North American history on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]

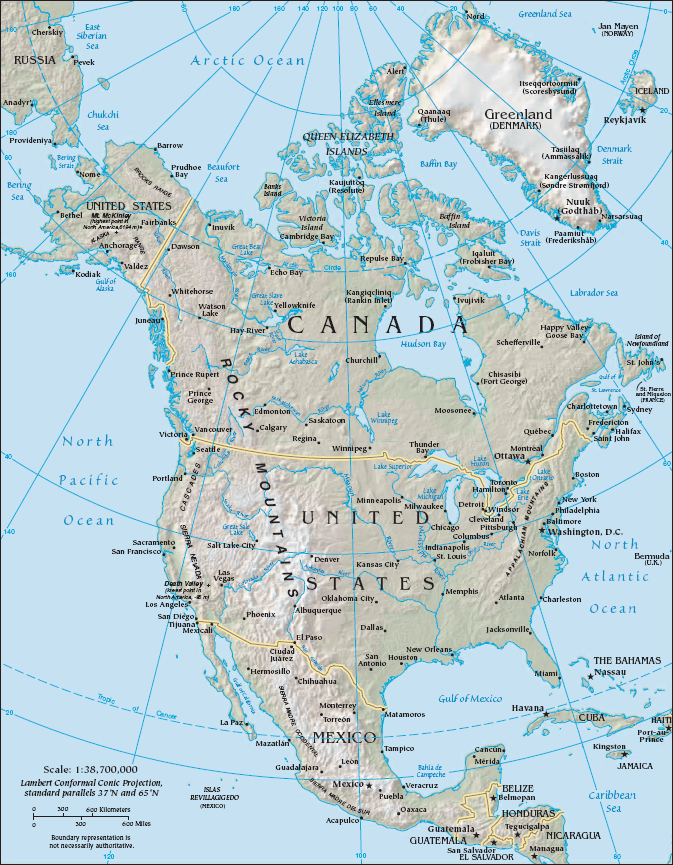 History of North America encompasses the past developments of people populating the continent of
History of North America encompasses the past developments of people populating the continent of
 The specifics of Paleo-Indians' migration to and throughout the Americas, including the exact dates and routes traveled, are subject to ongoing research and discussion. For years, the traditional theory has been that these early migrants moved into the Beringia land bridge between eastern Siberia and present-day Alaska around 40,000–17,000 years ago, when sea levels were significantly lowered due to the
The specifics of Paleo-Indians' migration to and throughout the Americas, including the exact dates and routes traveled, are subject to ongoing research and discussion. For years, the traditional theory has been that these early migrants moved into the Beringia land bridge between eastern Siberia and present-day Alaska around 40,000–17,000 years ago, when sea levels were significantly lowered due to the
This time range is a hot source of debate and promises to continue as such for years to come. The few agreements achieved to date are the origin from Central Asia, with widespread habitation of the Americas during the end of the last glacial period, or more specifically what is known as the
 There was limited
There was limited
 From the time of independence of the United States, that country expanded rapidly to the west, acquiring the massive Louisiana territory in 1803. Between 1810 and 1811 a Native confederacy under Tecumseh fought unsuccessfully to keep the Americans from pushing them out of the Great Lakes. Tecumseh's followers then went north into Canada, where they helped the British to block an American attempt to seize Canada during the
From the time of independence of the United States, that country expanded rapidly to the west, acquiring the massive Louisiana territory in 1803. Between 1810 and 1811 a Native confederacy under Tecumseh fought unsuccessfully to keep the Americans from pushing them out of the Great Lakes. Tecumseh's followers then went north into Canada, where they helped the British to block an American attempt to seize Canada during the

 History of North America encompasses the past developments of people populating the continent of
History of North America encompasses the past developments of people populating the continent of North America
North America is a continent in the Northern Hemisphere and almost entirely within the Western Hemisphere. It is bordered to the north by the Arctic Ocean, to the east by the Atlantic Ocean, to the southeast by South America and th ...
. While it was widely believed that continent first became a human habitat when people migrated across the Bering Sea
The Bering Sea (, ; rus, Бе́рингово мо́ре, r=Béringovo móre) is a marginal sea of the Northern Pacific Ocean. It forms, along with the Bering Strait, the divide between the two largest landmasses on Earth: Eurasia and The Am ...
40,000 to 17,000 years ago, recent discoveries may have pushed those estimates back at least another 90,000 years. People settled
A settler is a person who has migrated to an area and established a permanent residence there, often to colonize the area.
A settler who migrates to an area previously uninhabited or sparsely inhabited may be described as a pioneer.
Settle ...
throughout the continent, from the Inuit
Inuit (; iu, ᐃᓄᐃᑦ 'the people', singular: Inuk, , dual: Inuuk, ) are a group of culturally similar indigenous peoples inhabiting the Arctic and subarctic regions of Greenland, Labrador, Quebec, Nunavut, the Northwest Territorie ...
of the far north to the Mayans
The Maya peoples () are an ethnolinguistic group of indigenous peoples of Mesoamerica. The ancient Maya civilization was formed by members of this group, and today's Maya are generally descended from people who lived within that historical reg ...
and Aztecs
The Aztecs () were a Mesoamerican culture that flourished in central Mexico in the post-classic period from 1300 to 1521. The Aztec people included different ethnic groups of central Mexico, particularly those groups who spoke the Nahuatl ...
of the south. These complex communities each developed their own unique ways of life and cultures.
Records of European travel to North America begin with the Norse colonization in the tenth century AD. In 985, they founded a settlement on Greenland
Greenland ( kl, Kalaallit Nunaat, ; da, Grønland, ) is an island country in North America that is part of the Kingdom of Denmark. It is located between the Arctic and Atlantic oceans, east of the Canadian Arctic Archipelago. Greenland ...
(an often-overlooked part of North America) that persisted until the early 1400s. They also explored the east coast of Canada, but their settlements there were much smaller and shorter-lived. With the Age of Exploration
The Age of Discovery (or the Age of Exploration), also known as the early modern period, was a period largely overlapping with the Age of Sail, approximately from the 15th century to the 17th century in European history, during which seafaring ...
and the voyages of Christopher Columbus
Christopher Columbus
* lij, Cristoffa C(or)ombo
* es, link=no, Cristóbal Colón
* pt, Cristóvão Colombo
* ca, Cristòfor (or )
* la, Christophorus Columbus. (; born between 25 August and 31 October 1451, died 20 May 1506) was a ...
(starting 1492), Europeans began to arrive in the Americas in large numbers and to develop colonial ambitions for both North and South America. After Columbus, influxes of Europeans soon followed and overwhelmed the native population. North America became a staging ground for ongoing European rivalries. The continent was divided by three prominent European powers: England
England is a country that is part of the United Kingdom. It shares land borders with Wales to its west and Scotland to its north. The Irish Sea lies northwest and the Celtic Sea to the southwest. It is separated from continental Europe ...
, France
France (), officially the French Republic ( ), is a country primarily located in Western Europe. It also comprises of Overseas France, overseas regions and territories in the Americas and the Atlantic Ocean, Atlantic, Pacific Ocean, Pac ...
, and Spain
, image_flag = Bandera de España.svg
, image_coat = Escudo de España (mazonado).svg
, national_motto = '' Plus ultra'' (Latin)(English: "Further Beyond")
, national_anthem = (English: "Royal March")
, ...
. The influences of colonization by these states on North American cultures are still apparent today.
Conflict over resources on North America ensued in various wars between these powers, but, gradually, the new European colonies developed desires for independence. Revolutions, such as the American Revolution
The American Revolution was an ideological and political revolution that occurred in British America between 1765 and 1791. The Americans in the Thirteen Colonies formed independent states that defeated the British in the American Revoluti ...
and Mexican War of Independence
The Mexican War of Independence ( es, Guerra de Independencia de México, links=no, 16 September 1810 – 27 September 1821) was an armed conflict and political process resulting in Mexico's independence from Spain. It was not a single, co ...
, created new, independent states that came to dominate North America. The Canadian Confederation
Canadian Confederation (french: Confédération canadienne, link=no) was the process by which three British North American provinces, the Province of Canada, Nova Scotia, and New Brunswick, were united into one federation called the Dominio ...
formed in 1867, creating the modern political landscape of North America.
From the 19th to 21st centuries, North American states have developed increasingly deeper connections with each other. Although some conflicts have occurred, the continent has for the most part enjoyed peace and general cooperation between its states, as well as open commerce and trade between them. Modern developments include the opening of free trade agreements, extensive immigration from Mexico and Latin America, and drug trafficking concerns in these regions.
The beginning of North America
Quaternary glaciation
The Quaternary glaciation, also known as the Pleistocene glaciation, is an alternating series of glacial and interglacial periods during the Quaternary period that began 2.58 Ma (million years ago) and is ongoing. Although geologists describ ...
. These people are believed to have followed herds of now-extinct pleistocene
The Pleistocene ( , often referred to as the ''Ice age'') is the geological Epoch (geology), epoch that lasted from about 2,580,000 to 11,700 years ago, spanning the Earth's most recent period of repeated glaciations. Before a change was fina ...
megafauna
In terrestrial zoology, the megafauna (from Greek μέγας ''megas'' "large" and New Latin ''fauna'' "animal life") comprises the large or giant animals of an area, habitat, or geological period, extinct and/or extant. The most common thresho ...
along ice-free corridors that stretched between the Laurentide and Cordilleran ice sheets. Another route proposed is that, either on foot or using primitive boats, they migrated down the Pacific coast to South America
South America is a continent entirely in the Western Hemisphere and mostly in the Southern Hemisphere, with a relatively small portion in the Northern Hemisphere at the northern tip of the continent. It can also be described as the sou ...
. Evidence of the latter would since have been covered by a sea level rise
Globally, sea levels are rising due to human-caused climate change. Between 1901 and 2018, the globally averaged sea level rose by , or 1–2 mm per year on average.IPCC, 2019Summary for Policymakers InIPCC Special Report on the Ocean and Cr ...
of hundreds of meters following the last ice age.
Archaeologists contend that Paleo-Indian migration out of Beringia ( eastern Alaska), ranges from 40,000 to around 16,500 years ago.page 2This time range is a hot source of debate and promises to continue as such for years to come. The few agreements achieved to date are the origin from Central Asia, with widespread habitation of the Americas during the end of the last glacial period, or more specifically what is known as the
late glacial maximum
The Last Glacial Maximum (LGM), also referred to as the Late Glacial Maximum, was the most recent time during the Last Glacial Period that ice sheets were at their greatest extent.
Ice sheets covered much of Northern North America, Northern Eur ...
, around 16,000–13,000 years before present. However, older alternative theories exist, including migration from Europe.

Stone tools
A stone tool is, in the most general sense, any tool made either partially or entirely out of stone. Although stone tool-dependent societies and cultures still exist today, most stone tools are associated with prehistoric (particularly Stone Ag ...
, particularly projectile points and scrapers, are the primary evidence of early human activity in the Americas. Crafted lithic flake
In archaeology, a lithic flake is a "portion of rock removed from an objective piece by percussion or pressure,"Andrefsky, W. (2005) ''Lithics: Macroscopic Approaches to Analysis''. 2d Ed. Cambridge, Cambridge University Press and may also be ref ...
d tools are used by archaeologists
Archaeology or archeology is the scientific study of human activity through the recovery and analysis of material culture. The archaeological record consists of artifacts, architecture, biofacts or ecofacts, sites, and cultural landscapes ...
and anthropologists
An anthropologist is a person engaged in the practice of anthropology. Anthropology is the study of aspects of humans within past and present societies. Social anthropology, cultural anthropology and philosophical anthropology study the norms and ...
to classify cultural periods. Scientific evidence links indigenous Americans to Asian peoples, specifically eastern Siberian populations. Indigenous peoples of the Americas have been linked to North Asian populations by linguistic dialects, the distribution of blood types
Blood is a body fluid in the circulatory system of humans and other vertebrates that delivers necessary substances such as nutrients and oxygen to the cells, and transports metabolic waste products away from those same cells. Blood in the ...
, and in genetic composition as reflected by molecular data, such as DNA.
8,000–7,000 BCE (10,000–9,000 years ago) the climate stabilized, leading to a rise in population and lithic technology
In archaeology, lithic technology includes a broad array of techniques used to produce usable tools from various types of stone. The earliest stone tools were recovered from modern Ethiopia and were dated to between two-million and three-million ...
advances, resulting in a more sedentary lifestyle
Sedentary lifestyle is a Lifestyle (social sciences), lifestyle type, in which one is physically inactive and does little or no physical movement and or exercise. A person living a sedentary lifestyle is often sitting or lying down while enga ...
.
Pre-Columbian era
Before contact with Europeans, the indigenous peoples of North America were divided into many differentpolities
A polity is an identifiable political entity – a group of people with a collective identity, who are organized by some form of institutionalized social relations, and have a capacity to mobilize resources. A polity can be any other group of p ...
, from small bands of a few families to large empires. They lived in numerous culture areas, which roughly correspond to geographic and biological zones. Societies adapted their subsistence strategies to their homelands, and some societies were hunter-gatherers, some horticulturists
Horticulture is the branch of agriculture that deals with the art, science, technology, and business of plant cultivation. It includes the cultivation of fruits, vegetables, nuts, seeds, herbs, sprouts, mushrooms, algae, flowers, seaweeds and no ...
, some agriculturalist
An agriculturist, agriculturalist, agrologist, or agronomist (abbreviated as agr.), is a professional in the science, practice, and management of agriculture and agribusiness. It is a regulated profession in Canada, India, the Philippines, the ...
s, and many a mix of these. Native groups can also be classified by their language family
A language family is a group of languages related through descent from a common ''ancestral language'' or ''parental language'', called the proto-language of that family. The term "family" reflects the tree model of language origination in h ...
(e.g. Athapascan
Athabaskan (also spelled ''Athabascan'', ''Athapaskan'' or ''Athapascan'', and also known as Dene) is a large family of indigenous languages of North America, located in western North America in three areal language groups: Northern, Pacific ...
or Uto-Aztecan). It is important to note that people with similar languages did not always share the same material culture, nor were they always allies
An alliance is a relationship among people, groups, or states that have joined together for mutual benefit or to achieve some common purpose, whether or not explicit agreement has been worked out among them. Members of an alliance are called ...
.
The Archaic period in the Americas
Archaic is a period of time preceding a designated classical period, or something from an older period of time that is also not found or used currently:
*List of archaeological periods
**Archaic Sumerian language, spoken between 31st - 26th cent ...
saw a changing environment featuring a warmer more arid
A region is arid when it severely lacks available water, to the extent of hindering or preventing the growth and development of plant and animal life. Regions with arid climates tend to lack vegetation and are called xeric or desertic. Most ...
climate and the disappearance of the last megafauna. The majority of population groups at this time were still highly mobile hunter-gatherers; but now individual groups started to focus on resources available to them locally, thus with the passage of time there is a pattern of increasing regional generalization, for example the Southwest
The points of the compass are a set of horizontal, radially arrayed compass directions (or azimuths) used in navigation and cartography. A compass rose is primarily composed of four cardinal directions—north, east, south, and west—each sepa ...
, Arctic
The Arctic ( or ) is a polar region located at the northernmost part of Earth. The Arctic consists of the Arctic Ocean, adjacent seas, and parts of Canada (Yukon, Northwest Territories, Nunavut), Danish Realm (Greenland), Finland, Iceland, N ...
, Poverty Point culture
The Poverty Point culture is the archaeological culture of a prehistoric indigenous peoples who inhabited a portion of North America's lower Mississippi Valley and surrounding Gulf coast from about 1730 – 1350 BC.
Archeologists have identified ...
, Plains Arctic, Dalton
Dalton may refer to:
Science
* Dalton (crater), a lunar crater
* Dalton (program), chemistry software
* Dalton (unit) (Da), the atomic mass unit
* John Dalton, chemist, physicist and meteorologist
Entertainment
* Dalton (Buffyverse), minor ch ...
, and Plano traditions. This kind of regional adaptation became the norm, with reliance less on hunting and gathering among many cultures, with a more mixed economy of small game, fish, seasonally wild vegetables and harvested plant foods. Many groups continued as big game hunters, but their hunting traditions became more varied, and meat procurement methods more sophisticated.
The placement of artifacts and materials within an Archaic burial site indicated social differentiation based upon status in some groups.
Agriculture was invented independently in two regions of North America: the Eastern Woodlands
The Eastern Woodlands is a cultural area of the indigenous people of North America. The Eastern Woodlands extended roughly from the Atlantic Ocean to the eastern Great Plains, and from the Great Lakes region to the Gulf of Mexico, which is now p ...
and Mesoamerica
Mesoamerica is a historical region and cultural area in southern North America and most of Central America. It extends from approximately central Mexico through Belize, Guatemala, El Salvador, Honduras, Nicaragua, and northern Costa Rica ...
. The more southern cultural groups of North America were responsible for the domestication
Domestication is a sustained multi-generational relationship in which humans assume a significant degree of control over the reproduction and care of another group of organisms to secure a more predictable supply of resources from that group. ...
of many common crops now used around the world, such as tomatoes and squash
Squash may refer to:
Sports
* Squash (sport), the high-speed racquet sport also known as squash racquets
* Squash (professional wrestling), an extremely one-sided match in professional wrestling
* Squash tennis, a game similar to squash but pla ...
. Perhaps most importantly they domesticated one of the world's major staples, maize (corn). During the Plains Village period The Plains Village period or the Plains Village tradition is an archaeological period on the Great Plains from North Dakota down to Texas, spanning approximately 900/950 to 1780/1850 CE.
On the west and east, Plains villagers were bounded by the ...
, agriculture
Agriculture or farming is the practice of cultivating plants and livestock. Agriculture was the key development in the rise of sedentary human civilization, whereby farming of domesticated species created food surpluses that enabled people t ...
and bison-hunting were important to Great Plains tribes
Plains Indians or Indigenous peoples of the Great Plains and Canadian Prairies are the Native American tribes and First Nation band governments who have historically lived on the Interior Plains (the Great Plains and Canadian Prairies) of ...
.
As a result of the development of agriculture in the south, many important cultural advances were made there. For example, the Maya civilization
The Maya civilization () of the Mesoamerican people is known by its ancient temples and glyphs. Its Maya script is the most sophisticated and highly developed writing system in the pre-Columbian Americas. It is also noted for its art, a ...
developed a writing system
A writing system is a method of visually representing verbal communication, based on a script and a set of rules regulating its use. While both writing and speech are useful in conveying messages, writing differs in also being a reliable fo ...
, built huge pyramids, had a complex calendar, and developed the concept of zero
0 (zero) is a number representing an empty quantity. In place-value notation such as the Hindu–Arabic numeral system, 0 also serves as a placeholder numerical digit, which works by multiplying digits to the left of 0 by the radix, usual ...
500 years before anyone in the Old World. The Mayan culture was still present when the Spanish
Spanish might refer to:
* Items from or related to Spain:
**Spaniards are a nation and ethnic group indigenous to Spain
**Spanish language, spoken in Spain and many Latin American countries
**Spanish cuisine
Other places
* Spanish, Ontario, Can ...
arrived in Central America, but political dominance in the area had shifted to the Aztec Empire further north.
In the Southwest of North America, Hohokam and Ancestral Pueblo
The Ancestral Puebloans, also known as the Anasazi, were an ancient Native American culture that spanned the present-day Four Corners region of the United States, comprising southeastern Utah, northeastern Arizona, northwestern New Mexico, a ...
societies had been engaged in agricultural production with ditch irrigation and a sedentary village life for at least two millennia before the Spanish arrived in the 1540s. Upon the arrival of the Europeans in the "New World", native peoples found their culture changed drastically. As such, their affiliation with political and cultural groups changed as well, several linguistic groups went extinct, and others changed quite quickly. The name and cultures that Europeans recorded for the natives were not necessarily the same as the ones they had used a few generations before, or the ones in use today.
Arrival of Europeans
Early contact
 There was limited
There was limited contact
Contact may refer to:
Interaction Physical interaction
* Contact (geology), a common geological feature
* Contact lens or contact, a lens placed on the eye
* Contact sport, a sport in which players make contact with other players or objects
* ...
between North American people and the outside world before 1492. Several theoretical contacts have been proposed, but the earliest physical evidence comes from the Norse or Vikings
Vikings ; non, víkingr is the modern name given to seafaring people originally from Scandinavia (present-day Denmark, Norway and Sweden),
who from the late 8th to the late 11th centuries raided, pirated, traded and ...
. Erik the Red founded a colony on Greenland
Greenland ( kl, Kalaallit Nunaat, ; da, Grønland, ) is an island country in North America that is part of the Kingdom of Denmark. It is located between the Arctic and Atlantic oceans, east of the Canadian Arctic Archipelago. Greenland i ...
in 985 CE. Erik's son Leif Eriksson
Leif Erikson, Leiv Eiriksson, or Leif Ericson, ; Modern Icelandic: ; Norwegian: ''Leiv Eiriksson'' also known as Leif the Lucky (), was a Norse explorer who is thought to have been the first European to have set foot on continental North ...
is believed to have reached the Island of Newfoundland
Newfoundland (, ; french: link=no, Terre-Neuve, ; ) is a large island off the east coast of the North American mainland and the most populous part of the Canadian province of Newfoundland and Labrador. It has 29 percent of the province's land ...
circa 1000, naming the discovery Vinland
Vinland, Vineland, or Winland ( non, Vínland ᚠᛁᚾᛚᛅᚾᛏ) was an area of coastal North America explored by Vikings. Leif Erikson landed there around 1000 AD, nearly five centuries before the voyages of Christopher Columbus and John ...
. The only Norse site outside of Greenland yet discovered in North America is at L'Anse aux Meadows
L'Anse aux Meadows ( lit. Meadows Cove) is an archaeological site, first excavated in the 1960s, of a Norse settlement dating to approximately 1,000 years ago. The site is located on the northernmost tip of the island of Newfoundland in the ...
, Newfoundland and Labrador in Canada. All of the Norse colonies were eventually abandoned.
The Norse voyages did not become common knowledge in the Old World. Even the permanent settlement in Greenland, which persisted until the early 1400s, received little attention and Europeans remained largely ignorant of the existence of the Americas until 1492. As part of a general age of discovery
The Age of Discovery (or the Age of Exploration), also known as the early modern period, was a period largely overlapping with the Age of Sail, approximately from the 15th century to the 17th century in European history, during which seafarin ...
, Italian sailor Christopher Columbus
Christopher Columbus
* lij, Cristoffa C(or)ombo
* es, link=no, Cristóbal Colón
* pt, Cristóvão Colombo
* ca, Cristòfor (or )
* la, Christophorus Columbus. (; born between 25 August and 31 October 1451, died 20 May 1506) was a ...
proposed a voyage west from Europe to find a shorter route to Asia. He eventually received the backing of Isabella I
Isabella I ( es, Isabel I; 22 April 1451 – 26 November 1504), also called Isabella the Catholic (Spanish: ''la Católica''), was Queen of Castile from 1474 until her death in 1504, as well as Queen consort of Aragon from 1479 until 1504 by ...
and Ferdinand II, Queen and King of newly united Spain. In 1492 Columbus reached land in the Bahamas
The Bahamas (), officially the Commonwealth of The Bahamas, is an island country within the Lucayan Archipelago of the West Indies in the North Atlantic. It takes up 97% of the Lucayan Archipelago's land area and is home to 88% of the ar ...
.
Almost 500 years after the Norse, John Cabot explored the east coast of what would become Canada in 1497. Giovanni da Verrazzano
Giovanni da Verrazzano ( , , often misspelled Verrazano in English; 1485–1528) was an Italian ( Florentine) explorer of North America, in the service of King Francis I of France.
He is renowned as the first European to explore the Atlanti ...
explored the East Coast of North America from Florida to presumably Newfoundland in 1524. Jacques Cartier made a series of voyages on behalf of the French crown in 1534 and explored the St. Lawrence River
The St. Lawrence River (french: Fleuve Saint-Laurent, ) is a large river in the middle latitudes of North America. Its headwaters begin flowing from Lake Ontario in a (roughly) northeasterly direction, into the Gulf of St. Lawrence, connecting ...
.
Successful colonization
To understand what constitutes successful colonization, it is important to understand what colonization means. Colonization refers to large-scale population movements in which the migrants maintain strong links with their or their ancestors' former country, gaining significant advantages over other inhabitants of the territory by such links. When colonization takes place under the protection of clearly colonial political structures, it may most handily be called ''settler colonialism''. This often involves the settlers' entirely dispossessing earlier inhabitants, or instituting legal and other structures which systematically disadvantage them. Initially, European activity consisted mostly of trade and exploration. Eventually Europeans began to establish settlements. The three principal colonial powers in North America wereSpain
, image_flag = Bandera de España.svg
, image_coat = Escudo de España (mazonado).svg
, national_motto = ''Plus ultra'' (Latin)(English: "Further Beyond")
, national_anthem = (English: "Royal March")
, i ...
, England
England is a country that is part of the United Kingdom. It shares land borders with Wales to its west and Scotland to its north. The Irish Sea lies northwest and the Celtic Sea to the southwest. It is separated from continental Europe b ...
, and France
France (), officially the French Republic ( ), is a country primarily located in Western Europe. It also comprises of overseas regions and territories in the Americas and the Atlantic, Pacific and Indian Oceans. Its metropolitan area ...
, although eventually other powers such as the Netherlands
)
, anthem = ( en, "William of Nassau")
, image_map =
, map_caption =
, subdivision_type = Sovereign state
, subdivision_name = Kingdom of the Netherlands
, established_title = Before independence
, established_date = Spanish Netherl ...
and Sweden also received holdings on the continent.
Settlement by the Spanish started the European colonization of the Americas
During the Age of Discovery, a large scale European colonization of the Americas took place between about 1492 and 1800. Although the Norse had explored and colonized areas of the North Atlantic, colonizing Greenland and creating a short t ...
.Ward 1997, pp. 97–132 They gained control of most of the largest islands in the Caribbean and conquered the Aztec empire, gaining control of present-day Mexico and Central America. This was the beginning of the Spanish Empire
The Spanish Empire ( es, link=no, Imperio español), also known as the Hispanic Monarchy ( es, link=no, Monarquía Hispánica) or the Catholic Monarchy ( es, link=no, Monarquía Católica) was a colonial empire governed by Spain and its prede ...
in the New World. The first successful Spanish settlement in continental North America was Veracruz
Veracruz (), formally Veracruz de Ignacio de la Llave (), officially the Free and Sovereign State of Veracruz de Ignacio de la Llave ( es, Estado Libre y Soberano de Veracruz de Ignacio de la Llave), is one of the 31 states which, along with Me ...
founded by Hernán Cortés in 1519, followed by many other settlements in colonial New Spain, including Spanish Florida, Central America, New Mexico
)
, population_demonym = New Mexican ( es, Neomexicano, Neomejicano, Nuevo Mexicano)
, seat = Santa Fe
, LargestCity = Albuquerque
, LargestMetro = Tiguex
, OfficialLang = None
, Languages = English, Spanish ( New Mexican), Navajo, Ke ...
, and later California. The Spanish claimed all of North and South America (with the exception of Brazil), and no other European power challenged those claims by planting colonies until over a century after Spain's first settlements.
The first French settlements were Port Royal (1604) and Quebec City
Quebec City ( or ; french: Ville de Québec), officially Québec (), is the capital city of the Canadian province of Quebec. As of July 2021, the city had a population of 549,459, and the metropolitan area had a population of 839,311. It is t ...
(1608) in what is now Nova Scotia
Nova Scotia ( ; ; ) is one of the thirteen provinces and territories of Canada. It is one of the three Maritime provinces and one of the four Atlantic provinces. Nova Scotia is Latin for "New Scotland".
Most of the population are native Eng ...
and Quebec
Quebec ( ; )According to the Canadian government, ''Québec'' (with the acute accent) is the official name in Canadian French and ''Quebec'' (without the accent) is the province's official name in Canadian English is one of the thirtee ...
. The Fur Trade soon became the primary business on the continent and as a result transformed the indigenous North American ways of life.
The first permanent English settlements were at Jamestown (1607) (along with its satellite, Bermuda
)
, anthem = "God Save the King"
, song_type = National song
, song = "Hail to Bermuda"
, image_map =
, map_caption =
, image_map2 =
, mapsize2 =
, map_caption2 =
, subdivision_type = Sovereign state
, subdivision_name =
, es ...
in 1609) and Plymouth (1620), in what are today Virginia
Virginia, officially the Commonwealth of Virginia, is a state in the Mid-Atlantic and Southeastern regions of the United States, between the Atlantic Coast and the Appalachian Mountains. The geography and climate of the Commonwealth ar ...
and Massachusetts
Massachusetts (Massachusett: ''Muhsachuweesut Massachusett_writing_systems.html" ;"title="nowiki/> məhswatʃəwiːsət.html" ;"title="Massachusett writing systems">məhswatʃəwiːsət">Massachusett writing systems">məhswatʃəwiːsət'' En ...
respectively.
Further to the south, plantation slavery became the main industry of the West Indies
The West Indies is a subregion of North America, surrounded by the North Atlantic Ocean and the Caribbean Sea that includes 13 independent island countries and 18 dependencies and other territories in three major archipelagos: the Greate ...
, and this gave rise to the beginning of the Atlantic slave trade.
Colonial era
By the year 1663 theFrench crown
France was ruled by monarchs from the establishment of the Kingdom of West Francia in 843 until the end of the Second French Empire in 1870, with several interruptions.
Classical French historiography usually regards Clovis I () as the firs ...
had taken over control of New France
New France (french: Nouvelle-France) was the area colonized by France in North America, beginning with the exploration of the Gulf of Saint Lawrence by Jacques Cartier in 1534 and ending with the cession of New France to Great Britain and Spa ...
from the fur-trading companies, and the English charter colonies gave way to more metropolitan control. This ushered in a new era of more formalized colonialism in North America.
Rivalry between the European powers created a series of wars on the North American landmass that would have great impact on the development of the colonies. Territory often changed hands multiple times. Peace was not achieved until French forces in North America were vanquished at the Battle of the Plains of Abraham
The Battle of the Plains of Abraham, also known as the Battle of Quebec (french: Bataille des Plaines d'Abraham, Première bataille de Québec), was a pivotal battle in the Seven Years' War (referred to as the French and Indian War to describe ...
at Quebec City
Quebec City ( or ; french: Ville de Québec), officially Québec (), is the capital city of the Canadian province of Quebec. As of July 2021, the city had a population of 549,459, and the metropolitan area had a population of 839,311. It is t ...
, and France ceded most of her claims outside of the Caribbean. The end of the French presence in North America was a disaster for most Native nations in Eastern North America, who lost their major ally against the expanding Anglo-American settlement's. During Pontiac's Rebellion
Pontiac's War (also known as Pontiac's Conspiracy or Pontiac's Rebellion) was launched in 1763 by a loose confederation of Native Americans dissatisfied with British rule in the Great Lakes region following the French and Indian War (1754–176 ...
from 1763 to 1766, a confederation of Great Lakes-area tribes fought a somewhat successful campaign to defend their rights over their lands west of the Appalachian Mountains
The Appalachian Mountains, often called the Appalachians, (french: Appalaches), are a system of mountains in eastern to northeastern North America. The Appalachians first formed roughly 480 million years ago during the Ordovician Period. They ...
, which had been "reserved" for them under the Royal Proclamation of 1763
The Royal Proclamation of 1763 was issued by King George III on 7 October 1763. It followed the Treaty of Paris (1763), which formally ended the Seven Years' War and transferred French territory in North America to Great Britain. The Procla ...
.
Viceroyalty of New Spain (present-day Mexico) was the name of the viceroy
A viceroy () is an official who reigns over a polity in the name of and as the representative of the monarch of the territory. The term derives from the Latin prefix ''vice-'', meaning "in the place of" and the French word ''roy'', meaning " ...
-ruled territories of the Spanish Empire
The Spanish Empire ( es, link=no, Imperio español), also known as the Hispanic Monarchy ( es, link=no, Monarquía Hispánica) or the Catholic Monarchy ( es, link=no, Monarquía Católica) was a colonial empire governed by Spain and its prede ...
in Asia, North America and its peripheries from 1535 to 1821.
Revolutions
The coming of the American Revolution had a great impact across the continent. Most importantly it directly led to the creation of the United States of America. However, the associatedAmerican Revolutionary War
The American Revolutionary War (April 19, 1775 – September 3, 1783), also known as the Revolutionary War or American War of Independence, was a major war of the American Revolution. Widely considered as the war that secured the independence of t ...
was an important war that touched all corners of the region. The flight of the United Empire Loyalists
United Empire Loyalists (or simply Loyalists) is an honorific title which was first given by the 1st Lord Dorchester, the Governor of Quebec, and Governor General of The Canadas, to American Loyalists who resettled in British North America dur ...
led to the creation of English Canada
Canada comprises that part of the population within Canada, whether of British origin or otherwise, that speaks English.
The term ''English Canada'' can also be used for one of the following:
#Describing all the provinces of Canada tha ...
as a separate community
Meanwhile, Spain's hold on Mexico was weakening. Independence was declared in 1810 by Miguel Hidalgo
Don Miguel Gregorio Antonio Ignacio Hidalgo y Costilla y Gallaga Mandarte Villaseñor (8 May 1753 – 30 July 1811), more commonly known as Miguel Hidalgo y Costilla or Miguel Hidalgo (), was a Catholic priest, leader of the Mexican ...
, starting the ''Mexican War of Independence''. In 1813, José María Morelos
José María Teclo Morelos Pérez y Pavón () (30 September 1765 – 22 December 1815) was a Mexican Catholic priest, statesman and military leader who led the Mexican War of Independence movement, assuming its leadership after the execution of ...
and the Congress of Anáhuac signed the Solemn Act of the Declaration of Independence of Northern America
The Solemn Act of Northern America's Declaration of Independence ( es, Acta Solemne de la Declaración de Independencia de la América Septentrional) is the first Mexican legal historical document which established the separation of Mexico from S ...
, the first legal document where the separation of the New Spain with respect to Spain is proclaimed. Spain finally recognized Mexico's independence in 1821.
Expansion era
 From the time of independence of the United States, that country expanded rapidly to the west, acquiring the massive Louisiana territory in 1803. Between 1810 and 1811 a Native confederacy under Tecumseh fought unsuccessfully to keep the Americans from pushing them out of the Great Lakes. Tecumseh's followers then went north into Canada, where they helped the British to block an American attempt to seize Canada during the
From the time of independence of the United States, that country expanded rapidly to the west, acquiring the massive Louisiana territory in 1803. Between 1810 and 1811 a Native confederacy under Tecumseh fought unsuccessfully to keep the Americans from pushing them out of the Great Lakes. Tecumseh's followers then went north into Canada, where they helped the British to block an American attempt to seize Canada during the War of 1812
The War of 1812 (18 June 1812 – 17 February 1815) was fought by the United States, United States of America and its Indigenous peoples of the Americas, indigenous allies against the United Kingdom of Great Britain and Ireland, United Kingdom ...
. Following the war, British and Irish settlement in Canada increased dramatically.
US expansion was complicated by the division between "free" and "slave" states, which led to the Missouri Compromise
The Missouri Compromise was a federal legislation of the United States that balanced desires of northern states to prevent expansion of slavery in the country with those of southern states to expand it. It admitted Missouri as a slave state and ...
in 1820. Likewise, Canada faced a division between French and English
English usually refers to:
* English language
* English people
English may also refer to:
Peoples, culture, and language
* ''English'', an adjective for something of, from, or related to England
** English national ide ...
communities that led to the outbreak of civil strife in 1837. Mexico faced constant political tensions between liberals and conservatives, as well as the rebellion of the English-speaking region of Texas, which declared itself the Republic of Texas in 1836. In 1845 Texas joined the United States, which would later lead to the Mexican–American War
The Mexican–American War, also known in the United States as the Mexican War and in Mexico as the (''United States intervention in Mexico''), was an armed conflict between the United States and Mexico from 1846 to 1848. It followed the 1 ...
in 1846 that began American imperialism
American imperialism refers to the expansion of American political, economic, cultural, and media influence beyond the boundaries of the United States. Depending on the commentator, it may include imperialism through outright military conques ...
. As a result of conflict with Mexico, the United States made further territorial gains in California
California is a state in the Western United States, located along the Pacific Coast. With nearly 39.2million residents across a total area of approximately , it is the most populous U.S. state and the 3rd largest by area. It is also the m ...
and the Southwest.
Conflict, confederation, and invasion
The secession of theConfederate States
The Confederate States of America (CSA), commonly referred to as the Confederate States or the Confederacy was an unrecognized breakaway republic in the Southern United States that existed from February 8, 1861, to May 9, 1865. The Confeder ...
and the resulting civil war rocked American society. It eventually led to the end of slavery in the United States, the destruction and later reconstruction
Reconstruction may refer to:
Politics, history, and sociology
*Reconstruction (law), the transfer of a company's (or several companies') business to a new company
*'' Perestroika'' (Russian for "reconstruction"), a late 20th century Soviet Unio ...
of most of the South, and tremendous loss of life. From the conflict, the United States emerged as a powerful industrialized nation.
Partly as a response to the threat of American power, four of the Canadian colonies agreed to federate in 1867, creating the Dominion
The term ''Dominion'' is used to refer to one of several self-governing nations of the British Empire.
"Dominion status" was first accorded to Canada, Australia, New Zealand, Newfoundland, South Africa, and the Irish Free State at the 192 ...
of Canada. The new nation was not fully sovereign, but enjoyed considerable independence from Britain. With the addition of British Columbia
British Columbia (commonly abbreviated as BC) is the westernmost province of Canada, situated between the Pacific Ocean and the Rocky Mountains. It has a diverse geography, with rugged landscapes that include rocky coastlines, sandy beaches, ...
Canada would expand to the Pacific by 1871 and establish a transcontinental railway, the Canadian Pacific, by 1885.
In Mexico conflicts like the Reform War
The Reform War, or War of Reform ( es, Guerra de Reforma), also known as the Three Years' War ( es, Guerra de los Tres Años), was a civil war in Mexico lasting from January 11, 1858 to January 11, 1861, fought between liberals and conservativ ...
left the state weak, and open to foreign influence. This led to the Second French Empire
The Second French Empire (; officially the French Empire, ), was the 18-year Imperial Bonapartist regime of Napoleon III from 14 January 1852 to 27 October 1870, between the Second and the Third Republic of France.
Historians in the 1930 ...
to invade Mexico.
Late 19th century
In both the United States and Canada, the second half of the 19th century witnessed massive inflows of immigration to settle the West. These lands were not uninhabited however: in the United States the government fought numerousIndian Wars
The American Indian Wars, also known as the American Frontier Wars, and the Indian Wars, were fought by European governments and colonists in North America, and later by the United States and Canadian governments and American and Canadian settle ...
against the native inhabitants. In Canada, relations were more peaceful, as a result of the Numbered Treaties
The Numbered Treaties (or Post-Confederation Treaties) are a series of eleven treaties signed between the First Nations, one of three groups of Indigenous peoples in Canada, and the reigning monarch of Canada (Victoria, Edward VII or George V) ...
, but two rebellions broke out in 1870 and 1885 on the prairies. The British colony of Newfoundland became a dominion in 1907.
In Mexico, the entire era was dominated by the dictatorship of Porfirio Díaz.
World Wars era
World War I
As a part of theBritish Empire
The British Empire was composed of the dominions, colonies, protectorates, mandates, and other territories ruled or administered by the United Kingdom and its predecessor states. It began with the overseas possessions and trading posts e ...
Canada immediately was at war in 1914. Canada bore the brunt of several major battles during the early stages of the war including the use of poison gas
Many gases have toxic properties, which are often assessed using the LC50 (median lethal dose) measure. In the United States, many of these gases have been assigned an NFPA 704 health rating of 4 (may be fatal) or 3 (may cause serious or perman ...
attacks at Ypres
Ypres ( , ; nl, Ieper ; vls, Yper; german: Ypern ) is a Belgian city and municipality in the province of West Flanders. Though
the Dutch name is the official one, the city's French name is most commonly used in English. The municipality c ...
. Losses became grave, and the government eventually brought in conscription, despite the fact this was against the wishes of the majority of French Canadians. In the ensuing Conscription Crisis of 1917, riots broke out on the streets of Montreal
Montreal ( ; officially Montréal, ) is the second-most populous city in Canada and most populous city in the Canadian province of Quebec. Founded in 1642 as '' Ville-Marie'', or "City of Mary", it is named after Mount Royal, the triple ...
. In neighboring Newfoundland, the new dominion suffered a devastating loss on July 1, 1916, the First day on the Somme
The first day on the Somme, 1 July 1916, was the beginning of the Battle of Albert the name given by the British to the first two weeks of the 141 days of the Battle of the Somme () in the First World War. Nine corps of the French Sixth Ar ...
.
The United States stayed apart from the conflict until 1917, joining the Entente powers. The United States was then able to play a crucial role at the Paris Peace Conference of 1919
Paris () is the capital and most populous city of France, with an estimated population of 2,165,423 residents in 2019 in an area of more than 105 km² (41 sq mi), making it the 30th most densely populated city in the world in 2020. S ...
that shaped interwar
In the history of the 20th century, the interwar period lasted from 11 November 1918 to 1 September 1939 (20 years, 9 months, 21 days), the end of the First World War to the beginning of the Second World War. The interwar period was relativel ...
Europe.
Mexico was not part of the war as the country was embroiled in the Mexican Revolution at the time.
Interwar years
The 1920s brought an age of great prosperity in the United States, and to a lesser degree Canada. But theWall Street Crash of 1929
The Wall Street Crash of 1929, also known as the Great Crash, was a major American stock market crash that occurred in the autumn of 1929. It started in September and ended late in October, when share prices on the New York Stock Exchange coll ...
combined with drought
A drought is defined as drier than normal conditions.Douville, H., K. Raghavan, J. Renwick, R.P. Allan, P.A. Arias, M. Barlow, R. Cerezo-Mota, A. Cherchi, T.Y. Gan, J. Gergis, D. Jiang, A. Khan, W. Pokam Mba, D. Rosenfeld, J. Tierney, an ...
ushered in a period of economic hardship in the United States and Canada
Canada is a country in North America. Its ten provinces and three territories extend from the Atlantic Ocean to the Pacific Ocean and northward into the Arctic Ocean, covering over , making it the world's second-largest country by tot ...
.
From 1937 to 1949, this was a popular uprising against the anti-Catholic Mexican government of the time, set off specifically by the anti-clerical provisions of the Mexican Constitution of 1917
The Constitution of Mexico, formally the Political Constitution of the United Mexican States ( es, Constitución Política de los Estados Unidos Mexicanos), is the current constitution of Mexico. It was drafted in Santiago de Querétaro, in th ...
.
World War II
Once again Canada found itself at war before her neighbors, however even Canadian contributions were slight before the Japaneseattack on Pearl Harbor
The attack on Pearl HarborAlso known as the Battle of Pearl Harbor was a surprise military strike by the Imperial Japanese Navy Air Service upon the United States against the naval base at Pearl Harbor in Honolulu, Territory of Hawaii ...
. The entry of the United States into the war helped to tip the balance in favor of the Allies
An alliance is a relationship among people, groups, or states that have joined together for mutual benefit or to achieve some common purpose, whether or not explicit agreement has been worked out among them. Members of an alliance are called ...
. On August 19, 1942, a force of some 6000, largely Canadian, infantry was landed near the French channel port of Dieppe
Dieppe (; Norman: ''Dgieppe'') is a coastal commune in the Seine-Maritime department in the Normandy region of northern France.
Dieppe is a seaport on the English Channel at the mouth of the river Arques. A regular ferry service runs to N ...
. The German defenders under General von Rundstedt destroyed the invaders. 907 Canadians were killed and almost 2,500 captured (many wounded). Lessons learned in this abortive raid were put to good use 2 years later in the successful Normandy invasion.
Two Mexican tankers, transporting oil to the United States, were attacked and sunk by the Germans in the Gulf of Mexico
The Gulf of Mexico ( es, Golfo de México) is an ocean basin and a marginal sea of the Atlantic Ocean, largely surrounded by the North American continent. It is bounded on the northeast, north and northwest by the Gulf Coast of the United ...
waters, in 1942. The incident happened in spite of Mexico's neutrality at that time. This led Mexico to declare war on the Axis nations and enter the conflict.
The destruction of Europe wrought by the war vaulted all North American countries to more important roles in world affairs. The United States especially emerged as a "superpower".
Post-war
The early Cold War era saw the United States as the most powerful nation in a Western coalition of which Mexico and Canada were also a part. At home, the United States witnessed convulsive change especially in the area ofrace relations
Race relations is a sociological concept that emerged in Chicago in connection with the work of sociologist Robert E. Park and the Chicago race riot of 1919. Race relations designates a paradigm or field in sociology and a legal concept in the ...
. In Canada this was mirrored by the Quiet Revolution
The Quiet Revolution (french: Révolution tranquille) was a period of intense socio-political and socio-cultural change in French Canada which started in Quebec after the election of 1960, characterized by the effective secularization of govern ...
and the emergence of Quebec nationalism
Quebec nationalism or Québécois nationalism is a feeling and a political doctrine that prioritizes cultural belonging to, the defence of the interests of, and the recognition of the political legitimacy of the Québécois nation. It has been ...
.
Mexico experienced an era of huge economic growth after World War II, a heavy industrialization process and a growth of its middle class, a period known in Mexican history as the ''"El Milagro Mexicano"'' (Mexican miracle).
The Caribbean saw the beginnings of decolonization
Decolonization or decolonisation is the undoing of colonialism, the latter being the process whereby imperial nations establish and dominate foreign territories, often overseas. Some scholars of decolonization focus especially on separatism, in ...
, while on the largest island the Cuban Revolution
The Cuban Revolution ( es, Revolución Cubana) was carried out after the 1952 Cuban coup d'état which placed Fulgencio Batista as head of state and the failed mass strike in opposition that followed. After failing to contest Batista in co ...
introduced Cold War rivalries into Latin America.
In 1959 the non-contiguous
Contiguity or contiguous may refer to:
*Contiguous data storage, in computer science
*Contiguity (probability theory)
*Contiguity (psychology)
*Contiguous distribution of species, in biogeography
*Geographic contiguity of territorial land
*Contigu ...
US territories of Alaska
Alaska ( ; russian: Аляска, Alyaska; ale, Alax̂sxax̂; ; ems, Alas'kaaq; Yup'ik: ''Alaskaq''; tli, Anáaski) is a state located in the Western United States on the northwest extremity of North America. A semi-exclave of the U.S. ...
and Hawaii became US states.
Vietnam War and ''stagflation''
During this time the United States became involved in theVietnam War
The Vietnam War (also known by other names) was a conflict in Vietnam, Laos, and Cambodia from 1 November 1955 to the fall of Saigon on 30 April 1975. It was the second of the Indochina Wars and was officially fought between North Vietnam a ...
as part of the global Cold War. This war would later prove to be highly divisive in American society, and American troops were withdrawn from Indochina in 1975 with the Khmer Rouge's capture of Phnom Penh on April 17, the Vietnam People's Army
Vietnam or Viet Nam ( vi, Việt Nam, ), officially the Socialist Republic of Vietnam,., group="n" is a country in Southeast Asia, at the eastern edge of mainland Southeast Asia, with an area of and population of 96 million, making i ...
's capture of Saigon on April 30 and the Pathet Lao's capture of Vientiane
Vientiane ( , ; lo, ວຽງຈັນ, ''Viangchan'', ) is the capital and largest city of Laos. Vientiane is divided administratively into 9 cities with a total area of only approx. 3,920 square kilometres and is located on the banks of ...
on December 2.
Canada during this era was dominated by the leadership of Pierre Elliot Trudeau
Joseph Philippe Pierre Yves Elliott Trudeau ( , ; October 18, 1919 – September 28, 2000), also referred to by his initials PET, was a Canadian lawyer and politician who served as the 15th prime minister of Canada from 1968 to 1979 and ...
. Eventually in 1982 at the end of his tenure, Canada received a new constitution.
Both the United States and Canada experienced stagflation
In economics, stagflation or recession-inflation is a situation in which the inflation rate is high or increasing, the economic growth rate slows, and unemployment remains steadily high. It presents a dilemma for economic policy, since actio ...
, which eventually led to a revival in small-government politics.
The 1980s
Mexican presidents Miguel de la Madrid, in the early 1980s andCarlos Salinas de Gortari
Carlos Salinas de Gortari CYC DMN (; born 3 April 1948) is a Mexican economist and politician who served as 60th president of Mexico from 1988 to 1994. Affiliated with the Institutional Revolutionary Party (PRI), earlier in his career he wor ...
in the late 1980s, started implementing liberal economic strategies that were seen as a good move. However, Mexico experienced a strong economic recession in 1982 and the Mexican peso suffered a devaluation. Presidential elections held in 1988 were forecast to be very competitive and they were. Leftist candidate Cuauhtémoc Cárdenas
Cuauhtémoc Cárdenas Solórzano (; born 1 May 1934) is a Mexican prominent politician. The son of 51st President of Mexico Lázaro Cárdenas, he is a former Head of Government of Mexico City and a founder of the Party of the Democratic Revolut ...
, son of Lázaro Cárdenas one of the most beloved Mexican presidents, created a successful campaign and was reported as the leader in several opinion polls. On July 6, 1988, the day of the elections, a system shutdown of the IBM AS/400
The IBM AS/400 (Application System/400) is a family of midrange computers from IBM announced in June 1988 and released in August 1988. It was the successor to the System/36 and System/38 platforms, and ran the OS/400 operating system. Lower-cost ...
that the government was using to count the votes occurred, presumably by accident. The government simply stated that ''"se cayó el sistema"'' ("the system crashed"), to refer to the incident. When the system was finally restored, the PRI candidate Carlos Salinas was declared the official winner. It was the first time since the Revolution that a non-PRI candidate was so close to winning the presidency.
In the United States president Ronald Reagan attempted to move the United States back towards a hard anti-communist line in foreign affairs, in what his supporters saw as an attempt to assert moral leadership (compared to the Soviet Union
The Soviet Union,. officially the Union of Soviet Socialist Republics. (USSR),. was a List of former transcontinental countries#Since 1700, transcontinental country that spanned much of Eurasia from 1922 to 1991. A flagship communist state, ...
) in the world community. Domestically, Reagan attempted to bring in a package of privatization
Privatization (also privatisation in British English) can mean several different things, most commonly referring to moving something from the public sector into the private sector. It is also sometimes used as a synonym for deregulation when ...
and trickle down economics to stimulate the economy.
Canada's Brian Mulroney ran on a similar platform to Reagan, and also favored closer trade ties with the United States. This led to the Canada-United States Free Trade Agreement in January 1989.
Recent history
The End of the Cold War and the beginning of the era of sustained economic expansion coincided during the 1990s. On January 1, 1994, Canada, Mexico, and the United States signed the North American Free Trade Agreement, creating the world's largest free trade area. Quebec held a referendum in 1995 for national sovereignty in which 51% voted no to 49% yes. In 2000,Vicente Fox
Vicente Fox Quesada (; born 2 July 1942) is a Mexican businessman and politician who served as the 62nd president of Mexico from 1 December 2000 to 30 November 2006. After campaigning as a right-wing populist, Fox was elected president on the ...
became the first non- PRI candidate to win the Mexican presidency in over 70 years.
The optimism of the 1990s was shattered by the 9/11 attacks of 2001 on the United States, which prompted the 20-year period of military intervention war in Afghanistan
Afghanistan, officially the Islamic Emirate of Afghanistan,; prs, امارت اسلامی افغانستان is a landlocked country located at the crossroads of Central Asia and South Asia. Referred to as the Heart of Asia, it is bordere ...
, which Canada also participated in. Meanwhile, Canada and Mexico both did not support the United States later moves to invade Iraq
Iraq,; ku, عێراق, translit=Êraq officially the Republic of Iraq, '; ku, کۆماری عێراق, translit=Komarî Êraq is a country in Western Asia. It is bordered by Turkey to the north, Iran to the east, the Persian Gulf and K ...
.
In 2006, the drug war in Mexico evolved into an actual military conflict with each year more deadly than the last.
Starting in early 2008, the Great Recession
The Great Recession was a period of marked general decline, i.e. a recession, observed in national economies globally that occurred from late 2007 into 2009. The scale and timing of the recession varied from country to country (see map). At ...
in 3 North American nations began, which eventually triggered a worldwide recession in the Fall of 2008 and still has not recovered until 2009. In 2009, Barack Obama
Barack Hussein Obama II ( ; born August 4, 1961) is an American politician who served as the 44th president of the United States from 2009 to 2017. A member of the Democratic Party, Obama was the first African-American president of the ...
was inaugurated as the first African American to be President of the United States. 2 years later, Osama Bin Laden, the perpetrator of 9/11, was found and killed. On December 18, 2011, the Iraq War
{{Infobox military conflict
, conflict = Iraq War {{Nobold, {{lang, ar, حرب العراق (Arabic) {{Nobold, {{lang, ku, شەڕی عێراق ( Kurdish)
, partof = the Iraq conflict and the War on terror
, image ...
was declared formally over once the troops had pulled out.
In 2016, Donald Trump
Donald John Trump (born June 14, 1946) is an American politician, media personality, and businessman who served as the 45th president of the United States from 2017 to 2021.
Trump graduated from the Wharton School of the University of P ...
was elected 45th President, who defeated Hillary Clinton
Hillary Diane Rodham Clinton ( Rodham; born October 26, 1947) is an American politician, diplomat, and former lawyer who served as the 67th United States Secretary of State for President Barack Obama from 2009 to 2013, as a United States sen ...
in the 2016 election, and in 2017, he was sworn in as president. In early 2020, the United States confirmed the first case of the novel coronavirus
Novel coronavirus (nCoV) is a provisional name given to coronaviruses of medical significance before a permanent name is decided upon. Although coronaviruses are endemic in humans and infections normally mild, such as the common cold (caused by ...
, and later that month in March, North America went into national lockdown as the whole region was affected by the COVID-19 pandemic
The COVID-19 pandemic, also known as the coronavirus pandemic, is an ongoing global pandemic of coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) caused by severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2). The novel virus was first identi ...
. As of December 2021, three North American nations have suffered more than 1.3 million COVID-19 related deaths.
In 2020, Joe Biden was elected 46th President, who defeated Donald Trump
Donald John Trump (born June 14, 1946) is an American politician, media personality, and businessman who served as the 45th president of the United States from 2017 to 2021.
Trump graduated from the Wharton School of the University of P ...
in 2020 presidential election
This national electoral calendar for 2020 lists the national/federal elections held in 2020 in all sovereign states and their dependent territories. By-elections are excluded, though national referendums are included.
January
*5 January:
**C ...
, although Trump refused to concede the election, and on January 6, 2021, a group of his supporters stormed the United States Capitol in an unsuccessful effort to disrupt the presidential Electoral College vote count.
Also, Canadian Prime Minister Justin Trudeau
Justin Pierre James Trudeau ( , ; born December 25, 1971) is a Canadian politician who is the 23rd and current prime minister of Canada. He has served as the prime minister of Canada since 2015 and as the leader of the Liberal Party since 2 ...
called a snap election
A snap election is an election that is called earlier than the one that has been scheduled.
Generally, a snap election in a parliamentary system (the dissolution of parliament) is called to capitalize on an unusual electoral opportunity or to ...
in 2021 to try and increase the Liberal
Liberal or liberalism may refer to:
Politics
* a supporter of liberalism
** Liberalism by country
* an adherent of a Liberal Party
* Liberalism (international relations)
* Sexually liberal feminism
* Social liberalism
Arts, entertainment and m ...
s seat share and reach a majority government. The results of 2021 federal election were mostly unchanged from 2019 federal election, with the Liberals forming another minority government.
See also
*History of the Americas
The prehistory of the Americas (North, South, and Central America, and the Caribbean) begins with people migrating to these areas from Asia during the height of an ice age. These groups are generally believed to have been isolated from the peopl ...
* History of western civilization
Western civilization traces its roots back to Europe and the Mediterranean. It is linked to ancient Greece, the Roman Empire and with Medieval Western Christendom which emerged from the Middle Ages to experience such transformative episodes as ...
* ''Making North America'' (2015 PBS film)
By region
* American Old West *History of Central America
Central America is commonly said to include Guatemala, Belize, El Salvador, Honduras, Nicaragua, Costa Rica, and Panama. This definition matches modern political borders. Central America begins geographically in Mexico, at the Isthmus of Tehuantep ...
* History of Latin America
The term ''Latin America'' primarily refers to the Spanish- and Portuguese-speaking countries in the New World.
Before the arrival of Europeans in the late 15th and early 16th centuries, the region was home to many indigenous peoples, a number of ...
* History of New England
New England is the oldest clearly defined region of the United States, being settled more than 150 years before the American Revolution. The first English colony in New England, Plymouth Colony, was established in 1620 by Pilgrims fleeing religi ...
* History of the Caribbean
The history of the Caribbean reveals the significant role the region played in the colonial struggles of the European powers since the 15th century. In 1492, Christopher Columbus landed in the Caribbean and claimed the region for Spain. The ...
* History of the Southern United States
* History of the west coast of North America
The human history of the west coast of North America is believed to stretch back to the arrival of the earliest people over the Bering Strait, or alternately along a now-submerged coastal plain, through the development of significant pre-Columbi ...
* Histories of cities in the United States
Histories or, in Latin, Historiae may refer to:
* the plural of history
* ''Histories'' (Herodotus), by Herodotus
* ''The Histories'', by Timaeus
* ''The Histories'' (Polybius), by Polybius
* ''Histories'' by Gaius Sallustius Crispus (Sallust) ...
* History of cities in Mexico
* History of the US States
* Local history in Canada
References
Further reading
* Bennett, Norma V. (1997). ''Pioneer Legacy'', * Fernlund, Kevin Jon (2022). ''A Big History of North America, from Montezuma to Monroe.'' Columbia: University of Missouri Press. * Kane, Katie ''Nits Make Lice: Drogheda, Sand Creek, and the Poetics of Colonial Extermination'' ''Cultural Critique'', No. 42 (Spring, 1999), pp. 81–103 * Churchill, Ward (1997).''A Little Matter of Genocide'' City Lights Books {{DEFAULTSORT:History Of North America