Observer Badge on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
The Observer Badge is a military badge of the
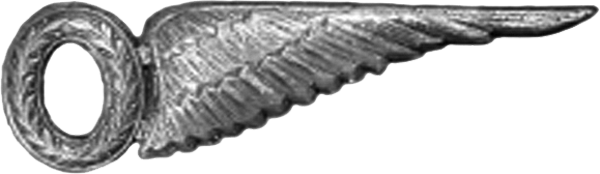 The original Observer Badge was a half-wing variation of the Aviator Badge worn by military pilots of the
The original Observer Badge was a half-wing variation of the Aviator Badge worn by military pilots of the
 Between 1919 and 1935 the design of the Observer Badge remained unchanged, and was issued to both airplane and lighter-than-air ratings. However, as
Between 1919 and 1935 the design of the Observer Badge remained unchanged, and was issued to both airplane and lighter-than-air ratings. However, as
 The Naval Aviation Observer Badge was first created in 1922, awarded to navigators and other support personnel on naval aircraft. The original badge was based on the design of the
The Naval Aviation Observer Badge was first created in 1922, awarded to navigators and other support personnel on naval aircraft. The original badge was based on the design of the  For a brief period starting in 1945, the Secretary of the Navy approved distinct insignia for Naval Aviation Observers with Navigation, Radar, Tactical, and Aerology specializations. These were abolished in favor of the standardized gold insignia/silver anchor/silver circle design.
In 1966 a new insignia was instituted, and by 1968 the Naval Aviation Observer Badge was replaced by the
For a brief period starting in 1945, the Secretary of the Navy approved distinct insignia for Naval Aviation Observers with Navigation, Radar, Tactical, and Aerology specializations. These were abolished in favor of the standardized gold insignia/silver anchor/silver circle design.
In 1966 a new insignia was instituted, and by 1968 the Naval Aviation Observer Badge was replaced by the
 With the creation of the
With the creation of the
Appendix 20
Washington DC, U.S. Department of the Navy Historical Center. * COMDTNOTE 1200. ''ALCOAST 401/03''
United States military badges
United States armed forces
The United States Armed Forces are the military forces of the United States. The armed forces consists of six service branches: the Army, Marine Corps, Navy, Air Force, Space Force, and Coast Guard. The president of the United States is ...
dating from the First World War
World War I (28 July 1914 11 November 1918), often abbreviated as WWI, was List of wars and anthropogenic disasters by death toll, one of the deadliest global conflicts in history. Belligerents included much of Europe, the Russian Empire, ...
. The badge was issued to co-pilots, navigators, and flight support personnel (as air observer
An air observer or aerial observer is an aircrew member whose duties are predominantly reconnaissance. The term originated in the First World War in the British Royal Flying Corps, and was maintained by its successor, the Royal Air Force. An ai ...
) who had received a variation in the training required for the standard Pilot's Badge. The Observer Badge survived through the Second World War
World War II or the Second World War, often abbreviated as WWII or WW2, was a world war that lasted from 1939 to 1945. It involved the vast majority of the world's countries—including all of the great powers—forming two opposi ...
and into the 1950s, at which time the concept of an Observer Badge was phased out in favor of the modern Aircrew Badge
The Aircrew Badge, commonly known as Wings, is a qualification badge of the United States military that is awarded by all five branches of armed services to personnel who serve as aircrew members on board military aircraft. The badge is inten ...
and Navigator-Observer Badges. In addition to wings for Naval Aviator
Naval aviation is the application of military air power by navies, whether from warships that embark aircraft, or land bases.
Naval aviation is typically projected to a position nearer the target by way of an aircraft carrier. Carrier-bas ...
s and Naval Flight Officer
A naval flight officer (NFO) is a commissioned officer in the United States Navy or United States Marine Corps who specializes in airborne weapons and sensor systems. NFOs are not pilots (naval aviators), but they may perform many "co-pilot" or ...
s, the United States Navy
The United States Navy (USN) is the maritime service branch of the United States Armed Forces and one of the eight uniformed services of the United States. It is the largest and most powerful navy in the world, with the estimated tonnage ...
still maintains an "Observer Badge" which is issued to flight-qualified mission specialists, such as a select number of meteorologists and intelligence officers in both the U.S. Navy and U.S. Marine Corps. The U.S. Air Force awards its USAF Observer Badge, which is identical to the USAF Navigator Badge, to Air Force officers who have qualified as NASA
The National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA ) is an independent agency of the US federal government responsible for the civil space program, aeronautics research, and space research.
NASA was established in 1958, succeedin ...
Space Shuttle
The Space Shuttle is a retired, partially reusable low Earth orbital spacecraft system operated from 1981 to 2011 by the U.S. National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA) as part of the Space Shuttle program. Its official program n ...
Mission Specialists, have flown an actual mission aboard the shuttle and/or the International Space Station
The International Space Station (ISS) is the largest Modular design, modular space station currently in low Earth orbit. It is a multinational collaborative project involving five participating space agencies: NASA (United States), Roscosmos ( ...
and who are otherwise not previously aeronautically rated as an Air Force pilot or navigator.
In the modern U.S. Armed Forces, the Observer Badge is rarely issued, but has seen a resurgence in the Air Forces of other countries, most notably the United Kingdom
The United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern Ireland, commonly known as the United Kingdom (UK) or Britain, is a country in Europe, off the north-western coast of the continental mainland. It comprises England, Scotland, Wales and ...
and Canada
Canada is a country in North America. Its ten provinces and three territories extend from the Atlantic Ocean to the Pacific Ocean and northward into the Arctic Ocean, covering over , making it the world's second-largest country by to ...
.
First World War
 The original Observer Badge was a half-wing variation of the Aviator Badge worn by military pilots of the
The original Observer Badge was a half-wing variation of the Aviator Badge worn by military pilots of the United States Army Air Service
The United States Army Air Service (USAAS)Craven and Cate Vol. 1, p. 9 (also known as the ''"Air Service"'', ''"U.S. Air Service"'' and before its legislative establishment in 1920, the ''"Air Service, United States Army"'') was the aerial war ...
and later the United States Army Air Corps
The United States Army Air Corps (USAAC) was the aerial warfare service component of the United States Army between 1926 and 1941. After World War I, as early aviation became an increasingly important part of modern warfare, a philosophical r ...
. The badge was mainly awarded to gunners, spotters, and navigators on the first armed military aircraft. With the advent of bombing
A bomb is an explosive weapon that uses the exothermic reaction of an explosive material to provide an extremely sudden and violent release of energy. Detonations inflict damage principally through ground- and atmosphere-transmitted mechanica ...
, the Observer Badge was also initially authorized for aircraft bombardiers. A new badge was soon created for these duties, however: the Bombing Aviator Badge {{Unreferenced, date=December 2009
The Bombardier Badge was a military badge of the United States military which was issued between the years of 1918 and 1949. The decoration was intended to recognize the military training and qualification req ...
.
Those rated as Balloon Observers were also eligible for the badge, and the badge was typically referred to as both the ''Airplane Observer Badge'' and the ''Balloon Observer Badge''. The design of the badge awarded was identical in both cases, and towards the end of the First World War was commonly referred to as the "Airplane and Balloon Observer Badge", although the ratings for which the badge was issued remained distinct.
Second World War
 Between 1919 and 1935 the design of the Observer Badge remained unchanged, and was issued to both airplane and lighter-than-air ratings. However, as
Between 1919 and 1935 the design of the Observer Badge remained unchanged, and was issued to both airplane and lighter-than-air ratings. However, as military aviation
Military aviation comprises military aircraft and other flying machines for the purposes of conducting or enabling aerial warfare, including national airlift ( air cargo) capacity to provide logistical supply to forces stationed in a war thea ...
developed, changes in the concept of an Airplane Observer necessitated the redesign of the Observer Badge with a corresponding change in the eligibility criteria. On 20 February 1940 the rating was changed to that of ''Combat Observer'', followed by redesignation as ''Aircraft Observer'' on 4 September 1942. Note that bombardiers that used the top secret SHORAN
SHORAN is an acronym for SHOrt RAnge Navigation, a type of electronic navigation and bombing system using a precision radar beacon. It was developed during World War II and the first stations were set up in Europe as the war was ending, and was o ...
also received the Observer Badge. They sat midship, where the radio operator would normally sit, since they used an electronic not optical bombsight.
By the time of the United States' entry into the Second World War, three Observer Badges were authorized by the Army Air Forces
The United States Army Air Forces (USAAF or AAF) was the major land-based aerial warfare service component of the United States Army and ''de facto'' aerial warfare service branch of the United States during and immediately after World War II ...
. The first was the Combat Observer Badge: in appearance an Aviator Badge with a large 'O' in the center. For Balloon Observers, a separate badge was created: the Observer Badge augmented with a balloon insignia.
The third and final version of the Observer Badge was the Technical Observer Badge, an Aviator Badge with a T and O motif in the center. The Technical Observer Badge was primarily awarded to flight engineering personnel assigned to assist the flight engineer
A flight engineer (FE), also sometimes called an air engineer, is the member of an aircraft's flight crew who monitors and operates its complex aircraft systems. In the early era of aviation, the position was sometimes referred to as the "air m ...
.
United States Navy, Marine Corps, and Coast Guard
 The Naval Aviation Observer Badge was first created in 1922, awarded to navigators and other support personnel on naval aircraft. The original badge was based on the design of the
The Naval Aviation Observer Badge was first created in 1922, awarded to navigators and other support personnel on naval aircraft. The original badge was based on the design of the Naval Aviator
Naval aviation is the application of military air power by navies, whether from warships that embark aircraft, or land bases.
Naval aviation is typically projected to a position nearer the target by way of an aircraft carrier. Carrier-bas ...
badge, but with a single wing on the left, and with the anchor surmounted by an "O" rather than a shield. In 1927 this insignia was superseded by a new device, identical to the Naval Aviator's wings, but in silver rather than gold.
This in turn was replaced by a gold insignia with a center device of a silver anchor within a silver circle, used from 1929 to 1968.
 For a brief period starting in 1945, the Secretary of the Navy approved distinct insignia for Naval Aviation Observers with Navigation, Radar, Tactical, and Aerology specializations. These were abolished in favor of the standardized gold insignia/silver anchor/silver circle design.
In 1966 a new insignia was instituted, and by 1968 the Naval Aviation Observer Badge was replaced by the
For a brief period starting in 1945, the Secretary of the Navy approved distinct insignia for Naval Aviation Observers with Navigation, Radar, Tactical, and Aerology specializations. These were abolished in favor of the standardized gold insignia/silver anchor/silver circle design.
In 1966 a new insignia was instituted, and by 1968 the Naval Aviation Observer Badge was replaced by the Naval Flight Officer Badge
The Naval Flight Officer insignia is a breast insignia of the United States military which is awarded to those aviators of the Navy, Marine Corps and Coast Guard who have qualified as Naval Flight Officers (NFO) based on successful completion of ...
. However, in lieu of being totally discontinued, the criteria for the Naval Aviation Observer insignia was modified again and granted to non-pilot/non-NFO aviation mission specialists such as in-flight Meteorologists or for Naval Intelligence or Cryptology officers who regularly fly as crew on selected naval aircraft. In this form the Naval Observer Badge is still in existence, but is alternatingly referred to by both its original name and, in the case of when worn by Meteorology officers, as the Flight Meteorologist Badge
The Flight Meteorologist insignia is a military badge decoration of the United States Navy which is issued to officers of the Restricted Line who are commissioned as weather and meteorology specialists. To be issued the insignia, an officer mu ...
. In the Marine Corps the badge is awarded to in-flight aircraft support personnel under its original name as the Naval Aviation Observer Badge for non-aeronautically designated officers flying in observer/spotter roles in Marine Corps aircraft.
The Coast Guard authorized the Aviation Mission Specialist designation on August 26, 2003 in COMDTNOTE 1200 (ALCOAST 401/03). Aerial Ice Observers (from the International Ice Patrol
The International Ice Patrol is an organization with the purpose of monitoring the presence of icebergs in the Atlantic and Arctic Oceans and reporting their movements for safety purposes. It is operated by United States Coast Guard but is f ...
) as well as Sensor System Operators, Tactical Systems Operators, Aviation Gunners and Aviation Medical Technicians are eligible for designation. Coast Guard Aviation Mission Specialist personnel also wear the same uniform insignia as Naval Aviation Observers. Permanent designation is attained at 200 hours for rotary wing and 400 hours for fixed wing specialists.
US Air Force Observer rating
United States Air Force
The United States Air Force (USAF) is the air service branch of the United States Armed Forces, and is one of the eight uniformed services of the United States. Originally created on 1 August 1907, as a part of the United States Army Si ...
in 1947, aviation observers were phased out and replaced by more highly trained specialists known as Aircrew personnel. The Aircrew Badge
The Aircrew Badge, commonly known as Wings, is a qualification badge of the United States military that is awarded by all five branches of armed services to personnel who serve as aircrew members on board military aircraft. The badge is inten ...
was created prior to the Second World War
World War II or the Second World War, often abbreviated as WWII or WW2, was a world war that lasted from 1939 to 1945. It involved the vast majority of the world's countries—including all of the great powers—forming two opposi ...
; but had only been awarded to enlisted personnel. Since the creation of the USAF Officer Aircrew Badge (an unrated award), the Navigator-Observer Badge has been issued to otherwise unrated officers who complete NASA Mission Specialist training with the aeronautical rating of Observer. On completion of an operational mission they may then apply to the Air Force Chief of Staff for the Astronaut
An astronaut (from the Ancient Greek (), meaning 'star', and (), meaning 'sailor') is a person trained, equipped, and deployed by a human spaceflight program to serve as a commander or crew member aboard a spacecraft. Although generally r ...
qualification that permits them to wear the USAF Navigator / Combat Systems Officer version of the Astronaut Badge
The United States Astronaut Badge is a badge of the United States, awarded to military and civilian personnel who have completed training and performed a successful spaceflight. A variation of the astronaut badge is also issued to civilians who ...
.
Civil Air Patrol
The title "Observer" is still used regularly in the U.S. Air Force Auxiliary, better known as theCivil Air Patrol
Civil Air Patrol (CAP) is a congressionally chartered, federally supported non-profit corporation that serves as the official civilian auxiliary of the United States Air Force (USAF). CAP is a volunteer organization with an aviation-minded mem ...
. Civil Air Patrol observers may act as the mission commander for aircrews engaged in search and rescue, homeland defense reconnaissance, or other Air Force-authorized missions, serving as the liaison between the sortie and mission base. Observers are trained in air navigation, radio communications, and other technical subjects such as aerial direction finding. The Civil Air Patrol badge for an observer looks almost identical to the CAP pilot badge, except that the observer device has an additional ''O'' or thin circle atop the central CAP emblem.
See also
* Badges of the United States Air Force *Badges of the United States Army
Badges of the United States Army are military decorations issued by the United States Department of the Army to soldiers who achieve a variety of qualifications and accomplishments while serving on active and reserve duty in the United States Arm ...
* Badges of the United States Coast Guard
Badges of the United States Coast Guard are issued by the Department of Homeland Security to members of the United States Coast Guard to denote certain qualifications, achievements, and postings to certain assignments. Prior to 2002, the issuanc ...
* Badges of the United States Marine Corps
* Badges of the United States Navy
Insignias and badges of the United States Navy are military badges issued by the United States Department of the Navy to naval service members who achieve certain qualifications and accomplishments while serving on both active and reserve duty ...
* Military badges of the United States
Military badges of the United States are awards authorized by the United States Armed Forces that signify rating, qualification, or accomplishment in several career fields, and also serve as identification devices for personnel occupying certain a ...
* Obsolete badges of the United States military
Obsolete badges of the United States military are a number of U.S. military insignia which were issued in the 20th and 21st centuries. After World War II many badges were phased out of the United States Armed Forces in favor of more modern milit ...
References
{{Reflist * Grossnick, Roy A. (1997). ''United States Naval Aviation 1910-1995''Appendix 20
Washington DC, U.S. Department of the Navy Historical Center. * COMDTNOTE 1200. ''ALCOAST 401/03''
United States military badges