exchange
* Communications in India
** Amateur radio in India
** Internet in India
*** Asia-Pacific Network Information Centre
* List of Indian companies, Companies of India
*Currency, Currency of India: Indian rupee, Rupee
**ISO 4217: INR
* Economic development in India
*
Economic history of India
India was the one of the largest economies in the world, for about two and a half millennia starting around the end of 1st millennium BC and ending around the beginning of British rule in India.
Around 500 BC, the Mahajanapadas minted punch-m ...
* Economic Survey of India
* Energy in India
* Finances of India
** Finance minister of India
** Finance Commission of India
** Five-Year Plans of India
** Union budget of India
**
Taxation in India
*** Central Excise (India)
* Health care in India
* Mining in India
* Poverty in India
* National Stock Exchange of India
* Tourism in India
* Transport in India
** List of airports in India, Airports in India
** Automobile industry in India
** Inland waterways of India
** Ports in India
** Rail transport in India
** Roads in India
* Water supply and sanitation in India

Economy & infrastructure of states
Education in India

Education in states
Tourism in India
Tourism in states
List of tourism in different states of India
File:Shikaras at Dal Lake.jpg, Shikkaras at Dal lake, Jammu and Kashmir, India.
File:Khajuraho.JPG, Khajuraho Temple, Madhya Pradesh, India.
File:India Goa Coastline Tiracol.jpg, Beach of Goa, India.
File:Gangotri Glacier.jpg, Gangotri Glacier, Uttarakhand, India.
File:A Tea Garden of Cachar, Assam..JPG, A Tea Garden of Cachar, Assam, India.
File:KAZIRANGA.JPG, Kaziranga National Park, Assam, India.
File:Kumbh Mela 2013 Sangam, Allahabd.jpg, Kumbh Mela Sangam, Allahabad, Uttar Pradesh, India.
File:Akshardham Delhi.jpg, Akshardham Temple, Delhi, India.
Image: India Gate in New Delhi 03-2016.jpg, India Gate, New Delhi.
File:Taj Mahal in March 2004.jpg, Taj Mahal, Agra, Uttar Pradesh, India.
File:Hunder-Ladakh Region, India.jpg, Ladakh is a popular mountaineering site for climbers and trekkers
File:White Rann of Kutch.jpg, The White Rann of Kutch, Gujarat
File:Thar Khuri.jpg, Thar Desert, Rajasthan.
See also
;
* List of international rankings
* Member state of the Commonwealth of Nations
* Member state of the Group of Twenty Finance Ministers and Central Bank Governors
* Member state of the United Nations
* Outline of Asia
* Outline of geography
References
External links
*
; Government
Official entry portalof the Government of India
Official directoryof Indian Government websites
; General reference
India ''The World Factbook''. Central Intelligence Agency.
* Encyclopædia Britannica entry o
India* BBC News, BBC country profile o
India* Library of Congress Country Studies entry o
India
; Other
Incredible India– The Official Tourism Website of Ministry of Tourism, Government of India
* Ministry of Petroleum and Natural Gas
*
India 4You– Directory of popular Indian websites.
{{DEFAULTSORT:India
India,
India-related lists,
Outlines of countries, India
Tourism in India
 The following outline is provided as an overview of, and topical guide to,
The following outline is provided as an overview of, and topical guide to,  *** High:
*** High:  *
*  *
*  * The northern mountains including the
* The northern mountains including the 
 *
*  ***
*** 

 * Command
** Commander-in-chief:
* Command
** Commander-in-chief: 

 *
*  *
* *
* 
 * Indian classical music
** Hindustani classical music
** Carnatic classical music
* Indian folk music
** Bhavageete
** Bhangra (music)
** Lavani
** Dandiya
** Baul music
* Qawwali
* Indian pop
* Indian hip hop
* Filmi
* Indian rock
* Sangeet Natak Akademi
* Thyagaraja Aradhana
* Cleveland Thyagaraja Aradhana
* Chembai sangeetha utsavam
* List of Indian playback singers
* Indian musical instruments
* Indian classical music
** Hindustani classical music
** Carnatic classical music
* Indian folk music
** Bhavageete
** Bhangra (music)
** Lavani
** Dandiya
** Baul music
* Qawwali
* Indian pop
* Indian hip hop
* Filmi
* Indian rock
* Sangeet Natak Akademi
* Thyagaraja Aradhana
* Cleveland Thyagaraja Aradhana
* Chembai sangeetha utsavam
* List of Indian playback singers
* Indian musical instruments

