Organoniobium chemistry on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Organoniobium chemistry is the chemistry of compounds containing niobium-
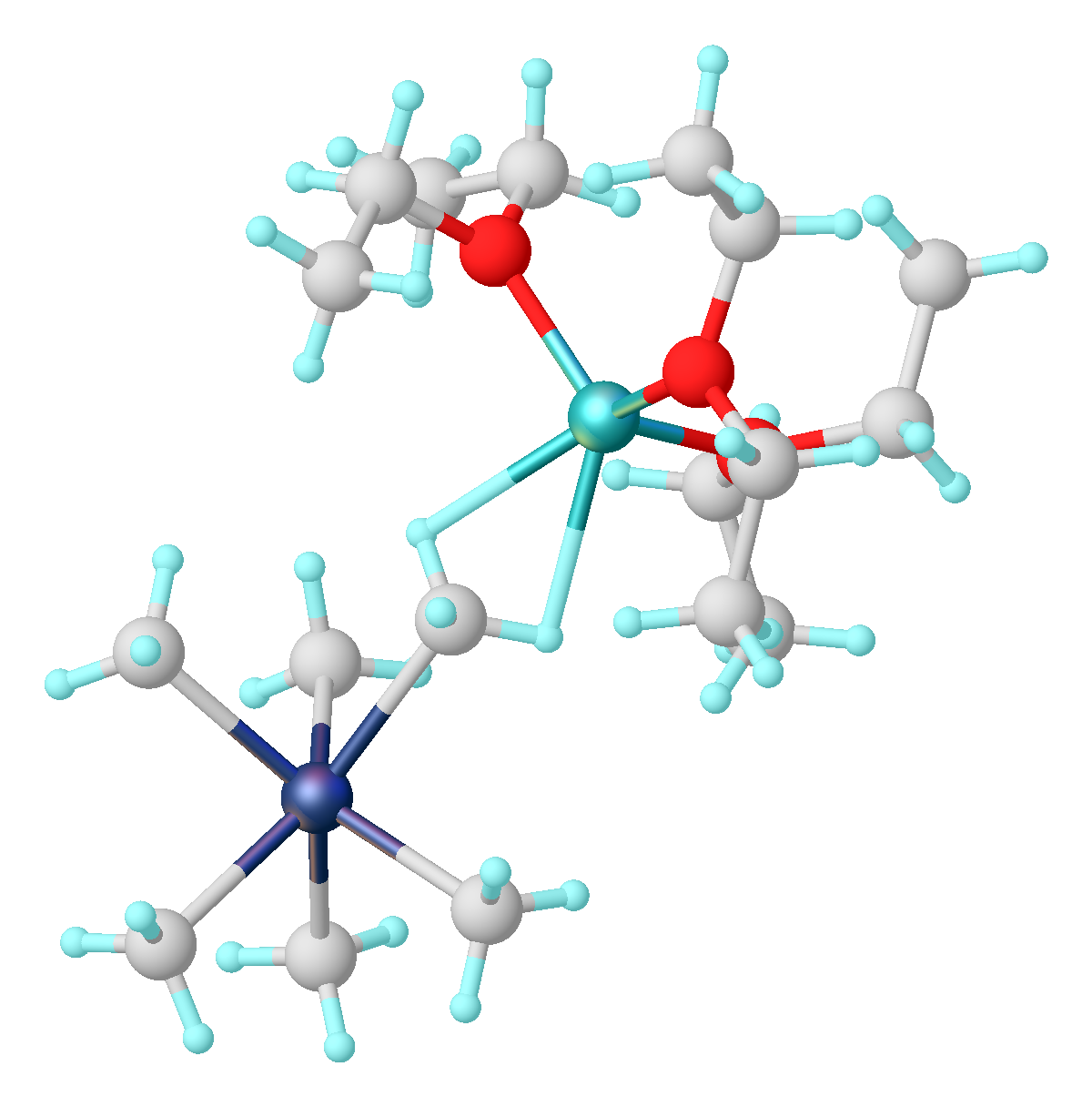
 Similar to other d2 transition metals, Nb(III) produce adducts with alkynes. These derivatives are sometimes called Nb(V) alkenediyls metallacyclopropenes.
These alkendiyl complexes function as latent dianion equivalents. They react with electrophiles to give alkene derivatives.
Similar to other d2 transition metals, Nb(III) produce adducts with alkynes. These derivatives are sometimes called Nb(V) alkenediyls metallacyclopropenes.
These alkendiyl complexes function as latent dianion equivalents. They react with electrophiles to give alkene derivatives.
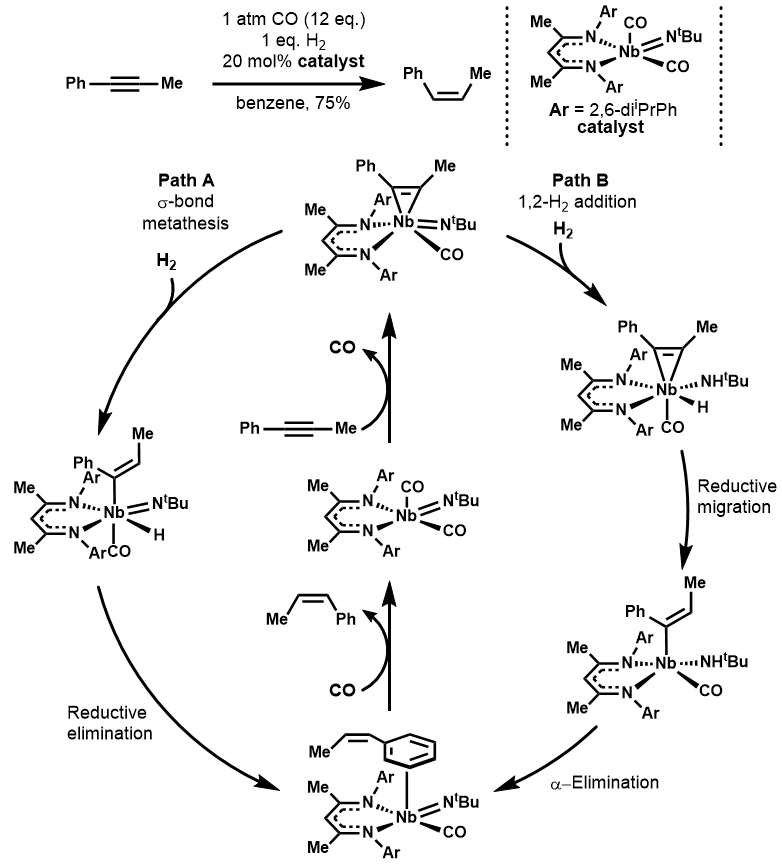
 An organoniobium catalyst has also been developed for (Z)-selective semihydrogenation of alkynes. The mechanistic pathway for this reaction is distinct from other transition metal catalyzed hydrogenations, proceeding through the Nb(V) metallocyclopropene which engages with hydrogen either through direct sigma-bond metathesis or outer sphere 1,2-addition.
An organoniobium catalyst has also been developed for (Z)-selective semihydrogenation of alkynes. The mechanistic pathway for this reaction is distinct from other transition metal catalyzed hydrogenations, proceeding through the Nb(V) metallocyclopropene which engages with hydrogen either through direct sigma-bond metathesis or outer sphere 1,2-addition.
carbon
Carbon () is a chemical element with the symbol C and atomic number 6. It is nonmetallic and tetravalent—its atom making four electrons available to form covalent chemical bonds. It belongs to group 14 of the periodic table. Carbon mak ...
(Nb-C) bonds. Compared to the other group 5 transition metal organometallics
''Organometallics'' is a biweekly journal published by the American Chemical Society. Its area of focus is organometallic and organometalloid chemistry. This peer-reviewed journal has an impact factor of 3.837 as reported by the 2021 Journal Cit ...
, the chemistry of organoniobium compounds most closely resembles that of organotantalum compounds. Organoniobium compounds of oxidation states +5, +4, +3, +2, +1, 0, -1, and -3 have been prepared, with the +5 oxidation state being the most common.
Compound classes

Carbonyls
Unlike vanadium, which forms the neutral hexacarbonyl, niobium does not easily form an analogous complex. The salts of the anionic binary carbonyl, , are however well characterized. They are obtained by reduction of under an atmosphere of CO.Alkyl
A wide variety of alkyl Nb compounds have been prepared. Low coordination number complexes require the absence of any β-hydrogen to prevent rapid β-hydride elimination. The simplest compounds are salts of , which is prepared by alkylation of usingmethyl lithium
Methyllithium is the simplest organolithium reagent with the empirical formula CH3Li. This s-block organometallic compound adopts an oligomeric structure both in solution and in the solid state. This highly reactive compound, invariably used in s ...
:
:
Cyclopentadienyl derivatives
The first organoniobium compound fully characterized was , however the paramagnetic Nb(IV) metallocenes such asniobocene dichloride
Niobocene dichloride is the organometallic compound with the formula (C5H5)2NbCl2, abbreviated Cp2NbCl2. This paramagnetic brown solid is a starting reagent for the synthesis of other organoniobium compounds. The compound adopts a pseudotetrahed ...
are more prevalent. Complexes are typically prepared by treatment of with NaCp to form the bis(cyclopentadienyl) complex followed by further functionalization. Derivatives of pentamethylcyclopentadiene
1,2,3,4,5-Pentamethylcyclopentadiene is a cyclic compound, cyclic diene with the formula C5Me5H (Me = CH3). 1,2,3,4,5-Pentamethylcyclopentadiene is the precursor to the ligand ''1,2,3,4,5-pentamethylcyclopentadienyl'', which is often denoted Cp* ...
are also known, such as .
Niobium carbonyls supported by Cp ligands can be prepared at various oxidation states of Nb and serve as useful precursors in niobium carbonyl chemistry.
Alkylidenes
Along with the related organotantalum species, niobium alkylidenes were among the first Scrock carbenes studied. The first syntheses of these complexes involved addition oforganolithium reagent
In organometallic chemistry, organolithium reagents are chemical compounds that contain carbon–lithium (C–Li) bonds. These reagents are important in organic synthesis, and are frequently used to transfer the organic group or the lithium atom ...
s lacking β-hydrogens into hindered Nb(V) complexes followed by α-proton elimination. As compared to tantalum alkylidenes, niobium alkylidenes are less thermally and hydrolytically stable.
Alkyne complexes
 Similar to other d2 transition metals, Nb(III) produce adducts with alkynes. These derivatives are sometimes called Nb(V) alkenediyls metallacyclopropenes.
These alkendiyl complexes function as latent dianion equivalents. They react with electrophiles to give alkene derivatives.
Similar to other d2 transition metals, Nb(III) produce adducts with alkynes. These derivatives are sometimes called Nb(V) alkenediyls metallacyclopropenes.
These alkendiyl complexes function as latent dianion equivalents. They react with electrophiles to give alkene derivatives.
Applications
No commercial applications of organoniobium compounds have been reported. They have found limited use in organic synthesis.Stoicheometric niobium reagents
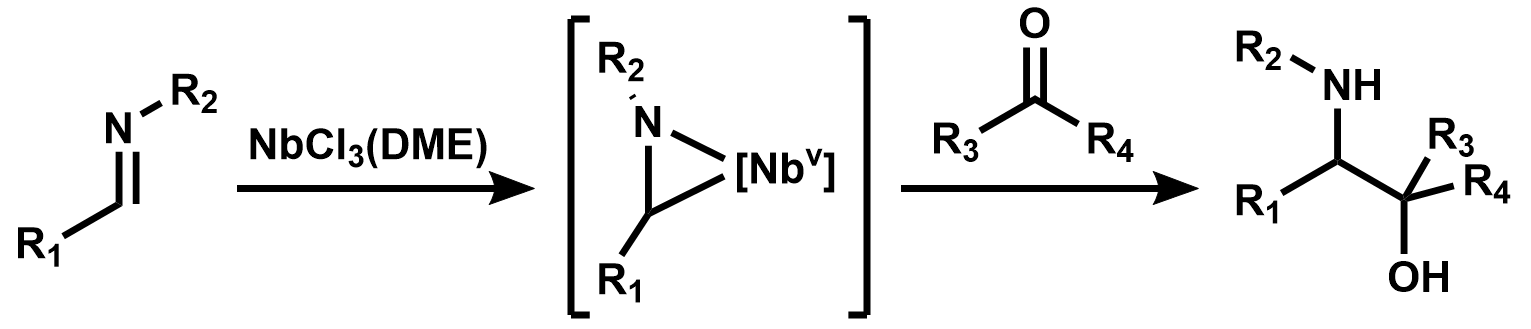
A prominent early synthetic application of organoniobium chemistry was the use ofdimethoxyethane
Dimethoxyethane, also known as glyme, monoglyme, dimethyl glycol, ethylene glycol dimethyl ether, dimethyl cellosolve, and DME, is a colorless, aprotic, and liquid ether that is used as a solvent, especially in batteries. Dimethoxyethane is mi ...
niobium trichloride, NbCl3(DME), as a reagent for the reductive coupling of imine
In organic chemistry, an imine ( or ) is a functional group or organic compound containing a carbon–nitrogen double bond (). The nitrogen atom can be attached to a hydrogen or an organic group (R). The carbon atom has two additional single bon ...
s with carbonyl compounds to form amino alcohol
In organic chemistry, alkanolamines are organic compounds that contain both hydroxyl () and amino (, , and ) functional groups on an alkane backbone. The term alkanolamine is a broad class term that is sometimes used as a subclassification.
Meth ...
s. This reagent has found further use in other pinacol
Pinacol is a white solid organic compound. It is a diol that has hydroxyl groups (-OH) on vicinal carbon atoms.
Preparation
It may be produced by the pinacol coupling reaction from
acetone:
Reactions
As a vicinal-diol, it can rearrange t ...
-type reductive couplings.

Catalytic reactions
A number of formal +2+2cycloaddition
In organic chemistry, a cycloaddition is a chemical reaction in which "two or more unsaturated molecules (or parts of the same molecule) combine with the formation of a cyclic adduct in which there is a net reduction of the bond multiplicity". T ...
s have been realized under Nb catalysis, including alkyne trimerizations and couplings of alkynes with alkenes or nitriles to form cyclohexadienes or pyridines, respectively. Typically a Nb(III) catalyst will form a Nb(V) metallocyclopropene with a terminal alkyne component and then engage in sequential migratory insertions and reductive elimination to furnish the six membered ring and regenerate the Nb(III).
 An organoniobium catalyst has also been developed for (Z)-selective semihydrogenation of alkynes. The mechanistic pathway for this reaction is distinct from other transition metal catalyzed hydrogenations, proceeding through the Nb(V) metallocyclopropene which engages with hydrogen either through direct sigma-bond metathesis or outer sphere 1,2-addition.
An organoniobium catalyst has also been developed for (Z)-selective semihydrogenation of alkynes. The mechanistic pathway for this reaction is distinct from other transition metal catalyzed hydrogenations, proceeding through the Nb(V) metallocyclopropene which engages with hydrogen either through direct sigma-bond metathesis or outer sphere 1,2-addition.

References