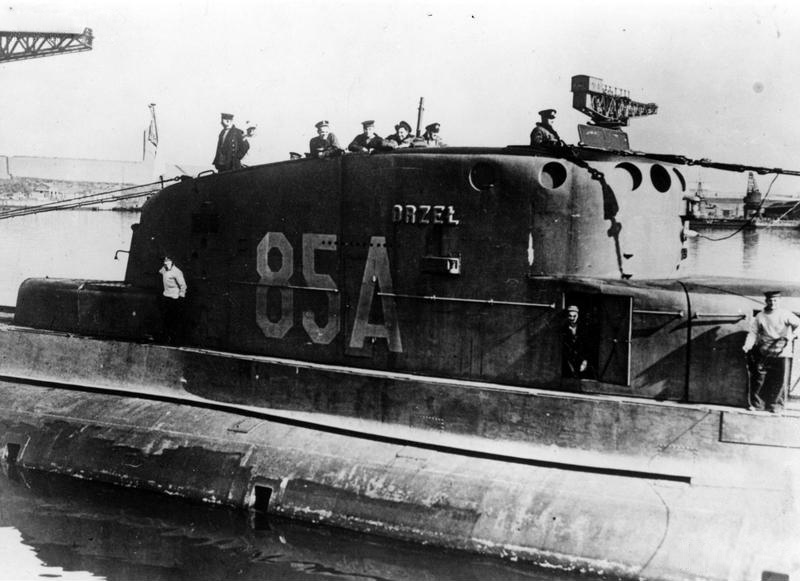
ORP Orzeł (1938) on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 ORP ''Orzeł'' was the
ORP ''Orzeł'' was the

 ''Orzel''s crew decided to head to
''Orzel''s crew decided to head to
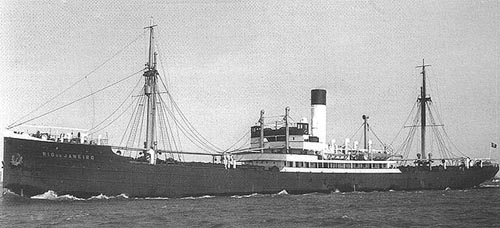 After a refit, ''Orzeł'' was assigned to the Royal Navy's 2nd Submarine Flotilla, and was assigned to patrol missions. Shortly after noon on 8 April 1940 she sank the clandestine German
After a refit, ''Orzeł'' was assigned to the Royal Navy's 2nd Submarine Flotilla, and was assigned to patrol missions. Shortly after noon on 8 April 1940 she sank the clandestine German
 On 23 May 1940, ''Orzeł'' departed on its seventh patrol in the central North Sea. On 1 and 2 June, radio messages were transmitted from the
On 23 May 1940, ''Orzeł'' departed on its seventh patrol in the central North Sea. On 1 and 2 June, radio messages were transmitted from the
Association of the "ORZEŁ" submarine search group
ORP Orzel
a concept album from Cold Fusion
Shipwreck Expeditions Association
{{DEFAULTSORT:Orzel Orzeł-class submarines World War II submarines of Poland Germany–Soviet Union relations World War II shipwrecks in the North Sea 1938 ships Maritime incidents in September 1939 Maritime incidents in May 1940 Missing submarines of World War II Ships built in Vlissingen Warships lost with all hands
 ORP ''Orzeł'' was the
ORP ''Orzeł'' was the lead ship
The lead ship, name ship, or class leader is the first of a series or class of ships all constructed according to the same general design. The term is applicable to naval ships and large civilian vessels.
Large ships are very complex and may ...
of her class of submarine
A submarine (or sub) is a watercraft capable of independent operation underwater. It differs from a submersible, which has more limited underwater capability. The term is also sometimes used historically or colloquially to refer to remotely op ...
s serving in the Polish Navy during World War II
World War II or the Second World War, often abbreviated as WWII or WW2, was a world war that lasted from 1939 to 1945. It involved the vast majority of the world's countries—including all of the great powers—forming two opposin ...
. Her name () means "Eagle
Eagle is the common name for many large birds of prey of the family Accipitridae. Eagles belong to several groups of genera, some of which are closely related. Most of the 68 species of eagle are from Eurasia and Africa. Outside this area, just ...
" in Polish
Polish may refer to:
* Anything from or related to Poland, a country in Europe
* Polish language
* Poles, people from Poland or of Polish descent
* Polish chicken
*Polish brothers (Mark Polish and Michael Polish, born 1970), American twin screenwr ...
. The boat is best known for the ''Orzeł'' incident, her escape from internment in neutral Estonia
Estonia, formally the Republic of Estonia, is a country by the Baltic Sea in Northern Europe. It is bordered to the north by the Gulf of Finland across from Finland, to the west by the sea across from Sweden, to the south by Latvia, a ...
during the early stages of the Second World War
World War II or the Second World War, often abbreviated as WWII or WW2, was a world war that lasted from 1939 to 1945. It involved the vast majority of the world's countries—including all of the great powers—forming two opposin ...
.
Construction
''Orzeł'' was laid down 14 August 1936 at theDutch
Dutch commonly refers to:
* Something of, from, or related to the Netherlands
* Dutch people ()
* Dutch language ()
Dutch may also refer to:
Places
* Dutch, West Virginia, a community in the United States
* Pennsylvania Dutch Country
People E ...
shipyard
A shipyard, also called a dockyard or boatyard, is a place where ships are built and repaired. These can be yachts, military vessels, cruise liners or other cargo or passenger ships. Dockyards are sometimes more associated with maintenance a ...
De Schelde, as the Job No. 205; launched on 15 January 1938, and commissioned on 2 February 1939. She was a modern design (designed by the joint venture of Polish and Dutch engineers), albeit quite large for the shallow waters of the Baltic Sea
The Baltic Sea is an arm of the Atlantic Ocean that is enclosed by Denmark, Estonia, Finland, Germany, Latvia, Lithuania, Poland, Russia, Sweden and the North and Central European Plain.
The sea stretches from 53°N to 66°N latitude and from ...
.
World War II
Polish Campaign
At the beginning of theinvasion of Poland
The invasion of Poland (1 September – 6 October 1939) was a joint attack on the Republic of Poland by Nazi Germany and the Soviet Union which marked the beginning of World War II. The German invasion began on 1 September 1939, one week aft ...
''Orzeł'' was docked in Oksywie
Oksywie (german: Oxhöft, csb, Òksëwiô) is a neighbourhood of the city of Gdynia, Pomeranian Voivodeship, northern Poland. Formerly a separate settlement, it is older than Gdynia by several centuries.
Etymology
Both the Polish and then Germ ...
. As per the Worek Plan
The Worek Plan (or ''Operation Worek'', pl, Plan Worek, literally ''Plan Sack'') was an operation of the Polish Navy in the first days of World War II, in which its five submarines formed a screen in order to prevent German naval forces fr ...
, the submarine was deployed on patrol in a designated strategic zone of the Baltic Sea. The crew received orders to attack the pre-dreadnought
Pre-dreadnought battleships were sea-going battleships built between the mid- to late- 1880s and 1905, before the launch of in 1906. The pre-dreadnought ships replaced the ironclad battleships of the 1870s and 1880s. Built from steel, prote ...
''Schleswig-Holstein
Schleswig-Holstein (; da, Slesvig-Holsten; nds, Sleswig-Holsteen; frr, Slaswik-Holstiinj) is the northernmost of the 16 states of Germany, comprising most of the historical duchy of Holstein and the southern part of the former Duchy of Sch ...
'', should it leave Danzig. With the situation rapidly deteriorating, ''Orzel'' abandoned its sector on 4 September and began to withdraw into the Baltic Sea
The Baltic Sea is an arm of the Atlantic Ocean that is enclosed by Denmark, Estonia, Finland, Germany, Latvia, Lithuania, Poland, Russia, Sweden and the North and Central European Plain.
The sea stretches from 53°N to 66°N latitude and from ...
. The submarine was attacked by the German minesweepers ''M3'' and ''M4'', damaged but evaded destruction that evening.
Escape to Britain
 ''Orzel''s crew decided to head to
''Orzel''s crew decided to head to Tallinn
Tallinn () is the most populous and capital city of Estonia. Situated on a bay in north Estonia, on the shore of the Gulf of Finland of the Baltic Sea, Tallinn has a population of 437,811 (as of 2022) and administratively lies in the Harju ' ...
, Estonia
Estonia, formally the Republic of Estonia, is a country by the Baltic Sea in Northern Europe. It is bordered to the north by the Gulf of Finland across from Finland, to the west by the sea across from Sweden, to the south by Latvia, a ...
as a result of the damage. ''Orzeł'' reached Tallinn on 14 September 1939. On 15 September the captain, Lieutenant-Commander
Lieutenant commander (also hyphenated lieutenant-commander and abbreviated Lt Cdr, LtCdr. or LCDR) is a commissioned officer rank in many navies. The rank is superior to a lieutenant and subordinate to a commander. The corresponding rank i ...
, was forced to leave the submarine to undergo hospital treatment for an unknown illness he had been suffering from since 8 September. Under the Hague Convention of 1907
The Hague Conventions of 1899 and 1907 are a series of international treaties and declarations negotiated at two international peace conferences at The Hague in the Netherlands. Along with the Geneva Conventions, the Hague Conventions were amon ...
, section XIII, Article 12, "belligerent ships" could enter a neutral port but were forbidden from remaining there for "more than twenty-four hours." At the insistence of Germany, the Estonian military authorities boarded the ship, interned the crew, confiscated all the navigation aids and maps, and commenced removing all her armaments. However, only fifteen of her twenty torpedoes were removed before the hoist cable parted; this was because it had been secretly sabotaged by her new commander, former chief officer
A chief mate (C/M) or chief officer, usually also synonymous with the first mate or first officer, is a licensed mariner and head of the deck department of a merchant ship. The chief mate is customarily a watchstander and is in charge of the ship ...
, Lieutenant
A lieutenant ( , ; abbreviated Lt., Lt, LT, Lieut and similar) is a commissioned officer rank in the armed forces of many nations.
The meaning of lieutenant differs in different militaries (see comparative military ranks), but it is often sub ...
Jan Grudzinski
Jan, JaN or JAN may refer to:
Acronyms
* Jackson, Mississippi (Amtrak station), US, Amtrak station code JAN
* Jackson-Evers International Airport, Mississippi, US, IATA code
* Jabhat al-Nusra (JaN), a Syrian militant group
* Japanese Article Numb ...
.
The crew of ''Orzeł'' conspired together to carry out a daring escape. Around midnight on 18 September, the submarine's Estonian guards were overpowered, the mooring lines were cut, and ''Orzeł'' got under way. The alarm was raised, and her conning tower was peppered by machine-gun fire. Running half-submerged, ''Orzeł'' ran aground on a bar at the harbour mouth, where artillery fire damaged her wireless equipment. Grudzinski managed to get the boat off the bar by blowing her tanks, and she proceeded out of the Gulf of Finland, intending to sail for a British port, the crew having heard a radio report that the Polish submarine had been welcomed in Britain.
''Orzel'' escaped from Tallinn with two Estonian guards on board as hostages. The Estonian and German press covering the ''Orzeł'' incident declared the two captured guards missing at sea. Grudzinski set them ashore in Sweden
Sweden, formally the Kingdom of Sweden,The United Nations Group of Experts on Geographical Names states that the country's formal name is the Kingdom of SwedenUNGEGN World Geographical Names, Sweden./ref> is a Nordic country located on ...
, providing them with clothing, money, and food for their safe return to homeland. The Polish crew believed that "those returning from the underworld deserve to travel first class only". The escape of the submarine ''Orzeł'' was used by the Soviet Union
The Soviet Union,. officially the Union of Soviet Socialist Republics. (USSR),. was a transcontinental country that spanned much of Eurasia from 1922 to 1991. A flagship communist state, it was nominally a federal union of fifteen national ...
and Germany
Germany,, officially the Federal Republic of Germany, is a country in Central Europe. It is the second most populous country in Europe after Russia, and the most populous member state of the European Union. Germany is situated betwe ...
to challenge Estonian neutrality.
Since ''Orzeł''s navigational charts had all been removed by the Estonian authorities, Captain Grudzinski resolved to stop a German ship and take her charts. However, the only German vessels encountered were warships rather than merchantmen. The submarine's sole remaining navigational aid was a list of lighthouses, and using these as a reference, ''Orzeł'' followed a course along the Baltic coast, around Denmark, and out into the North Sea where she came under attack by British as well as German forces, since without her wireless equipment she had no means of identifying herself.
Forty days after she had originally sailed from Gdynia, ''Orzeł'' made landfall, off the east coast of Scotland. She lay on the bottom until emergency repairs were made to the radio, then surfaced to transmit a message in English. A Royal Navy
The Royal Navy (RN) is the United Kingdom's naval warfare force. Although warships were used by English and Scottish kings from the early medieval period, the first major maritime engagements were fought in the Hundred Years' War against F ...
destroyer then came out and escorted her into port, to the surprise of the British who had thought her sunk already weeks earlier.
''Orzeł'' sank no enemy vessels during her journey from Estonia to Britain, but Soviet authorities blamed her for sinking the Soviet tanker ''Metallist'' in Narva Bay
The Narva Bay ( et, Narva laht, russian: Нарвский залив) (also the ''Gulf of Narva'' and the ''Narva Estuary'') is a bay in the southern part of the Gulf of Finland divided between Estonia and Russia.
Geography
The Kurgalsky Pe ...
on 26 September, and used the incident as a pretext for the Soviet invasion of Estonia.
Norwegian Campaign
 After a refit, ''Orzeł'' was assigned to the Royal Navy's 2nd Submarine Flotilla, and was assigned to patrol missions. Shortly after noon on 8 April 1940 she sank the clandestine German
After a refit, ''Orzeł'' was assigned to the Royal Navy's 2nd Submarine Flotilla, and was assigned to patrol missions. Shortly after noon on 8 April 1940 she sank the clandestine German troopship
A troopship (also troop ship or troop transport or trooper) is a ship used to carry soldiers, either in peacetime or wartime. Troopships were often drafted from commercial shipping fleets, and were unable land troops directly on shore, typicall ...
off the small harbour village of Lillesand
Lillesand () is municipality in Agder county, Norway. It is part of the traditional district of Sørlandet. The administrative center of the municipality is the town of Lillesand. Some of the larger villages in Lillesand municipality include ...
in southern Norway, killing hundreds of German troops intended for the invasion of Norway
Norway, officially the Kingdom of Norway, is a Nordic country in Northern Europe, the mainland territory of which comprises the western and northernmost portion of the Scandinavian Peninsula. The remote Arctic island of Jan Mayen and t ...
. ''Rio de Janeiro'' was heading to Bergen
Bergen (), historically Bjørgvin, is a city and municipality in Vestland county on the west coast of Norway. , its population is roughly 285,900. Bergen is the second-largest city in Norway. The municipality covers and is on the peninsula of ...
in order to take part in the initial landings of Operation Weserübung
Operation Weserübung (german: Unternehmen Weserübung , , 9 April – 10 June 1940) was Germany's assault on Denmark and Norway during the Second World War and the opening operation of the Norwegian Campaign.
In the early morning of 9 Ap ...
– the invasion of Norway
Norway, officially the Kingdom of Norway, is a Nordic country in Northern Europe, the mainland territory of which comprises the western and northernmost portion of the Scandinavian Peninsula. The remote Arctic island of Jan Mayen and t ...
and opening move of the Norwegian Campaign. News that several hundred German soldiers were rescued by the Norwegian Navy and some had admitted their intention to occupy Norway reached the Norwegian parliament that evening, but the news was dismissed and no steps were taken to alert their Navy or Coast Guard of the impending invasion. Two days later ''Orzeł'' fired a torpedo at a German minesweeper V 705; however, she was forced to dive before the sinking of the German ship could be confirmed. The ship was not damaged by the torpedoes.
Loss
 On 23 May 1940, ''Orzeł'' departed on its seventh patrol in the central North Sea. On 1 and 2 June, radio messages were transmitted from the
On 23 May 1940, ''Orzeł'' departed on its seventh patrol in the central North Sea. On 1 and 2 June, radio messages were transmitted from the Rosyth Naval base
Rosyth Dockyard is a large naval dockyard on the Firth of Forth at Rosyth, Fife, Scotland, owned by Babcock Marine, which formerly undertook refitting of Royal Navy surface vessels and submarines. Before its privatisation in the 1990s it was ...
ordering the boat to alter its patrol area and proceed to the Skagerrak
The Skagerrak (, , ) is a strait running between the Jutland peninsula of Denmark, the southeast coast of Norway and the west coast of Sweden, connecting the North Sea and the Kattegat sea area through the Danish Straits to the Baltic Sea.
The ...
(the strait
A strait is an oceanic landform connecting two seas or two other large areas of water. The surface water generally flows at the same elevation on both sides and through the strait in either direction. Most commonly, it is a narrow ocean channe ...
separating Norway
Norway, officially the Kingdom of Norway, is a Nordic country in Northern Europe, the mainland territory of which comprises the western and northernmost portion of the Scandinavian Peninsula. The remote Arctic island of Jan Mayen and t ...
and Sweden
Sweden, formally the Kingdom of Sweden,The United Nations Group of Experts on Geographical Names states that the country's formal name is the Kingdom of SwedenUNGEGN World Geographical Names, Sweden./ref> is a Nordic country located on ...
from the Danish
Danish may refer to:
* Something of, from, or related to the country of Denmark
People
* A national or citizen of Denmark, also called a "Dane," see Demographics of Denmark
* Culture of Denmark
* Danish people or Danes, people with a Danish ance ...
Jutland peninsula
Jutland ( da, Jylland ; german: Jütland ; ang, Ēota land ), known anciently as the Cimbric or Cimbrian Peninsula ( la, Cimbricus Chersonesus; da, den Kimbriske Halvø, links=no or ; german: Kimbrische Halbinsel, links=no), is a peninsula of ...
). No radio signals had been received from her since she had sailed, and on 5 June ''Orzeł'' was ordered to return to base. No reception was acknowledged. On 8 June 1940 the submarine was officially declared lost. The true cause is unknown, although it is commonly believed ''Orzeł'' most likely struck a British or German sea mine
A naval mine is a self-contained explosive device placed in water to damage or destroy surface ships or submarines. Unlike depth charges, mines are deposited and left to wait until they are triggered by the approach of, or contact with, any ve ...
in or near the Skagerrak. Another theory suggests the boat may have been sunk mistakenly by a British aircraft.
Search for the wreck
Between 2008 and 2017 a number of Polish expeditions, both private and public-funded, searched the region of North Sea where she went missing with the hope of finding her final resting place. Wrecks of various other ships have been located, but ''Orzeł'' has not been among them and ultimately the fate of the ship remains unknown. In June 2013 the Polish Navy, following reports of a wreck of an unknown large submarine found in the North Sea, conducted one more expedition to check whether the ship could be ''Orzeł''. The wreck was surveyed and identified as . In 2017 another private expedition found a previously unknown wreck which they identified to be most likely based on sonar data. On May 23, 2020, 80 years after ''Orzeł'' left on its final patrol, the Shipwreck Expeditions Association announced a partnership to search for the wreck in conjunction with theMaritime University of Szczecin
The Maritime University of Szczecin ( pl, Politechnika Morska w Szczecinie; ''Akademia Morska'' until 2022) is a public university in Szczecin, Poland. The profile of the university is maritime industry, maritime education.
The University struct ...
with the assistance from the Chancellery of the Prime Minister of the Republic of Poland and the Ministry of Maritime Economy and Inland Navigation.
The search is currently entering the logistics and preparations phase for the first expedition.
See also
* ''The Eagle'' (1959 film)References
External links
* http://crolick.website.pl/orporzel/Association of the "ORZEŁ" submarine search group
ORP Orzel
a concept album from Cold Fusion
Shipwreck Expeditions Association
{{DEFAULTSORT:Orzel Orzeł-class submarines World War II submarines of Poland Germany–Soviet Union relations World War II shipwrecks in the North Sea 1938 ships Maritime incidents in September 1939 Maritime incidents in May 1940 Missing submarines of World War II Ships built in Vlissingen Warships lost with all hands