Nursing assessment on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Nursing assessment is the gathering of information about a
 The patient history and interview is considered to be subjective but still of high importance when combined with objective measurements. High quality interviewing strategies include the use of
The patient history and interview is considered to be subjective but still of high importance when combined with objective measurements. High quality interviewing strategies include the use of
 A nursing assessment includes a
A nursing assessment includes a
 *hair: quantity, location, distribution, texture
*nails: shape and color, presence of clubbing
*lesions: type, location, arrangement, color of lesions, drainage, depth, width, length
*texture, moisture, color, elasticity, turgor
*hair: quantity, location, distribution, texture
*nails: shape and color, presence of clubbing
*lesions: type, location, arrangement, color of lesions, drainage, depth, width, length
*texture, moisture, color, elasticity, turgor
 The main areas considered in a
The main areas considered in a
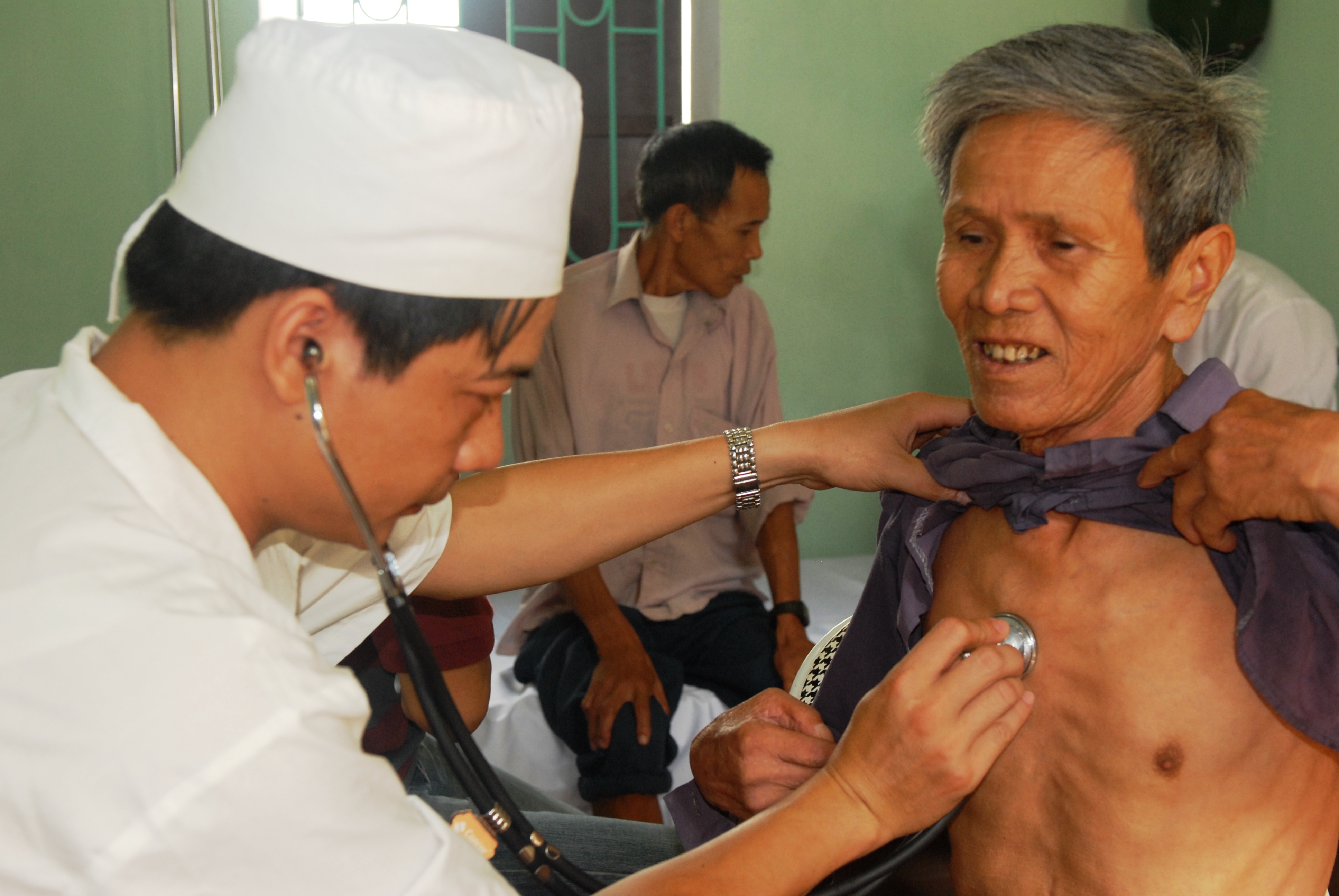 A range of instruments and tools have been developed to assist nurses in their assessment role. These include: the index of independence in
A range of instruments and tools have been developed to assist nurses in their assessment role. These include: the index of independence in
Patient Initial Assessment
/ref>External links
Glasgow coma scale
Morse Fall Assessment
An assessment tool to determine and quantify persons as low, mid, and high risk for falls.
Pressure Ulcer Staging Guide
from the Wound Care Institute
National Pressure Ulcer Advisory Panel
CETL, Clinical and Communication Skills, Barts and City University of London.
CETL, Clinical and Communication. Barts and City University of London.
CETL, Clinical and Communication. Barts and City University of London.
ATI Nursing Education. {{DEFAULTSORT:Nursing Assessment Assessment, Nursing Physical examination
patient
A patient is any recipient of health care services that are performed by healthcare professionals. The patient is most often ill or injured and in need of treatment by a physician, nurse, optometrist, dentist, veterinarian, or other heal ...
's physiological
Physiology (; ) is the scientific study of functions and mechanisms in a living system. As a sub-discipline of biology, physiology focuses on how organisms, organ systems, individual organs, cells, and biomolecules carry out the chemica ...
, psychological
Psychology is the scientific study of mind and behavior. Psychology includes the study of conscious and unconscious phenomena, including feelings and thoughts. It is an academic discipline of immense scope, crossing the boundaries bet ...
, sociological
Sociology is a social science that focuses on society, human social behavior, patterns of social relationships, social interaction, and aspects of culture associated with everyday life. It uses various methods of empirical investigation and ...
, and spiritual status by a licensed Registered Nurse
A registered nurse (RN) is a nurse who has graduated or successfully passed a nursing program from a recognized nursing school and met the requirements outlined by a country, state, province or similar government-authorized licensing body to o ...
. Nursing assessment is the first step in the nursing process. A section of the nursing assessment may be delegated to certified nurses aides. Vitals and EKG's may be delegated to certified nurses aides or nursing techs. (Nurse Journal, 2017) It differs from a medical diagnosis. In some instances, the nursing assessment is very broad in scope and in other cases it may focus on one body system or mental health
Mental health encompasses emotional, psychological, and social well-being, influencing cognition, perception, and behavior. It likewise determines how an individual handles Stress (biology), stress, interpersonal relationships, and decision-maki ...
. Nursing assessment is used to identify current and future patient care needs. It incorporates the recognition of normal versus abnormal body physiology. Prompt recognition of pertinent changes along with the skill of critical thinking allows the nurse to identify and prioritize appropriate interventions. An assessment format may already be in place to be used at specific facilities and in specific circumstances.
The client interview
Before assessment can begin the nurse must establish a professional and therapeutic mode of communication. This develops rapport and lays the foundation of a trusting, non-judgmental relationship. This will also assure that the person will be as comfortable as possible when revealing personal information. A common method of initiating therapeutic communication by the nurse is to have the nurse introduce herself or himself. The interview proceeds to asking the client how they wish to be addressed and the general nature of the topics that will be included in the interview. The therapeutic communication methods of nursing assessment takes into account developmental stage (toddler vs. the elderly), privacy, distractions, age-related impediments to communication such as sensory deficits and language, place, time, non-verbal cues. Therapeutic communication is also facilitated by avoiding the use of medical jargon and instead using common terms used by the patient. During the first part of the personal interview, thenurse
Nursing is a profession within the health care sector focused on the care of individuals, families, and communities so they may attain, maintain, or recover optimal health and quality of life. Nurses may be differentiated from other health ...
carries out an analysis of the patient needs. In many cases, the client requires a focused assessment rather than a comprehensive nursing assessment of the entire bodily systems. In the focused assessment, the major complaint is assessed. The nurse may employ the use of acronyms performing the assessment:
*OLDCART
**Onset of health concern or complaint
**Location of pain or other symptoms related to the area of the body involved
**Duration of health concern or complaint
**Characteristics
**Aggravating factors or what makes the concern or complaint worse
**Relieving factors or what makes the concern or complaint better
**Treatments or what treatments were tried in the past or ongoing
Patient history and interview
 The patient history and interview is considered to be subjective but still of high importance when combined with objective measurements. High quality interviewing strategies include the use of
The patient history and interview is considered to be subjective but still of high importance when combined with objective measurements. High quality interviewing strategies include the use of open-ended question
An open-ended question is a question that cannot be answered with a "yes" or "no" response, or with a static response. Open-ended questions are phrased as a statement which requires a longer response. The response can be compared to information th ...
s. Open-ended questions are those that cannot be answered with a simple "yes" or "no" response. If the person is unable to respond, then family or caregivers will be given the opportunity to answer the questions.
The typical nursing assessment in the clinical setting will be the collection of data about the following:
*present complaint and nature of symptoms
*onset of symptoms
*severity of symptoms
*classifying symptoms as acute or chronic
*health history
*family history
*social history
*current medical and/or nursing management
*understanding of medical and nursing plans
*perception of illness
In addition, the nursing assessment may include reviewing the results of laboratory values such as blood work and urine analysis. Medical records of the client assist to determine the baseline measures related to their health.
In some instances, the nursing assessment will not incorporate the typical patient history
The medical history, case history, or anamnesis (from Greek: ἀνά, ''aná'', "open", and μνήσις, ''mnesis'', "memory") of a patient is information gained by a physician by asking specific questions, either to the patient or to other peo ...
and interview if prioritization indicates that immediate action is urgent to preserve the airway, breathing and circulation. This is also known as triage
In medicine, triage () is a practice invoked when acute care cannot be provided for lack of resources. The process rations care towards those who are most in need of immediate care, and who benefit most from it. More generally it refers to prio ...
and is used in emergency rooms and medical team disaster response situations. The patient history is documented through a personal interview with the client and/or the client's family. If there is an urgent need for a focused assessment, the most obvious or troubling complaint will be addressed first. This is especially important in the case of extreme pain.
Physical examination
 A nursing assessment includes a
A nursing assessment includes a physical examination
In a physical examination, medical examination, or clinical examination, a medical practitioner examines a patient for any possible medical signs or symptoms of a medical condition. It generally consists of a series of questions about the pati ...
: the observation or measurement of signs, which can be observed or measured, or symptoms
Signs and symptoms are the observed or detectable signs, and experienced symptoms of an illness, injury, or condition. A sign for example may be a higher or lower temperature than normal, raised or lowered blood pressure or an abnormality showi ...
such as nausea
Nausea is a diffuse sensation of unease and discomfort, sometimes perceived as an urge to vomit. While not painful, it can be a debilitating symptom if prolonged and has been described as placing discomfort on the chest, abdomen, or back of th ...
or vertigo
Vertigo is a condition where a person has the sensation of movement or of surrounding objects moving when they are not. Often it feels like a spinning or swaying movement. This may be associated with nausea, vomiting, sweating, or difficulties w ...
, which can be felt by the patient.
The techniques used may include inspection, palpation
Palpation is the process of using one's hands to check the body, especially while perceiving/diagnosing a disease or illness. Usually performed by a health care practitioner, it is the process of feeling an object in or on the body to determine ...
, auscultation
Auscultation (based on the Latin verb ''auscultare'' "to listen") is listening to the internal sounds of the body, usually using a stethoscope. Auscultation is performed for the purposes of examining the circulatory and respiratory systems (he ...
and percussion
A percussion instrument is a musical instrument that is sounded by being struck or scraped by a beater including attached or enclosed beaters or rattles struck, scraped or rubbed by hand or struck against another similar instrument. Exc ...
in addition to the "vital signs" of temperature
Temperature is a physical quantity that expresses quantitatively the perceptions of hotness and coldness. Temperature is measured with a thermometer.
Thermometers are calibrated in various temperature scales that historically have relied o ...
, blood pressure
Blood pressure (BP) is the pressure of circulating blood against the walls of blood vessels. Most of this pressure results from the heart pumping blood through the circulatory system. When used without qualification, the term "blood pressure ...
, pulse
In medicine, a pulse represents the tactile arterial palpation of the cardiac cycle (heartbeat) by trained fingertips. The pulse may be palpated in any place that allows an artery to be compressed near the surface of the body, such as at the n ...
and respiratory rate
The respiratory rate is the rate at which breathing occurs; it is set and controlled by the respiratory center of the brain. A person's respiratory rate is usually measured in breaths per minute.
Measurement
The respiratory rate in humans is me ...
, and further examination of the body systems such as the cardiovascular
The blood circulatory system is a system of organs that includes the heart, blood vessels, and blood which is circulated throughout the entire body of a human or other vertebrate. It includes the cardiovascular system, or vascular system, tha ...
or musculoskeletal
The human musculoskeletal system (also known as the human locomotor system, and previously the activity system) is an organ system that gives humans the ability to move using their muscular and skeletal systems. The musculoskeletal system prov ...
systems.
Focused assessment
Neurovascular assessment
The nurse conducts a neurovascular assessment to determine sensory and muscular function of the arms and legs in addition to peripheral circulation. The focused neurovascular assessment includes the objective observation of pulses, capillary refill, skin color and temperature, and sensation. During the neurovascular assessment the measures between extremities are compared. A neurovascular assessment is an evaluation of the extremities along with sensory, circulation and motor function.Mental status
During the assessment, interactions and functioning are evaluated and documented. Those specific items assessed include: *orientation, memory, * mood, depression,anxiety
Anxiety is an emotion which is characterized by an unpleasant state of inner turmoil and includes feelings of dread over anticipated events. Anxiety is different than fear in that the former is defined as the anticipation of a future threat wh ...
, coherence
Coherence, coherency, or coherent may refer to the following:
Physics
* Coherence (physics), an ideal property of waves that enables stationary (i.e. temporally and spatially constant) interference
* Coherence (units of measurement), a deriv ...
, hallucination
A hallucination is a perception in the absence of an external stimulus that has the qualities of a real perception. Hallucinations are vivid, substantial, and are perceived to be located in external objective space. Hallucination is a combinati ...
s, illusion
An illusion is a distortion of the senses, which can reveal how the mind normally organizes and interprets sensory stimulation. Although illusions distort the human perception of reality, they are generally shared by most people.
Illusions may oc ...
s, insight
Insight is the understanding of a specific cause and effect within a particular context. The term insight can have several related meanings:
*a piece of information
*the act or result of understanding the inner nature of things or of seeing intui ...
* speech patterns (rate, clarity clanging
In psychology and psychiatry, clanging or clang association refers to a mode of speech characterized by association of words based upon sound rather than concepts. For example, this may include compulsive rhyming or alliteration without apparent l ...
)
*grooming, personal hygiene, appropriateness of clothing
*response to verbal and tactile stimuli, level of consciousness, and alertness
*posture, gait, appropriateness of movements
Pain
Pain is no longer being identified as the fifth vital sign due to the prevalence of opioid abuse and over-prescribing of narcotic pain relievers. However, assessment for pain is still very important. Assessment of a patient's experience of pain is a crucial component in providing effective pain management. Pain is not a simple sensation that can be easily assessed and measured. Nurses should be aware of the many factors that can influence the patient's overall experience and expression of pain, and these should be considered during the assessment process. Systematic process of pain assessment, measurement, and re-assessment (re-evaluation), enhances the healthcare teams' ability to achieve. Pain is assessed for its provocative and palliative associations; quality, region/radiation, severity (numerical scale or pictorial, Wong-Baker Faces scale); and time—of onset, duration, frequency, and length of provocative and relief measures.Integument
 *hair: quantity, location, distribution, texture
*nails: shape and color, presence of clubbing
*lesions: type, location, arrangement, color of lesions, drainage, depth, width, length
*texture, moisture, color, elasticity, turgor
*hair: quantity, location, distribution, texture
*nails: shape and color, presence of clubbing
*lesions: type, location, arrangement, color of lesions, drainage, depth, width, length
*texture, moisture, color, elasticity, turgor
Head
*scalp, facial symmetry, sensation *eyes **acuity **eyelids **lacrimal glands **conjunctiva **visual fields **peripheral vision **sclera **size, shape, symmetry, pupil reactions **movement (cranial nerves) * ears **external structure **inner ear **eardrum **hearing (frequencies of sound detected) *dentationPsychosocial assessment
psychological examination
Psychological evaluation is a method to assess an individual's behavior, personality, cognitive abilities, and several other domains. A common reason for a psychological evaluation is to identify psychological factors that may be inhibiting a pers ...
are intellectual health and emotional health. Assessment of cognitive function, checking for hallucinations and delusions, measuring concentration levels, and inquiring into the client's hobbies and interests constitute an intellectual health assessment. Emotional health is assessed by observing and inquiring about how the client feels and what he does in response to these feelings. The psychological examination may also include the client's perceptions (why they think they are being assessed or have been referred, what they hope to gain from the meeting). Religion and beliefs are also important areas to consider. The need for a physical health assessment is always included in any psychological examination to rule out structural damage or anomalies.
Safety
*environment *ambulatory aidsCultural assessment
The nursing cultural assessment will identify factors that may impede or facilitate the implementation of a nursing diagnosis. Cultural factors have a major impact on the nursing assessment. Some of the information obtained during the interview include: *ethnic origin *primary language *second language *the need for an interpreter *the client's main support system(s) *family living arrangements *Who is the major decision maker in the family? What are the family members' roles within the family *Describe religious beliefs and practices *Are there any religious requirements/restrictions that place limitations on the client's care? *Who in the family takes responsibility for health concerns? *Describe any special health beliefs and practices: *From whom does family usually seek medical assistance in time of need? *Describe client's usual emotional/behavioral response to: Anxiety: Anger: Loss/change/failure: Pain: Fear: *Describe any topics that are particularly sensitive or that the client is unwilling to discuss (because of cultural taboos): *Describe any activities in which the client is unwilling to participate (because of cultural customs or taboos): *What are the client's personal feelings regarding touch? *What are the client's personal feelings regarding eye contact? *What is the client's personal orientation to time? (past, present, future) *Describe any particular illnesses to which the client may be bioculturally susceptible (e.g., hypertension and sickle cell anemia in *African Americans): *Describe any nutritional deficiencies to which the client may be bioculturally susceptible (e.g.,lactose intolerance
Lactose intolerance is a common condition caused by a decreased ability to digest lactose, a sugar found in dairy products. Those affected vary in the amount of lactose they can tolerate before symptoms develop. Symptoms may include abdominal pai ...
in Native and Asian Americans)
*Are there any foods the client requests or refuses because of cultural beliefs related to this illness (e.g., "hot" and "cold" foods for Latino Americans and Asian Americans)?
Assessment tools
 A range of instruments and tools have been developed to assist nurses in their assessment role. These include: the index of independence in
A range of instruments and tools have been developed to assist nurses in their assessment role. These include: the index of independence in activities of daily living
Activity may refer to:
* Action (philosophy), in general
* Human activity: human behavior, in sociology behavior may refer to all basic human actions, economics may study human economic activities and along with cybernetics and psychology may s ...
, the Barthel index, the Crighton Royal behaviour rating scale, the Clifton assessment procedures for the elderly, the general health questionnaire, and the geriatric mental health state schedule.
Other assessment tools may focus on a specific aspect of the patient's care. For example, the Waterlow score and the Braden scale deals with a patient's risk of developing a Pressure ulcer
Pressure ulcers, also known as pressure sores, bed sores or pressure injuries, are localised damage to the skin and/or underlying tissue that usually occur over a bony prominence as a result of usually long-term pressure, or pressure in combi ...
(decubitus ulcer), the Glasgow Coma Scale
The Glasgow Coma Scale (GCS) is a clinical scale used to reliably measure a person's level of consciousness after a brain injury.
The GCS assesses a person based on their ability to perform eye movements, speak, and move their body. These thr ...
measures the conscious state of a person, and various pain scale
A pain scale measures a patient's pain intensity or other features. Pain scales are a common communication tool in medical contexts, and are used in a variety of medical settings. Pain scales are a necessity to assist with better assessment of pai ...
s exist to assess the "fifth vital sign".
The use of medical equipment is routinely employed to conduct a nursing assessment. These include, the otoscope, thermometer, stethoscope, penlight, sphygmomanometer
A sphygmomanometer ( ), a blood pressure monitor, or blood pressure gauge, is a device used to measure blood pressure, composed of an inflatable cuff to collapse and then release the artery under the cuff in a controlled manner, and a mercury ...
, bladder scanner, speculum, and eye charts. Besides the interviewing process, the nursing assessment utilizes certain techniques to collect information such as observation, auscultation, palpation and percussion.
See also
*Assessment (disambiguation)
Assessment may refer to:
Healthcare
*Health assessment, identifies needs of the patient and how those needs will be addressed
* Nursing assessment, gathering information about a patient's physiological, psychological, sociological, and spiritual ...
* Nursing diagnosis A nursing diagnosis may be part of the nursing process and is a clinical judgment about individual, family, or community experiences/responses to actual or potential health problems/life processes. Nursing diagnoses foster the nurse's independent p ...
References
Bibliography
*Ackley, Betty (2010). Nursing diagnosis handbook : an evidence-based guide to planning care. Maryland Heights, Mo: Mosby. . * Amico, Donita (2016). Health & physical assessment in nursing. Boston: Pearson. . * Bates, Barbara (1995). A pocket guide to physical examination and history taking. Philadelphia: Lippincott. . *Habich, Michele, and MariJo Letizia. 2015. "Pediatric Pain Assessment In the Emergency Department: A Nursing Evidence-Based Practice Protocol." Pediatric Nursing 41, no. 4: 198–202. * Henry, Norma Jean, Mendy McMichael, Janean Johnson, Agnes DiStasi, Brenda S. Ball, Honey C. Holman, Mary Jane Janowski, Marsha S. Barlow, Peggy Leehy and Terri Lemon (2016). Fundamentals for Nursing, Review Module Edition 9.0. Assessment Technologies Institute. . * Kozier, Barbara (2012). Kozier & Erb's fundamentals of nursing : concepts, process, and practice. Boston: Pearson. . * Longe, Jacqueline (2006). The Gale encyclopedia of nursing & allied health. Detroit: Thomson Gale. . * Potter, Patricia (2013). Fundamentals of nursing. St. Louis, Mo: Mosby Elsevier. .* Smith, Sandra (2008). Clinical nursing skills : basic to advanced skills. Upper Saddle River, N.J: Pearson Prentice Hall. . * Smith, Sandra (2002). Photo guide of nursing skills. Upper Saddle River, N.J: Prentice Hall. . * Taylor, Carol (2015). Fundamentals of nursing : the art and science of person-centered nursing care. Philadelphia: Wolters Kluwer Health. * Townsend, Mary (2015). Psychiatric nursing : assessment, care plans, and medications. Philadelphia: F.A. Davis Company. . * Weber, Janet (2014). Nurses' handbook of health assessment. Philadelphia: Wolters Kluwer/Lippincott Williams & Wilkins Health. .Journals
* Schreiber, Mary L. Evidence-Based Practice. ''Neurovascular Assessment: An Essential Nursing Focus.'' MEDSURG Nursing (MEDSURG NURS), Jan/Feb2016; 25(1): 55–57. *Further reading
* Harkreader, Helen and Mary Ann Hogan. Fundamentals of Nursing: Caring and Clinical Judgement. (2003) W B Saunders Co./ref>External links
Glasgow coma scale
Morse Fall Assessment
An assessment tool to determine and quantify persons as low, mid, and high risk for falls.
Pressure Ulcer Staging Guide
from the Wound Care Institute
National Pressure Ulcer Advisory Panel
CETL, Clinical and Communication Skills, Barts and City University of London.
CETL, Clinical and Communication. Barts and City University of London.
CETL, Clinical and Communication. Barts and City University of London.
ATI Nursing Education. {{DEFAULTSORT:Nursing Assessment Assessment, Nursing Physical examination