Open System Environment Reference Model on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 Open-system environment (OSE) reference model (RM) or ''OSE reference model'' (OSE/RM) is a 1990 reference model for enterprise architecture. It provides a
Open-system environment (OSE) reference model (RM) or ''OSE reference model'' (OSE/RM) is a 1990 reference model for enterprise architecture. It provides a
STANDARDS FOR OPEN SYSTEMS: MORE FLEXIBILITY FOR FEDERAL USERS
NIST Bulletin 1996. Accessed 13 Dec 2008.
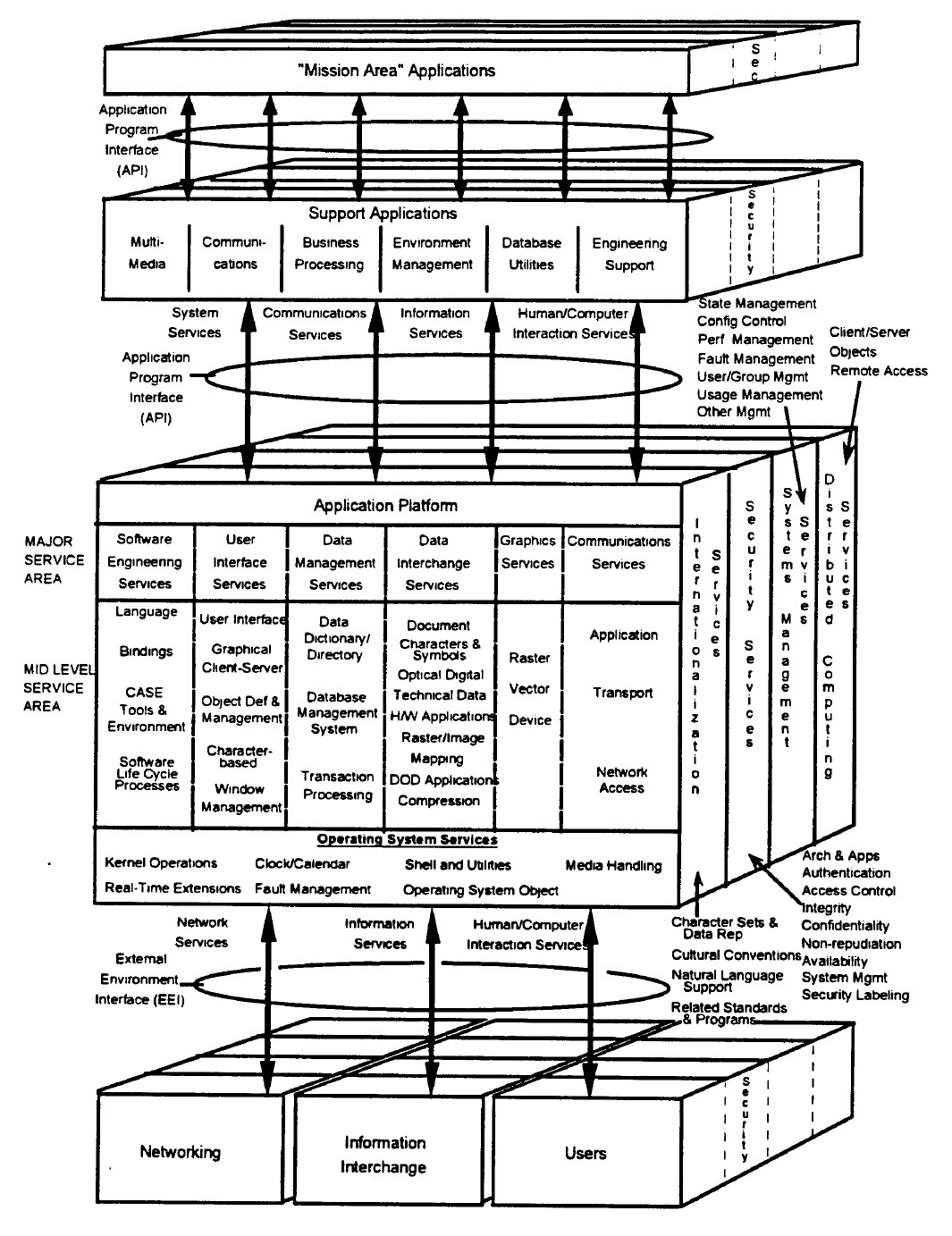
 The Application Portability Profile (APP) is an OSE profile designed for use by the U.S. Government. It covers a broad range of application software domains of interest to many Federal agencies, but it does not include every domain within the U.S. Government’s application inventory. The individual standards and specifications in the APP define data formats, interfaces, protocols, or a mix of these elements.
The services defined in the APP tend to fall into broad service areas. These service areas are:
* Operating system services (OS)
* Human/computer interface services (HCI)
* Data management services (DM)
* Data interchange services (DI)
* Software engineering services (SWE)
* Graphics services (GS)
* Network services (NS)
Each service area is defined in the following sections. The figure illustrates where each of these services areas relates to the OSE/RM. Assume that
The Application Portability Profile (APP) is an OSE profile designed for use by the U.S. Government. It covers a broad range of application software domains of interest to many Federal agencies, but it does not include every domain within the U.S. Government’s application inventory. The individual standards and specifications in the APP define data formats, interfaces, protocols, or a mix of these elements.
The services defined in the APP tend to fall into broad service areas. These service areas are:
* Operating system services (OS)
* Human/computer interface services (HCI)
* Data management services (DM)
* Data interchange services (DI)
* Software engineering services (SWE)
* Graphics services (GS)
* Network services (NS)
Each service area is defined in the following sections. The figure illustrates where each of these services areas relates to the OSE/RM. Assume that
 Basically, the open-system environment model is a basic building block of several technical reference models and technical architecture. A
Basically, the open-system environment model is a basic building block of several technical reference models and technical architecture. A
at acf.hhs.gov. Accessed 12 Dec 2008. A technical reference model can be defined as a taxonomy of services arranged according to a conceptual model, such as the Open System Environment model. The enumerated services are specific to those needed to support the technology computing style (e.g., distributed object computing) and the industry/business application needs (e.g., Human Services, financial).
 Open-system environment (OSE) reference model (RM) or ''OSE reference model'' (OSE/RM) is a 1990 reference model for enterprise architecture. It provides a
Open-system environment (OSE) reference model (RM) or ''OSE reference model'' (OSE/RM) is a 1990 reference model for enterprise architecture. It provides a framework
A framework is a generic term commonly referring to an essential supporting structure which other things are built on top of.
Framework may refer to:
Computing
* Application framework, used to implement the structure of an application for an op ...
for describing open system concepts and defining a lexicon of terms, that can be agreed upon generally by all interested parties.
This reference model is meant as an environment model, complementary to the POSIX
The Portable Operating System Interface (POSIX) is a family of standards specified by the IEEE Computer Society for maintaining compatibility between operating systems. POSIX defines both the system- and user-level application programming in ...
architecture for open systems. It offers an extensible framework that allows services, interfaces, protocols, and supporting data formats to be defined in terms of nonproprietary specifications that evolve through open (public), consensus-based forums. This reference model served in the 1990s as a basic building block of several technical reference models and technical architectures.
In 1996 this reference model was standardized in the ISO/IEC TR 14252 titled "Information technology -- Guide to the POSIX Open System Environment (OSE)".
History
The development of the open-system environment reference model started early 1990s by theNIST
The National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) is an agency of the United States Department of Commerce whose mission is to promote American innovation and industrial competitiveness. NIST's activities are organized into physical sci ...
as refinement of the POSIX
The Portable Operating System Interface (POSIX) is a family of standards specified by the IEEE Computer Society for maintaining compatibility between operating systems. POSIX defines both the system- and user-level application programming in ...
(Portable Operating System Interface) standard. POSIX is a standard for maintaining compatibility between operating systems, and addresses interoperation for communications, computing, and entertainment infrastructure. Its development started late 1980s by the POSIX Working Group 1003.0 of the Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers
The Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers (IEEE) is a 501(c)(3) professional association for electronic engineering and electrical engineering (and associated disciplines) with its corporate office in New York City and its operation ...
(IEEE).
The NIST hosted workshops and conducts other support activities to assist users in addressing open systems requirements, preparing for the use of new technology, and identifying the international, national, industry and other open specifications that are available for building open systems frameworks, such as the government's applications portability profile for the open-system environment.
NIST sponsors the semiannual Users' Forum on Application Portability Profile (APP) and Open System Environment (OSE) to exchange information and respond to NIST proposals regarding the evaluation and adoption of an integrated set of standards to support the APP and OSE. The quarterly Open Systems Environment Implementors' Workshop (OIW), co-sponsored by NIST and the Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers
The Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers (IEEE) is a 501(c)(3) professional association for electronic engineering and electrical engineering (and associated disciplines) with its corporate office in New York City and its operation ...
(IEEE) Computer Society, provides a public international technical forum for the timely development of implementation agreements based on emerging OSE standards.NIST Bulletin 1996. Accessed 13 Dec 2008.
OSE/RM topics
The open-system environment (OSE) forms an extensible framework that allows services, interfaces, protocols, and supporting data formats to be defined in terms of nonproprietary specifications that evolve through open (public), consensus-based forums. A selected suite of specifications that defines these interfaces, services, protocols, and data formats for a particular class or domain of applications is called a profile. Two types of elements are used in the model: entities consisting of the application software, application platform, and platform external environment; and interfaces including the application program interface and external environment interface.APP service areas
 The Application Portability Profile (APP) is an OSE profile designed for use by the U.S. Government. It covers a broad range of application software domains of interest to many Federal agencies, but it does not include every domain within the U.S. Government’s application inventory. The individual standards and specifications in the APP define data formats, interfaces, protocols, or a mix of these elements.
The services defined in the APP tend to fall into broad service areas. These service areas are:
* Operating system services (OS)
* Human/computer interface services (HCI)
* Data management services (DM)
* Data interchange services (DI)
* Software engineering services (SWE)
* Graphics services (GS)
* Network services (NS)
Each service area is defined in the following sections. The figure illustrates where each of these services areas relates to the OSE/RM. Assume that
The Application Portability Profile (APP) is an OSE profile designed for use by the U.S. Government. It covers a broad range of application software domains of interest to many Federal agencies, but it does not include every domain within the U.S. Government’s application inventory. The individual standards and specifications in the APP define data formats, interfaces, protocols, or a mix of these elements.
The services defined in the APP tend to fall into broad service areas. These service areas are:
* Operating system services (OS)
* Human/computer interface services (HCI)
* Data management services (DM)
* Data interchange services (DI)
* Software engineering services (SWE)
* Graphics services (GS)
* Network services (NS)
Each service area is defined in the following sections. The figure illustrates where each of these services areas relates to the OSE/RM. Assume that software engineering
Software engineering is a systematic engineering approach to software development.
A software engineer is a person who applies the principles of software engineering to design, develop, maintain, test, and evaluate computer software. The term '' ...
services are applicable in all areas. Each of the APP service areas addresses specific components around which interface, data format, or protocol specifications have been or will be defined. Security and management services are common to all of the
service areas and pervade these areas in one or more forms.
Classes of interfaces
There are two classes of interfaces in the OSE reference model: the application program interface and the external environment interface: * ''Application programming interface
An application programming interface (API) is a way for two or more computer programs to communicate with each other. It is a type of software interface, offering a service to other pieces of software. A document or standard that describes how ...
(API)'' : The API is the interface between the application software and the application platform. Its primary function is to support portability of application software. An API is categorized in accordance with the types of service accessible via that API. There are four types of API services in the OSE/RM:
** Human/computer interface services
** Information interchange services
** Communication services
** Internal system services
* ''External environment interface (EEI)'' : The EEI is the interface that supports information transfer between the application platform and the external environment, and between applications executing on the same platform. Consisting chiefly of protocols and supporting data formats, the EEI supports interoperability to a large extent. An EEI is categorized in accordance with the type of information transfer services provided.
OSE profile
A profile consists of a selected list of standards and other specifications that define a complement of services made available to applications in a specific domain. Examples of domains might include a workstation environment, an embedded process control environment, a distributed environment, a transaction processing environment, or an office automation environment, to name a few. Each of these environments has a different cross-section of service requirements that can be specified independently from the others. Each service, however, is defined in a standard form across all environments. An OSE profile is composed of a selected list of open (public), consensus-based standards and specifications that define services in the OSE/RM. Restricting a profile to a specific domain or group of domains that are of interest to an individual organization results in the definition of an organizational profile.OSE reference model entities
The three classes of OSE reference model entities are described as follows: * ''Application software'' : Within the context of the OSE Reference Model, the application software includes data, documentation, and training, as well as programs. * ''Application platform'' : The application platform is composed of the collection of hardware and software components that provide the generic application and system services. * ''Platform external environment'' : The platform external environment consists of those system elements that are external to the application software and the application platform (e.g., services provided by other platforms or peripheral devices).Types of information transfer services
There are three types of information transfer services. These are transfer services to and from: * Human users * External data stores * Other application platforms In its simplest form, the OSE/RM illustrates a straightforward user-supplier relationship: the application software is the user of services and the application platform/ external environment entities are the suppliers. The API and EEI define the services that are provided.Applications
 Basically, the open-system environment model is a basic building block of several technical reference models and technical architecture. A
Basically, the open-system environment model is a basic building block of several technical reference models and technical architecture. A technical architecture
Information technology architecture is the process of development of methodical information technology specifications, models and guidelines, using a variety of information technology notations, for example Unified Modeling Language (UML), within ...
identifies and describes the types of applications, platforms, and external entities; their interfaces; and their services; as well as the context within which the entities interoperate.
A technical architecture is based on:
* a Technical Reference Model (TRM); and
* the selected standards that further describe the TRM elements (the profile).
The technical architecture is the basis for selecting and implementing the infrastructure to establish the target architecture.Consolidated Definitions and Referencesat acf.hhs.gov. Accessed 12 Dec 2008. A technical reference model can be defined as a taxonomy of services arranged according to a conceptual model, such as the Open System Environment model. The enumerated services are specific to those needed to support the technology computing style (e.g., distributed object computing) and the industry/business application needs (e.g., Human Services, financial).
See also
* Enterprise architecture framework * Federal enterprise architecture * GERAM * TAFIM *TOGAF
The Open Group Architecture Framework (TOGAF) is the most used framework for enterprise architecture as of 2020 that provides an approach for designing, planning, implementing, and governing an enterprise information technology architecture. TOG ...
References
Further reading
{{Commonscat, Open System Environment Reference Model * Department of Defense (1996). ''Technical Architecture Framework for Information Management. Vol. 2, Technical Reference Model''. * Defense Information Systems Agency (2001). ''DoD Technical Reference Model, Version 2.0,'' April 9, 2001. * Gary Fisher (1993). ''Application Portability Profile (APP) : The U.S. Government’s Open System Environment Profile OSE/1 Version 2.0''. NIST Special Publication 500-210, June 1993. * IEEE P1003.22 ''Draft Guide for POSIX Open Systems Environment—A Security Framework'' Reference models Enterprise modelling