Odontogenic keratocyst on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
An odontogenic keratocyst is a rare and

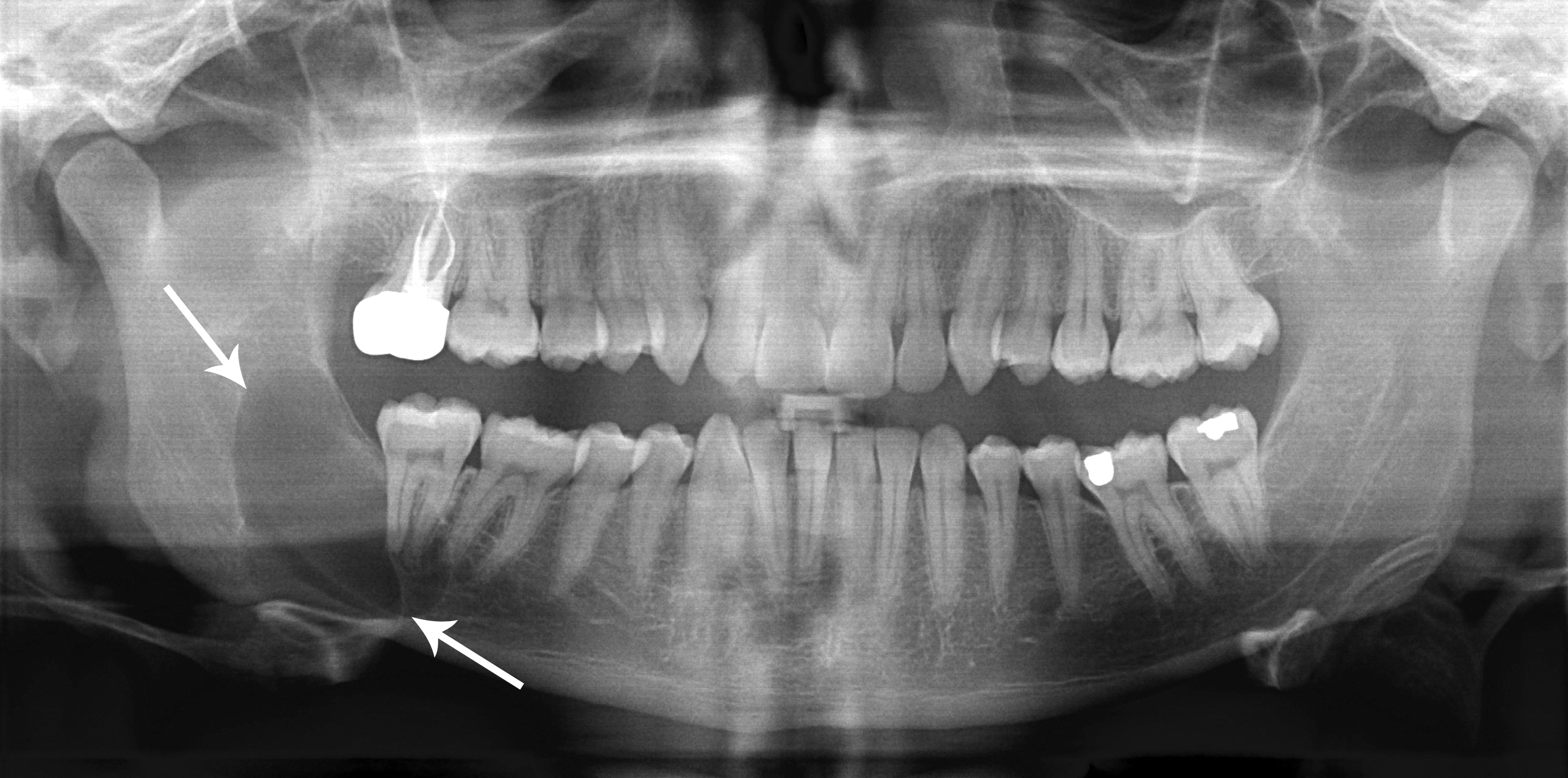 Diagnosis is usually radiological. However, definitive diagnosis is through
Diagnosis is usually radiological. However, definitive diagnosis is through
File:Keratocystic odontogenic tumour - 2 - intermed mag.jpg, Intermediate magnification of an odontogenic keratocyst showing a folded cyst.
File:Keratocystic odontogenic tumour - intermed mag.jpg, Intermediate magnification of an odontogenic keratocyst
File:Keratocystic odontogenic tumour - 2 - high mag.jpg, High magnification of an odontogenic keratocyst.
 As the condition is quite rare, opinions among experts about how to treat OKCs differ. A 2015 Cochrane review found that there is currently no high quality evidence to suggest the effectiveness of specific treatments for the treatment of odontogenic keratocysts. Treatment depends on extent of multilocularity and cyst. Small multilocular and unilocular cysts can be treated more conservatively through enucleation and curretage. Treatment options for KTOC may vary according to its size, extent, site, and adjacent structures.
Treatment options:
*Surgical enucleation: surgical removal of the entire epithelial lining of the cyst.
*Marsupialisation followed by enucleation: this method is carried out by surgeons for larger cysts.
*
As the condition is quite rare, opinions among experts about how to treat OKCs differ. A 2015 Cochrane review found that there is currently no high quality evidence to suggest the effectiveness of specific treatments for the treatment of odontogenic keratocysts. Treatment depends on extent of multilocularity and cyst. Small multilocular and unilocular cysts can be treated more conservatively through enucleation and curretage. Treatment options for KTOC may vary according to its size, extent, site, and adjacent structures.
Treatment options:
*Surgical enucleation: surgical removal of the entire epithelial lining of the cyst.
*Marsupialisation followed by enucleation: this method is carried out by surgeons for larger cysts.
*
benign
Malignancy () is the tendency of a medical condition to become progressively worse.
Malignancy is most familiar as a characterization of cancer. A ''malignant'' tumor contrasts with a non-cancerous ''benign'' tumor in that a malignancy is not s ...
but locally aggressive developmental cyst
A cyst is a closed sac, having a distinct envelope and division compared with the nearby tissue. Hence, it is a cluster of cells that have grouped together to form a sac (like the manner in which water molecules group together to form a bubble) ...
. It most often affects the posterior mandible
In anatomy, the mandible, lower jaw or jawbone is the largest, strongest and lowest bone in the human facial skeleton. It forms the lower jaw and holds the lower teeth in place. The mandible sits beneath the maxilla. It is the only movable bone ...
and most commonly presents in the third decade of life. Odontogenic keratocysts make up around 19% of jaw cysts.
In the WHO
Who or WHO may refer to:
* Who (pronoun), an interrogative or relative pronoun
* Who?, one of the Five Ws in journalism
* World Health Organization
Arts and entertainment Fictional characters
* Who, a creature in the Dr. Seuss book '' Horton He ...
/ IARC classification of head and neck pathology, this clinical entity had been known for years as the odontogenic keratocyst; it was reclassified as keratocystic odontogenic tumour (KCOT) from 2005 to 2017. In 2017 it reverted to the earlier name, as the new WHO/IARC classification reclassified OKC back into the cystic category. Under The WHO/IARC classification, Odontogenic Keratocyst underwent the reclassification as it is no longer considered a neoplasm due to a lack of quality evidence regarding this hypothesis, especially with respect to clonality. Within the Head and Neck pathology community there is still controversy surrounding the reclassification, with some pathologists still considering Odontogenic Keratocyst as a neoplasm in line with the previous classification.
Signs and symptoms
Odontogenic keratocysts can occur at any age, however they are more common in the third to sixth decades. The male to female ratio is approximately 2:1. The majority are found in the mandible, with half occurring at the angle of the mandible. Early odontogenic keratocysts usually do not display symptoms. Typically, clinical signs and symptoms present with bony expansion, or infection. However, bony expansion is uncommon as odontogenic keratocysts grow due to increased epithelial turnover rather than osmotic pressure. When symptoms are present they usually take the form of pain, swelling and discharge due to secondary infection. Odontogenic keratocysts are usually noted as incidental radiographic findings. Radiographically they can be seen as unilocular or multilocular radiolucencies. They can be mistaken for other cysts such as residual cysts or adentigerous cyst
Dentigerous cyst, also known as follicular cyst is an epithelial-lined developmental cyst formed by accumulation of fluid between the reduced enamel epithelium and crown of an unerupted tooth. It is formed when there is an alteration in the redu ...
if they occur over an unerupted tooth.
Pathogenesis
Odontogenic keratocysts originate from the odontogenic epithelium (dental lamina
The dental lamina is a band of epithelial tissue seen in histologic sections of a developing tooth. The dental lamina is first evidence of tooth development and begins (in humans) at the sixth week in utero or three weeks after the rupture of th ...
) in the alveolus left from tooth development stages. They are mainly thought to arise from rests of Serres.
Genetics
Sporadic (non-syndromic) and syndromic OKCs are associated with mutations in thegene
In biology, the word gene (from , ; "... Wilhelm Johannsen coined the word gene to describe the Mendelian units of heredity..." meaning ''generation'' or ''birth'' or ''gender'') can have several different meanings. The Mendelian gene is a b ...
'' PTCH'' found on chromosome 9
Chromosome 9 is one of the 23 pairs of chromosomes in humans. Humans normally have two copies of this chromosome, as they normally do with all chromosomes. Chromosome 9 spans about 138 million base pairs of nucleic acids (the building blocks of D ...
q, which is part of the Hedgehog signaling pathway
The Hedgehog signaling pathway is a signaling pathway that transmits information to embryonic cells required for proper cell differentiation. Different parts of the embryo have different concentrations of hedgehog signaling proteins. The pathwa ...
. ''PTCH'' is a tumour suppressor gene
A tumor suppressor gene (TSG), or anti-oncogene, is a gene that regulates a cell during cell division and replication. If the cell grows uncontrollably, it will result in cancer. When a tumor suppressor gene is mutated, it results in a loss or red ...
. Loss of ''PTCH'' activity leads to a brake in the cell cycle
The cell cycle, or cell-division cycle, is the series of events that take place in a cell that cause it to divide into two daughter cells. These events include the duplication of its DNA (DNA replication) and some of its organelles, and sub ...
. A third of OKCs show mutations in ''PTCH'', resulting in the cyst epithelium undergoing highly proliferative activity. This leads to growth of the cyst wall and when removed favours recurrence if following incomplete removal of the epithelium.
Nevoid basal-cell carcinoma syndrome
Multiple odontogenic keratocysts are a feature, and major diagnostic criteria, of nevoid basal cell carcinoma syndrome (NBCCS, also known as Gorlin-Goltz Syndrome). Almost all individuals with NBCCS have odontogenic keratocysts which require numerous treatments. Consideration of the syndrome needs to be taken into account if found in children or if multiple OKCs are present; diagnosis of multiple OKCs in a child necessitates referral for genetic evaluation. Histologically, the cysts are indistinguishable to non-syndromic cysts and over 80% will have ''PTCH'' mutations.Diagnosis
 Diagnosis is usually radiological. However, definitive diagnosis is through
Diagnosis is usually radiological. However, definitive diagnosis is through biopsy
A biopsy is a medical test commonly performed by a surgeon, interventional radiologist, or an interventional cardiologist. The process involves extraction of sample cells or tissues for examination to determine the presence or extent of a dise ...
. Aspirational biopsy of odontogenic keratocysts contains a greasy fluid which is pale in colour and contains keratotic squames. Protein content of cyst fluid below 4g% is diagnostic of odontogenic keratocysts. Smaller and unilocular lesions resembling other types of cysts may require a biopsy to confirm the diagnosis. On a CT scan, the radiodensity
Radiodensity (or radiopacity) is opacity to the radio wave and X-ray portion of the electromagnetic spectrum: that is, the relative inability of those kinds of electromagnetic radiation to pass through a particular material. Radiolucency or hypod ...
of a keratocystic odontogenic tumour is about 30 Hounsfield unit The Hounsfield scale , named after Sir Godfrey Hounsfield, is a quantitative scale for describing radiodensity. It is frequently used in CT scans, where its value is also termed CT number.
Definition
The Hounsfield unit (HU) scale is a linear tr ...
s, which is about the same as ameloblastoma
Ameloblastoma is a rare, benign or cancerous tumor of odontogenic epithelium ( ameloblasts, or outside portion, of the teeth during development) much more commonly appearing in the lower jaw than the upper jaw. It was recognized in 1827 by Cusack ...
s. However, ameloblastomas show more bone expansion and seldom show high density areas.
Radiographs of odontogenic keratocysts show well-defined radiolucent areas with rounded or scalloped margins which are well demarcated. These areas can be multilocular or unilocular. The growth pattern of the lesion is very characteristic from which a diagnosis can be made as there is growth and spread both forward and backward along the medullary cavity with little expansion. No resorption of teeth or inferior dental canal and minimal displacement of teeth is seen. Due to lack of expansion of the odontogenic keratocyst, the lesion can be very large when radiographically discovered.
Differential diagnosis
Radiologically * Odontogenic myxoma *Ameloblastoma
Ameloblastoma is a rare, benign or cancerous tumor of odontogenic epithelium ( ameloblasts, or outside portion, of the teeth during development) much more commonly appearing in the lower jaw than the upper jaw. It was recognized in 1827 by Cusack ...
* Central giant-cell granuloma
* Adenomatoid odontogenic tumor
*Dentigerous cyst
Dentigerous cyst, also known as follicular cyst is an epithelial-lined developmental cyst formed by accumulation of fluid between the reduced enamel epithelium and crown of an unerupted tooth. It is formed when there is an alteration in the redu ...
(follicular cyst)
Histologically
* Orthokeratocyst
* Radicular cyst (particularly if the OKC is very inflamed)
*Ameloblastoma
Ameloblastoma is a rare, benign or cancerous tumor of odontogenic epithelium ( ameloblasts, or outside portion, of the teeth during development) much more commonly appearing in the lower jaw than the upper jaw. It was recognized in 1827 by Cusack ...
Histology
Odontogenic keratocysts have a diagnostic histological appearance. Under themicroscope
A microscope () is a laboratory instrument used to examine objects that are too small to be seen by the naked eye. Microscopy is the science of investigating small objects and structures using a microscope. Microscopic means being invisi ...
, OKCs vaguely resemble keratinized
Keratin () is one of a family of structural fibrous proteins also known as ''scleroproteins''. Alpha-keratin (α-keratin) is a type of keratin found in vertebrates. It is the key structural material making up scales, hair, nails, feathers, h ...
squamous epithelium
Epithelium or epithelial tissue is one of the four basic types of animal tissue, along with connective tissue, muscle tissue and nervous tissue. It is a thin, continuous, protective layer of compactly packed cells with a little intercellula ...
; however, they lack rete ridges and often have an artifactual separation from their basement membrane.
The fibrous wall of the cyst is usually thin and uninflamed. The epithelial lining is thin with even thickness and parakeratinised with columnar cells
Epithelium or epithelial tissue is one of the four basic types of animal tissue, along with connective tissue, muscle tissue and nervous tissue. It is a thin, continuous, protective layer of compactly packed cells with a little intercellula ...
in the basal layer which have focal reverse polarisation (nuclei are on the opposite pole of the cell). The basal cells are an indication of the odontogenic origin as they resemble pre-ameloblasts. The epithelium can separate from the wall, resulting in islands of epithelium. These can go on to form 'satellite' or 'daughter' cysts, leading to an overall multilocular cyst. Presence of daughter cysts is particularly seen in those with NBCCS. Inflamed cysts show hyperplastic
Hyperplasia (from ancient Greek ὑπέρ ''huper'' 'over' + πλάσις ''plasis'' 'formation'), or hypergenesis, is an enlargement of an organ or tissue caused by an increase in the amount of organic tissue that results from cell proliferatio ...
epithelium which is no longer characteristic of OKCs and can have resemblance to radicular cysts instead. Due to areas of focal inflammation, a larger biopsy is required for correct diagnosis of odontogenic keratocysts.
Treatment
 As the condition is quite rare, opinions among experts about how to treat OKCs differ. A 2015 Cochrane review found that there is currently no high quality evidence to suggest the effectiveness of specific treatments for the treatment of odontogenic keratocysts. Treatment depends on extent of multilocularity and cyst. Small multilocular and unilocular cysts can be treated more conservatively through enucleation and curretage. Treatment options for KTOC may vary according to its size, extent, site, and adjacent structures.
Treatment options:
*Surgical enucleation: surgical removal of the entire epithelial lining of the cyst.
*Marsupialisation followed by enucleation: this method is carried out by surgeons for larger cysts.
*
As the condition is quite rare, opinions among experts about how to treat OKCs differ. A 2015 Cochrane review found that there is currently no high quality evidence to suggest the effectiveness of specific treatments for the treatment of odontogenic keratocysts. Treatment depends on extent of multilocularity and cyst. Small multilocular and unilocular cysts can be treated more conservatively through enucleation and curretage. Treatment options for KTOC may vary according to its size, extent, site, and adjacent structures.
Treatment options:
*Surgical enucleation: surgical removal of the entire epithelial lining of the cyst.
*Marsupialisation followed by enucleation: this method is carried out by surgeons for larger cysts.
*Curettage
Curettage ( or ), in medical procedures, is the use of a curette (French, meaning scoop Mosby's Medical, Nursing & Allied Health Dictionary, Fourth Edition, Mosby-Year Book 1994, p. 422) to remove tissue by scraping or scooping.
Curettages are ...
involving simple excision and scraping-out of cavity.
* Carnoy's solution fixative (ethanol, chloroform and acetic acid) which is usually used in conjunction with excision and curretage. Cavity wall can be treated with the fixative either before enucleation to kill the lining of the wall or added after curretage to bony walls, killing any residual epithelial cells to a depth of 1-2mm. Used with care near mandibular canal and the neurovascular bundle within.
* Marsupialization which involves the surgical opening of the cyst cavity and a creation of a marsupial
Marsupials are any members of the mammalian infraclass Marsupialia. All extant marsupials are endemic to Australasia, Wallacea and the Americas. A distinctive characteristic common to most of these species is that the young are carried in a ...
-like pouch. This allows the cavity to be in contact with the outside of the cyst for an extended period of time. Marsupialisation results in slow shrinkage of the cyst allowing later enucleation. However, resolution can take up to 20 months and patients are required to clean the open cavity and irrigate it.
* Peripheral ostectomy after curettage and/or enucleation. Extensive cysts may require a bone graft after bone resection and reconstruction of the area.
*Simple excision
* Enucleation and cryotherapy
Cryotherapy, sometimes known as cold therapy, is the local or general use of low temperatures in medical therapy. Cryotherapy may be used to treat a variety of tissue lesions. The most prominent use of the term refers to the surgical treatment, s ...
. Decompression followed by enucleation has been shown to be most successful with lowest recurrence rates.
* Topical application of 5FU after enucleation
*Ostectomy or En – bloc resection: in addition to the above treatments, these may be required due to the issue of recurrence. Ostectomy is removal of peripheral bone. En – block resection is removal of the cyst with the surrounding tissue. Extensive cysts may require a bone graft after bone resection and reconstruction of the area.
Follow-up
Annual radiographic review has been recommended. Long-term clinical follow-up is also recommended due to recurrences occurring many years after treatment.Recurrence and neoplastic nature
Malignant transformation
Malignant transformation is the process by which cells acquire the properties of cancer. This may occur as a primary process in normal tissue, or secondarily as ''malignant degeneration'' of a previously existing benign tumor.
Causes
There are ...
to squamous cell carcinoma may occur, but is unusual.
Recurrence is likely when treated by simple enucleation. Contributing causes include thin and fragile epithelium leading to incomplete removal, cyst extensions extending into cancellous bone, satellite cysts found in the wall, experience of the surgeon, formation of further new cysts from other remnants of the dental epithelium. With current treatment techniques the recurrence rate is around 2-3% but can be as high as 50%. Recurrence can occur as early as 5 years and as late as 40 years after removal. Recurrence is usually seen within 5 years of treatment. Early findings of recurrence can be easily treated with minor surgery and curretage. Any fragment of the cyst that is left behind has the potential to survive and grow. Therefore, the success of enucleation depends on how well the cyst is removed. Larger cysts have a higher rate of recurrence after enucleation as they are more difficult to remove.
Pronto genie keratocysts are well known to recur in the posterior mandible
In anatomy, the mandible, lower jaw or jawbone is the largest, strongest and lowest bone in the human facial skeleton. It forms the lower jaw and holds the lower teeth in place. The mandible sits beneath the maxilla. It is the only movable bone ...
. A substantial amount of odontogenic keratocysts also recur in the tooth-bearing area of the jaws, requiring attention from clinicians.
The neoplastic
A neoplasm () is a type of abnormal and excessive growth of tissue. The process that occurs to form or produce a neoplasm is called neoplasia. The growth of a neoplasm is uncoordinated with that of the normal surrounding tissue, and persists ...
nature of odontogenic keratocysts has been debated. Due to high recurrence rate, late detection when the cyst has grown very large and causation by tumour suppressor gene
A tumor suppressor gene (TSG), or anti-oncogene, is a gene that regulates a cell during cell division and replication. If the cell grows uncontrollably, it will result in cancer. When a tumor suppressor gene is mutated, it results in a loss or red ...
inactivation, some have classified OKCs as benign neoplasms. The best evidence to suggest that this type of cyst is not a neoplasm is that it responds very well to marsupialisation.
See also
* Cysts of the jawsReferences
External links
{{DEFAULTSORT:Keratocystic Odontogenic Tumour Jaw disorders Odontogenic tumors