Natural history of Minnesota on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 The natural history of Minnesota covers many plant and animal species in the
The natural history of Minnesota covers many plant and animal species in the
 Much of Minnesota's northern forest has been logged, leaving only a few patches of old-growth forest today in areas such as in the
Much of Minnesota's northern forest has been logged, leaving only a few patches of old-growth forest today in areas such as in the

 Historic (and modern) loss of habitat, as well as overharvesting, has affected some native mammals to the point of
Historic (and modern) loss of habitat, as well as overharvesting, has affected some native mammals to the point of
 The natural history of Minnesota covers many plant and animal species in the
The natural history of Minnesota covers many plant and animal species in the U.S. state
In the United States, a state is a constituent political entity, of which there are 50. Bound together in a political union, each state holds governmental jurisdiction over a separate and defined geographic territory where it shares its sove ...
of Minnesota
Minnesota () is a state in the upper midwestern region of the United States. It is the 12th largest U.S. state in area and the 22nd most populous, with over 5.75 million residents. Minnesota is home to western prairies, now given over to ...
. The continental climate and location of Minnesota at the physiographic
Physical geography (also known as physiography) is one of the three main branches of geography. Physical geography is the branch of natural science which deals with the processes and patterns in the natural environment such as the atmosphere, ...
intersection of the Laurentian and the Interior Plains
The Interior Plains is a vast physiographic region that spreads across the Laurentian craton of central North America, extending along the east flank of the Rocky Mountains from the Gulf Coast region to the Arctic Beaufort Sea. In Canada, it en ...
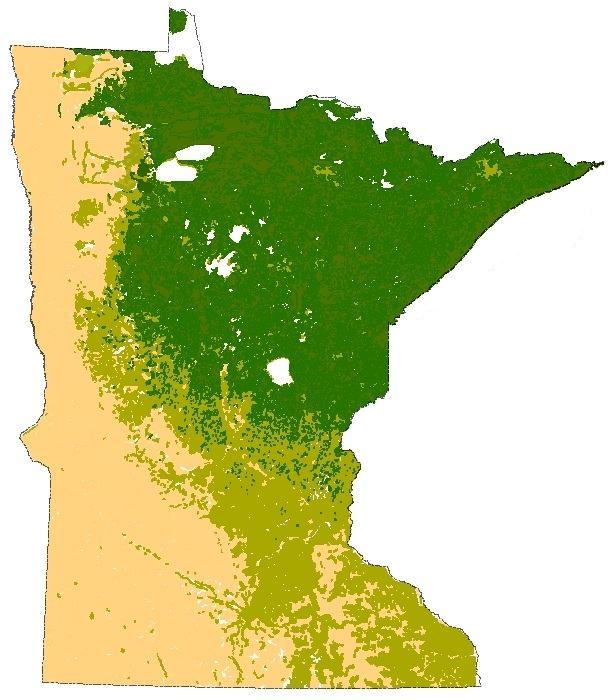
influences its plant and animal life. Three of North America's biome
A biome () is a biogeographical unit consisting of a biological community that has formed in response to the physical environment in which they are found and a shared regional climate. Biomes may span more than one continent. Biome is a broader ...
s converge in Minnesota: prairie grasslands in the southwestern and western parts of the state, the eastern temperate deciduous forest
Temperate deciduous or temperate broad-leaf forests are a variety of temperate forest 'dominated' by trees that lose their leaves each year. They are found in areas with warm moist summers and cool winters. The six major areas of this forest type ...
s in the east-central and the southeast, and the coniferous forest
Conifers are a group of cone-bearing seed plants, a subset of gymnosperms. Scientifically, they make up the division Pinophyta (), also known as Coniferophyta () or Coniferae. The division contains a single extant class, Pinopsida. All exta ...
in the north-central and northeast.
Ecoregions
Anecoregion
An ecoregion (ecological region) or ecozone (ecological zone) is an ecologically and geographically defined area that is smaller than a bioregion, which in turn is smaller than a biogeographic realm. Ecoregions cover relatively large areas of ...
is an area uniquely defined by environmental conditions and natural features. Ecoregions in Minnesota were largely influenced by the unique glacial history, geology
Geology () is a branch of natural science concerned with Earth and other astronomical objects, the features or rocks of which it is composed, and the processes by which they change over time. Modern geology significantly overlaps all other Ea ...
, soil type, land use
Land use involves the management and modification of natural environment or wilderness into built environment such as settlements and semi-natural habitats such as arable fields, pastures, and managed woods. Land use by humans has a long ...
, and climate
Climate is the long-term weather pattern in an area, typically averaged over 30 years. More rigorously, it is the mean and variability of meteorological variables over a time spanning from months to millions of years. Some of the meteorologi ...
of the state. The United States Environmental Protection Agency
The Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) is an independent executive agency of the United States federal government tasked with environmental protection matters. President Richard Nixon proposed the establishment of EPA on July 9, 1970; it ...
, Minnesota Department of Natural Resources
The Minnesota Department of Natural Resources, or Minnesota DNR, is the agency of the U.S. state of Minnesota charged with conserving and managing the state's natural resources. The agency maintains areas such as state parks, state forests, recr ...
, and World Wildlife Fund
The World Wide Fund for Nature Inc. (WWF) is an international non-governmental organization founded in 1961 that works in the field of wilderness preservation and the reduction of human impact on the environment. It was formerly named the Wo ...
maintain separate classifications of the state's ecoregions. Although different, they generally agree on delineating between the coniferous forest
Conifers are a group of cone-bearing seed plants, a subset of gymnosperms. Scientifically, they make up the division Pinophyta (), also known as Coniferophyta () or Coniferae. The division contains a single extant class, Pinopsida. All exta ...
in the north-central portion and the Arrowhead
An arrowhead or point is the usually sharpened and hardened tip of an arrow, which contributes a majority of the projectile mass and is responsible for impacting and penetrating a target, as well as to fulfill some special purposes such as sign ...
, a temperate deciduous forest
Temperate deciduous or temperate broad-leaf forests are a variety of temperate forest 'dominated' by trees that lose their leaves each year. They are found in areas with warm moist summers and cool winters. The six major areas of this forest type ...
in the central and southeast, and the tallgrass prairie
The tallgrass prairie is an ecosystem native to central North America. Historically, natural and anthropogenic fire, as well as grazing by large mammals (primarily bison) provided periodic disturbances to these ecosystems, limiting the encroachm ...
in the southern and western portions of the state. The northern coniferous forests are a vast wilderness of pine
A pine is any conifer tree or shrub in the genus ''Pinus'' () of the family Pinaceae. ''Pinus'' is the sole genus in the subfamily Pinoideae. The World Flora Online created by the Royal Botanic Gardens, Kew and Missouri Botanical Garden accepts ...
and spruce trees mixed with patchy stands of birch
A birch is a thin-leaved deciduous hardwood tree of the genus ''Betula'' (), in the family Betulaceae, which also includes alders, hazels, and hornbeams. It is closely related to the beech- oak family Fagaceae. The genus ''Betula'' contains ...
and poplar.
Flora
 Much of Minnesota's northern forest has been logged, leaving only a few patches of old-growth forest today in areas such as in the
Much of Minnesota's northern forest has been logged, leaving only a few patches of old-growth forest today in areas such as in the Chippewa National Forest
Chippewa National Forest is a National Forest located in north central Minnesota, United States, in the counties of Itasca, Cass and Beltrami. Forest headquarters are located in Cass Lake, Minnesota. There are local ranger district offices i ...
and the Superior National Forest
Superior National Forest, part of the United States National Forest system, is located in the Arrowhead Region of the state of Minnesota between the Canada–United States border and the north shore of Lake Superior. The area is part of the grea ...
where the Boundary Waters Canoe Area Wilderness
The Boundary Waters Canoe Area Wilderness (BWCAW or BWCA) is a wilderness area within the Superior National Forest in the northeastern part of the US state of Minnesota under the administration of the U.S. Forest Service. A mixture of forests ...
has some of unlogged land. Although logging continues, regrowth keeps about one third of the state forested.
Flora listed as threatened on the United States Fish and Wildlife Service list of endangered species include the Prairie bush-clover (''Lespedeza leptostachya''), the Western Prairie Fringed Orchid (''Platanthera praeclara''), and Leedy's roseroot (''Rhodiola integrifolia ssp. leedyi''), and the Dwarf trout lily (''Erythronium propullans'').
Fauna

 Historic (and modern) loss of habitat, as well as overharvesting, has affected some native mammals to the point of
Historic (and modern) loss of habitat, as well as overharvesting, has affected some native mammals to the point of extirpation
Local extinction, also known as extirpation, refers to a species (or other taxon) of plant or animal that ceases to exist in a chosen geographic area of study, though it still exists elsewhere. Local extinctions are contrasted with global extinct ...
, including the bison (disappeared in the mid-1800s; the last bison was reported in southwest Minnesota in 1879; a non-wild population exists in Blue Mounds State Park), cougar (though vagrant
Vagrancy is the condition of homelessness without regular employment or income. Vagrants (also known as bums, vagabonds, rogues, tramps or drifters) usually live in poverty and support themselves by begging, scavenging, petty theft, temporar ...
individuals are becoming more common), wolverine
The wolverine (), (''Gulo gulo''; ''Gulo'' is Latin for " glutton"), also referred to as the glutton, carcajou, or quickhatch (from East Cree, ''kwiihkwahaacheew''), is the largest land-dwelling species of the family Mustelidae. It is a muscul ...
, and the boreal woodland caribou
The boreal woodland caribou (''Rangifer tarandus caribou''; but subject to a recent taxonomic revision. See Reindeer: taxonomy), also known as woodland caribou, boreal forest caribou and forest-dwelling caribou, is a North American subspecies of ...
(extirpated from all the Lower 48). Whitetail deer
The white-tailed deer (''Odocoileus virginianus''), also known as the whitetail or Virginia deer, is a medium-sized deer native to North America, Central America, and South America as far south as Peru and Bolivia. It has also been introduced t ...
and bobcats thrive; the state has the nation's largest population of wolves
The wolf (''Canis lupus''; : wolves), also known as the gray wolf or grey wolf, is a large canine native to Eurasia and North America. More than thirty subspecies of ''Canis lupus'' have been recognized, and gray wolves, as popularly un ...
(specifically timber wolves) outside of Alaska
Alaska ( ; russian: Аляска, Alyaska; ale, Alax̂sxax̂; ; ems, Alas'kaaq; Yup'ik: ''Alaskaq''; tli, Anáaski) is a state located in the Western United States on the northwest extremity of North America. A semi-exclave of the U.S. ...
, and also supports healthy populations of black bear
Black bear or Blackbear may refer to:
Animals
* American black bear (''Ursus americanus''), a North American bear species
* Asian black bear (''Ursus thibetanus''), an Asian bear species
Music
* Black Bear (band), a Canadian First Nations group ...
s, elk, Canada lynx
The Canada lynx (''Lynx canadensis''), or Canadian lynx, is a medium-sized North American lynx that ranges across Alaska, Canada, and northern areas of the contiguous United States. It is characterized by its long, dense fur, triangular ears ...
, American martens, fisher
Fisher is an archaic term for a fisherman, revived as gender-neutral.
Fisher, Fishers or The Fisher may also refer to:
Places
Australia
*Division of Fisher, an electoral district in the Australian House of Representatives, in Queensland
*Elect ...
s, and moose
The moose (in North America) or elk (in Eurasia) (''Alces alces'') is a member of the New World deer subfamily and is the only species in the genus ''Alces''. It is the largest and heaviest extant species in the deer family. Most adult ma ...
.
Located on the Mississippi Flyway
The Mississippi Flyway is a bird migration route that generally follows the Mississippi, Missouri, and Lower Ohio Rivers in the United States across the western Great Lakes to the Mackenzie River and Hudson Bay in Canada. The main endpoints of ...
, Minnesota hosts migratory waterfowl such as geese
A goose ( : geese) is a bird of any of several waterfowl species in the family Anatidae. This group comprises the genera '' Anser'' (the grey geese and white geese) and ''Branta'' (the black geese). Some other birds, mostly related to the she ...
and ducks, and game birds such as grouse
Grouse are a group of birds from the order Galliformes, in the family Phasianidae. Grouse are presently assigned to the tribe Tetraonini (formerly the subfamily Tetraoninae and the family Tetraonidae), a classification supported by mitochondria ...
, pheasants
Pheasants ( ) are birds of several genera within the family Phasianidae in the order Galliformes. Although they can be found all over the world in introduced (and captive) populations, the pheasant genera native range is restricted to Eurasia ...
, and turkeys
The turkey is a large bird in the genus ''Meleagris'', native to North America. There are two extant turkey species: the wild turkey (''Meleagris gallopavo'') of eastern and central North America and the ocellated turkey (''Meleagris ocellat ...
. It is home to the largest population of bald eagles in the contiguous United States following a large increase in conservation efforts and breeding areas since 1989, with an estimated 30 active nests in the Twin Cities
Twin cities are a special case of two neighboring cities or urban centres that grow into a single conurbation – or narrowly separated urban areas – over time. There are no formal criteria, but twin cities are generally comparable in sta ...
alone. The red-tailed hawk
The red-tailed hawk (''Buteo jamaicensis'') is a bird of prey that breeds throughout most of North America, from the interior of Alaska and northern Canada to as far south as Panama and the West Indies. It is one of the most common members wit ...
thrives in Minnesota woodlands, swamps, and prairies, where rodent populations are high. Although they do not nest in the state, snowy owls
The snowy owl (''Bubo scandiacus''), also known as the polar owl, the white owl and the Arctic owl, is a large, white owl of the true owl family. Snowy owls are native to the Arctic regions of both North America and the Palearctic, breeding mos ...
migrate to Minnesota from the arctic tundra
In physical geography, tundra () is a type of biome where tree growth is hindered by frigid temperatures and short growing seasons. The term ''tundra'' comes through Russian (') from the Kildin Sámi word (') meaning "uplands", "treeless mou ...
to hunt voles
Voles are small rodents that are relatives of lemmings and hamsters, but with a stouter body; a longer, hairy tail; a slightly rounder head; smaller eyes and ears; and differently formed molars (high-crowned with angular cusps instead of lo ...
, mice, and rabbits. The number of snowy owls in the state in any given winter depends greatly on the winter conditions of the snowy owl's natural habitat, in areas such as Canada
Canada is a country in North America. Its ten provinces and three territories extend from the Atlantic Ocean to the Pacific Ocean and northward into the Arctic Ocean, covering over , making it the world's second-largest country by tot ...
and Alaska
Alaska ( ; russian: Аляска, Alyaska; ale, Alax̂sxax̂; ; ems, Alas'kaaq; Yup'ik: ''Alaskaq''; tli, Anáaski) is a state located in the Western United States on the northwest extremity of North America. A semi-exclave of the U.S. ...
.
The state fish, the walleye
The walleye (''Sander vitreus'', synonym ''Stizostedion vitreum''), also called the yellow pike or yellow pickerel, is a freshwater perciform fish native to most of Canada and to the Northern United States. It is a North American close relat ...
, is found in all parts of Minnesota. The walleye fishing season begins on the second Saturday of May, the time of year when the fish begin spawning. Walleye are especially active on cloudy days and after sunset, as well as during the autumn, when they feed heavily to prepare for winter. They naturally reproduce in 260 lakes throughout the state, and are stocked in 1,300 other lakes by the Minnesota Department of Natural Resources
The Minnesota Department of Natural Resources, or Minnesota DNR, is the agency of the U.S. state of Minnesota charged with conserving and managing the state's natural resources. The agency maintains areas such as state parks, state forests, recr ...
. The lakes contain other sport fish such as smallmouth and largemouth bass, muskellunge
The muskellunge ''(Esox masquinongy)'', often shortened to muskie, musky or lunge is a species of large freshwater predatory fish native to North America. It is the largest member of the pike family, Esocidae.
Origin of name
The name "muskell ...
, and northern pike
The northern pike (''Esox lucius'') is a species of carnivorous fish of the genus ''Esox'' (the pikes). They are typical of brackish and fresh waters of the Northern Hemisphere (''i.e.'' holarctic in distribution). They are known simply as a p ...
, and streams in the southeast are populated by brook
A brook is a small river or natural stream of fresh water. It may also refer to:
Computing
*Brook, a programming language for GPU programming based on C
*Brook+, an explicit data-parallel C compiler
*BrookGPU, a framework for GPGPU programming ...
, brown
Brown is a color. It can be considered a composite color, but it is mainly a darker shade of orange. In the CMYK color model used in printing or painting, brown is usually made by combining the colors orange and black. In the RGB color model us ...
, and rainbow trout.
References
{{Portal, United States Environment of Minnesota