Old Prussians on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Old Prussians, Baltic Prussians or simply Prussians ( Old Prussian: ''prūsai''; german: Pruzzen or ''Prußen''; la, Pruteni; lv, prūši; lt, prūsai; pl, Prusowie; csb, Prësowié) were an indigenous tribe among the
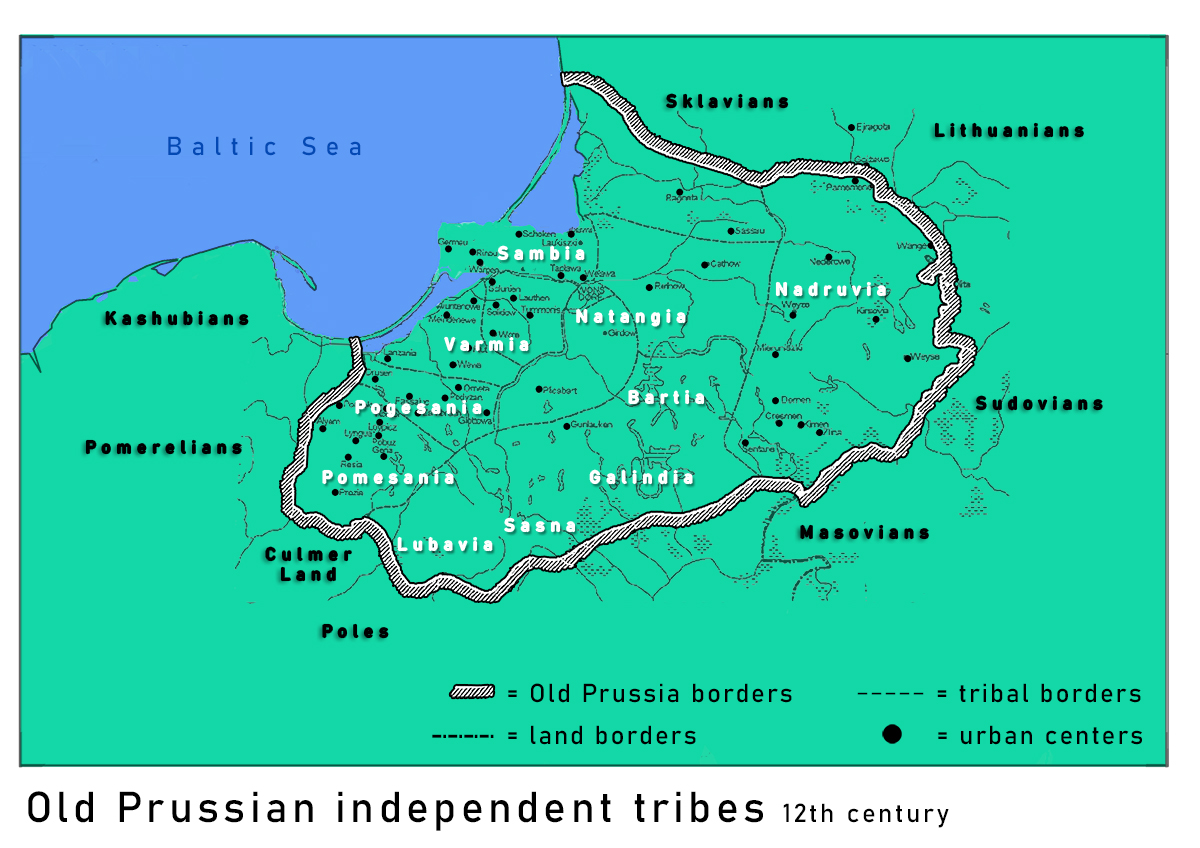
 The original Old Prussian settlement area in the western Baltics, as well as that of the eastern Balts, was much larger than in historical times. The archaeological documentation and associated finds confirm uninterrupted presence from the
The original Old Prussian settlement area in the western Baltics, as well as that of the eastern Balts, was much larger than in historical times. The archaeological documentation and associated finds confirm uninterrupted presence from the
English translation
describes a ninth century voyage by traveller and trader
 Characterized as a humble people, who dressed plainly, the Old Prussians were ''distinguished for their valor and great bodily strength''. They generally rejected luxury, yet were very hospitable, and enjoyed celebrating and drinking excessively, usually
Characterized as a humble people, who dressed plainly, the Old Prussians were ''distinguished for their valor and great bodily strength''. They generally rejected luxury, yet were very hospitable, and enjoyed celebrating and drinking excessively, usually
 The Stone babas, found all over Old Prussia, have for centuries caused considerable speculation and dissent among scholars. Beginning with a lack of confirmation about their original location and context, all subsequent questions on their age, the chronology of the objects, an exact definition of their function, their provenance, pointing to which cultural influence have not been addressed until the late 19th century. A majority of past and present researchers agree the babas were created between the 8th and 13th centuries...as a ''result of a long cultural process among the population of early Iron Age area of the south-eastern Baltic coast, which was affected by both the early traditions of the local craft and inspirations from countries already under
The Stone babas, found all over Old Prussia, have for centuries caused considerable speculation and dissent among scholars. Beginning with a lack of confirmation about their original location and context, all subsequent questions on their age, the chronology of the objects, an exact definition of their function, their provenance, pointing to which cultural influence have not been addressed until the late 19th century. A majority of past and present researchers agree the babas were created between the 8th and 13th centuries...as a ''result of a long cultural process among the population of early Iron Age area of the south-eastern Baltic coast, which was affected by both the early traditions of the local craft and inspirations from countries already under
 ''"Because they did not know God, therefore, in their error, they worshipped every creature as divine, namely the sun, moon and stars, thunder, birds, even four-legged animals, even the toad. They also had forests, fields and bodies of water, which they held so sacred that they neither chopped wood nor dared to cultivate fields or fish in them. "'' –
''"Because they did not know God, therefore, in their error, they worshipped every creature as divine, namely the sun, moon and stars, thunder, birds, even four-legged animals, even the toad. They also had forests, fields and bodies of water, which they held so sacred that they neither chopped wood nor dared to cultivate fields or fish in them. "'' –

 Numerous knights from throughout Catholic Europe joined in the
Numerous knights from throughout Catholic Europe joined in the
Chronica terrae Prussiae
Lecture about Prussians & Their Mythology
The Old Prussians: the Lost Relatives of Latvians and Lithuanians
Milestones of Baltic Prussian History
Modern Prusai-Communities' Map of the land of Old Prussians
Dictionary of reconstructed Prussian language
Comparative Phonology and Morphology of the Baltic Languages
{{Authority control People from Prussia proper Historical ethnic groups of Europe Indigenous peoples of Europe Historical Baltic peoples
Baltic
Baltic may refer to:
Peoples and languages
*Baltic languages, a subfamily of Indo-European languages, including Lithuanian, Latvian and extinct Old Prussian
*Balts (or Baltic peoples), ethnic groups speaking the Baltic languages and/or originatin ...
peoples that inhabited the region of Prussia, at the south-eastern shore of the Baltic Sea
The Baltic Sea is an arm of the Atlantic Ocean that is enclosed by Denmark, Estonia, Finland, Germany, Latvia, Lithuania, Poland, Russia, Sweden and the North and Central European Plain.
The sea stretches from 53°N to 66°N latitude and from ...
between the Vistula Lagoon
The Vistula Lagoon ( pl, Zalew Wiślany; russian: Калининградский залив, transliterated: ''Kaliningradskiy Zaliv''; german: Frisches Haff; lt, Aistmarės) is a brackish water lagoon on the Baltic Sea roughly 56 miles (90 ...
to the west and the Curonian Lagoon
The Curonian Lagoon (or Bay, Gulf; russian: Куршский залив, lt, Kuršių marios, pl, Zalew Kuroński, german: Kurisches Haff, lv, Kuršu joma) is a freshwater lagoon separated from the Baltic Sea by the Curonian Spit. Its surfac ...
to the east. The Old Prussians, who spoke an Indo-European
The Indo-European languages are a language family native to the overwhelming majority of Europe, the Iranian plateau, and the northern Indian subcontinent. Some European languages of this family, English, French, Portuguese, Russian, Du ...
language now known as Old Prussian and worshipped pre-Christian deities
A deity or god is a supernatural being who is considered divine or sacred. The ''Oxford Dictionary of English'' defines deity as a god or goddess, or anything revered as divine. C. Scott Littleton defines a deity as "a being with powers greater ...
, lent their name, despite very few commonalities, to the later, predominantly Low German-speaking inhabitants of the region.
The duchy of the Polans under Mieszko I
Mieszko I (; – 25 May 992) was the first ruler of Poland and the founder of the first independent Polish state, the Duchy of Poland. His reign stretched from 960 to his death and he was a member of the Piast dynasty, a son of Siemomysł and ...
, which was the predecessor of the Kingdom of Poland, first attempted to conquer and baptize the Baltic tribes during the 10th century, but repeatedly encountered strong resistance. Not until the 13th century were the Old Prussians subjugated and their lands conquered by the Teutonic Order
The Order of Brothers of the German House of Saint Mary in Jerusalem, commonly known as the Teutonic Order, is a Catholic religious institution founded as a military society in Acre, Kingdom of Jerusalem. It was formed to aid Christians on ...
. The remaining Old Prussians were assimilated during the following two centuries. The old Prussian language, largely undocumented, was effectively extinct by the 17th century.
The original territory of the Old Prussians prior to the first clashes with the Polans consisted of central and southern West
West or Occident is one of the four cardinal directions or points of the compass. It is the opposite direction from east and is the direction in which the Sun sets on the Earth.
Etymology
The word "west" is a Germanic word passed into some ...
and East Prussia
East Prussia ; german: Ostpreißen, label= Low Prussian; pl, Prusy Wschodnie; lt, Rytų Prūsija was a province of the Kingdom of Prussia from 1773 to 1829 and again from 1878 (with the Kingdom itself being part of the German Empire from 187 ...
, equivalent to parts of the modern areas of the Pomeranian Voivodeship
Pomeranian Voivodeship, Pomorskie Region, or Pomerania Province ( Polish: ''Województwo pomorskie'' ; ( Kashubian: ''Pòmòrsczé wòjewództwò'' ), is a voivodeship, or province, in northwestern Poland. The provincial capital is Gdańsk.
Th ...
and Warmian-Masurian Voivodeship
Warmian-Masurian Voivodeship or Warmia-Masuria Province or Warmia-Mazury Province (in pl, Województwo warmińsko-mazurskie, is a voivodeship (province) in northeastern Poland. Its capital and largest city is Olsztyn. The voivodeship has an ar ...
in Poland
Poland, officially the Republic of Poland, is a country in Central Europe. It is divided into 16 administrative provinces called voivodeships, covering an area of . Poland has a population of over 38 million and is the fifth-most populou ...
, the Kaliningrad Oblast
Kaliningrad Oblast (russian: Калинингра́дская о́бласть, translit=Kaliningradskaya oblast') is the westernmost federal subject of Russia. It is a semi-exclave situated on the Baltic Sea. The largest city and admin ...
in Russia
Russia (, , ), or the Russian Federation, is a transcontinental country spanning Eastern Europe and Northern Asia. It is the largest country in the world, with its internationally recognised territory covering , and encompassing one-ei ...
and the southern Klaipėda Region
The Klaipėda Region ( lt, Klaipėdos kraštas) or Memel Territory (german: Memelland or ''Memelgebiet'') was defined by the 1919 Treaty of Versailles in 1920 and refers to the northernmost part of the German province of East Prussia, when as ...
in Lithuania
Lithuania (; lt, Lietuva ), officially the Republic of Lithuania ( lt, Lietuvos Respublika, links=no ), is a country in the Baltic region of Europe. It is one of three Baltic states and lies on the eastern shore of the Baltic Sea. Lithuania ...
. The territory was also inhabited by Scalovians, a tribe related to the Prussians, Curonians
:''The Kursenieki are also sometimes known as Curonians.''
The Curonians or Kurs ( lv, kurši; lt, kuršiai; german: Kuren; non, Kúrir; orv, кърсь) were a Baltic tribe living on the shores of the Baltic Sea in what are now the western ...
and Eastern Balts.
Etymology
The name of the Old Prussians has its origin intoponymy
Toponymy, toponymics, or toponomastics is the study of ''toponyms'' ( proper names of places, also known as place names and geographic names), including their origins, meanings, usage and types. Toponym is the general term for a proper name of ...
, as the word ''Prūsas'' (a Prussian) can be derived from the term for a body of water, an understandable convention in a coastal region dotted with thousands of lakes, streams and swamps ( Masuria). To the south, the terrain runs into the vast wetlands of the Pripet Marshes
__NOTOC__
The Pinsk Marshes ( be, Пінскія балоты, ''Pinskiya baloty''), also known as the Pripet Marshes ( be, Прыпяцкія балоты, ''Prypiackija baloty''), the Polesie Marshes, and the Rokitno Marshes, are a vast natural ...
at the headwaters of the Dnieper River
}
The Dnieper () or Dnipro (); , ; . is one of the major transboundary rivers of Europe, rising in the Valdai Hills near Smolensk, Russia, before flowing through Belarus and Ukraine to the Black Sea. It is the longest river of Ukraine an ...
, which has been an effective natural barrier throughout the millennia.
Writing in 98 CE, Roman historian Tacitus
Publius Cornelius Tacitus, known simply as Tacitus ( , ; – ), was a Roman historian and politician. Tacitus is widely regarded as one of the greatest Roman historians by modern scholars.
The surviving portions of his two major works—the ...
described the pagan '' Aesti'' who lived somewhere by the Baltic Sea coast and east of the Vistula estuary. It has been suggested that the name ''Aesti'' could be etymologically related to the modern toponym Estonians
Estonians or Estonian people ( et, eestlased) are a Finnic ethnic group native to Estonia who speak the Estonian language.
The Estonian language is spoken as the first language by the vast majority of Estonians; it is closely related to othe ...
. On the other hand, the Old Prussian and modern Lithuanian names for localities, such as the Vistula Lagoon
The Vistula Lagoon ( pl, Zalew Wiślany; russian: Калининградский залив, transliterated: ''Kaliningradskiy Zaliv''; german: Frisches Haff; lt, Aistmarės) is a brackish water lagoon on the Baltic Sea roughly 56 miles (90 ...
, ''Aīstinmari'' and ''Aistmarės'', respectively, also appear to derive from ''Aesti'' and ''mari'' ("lagoon
A lagoon is a shallow body of water separated from a larger body of water by a narrow landform, such as reefs, barrier islands, barrier peninsulas, or isthmuses. Lagoons are commonly divided into '' coastal lagoons'' (or ''barrier lagoons ...
" or "fresh-water bay"), which suggests that the area around the lagoon had links with the ''Aesti''.
The original settlers tended to name their assets after surrounding localities (streams, lakes, seas, forests, etc). The clan or tribal entity into which their descendants later were organized continued to use the names. This source is perhaps the one used in the very name of ''Prusa'' (Prussia), for which an earlier ''Brus-'' is found in the map of the Bavarian Geographer. In Tacitus' ''Germania
Germania ( ; ), also called Magna Germania (English: ''Great Germania''), Germania Libera (English: ''Free Germania''), or Germanic Barbaricum to distinguish it from the Roman province of the same name, was a large historical region in north-c ...
'', the Lugii
The Lugii (or ''Lugi'', ''Lygii'', ''Ligii'', ''Lugiones'', ''Lygians'', ''Ligians'', ''Lugians'', or ''Lougoi'') were a large tribal confederation mentioned by Roman authors living in ca. 100 BC–300 AD in Central Europe, north of the Sude ...
Buri are mentioned living within the eastern range of the Germans. Lugi may descend from Pokorny's ''*leug-'' (2), "black, swamp" (Page 686), while ''Buri'' is perhaps the "Prussian" root.
The name of ''Pameddi'', the ( Pomesania) tribe is derived from the words ''pa'' ("by" or "near") and ''meddin'' ("forest") or ''meddu'' ("honey"), which can be traced to the Proto-Indo-European
Proto-Indo-European (PIE) is the reconstructed common ancestor of the Indo-European language family. Its proposed features have been derived by linguistic reconstruction from documented Indo-European languages. No direct record of Proto-Indo ...
root ''*medhu-''. Nadruvia may be a compound of the words ''na'' ("by" or "on") and ''drawē'' ("wood") or ''nad'' ("above") and the root ''*reu-'' ("flow" or "river"). The name of the Bartians, a Prussian tribe, and the name of the Bārta river in Latvia are possibly cognate
In historical linguistics, cognates or lexical cognates are sets of words in different languages that have been inherited in direct descent from an etymological ancestor in a common parent language. Because language change can have radical ef ...
s.
In the second century AD, the geographer Claudius Ptolemy
Claudius Ptolemy (; grc-gre, Πτολεμαῖος, ; la, Claudius Ptolemaeus; AD) was a mathematician, astronomer, astrologer, geographer, and music theorist, who wrote about a dozen scientific treatises, three of which were of importanc ...
listed some ''Borusci'' living in European Sarmatia (in his ''Eighth Map of Europe''), which was separated from Germania by the ''Vistula Flumen''. His map is very confusing in that region, but the Borusci seem further east than the Prussians, which would have been under the ''Gythones'' (Goths
The Goths ( got, 𐌲𐌿𐍄𐌸𐌹𐌿𐌳𐌰, translit=''Gutþiuda''; la, Gothi, grc-gre, Γότθοι, Gótthoi) were a Germanic people who played a major role in the fall of the Western Roman Empire and the emergence of medieval Euro ...
) at the mouth of the Vistula. The '' Aesti'' recorded by Tacitus
Publius Cornelius Tacitus, known simply as Tacitus ( , ; – ), was a Roman historian and politician. Tacitus is widely regarded as one of the greatest Roman historians by modern scholars.
The surviving portions of his two major works—the ...
, were 450 years later recorded by Jordanes
Jordanes (), also written as Jordanis or Jornandes, was a 6th-century Eastern Roman bureaucrat widely believed to be of Gothic descent who became a historian later in life. Late in life he wrote two works, one on Roman history ('' Romana'') an ...
as part of the Gothic Empire.
Organization

 The original Old Prussian settlement area in the western Baltics, as well as that of the eastern Balts, was much larger than in historical times. The archaeological documentation and associated finds confirm uninterrupted presence from the
The original Old Prussian settlement area in the western Baltics, as well as that of the eastern Balts, was much larger than in historical times. The archaeological documentation and associated finds confirm uninterrupted presence from the Iron Age
The Iron Age is the final epoch of the three-age division of the prehistory and protohistory of humanity. It was preceded by the Stone Age ( Paleolithic, Mesolithic, Neolithic) and the Bronze Age ( Chalcolithic). The concept has been mostly ...
(fifth century BC) to the successive conquest by Slavic tribes, beginning in the Migration Period
The Migration Period was a period in European history marked by large-scale migrations that saw the fall of the Western Roman Empire and subsequent settlement of its former territories by various tribes, and the establishment of the post-Roma ...
.
Permanent recorded Baltic
Baltic may refer to:
Peoples and languages
*Baltic languages, a subfamily of Indo-European languages, including Lithuanian, Latvian and extinct Old Prussian
*Balts (or Baltic peoples), ethnic groups speaking the Baltic languages and/or originatin ...
history begins in the 10th century with the failed Christianisation by Adalbert of Prague (997 CE.), the first conquest attempts at the expense of the Old Prussians by the duchy of the Polans under Mieszko I
Mieszko I (; – 25 May 992) was the first ruler of Poland and the founder of the first independent Polish state, the Duchy of Poland. His reign stretched from 960 to his death and he was a member of the Piast dynasty, a son of Siemomysł and ...
and the Duchy of Greater Poland
The Duchy of Greater Poland was a district principality in Greater Poland that was a fiefdom of the Kingdom of Poland. It was formed in 1138 from the territories of the Kingdom of Poland, following its fragmentation started by the testament of ...
under his son Bolesław, as a number of border areas were eventually lost.
Around the year 1,000 CE. to the West of the Old Prussians lived the Kashubians
The Kashubians ( csb, Kaszëbi; pl, Kaszubi; german: Kaschuben), also known as Cassubians or Kashubs, are a Lechitic ( West Slavic) ethnic group native to the historical region of Pomerania, including its eastern part called Pomerelia, in nor ...
and Pomeranians, the Poles
Poles,, ; singular masculine: ''Polak'', singular feminine: ''Polka'' or Polish people, are a West Slavic nation and ethnic group, who share a common history, culture, the Polish language and are identified with the country of Poland in ...
to the south, the Sudovians
Yotvingians (also called: Sudovians, Jatvians, or Jatvingians; Yotvingian: ''Jotvingai''; lt, Jotvingiai, ; lv, Jātvingi; pl, Jaćwingowie, be, Яцвягі, ger, Sudauer) were a Western Baltic people who were closely tied to the Old Prus ...
(sometimes considered a separate people, other times regarded as a Prussian tribe) to the east and south-east, the Skalvians to the north, and the Lithuanians
Lithuanians ( lt, lietuviai) are a Baltic ethnic group. They are native to Lithuania, where they number around 2,378,118 people. Another million or two make up the Lithuanian diaspora, largely found in countries such as the United States, Unite ...
to the northeast.
The smallest social unit in Baltic lands was the ''laūks'', a word attested in Old Prussian as "field", which were small family oriented settlements, households and the surrounding fields, only separated from one another by uninhabited areas of forest, swamp and marsh. The word appears as a segment in Baltic settlement names, especially in Curonian,It varies in spellings, including ''-laukas'', ''-laukis'', and ''lauks''. and is found in Old Prussian placenames such as in ''Stablack'', from ''stabs'' (stone) + ''laūks'' (field, thus ''stone field''). The plural is not attested in Old Prussian, but the Lithuanian plural of ''laukas'' ("field") is ''laukai''.
A ''laūks'' was also formed by a group of farms, that shared economic interests and a desire for safety, ruled by a male head of the family and centred on strongholds or hill forts. The supreme power resided in general gatherings of all adult males, who discussed important matters concerning the community and elected the leader and chief; the leader was responsible for the supervision of the everyday matters, while the chief (the ''rikīs'') was in charge of the road and watchtower building, and border defense, undertaken by ''Vidivarii The Vidivarii are described by Jordanes in his Getica as a melting pot of tribes who in the mid-6th century lived at the lower Vistula: Mayke de Jong, Frans Theuws, Carine van Rhijn, ''Topographies of Power in the Early Middle Ages'', BRILL, 2001, p ...
''.
The head of a household was the ''buttataws'' (literally, the ''house father'', from ''buttan'', meaning ''home'', and ''taws'', meaning ''father''). Larger political and territorial organisations, called ''terrula'' in Latin (a small land), existed in the early 13th century in the territories which later comprised Prussia, Latvia and Lithuania and centred on strongholds or hill forts. Such a political territorial unit covered up to and could have up to 2,000 inhabitants. They were known as ''pulka'', comprising a dozen or so laukses.
Because the Baltic tribes inhabiting Prussia never formed a common political and territorial organisation, they had no reason to adopt a common ethnic or national name. Instead they used the name of the region from which they came — Galindians, Sambians, Bartians, Nadruvians
The Nadruvians were a now-extinct Prussian tribe. They lived in Nadruvia (alternative spellings include: ''Nadruva'', ''Nadrowite'', ''Nadrovia'', ''Nadrauen'', ''Nadravia'', ''Nadrow'' and ''Nadra''), a large territory in northernmost Prussia. Th ...
, Natangians, Scalovians, Sudovians
Yotvingians (also called: Sudovians, Jatvians, or Jatvingians; Yotvingian: ''Jotvingai''; lt, Jotvingiai, ; lv, Jātvingi; pl, Jaćwingowie, be, Яцвягі, ger, Sudauer) were a Western Baltic people who were closely tied to the Old Prus ...
, etc. It is not known when and how the first general names came into being. This lack of unity weakened them severely, similar to the condition of Germany
Germany,, officially the Federal Republic of Germany, is a country in Central Europe. It is the second most populous country in Europe after Russia, and the most populous member state of the European Union. Germany is situated betwee ...
during the Middle Ages
In the history of Europe, the Middle Ages or medieval period lasted approximately from the late 5th to the late 15th centuries, similar to the post-classical period of global history. It began with the fall of the Western Roman Empire ...
.
According to Jan Długosz
Jan Długosz (; 1 December 1415 – 19 May 1480), also known in Latin as Johannes Longinus, was a Polish priest, chronicler, diplomat, soldier, and secretary to Bishop Zbigniew Oleśnicki of Kraków. He is considered Poland's first histo ...
, the Prussians, Samogitians
Samogitians ( Samogitian: ''žemaitē'', lt, žemaičiai, lv, žemaiši) are an ethnographic group of Lithuanians of the Samogitia region, an ethnographic region of Lithuania. Many speak the Samogitian language, which in Lithuania is mostly co ...
, and Lithuanians
Lithuanians ( lt, lietuviai) are a Baltic ethnic group. They are native to Lithuania, where they number around 2,378,118 people. Another million or two make up the Lithuanian diaspora, largely found in countries such as the United States, Unite ...
were the same tribe.
The Prussian tribal structure is well attested in the '' Chronicon terrae Prussiae'' of contemporary author Peter of Dusburg Peter of Dusburg (german: Peter von Dusburg; la, Petrus de Dusburg; died after 1326), also known as Peter of Duisburg, was a Priest-Brother and chronicler of the Teutonic Knights. He is known for writing the ''Chronicon terrae Prussiae'', which des ...
, a chronicler of the Teutonic Order
The Order of Brothers of the German House of Saint Mary in Jerusalem, commonly known as the Teutonic Order, is a Catholic religious institution founded as a military society in Acre, Kingdom of Jerusalem. It was formed to aid Christians on ...
. The work is dated to 1326. He lists eleven lands and ten tribes, which were named on a geographical basis. These were:
Culture, religion and customs
The Voyages of Ohthere and Wulfstan (inAnglo-Saxon
The Anglo-Saxons were a cultural group who inhabited England in the Early Middle Ages. They traced their origins to settlers who came to Britain from mainland Europe in the 5th century. However, the ethnogenesis of the Anglo-Saxons happened wit ...
)English translation
describes a ninth century voyage by traveller and trader
Wulfstan of Hedeby
Wulfstan of Hedeby was a late ninth century traveller and trader. His travel accounts, as well as those of another trader, Ohthere of Hålogaland, were included in the '' Old English Orosius''. It is unclear if Wulfstan was English or indeed if ...
to the land of the Old Prussians. He observes their funeral
A funeral is a ceremony connected with the final disposition of a corpse, such as a burial or cremation, with the attendant observances. Funerary customs comprise the complex of beliefs and practices used by a culture to remember and respect ...
customs.
Customs
 Characterized as a humble people, who dressed plainly, the Old Prussians were ''distinguished for their valor and great bodily strength''. They generally rejected luxury, yet were very hospitable, and enjoyed celebrating and drinking excessively, usually
Characterized as a humble people, who dressed plainly, the Old Prussians were ''distinguished for their valor and great bodily strength''. They generally rejected luxury, yet were very hospitable, and enjoyed celebrating and drinking excessively, usually mead
Mead () is an alcoholic beverage made by fermenting honey mixed with water, and sometimes with added ingredients such as fruits, spices, grains, or hops. The alcoholic content ranges from about 3.5% ABV to more than 20%. The defining characte ...
. Wulfstan of Hedeby
Wulfstan of Hedeby was a late ninth century traveller and trader. His travel accounts, as well as those of another trader, Ohthere of Hålogaland, were included in the '' Old English Orosius''. It is unclear if Wulfstan was English or indeed if ...
, who visited the trading town of Truso at the Vistula Lagoon
The Vistula Lagoon ( pl, Zalew Wiślany; russian: Калининградский залив, transliterated: ''Kaliningradskiy Zaliv''; german: Frisches Haff; lt, Aistmarės) is a brackish water lagoon on the Baltic Sea roughly 56 miles (90 ...
, observed that wealthy people drank fermented mare's milk kumis
''Kumis'' (also spelled ''kumiss'' or ''koumiss'' or ''kumys'', see other transliterations and cognate words below under terminology and etymology – otk, airag kk, қымыз, ''qymyz'') mn, айраг, ''ääryg'') is a fermented dairy ...
instead of mead
Mead () is an alcoholic beverage made by fermenting honey mixed with water, and sometimes with added ingredients such as fruits, spices, grains, or hops. The alcoholic content ranges from about 3.5% ABV to more than 20%. The defining characte ...
. According to Adam of Bremen, the Samians are said to have consumed horse blood as well as horse milk. He also mentions that horse meat was eaten.
Women held no powerful positions among the Old Prussians and, according to Peter von Dusburg, were treated like servants, forbidden to share the husband's table. Commercial marriage was widespread and after the husband's death, the widow fell to the son, like other inheritance. In addition, polygyny (up to three wives) was widespread. Adultery was a serious crime, punishable with death. After the submission, commercial marriage and polygyny were forbidden.
Burial customs
According to archaeological evidence, pre-Christian burial customs changed over the centuries. During the Iron Age (5th century BC – 1st century AD), the western Baltickurgan
A kurgan is a type of tumulus constructed over a grave, often characterized by containing a single human body along with grave vessels, weapons and horses. Originally in use on the Pontic–Caspian steppe, kurgans spread into much of Central As ...
and barrow culture was widespread among the Old Prussians. It was then that cremation in urns appeared. Grave mounds were raised over stone cells for up to 30 urns, or stone boxes for the urns were buried in Bronze Age
The Bronze Age is a historic period, lasting approximately from 3300 BC to 1200 BC, characterized by the use of bronze, the presence of writing in some areas, and other early features of urban civilization. The Bronze Age is the second pri ...
style barrows.
During the early phase of imperial Rome, shallow graves appeared in which the corpse was buried in tree coffins. Cremation with urns spread from the third century onwards. Except for the Samians and Sudauers, where shallow grave fields existed until Christianization, cremation pits without urns increasingly became the only form of burials among the Prussians. However, different forms of burial could occur side by side at the same time.
Stone babas
Christian
Christians () are people who follow or adhere to Christianity, a monotheistic Abrahamic religion based on the life and teachings of Jesus Christ. The words ''Christ'' and ''Christian'' derive from the Koine Greek title ''Christós'' (Χρι� ...
influence.'' icref name=baba>
Old Prussian religion
 ''"Because they did not know God, therefore, in their error, they worshipped every creature as divine, namely the sun, moon and stars, thunder, birds, even four-legged animals, even the toad. They also had forests, fields and bodies of water, which they held so sacred that they neither chopped wood nor dared to cultivate fields or fish in them. "'' –
''"Because they did not know God, therefore, in their error, they worshipped every creature as divine, namely the sun, moon and stars, thunder, birds, even four-legged animals, even the toad. They also had forests, fields and bodies of water, which they held so sacred that they neither chopped wood nor dared to cultivate fields or fish in them. "'' – Peter of Dusburg Peter of Dusburg (german: Peter von Dusburg; la, Petrus de Dusburg; died after 1326), also known as Peter of Duisburg, was a Priest-Brother and chronicler of the Teutonic Knights. He is known for writing the ''Chronicon terrae Prussiae'', which des ...
: Chronicon terrae Prussiae III,5 ,53
Baltic paganism has been described as a form of ''polydoxy'' – a belief in the sacredness of all-natural forces and phenomena, not personified but possess their own spirits and magical powers. Practically, the world is inhabited by a limitless number of spirits and demons that includes a belief in the afterlife, the soul and worship of ancestors characterised by specific cults and their associated rituals. Other authors have argued for a well developed, sophisticated Old Prussian polytheism with a clearly defined pantheon of gods.
The highest priest ''Kriwe-Kriwajto
''Kriwe Kriwaito'' ( lv, krīvu krīvs, lt, krivių krivaitis) or simply ''Kriwe'' ( lv, krīvs, lt, krivis) was the chief priest in the Baltic mythology. Known primarily from the dubious 16th-century writings of Simon Grunau, the concept of ''k ...
'' was to be in permanent connection with the spirits of the dead ancestors. He lived in a sacred grove, the ''Romove'', a place off limit for anyone but elite clergy. Each district was headed by its ''Kriwe'', who also served as lawgiver and judge. The ''Kriwe-Kriwajto's'' next in rank, the ''Siggonen'' were expected to maintain the healthy spiritual connection with natural sacred sites, like springs and trees. The ''Wurskaiten'' – priests of lower rank – were supposed to superintend rites and ceremonies.
Christianisation
With the submission to theTeutonic Order
The Order of Brothers of the German House of Saint Mary in Jerusalem, commonly known as the Teutonic Order, is a Catholic religious institution founded as a military society in Acre, Kingdom of Jerusalem. It was formed to aid Christians on ...
in 1231, the Old Prussians were Christianised
Christianization ( or Christianisation) is to make Christian; to imbue with Christian principles; to become Christian. It can apply to the conversion of an individual, a practice, a place or a whole society. It began in the Roman Empire, conti ...
. How long the old paganism
Paganism (from classical Latin ''pāgānus'' "rural", "rustic", later "civilian") is a term first used in the fourth century by early Christians for people in the Roman Empire who practiced polytheism, or ethnic religions other than Judaism. I ...
lived on cannot be inferred from the sources. Pagan customs are said to have lasted the longest with the remote Sudauers. In the 16th century, the so-called Sudovian Book (''Sudauerbüchlein'') was created, which described a list of gods, "pagan" festivals and goat sanctification. However, researchers argue that this little book misinterpreted traditional folk customs as 'pagan' in the context of the Reformation
The Reformation (alternatively named the Protestant Reformation or the European Reformation) was a major movement within Western Christianity in 16th-century Europe that posed a religious and political challenge to the Catholic Church and in ...
.
History

Cassiodorus
Magnus Aurelius Cassiodorus Senator (c. 485 – c. 585), commonly known as Cassiodorus (), was a Roman statesman, renowned scholar of antiquity, and writer serving in the administration of Theodoric the Great, king of the Ostrogoths. ''Senator'' ...
' ''Variae'', published in 537, contains a letter written by Cassiodorus in the name of Theodoric the Great
Theodoric (or Theoderic) the Great (454 – 30 August 526), also called Theodoric the Amal ( got, , *Þiudareiks; Greek: , romanized: ; Latin: ), was king of the Ostrogoths (471–526), and ruler of the independent Ostrogothic Kingdom of Italy ...
, addressed to the ''Aesti'':
The Old Prussians are called ''Brus'' by the Bavarian Geographer in the ninth century.
More extensive mention of the Old Prussians in historical sources is in connection with Adalbert of Prague, who was sent by Bolesław I of Poland. Adalbert was slain in 997 during a missionary effort to Christianize
Christianization ( or Christianisation) is to make Christian; to imbue with Christian principles; to become Christian. It can apply to the conversion of an individual, a practice, a place or a whole society. It began in the Roman Empire, conti ...
the Prussians. As soon as the first Polish dukes had been established with Mieszko I
Mieszko I (; – 25 May 992) was the first ruler of Poland and the founder of the first independent Polish state, the Duchy of Poland. His reign stretched from 960 to his death and he was a member of the Piast dynasty, a son of Siemomysł and ...
in 966, they undertook a number of conquests and crusades not only against Prussians and the closely related Sudovians
Yotvingians (also called: Sudovians, Jatvians, or Jatvingians; Yotvingian: ''Jotvingai''; lt, Jotvingiai, ; lv, Jātvingi; pl, Jaćwingowie, be, Яцвягі, ger, Sudauer) were a Western Baltic people who were closely tied to the Old Prus ...
, but against the Pomeranians and Wends as well.
Beginning in 1147, the Polish duke Bolesław IV the Curly
Bolesław IV the Curly (; 1122 – 5 January 1173), a member of the Piast dynasty, was Duke of Masovia from 1138 and High Duke of Poland from 1146 until his death.
Early life
Bolesław was the third son of Duke Bolesław III Wrymouth of Polan ...
(securing the help of Ruthenian troops) tried to subdue Prussia, supposedly as punishment for the close cooperation of Prussians with Władysław II the Exile : ''This article refers to the 12th century Polish monarch. For the 14th century founder of the Jagiellon dynasty, see Jogaila, and for other monarchs with similar names, see Ladislaus II (disambiguation).''
Vladislaus II the Exile ( pl, Władys ...
. The only source is unclear about the results of his attempts, vaguely only mentioning that the Prussians were defeated. Whatever were the results, in 1157 some Prussian troops supported the Polish army in their fight against Emperor Frederick Barbarossa
Frederick Barbarossa (December 1122 – 10 June 1190), also known as Frederick I (german: link=no, Friedrich I, it, Federico I), was the Holy Roman Emperor from 1155 until his death 35 years later. He was elected King of Germany in Frankfurt ...
. In 1166 two Polish dukes, Bolesław IV and his younger brother Henry, came into Prussia, again over the Ossa River. The prepared Prussians led the Polish army, under the leadership of Henry, into an area of marshy morass. Whoever did not drown was felled by an arrow or by throwing clubs, and nearly all Polish troops perished. From 1191 to 1193 Casimir II the Just
Casimir II the Just ( pl, Kazimierz II Sprawiedliwy; 28 October 1138 – 5 May 1194) was a Lesser Polish Duke of Wiślica from 1166–1173, and of Sandomierz after 1173. He became ruler over the Polish Seniorate Province at Kraków and thereby Hi ...
invaded Prussia, this time along the river Drewenz ( Drwęca). He forced some of the Prussian tribes to pay tribute and then withdrew.
Several attacks by Konrad of Masovia in the early 13th century were also successfully repelled by the Prussians. In 1209 Pope Innocent III
Pope Innocent III ( la, Innocentius III; 1160 or 1161 – 16 July 1216), born Lotario dei Conti di Segni (anglicized as Lothar of Segni), was the head of the Catholic Church and ruler of the Papal States from 8 January 1198 to his death in 16 ...
commissioned the Cistercian
The Cistercians, () officially the Order of Cistercians ( la, (Sacer) Ordo Cisterciensis, abbreviated as OCist or SOCist), are a Catholic religious order of monks and nuns that branched off from the Benedictines and follow the Rule of Saint B ...
monk Christian of Oliva with the conversion of the pagan Prussians. In 1215, Christian was installed as the first bishop of Prussia. The Duchy of Masovia, and especially the region of Culmerland, become the object of constant Prussian counter-raids. In response, Konrad I of Masovia
Konrad I of Masovia (ca. 1187/88 – 31 August 1247), from the Polish Piast dynasty, was the sixth Duke of Masovia and Kuyavia from 1194 until his death as well as High Duke of Poland from 1229 to 1232 and again from 1241 to 1243.
Life
Konrad wa ...
called on the Pope
The pope ( la, papa, from el, πάππας, translit=pappas, 'father'), also known as supreme pontiff ( or ), Roman pontiff () or sovereign pontiff, is the bishop of Rome (or historically the patriarch of Rome), head of the worldwide Cathol ...
for aid several times, and founded a military order (the Order of Dobrzyń) before calling on the Teutonic Order
The Order of Brothers of the German House of Saint Mary in Jerusalem, commonly known as the Teutonic Order, is a Catholic religious institution founded as a military society in Acre, Kingdom of Jerusalem. It was formed to aid Christians on ...
. The results were edicts calling for Northern Crusades
The Northern Crusades or Baltic Crusades were Christian colonization and Christianization campaigns undertaken by Catholic Christian military orders and kingdoms, primarily against the pagan Baltic, Finnic and West Slavic peoples around th ...
against the Prussians.
In 1224, Emperor Frederick II proclaimed that he himself and the Empire
An empire is a "political unit" made up of several territories and peoples, "usually created by conquest, and divided between a dominant center and subordinate peripheries". The center of the empire (sometimes referred to as the metropole) ex ...
took the population of Prussia and the neighboring provinces under their direct protection; the inhabitants were declared to be ''Reichsfrei
Imperial immediacy (german: Reichsfreiheit or ') was a privileged constitutional and political status rooted in German feudal law under which the Imperial estates of the Holy Roman Empire such as Imperial cities, prince-bishoprics and secular pri ...
e'', to be subordinated directly to the Church and the Empire only, and exempted from service to and the jurisdiction of other dukes. The Teutonic Order
The Order of Brothers of the German House of Saint Mary in Jerusalem, commonly known as the Teutonic Order, is a Catholic religious institution founded as a military society in Acre, Kingdom of Jerusalem. It was formed to aid Christians on ...
, officially subject directly to the Popes, but also under the control of the empire, took control of much of the Baltic, establishing their own monastic state in Prussia.
In 1230, following the Golden Bull of Rimini, Grand Master Hermann von Salza
Hermann von Salza (or Herman of Salza; c. 1165 – 20 March 1239) was the fourth Grand Master of the Teutonic Knights, serving from 1210 to 1239. A skilled diplomat with ties to the Holy Roman Emperor and the Pope, Hermann oversaw the expansio ...
and Duke Konrad I of Masovia
Konrad I of Masovia (ca. 1187/88 – 31 August 1247), from the Polish Piast dynasty, was the sixth Duke of Masovia and Kuyavia from 1194 until his death as well as High Duke of Poland from 1229 to 1232 and again from 1241 to 1243.
Life
Konrad wa ...
launched the Prussian Crusade
The Prussian Crusade was a series of 13th-century campaigns of Roman Catholic crusaders, primarily led by the Teutonic Knights, to Christianize under duress the pagan Old Prussians. Invited after earlier unsuccessful expeditions against the Pr ...
, a joint invasion of Prussia to Christianise the Baltic Old Prussians. The Order then created the independent Monastic State of the Teutonic Knights in the conquered territory and subsequently conquered Courland, Livonia, and Estonia. The Dukes of Poland accused the Order of holding lands illegally.
During an attack on Prussia in 1233, over 21,000 crusaders took part, of which the burggrave of Magdeburg brought 5,000 warriors, Duke Henry of Silesia
Silesia (, also , ) is a historical region of Central Europe that lies mostly within Poland, with small parts in the Czech Silesia, Czech Republic and Germany. Its area is approximately , and the population is estimated at around 8,000,000. S ...
3,000, Duke Konrad of Masovia 4,000, Duke Casimir of Kuyavia 2,000, Duke Wladyslaw of Greater Poland 2,200 and Dukes of Pomerania 5,000 warriors. The main battle took place at the Sirgune River and the Prussians suffered a decisive defeat. The Prussians took the Christian bishop and imprisoned him for several years.
 Numerous knights from throughout Catholic Europe joined in the
Numerous knights from throughout Catholic Europe joined in the Prussian Crusade
The Prussian Crusade was a series of 13th-century campaigns of Roman Catholic crusaders, primarily led by the Teutonic Knights, to Christianize under duress the pagan Old Prussians. Invited after earlier unsuccessful expeditions against the Pr ...
s, which lasted sixty years. Many of the native Prussians from Sudovia who survived were resettled in Samland; Sudauer Winkel was named after them. Frequent revolts, including a major rebellion in 1286, were defeated by the Teutonic Knights. In 1283, according
to the chronicler of the Teutonic Knights, Peter of Dusburg, the conquest of the Prussians ended and the war with the Lithuanians began.
In 1243, papal legate William of Modena divided Prussia into four bishoprics — Culm, Pomesania, Ermland, and Samland — under the Bishopric of Riga
The Archbishopric of Riga ( la, Archiepiscopatus Rigensis, nds, Erzbisdom Riga) was an archbishopric in Medieval Livonia, a subject to the Holy See. It was established in 1186 as the bishopric of Livonia at Ikšķile, then after moving to Ri ...
. Prussians were baptised at the Archbishopric of Magdeburg
The Archbishopric of Magdeburg was a Roman Catholic archdiocese (969–1552) and Prince-Archbishopric (1180–1680) of the Holy Roman Empire centered on the city of Magdeburg on the Elbe River.
Planned since 955 and established in 968, the R ...
, while Germans
, native_name_lang = de
, region1 =
, pop1 = 72,650,269
, region2 =
, pop2 = 534,000
, region3 =
, pop3 = 157,000
3,322,405
, region4 =
, pop4 = ...
and Dutch settlers colonized the lands of the native Prussians; Poles
Poles,, ; singular masculine: ''Polak'', singular feminine: ''Polka'' or Polish people, are a West Slavic nation and ethnic group, who share a common history, culture, the Polish language and are identified with the country of Poland in ...
and Lithuanians
Lithuanians ( lt, lietuviai) are a Baltic ethnic group. They are native to Lithuania, where they number around 2,378,118 people. Another million or two make up the Lithuanian diaspora, largely found in countries such as the United States, Unite ...
also settled in southern and eastern Prussia, respectively. Significant pockets of Old Prussians were left in a matrix of Germans throughout Prussia and in what is now the Kaliningrad Oblast
Kaliningrad Oblast (russian: Калинингра́дская о́бласть, translit=Kaliningradskaya oblast') is the westernmost federal subject of Russia. It is a semi-exclave situated on the Baltic Sea. The largest city and admin ...
.
The monks and scholars of the Teutonic Order took an interest in the language spoken by the Prussians and tried to record it. In addition, missionaries needed to communicate with the Prussians in order to convert them. Records of the Old Prussian language therefore survive; along with little-known Galindian and better-known Sudovian
Sudovian (also known as Yotvingian, or Jatvingian) was a Western Baltic language of Northeastern Europe. Sudovian was closely related to Old Prussian. It was formerly spoken southwest of the Nemunas river in what is now Lithuania, east of Gali ...
, these records are all that remain of the West Baltic language group. As might be expected, it is a very archaic Baltic language.
Old Prussians resisted the Teutonic Knights and received help from the Grand Duchy of Lithuania
The Grand Duchy of Lithuania was a European state that existed from the 13th century to 1795, when the territory was Partitions of Poland, partitioned among the Russian Empire, the Kingdom of Prussia, and the Habsburg Empire, Habsburg Empire of ...
during the 13th century in their quest to free themselves of the military order. In 1525 Grand Master Albert of Brandenburg-Ansbach secularized the Order's Prussian territories into the Protestant Duchy of Prussia
The Duchy of Prussia (german: Herzogtum Preußen, pl, Księstwo Pruskie, lt, Prūsijos kunigaikštystė) or Ducal Prussia (german: Herzogliches Preußen, link=no; pl, Prusy Książęce, link=no) was a duchy in the region of Prussia establish ...
, a vassal of the crown of Poland. During the Reformation
The Reformation (alternatively named the Protestant Reformation or the European Reformation) was a major movement within Western Christianity in 16th-century Europe that posed a religious and political challenge to the Catholic Church and in ...
, Lutheranism
Lutheranism is one of the largest branches of Protestantism, identifying primarily with the theology of Martin Luther, the 16th-century German monk and Protestant Reformers, reformer whose efforts to reform the theology and practice of the Cathol ...
spread throughout the territories, officially in the Duchy of Prussia and unofficially in the Polish province of Royal Prussia, while Catholicism survived in the Prince-Bishopric of Warmia, the territory of secular rule comprising a third of the then Diocese of Warmia
The Roman Catholic Archdiocese of Warmia ( pl, Archidiecezja warmińska, german: Erzdiözese Ermland) is a Metropolitan archdiocese of the Latin Rite of the Roman Catholic Church in the Warmian-Masurian Voivodeship, Poland.
The archbishop has his ...
. With Protestantism came the use of the vernacular
A vernacular or vernacular language is in contrast with a "standard language". It refers to the language or dialect that is spoken by people that are inhabiting a particular country or region. The vernacular is typically the native language, n ...
in church services instead of Latin
Latin (, or , ) is a classical language belonging to the Italic languages, Italic branch of the Indo-European languages. Latin was originally a dialect spoken in the lower Tiber area (then known as Latium) around present-day Rome, but through ...
, so Albert had the Catechism
A catechism (; from grc, κατηχέω, "to teach orally") is a summary or exposition of doctrine and serves as a learning introduction to the Sacraments traditionally used in catechesis, or Christian religious teaching of children and adul ...
s translated into Old Prussian.
Because of the conquest of the Old Prussians by Germans, the Old Prussian language probably became extinct in the beginning of the 18th century with the devastation of the rural population by plagues and the assimilation of the nobility and the larger population with Germans or Lithuanians. However, translations of the Bible, Old Prussian poems, and some other texts survived and have enabled scholars to reconstruct the language.
References
External links
Chronica terrae Prussiae
Lecture about Prussians & Their Mythology
The Old Prussians: the Lost Relatives of Latvians and Lithuanians
Milestones of Baltic Prussian History
Modern Prusai-Communities' Map of the land of Old Prussians
Dictionary of reconstructed Prussian language
Comparative Phonology and Morphology of the Baltic Languages
{{Authority control People from Prussia proper Historical ethnic groups of Europe Indigenous peoples of Europe Historical Baltic peoples