Nikolay Muravyov-Amursky on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Count Nikolay Nikolayevich Muravyov-Amursky (also spelled as Nikolai Nikolaevich Muraviev-Amurskiy; russian: link=no, Никола́й Никола́евич Муравьёв-Аму́рский; – ) was a Russian general, statesman and diplomat, who played a major role in the
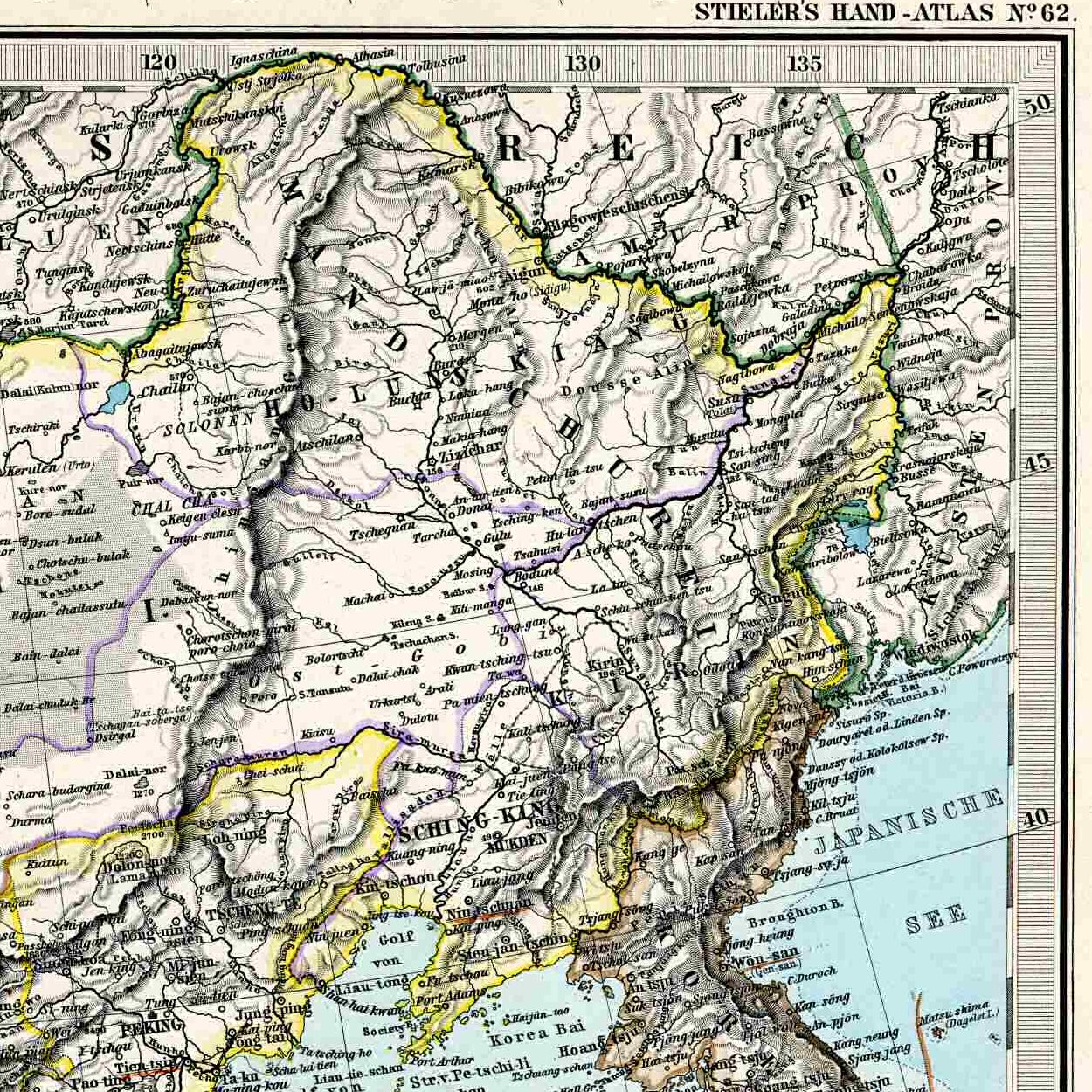 .
In 1840, Muravyov was assigned to command one of the sections of the
.
In 1840, Muravyov was assigned to command one of the sections of the
 On September 5, 1847, Muravyov was appointed the governor-general of
On September 5, 1847, Muravyov was appointed the governor-general of  On , Tsar Nicholas I authorized Muravyov to carry the negotiations with the Chinese regarding establishing a border along the Amur River and to transport troops to the Amur's estuary. From 1854–58, Muravyov assisted Gennady Nevelskoy in achieving that goal. The first expedition took place in May 1854. A fleet of 77 barges and rafts, led by the steamship ''Argun'', sailed down to the Amur's estuary. Due to the
On , Tsar Nicholas I authorized Muravyov to carry the negotiations with the Chinese regarding establishing a border along the Amur River and to transport troops to the Amur's estuary. From 1854–58, Muravyov assisted Gennady Nevelskoy in achieving that goal. The first expedition took place in May 1854. A fleet of 77 barges and rafts, led by the steamship ''Argun'', sailed down to the Amur's estuary. Due to the
Николай Николаевич Муравьёв-Амурский
(Nikolay Nikolayevich Muravyov-Amursky). ''Алфавит'' (''Alfavit'') newspaper, No. 30, 2000 The new territories acquired by Russia included
 In 1891, a bronze statue of Muravyov was erected on one of the Amur River's cliffs near
In 1891, a bronze statue of Muravyov was erected on one of the Amur River's cliffs near
online
* Bassin, Mark. ''Imperial visions: nationalist imagination and geographical expansion in the Russian Far East, 1840–1865'' (Cambridge University Press, 1999). * Gibson, James R. "The Significance of Siberia to Tsarist Russia." ''Canadian Slavonic Papers'' 14.3 (1972): 442–453. {{DEFAULTSORT:Muravyov-Amursky, Nikolay 1809 births 1881 deaths Military personnel from Saint Petersburg Politicians of the Russian Empire Members of the State Council (Russian Empire) Counts of the Russian Empire Primorsky Krai Explorers from the Russian Empire Russian people of the November Uprising Diplomats from Saint Petersburg
expansion
Expansion may refer to:
Arts, entertainment and media
* ''L'Expansion'', a French monthly business magazine
* ''Expansion'' (album), by American jazz pianist Dave Burrell, released in 2004
* ''Expansions'' (McCoy Tyner album), 1970
* ''Expansio ...
of the Russian Empire
The Russian Empire was an empire and the final period of the Russian monarchy from 1721 to 1917, ruling across large parts of Eurasia. It succeeded the Tsardom of Russia following the Treaty of Nystad, which ended the Great Northern War. ...
into the Amur River
The Amur (russian: река́ Аму́р, ), or Heilong Jiang (, "Black Dragon River", ), is the world's List of longest rivers, tenth longest river, forming the border between the Russian Far East and Northeast China, Northeastern China (Inne ...
basin and to the shores of the Sea of Japan
The Sea of Japan is the marginal sea between the Japanese archipelago, Sakhalin, the Korean Peninsula, and the mainland of the Russian Far East. The Japanese archipelago separates the sea from the Pacific Ocean. Like the Mediterranean Sea, it h ...
.
The surname Muravyov has also been transcribed as Muravyev or Murav'ev.
Early life and career
Nikolay Muravyov was born inSaint Petersburg
Saint Petersburg ( rus, links=no, Санкт-Петербург, a=Ru-Sankt Peterburg Leningrad Petrograd Piter.ogg, r=Sankt-Peterburg, p=ˈsankt pʲɪtʲɪrˈburk), formerly known as Petrograd (1914–1924) and later Leningrad (1924–1991), i ...
and graduated from the Page Corps
The Page Corps (russian: Пажеский корпус; french: Corps des Pages) was a military academy in Imperial Russia, which prepared sons of the nobility and of senior officers for military service. Similarly, the Imperial School of Jurispr ...
in 1827. He participated in the Siege of Varna
The siege of Varna (July–September 29, 1828) was a battle during the Russo-Turkish War, 1828–1829.
History
Varna was held by the Ottoman army. An approach to Varna by Russian forces was first attempted on June 28, but the Russian ava ...
in the Russo-Turkish War
The Russo-Turkish wars (or Ottoman–Russian wars) were a series of twelve wars fought between the Russian Empire and the Ottoman Empire between the 16th and 20th centuries. It was one of the longest series of military conflicts in European histo ...
in 1828–1829, and later in suppression of the November Uprising
The November Uprising (1830–31), also known as the Polish–Russian War 1830–31 or the Cadet Revolution,
was an armed rebellion in the heartland of partitioned Poland against the Russian Empire. The uprising began on 29 November 1830 in W ...
in Poland
Poland, officially the Republic of Poland, is a country in Central Europe. It is divided into 16 administrative provinces called voivodeships, covering an area of . Poland has a population of over 38 million and is the fifth-most populous ...
in 1831. Due to health reasons, he retired from the military in 1833 and returned home to manage his father's estate. However, he returned to active duty in 1838, as General Golovin's aide-de-camp, to serve in the Caucasus
The Caucasus () or Caucasia (), is a region between the Black Sea and the Caspian Sea, mainly comprising Armenia, Azerbaijan, Georgia, and parts of Southern Russia. The Caucasus Mountains, including the Greater Caucasus range, have historically ...
region. During one of the campaigns against the mountain people
Hill people, also referred to as mountain people, is a general term for people who live in the hills and mountains.
This includes all rugged land above and all land (including plateaus) above elevation.
The climate is generally harsh, with s ...
Muravyov was wounded.
 .
In 1840, Muravyov was assigned to command one of the sections of the
.
In 1840, Muravyov was assigned to command one of the sections of the Black Sea
The Black Sea is a marginal mediterranean sea of the Atlantic Ocean lying between Europe and Asia, east of the Balkans, south of the East European Plain, west of the Caucasus, and north of Anatolia. It is bounded by Bulgaria, Georgia, Roma ...
coast defense lines, during which time he participated in the suppression of the Ubykh people
The Ubykh ( Ubykh: Пэху / Туахы, ''Pəxu / Tuaxy''; , ''Ubyx''; russian: Убыхи; tr, Ubıhlar / Vubıhlar) are one of the twelve Circassian tribes, representing one of the twelve stars on the green-and-gold Circassian flag. Along w ...
.
Muravyov was promoted in rank to major-general in 1841, but had to permanently retire from the military due to illness. He transferred to the Ministry of Internal Affairs and was appointed as an acting military and civil governor of Tula province in 1846. Eager in his willingness to improve the province's state of affairs, he proposed to establish the governorate agricultural society.
Muravyov was the first governor to propose Tsar
Tsar ( or ), also spelled ''czar'', ''tzar'', or ''csar'', is a title used by East Slavs, East and South Slavs, South Slavic monarchs. The term is derived from the Latin word ''Caesar (title), caesar'', which was intended to mean "emperor" i ...
Nicholas I to abolish serfdom
Serfdom was the status of many peasants under feudalism, specifically relating to manorialism, and similar systems. It was a condition of debt bondage and indentured servitude with similarities to and differences from slavery, which develop ...
; a motion signed by nine local land-owners. While the tsar did nothing about the petition, from then on he always referred to Muravyov as a "liberal" and a "democrat".
Government of East Siberia
 On September 5, 1847, Muravyov was appointed the governor-general of
On September 5, 1847, Muravyov was appointed the governor-general of Irkutsk
Irkutsk ( ; rus, Иркутск, p=ɪrˈkutsk; Buryat language, Buryat and mn, Эрхүү, ''Erhüü'', ) is the largest city and administrative center of Irkutsk Oblast, Russia. With a population of 617,473 as of the 2010 Census, Irkutsk is ...
and Yeniseysk
Yeniseysk ( rus, Енисейск, p=jɪnʲɪˈsʲejsk) is a town in Krasnoyarsk Krai, Russia, located on the Yenisei River. Population: 20,000 (1970).
History
Yeniseysk was founded in 1619 as a stockaded town—the first town on the Yenise ...
(Eastern Siberia
Siberia ( ; rus, Сибирь, r=Sibir', p=sʲɪˈbʲirʲ, a=Ru-Сибирь.ogg) is an extensive region, geographical region, constituting all of North Asia, from the Ural Mountains in the west to the Pacific Ocean in the east. It has been a ...
). His appointment was a subject of much controversy, as it was unusual for a person of his age (only 38 at the time) to be put in charge of such a vast territory. Contrary to the views of Karl Nesselrode
Karl Robert Reichsgraf von Nesselrode-Ehreshoven, also known as Charles de Nesselrode ( Russian: Карл Васильевич Нессельроде, ''Karl Vasilyevich Nesselrode''; 14 December 1780 – 23 March 1862) was a Russian German diplo ...
, the Russian Foreign Minister
The Minister of Foreign Affairs of the Russian Federation is a high-ranking Russian government official who heads the Ministry of Foreign Affairs of the Russian Federation. The foreign minister is one of the five so-called 'presidential' minist ...
, Muravyov was personally instructed by Tsar Nicholas I to press for an advantage against China. Muravyov's first action as governor-general was to put end to the embezzlement of public funds. He also mandated the study of the Russian language
Russian (russian: русский язык, russkij jazyk, link=no, ) is an East Slavic languages, East Slavic language mainly spoken in Russia. It is the First language, native language of the Russians, and belongs to the Indo-European langua ...
in schools for native Siberian and Far Eastern peoples. He pursued the exploration and settlement of the territories north of the Amur River
The Amur (russian: река́ Аму́р, ), or Heilong Jiang (, "Black Dragon River", ), is the world's List of longest rivers, tenth longest river, forming the border between the Russian Far East and Northeast China, Northeastern China (Inne ...
, often utilizing the help of political exiles. Many of his actions were aimed to expand commerce in the Far Eastern region. Seeing religion as a powerful form of control over the local population, he favored the building of new Christian churches and promoted local religious beliefs such as shamanism
Shamanism is a religious practice that involves a practitioner (shaman) interacting with what they believe to be a Spirit world (Spiritualism), spirit world through Altered state of consciousness, altered states of consciousness, such as tranc ...
and Buddhism
Buddhism ( , ), also known as Buddha Dharma and Dharmavinaya (), is an Indian religion or philosophical tradition based on teachings attributed to the Buddha. It originated in northern India as a -movement in the 5th century BCE, and gra ...
.
After the 1689 Treaty of Nerchinsk
The Treaty of Nerchinsk () of 1689 was the first treaty between the Tsardom of Russia and the Qing dynasty of China. The Russians gave up the area north of the Amur River as far as the Stanovoy Range and kept the area between the Argun River ...
, Russia lost the right to navigate the Amur River
The Amur (russian: река́ Аму́р, ), or Heilong Jiang (, "Black Dragon River", ), is the world's List of longest rivers, tenth longest river, forming the border between the Russian Far East and Northeast China, Northeastern China (Inne ...
. Muravyov insisted on conducting an aggressive policy with China despite strong resistance from St Petersburg officials, who feared a breakdown in relations between the two countries. Nevertheless, because the lower reaches of the Amur River were, in fact, being claimed by the Russians, several expeditions organized by Gennady Nevelskoy
Gennady Ivanovich Nevelskoy (; in Drakino, now in Soligalichsky District, Kostroma Oblast – in St. Petersburg) was a Russian navigator.
In 1848 Nevelskoy set out in command of what became the to the area of the present-day ...
had been approved by the government. In 1851–1853, several expeditions were sent to the Amur Liman
The Amur Liman is a liman of the Amur River, the northern part of the Strait of Tartary between Eurasia and Sakhalin. It connects the Sakhalin Gulf of the Sea of Okhotsk with the main body of the Strait of Tartary via the Nevelskoy Strait.
"A ...
and Sakhalin
Sakhalin ( rus, Сахали́н, r=Sakhalín, p=səxɐˈlʲin; ja, 樺太 ''Karafuto''; zh, c=, p=Kùyèdǎo, s=库页岛, t=庫頁島; Manchu: ᠰᠠᡥᠠᠯᡳᠶᠠᠨ, ''Sahaliyan''; Orok: Бугата на̄, ''Bugata nā''; Nivkh: ...
, with Russian settlements being established in those areas.
 On , Tsar Nicholas I authorized Muravyov to carry the negotiations with the Chinese regarding establishing a border along the Amur River and to transport troops to the Amur's estuary. From 1854–58, Muravyov assisted Gennady Nevelskoy in achieving that goal. The first expedition took place in May 1854. A fleet of 77 barges and rafts, led by the steamship ''Argun'', sailed down to the Amur's estuary. Due to the
On , Tsar Nicholas I authorized Muravyov to carry the negotiations with the Chinese regarding establishing a border along the Amur River and to transport troops to the Amur's estuary. From 1854–58, Muravyov assisted Gennady Nevelskoy in achieving that goal. The first expedition took place in May 1854. A fleet of 77 barges and rafts, led by the steamship ''Argun'', sailed down to the Amur's estuary. Due to the Crimean War
The Crimean War, , was fought from October 1853 to February 1856 between Russia and an ultimately victorious alliance of the Ottoman Empire, France, the United Kingdom and Piedmont-Sardinia.
Geopolitical causes of the war included the de ...
, a portion of the fleet was then sent to Kamchatka
The Kamchatka Peninsula (russian: полуостров Камчатка, Poluostrov Kamchatka, ) is a peninsula in the Russian Far East, with an area of about . The Pacific Ocean and the Sea of Okhotsk make up the peninsula's eastern and wes ...
's Avacha Bay
Avacha Bay (russian: Авачинская губа, Авачинская бухта) is a Pacific Ocean bay on the southeastern coast of the Kamchatka Peninsula. It is long and wide (at the mouth), with a maximum depth of .
The Avacha River flo ...
, where a series of artillery batteries
In military organizations, an artillery battery is a unit or multiple systems of artillery, mortar systems, rocket artillery, multiple rocket launchers, surface-to-surface missiles, ballistic missiles, cruise missiles, etc., so grouped to facil ...
was established to defend the peninsula. The batteries played a major role in defending the city of Petropavlovsk (see Siege of Petropavlovsk), which was attacked by the English and French forces.
The 1855 expedition transported the first Russian settlers to the Amur's estuary. Muravyov started negotiations with the Chinese about that time.
Treaty of Aigun
During the last expedition of 1858, Muravyov concluded theTreaty of Aigun
The Treaty of Aigun (Russian: Айгунский договор; ) was an 1858 treaty between the Russian Empire and the Qing dynasty that established much of the modern border between the Russian Far East and China by ceding much of Manchuria ( ...
with the Qing
The Qing dynasty ( ), officially the Great Qing,, was a Manchu-led imperial dynasty of China and the last orthodox dynasty in Chinese history. It emerged from the Later Jin dynasty founded by the Jianzhou Jurchens, a Tungusic-speaki ...
official
Yishan. The Chinese were initially against setting any kinds of boundaries along the Amur River, preferring the ''status quo'' of keeping the adjacent territories under joint control of Russia and China. Muravyov, however, was able to persuade the Chinese that Russia's intentions were peaceful and constructive. The Treaty of Aigun effectively recognized the Amur River as the boundary between Russia and Qing Empire and granted Russia free access to the Pacific Ocean. For this, Muravyov was granted the title of Count Amursky (i.e., "of the Amur River"). According to an article by the Russian novelist Vladimir Barayev, the signing of the treaty was celebrated by grandiose illumination in Peking
}
Beijing ( ; ; ), alternatively romanized as Peking ( ), is the capital of the People's Republic of China. It is the center of power and development of the country. Beijing is the world's most populous national capital city, with over 21 ...
and festivities in major Siberian cities.Vladimir Barayev,Николай Николаевич Муравьёв-Амурский
(Nikolay Nikolayevich Muravyov-Amursky). ''Алфавит'' (''Alfavit'') newspaper, No. 30, 2000 The new territories acquired by Russia included
Priamurye
Amur Oblast ( rus, Аму́рская о́бласть, r=Amurskaya oblast, p=ɐˈmurskəjə ˈobləsʲtʲ) is a federal subject of Russia (an oblast), located on the banks of the Amur and Zeya Rivers in the Russian Far East. The administrative ...
and most of the territories of modern Primorsky and Khabarovsk
Khabarovsk ( rus, Хабaровск, a=Хабаровск.ogg, r=Habárovsk, p=xɐˈbarəfsk) is the largest types of inhabited localities in Russia, city and the administrative centre of Khabarovsk Krai, Russia,Law #109 located from the China ...
krai
A krai or kray (; russian: край, , ''kraya'') is one of the types of federal subjects of modern Russia, and was a type of geographical administrative division in the Russian Empire and the Russian SFSR.
Etymologically, the word is relat ...
s (territories).
The Treaty of Aigun was confirmed and expanded by the provisions of the Beijing Treaty of 1860, which granted Russia right to the Ussuri krai
Ussuri krai () is an unofficial name for a part of Primorsky Krai and Khabarovsky Krai that consisted of the Ussuri and South-Ussuri Okrugs. The name was often used in the late Russian Empire. The name comes from the fact that Ussuri River is loc ...
and southern parts of Primorye
Primorsky Krai (russian: Приморский край, r=Primorsky kray, p=prʲɪˈmorskʲɪj kraj), informally known as Primorye (, ), is a federal subject (a krai) of Russia, located in the Far East region of the country and is a part of t ...
.
As a governor general of Eastern Siberia, Muravyov-Amursky made numerous attempts to settle the shores of the Amur River. These attempts were mostly unsuccessful as very few people wanted to move to the Amur voluntarily. Muravyov had to transfer several Baikal Cossacks detachments to populate the area. Also unsuccessful were attempts to organize steamboat transportation on the Amur and to build a postal road.
As the main objection of the St. Petersburg officials against taking over the left bank of the Amur was lack of people to defend the new territories, Muravyov-Amursky successfully petitioned to free Nerchinsk
Nerchinsk ( rus, Не́рчинск; bua, Нэршүү, ''Nershüü''; mn, Нэрчүү, ''Nerchüü''; mnc, m=, v=Nibcu, a=Nibqu; zh, t=涅尔琴斯克(尼布楚), p=Niè'ěrqínsīkè (Níbùchǔ)) is a town and the administrative ce ...
peasants from mandatory works in the ore mines. With these people, a 12,000 corps of Amur Cossacks
The Amur Cossack Host (russian: Амурское казачье войско) was a Cossack host created in the Amur region and Primorye in the 1850s on the basis of the Cossacks relocated from the Transbaikal region and freed miners of Nerchinsk r ...
was formed and used to settle some of the lands, the military core being the Cossack
The Cossacks , es, cosaco , et, Kasakad, cazacii , fi, Kasakat, cazacii , french: cosaques , hu, kozákok, cazacii , it, cosacchi , orv, коза́ки, pl, Kozacy , pt, cossacos , ro, cazaci , russian: казаки́ or ...
s transferred from the Transbaikalia
Transbaikal, Trans-Baikal, Transbaikalia ( rus, Забайка́лье, r=Zabaykalye, p=zəbɐjˈkalʲjɪ), or Dauria (, ''Dauriya'') is a mountainous region to the east of or "beyond" (trans-) Lake Baikal in Far Eastern Russia.
The steppe and ...
.
Muravyov-Amursky retired from his post of governor general in 1861 after his proposal to divide Eastern Siberia into two separate governorates general was declined. He was appointed as a member of the State Council State Council may refer to:
Government
* State Council of the Republic of Korea, the national cabinet of South Korea, headed by the President
* State Council of the People's Republic of China, the national cabinet and chief administrative auth ...
. In 1868, he moved to Paris, France, where he lived until his death in 1881, visiting Russia only occasionally to participate in the State Council meetings.
Commemorations
 In 1891, a bronze statue of Muravyov was erected on one of the Amur River's cliffs near
In 1891, a bronze statue of Muravyov was erected on one of the Amur River's cliffs near Khabarovsk
Khabarovsk ( rus, Хабaровск, a=Хабаровск.ogg, r=Habárovsk, p=xɐˈbarəfsk) is the largest types of inhabited localities in Russia, city and the administrative centre of Khabarovsk Krai, Russia,Law #109 located from the China ...
. In 1929, it was taken off and replaced with a statue of Lenin
Vladimir Ilyich Ulyanov. ( 1870 – 21 January 1924), better known as Vladimir Lenin,. was a Russian revolutionary, politician, and political theorist. He served as the first and founding head of government of Soviet Russia from 1917 to 19 ...
, which stood there until 1989. The Muravyov-Amursky memorial was restored in 1993.
In 1992, the remains of Muravyov-Amursky were brought from Paris to be re-buried in the central part of Vladivostok
Vladivostok ( rus, Владивосто́к, a=Владивосток.ogg, p=vɫədʲɪvɐˈstok) is the largest city and the administrative center of Primorsky Krai, Russia. The city is located around the Zolotoy Rog, Golden Horn Bay on the Sea ...
, which stands on the Muravyov-Amursky Peninsula
The Muravyov-Amursky Peninsula (Russian: полуостров Муравьёва-Амурского) is a peninsula in Primorsky Krai, Russia, located in the Peter the Great Gulf of the Sea of Japan. Vladivostok, the administrative center of Primo ...
, named after this statesman. In 2012 a bronze statue of the governor was installed over the tomb, overlooking the Zolotoy Rog
Zolotoy Rog (russian: Золотой Рог) or the Golden Horn Bay, is a sheltered horn-shaped bay of the Sea of Japan, located in coastal Primorsky Krai within the Russian Far East. Vladivostok, that lies on the hills at the head of the bay, ...
bay, which he visited in 1850s.
The Khabarovsk monument—along with the Khabarovsk Bridge
Khabarovsk Bridge is a road and rail bridge built in 1999. It crosses the Amur River in eastern Russia, and connects the urban-type settlement of Imeni Telmana in the Jewish Autonomous Oblast with the city of Khabarovsk in Khabarovsk Krai. Until ...
over the Amur River—is depicted on the 5000 ruble
The ruble (American English) or rouble (Commonwealth English) (; rus, рубль, p=rublʲ) is the currency unit of Belarus and Russia. Historically, it was the currency of the Russian Empire and of the Soviet Union.
, currencies named ''rub ...
banknote issued by the Central Bank of the Russian Federation
The Central Bank of the Russian Federation (CBR; ), doing business as the Bank of Russia (russian: Банк России}), is the central bank of the Russian Federation. The bank was established on July 13, 1990. The predecessor of the bank can ...
on July 31, 2006.
Notes and references
See also
*Amur Annexation
The Amur Annexation was the annexation of the southeast corner of Siberia by the Russian Empire in 1858–1860 through a series of unequal treaties forced upon the Qing dynasty of China. The two areas involved are Priamurye between the Amur River ...
Further reading
* Bassin, Mark. "Inventing Siberia: visions of the Russian East in the early nineteenth century." ''American Historical Review'' 96.3 (1991): 763–794online
* Bassin, Mark. ''Imperial visions: nationalist imagination and geographical expansion in the Russian Far East, 1840–1865'' (Cambridge University Press, 1999). * Gibson, James R. "The Significance of Siberia to Tsarist Russia." ''Canadian Slavonic Papers'' 14.3 (1972): 442–453. {{DEFAULTSORT:Muravyov-Amursky, Nikolay 1809 births 1881 deaths Military personnel from Saint Petersburg Politicians of the Russian Empire Members of the State Council (Russian Empire) Counts of the Russian Empire Primorsky Krai Explorers from the Russian Empire Russian people of the November Uprising Diplomats from Saint Petersburg