Neon art on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 Neon lighting consists of brightly glowing, electrified glass tubes or bulbs that contain
Neon lighting consists of brightly glowing, electrified glass tubes or bulbs that contain
 Neon is a
Neon is a  These neon tubes were essentially in their contemporary form. The outer diameters for the glass tubing used in neon lighting ranges from 9 to 25 mm; with standard electrical equipment, the tubes can be as long as . The pressure of the gas inside ranges from 3 to 20
These neon tubes were essentially in their contemporary form. The outer diameters for the glass tubing used in neon lighting ranges from 9 to 25 mm; with standard electrical equipment, the tubes can be as long as . The pressure of the gas inside ranges from 3 to 20
 When Georges Claude demonstrated an impressive, practical form of neon tube lighting in 1910, he apparently envisioned that it would be used as a form of lighting, which had been the application of the earlier Moore tubes that were based on nitrogen and carbon dioxide discharges. Claude's 1910 demonstration of neon lighting at the '' Grand Palais'' (Grand Palace) in Paris lit a
When Georges Claude demonstrated an impressive, practical form of neon tube lighting in 1910, he apparently envisioned that it would be used as a form of lighting, which had been the application of the earlier Moore tubes that were based on nitrogen and carbon dioxide discharges. Claude's 1910 demonstration of neon lighting at the '' Grand Palais'' (Grand Palace) in Paris lit a  The Second World War (1939–1945) arrested new sign installations around most of the world. Following the war, the industry resumed. Marcus Thielen writes of this era, "...after World War II, government programs were established to help re-educate soldiers. The Egani Institute (New York City) was one of few schools in the country that taught neon-trade secrets. The American streamlined design from the 1950s would be unimaginable without the use of neon." The development of
The Second World War (1939–1945) arrested new sign installations around most of the world. Following the war, the industry resumed. Marcus Thielen writes of this era, "...after World War II, government programs were established to help re-educate soldiers. The Egani Institute (New York City) was one of few schools in the country that taught neon-trade secrets. The American streamlined design from the 1950s would be unimaginable without the use of neon." The development of
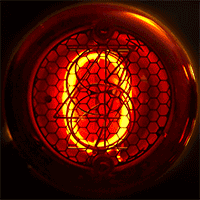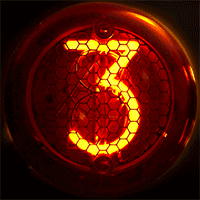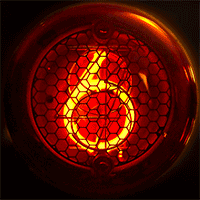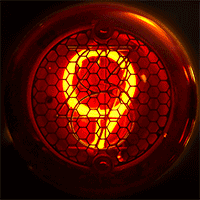 In neon glow lamps, the luminous region of the gas is a thin, "negative glow" region immediately adjacent to a negatively charged electrode (or "cathode"); the positively charged electrode ("anode") is quite close to the cathode. These features distinguish glow lamps from the much longer and brighter "positive column" luminous regions in neon tube lighting. The energy dissipation in the lamps when they are glowing is very low (about 0.1 W), hence the distinguishing term cold-cathode lighting.
Some of the applications of neon lamps include:
*Pilot lamps that indicate the presence of electrical power in an appliance or instrument (e.g. an electric coffee pot or power supply).
*Decorative (or "figural") lamps in which the cathode is shaped as a flower, animal, etc.. The figures inside these lamps were typically painted with phosphorescent paints to achieve a variety of colors.
*Active electronic circuits such as electronic oscillators, timers, memory elements, etc..
*Intricate electronic displays such as the
In neon glow lamps, the luminous region of the gas is a thin, "negative glow" region immediately adjacent to a negatively charged electrode (or "cathode"); the positively charged electrode ("anode") is quite close to the cathode. These features distinguish glow lamps from the much longer and brighter "positive column" luminous regions in neon tube lighting. The energy dissipation in the lamps when they are glowing is very low (about 0.1 W), hence the distinguishing term cold-cathode lighting.
Some of the applications of neon lamps include:
*Pilot lamps that indicate the presence of electrical power in an appliance or instrument (e.g. an electric coffee pot or power supply).
*Decorative (or "figural") lamps in which the cathode is shaped as a flower, animal, etc.. The figures inside these lamps were typically painted with phosphorescent paints to achieve a variety of colors.
*Active electronic circuits such as electronic oscillators, timers, memory elements, etc..
*Intricate electronic displays such as the
 Neon lighting consists of brightly glowing, electrified glass tubes or bulbs that contain
Neon lighting consists of brightly glowing, electrified glass tubes or bulbs that contain rarefied
Rarefaction is the reduction of an item's density, the opposite of compression. Like compression, which can travel in waves (sound waves, for instance), rarefaction waves also exist in nature. A common rarefaction wave is the area of low relati ...
neon or other gases. Neon lights are a type of cold cathode
A cold cathode is a cathode that is not electrically heated by a filament.A negatively charged electrode emits electrons or is the positively charged terminal. For more, see field emission. A cathode may be considered "cold" if it emits more el ...
gas-discharge light. A neon tube is a sealed glass tube with a metal electrode
An electrode is an electrical conductor used to make contact with a nonmetallic part of a circuit (e.g. a semiconductor, an electrolyte, a vacuum or air). Electrodes are essential parts of batteries that can consist of a variety of materials d ...
at each end, filled with one of a number of gases at low pressure. A high potential of several thousand volt
The volt (symbol: V) is the unit of electric potential, electric potential difference (voltage), and electromotive force in the International System of Units (SI). It is named after the Italian physicist Alessandro Volta (1745–1827).
Defin ...
s applied to the electrodes ionizes
Ionization, or Ionisation is the process by which an atom or a molecule acquires a negative or positive charge by gaining or losing electrons, often in conjunction with other chemical changes. The resulting electrically charged atom or molecule i ...
the gas in the tube, causing it to emit colored light. The color of the light depends on the gas in the tube. Neon lights were named for neon, a noble gas
The noble gases (historically also the inert gases; sometimes referred to as aerogens) make up a class of chemical elements with similar properties; under standard conditions, they are all odorless, colorless, monatomic gases with very low ch ...
which gives off a popular orange light, but other gases and chemicals are used to produce other colors, such as hydrogen
Hydrogen is the chemical element with the symbol H and atomic number 1. Hydrogen is the lightest element. At standard conditions hydrogen is a gas of diatomic molecules having the formula . It is colorless, odorless, tasteless, non-toxic ...
(red), helium
Helium (from el, ἥλιος, helios, lit=sun) is a chemical element with the symbol He and atomic number 2. It is a colorless, odorless, tasteless, non-toxic, inert, monatomic gas and the first in the noble gas group in the periodic table. ...
(yellow), carbon dioxide
Carbon dioxide ( chemical formula ) is a chemical compound made up of molecules that each have one carbon atom covalently double bonded to two oxygen atoms. It is found in the gas state at room temperature. In the air, carbon dioxide is trans ...
(white), and mercury (blue). Neon tubes can be fabricated in curving artistic shapes, to form letters or pictures. They are mainly used to make dramatic, multicolored glowing signage
Signage is the design or use of signs and symbols to communicate a message. A signage also means signs ''collectively'' or being considered as a group. The term ''signage'' is documented to have been popularized in 1975 to 1980.
Signs are any ...
for advertising, called neon sign
In the signage industry, neon signs are electric signs lighted by long luminous gas-discharge tubes that contain rarefied neon or other gases. They are the most common use for neon lighting, which was first demonstrated in a modern form in D ...
s, which were popular from the 1920s to 1960s and again in the 1980s.
The term can also refer to the miniature neon glow lamp, developed in 1917, about seven years after neon tube lighting. While neon tube lights are typically meters long, the neon lamps can be less than one centimeter in length and glow much more dimly than the tube lights. They are still in use as small indicator lights. Through the 1970s, neon glow lamps were widely used for numerical displays in electronics, for small decorative lamps, and as signal processing devices in circuitry. While these lamps are now antiques, the technology of the neon glow lamp developed into contemporary plasma display
A plasma display panel (PDP) is a type of flat panel display that uses small cells containing plasma: ionized gas that responds to electric fields. Plasma televisions were the first large (over 32 inches diagonal) flat panel displays to be releas ...
s and televisions
Television, sometimes shortened to TV, is a telecommunication medium for transmitting moving images and sound. The term can refer to a television set, or the medium of television transmission. Television is a mass medium for advertising, ...
.
Neon was discovered in 1898 by the British scientists William Ramsay
Sir William Ramsay (; 2 October 1852 – 23 July 1916) was a Scottish chemist who discovered the noble gases and received the Nobel Prize in Chemistry in 1904 "in recognition of his services in the discovery of the inert gaseous element ...
and Morris W. Travers. After obtaining pure neon from the atmosphere, they explored its properties using an "electrical gas-discharge" tube that was similar to the tubes used for neon signs today. Georges Claude, a French engineer and inventor, presented neon tube lighting in essentially its modern form at the Paris Motor Show
The Paris Motor Show (french: Mondial de l'Automobile) is a biennial auto show in Paris. Held during October, it is one of the most important auto shows, often with many new production automobile and concept car debuts. The show presently take ...
, December 3–18, 1910.The dates of the 1910 Paris Motor Show are incorporated into this poster for the show. Claude lit the peristyle
In ancient Greek and Roman architecture, a peristyle (; from Greek ) is a continuous porch formed by a row of columns surrounding the perimeter of a building or a courtyard. Tetrastoön ( grc, τετράστῳον or τετράστοον, lit=f ...
of the '' Grand Palais'' in Paris with neon tubes; this webpage includes a contemporary photograph that gives an impression of the effect. The webpage is part of an extensive selection of images of neon lighting; see Claude, sometimes called "the Edison of France", had a near monopoly on the new technology, which became very popular for signage and displays in the period 1920-1940. Neon lighting was an important cultural phenomenon in the United States in that era; As explained in this article, Claude did not discover neon. by 1940, the downtowns of nearly every city in the US were bright with neon signage, and Times Square
Times Square is a major commercial intersection, tourist destination, entertainment hub, and neighborhood in Midtown Manhattan, New York City. It is formed by the junction of Broadway, Seventh Avenue, and 42nd Street. Together with adjacent ...
in New York City was known worldwide for its neon extravagances. There were 2,000 shops nationwide designing and fabricating neon signs. The popularity, intricacy, and scale of neon signage for advertising declined in the U.S. following the Second World War (1939–1945), but development continued vigorously in Japan, Iran, and some other countries. In recent decades architects and artists, in addition to sign designers, have again adopted neon tube lighting as a component in their works.
Neon lighting is closely related to fluorescent lighting
A fluorescent lamp, or fluorescent tube, is a low-pressure mercury-vapor gas-discharge lamp that uses fluorescence to produce visible light. An electric current in the gas excites mercury vapor, which produces short-wave ultraviolet ligh ...
, which developed about 25 years after neon tube lighting. In fluorescent lights, the light emitted by rarefied gases within a tube is used exclusively to excite fluorescent materials that coat the tube, which then shine with their own colors that become the tube's visible, usually white, glow. Fluorescent coatings and glasses are also an option for neon tube lighting, but are usually selected to obtain bright colors.
History and science
 Neon is a
Neon is a noble gas
The noble gases (historically also the inert gases; sometimes referred to as aerogens) make up a class of chemical elements with similar properties; under standard conditions, they are all odorless, colorless, monatomic gases with very low ch ...
chemical element
A chemical element is a species of atoms that have a given number of protons in their nuclei, including the pure substance consisting only of that species. Unlike chemical compounds, chemical elements cannot be broken down into simpler sub ...
and an inert gas
An inert gas is a gas that does not readily undergo chemical reactions with other chemical substances and therefore does not readily form chemical compounds. The noble gases often do not react with many substances and were historically referred to ...
that is a minor component of the Earth's atmosphere. It was discovered in 1898 by the British scientists William Ramsay
Sir William Ramsay (; 2 October 1852 – 23 July 1916) was a Scottish chemist who discovered the noble gases and received the Nobel Prize in Chemistry in 1904 "in recognition of his services in the discovery of the inert gaseous element ...
and Morris W. Travers. When Ramsay and Travers had succeeded in obtaining pure neon from the atmosphere, they explored its properties using an "electrical gas-discharge" tube that was similar to the tubes used today for neon signs. Travers later wrote, "the blaze of crimson light from the tube told its own story and was a sight to dwell upon and never forget." The procedure of examining the colors of the light emitted from gas-discharge (or "Geissler" tubes) was well known at the time, since the colors of light (the "spectral lines") emitted by a gas discharge tube are, essentially, fingerprints that identify the gases inside.
Immediately following neon's discovery, neon tubes were used as scientific instruments and novelties. However, the scarcity of purified neon gas precluded its prompt application for electrical gas-discharge lighting along the lines of Moore tubes, which used more common nitrogen
Nitrogen is the chemical element with the symbol N and atomic number 7. Nitrogen is a nonmetal and the lightest member of group 15 of the periodic table, often called the pnictogens. It is a common element in the universe, estimated at se ...
or carbon dioxide
Carbon dioxide ( chemical formula ) is a chemical compound made up of molecules that each have one carbon atom covalently double bonded to two oxygen atoms. It is found in the gas state at room temperature. In the air, carbon dioxide is trans ...
as the working gas, and enjoyed some commercial success in the US in the early 1900s. After 1902, Georges Claude's company in France, Air Liquide
Air Liquide S.A. (; ; literally "liquid air"), is a French multinational company which supplies industrial gases and services to various industries including medical, chemical and electronic manufacturers. Founded in 1902, after Linde it is ...
, began producing industrial quantities of neon as a byproduct of the air liquefaction business. From December 3 to 18, 1910, Claude demonstrated two large ( long), bright red neon tubes at the Paris Motor Show
The Paris Motor Show (french: Mondial de l'Automobile) is a biennial auto show in Paris. Held during October, it is one of the most important auto shows, often with many new production automobile and concept car debuts. The show presently take ...
.
Torr
The torr (symbol: Torr) is a unit of pressure based on an absolute scale, defined as exactly of a standard atmosphere (). Thus one torr is exactly (≈ ).
Historically, one torr was intended to be the same as one " millimeter of merc ...
(0.4–3 kPa), which corresponds to a partial vacuum in the tubing. Claude had also solved two technical problems that substantially shortened the working life of neon and some other gas discharge tubes, and effectively gave birth to a neon lighting industry. In 1915, a US patent was issued to Claude covering the design of the electrodes for gas-discharge lighting; this patent became the basis for the monopoly held in the US by his company, Claude Neon Lights, for neon signs through the early 1930s.
Claude's patents envisioned the use of gases such as argon
Argon is a chemical element with the symbol Ar and atomic number 18. It is in group 18 of the periodic table and is a noble gas. Argon is the third-most abundant gas in Earth's atmosphere, at 0.934% (9340 ppmv). It is more than twice as ...
and mercury vapor to create different colors beyond those produced by neon. For instance, mixing metallic mercury with neon gas creates blue. Green can then be achieved using uranium (yellow) glass. White and gold can also be created by adding argon and helium
Helium (from el, ἥλιος, helios, lit=sun) is a chemical element with the symbol He and atomic number 2. It is a colorless, odorless, tasteless, non-toxic, inert, monatomic gas and the first in the noble gas group in the periodic table. ...
. In the 1920s, fluorescent glasses and coatings were developed to further expand the range of colors and effects for tubes with argon gas or argon-neon mixtures; generally, the fluorescent coatings are used with an argon/mercury-vapor mixture, which emits ultraviolet
Ultraviolet (UV) is a form of electromagnetic radiation with wavelength from 10 nm (with a corresponding frequency around 30 PHz) to 400 nm (750 THz), shorter than that of visible light, but longer than X-rays. UV radiation ...
light that activates the fluorescent coatings. By the 1930s, the colors from combinations of neon tube lights had become satisfactory for some general interior lighting applications, and achieved some success in Europe, but not in the US. Since the 1950s, the development of phosphors for color televisions has created nearly 100 new colors for neon tube lighting.
Around 1917, Daniel McFarlan Moore
Daniel McFarlan Moore (February 27, 1869 – June 15, 1936) was a U.S. electrical engineer and inventor. He developed a novel light source, the "Moore lamp", and a business that produced them in the early 1900s. The Moore lamp was the first co ...
, then working at the General Electric Company, developed the miniature neon lamp
A neon lamp (also neon glow lamp) is a miniature gas discharge lamp. The lamp typically consists of a small glass capsule that contains a mixture of neon and other gases at a low pressure and two electrodes (an anode and a cathode). When suff ...
. The glow lamp has a very different design than the much larger neon tubes used for signage; the difference was sufficient that a separate US patent was issued for the lamp in 1919. A Smithsonian Institution website notes, "These small, low power devices use a physical principle called 'coronal discharge'." Moore mounted two electrodes close together in a bulb and added neon or argon gas. The electrodes would glow brightly in red or blue, depending on the gas, and the lamps lasted for years. Since the electrodes could take almost any shape imaginable, a popular application has been fanciful decorative lamps. Glow lamps found practical use as electronic components, and as indicators in instrument panels and in many home appliances until the acceptance of light-emitting diodes (LEDs) starting in the 1970s."
Although some neon lamps themselves are now antiques, and their use in electronics has declined markedly, the technology has continued to develop in artistic and entertainment contexts. Neon lighting technology has been reshaped from long tubes into thin flat panels used for plasma display
A plasma display panel (PDP) is a type of flat panel display that uses small cells containing plasma: ionized gas that responds to electric fields. Plasma televisions were the first large (over 32 inches diagonal) flat panel displays to be releas ...
s and plasma television sets.
Neon tube lighting and signs
 When Georges Claude demonstrated an impressive, practical form of neon tube lighting in 1910, he apparently envisioned that it would be used as a form of lighting, which had been the application of the earlier Moore tubes that were based on nitrogen and carbon dioxide discharges. Claude's 1910 demonstration of neon lighting at the '' Grand Palais'' (Grand Palace) in Paris lit a
When Georges Claude demonstrated an impressive, practical form of neon tube lighting in 1910, he apparently envisioned that it would be used as a form of lighting, which had been the application of the earlier Moore tubes that were based on nitrogen and carbon dioxide discharges. Claude's 1910 demonstration of neon lighting at the '' Grand Palais'' (Grand Palace) in Paris lit a peristyle
In ancient Greek and Roman architecture, a peristyle (; from Greek ) is a continuous porch formed by a row of columns surrounding the perimeter of a building or a courtyard. Tetrastoön ( grc, τετράστῳον or τετράστοον, lit=f ...
of this large exhibition space. Claude's associate, Jacques Fonseque, realized the possibilities for a business based on signage and advertising. By 1913 a large sign for the vermouth Cinzano
Cinzano () is an Italian brand of vermouth, a brand owned since 1999 by Gruppo Campari.
History
Cinzano vermouths date back to 1757 and the Turin herbal shop of two brothers, Giovanni Giacomo and Carlo Stefano Cinzano, who created a new "verm ...
illuminated the night sky in Paris, and by 1919 the entrance to the Paris Opera was adorned with neon tube lighting.
Neon signage was received with particular enthusiasm in the United States. In 1923, Earle C. Anthony purchased two neon signs from Claude for his Packard car dealership in Los Angeles, California; these literally stopped traffic. Claude's US patents had secured him a monopoly on neon signage, and following Anthony's success with neon signs, many companies arranged franchises with Claude to manufacture neon signs. In many cases companies were given exclusive licenses for the production of neon signs in a given geographical area; by 1931, the value of the neon sign business was $16.9 million, of which a significant percentage was paid to Claude Neon Lights, Inc. by the franchising arrangements. Claude's principal patent expired in 1932, which led to a great expansion in the production of neon signage. The industry's sales in 1939 were about $22.0 million; the expansion in volume from 1931 to 1939 was much larger than the ratio of sales in the two years suggests.
Rudi Stern has written, "The 1930s were years of great creativity for neon, a period when many design and animation techniques were developed. ... Men like O. J. Gude and, in particular, Douglas Leigh
Douglas Leigh (May 24, 1907 – December 14, 1999) was an American advertising executive and lighting designer, and a pioneer in signage and outdoor advertising. He is famous for making New York City's Times Square the site of some of the worl ...
took neon advertising further than Georges Claude and his associates had ever envisioned. Leigh, who conceived and created the archetypal Times Square spectacular, experimented with displays that incorporated smells, fog, and sounds as part of their total effect. ... Much of the visual excitement of Times Square in the thirties was a result of Leigh's genius as a kinetic and luminal artist." Major cities throughout the United States and in several other countries also had elaborate displays of neon signs. Events such as the Chicago Century of Progress Exposition (1933–34), the Paris World's Fair (1937) and New York World's Fair (1939) were remarkable for their extensive use of neon tubes as architectural features. Stern has argued that the creation of "glorious" neon displays for movie theaters led to an association of the two, "One's joy in going to the movies became inseparably associated with neon."
 The Second World War (1939–1945) arrested new sign installations around most of the world. Following the war, the industry resumed. Marcus Thielen writes of this era, "...after World War II, government programs were established to help re-educate soldiers. The Egani Institute (New York City) was one of few schools in the country that taught neon-trade secrets. The American streamlined design from the 1950s would be unimaginable without the use of neon." The development of
The Second World War (1939–1945) arrested new sign installations around most of the world. Following the war, the industry resumed. Marcus Thielen writes of this era, "...after World War II, government programs were established to help re-educate soldiers. The Egani Institute (New York City) was one of few schools in the country that taught neon-trade secrets. The American streamlined design from the 1950s would be unimaginable without the use of neon." The development of Las Vegas, Nevada
Las Vegas (; Spanish for "The Meadows"), often known simply as Vegas, is the 25th-most populous city in the United States, the most populous city in the state of Nevada, and the county seat of Clark County. The city anchors the Las Vega ...
as a resort city is inextricably linked with neon signage; Tom Wolfe
Thomas Kennerly Wolfe Jr. (March 2, 1930 – May 14, 2018)Some sources say 1931; ''The New York Times'' and Reuters both initially reported 1931 in their obituaries before changing to 1930. See and was an American author and journalist widely ...
wrote in 1965, "Las Vegas is the only city in the world whose skyline is made neither of buildings, like New York, nor of trees, like Wilbraham, Massachusetts
Wilbraham is a town in Hampden County, Massachusetts, United States. It is a suburb of the City of Springfield, and part of the Springfield Metropolitan Statistical Area. The population was 14,613 at the 2020 census.
Part of the town comprises ...
, but signs. One can look at Las Vegas from a mile away on route 91 and see no buildings, no trees, only signs. But such signs! They tower. They revolve, they oscillate, they soar in shapes before which the existing vocabulary of art history is helpless."
Overall, however, neon displays became less fashionable, and some cities discouraged their construction with ordinances. Nelson Algren
Nelson Algren (born Nelson Ahlgren Abraham; March 28, 1909 – May 9, 1981) was an American writer. His 1949 novel ''The Man with the Golden Arm'' won the National Book Award and was adapted as the 1955 film of the same name.
Algren articulated ...
titled his 1947 collection of short stories '' The Neon Wilderness'' (as a synonym of "urban jungle" for Chicago
(''City in a Garden''); I Will
, image_map =
, map_caption = Interactive Map of Chicago
, coordinates =
, coordinates_footnotes =
, subdivision_type = Country
, subdivision_name ...
). Margalit Fox
Margalit Fox (born 1961) is an American writer. She began her career in publishing in the 1980s, before switching to journalism in the 1990s. She joined the obituary department of ''The New York Times'' in 2004, and authored over 1,400 obituarie ...
has written, "... after World War II, as neon signs were replaced increasingly by fluorescent-lighted plastic, the art of bending colored tubes into sinuous, gas-filled forms began to wane." A dark age persisted at least through the 1970s, when artists adopted neon with enthusiasm; in 1979 Rudi Stern published his manifesto, ''Let There Be Neon''. Marcus Thielen wrote in 2005, on the 90th anniversary of the US patent issued to Georges Claude, "The demand for the use of neon and cold cathode in architectural applications is growing, and the introduction of new techniques like fiber optics and LED—into the sign market have strengthened, rather than replaced, neon technology. The evolution of the 'waste' product neon tube remains incomplete 90 years after the patent was filed."
Neon glow lamps and plasma displays
 In neon glow lamps, the luminous region of the gas is a thin, "negative glow" region immediately adjacent to a negatively charged electrode (or "cathode"); the positively charged electrode ("anode") is quite close to the cathode. These features distinguish glow lamps from the much longer and brighter "positive column" luminous regions in neon tube lighting. The energy dissipation in the lamps when they are glowing is very low (about 0.1 W), hence the distinguishing term cold-cathode lighting.
Some of the applications of neon lamps include:
*Pilot lamps that indicate the presence of electrical power in an appliance or instrument (e.g. an electric coffee pot or power supply).
*Decorative (or "figural") lamps in which the cathode is shaped as a flower, animal, etc.. The figures inside these lamps were typically painted with phosphorescent paints to achieve a variety of colors.
*Active electronic circuits such as electronic oscillators, timers, memory elements, etc..
*Intricate electronic displays such as the
In neon glow lamps, the luminous region of the gas is a thin, "negative glow" region immediately adjacent to a negatively charged electrode (or "cathode"); the positively charged electrode ("anode") is quite close to the cathode. These features distinguish glow lamps from the much longer and brighter "positive column" luminous regions in neon tube lighting. The energy dissipation in the lamps when they are glowing is very low (about 0.1 W), hence the distinguishing term cold-cathode lighting.
Some of the applications of neon lamps include:
*Pilot lamps that indicate the presence of electrical power in an appliance or instrument (e.g. an electric coffee pot or power supply).
*Decorative (or "figural") lamps in which the cathode is shaped as a flower, animal, etc.. The figures inside these lamps were typically painted with phosphorescent paints to achieve a variety of colors.
*Active electronic circuits such as electronic oscillators, timers, memory elements, etc..
*Intricate electronic displays such as the Nixie tube
A Nixie tube ( ), or cold cathode display, is an electronic device used for displaying numerals or other information using glow discharge.
The glass tube contains a wire-mesh anode and multiple cathodes, shaped like numerals or other symbo ...
(see photograph).
The small size of the negative glow region of a neon lamp, and the flexible electronic properties that were exploited in electronic circuits, led to the adoption of this technology for the earliest plasma panel displays. The first monochrome dot-matrix plasma panel displays were developed in 1964 at the University of Illinois for the PLATO educational computing system. They had the characteristic color of the neon lamp; their inventors, Donald L. Bitzer, H. Gene Slottow, and Robert H. Wilson, had achieved a working computer display that remembered its own state, and did not require constant refreshing from the central computer system. The relationship between these early monochrome displays and contemporary, color plasma displays and televisions was described by Larry F. Weber in 2006, "All plasma TVs on the market today have the same features that were demonstrated in the first plasma display which was a device with only a single cell. These features include alternating sustain voltage, dielectric layer, wall charge, and a neon-based gas mixture." As in colored neon lamps, plasma displays use a gas mixture that emits ultraviolet light. Each pixel has a phosphor that emits one of the display's base colors.
Neon lighting and artists in light
The mid to late 1980s was a period of resurgence in neon production. Sign companies developed a new type of signage called channel lettering, in which individual letters were fashioned from sheet metal. While the market for neon lighting in outdoor advertising signage has declined since the mid twentieth century, in recent decades neon lighting has been used consciously in art, both in individual objects and integrated into architecture.Frank Popper
Frank Popper (17 April 1918 – 12 July 2020) was a Czech-born French-British historian of art and technology and Professor Emeritus of Aesthetics and the Science of Art at the University of Paris VIII. He was decorated with the medal of the L ...
traces the use of neon lighting as the principal element in artworks to Gyula Košice's late 1940s work in Argentina. Among the later artists whom Popper notes in a brief history of neon lighting in art are Stephen Antonakos
Stephen Antonakos ( el, Στυλιανός Αντωνάκος; November 1, 1926 in Agios Nikolaos, Laconia, Greece – August 17, 2013 in New York City) was a Greek born American sculptor most well known for his abstract sculptures often incorporat ...
, the conceptual artists Billy Apple
Billy Apple (born Barrie Bates; 31 December 19356 September 2021) was a New Zealand/USA artist, whose work is associated with the British and New York schools of pop art in the 1960s and NY's Conceptual Art movement in the 1970s. He worked alo ...
, Joseph Kosuth
Joseph Kosuth (; born January 31, 1945), an American conceptual artist, lives in New York and London,
, Bruce Nauman
Bruce Nauman (born December 6, 1941) is an American artist. His practice spans a broad range of media including sculpture, photography, neon, video, drawing, printmaking, and performance. Nauman lives near Galisteo, New Mexico.
Life and work ...
, Martial Raysse, Chryssa
Chryssa Vardea-Mavromichali ( el, Χρύσα Βαρδέα-Μαυρομιχάλη; December 31, 1933 – December 23, 2013) was a Greek American artist who worked in a wide variety of media. An American art pioneer in light art and luminist scu ...
, Piotr Kowalski, Maurizio Nannucci
Maurizio Nannucci (born 1939, in Florence, Italy) is an Italian contemporary artist. Lives and works in Florence and South Baden, Germany. Nannucci's work includes: photography, video, neon installations, sound installation, artist's books, and ed ...
and François Morellet in addition to Lucio Fontana or Mario Merz
Mario Merz (1 January 1925 – 9 November 2003) was an Italian artist, and husband of Marisa Merz.
Life
Born in Milan, Merz started drawing during World War II, when he was imprisoned for his activities with the ''Giustizia e Libertà'' antif ...
.
Several museums in the United States are now devoted to neon lighting and art, including the Museum of Neon Art
The Museum of Neon Art (MONA) is an institution that exists to encourage learning and curiosity through the preservation, collection, and interpretation of neon art. The first museum devoted to art that incorporates neon lighting, it exclusively e ...
(founded by neon artist Lili Lakich
Liliana Diane Lakich (born June 4, 1944) is an American artist, best known for her work in neon sculpture. As a child, she had been fascinated by neon advertising, and she built her career around illuminated art, with its special emotional power ...
, Los Angeles, 1981), the Neon Museum
The Neon Museum in Las Vegas, Nevada, United States, features signs from old casinos and other businesses displayed outdoors on 2.62 acres. The museum features a restored lobby shell from the defunct La Concha Motel as its visitors' center, whic ...
(Las Vegas, founded 1996), the American Sign Museum
The American Sign Museum in Cincinnati, Ohio, preserves, archives, and displays a collection of signs. The museum also displays the equipment utilized in the design and manufacture of signs. Tod Swormstedt began working on the museum in 1999. It o ...
(Cincinnati, founded 1999). These museums restore and display historical signage that was originally designed as advertising, in addition to presenting exhibits of neon art. Several books of photographs have also been published to draw attention to neon lighting as art. A collection of photographs of neon signs from cities around the world, most unannotated. In 1994, Christian Schiess has published an anthology of photographs and interviews devoted to fifteen "light artists". Schiess' anthology includes Stephen Antonakos, Valerij Bugrov, Chris Freeman, Peter Freeman, Michael Hayden, Craig Kraft, Dante Leonelli, Cork Marcheschi, Bill Parker, Alejandro & Moira Siña (Sinha), Keith Sonnier
Keith Sonnier (July 31, 1941 – July 18, 2020) was a postminimalist sculptor, performance artist, video and light artist. Sonnier was one of the first artists to use light in sculpture in the 1960s. With his use of neon in combination with epheme ...
, and Willem Volkersz.
List of neon light artists
*Billy Apple
Billy Apple (born Barrie Bates; 31 December 19356 September 2021) was a New Zealand/USA artist, whose work is associated with the British and New York schools of pop art in the 1960s and NY's Conceptual Art movement in the 1970s. He worked alo ...
(1935) New Zealand / USA
* Frida Blumenberg (1935) South Africa
* Chryssa
Chryssa Vardea-Mavromichali ( el, Χρύσα Βαρδέα-Μαυρομιχάλη; December 31, 1933 – December 23, 2013) was a Greek American artist who worked in a wide variety of media. An American art pioneer in light art and luminist scu ...
(1962) Greek-American
* Michael Flechtner (1951) US
* Michael Hayden (1943) Canada
* Joseph Kosuth
Joseph Kosuth (; born January 31, 1945), an American conceptual artist, lives in New York and London,
(1965) US
* Piotr Kowalski (1927) Poland, France
* Brigitte Kowanz
Brigitte Kowanz (13 April 1957 – 28 January 2022) was an Austrian artist. Kowanz studied from 1975 to 1980 at the University of Applied Arts Vienna. She was Professor of Transmedial Art there from 1997.
Works
Since the 1980s, Brigitte Kowanz ...
(1957) Austria
* Lili Lakich
Liliana Diane Lakich (born June 4, 1944) is an American artist, best known for her work in neon sculpture. As a child, she had been fascinated by neon advertising, and she built her career around illuminated art, with its special emotional power ...
(1944) US
* Mario Merz
Mario Merz (1 January 1925 – 9 November 2003) was an Italian artist, and husband of Marisa Merz.
Life
Born in Milan, Merz started drawing during World War II, when he was imprisoned for his activities with the ''Giustizia e Libertà'' antif ...
(1925) Italy
* Victor Millonzi (1915) US
* Maurizio Nannucci
Maurizio Nannucci (born 1939, in Florence, Italy) is an Italian contemporary artist. Lives and works in Florence and South Baden, Germany. Nannucci's work includes: photography, video, neon installations, sound installation, artist's books, and ed ...
(1939) Italy
* Bruce Nauman
Bruce Nauman (born December 6, 1941) is an American artist. His practice spans a broad range of media including sculpture, photography, neon, video, drawing, printmaking, and performance. Nauman lives near Galisteo, New Mexico.
Life and work ...
(1941) US
* Carla O'Brien Australia LED neon flex
* Bill Parker (1950) US - plasma lamp
* Stepan Ryabchenko (1987) Ukraine
* Lisa Schulte (1956) US
* Keith Sonnier
Keith Sonnier (July 31, 1941 – July 18, 2020) was a postminimalist sculptor, performance artist, video and light artist. Sonnier was one of the first artists to use light in sculpture in the 1960s. With his use of neon in combination with epheme ...
(1941) US
* Rudi Stern (1936) US
* Tim White-Sobieski (1961) Poland
See also
* Crackle tube *Plasma globe
A plasma globe or plasma lamp is a clear glass container filled with a mixture of various noble gases with a high-voltage electrode in the center of the container.
When voltage is applied, a plasma is formed within the container. Plasma filam ...
References
Further reading
*Len Davidson operated a neon museum in Philadelphia until 2006; the museum exhibited pieces from his large private collection. See {{Authority control