Orthomyxovirus on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
''Orthomyxoviridae'' (from
 The influenzavirus
The influenzavirus
 Viruses of the family ''Orthomyxoviridae'' contain six to eight segments of linear
Viruses of the family ''Orthomyxoviridae'' contain six to eight segments of linear
 Typically, influenza is transmitted from infected mammals through the air by coughs or sneezes, creating aerosols containing the virus, and from infected birds through their
Typically, influenza is transmitted from infected mammals through the air by coughs or sneezes, creating aerosols containing the virus, and from infected birds through their  Orthomyxoviridae viruses are one of two RNA viruses that replicate in the nucleus (the other being
Orthomyxoviridae viruses are one of two RNA viruses that replicate in the nucleus (the other being
 Influenza A viruses are further classified, based on the viral surface proteins
Influenza A viruses are further classified, based on the viral surface proteins
 Influenza B virus is almost exclusively a human pathogen, and is less common than influenza A. The only other animal known to be susceptible to influenza B infection is the
Influenza B virus is almost exclusively a human pathogen, and is less common than influenza A. The only other animal known to be susceptible to influenza B infection is the
 Vaccines and drugs are available for the prophylaxis and treatment of influenza virus infections. Vaccines are composed of either inactivated or live attenuated virions of the H1N1 and H3N2 human influenza A viruses, as well as those of influenza B viruses. Because the antigenicities of the wild viruses evolve, vaccines are reformulated annually by updating the seed strains.
When the antigenicities of the seed strains and wild viruses do not match, vaccines fail to protect the vaccinees. In addition, even when they do match, escape mutants are often generated.
Drugs available for the treatment of influenza include
Vaccines and drugs are available for the prophylaxis and treatment of influenza virus infections. Vaccines are composed of either inactivated or live attenuated virions of the H1N1 and H3N2 human influenza A viruses, as well as those of influenza B viruses. Because the antigenicities of the wild viruses evolve, vaccines are reformulated annually by updating the seed strains.
When the antigenicities of the seed strains and wild viruses do not match, vaccines fail to protect the vaccinees. In addition, even when they do match, escape mutants are often generated.
Drugs available for the treatment of influenza include
Health-EU Portal
EU work to prepare a global response to influenza.
Influenza Research Database
Database of influenza genomic sequences and related information.
EU coordination on Pandemic (H1N1) 2009
3D Influenza-virus-related structures from the EM Data Bank (EMDB)
Virus Taxonomy: 2020 Release
International Committee on Taxonomy of Viruses (ICTV) {{Taxonbar, from=Q287246 Virus families
Greek
Greek may refer to:
Greece
Anything of, from, or related to Greece, a country in Southern Europe:
*Greeks, an ethnic group.
*Greek language, a branch of the Indo-European language family.
**Proto-Greek language, the assumed last common ancestor ...
ὀρθός, ''orthós'' 'straight' + μύξα, ''mýxa'' 'mucus
Mucus ( ) is a slippery aqueous secretion produced by, and covering, mucous membranes. It is typically produced from cells found in mucous glands, although it may also originate from mixed glands, which contain both serous and mucous cells. It ...
') is a family of negative-sense
In molecular biology and genetics, the sense of a nucleic acid molecule, particularly of a strand of DNA or RNA, refers to the nature of the roles of the strand and its complementarity (molecular biology), complement in specifying a sequence of am ...
RNA viruses. It includes seven genera: '' Alphainfluenzavirus'', '' Betainfluenzavirus'', '' Gammainfluenzavirus'', '' Deltainfluenzavirus'', '' Isavirus'', ''Thogotovirus
''Thogotovirus'' is a genus of enveloped RNA viruses, one of seven genera in the virus family '' Orthomyxoviridae''. Their single-stranded, negative-sense RNA genome has six or seven segments. Thogotoviruses are distinguished from most other ...
'', and ''Quaranjavirus
''Quaranjavirus'' is a genus of viral envelope, enveloped RNA viruses, one of seven genera in the virus family ''Orthomyxoviridae''. The genome is single-stranded, sense (molecular biology), negative-sense segmented RNA, generally with six segme ...
''. The first four genera contain viruses that cause influenza in bird
Birds are a group of warm-blooded vertebrates constituting the class Aves (), characterised by feathers, toothless beaked jaws, the laying of hard-shelled eggs, a high metabolic rate, a four-chambered heart, and a strong yet lightweig ...
s (see also avian influenza
Avian influenza, known informally as avian flu or bird flu, is a variety of influenza caused by viruses adapted to birds.
) and mammals, including humans. Isaviruses infect salmon
Salmon () is the common name for several commercially important species of euryhaline ray-finned fish from the family Salmonidae, which are native to tributaries of the North Atlantic (genus ''Salmo'') and North Pacific (genus '' Oncorhy ...
; the thogotoviruses are arbovirus
Arbovirus is an informal name for any virus that is transmitted by arthropod vectors. The term ''arbovirus'' is a portmanteau word (''ar''thropod-''bo''rne ''virus''). ''Tibovirus'' (''ti''ck-''bo''rne ''virus'') is sometimes used to more sp ...
es, infecting vertebrate
Vertebrates () comprise all animal taxa within the subphylum Vertebrata () (chordates with backbones), including all mammals, birds, reptiles, amphibians, and fish. Vertebrates represent the overwhelming majority of the phylum Chordata, with c ...
s and invertebrate
Invertebrates are a paraphyletic group of animals that neither possess nor develop a vertebral column (commonly known as a ''backbone'' or ''spine''), derived from the notochord. This is a grouping including all animals apart from the chordate ...
s (such as tick
Ticks (order Ixodida) are parasitic arachnids that are part of the mite superorder Parasitiformes. Adult ticks are approximately 3 to 5 mm in length depending on age, sex, species, and "fullness". Ticks are external parasites, living by ...
s and mosquito
Mosquitoes (or mosquitos) are members of a group of almost 3,600 species of small flies within the family Culicidae (from the Latin ''culex'' meaning " gnat"). The word "mosquito" (formed by ''mosca'' and diminutive ''-ito'') is Spanish for "li ...
es). The Quaranjaviruses are also arbovirus
Arbovirus is an informal name for any virus that is transmitted by arthropod vectors. The term ''arbovirus'' is a portmanteau word (''ar''thropod-''bo''rne ''virus''). ''Tibovirus'' (''ti''ck-''bo''rne ''virus'') is sometimes used to more sp ...
es, infecting vertebrates (birds) and invertebrates (arthropod
Arthropods (, (gen. ποδός)) are invertebrate animals with an exoskeleton, a segmented body, and paired jointed appendages. Arthropods form the phylum Arthropoda. They are distinguished by their jointed limbs and cuticle made of chiti ...
s).
The four genera of Influenza virus that infect vertebrates, which are identified by antigenic differences in their nucleoprotein
Nucleoproteins are proteins conjugated with nucleic acids (either DNA or RNA). Typical nucleoproteins include ribosomes, nucleosomes and viral nucleocapsid proteins.
Structures
Nucleoproteins tend to be positively charged, facilitating int ...
and matrix protein
Viral matrix proteins are structural proteins linking the viral envelope with the virus core. They play a crucial role in virus assembly, and interact with the RNP complex as well as with the viral membrane. They are found in many enveloped viruses ...
, are as follows:
* '' Alphainfluenzavirus'' infects humans, other mammals, and birds, and causes all flu pandemics
* '' Betainfluenzavirus'' infects humans and seals
* '' Gammainfluenzavirus'' infects humans and pig
The pig (''Sus domesticus''), often called swine, hog, or domestic pig when distinguishing from other members of the genus '' Sus'', is an omnivorous, domesticated, even-toed, hoofed mammal. It is variously considered a subspecies of ''Sus ...
s
* '' Deltainfluenzavirus'' infects pigs and cattle
Cattle (''Bos taurus'') are large, domesticated, cloven-hooved, herbivores. They are a prominent modern member of the subfamily Bovinae and the most widespread species of the genus ''Bos''. Adult females are referred to as cows and adult ma ...
.
Structure
 The influenzavirus
The influenzavirus virion
A virus is a submicroscopic infectious agent that replicates only inside the living cells of an organism. Viruses infect all life forms, from animals and plants to microorganisms, including bacteria and archaea.
Since Dmitri Ivanovsky's ...
is pleomorphic; the viral envelope
A viral envelope is the outermost layer of many types of viruses. It protects the genetic material in their life cycle when traveling between host cells. Not all viruses have envelopes.
Numerous human pathogenic viruses in circulation are encase ...
can occur in spherical and filamentous forms. In general, the virus's morphology is ellipsoidal with particles 100–120 nm in diameter, or filamentous with particles 80–100 nm in diameter and up to 20 µm long. There are approximately 500 distinct spike-like surface projections in the envelope each projecting 10–14 nm from the surface with varying surface densities. The major glycoprotein (HA) spike is interposed irregularly by clusters of neuraminidase
Exo-α-sialidase (EC 3.2.1.18, sialidase, neuraminidase; systematic name acetylneuraminyl hydrolase) is a glycoside hydrolase that cleaves the glycosidic linkages of neuraminic acids:
: Hydrolysis of α-(2→3)-, α-(2→6)-, α-(2→8)- glyc ...
(NA) spikes, with a ratio of HA to NA of about 10 to 1.
The viral envelope composed of a lipid bilayer
The lipid bilayer (or phospholipid bilayer) is a thin polar membrane made of two layers of lipid molecules. These membranes are flat sheets that form a continuous barrier around all cells. The cell membranes of almost all organisms and many vir ...
membrane in which the glycoprotein spikes are anchored encloses the nucleocapsids; nucleoproteins of different size classes with a loop at each end; the arrangement within the virion is uncertain. The ribonuclear proteins are filamentous and fall in the range of 50–130 nm long and 9–15 nm in diameter with helical symmetry.
Genome
 Viruses of the family ''Orthomyxoviridae'' contain six to eight segments of linear
Viruses of the family ''Orthomyxoviridae'' contain six to eight segments of linear negative-sense
In molecular biology and genetics, the sense of a nucleic acid molecule, particularly of a strand of DNA or RNA, refers to the nature of the roles of the strand and its complementarity (molecular biology), complement in specifying a sequence of am ...
single stranded RNA. They have a total genome length that is 10,000–14,600 nucleotide
Nucleotides are organic molecules consisting of a nucleoside and a phosphate. They serve as monomeric units of the nucleic acid polymers – deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) and ribonucleic acid (RNA), both of which are essential biomolecule ...
s (nt). The influenza A genome
In the fields of molecular biology and genetics, a genome is all the genetic information of an organism. It consists of nucleotide sequences of DNA (or RNA in RNA viruses). The nuclear genome includes protein-coding genes and non-coding g ...
, for instance, has eight pieces of segmented negative-sense RNA (13.5 kilobases total).
The best-characterised of the influenzavirus proteins are hemagglutinin
In molecular biology, hemagglutinins (or ''haemagglutinin'' in British English) (from the Greek , 'blood' + Latin , 'glue') are receptor-binding membrane fusion glycoproteins produced by viruses in the '' Paramyxoviridae'' family. Hemagglutinins a ...
and neuraminidase
Exo-α-sialidase (EC 3.2.1.18, sialidase, neuraminidase; systematic name acetylneuraminyl hydrolase) is a glycoside hydrolase that cleaves the glycosidic linkages of neuraminic acids:
: Hydrolysis of α-(2→3)-, α-(2→6)-, α-(2→8)- glyc ...
, two large glycoproteins found on the outside of the viral particles. Hemagglutinin is a lectin that mediates binding of the virus to target cells and entry of the viral genome into the target cell. In contrast, neuraminidase is an enzyme
Enzymes () are proteins that act as biological catalysts by accelerating chemical reactions. The molecules upon which enzymes may act are called substrates, and the enzyme converts the substrates into different molecules known as products ...
involved in the release of progeny virus from infected cells, by cleaving sugars that bind the mature viral particles. The hemagglutinin (H) and neuraminidase (N) protein
Proteins are large biomolecules and macromolecules that comprise one or more long chains of amino acid residues. Proteins perform a vast array of functions within organisms, including catalysing metabolic reactions, DNA replication, res ...
s are key targets for antibodies and antiviral drugs, and they are used to classify the different serotypes of influenza A viruses, hence the ''H'' and ''N'' in ''H5N1''.
The genome sequence has terminal repeated sequences; repeated at both ends. Terminal repeats at the 5′-end 12–13 nucleotides long. Nucleotide sequences of 3′-terminus identical; the same in genera of same family; most on RNA (segments), or on all RNA species. Terminal repeats at the 3′-end 9–11 nucleotides long. Encapsidated nucleic acid is solely genomic. Each virion may contain defective interfering copies. In Influenza A (H1N1) PB1-F2 is produced from an alternative reading frame in PB1. The M and NS genes produce two different genes via alternative splicing.
Replication cycle
droppings
Feces ( or faeces), known colloquially and in slang as poo and poop, are the solid or semi-solid remains of food that was not digested in the small intestine, and has been broken down by bacteria in the large intestine. Feces contain a relati ...
. Influenza can also be transmitted by saliva, nasal secretions, feces and blood
Blood is a body fluid in the circulatory system of humans and other vertebrates that delivers necessary substances such as nutrients and oxygen to the cells, and transports metabolic waste products away from those same cells. Blood in the cir ...
. Infections occur through contact with these bodily fluids or with contaminated surfaces. Out of a host, flu viruses can remain infectious for about one week at human body temperature, over 30 days at , and indefinitely at very low temperatures (such as lakes in northeast Siberia
Siberia ( ; rus, Сибирь, r=Sibir', p=sʲɪˈbʲirʲ, a=Ru-Сибирь.ogg) is an extensive region, geographical region, constituting all of North Asia, from the Ural Mountains in the west to the Pacific Ocean in the east. It has been a ...
). They can be inactivated easily by disinfectants and detergents.
The viruses bind to a cell through interactions between its hemagglutinin
In molecular biology, hemagglutinins (or ''haemagglutinin'' in British English) (from the Greek , 'blood' + Latin , 'glue') are receptor-binding membrane fusion glycoproteins produced by viruses in the '' Paramyxoviridae'' family. Hemagglutinins a ...
glycoprotein and sialic acid sugars on the surfaces of epithelial cells
Epithelium or epithelial tissue is one of the four basic types of animal tissue, along with connective tissue, muscle tissue and nervous tissue. It is a thin, continuous, protective layer of compactly packed cells with a little intercell ...
in the lung and throat (Stage 1 in infection figure). The cell imports the virus by endocytosis. In the acidic endosome
Endosomes are a collection of intracellular sorting organelles in eukaryotic cells. They are parts of endocytic membrane transport pathway originating from the trans Golgi network. Molecules or ligands internalized from the plasma membrane can ...
, part of the hemagglutinin protein fuses the viral envelope with the vacuole's membrane, releasing the viral RNA (vRNA) molecules, accessory proteins and RNA-dependent RNA polymerase into the cytoplasm
In cell biology, the cytoplasm is all of the material within a eukaryotic cell, enclosed by the cell membrane, except for the cell nucleus. The material inside the nucleus and contained within the nuclear membrane is termed the nucleoplasm. ...
(Stage 2). These proteins and vRNA form a complex that is transported into the cell nucleus, where the RNA-dependent RNA polymerase begins transcribing complementary positive-sense cRNA (Steps 3a and b). The cRNA is either exported into the cytoplasm and translated (step 4), or remains in the nucleus. Newly synthesised viral proteins are either secreted through the Golgi apparatus
The Golgi apparatus (), also known as the Golgi complex, Golgi body, or simply the Golgi, is an organelle found in most eukaryotic cells. Part of the endomembrane system in the cytoplasm, it packages proteins into membrane-bound vesicles ...
onto the cell surface (in the case of neuraminidase and hemagglutinin, step 5b) or transported back into the nucleus to bind vRNA and form new viral genome particles (step 5a). Other viral proteins have multiple actions in the host cell, including degrading cellular mRNA
In molecular biology, messenger ribonucleic acid (mRNA) is a single-stranded molecule of RNA that corresponds to the genetic sequence of a gene, and is read by a ribosome in the process of synthesizing a protein.
mRNA is created during the ...
and using the released nucleotide
Nucleotides are organic molecules consisting of a nucleoside and a phosphate. They serve as monomeric units of the nucleic acid polymers – deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) and ribonucleic acid (RNA), both of which are essential biomolecule ...
s for vRNA synthesis and also inhibiting translation of host-cell mRNAs.
Negative-sense vRNAs that form the genome
In the fields of molecular biology and genetics, a genome is all the genetic information of an organism. It consists of nucleotide sequences of DNA (or RNA in RNA viruses). The nuclear genome includes protein-coding genes and non-coding g ...
s of future viruses, RNA-dependent RNA transcriptase, and other viral proteins are assembled into a virion. Hemagglutinin and neuraminidase molecules cluster into a bulge in the cell membrane. The vRNA and viral core proteins leave the nucleus and enter this membrane protrusion (step 6). The mature virus buds off from the cell in a sphere of host phospholipid membrane, acquiring hemagglutinin and neuraminidase with this membrane coat (step 7). As before, the viruses adhere to the cell through hemagglutinin; the mature viruses detach once their neuraminidase
Exo-α-sialidase (EC 3.2.1.18, sialidase, neuraminidase; systematic name acetylneuraminyl hydrolase) is a glycoside hydrolase that cleaves the glycosidic linkages of neuraminic acids:
: Hydrolysis of α-(2→3)-, α-(2→6)-, α-(2→8)- glyc ...
has cleaved sialic acid residues from the host cell. After the release of new influenza virus, the host cell dies.
 Orthomyxoviridae viruses are one of two RNA viruses that replicate in the nucleus (the other being
Orthomyxoviridae viruses are one of two RNA viruses that replicate in the nucleus (the other being retroviridae
A retrovirus is a type of virus that inserts a DNA copy of its RNA genome into the DNA of a host cell that it invades, thus changing the genome of that cell. Once inside the host cell's cytoplasm, the virus uses its own reverse transcriptase ...
). This is because the machinery of orthomyxo viruses cannot make their own mRNAs. They use cellular RNAs as primers for initiating the viral mRNA synthesis in a process known as cap snatching
The first step of transcription for some negative, single-stranded RNA viruses is cap snatching, in which the first 10 to 20 residues of a host cell RNA are removed (snatched) and used as the 5′ cap and primer to initiate the synthesis of the na ...
. Once in the nucleus, the RNA Polymerase Protein PB2 finds a cellular pre-mRNA and binds to its 5′ capped end. Then RNA Polymerase PA cleaves off the cellular mRNA near the 5′ end and uses this capped fragment as a primer for transcribing the rest of the viral RNA genome in viral mRNA. This is due to the need of mRNA to have a 5′ cap in order to be recognized by the cell's ribosome for translation.
Since RNA proofreading enzymes are absent, the RNA-dependent RNA transcriptase makes a single nucleotide insertion error roughly every 10 thousand nucleotides, which is the approximate length of the influenza vRNA. Hence, nearly every newly manufactured influenza virus will contain a mutation in its genome. The separation of the genome into eight separate segments of vRNA allows mixing (reassortment
Reassortment is the mixing of the genetic material of a species into new combinations in different individuals. Several different processes contribute to reassortment, including assortment of chromosomes, and chromosomal crossover. It is particul ...
) of the genes if more than one variety of influenza virus has infected the same cell (superinfection
A superinfection is a second infection superimposed on an earlier one, especially by a different microbial agent of exogenous or endogenous origin, that is resistant to the treatment being used against the first infection. Examples of this in bact ...
). The resulting alteration in the genome segments packaged into viral progeny confers new behavior, sometimes the ability to infect new host species or to overcome protective immunity of host populations to its old genome (in which case it is called an antigenic shift).
Classification
In aphylogenetic
In biology, phylogenetics (; from Greek φυλή/ φῦλον [] "tribe, clan, race", and wikt:γενετικός, γενετικός [] "origin, source, birth") is the study of the evolutionary history and relationships among or within groups o ...
-based taxonomy
Taxonomy is the practice and science of categorization or classification.
A taxonomy (or taxonomical classification) is a scheme of classification, especially a hierarchical classification, in which things are organized into groups or types. ...
, the category RNA virus includes the subcategory negative-sense ssRNA virus
Baltimore classification is a system used to classify viruses based on their manner of messenger RNA (mRNA) synthesis. By organizing viruses based on their manner of mRNA production, it is possible to study viruses that behave similarly as a dis ...
, which includes the order '' Articulavirales'', and the family ''Orthomyxoviridae''. The genera-associated species and serotypes of ''Orthomyxoviridae'' are shown in the following table.
Types
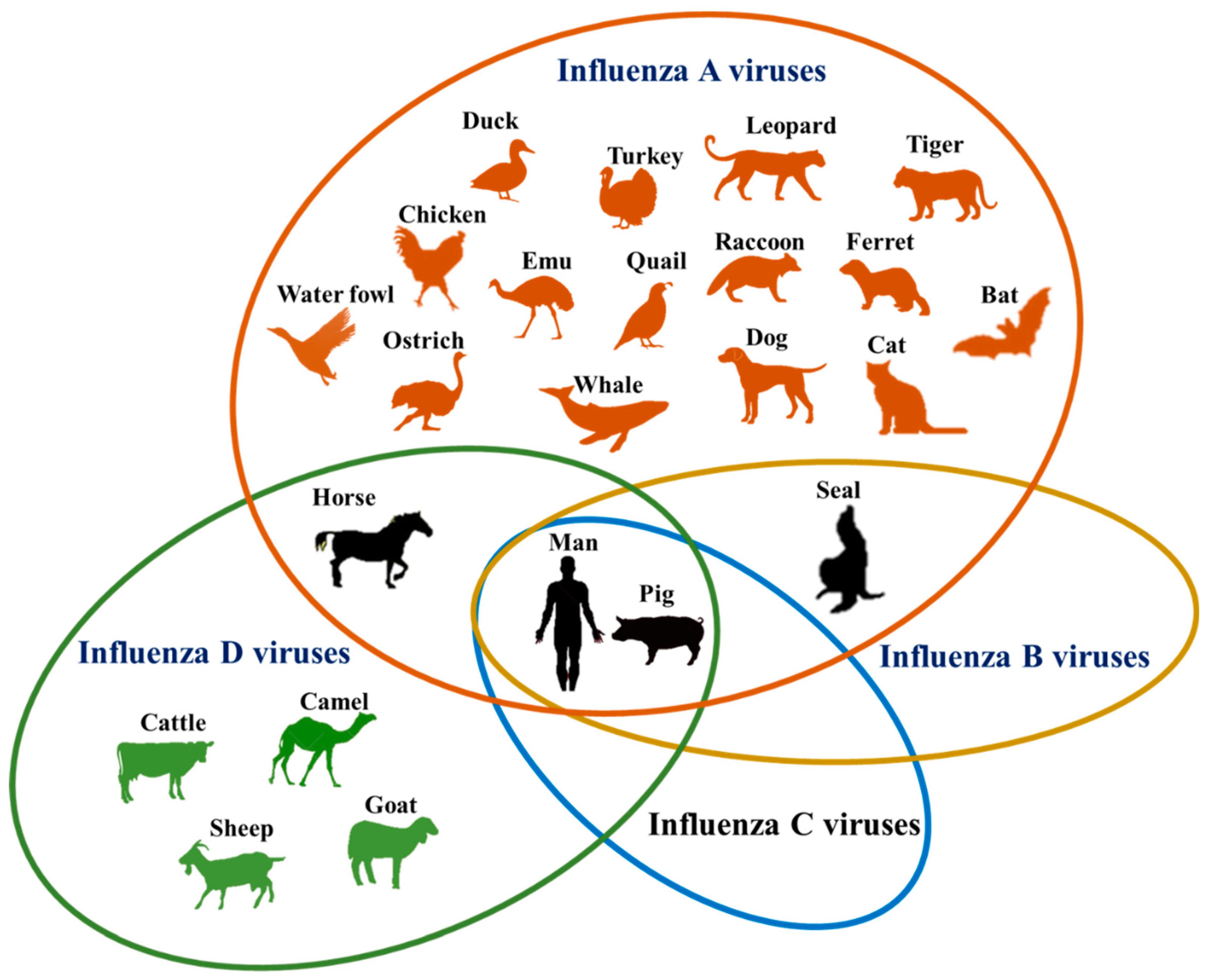
There are four genera of influenza virus, each containing only a single species, or type. Influenza A and C infect a variety of species (including humans), while influenza B almost exclusively infects humans, and influenza D infects cattle and pigs.Influenza A
hemagglutinin
In molecular biology, hemagglutinins (or ''haemagglutinin'' in British English) (from the Greek , 'blood' + Latin , 'glue') are receptor-binding membrane fusion glycoproteins produced by viruses in the '' Paramyxoviridae'' family. Hemagglutinins a ...
(HA or H) and neuraminidase
Exo-α-sialidase (EC 3.2.1.18, sialidase, neuraminidase; systematic name acetylneuraminyl hydrolase) is a glycoside hydrolase that cleaves the glycosidic linkages of neuraminic acids:
: Hydrolysis of α-(2→3)-, α-(2→6)-, α-(2→8)- glyc ...
(NA or N). 18 HA subtypes (or serotypes) and 11 NA subtypes of influenza A virus have been isolated in nature. Among these, the HA subtype 1-16 and NA subtype 1-9 are found in wild waterfowl and shorebirds and the HA subtypes 17-18 and NA subtypes 10-11 have only been isolated from bats.
Further variation exists; thus, specific influenza strain isolates are identified by a standard nomenclature specifying virus type, geographical location where first isolated, sequential number of isolation, year of isolation, and HA and NA subtype.
Examples of the nomenclature are:
# A/Brisbane/59/2007 (H1N1)
# A/Moscow/10/99 (H3N2).
The type A influenza viruses are the most virulent human pathogens among the three influenza types and cause the most severe disease. It is thought that all influenza A viruses causing outbreaks or pandemics originate from wild aquatic birds. All influenza A virus pandemics since the 1900's were caused by Avian influenza
Avian influenza, known informally as avian flu or bird flu, is a variety of influenza caused by viruses adapted to birds.
, through Reassortment
Reassortment is the mixing of the genetic material of a species into new combinations in different individuals. Several different processes contribute to reassortment, including assortment of chromosomes, and chromosomal crossover. It is particul ...
with human influenza strains (seasonal flu) or through adaptation in a mixing vessel (see 2009 swine flu pandemic
The 2009 swine flu pandemic, caused by the H1N1 influenza virus and declared by the World Health Organization (WHO) from June 2009 to August 2010, is the third recent flu pandemic involving the H1N1 virus (the first being the 1918–1920 Sp ...
). The serotypes that have been confirmed in humans
Humans (''Homo sapiens'') are the most abundant and widespread species of primate, characterized by bipedalism and exceptional cognitive skills due to a large and complex brain. This has enabled the development of advanced tools, culture, ...
, ordered by the number of confirmed human deaths, are:
* H1N1
In virology, influenza A virus subtype H1N1 (A/H1N1) is a subtype of influenza A virus. Major outbreaks of H1N1 strains in humans include the Spanish flu, the 1977 Russian flu pandemic and the 2009 swine flu pandemic. It is an orthomyxoviru ...
caused "Spanish flu
The 1918–1920 influenza pandemic, commonly known by the misnomer Spanish flu or as the Great Influenza epidemic, was an exceptionally deadly global influenza pandemic caused by the H1N1 influenza A virus. The earliest documented case wa ...
" in 1918 and "Swine flu
Swine influenza is an infection caused by any of several types of swine influenza viruses. Swine influenza virus (SIV) or swine-origin influenza virus (S-OIV) refers to any strain of the influenza family of viruses that is endemic in pigs. As ...
" in 2009.
* H2N2 caused "Asian Flu".
* H3N2
Influenza A virus subtype H3N2 (A/H3N2) is a subtype of viruses that causes influenza (flu). H3N2 viruses can infect birds and mammals. In birds, humans, and pigs, the virus has mutated into many strains. In years in which H3N2 is the predomina ...
caused " Hong Kong Flu".
* H5N1
Influenza A virus subtype H5N1 (A/H5N1) is a subtype of the influenza A virus which can cause illness in humans and many other animal species. A bird-adapted strain of H5N1, called HPAI A(H5N1) for highly pathogenic avian influenza virus of type ...
, "avian" or "bird flu".
* H7N7 has unusual zoonotic potential.
* H1N2
Influenza A virus subtype H1N2 (A/H1N2) is a subtype of the species Influenza A virus (sometimes called bird flu virus). It is currently endemic in pig populations and is occasionally seen in humans.
The virus does not cause more severe illne ...
infects pigs and humans.
* H9N2
Influenza A virus subtype H9N2 (A/H9N2) is a subtype of the species Influenza A virus ( bird flu virus).
Since 1998 a total of 86 cases of human infection with H9N2 viruses have been reported.
Infection in birds
H9N2 is the most common subtype ...
, H7N2
Influenza A virus subtype H7N2 (A/H7N2) is a subtype of the species Influenza A virus. This subtype is one of several sometimes called bird flu virus. H7N2 is considered a low pathogenicity avian influenza (LPAI) virus. With this in mind, H5 & ...
, H7N3, H10N7.
Influenza B
 Influenza B virus is almost exclusively a human pathogen, and is less common than influenza A. The only other animal known to be susceptible to influenza B infection is the
Influenza B virus is almost exclusively a human pathogen, and is less common than influenza A. The only other animal known to be susceptible to influenza B infection is the seal
Seal may refer to any of the following:
Common uses
* Pinniped, a diverse group of semi-aquatic marine mammals, many of which are commonly called seals, particularly:
** Earless seal, or "true seal"
** Fur seal
* Seal (emblem), a device to imp ...
. This type of influenza mutates at a rate 2–3 times lower than type A and consequently is less genetically diverse, with only one influenza B serotype. As a result of this lack of antigen
In immunology, an antigen (Ag) is a molecule or molecular structure or any foreign particulate matter or a pollen grain that can bind to a specific antibody or T-cell receptor. The presence of antigens in the body may trigger an immune respons ...
ic diversity, a degree of immunity to influenza B is usually acquired at an early age. However, influenza B mutates enough that lasting immunity is not possible. This reduced rate of antigenic change, combined with its limited host range (inhibiting cross species antigenic shift), ensures that pandemics of influenza B do not occur.
Influenza C
The influenza C virus infectshuman
Humans (''Homo sapiens'') are the most abundant and widespread species of primate, characterized by bipedalism and exceptional cognitive skills due to a large and complex brain. This has enabled the development of advanced tools, cultu ...
s and pig
The pig (''Sus domesticus''), often called swine, hog, or domestic pig when distinguishing from other members of the genus '' Sus'', is an omnivorous, domesticated, even-toed, hoofed mammal. It is variously considered a subspecies of ''Sus ...
s, and can cause severe illness and local epidemic
An epidemic (from Greek ἐπί ''epi'' "upon or above" and δῆμος ''demos'' "people") is the rapid spread of disease to a large number of patients among a given population within an area in a short period of time.
Epidemics of infectious ...
s. However, influenza C is less common than the other types and usually causes mild disease in children.
Influenza D
This is a genus that was classified in 2016, the members of which were first isolated in 2011. This genus appears to be most closely related to Influenza C, from which it diverged several hundred years ago. There are at least two extant strains of this genus. The main hosts appear to be cattle, but the virus has been known to infect pigs as well.Viability and disinfection
Mammalian influenza viruses tend to be labile, but can survive several hours in mucus. Avian influenza virus can survive for 100 days in distilled water at room temperature, and 200 days at . The avian virus is inactivated more quickly in manure, but can survive for up to 2 weeks in feces on cages. Avian influenza viruses can survive indefinitely when frozen. Influenza viruses are susceptible to bleach, 70% ethanol, aldehydes, oxidizing agents, and quaternary ammonium compounds. They are inactivated by heat of for minimum of 60 minutes, as well as by low pH <2.Vaccination and prophylaxis
 Vaccines and drugs are available for the prophylaxis and treatment of influenza virus infections. Vaccines are composed of either inactivated or live attenuated virions of the H1N1 and H3N2 human influenza A viruses, as well as those of influenza B viruses. Because the antigenicities of the wild viruses evolve, vaccines are reformulated annually by updating the seed strains.
When the antigenicities of the seed strains and wild viruses do not match, vaccines fail to protect the vaccinees. In addition, even when they do match, escape mutants are often generated.
Drugs available for the treatment of influenza include
Vaccines and drugs are available for the prophylaxis and treatment of influenza virus infections. Vaccines are composed of either inactivated or live attenuated virions of the H1N1 and H3N2 human influenza A viruses, as well as those of influenza B viruses. Because the antigenicities of the wild viruses evolve, vaccines are reformulated annually by updating the seed strains.
When the antigenicities of the seed strains and wild viruses do not match, vaccines fail to protect the vaccinees. In addition, even when they do match, escape mutants are often generated.
Drugs available for the treatment of influenza include Amantadine
Amantadine, sold under the brand name Gocovri among others, is a medication used to treat dyskinesia associated with parkinsonism and influenza caused by type A influenzavirus, though its use for the latter is no longer recommended due to wi ...
and Rimantadine
Rimantadine ( INN, sold under the trade name 'Flumadine'') is an orally administered antiviral drug used to treat, and in rare cases prevent, influenzavirus A infection. When taken within one to two days of developing symptoms, rimantadine can s ...
, which inhibit the uncoating of virions by interfering with M2, and Oseltamivir (marketed under the brand name Tamiflu), Zanamivir
Zanamivir is a medication used to treat and prevent influenza caused by influenza A and influenza B viruses. It is a neuraminidase inhibitor and was developed by the Australian biotech firm Biota Holdings. It was licensed to Glaxo in 1990 and ap ...
, and Peramivir
Peramivir (trade name Rapivab) is an antiviral drug developed by BioCryst Pharmaceuticals for the treatment of influenza. Peramivir is a neuraminidase inhibitor, acting as a transition-state analogue inhibitor of influenza neuraminidase and th ...
, which inhibit the release of virions from infected cells by interfering with NA. However, escape mutants are often generated for the former drug and less frequently for the latter drug.
See also
* Influenza-like illnessReferences
Further reading
*External links
Health-EU Portal
EU work to prepare a global response to influenza.
Influenza Research Database
Database of influenza genomic sequences and related information.
EU coordination on Pandemic (H1N1) 2009
3D Influenza-virus-related structures from the EM Data Bank (EMDB)
Virus Taxonomy: 2020 Release
International Committee on Taxonomy of Viruses (ICTV) {{Taxonbar, from=Q287246 Virus families