Operation Olympic on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Operation Downfall was the proposed Allied plan for the invasion of the
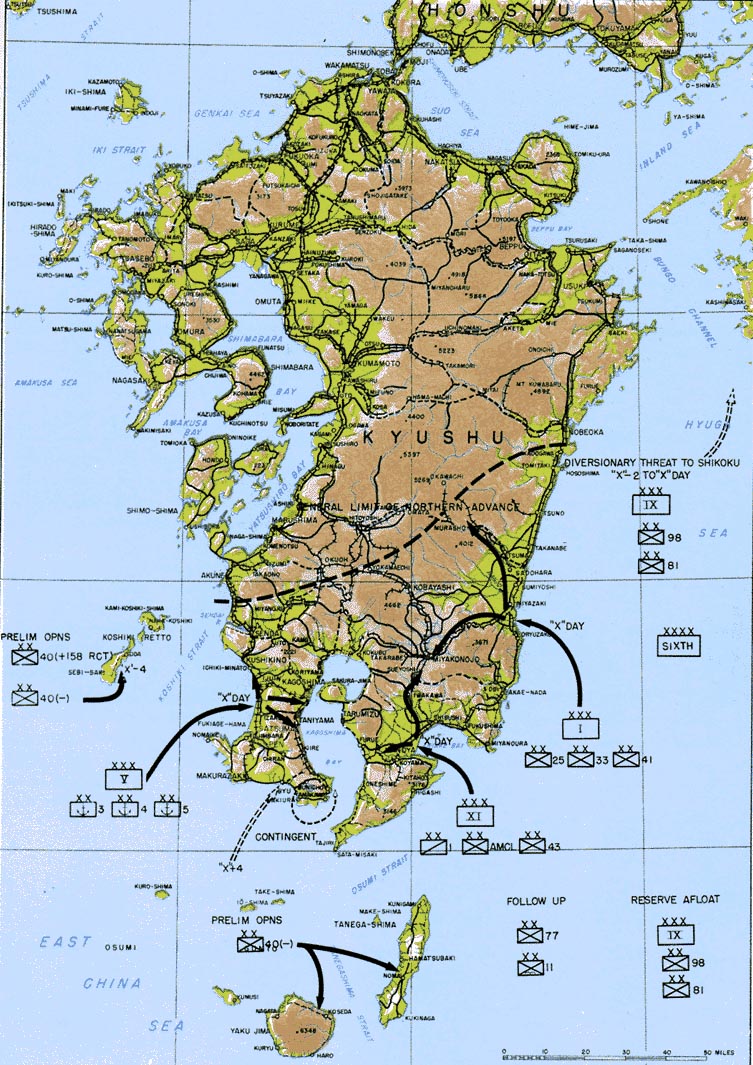
 Operation Olympic, the invasion of Kyūshū, was to begin on "X-Day", which was scheduled for 1 November 1945. The combined Allied naval armada would have been the largest ever assembled, including 42 aircraft carriers, 24 battleships, and 400 destroyers and
Operation Olympic, the invasion of Kyūshū, was to begin on "X-Day", which was scheduled for 1 November 1945. The combined Allied naval armada would have been the largest ever assembled, including 42 aircraft carriers, 24 battleships, and 400 destroyers and
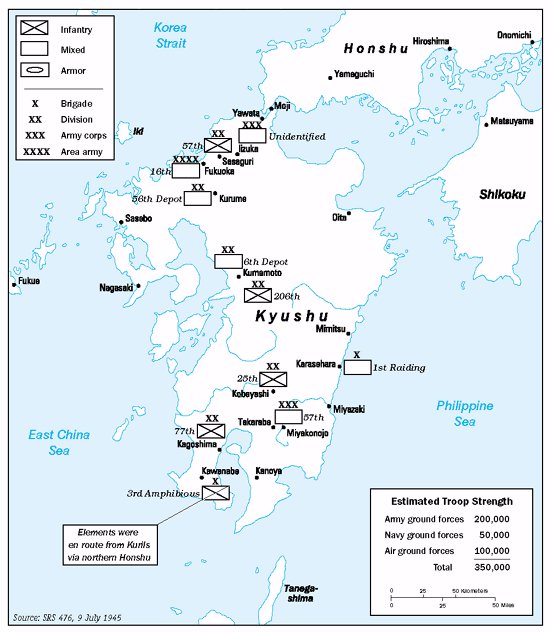
 Meanwhile, the Japanese had their own plans. Initially, they were concerned about an invasion during the summer of 1945. However, the Battle of Okinawa went on for so long that they concluded the Allies would not be able to launch another operation before the typhoon season, during which the weather would be too risky for amphibious operations. Japanese intelligence predicted fairly closely where the invasion would take place: southern Kyūshū at Miyazaki, Ariake Bay and/or the Satsuma Peninsula.
While Japan no longer had a realistic prospect of winning the war, Japan's leaders believed they could make the cost of invading and occupying the Home Islands too high for the Allies to accept, which would lead to some sort of
Meanwhile, the Japanese had their own plans. Initially, they were concerned about an invasion during the summer of 1945. However, the Battle of Okinawa went on for so long that they concluded the Allies would not be able to launch another operation before the typhoon season, during which the weather would be too risky for amphibious operations. Japanese intelligence predicted fairly closely where the invasion would take place: southern Kyūshū at Miyazaki, Ariake Bay and/or the Satsuma Peninsula.
While Japan no longer had a realistic prospect of winning the war, Japan's leaders believed they could make the cost of invading and occupying the Home Islands too high for the Allies to accept, which would lead to some sort of
Retrieved 23 August 2015. However, the IJN lacked enough fuel for further sorties by its capital ships, planning instead to use their anti-aircraft firepower to defend naval installations while docked in port. Despite its inability to conduct large-scale fleet operations, the IJN still maintained a fleet of thousands of warplanes and possessed nearly 2 million personnel in the Home Islands, ensuring it a large role in the coming defensive operation. In addition, Japan had about 100 ''Kōryū''-class
Total mobilized: 3,150,000
Kyushu – 900,000
Kanto (Tokyo) – 950,000
Korea – 247,000
For the Decisive Battle
Kyushu – 990,000
Kanto – 1,280,000
 Unknown to the Americans, the
Unknown to the Americans, the
The Final Months of the War with Japan.
Retrieved 23 August 2015 Nearly 500,000
Operation Downfall
'". Houghton Mifflin Reader's Companion to Military History. * Bauer, K. Jack, "
Operation Downfall: Olympic, Coronet
World War II in the Pacific, The Invasion of Japan''". ww2pacific.com. * * . * Hoyt, Austin, ''
Victory in the Pacific
'';
Waiting for the invasion
(notes on Japanese preparations for an American invasion) * Pearlman, Michael D.,
''Unconditional Surrender, Demobilization, and the Atomic Bomb''
; Combat Studies Institute, U.S. Army Command and General Staff College, 1996. * . {{DEFAULTSORT:Downfall Japan campaign World War II operations and battles of the Pacific theatre Cancelled invasions Operation Downfall Cancelled military operations of World War II Cancelled military operations involving the United States Cancelled military operations involving the United Kingdom United States Marine Corps in World War II Military operations of World War II
Japanese home islands
The Japanese archipelago (Japanese: 日本列島, ''Nihon rettō'') is a group of 6,852 islands that form the country of Japan, as well as the Russian island of Sakhalin. It extends over from the Sea of Okhotsk in the northeast to the East Chin ...
near the end of World War II. The planned operation was canceled when Japan surrendered following the atomic bombings of Hiroshima and Nagasaki, the Soviet declaration of war, and the invasion of Manchuria. The operation had two parts: Operation Olympic and Operation Coronet. Set to begin in November 1945, Operation Olympic was intended to capture the southern third of the southernmost main Japanese island, Kyūshū, with the recently captured island of Okinawa
is a prefecture of Japan. Okinawa Prefecture is the southernmost and westernmost prefecture of Japan, has a population of 1,457,162 (as of 2 February 2020) and a geographic area of 2,281 km2 (880 sq mi).
Naha is the capital and largest city ...
to be used as a staging area. In early 1946 would come Operation Coronet, the planned invasion of the Kantō Plain
The is the largest plain in Japan, and is located in the Kantō region of central Honshū. The total area of 17,000 km2 covers more than half of the region extending over Tokyo, Saitama Prefecture, Kanagawa Prefecture, Chiba Prefecture, ...
, near Tokyo
Tokyo (; ja, 東京, , ), officially the Tokyo Metropolis ( ja, 東京都, label=none, ), is the capital and List of cities in Japan, largest city of Japan. Formerly known as Edo, its metropolitan area () is the most populous in the world, ...
, on the main Japanese island of Honshu. Airbases on Kyūshū captured in Operation Olympic would allow land-based air support for Operation Coronet. If Downfall had taken place, it would have been the largest amphibious operation in history, surpassing D-Day.
Japan's geography made this invasion plan quite obvious to the Japanese as well; they were able to accurately predict the Allied invasion plans and thus adjust their defensive plan, Operation Ketsugō, accordingly. The Japanese planned an all-out defense of Kyūshū, with little left in reserve for any subsequent defense operations. Casualty predictions varied widely, but were extremely high. Depending on the degree to which Japanese civilians would have resisted the invasion, estimates ran up into the millions for Allied casualties.
Planning
Responsibility for the planning of Operation Downfall fell to American commanders Fleet Admiral Chester Nimitz, General of the Army Douglas MacArthur and the Joint Chiefs of Staff—Fleet AdmiralsErnest King
Ernest Joseph King (23 November 1878 – 25 June 1956) was an American naval officer who served as Commander in Chief, United States Fleet (COMINCH) and Chief of Naval Operations (CNO) during World War II. As COMINCH-CNO, he directed the U ...
and William D. Leahy, and Generals of the Army George Marshall
George Catlett Marshall Jr. (December 31, 1880 – October 16, 1959) was an American army officer and statesman. He rose through the United States Army to become Chief of Staff of the United States Army, Chief of Staff of the US Army under Pre ...
and Hap Arnold
Henry Harley Arnold (June 25, 1886 – January 15, 1950) was an American general officer holding the ranks of General of the Army and later, General of the Air Force. Arnold was an aviation pioneer, Chief of the Air Corps (1938–1941), ...
(the latter being the commander of the U.S. Army Air Forces).
At the time, the development of the atomic bomb was a very closely guarded secret (not even then-Vice President Harry Truman
Harry S. Truman (May 8, 1884December 26, 1972) was the 33rd president of the United States, serving from 1945 to 1953. A leader of the Democratic Party, he previously served as the 34th vice president from January to April 1945 under Franklin ...
knew of its existence until he became President), known only to a few top officials outside the Manhattan Project, and the initial planning for the invasion of Japan did not take its existence into consideration. Once the atomic bomb became available, General Marshall envisioned using it to support the invasion if sufficient numbers could be produced in time.
The Pacific War was not under a single Allied commander-in-chief (C-in-C). Allied command was divided into regions: by 1945, for example, Chester Nimitz was the Allied C-in-C Pacific Ocean Areas
Pacific Ocean Areas was a major Allied military command in the Pacific Ocean theater of World War II. It was one of four major Allied commands during the Pacific War, and one of three United States commands in the Asiatic-Pacific Theater. Admir ...
, while Douglas MacArthur was Supreme Allied Commander, South West Pacific Area
South West Pacific Area (SWPA) was the name given to the Allied supreme military command in the South West Pacific Theatre of World War II. It was one of four major Allied commands in the Pacific War. SWPA included the Philippines, Borneo, the ...
, and Admiral Louis Mountbatten was the Supreme Allied Commander, South East Asia Command
South East Asia Command (SEAC) was the body set up to be in overall charge of Allied operations in the South-East Asian Theatre during the Second World War.
History Organisation
The initial supreme commander of the theatre was General Sir A ...
. A unified command was deemed necessary for an invasion of Japan. Interservice rivalry
Interservice rivalry is the rivalry between different branches of a country's armed forces, in other words the competition for limited resources among a nation's land, naval, coastal, air, and space forces. The term also applies to the rival ...
over who it should be (the United States Navy
The United States Navy (USN) is the maritime service branch of the United States Armed Forces and one of the eight uniformed services of the United States. It is the largest and most powerful navy in the world, with the estimated tonnage ...
wanted Nimitz, but the United States Army
The United States Army (USA) is the land warfare, land military branch, service branch of the United States Armed Forces. It is one of the eight Uniformed services of the United States, U.S. uniformed services, and is designated as the Army o ...
wanted MacArthur) was so serious that it threatened to derail planning. Ultimately, the Navy partially conceded, and MacArthur was to be given total command of all forces if circumstances made it necessary.
Considerations
The primary considerations that the planners had to deal with were time and casualties—how they could force Japan's surrender as quickly as possible with as few Allied casualties as possible. Prior to the First Quebec Conference, a joint CanadianBritishAmerican planning team produced a plan ("Appreciation and Plan for the Defeat of Japan") which did not call for an invasion of the Japanese Home Islands until 1947–48. The American Joint Chiefs of Staff believed that prolonging the war to such an extent was dangerous for national morale. Instead, at the Quebec conference, the Combined Chiefs of Staff agreed that Japan should be forced to surrender not more than one year after Germany's surrender. The United States Navy urged the use of ablockade
A blockade is the act of actively preventing a country or region from receiving or sending out food, supplies, weapons, or communications, and sometimes people, by military force.
A blockade differs from an embargo or sanction, which are leg ...
and airpower to bring about Japan's capitulation. They proposed operations to capture airbases in nearby Shanghai
Shanghai (; , , Standard Mandarin pronunciation: ) is one of the four direct-administered municipalities of the People's Republic of China (PRC). The city is located on the southern estuary of the Yangtze River, with the Huangpu River flowin ...
, China, and Korea
Korea ( ko, 한국, or , ) is a peninsular region in East Asia. Since 1945, it has been divided at or near the 38th parallel, with North Korea (Democratic People's Republic of Korea) comprising its northern half and South Korea (Republic o ...
, which would give the United States Army Air Forces a series of forward airbases from which to bombard Japan into submission. The Army, on the other hand, argued that such a strategy could "prolong the war indefinitely" and expend lives needlessly, and therefore that an invasion was necessary. They supported mounting a large-scale thrust directly against the Japanese homeland, with none of the side operations that the Navy had suggested. Ultimately, the Army's viewpoint prevailed.
Physically, Japan made an imposing target, distant from other landmasses and with very few beaches geographically suitable for sea-borne invasion. Only Kyūshū (the southernmost island of Japan) and the beaches of the Kantō Plain
The is the largest plain in Japan, and is located in the Kantō region of central Honshū. The total area of 17,000 km2 covers more than half of the region extending over Tokyo, Saitama Prefecture, Kanagawa Prefecture, Chiba Prefecture, ...
(both southwest and southeast of Tokyo
Tokyo (; ja, 東京, , ), officially the Tokyo Metropolis ( ja, 東京都, label=none, ), is the capital and List of cities in Japan, largest city of Japan. Formerly known as Edo, its metropolitan area () is the most populous in the world, ...
) were realistic invasion zones. The Allies decided to launch a two-stage invasion. Operation Olympic would attack southern Kyūshū. Airbases would be established, which would give cover for Operation Coronet, the attack on Tokyo Bay.
Assumptions
While the geography of Japan was known, the U.S. military planners had to estimate the defending forces that they would face. Based on intelligence available early in 1945, their assumptions included the following: * "That operations in this area will be opposed not only by the available organized military forces of the Empire, but also by a fanatically hostile population." * "That approximately three (3) hostile divisions will be disposed in Southern Kyushu and an additional three (3) in Northern Kyushu at initiation of the Olympic operation." * "That total hostile forces committed against Kyushu operations will not exceed eight (8) to ten (10) divisions and that this level will be speedily attained." * "That approximately twenty-one (21) hostile divisions, including depot divisions, will be on Honshu at the initiation of oronetand that fourteen (14) of these divisions may be employed in the Kanto Plain area." * "That the enemy may withdraw his land-based air forces to the Asiatic Mainland for protection from our neutralizing attacks. That under such circumstances he can possibly amass from 2,000 to 2,500 planes in that area by exercising a rigid economy, and that this force can operate against Kyushu landings by staging through homeland fields."Olympic

 Operation Olympic, the invasion of Kyūshū, was to begin on "X-Day", which was scheduled for 1 November 1945. The combined Allied naval armada would have been the largest ever assembled, including 42 aircraft carriers, 24 battleships, and 400 destroyers and
Operation Olympic, the invasion of Kyūshū, was to begin on "X-Day", which was scheduled for 1 November 1945. The combined Allied naval armada would have been the largest ever assembled, including 42 aircraft carriers, 24 battleships, and 400 destroyers and destroyer escort
Destroyer escort (DE) was the United States Navy mid-20th-century classification for a warship designed with the endurance necessary to escort mid-ocean convoys of merchant marine ships.
Development of the destroyer escort was promoted by th ...
s. Fourteen U.S. divisions and a "division-equivalent" (two regimental combat teams) were scheduled to take part in the initial landings. Using Okinawa
is a prefecture of Japan. Okinawa Prefecture is the southernmost and westernmost prefecture of Japan, has a population of 1,457,162 (as of 2 February 2020) and a geographic area of 2,281 km2 (880 sq mi).
Naha is the capital and largest city ...
as a staging base, the objective would have been to seize the southern portion of Kyūshū. This area would then be used as a further staging point to attack Honshu in Operation Coronet.
Olympic was also to include a deception plan, known as Operation Pastel. Pastel was designed to convince the Japanese that the Joint Chiefs had rejected the notion of a direct invasion and instead were going to attempt to encircle and bombard Japan. This would require capturing bases in Formosa, along the Chinese coast, and in the Yellow Sea area.
Tactical air support was to be the responsibility of the Fifth, Seventh
Seventh is the ordinal form of the number seven.
Seventh may refer to:
* Seventh Amendment to the United States Constitution
* A fraction (mathematics), , equal to one of seven equal parts
Film and television
*"The Seventh", a second-season e ...
, and Thirteenth Air Forces. These were responsible for attacking Japanese airfields and transportation arteries on Kyushu and Southern Honshu (e.g. the Kanmon Tunnel) and for gaining and maintaining air superiority over the beaches. The task of strategic bombing fell on the United States Strategic Air Forces in the Pacific (USASTAF)—a formation which comprised the Eighth and Twentieth air forces, as well as the British Tiger Force. USASTAF and Tiger Force were to remain active through Operation Coronet. The Twentieth Air Force
The Twentieth Air Force (Air Forces Strategic) (20th AF) is a numbered air force of the United States Air Force Global Strike Command (AFGSC). It is headquartered at Francis E. Warren Air Force Base, Wyoming.
20 AF's primary mission is Interco ...
was to have continued its role as the main Allied strategic bomber force used against the Japanese home islands, operating from airfields in the Mariana Islands. Following the end of the war in Europe in May 1945, plans were also made to transfer some of the heavy bomber groups of the veteran Eighth Air Force to airbases on Okinawa to conduct strategic bombing raids in coordination with the Twentieth. The Eighth was to upgrade their B-17 Flying Fortresses and B-24 Liberators to B-29 Superfortresses (the group received its first B-29 on 8 August 1945).
Before the main invasion, the offshore islands of Tanegashima
is one of the Ōsumi Islands belonging to Kagoshima Prefecture, Japan. The island, 444.99 km2 in area, is the second largest of the Ōsumi Islands, and has a population of 33,000 people. Access to the island is by ferry, or by air to Ne ...
, Yakushima, and the Koshikijima Islands
The in the East China Sea are an island chain located 38 km west of the port city of Ichikikushikino, Kagoshima.
Major islands
Minor islands
All minor islands are currently (as in 2017) uninhabited.
#seems to undergo significant eros ...
were to be taken, starting on X-5. The invasion of Okinawa had demonstrated the value of establishing secure anchorages close at hand, for ships not needed off the landing beaches and for ships damaged by air attack.
Kyūshū was to be invaded by the Sixth United States Army
Sixth Army is a theater army of the United States Army. The Army service component command of United States Southern Command, its area of responsibility includes 31 countries and 15 areas of special sovereignty in Central and South America and ...
at three points: Miyazaki, Ariake Ariake (有明: "daybreak") may refer to:
Places in Japan
*Ariake, Kagoshima, a former town in Kagoshima Prefecture
*Ariake, Kumamoto, a former town in Kumamoto Prefecture
*Ariake, Saga, a former town in Saga Prefecture
*Ariake, Tokyo, a district w ...
, and Kushikino. If a clock were drawn on a map of Kyūshū, these points would roughly correspond to 4, 5, and 7 o'clock, respectively. The 35 landing beaches were all named for automobiles: Austin, Buick, Cadillac, and so on through to Stutz, Winton, and Zephyr. With one corps
Corps (; plural ''corps'' ; from French , from the Latin "body") is a term used for several different kinds of organization. A military innovation by Napoleon I, the formation was first named as such in 1805. The size of a corps varies great ...
assigned to each landing, the invasion planners assumed that the Americans would outnumber the Japanese by roughly three to one. In early 1945, Miyazaki was virtually undefended, while Ariake, with its good nearby harbor, was heavily defended.
The invasion was not intended to conquer the entire island, just the southernmost third of it, as indicated by the dashed line on the map labeled "general limit of northern advance". Southern Kyūshū would offer a staging ground and a valuable airbase for Operation Coronet.
After the name Operation Olympic was compromised by being sent out in unsecured code, the name Operation Majestic was adopted.
Coronet
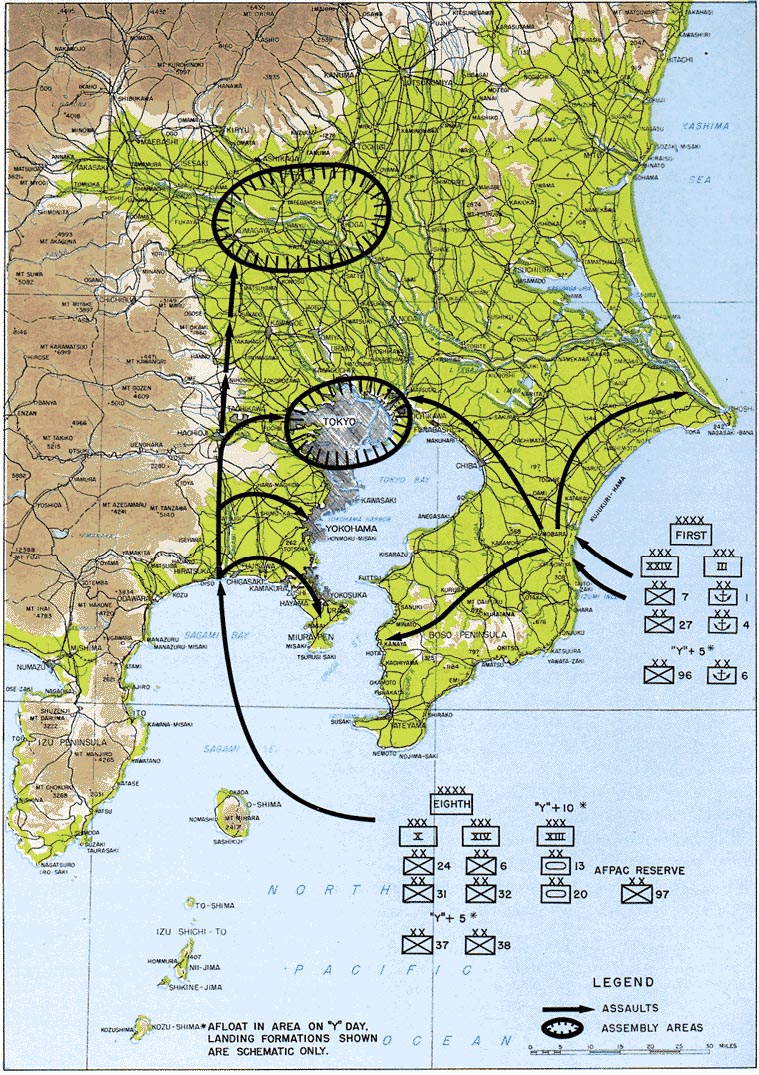
Operation Coronet, the invasion of Honshu at theKantō Plain
The is the largest plain in Japan, and is located in the Kantō region of central Honshū. The total area of 17,000 km2 covers more than half of the region extending over Tokyo, Saitama Prefecture, Kanagawa Prefecture, Chiba Prefecture, ...
south of the capital, was to begin on "Y-Day", which was tentatively scheduled for 1 March 1946. Coronet would have been even larger than Olympic, with up to 45 U.S. divisions assigned for both the initial landing and follow-up. (The Overlord invasion of Normandy, by comparison, deployed 12 divisions in the initial landings.) In the initial stage, the First Army would have invaded at Kujūkuri Beach
is a sandy beach that occupies much of the northeast coast of the Bōsō Peninsula in Chiba Prefecture, Japan. The beach is approximately long, making it the second longest beach in Japan. Kujūkuri Beach is a popular swimming and surfing dest ...
, on the Bōsō Peninsula
The is a peninsula that encompasses the entirety of Chiba Prefecture on Honshu, the largest island of Japan. It is part of the Greater Tokyo Area. It forms the eastern edge of Tokyo Bay, separating it from the Pacific Ocean. The peninsula covers ...
, while the Eighth Army invaded at Hiratsuka
260px, Hiratsuka City Hall
is a city located in Kanagawa Prefecture, Japan. , the city had an estimated population of 257,316 and a population density of 3800 persons per km². The total area of the city is .
Geography
Hiratsuka is located ...
, on Sagami Bay
lies south of Kanagawa Prefecture in Honshu, central Japan, contained within the scope of the Miura Peninsula, in Kanagawa, to the east, the Izu Peninsula, in Shizuoka Prefecture, to the west, and the Shōnan coastline to the north, while th ...
; these armies would have comprised 25 divisions between them. Later, a follow-up force of up to 20 additional U.S. divisions and up to 5 or more British Commonwealth divisions would have landed as reinforcements. The Allied forces would then have driven north and inland, encircling Tokyo and pressing on toward Nagano.
Redeployment
Olympic was to be mounted with resources already present in the Pacific, including theBritish Pacific Fleet
The British Pacific Fleet (BPF) was a Royal Navy formation that saw action against Japan during the Second World War. The fleet was composed of empire naval vessels. The BPF formally came into being on 22 November 1944 from the remaining ships o ...
, a Commonwealth formation that included at least eighteen aircraft carriers (providing 25% of the Allied air power) and four battleships.
Tiger Force, a joint Commonwealth long-range heavy bomber unit, was to be transferred from RAF
The Royal Air Force (RAF) is the United Kingdom's air and space force. It was formed towards the end of the First World War on 1 April 1918, becoming the first independent air force in the world, by regrouping the Royal Flying Corps (RFC) and ...
, RAAF
"Through Adversity to the Stars"
, colours =
, colours_label =
, march =
, mascot =
, anniversaries = RAAF Anniversary Commemoration ...
, RCAF
The Royal Canadian Air Force (RCAF; french: Aviation royale canadienne, ARC) is the air and space force of Canada. Its role is to "provide the Canadian Forces with relevant, responsive and effective airpower". The RCAF is one of three environm ...
and RNZAF units and personnel serving with RAF Bomber Command in Europe. In 1944, early planning proposed a force of 500–1,000 aircraft, including units dedicated to aerial refueling. Planning was later scaled back to 22 squadrons and, by the time the war ended, to 10 squadrons: between 120 and 150 Avro Lancasters/ Lincolns, operating out of airbases on Okinawa. Tiger Force was to have included the elite 617 Squadron
Number 617 Squadron is a Royal Air Force aircraft squadron, originally based at RAF Scampton in Lincolnshire and currently based at RAF Marham in Norfolk. It is commonly known as "''The Dambusters''", for its actions during Operation Chastis ...
, also known as "The Dambusters", which carried out specialist bombing operations.
Initially, US planners also did not plan to use any non-US Allied ground forces in Operation Downfall. Had reinforcements been needed at an early stage of Olympic, they would have been diverted from US forces being assembled for Coronet—for which there was to be a massive redeployment of units from the US Army's Southwest Pacific
The points of the compass are a set of horizontal, radially arrayed compass directions (or azimuths) used in navigation and cartography. A compass rose is primarily composed of four cardinal directions—north, east, south, and west—each sepa ...
, China-Burma-India and European commands, among others. These would have included spearheads of the war in Europe such as the US First Army (15 divisions) and the Eighth Air Force. These redeployments would have been complicated by the simultaneous demobilization and replacement of highly experienced, time-served personnel, which would have drastically reduced the combat effectiveness of many units. The Australian government had asked at an early stage for the inclusion of an Australian Army infantry division in the first wave (Olympic). This was rejected by U.S. commanders and even the initial plans for Coronet, according to U.S. historian John Ray Skates, did not envisage that units from Commonwealth or other Allied armies would be landed on the Kantō Plain in 1946. The first official "plans indicated that assault, followup, and reserve units would all come from US forces".
By mid-1945—when plans for Coronet were being reworked—many other Allied countries had, according to Skates, "offered ground forces, and a debate developed" amongst Western Allied political and military leaders, "over the size, mission, equipment, and support of these contingents". Following negotiations, it was decided that Coronet would include a joint Commonwealth Corps, made up of infantry divisions from the Australian
Australian(s) may refer to:
Australia
* Australia, a country
* Australians, citizens of the Commonwealth of Australia
** European Australians
** Anglo-Celtic Australians, Australians descended principally from British colonists
** Aboriginal A ...
, British
British may refer to:
Peoples, culture, and language
* British people, nationals or natives of the United Kingdom, British Overseas Territories, and Crown Dependencies.
** Britishness, the British identity and common culture
* British English, ...
and Canadian armies. Reinforcements would have been available from those countries, as well as other parts of the Commonwealth. However, MacArthur blocked proposals to include an Indian Army division because of differences in language, organization, composition, equipment, training and doctrine. He also recommended that the corps be organized along the lines of a U.S. corps, should use only U.S. equipment and logistics, and should train in the U.S. for six months before deployment; these suggestions were accepted. The British Government suggested that: Lieutenant-General Sir Charles Keightley
General Sir Charles Frederic Keightley, (24 June 1901 – 17 June 1974) was a senior British Army officer who served during and following the Second World War. After serving with distinction during the Second World War – becoming, in 1944, th ...
should command the Commonwealth Corps, a combined Commonwealth fleet should be led by Vice-Admiral Sir William Tennant, and that—as Commonwealth air units would be dominated by the RAAF – the Air Officer Commanding should be Australian. However, the Australian government questioned the appointment of an officer with no experience in fighting the Japanese, such as Keightley and suggested that Lieutenant General Leslie Morshead
Lieutenant General Sir Leslie James Morshead, (18 September 1889 – 26 September 1959) was an Australian soldier, teacher, businessman, and farmer, whose military career spanned both world wars. During the Second World War, he led the Aust ...
, an Australian who had been carrying out the New Guinea
New Guinea (; Hiri Motu: ''Niu Gini''; id, Papua, or , historically ) is the world's second-largest island with an area of . Located in Oceania in the southwestern Pacific Ocean, the island is separated from Australia by the wide Torr ...
and Borneo campaigns, should be appointed. The war ended before the details of the corps were finalized.
Projected initial commitment
Figures for Coronet exclude values for both the immediate strategic reserve of 3 divisions as well as the 17 division strategic reserve in the U.S. and any British/Commonwealth forces.Operation Ketsugō

 Meanwhile, the Japanese had their own plans. Initially, they were concerned about an invasion during the summer of 1945. However, the Battle of Okinawa went on for so long that they concluded the Allies would not be able to launch another operation before the typhoon season, during which the weather would be too risky for amphibious operations. Japanese intelligence predicted fairly closely where the invasion would take place: southern Kyūshū at Miyazaki, Ariake Bay and/or the Satsuma Peninsula.
While Japan no longer had a realistic prospect of winning the war, Japan's leaders believed they could make the cost of invading and occupying the Home Islands too high for the Allies to accept, which would lead to some sort of
Meanwhile, the Japanese had their own plans. Initially, they were concerned about an invasion during the summer of 1945. However, the Battle of Okinawa went on for so long that they concluded the Allies would not be able to launch another operation before the typhoon season, during which the weather would be too risky for amphibious operations. Japanese intelligence predicted fairly closely where the invasion would take place: southern Kyūshū at Miyazaki, Ariake Bay and/or the Satsuma Peninsula.
While Japan no longer had a realistic prospect of winning the war, Japan's leaders believed they could make the cost of invading and occupying the Home Islands too high for the Allies to accept, which would lead to some sort of armistice
An armistice is a formal agreement of warring parties to stop fighting. It is not necessarily the end of a war, as it may constitute only a cessation of hostilities while an attempt is made to negotiate a lasting peace. It is derived from the ...
rather than total defeat. The Japanese plan for defeating the invasion was called ("Operation Codename Decisive"). The Japanese planned to commit the entire population of Japan to resisting the invasion, and from June 1945 onward, a propaganda campaign calling for "The Glorious Death of One Hundred Million" commenced. The main message of "The Glorious Death of One Hundred Million" campaign was that it was "glorious to die for the holy emperor of Japan, and every Japanese man, woman, and child should die for the Emperor when the Allies arrived". While this was not realistic, both American and Japanese officers at the time predicted a Japanese death toll in the millions. From the Battle of Saipan onward, Japanese propaganda intensified the glory of patriotic death and depicted the Americans as merciless "white devils". During the Battle of Okinawa, Japanese officers had ordered civilians unable to fight to commit suicide rather than fall into American hands, and all available evidence suggests the same orders would have been given in the home islands. The Japanese were secretly constructing an underground headquarters in Matsushiro, Nagano Prefecture, to shelter the Emperor and the Imperial General Staff during an invasion. In planning for Operation Ketsugo, IGHQ overestimated the strength of the invading forces: while the Allied invasion plan called for fewer than 70 divisions, the Japanese expected up to 90.
''Kamikaze''
Admiral Matome Ugaki was recalled to Japan in February 1945 and given command of the Fifth Air Fleet on Kyūshū. The Fifth Air Fleet was assigned the task of '' kamikaze'' attacks against ships involved in the invasion of Okinawa,Operation Ten-Go
, also known as Operation Heaven One (or Ten-ichi-gō 天一号), was the last major Japanese naval operation in the Pacific Theater of World War II. The resulting engagement is also known as the Battle of the East China Sea.
In April 1945, t ...
, and began training pilots and assembling aircraft for the defense of Kyūshū, the first invasion target.
The Japanese defense relied heavily on ''kamikaze'' planes. In addition to fighters and bombers, they reassigned almost all of their trainers for the mission. More than 10,000 aircraft were ready for use in July (with more by October), as well as hundreds of newly built small suicide boats to attack Allied ships offshore.
Up to 2,000 ''kamikaze'' planes launched attacks during the Battle of Okinawa, achieving approximately one hit per nine attacks. At Kyūshū, because of the more favorable circumstances (such as terrain that would reduce the Allies' radar advantage), they hoped to raise that to one for six by overwhelming the US defenses with large numbers of ''kamikaze'' attacks within a period of hours. The Japanese estimated that the planes would sink more than 400 ships; since they were training the pilots to target transports rather than carriers and destroyers, the casualties would be disproportionately greater than at Okinawa. One staff study estimated that the ''kamikazes'' could destroy a third to half of the invasion force before landing.
Admiral Ernest King
Ernest Joseph King (23 November 1878 – 25 June 1956) was an American naval officer who served as Commander in Chief, United States Fleet (COMINCH) and Chief of Naval Operations (CNO) during World War II. As COMINCH-CNO, he directed the U ...
, Commander-in-Chief of the U.S Navy, was so concerned about losses from ''kamikaze'' attacks that he and other senior naval officers argued for canceling Operation Downfall, and instead continuing the fire-bombing campaign against Japanese cities and the blockade of food and supplies until the Japanese surrendered. However, General George Marshall
George Catlett Marshall Jr. (December 31, 1880 – October 16, 1959) was an American army officer and statesman. He rose through the United States Army to become Chief of Staff of the United States Army, Chief of Staff of the US Army under Pre ...
argued that forcing surrender this way might take several years, if ever. Accordingly, Marshall and United States Secretary of the Navy Frank Knox concluded the Americans would have to invade Japan to end the war, regardless of casualties.
Naval forces
Despite the shattering damage it had absorbed by this stage of the war, theImperial Japanese Navy
The Imperial Japanese Navy (IJN; Kyūjitai: Shinjitai: ' 'Navy of the Greater Japanese Empire', or ''Nippon Kaigun'', 'Japanese Navy') was the navy of the Empire of Japan from 1868 to 1945, when it was dissolved following Japan's surrend ...
, by then organized under the Navy General Command, was determined to inflict as much damage on the Allies as possible. Remaining major warships numbered four battleships (all damaged), five damaged aircraft carriers, two cruisers, 23 destroyers, and 46 submarines.Japanese Monograph No. 85 p. 16Retrieved 23 August 2015. However, the IJN lacked enough fuel for further sorties by its capital ships, planning instead to use their anti-aircraft firepower to defend naval installations while docked in port. Despite its inability to conduct large-scale fleet operations, the IJN still maintained a fleet of thousands of warplanes and possessed nearly 2 million personnel in the Home Islands, ensuring it a large role in the coming defensive operation. In addition, Japan had about 100 ''Kōryū''-class
midget submarine
A midget submarine (also called a mini submarine) is any submarine under 150 tons, typically operated by a crew of one or two but sometimes up to six or nine, with little or no on-board living accommodation. They normally work with mother ships, ...
s, 300 smaller ''Kairyū''-class midget submarines, 120 ''Kaiten
were crewed torpedoes and suicide craft, used by the Imperial Japanese Navy in the final stages of World War II.
History
In recognition of the unfavorable progress of the war, towards the end of 1943 the Japanese high command considered s ...
'' manned torpedoes, and 2,412 '' Shin'yō'' suicide motorboats. Unlike the larger ships, these, together with the destroyers and fleet submarines, were expected to see extensive action defending the shores, with a view to destroying about 60 Allied transports.
The Navy trained a unit of frogmen
A frogman is someone who is trained in scuba diving or swimming underwater in a tactical capacity that includes military, and in some European countries, police work. Such personnel are also known by the more formal names of combat diver, comb ...
to serve as suicide bombers, the Fukuryu. They were to be armed with contact-fuzed mines, and to dive under landing craft and blow them up. An inventory of mines was anchored to the sea bottom off each potential invasion beach for their use by the suicide divers, with up to 10,000 mines planned. Some 1,200 suicide divers had been trained before the Japanese surrender.
Ground forces
The two defensive options against amphibious invasion are strong defense of the beaches and defense in depth. Early in the war (such as at Tarawa), the Japanese employed strong defenses on the beaches with little or no manpower in reserve, but this tactic proved vulnerable to pre-invasionshore bombardment
Naval gunfire support (NGFS) (also known as shore bombardment) is the use of naval artillery to provide fire support for amphibious assault and other troops operating within their range. NGFS is one of a number of disciplines encompassed by t ...
. Later at Peleliu
Peleliu (or Beliliou) is an island in the island nation of Palau. Peleliu, along with two small islands to its northeast, forms one of the sixteen states of Palau. The island is notable as the location of the Battle of Peleliu in World War II.
H ...
, Iwo Jima, and Okinawa, they switched strategies and dug in their forces in the most defensible terrain.
For the defense of Kyūshū, the Japanese took an intermediate posture, with the bulk of their defensive forces a few kilometers inland, back far enough to avoid complete exposure to naval bombardment, but close enough that the Americans could not establish a secure foothold before engaging them. The counteroffensive forces were still farther back, prepared to move against the largest landing.
In March 1945, there was only one combat division in Kyūshū. Over the next four months, the Imperial Japanese Army transferred forces from Manchuria, Korea
Korea ( ko, 한국, or , ) is a peninsular region in East Asia. Since 1945, it has been divided at or near the 38th parallel, with North Korea (Democratic People's Republic of Korea) comprising its northern half and South Korea (Republic o ...
, and northern Japan, while raising other forces in place. By August, they had 14 divisions and various smaller formations, including three tank brigades, for a total of 900,000 men. Although the Japanese were able to muster new soldiers, equipping them was more difficult. By August, the Japanese Army had the equivalent of 65 divisions in the homeland but only enough equipment for 40 and ammunition for 30.
The Japanese did not formally decide to stake everything on the outcome of the Battle of Kyūshū, but they concentrated their assets to such a degree that there would be little left in reserve. By one estimate, the forces in Kyūshū had 40% of all the ammunition in the Home Islands.
In addition, the Japanese had organized the Volunteer Fighting Corps, which included all healthy men aged 15 to 60 and women 17 to 40 for a total of 28 million people, for combat support and, later, combat jobs. Weapons, training and uniforms were generally lacking: many were armed with nothing better than antiquated firearms, molotov cocktail
A Molotov cocktail (among several other names – ''see other names'') is a hand thrown incendiary weapon constructed from a frangible container filled with flammable substances equipped with a fuse (typically a glass bottle filled with fla ...
s, longbows, swords, knives, bamboo or wooden spears, and even clubs and truncheons: they were expected to make do with what they had. One mobilized high school girl, Yukiko Kasai, found herself issued an awl and told, "Even killing one American soldier will do. ... You must aim for the abdomen." They were expected to serve as a "second defense line" during the Allied invasion, and to conduct guerrilla warfare in urban areas and mountains.
The Japanese command intended to organize its Army personnel according to the following plan:
Allied re-evaluation of Operation Olympic
Air threat
US military intelligence initially estimated the number of Japanese aircraft to be around 2,500. The Okinawa experience was bad for the US—almost two fatalities and a similar number wounded per sortie—and Kyūshū was likely to be worse. To attack the ships off Okinawa, Japanese planes had to fly long distances over open water; to attack the ships off Kyūshū, they could fly overland and then short distances out to the landing fleets. Gradually, intelligence learned that the Japanese were devoting all their aircraft to the ''kamikaze'' mission and taking effective measures to conserve them until the battle. An Army estimate in May was 3,391 planes; in June, 4,862; in August, 5,911. A July Navy estimate, abandoning any distinction between training and combat aircraft, was 8,750; in August, 10,290. By the time the war ended, the Japanese actually possessed some 12,700 aircraft in the Home Islands, roughly half kamikazes. Allied counter-''kamikaze'' preparations were known as theBig Blue Blanket
The big blue blanket was an air defense system devised by John Thach during World War II for protecting American warships from attack by Japanese kamikazes.
History and tactics
As the American island hopping campaign got closer to Japan, the Jap ...
. This involved adding more fighter squadrons to the carriers in place of torpedo and dive bombers, and converting B-17s into airborne radar picket
A radar picket is a radar-equipped station, ship, submarine, aircraft, or vehicle used to increase the radar detection range around a nation or military (including naval) force to protect it from surprise attack, typically air attack, or from cr ...
s in a manner similar to present-day AWACS. Nimitz planned a pre-invasion feint, sending a fleet to the invasion beaches a couple of weeks before the real invasion, to lure out the Japanese on their one-way flights, who would then find ships bristling with anti-aircraft guns instead of the valuable, vulnerable transports.
The main defense against Japanese air attacks would have come from the massive fighter forces being assembled in the Ryukyu Islands. The US Army Fifth and Seventh Air Force
The Seventh Air Force (Air Forces Korea) (7 AF) is a Numbered Air Force of the United States Pacific Air Forces (PACAF). It is headquartered at Osan Air Base, South Korea.
The command's mission is to plan and direct air component operations in ...
s and US Marine air units had moved into the islands immediately after the invasion, and air strength had been increasing in preparation for the all-out assault on Japan. In preparation for the invasion, an air campaign against Japanese airfields and transportation arteries had commenced before the Japanese surrender.
Ground threat
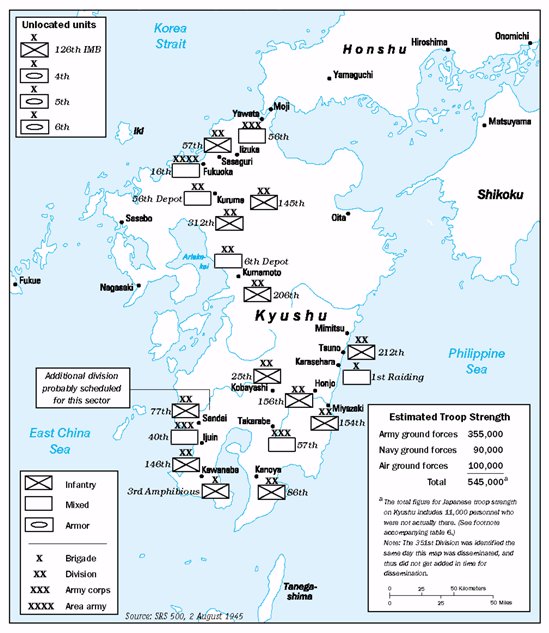
Through April, May, and June, Allied intelligence followed the buildup of Japanese ground forces, including five divisions added to Kyūshū, with great interest, but also some complacency, still projecting that in November the total for Kyūshū would be about 350,000 servicemen. That changed in July, with the discovery of four new divisions and indications of more to come. By August, the count was up to 600,000, and Magic cryptanalysis had identified nine divisions in southern Kyūshū—three times the expected number and still a serious underestimate of the actual Japanese strength. Estimated troop strength in early July was 350,000, rising to 545,000 in early August. By the time of surrender, the Japanese had over 735,000 military personnel either in position or in various stages of deployment on Kyushu alone. The total strength of the Japanese military in the Home Islands amounted to 4,335,500, of whom 2,372,700 were in the Army and 1,962,800 in the Navy. The buildup of Japanese troops on Kyūshū led American war planners, most importantly General George Marshall, to consider drastic changes to Olympic, or replacing it with a different invasion plan.Chemical weapons
Fears of "an Okinawa from one end of Japan to the other" encouraged the Allies to consider unconventional weapons, including chemical warfare. Widespread chemical warfare was considered against Japan's population and food crops. While large quantities of gas munitions were manufactured and plans were drawn, it is unlikely they would have been used. Richard B. Frank states that when the proposal reached Truman in June 1945, he vetoed the use of chemical weapons against personnel; their use against crops, however, remained under consideration. According toEdward J. Drea
Edward John Drea (born 24 February 1944) is an American military historian. He deals especially with the Imperial Japanese Army and the Pacific War.
Early life and education
Edward John Drea was born in Buffalo, New York, on 24 February 1944. ...
, the strategic use of chemical weapons on a massive scale was not seriously studied or proposed by any senior American leader; rather, they debated the ''tactical'' use of chemical weapons against pockets of Japanese resistance.
Although chemical warfare had been outlawed by the Geneva Protocol
The Protocol for the Prohibition of the Use in War of Asphyxiating, Poisonous or other Gases, and of Bacteriological Methods of Warfare, usually called the Geneva Protocol, is a treaty prohibiting the use of chemical and biological weapons in ...
, neither the United States nor Japan was a signatory at the time. While the US had promised never to initiate gas warfare, Japan had used gas against the Chinese earlier in the war.
In addition to use against people, the U.S. military considered chemical attacks to kill crops in an attempt to starve the Japanese into submission. The Army began experimenting with compounds to destroy crops in April 1944, and within one year had narrowed over 1,000 agents to nine promising ones containing phenoxyacetic acids. One compound designated LN-8 performed best in tests and went into mass production. Dropping or spraying the herbicide was deemed most effective; a July 1945 test from an SPD Mark 2 bomb, originally crafted to hold biological weapons like anthrax or ricin, had the shell burst open in the air to scatter the chemical agent. By the time the war ended, the Army was still trying to determine the optimal dispersal height to cover a wide enough area. The ingredients in LN-8 and another tested compound would later be used to create Agent Orange, used during the Vietnam War
The Vietnam War (also known by other names) was a conflict in Vietnam, Laos, and Cambodia from 1 November 1955 to the fall of Saigon on 30 April 1975. It was the second of the Indochina Wars and was officially fought between North Vietnam a ...
.
Nuclear weapons
On Marshall's orders, Major General John E. Hull looked into the tactical use of nuclear weapons for the invasion of the Japanese home islands, even after the dropping of two strategic atomic bombs on Japan (Marshall did not think that the Japanese would capitulate immediately). Colonel Lyle E. Seeman reported that at least seven Fat Man-type plutonium implosion bombs would be available by X-Day, which could be dropped on defending forces. Seeman advised that American troops not enter an area hit by a bomb for "at least 48 hours"; the risk ofnuclear fallout
Nuclear fallout is the residual radioactive material propelled into the upper atmosphere following a nuclear blast, so called because it "falls out" of the sky after the explosion and the shock wave has passed. It commonly refers to the radioac ...
was not well understood, and such a short time after detonation would have exposed American troops to substantial radiation.
Ken Nichols, the District Engineer of the Manhattan Engineer District, wrote that at the beginning of August 1945, " anning for the invasion of the main Japanese home islands had reached its final stages, and if the landings actually took place, we might supply about fifteen atomic bombs to support the troops." An air burst above the ground had been chosen for the (Hiroshima) bomb to achieve maximum blast effects, and to minimize residual radiation on the ground, as it was hoped that American troops would soon occupy the city.
Alternative targets
The Joint Staff planners, taking note of the extent to which the Japanese had concentrated on Kyūshū at the expense of the rest of Japan, considered alternate places to invade such as the island ofShikoku
is the smallest of the four main islands of Japan. It is long and between wide. It has a population of 3.8 million (, 3.1%). It is south of Honshu and northeast of Kyushu. Shikoku's ancient names include ''Iyo-no-futana-shima'' (), '' ...
, northern Honshu at Sendai, or Ominato. They also considered skipping the preliminary invasion and going directly at Tokyo. Attacking northern Honshu would have the advantage of a much weaker defense but had the disadvantage of giving up land-based air support (except the B-29s) from Okinawa
is a prefecture of Japan. Okinawa Prefecture is the southernmost and westernmost prefecture of Japan, has a population of 1,457,162 (as of 2 February 2020) and a geographic area of 2,281 km2 (880 sq mi).
Naha is the capital and largest city ...
.
Prospects for Olympic
General Douglas MacArthur dismissed any need to change his plans: However, AdmiralErnest King
Ernest Joseph King (23 November 1878 – 25 June 1956) was an American naval officer who served as Commander in Chief, United States Fleet (COMINCH) and Chief of Naval Operations (CNO) during World War II. As COMINCH-CNO, he directed the U ...
, Chief of Naval Operations, was prepared to oppose proceeding with the invasion, with Admiral Nimitz's concurrence, which would have set off a major dispute within the US government.
Soviet intentions
 Unknown to the Americans, the
Unknown to the Americans, the Soviet Union
The Soviet Union,. officially the Union of Soviet Socialist Republics. (USSR),. was a List of former transcontinental countries#Since 1700, transcontinental country that spanned much of Eurasia from 1922 to 1991. A flagship communist state, ...
also considered invading a major Japanese island, Hokkaido
is Japan's second largest island and comprises the largest and northernmost prefecture, making up its own region. The Tsugaru Strait separates Hokkaidō from Honshu; the two islands are connected by the undersea railway Seikan Tunnel.
The lar ...
, by the end of August 1945, which would have put pressure on the Allies to act sooner than November.
In the early years of World War II, the Soviets had planned on building a huge navy to catch up with the Western world
The Western world, also known as the West, primarily refers to the various nations and states in the regions of Europe, North America, and Oceania.
. However, the German invasion of the Soviet Union
Operation Barbarossa (german: link=no, Unternehmen Barbarossa; ) was the invasion of the Soviet Union by Nazi Germany and many of its Axis allies, starting on Sunday, 22 June 1941, during the Second World War. The operation, code-named afte ...
in June 1941 forced the suspension of this plan: the Soviets had to divert most of their resources to fighting the Germans and their allies, primarily on land, throughout most of the war, leaving their navy relatively poorly equipped. As a result, in Project Hula
Project Hula was a program during World War II in which the United States transferred naval vessels to the Soviet Union in anticipation of the Soviets eventually joining the war against Japan, specifically in preparation for planned Soviet inv ...
(1945), the United States transferred about 100 naval vessels out of the 180 planned to the Soviet Union in preparation for the planned Soviet entry into the war against Japan. The transferred vessels included amphibious assault ship
An amphibious assault ship is a type of amphibious warfare ship employed to land and support ground forces on enemy territory by an amphibious assault. The design evolved from aircraft carriers converted for use as helicopter carriers (and, a ...
s.
At the Yalta Conference (February 1945), the Allies had agreed that the Soviet Union would take the southern part of the island of Sakhalin, which Russia
Russia (, , ), or the Russian Federation, is a transcontinental country spanning Eastern Europe and Northern Asia. It is the largest country in the world, with its internationally recognised territory covering , and encompassing one-eig ...
had ceded to Japan in the Treaty of Portsmouth after the 1904–1905 Russo-Japanese War
The Russo-Japanese War ( ja, 日露戦争, Nichiro sensō, Japanese-Russian War; russian: Ру́сско-япóнская войнá, Rússko-yapónskaya voyná) was fought between the Empire of Japan and the Russian Empire during 1904 and 1 ...
(the Soviets already controlled the northern part), and the Kuril Islands, which had been assigned to Japan in the 1875 Treaty of St. Petersburg. On the other hand, no agreement envisaged Soviet participation in the invasion of Japan itself.
The Japanese had ''kamikaze'' aircraft in southern Honshu and Kyushu which would have opposed operations Olympic and Coronet. It is unknown to what extent they could have opposed Soviet landings in the far north of Japan. For comparative purposes, about 1,300 Western Allied
The Allies, formally referred to as the Declaration by United Nations, United Nations from 1942, were an international Coalition#Military, military coalition formed during the World War II, Second World War (1939–1945) to oppose the Axis ...
ships deployed during the Battle of Okinawa (April–June 1945). In total, 368 ships, including 120 amphibious craft, were badly damaged, and another 28, including 15 landing ships and 12 destroyers, were sunk, mostly by ''kamikazes''. The Soviets, however, had fewer than 400 ships, most of them not equipped for amphibious assault, when they declared war on Japan on 8 August 1945.
For Operation Downfall, the US military envisaged requiring more than 30 divisions for a successful invasion of the Japanese home islands. In comparison, the Soviet Union had about 11 divisions available, comparable to the 14 divisions the US estimated that it would require to invade southern Kyushu. The Soviet invasion of the Kuril Islands (18 August – 1 September 1945) took place after Japan's capitulation on 15 August. However, the Japanese forces in those islands resisted quite fiercely although some of them proved unwilling to fight after Japan's surrender on 15 August. In the Battle of Shumshu (18–23 August 1945), the Soviet Red Army had 8,821 troops that were not supported by tanks and without back-up from larger warships. The well-established Japanese garrison had 8,500 troops and fielded about 77 tanks. The battle lasted one day, with minor combat actions going on for four more after the official surrender of Japan and the garrison, during which the attacking Soviet forces lost over 516 troops and five of the 16 landing ships (many of these formerly belonged to the US Navy and were later given to the Soviet Union) to Japanese coastal artillery, and the Japanese lost over 256 troops. Soviet casualties during the Battle of Shumshu totaled up to 1,567, and the Japanese suffered 1,018 casualties, making Shumshu the only battle in the 1945 Soviet–Japanese War
The Soviet–Japanese War (russian: Советско-японская война; ja, ソ連対日参戦, soren tai nichi sansen, Soviet Union entry into war against Japan), known in Mongolia as the Liberation War of 1945 (), was a military ...
in which Soviet losses exceeded those of the Japanese, in stark contrast to overall Soviet-Japanese casualty rates in land-based fighting in Manchuria.
During World War II, the Japanese had a naval base
A naval base, navy base, or military port is a military base, where warships and naval ships are docked when they have no mission at sea or need to restock. Ships may also undergo repairs. Some naval bases are temporary homes to aircraft that u ...
at Paramushiro
Paramushir (russian: Парамушир, Paramushir, ja, 幌筵島, Paramushiru-tō, ain, パラムシㇼ, translit=Para=mu=sir) is a volcanic island in the northern portion of Kuril Islands chain in the Sea of Okhotsk in the northwest Pacific Oc ...
in the Kuril Islands and several bases in Hokkaido. Since Japan and the Soviet Union maintained a state of wary neutrality until the Soviet declaration of war on Japan in August 1945, Japanese observers based in Japanese-held territories in Manchuria, Korea, Sakhalin, and the Kuril Islands constantly watched the port of Vladivostok and other seaports
A port is a maritime facility comprising one or more wharves or loading areas, where ships load and discharge cargo and passengers. Although usually situated on a sea coast or estuary, ports can also be found far inland, such as Ha ...
in the Soviet Union.
According to Thomas B. Allen and Norman Polmar, the Soviets had carefully drawn up detailed plans for the Far East invasions, except that the landing for Hokkaido "existed in detail" only in Stalin's mind and that it was "unlikely that Stalin had interests in taking Manchuria and even taking on Hokkaido. Even if he wanted to grab as much territory in Asia as possible, he was too much focused on establishing a beachhead in Europe more so than Asia."
Estimated casualties
Because the U.S. military planners assumed "that operations in this area will be opposed not only by the available organized military forces of the Empire, but also by a fanatically hostile population", high casualties were thought to be inevitable, but nobody knew with certainty how high. Several estimates were made, but varied widely in numbers, assumptions and purposes, which included advocating and opposing the invasion. The estimated casualty figures later became a crucial point in postwar debate over the atomic bombings of Hiroshima and Nagasaki. On 15 January 1945, the U.S. Army Service Forces released a document, "Redeployment of the United States Army after the Defeat of Germany." In it, they estimate that during the 18 month period after June 1945 (that is, through December 1946), the Army would be required to furnish replacements for 43,000 dead and evacuated wounded every month. From analysis of the replacement schedule and projected strengths in overseas theaters, it suggested that Army losses alone in those categories, excluding the Navy and Marine Corps, would be approximately 863,000 through the first part of 1947, of whom 267,000 would be killed or missing. This likewise excludes wounded who would be treated in-theater during an initial window of 30 days, later to be expanded to 120 days. In preparation for Operation Olympic, the invasion of southern Kyushu, various figures and organizations made casualty estimates based on the terrain, strength, and disposition of known Japanese forces. However, as reported Japanese strength in the Home Islands continued to climb and Japanese military performance increased, so too did the casualty estimates. In April 1945, the Joint Chiefs of Staff formally adopted a planning paper giving a range of possible casualties based on experience in both Europe and the Pacific. These ranged from 0.42 dead and missing and 2.16 total casualties per 1000 men per day under the "European Experience" to 1.95 dead and missing and 7.45 total casualties per 1000 men per day under the "Pacific Experience." This assessment included neither casualties suffered ''after'' the 90-day mark (US planners envisioned switching to the tactical ''defensive'' by X+120), nor personnel losses at sea from Japanese air attacks. In order to sustain the campaign on Kyushu, planners estimated a replacement stream of 100,000 men per month would be necessary, a figure achievable even after the partial demobilization following the defeat of Germany. As time went on, other US leaders made estimates of their own: In a letter to GeneralCurtis LeMay
Curtis Emerson LeMay (November 15, 1906 – October 1, 1990) was an American Air Force general who implemented a controversial strategic bombing campaign in the Pacific theater of World War II. He later served as Chief of Staff of the U.S. Air ...
when LeMay assumed command of the B-29 force on Guam, General Lauris Norstad told LeMay that if an invasion took place, it would cost the US "half a million" dead.
In May, Admiral Nimitz's staff estimated 49,000 U.S casualties in the first 30 days of Operation Olympic, including 5,000 at sea.
A study done by General MacArthur's staff in June estimated 23,000 US casualties in the first 30 days of Olympic and 125,000 after 120 days, fighting an assumed Japanese force of 300,000 (in actuality some 917,000 Japanese troops were on Kyushu,). When these figures were questioned by General Marshall, MacArthur submitted a revised estimate of 105,000, in part by deducting wounded men able to return to duty.
In a conference with President Truman on June 18, Marshall, taking the Battle of Luzon
The Battle of Luzon ( tl, Labanan sa Luzon; ja, ルソン島の戦い; es, Batalla de Luzón) was a land battle of the Pacific Theater of Operations of World War II by the Allied forces of the U.S., its colony the Philippines, and allies agai ...
as the best model for Olympic, thought the Americans would suffer 31,000 casualties in the first 30 days and ultimately 20% of Japanese casualties, which he estimated would include the entire Japanese force. This implied a total of 70,000 American casualties in the battle of Kyushu using the June projection of 350,000 Japanese defenders. Admiral Leahy, more impressed by the Battle of Okinawa, thought the American forces would suffer a 35% casualty rate (implying an ultimate toll of 268,000). Admiral King thought that casualties in the first 30 days would fall between Luzon and Okinawa, i.e., between 31,000 and 41,000. Of these estimates, only Nimitz's included losses of the forces at sea, though kamikazes had inflicted 1.78 fatalities and a similar number of wounded per kamikaze pilot in the Battle of Okinawa, and troop transports off Kyūshū would have been much more exposed.
In July MacArthur's Intelligence Chief, Maj. Gen. Charles A. Willoughby, warned of between 210,000 and 280,000 battle casualties in the push to the "stop line" one-third of the way up Kyushu. Even when rounded down to a conservative 200,000, this figure implied a total of nearly 500,000 all-causes losses, of whom perhaps 50,000 might return to duty after light to moderate care.
The US Sixth Army, the formation tasked with carrying out the major land fighting on Kyushu, estimated a figure of 394,859 casualties serious enough to be permanently removed from unit roll calls during the first 120 days on Kyushu, barely enough to avoid outstripping the planned replacement stream.
Secretary of War Henry L. Stimson stated "We shall in my opinion have to go through an even more bitter finish fight than in Germany. We shall incur the losses incident to such a war and we shall leave the Japanese islands even more thoroughly destroyed than was the case with Germany." From D-Day to V-E Day, the Western Allies alone suffered some 766,294 casualties.
A study done for Stimson's staff by William Shockley estimated that invading Japan would cost 1.7–4 million American casualties, including 400,000–800,000 fatalities, and five to ten million Japanese fatalities. The key assumption was large-scale participation by civilians in the defense of Japan.
Japanese military directives ordered the execution of all POWs being held if Japan was ever invaded. Towards the end of the war about 100,000 Allied prisoners were in Japanese custody.
Outside the government, well-informed civilians were also making guesses. Kyle Palmer, war correspondent for the ''Los Angeles Times
The ''Los Angeles Times'' (abbreviated as ''LA Times'') is a daily newspaper that started publishing in Los Angeles in 1881. Based in the LA-adjacent suburb of El Segundo since 2018, it is the sixth-largest newspaper by circulation in the U ...
'', said half a million to a million Americans would die by the end of the war. Herbert Hoover, in memorandums submitted to Truman and Stimson, also estimated 500,000 to 1,000,000 fatalities, which were believed to be conservative estimates; however, it is not known if Hoover discussed these specific figures in his meetings with Truman. The Chief of the Army Operations Division thought them "entirely too high" under "our present plan of campaign."
The Battle of Okinawa was one of the bloodiest in the Pacific, with an estimated total of over 82,000 direct casualties on both sides: 14,009 Allied deaths and 77,417 Japanese soldiers.Okinawa Prefecture. ''The Cornerstone of Peace: Number of Names Inscribed''. http://www.pref.okinawa.jp/site/kodomo/heiwadanjo/heiwa/7812.html (accessed February 4, 2017)
Allied grave registration forces counted 110,071 dead bodies of Japanese soldiers, but this included conscripted Okinawans wearing Japanese uniforms. 149,425 Okinawans were killed, committed suicide or went missing, which was one-half of the estimated pre-war local population of 300,000.
The Battle resulted in 72,000 US casualties in 82 days, of whom 12,510 were killed or missing (this figure excludes the several thousand US soldiers who died after the battle indirectly, from their wounds). The entire island of Okinawa is . If the US casualty rate during the invasion of Japan had been only 5% as high per unit area as it was at Okinawa, the US would still have lost 297,000 soldiers (killed or missing).
In evaluating these estimates, especially those based on projected Japanese troop strength (such as General MacArthur's), it is important to consider what was known about the state of Japanese defenses at the time, as well as the actual condition of those defenses (MacArthur's staff believed Japanese manpower on Kyushu to be roughly 300,000).Retrieved 23 August 2015 Nearly 500,000
Purple Heart
The Purple Heart (PH) is a United States military decoration awarded in the name of the President to those wounded or killed while serving, on or after 5 April 1917, with the U.S. military. With its forerunner, the Badge of Military Merit, ...
medals (awarded for combat casualties) were manufactured in anticipation of the casualties resulting from the invasion of Japan; the number exceeded that of all American military casualties of the 65 years following the end of World War II
World War II or the Second World War, often abbreviated as WWII or WW2, was a world war that lasted from 1939 to 1945. It involved the vast majority of the world's countries—including all of the great powers—forming two opposing ...
, including the Korean
Korean may refer to:
People and culture
* Koreans, ethnic group originating in the Korean Peninsula
* Korean cuisine
* Korean culture
* Korean language
**Korean alphabet, known as Hangul or Chosŏn'gŭl
**Korean dialects and the Jeju language
** ...
and Vietnam War
The Vietnam War (also known by other names) was a conflict in Vietnam, Laos, and Cambodia from 1 November 1955 to the fall of Saigon on 30 April 1975. It was the second of the Indochina Wars and was officially fought between North Vietnam a ...
s. In 2003, there were still 120,000 of these Purple Heart medals in stock. There were so many left that combat units in Iraq
Iraq,; ku, عێراق, translit=Êraq officially the Republic of Iraq, '; ku, کۆماری عێراق, translit=Komarî Êraq is a country in Western Asia. It is bordered by Turkey to the north, Iran to the east, the Persian Gulf and K ...
and Afghanistan
Afghanistan, officially the Islamic Emirate of Afghanistan,; prs, امارت اسلامی افغانستان is a landlocked country located at the crossroads of Central Asia and South Asia. Referred to as the Heart of Asia, it is bordere ...
were able to keep Purple Hearts on hand for immediate award to soldiers wounded in the field.
Available equipment for defenders
Following the surrender and demobilization of Japan, vast amounts of war matériel were turned over to the US occupation forces in the Japanese Home Islands and South Korea. While some totals (particularly for items such as swords and small arms) may be inexact because of the problems of collection and the activities of the black market, the amount of military equipment available to the Japanese in and around the Home Islands by August 1945 was roughly as follows:See also
* ''1945'' – Alternate history novel byRobert Conroy
Joseph Robert Conroy (August 24, 1938 – December 30, 2014) was an author of alternate history novels.
Life
After he got an MBA, Conroy was a professor at Macomb Community College and taught business and economic history.
Following his early ...
depicting Operation Downfall
* '' The Burning Mountain'' – Alternate history novel by Alfred Coppel depicting the operation in the wake of a failed Manhattan Project
* Operation Sea Lion
Operation Sea Lion, also written as Operation Sealion (german: Unternehmen Seelöwe), was Nazi Germany's code name for the plan for an invasion of the United Kingdom during the Battle of Britain in the Second World War. Following the Battle o ...
– The planned German invasion of the United Kingdom
The United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern Ireland, commonly known as the United Kingdom (UK) or Britain, is a country in Europe, off the north-western coast of the European mainland, continental mainland. It comprises England, Scotlan ...
* Operation Unthinkable – British plans for war against the Soviet Union
The Soviet Union,. officially the Union of Soviet Socialist Republics. (USSR),. was a List of former transcontinental countries#Since 1700, transcontinental country that spanned much of Eurasia from 1922 to 1991. A flagship communist state, ...
References
Notes
Bibliography
* * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * *External links
* Allen, Thomas B., "Operation Downfall
'". Houghton Mifflin Reader's Companion to Military History. * Bauer, K. Jack, "
Operation Downfall: Olympic, Coronet
World War II in the Pacific, The Invasion of Japan''". ww2pacific.com. * * . * Hoyt, Austin, ''
American Experience
''American Experience'' is a television program airing on the Public Broadcasting Service (PBS) in the United States. The program airs documentaries, many of which have won awards, about important or interesting events and people in American his ...
'': Victory in the Pacific
'';
PBS
The Public Broadcasting Service (PBS) is an American public broadcaster and non-commercial, free-to-air television network based in Arlington, Virginia. PBS is a publicly funded nonprofit organization and the most prominent provider of educat ...
documentary.
* Japanese Monograph No. 23,Waiting for the invasion
(notes on Japanese preparations for an American invasion) * Pearlman, Michael D.,
''Unconditional Surrender, Demobilization, and the Atomic Bomb''
; Combat Studies Institute, U.S. Army Command and General Staff College, 1996. * . {{DEFAULTSORT:Downfall Japan campaign World War II operations and battles of the Pacific theatre Cancelled invasions Operation Downfall Cancelled military operations of World War II Cancelled military operations involving the United States Cancelled military operations involving the United Kingdom United States Marine Corps in World War II Military operations of World War II