Native American cuisine on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 Indigenous cuisine of the Americas includes all
Indigenous cuisine of the Americas includes all
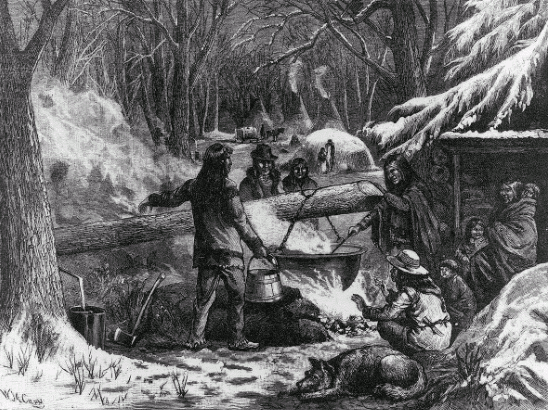


 *
* * Piki bread, from the
* Piki bread, from the
File:Albuquerque -- Indian Pueblo Kitchen.jpg, Indian Pueblo Kitchen (Albuquerque, NM)
Indian Fry Bread Taco.jpg, Tocabe (Denver, CO)
File:National Museum of the American Indian cafe 5.jpg, Mitsitam Native Foods Café (Washington, D.C.)
You Are On Native Land neon sign at Owamni by The Sioux Chef in Minneapolis, Minnesota.jpg, Owamni (Minneapolis, MN)
Three Sisters Saute at Thirty Nine Restaurant at First Americans Museum Oklahoma City.jpg, Thirty Nine Restaurant (Oklahoma City, OK)
Vincent Medina at Cafe Ohlone in Berkeley, 2020.jpg, Cafe Ohlone (Berkeley, CA)
File:Matsunaga-2017-red-ink-bison-6820 (27121055349).jpg, Café Gozhóó (Whiteriver, Navajo County, AZ)
 This region comprises the cultures of the
This region comprises the cultures of the

 The pre-Spanish colonization of the Americas, conquest cuisine of the Indigenous peoples of the Americas, Indigenous peoples of Mesoamerica made a major contribution to shaping modern-day
The pre-Spanish colonization of the Americas, conquest cuisine of the Indigenous peoples of the Americas, Indigenous peoples of Mesoamerica made a major contribution to shaping modern-day




 The earliest utensils, including bowls, knives, spoons, grinders, and griddles, were made from all kinds of materials, such as rock and animal bone. Gourds were also initially cultivated, hollowed, and dried to be used as bowls, spoons, ladles, and storage containers.
Many Indigenous cultures also developed elaborate ceramics for making bowls and cooking pots, and basketry for making containers. Nobility in the Andean and Mesoamerican civilizations were even known to have utensils and vessels smelted from gold, silver, copper, or other minerals.
*Batan (stone), ''Batan'', an Andean grinding slab used in conjunction with a small stone ''uña''
*''Burén'', a clay griddle used by the
The earliest utensils, including bowls, knives, spoons, grinders, and griddles, were made from all kinds of materials, such as rock and animal bone. Gourds were also initially cultivated, hollowed, and dried to be used as bowls, spoons, ladles, and storage containers.
Many Indigenous cultures also developed elaborate ceramics for making bowls and cooking pots, and basketry for making containers. Nobility in the Andean and Mesoamerican civilizations were even known to have utensils and vessels smelted from gold, silver, copper, or other minerals.
*Batan (stone), ''Batan'', an Andean grinding slab used in conjunction with a small stone ''uña''
*''Burén'', a clay griddle used by the






 *Pronghorn, Antelope
*Armadillo
*Badger
*Bear
*Beaver
*Bighorn sheep
*American bison, Bison—originally found throughout most of the North American plains
*Burro—European import
*Camel—extinct in the Americas
*Capybara
*Cattle—European import
*Chipmunk
*Deer
*Dove
*Duck
*Elk
*Ants
*Geese
*Ground hog
*Grouse
*''Guanaco''—hunted in South America by hunter-gatherer societies, for ex. in Patagonia until the 19th century
*Guinea pig—domesticated in the Andes
*Hog (swine), Hog—important European import
*Mexican honey wasp, Honey wasp—''Brachygastra mellifica'', ''Brachygastra lecheguana'', and ''Polybia occidentalis'', a source of honey found from the Southwestern United States to Argentina
*Horse—although imported by Europeans, the horse was still very important to Indigenous cultures throughout the Americas (famously on the North American Plains) in the historic era
*''Hutia''
*Iguana
*
*Pronghorn, Antelope
*Armadillo
*Badger
*Bear
*Beaver
*Bighorn sheep
*American bison, Bison—originally found throughout most of the North American plains
*Burro—European import
*Camel—extinct in the Americas
*Capybara
*Cattle—European import
*Chipmunk
*Deer
*Dove
*Duck
*Elk
*Ants
*Geese
*Ground hog
*Grouse
*''Guanaco''—hunted in South America by hunter-gatherer societies, for ex. in Patagonia until the 19th century
*Guinea pig—domesticated in the Andes
*Hog (swine), Hog—important European import
*Mexican honey wasp, Honey wasp—''Brachygastra mellifica'', ''Brachygastra lecheguana'', and ''Polybia occidentalis'', a source of honey found from the Southwestern United States to Argentina
*Horse—although imported by Europeans, the horse was still very important to Indigenous cultures throughout the Americas (famously on the North American Plains) in the historic era
*''Hutia''
*Iguana
*
Traditional Chiricahua recipes
American Indian Health and Diet Project
{{DEFAULTSORT:Indigenous Cuisine of the Americas Indigenous cuisine of the Americas, Indigenous culture of the Americas, Cuisine Native American culture, Cuisine Native American cuisine, Latin American cuisine North American cuisine First Nations culture
 Indigenous cuisine of the Americas includes all
Indigenous cuisine of the Americas includes all cuisine
A cuisine is a style of cooking characterized by distinctive ingredients, techniques and dishes, and usually associated with a specific culture or geographic region. Regional food preparation techniques, customs, and ingredients combine to ...
s and food
Food is any substance consumed by an organism for nutritional support. Food is usually of plant, animal, or fungal origin, and contains essential nutrients, such as carbohydrates, fats, proteins, vitamins, or minerals. The substance is in ...
practices of the Indigenous peoples of the Americas
The Indigenous peoples of the Americas are the inhabitants of the Americas before the arrival of the European settlers in the 15th century, and the ethnic groups who now identify themselves with those peoples.
Many Indigenous peoples of the A ...
. Contemporary Native peoples retain a varied culture of traditional foods, along with the addition of some post-contact foods that have become customary and even iconic of present-day Indigenous American social gatherings (for example, frybread). Foods like cornbread
Cornbread is a quick bread made with cornmeal, associated with the cuisine of the Southern United States, with origins in Native American cuisine. It is an example of batter bread. Dumplings and pancakes made with finely ground cornmeal are ...
, turkey
Turkey ( tr, Türkiye ), officially the Republic of Türkiye ( tr, Türkiye Cumhuriyeti, links=no ), is a transcontinental country located mainly on the Anatolian Peninsula in Western Asia, with a small portion on the Balkan Peninsula ...
, cranberry
Cranberries are a group of evergreen dwarf shrubs or trailing vines in the subgenus ''Oxycoccus'' of the genus '' Vaccinium''. In Britain, cranberry may refer to the native species '' Vaccinium oxycoccos'', while in North America, cranberry ...
, blueberry
Blueberries are a widely distributed and widespread group of perennial flowering plants with blue or purple berries. They are classified in the section ''Cyanococcus'' within the genus '' Vaccinium''. ''Vaccinium'' also includes cranberries ...
, hominy
Hominy (Spanish: maíz molido; literally meaning "milled corn") is a food produced from dried maize (corn) kernels that have been treated with an alkali, in a process called nixtamalization ( is the Nahuatl word for "hominy"). "Lye hominy" is a ...
and mush have been adopted into the cuisine of the broader United States population from Native American cultures.
In other cases, documents from the early periods of Indigenous American contact with European, African, and Asian peoples have allowed the recovery and revitalization of Indigenous food practices that had formerly passed out of popularity.
The most important Indigenous American crops have generally included Indian corn
Flint corn (''Zea mays'' var. ''indurata''; also known as Indian corn or sometimes calico corn) is a variant of maize, the same species as common corn. Because each kernel has a hard outer layer to protect the soft endosperm, it is likened to bei ...
(or maize
Maize ( ; ''Zea mays'' subsp. ''mays'', from es, maíz after tnq, mahiz), also known as corn (North American English, North American and Australian English), is a cereal grain first domesticated by indigenous peoples of Mexico, indigenous ...
, from the Taíno
The Taíno were a historic Indigenous peoples of the Caribbean, indigenous people of the Caribbean whose culture has been continued today by Taíno descendant communities and Taíno revivalist communities. At the time of European contact in the ...
name for the plant), beans, squash, pumpkins, sunflowers, wild rice, sweet potatoes, tomatoes, peppers, peanuts, avocados, papayas, potatoes and chocolate.
Indigenous cuisine of the Americas uses domesticated and wild native ingredients. As the Americas cover a large range of biome
A biome () is a biogeographical unit consisting of a biological community that has formed in response to the physical environment in which they are found and a shared regional climate. Biomes may span more than one continent. Biome is a broader ...
s, and there are more than 574 currently federally recognized
This is a list of federally recognized tribes in the contiguous United States of America. There are also federally recognized Alaska Native tribes. , 574 Indian tribes were legally recognized by the Bureau of Indian Affairs (BIA) of the United ...
Native American tribes in the US alone, Indigenous cuisine can vary significantly by region and culture. For example, North American Native cuisine differs from Southwestern
The points of the compass are a set of horizontal, radially arrayed compass directions (or azimuths) used in navigation and cartography. A compass rose is primarily composed of four cardinal directions—north, east, south, and west—each sep ...
and Mexican cuisine
Mexican cuisine consists of the cooking cuisines and traditions of the modern country of Mexico. Its earliest roots lie in Mesoamerican cuisine. Its ingredients and methods begin with the first agricultural communities such as the Olmec and ...
in its simplicity and directness of flavor.
Background: History, Tradition, and Harvest
In traditional tribal societies, the gathering of shellfish, wild plants, berries and seeds is often done by women. Native Americans located in the forests and woodlands had a wide variety of plant options. Native Americans who gathered much of the forest had access to many of the sustainable resources including, flesby fruits, roots and tubers, and greens. Available greenery changed year to year, depending on weather conditions and the production cycle of perennial resources such as nut-bearing trees. A popular source of meat, that offered a great amount of nutrition that Native Americans hunted were Bison, which were most traditional and important for thePlains Indians
Plains Indians or Indigenous peoples of the Great Plains and Canadian Prairies are the Native American tribes and First Nation band governments who have historically lived on the Interior Plains (the Great Plains and Canadian Prairies) of ...
in the area between the Mississippi River
The Mississippi River is the List of longest rivers of the United States (by main stem), second-longest river and chief river of the second-largest Drainage system (geomorphology), drainage system in North America, second only to the Hudson B ...
and the Rocky Mountains
The Rocky Mountains, also known as the Rockies, are a major mountain range and the largest mountain system in North America. The Rocky Mountains stretch in straight-line distance from the northernmost part of western Canada, to New Mexico ...
.
Each Native American territory encompasses considerable regional and temporal variation in topography, climate, and ecology. There have also been temporal and regional differences in Native American lifeways, including their subsistence practices and preparation.
Recipes were initially passed down through oral tradition. Over a period of hundreds of years, some tribes migrated into different climate zones
Climate classifications are systems that categorize the world's climates. A climate classification may correlate closely with a biome classification, as climate is a major influence on life in a region. One of the most used is the Köppen climate ...
, so by the time European settlers recorded these recipes the cuisine had probably adapted to use local ingredients. Some anthropologists propose that the southwestern Eastern Pueblo, Hopi
The Hopi are a Native American ethnic group who primarily live on the Hopi Reservation in northeastern Arizona, United States. As of the 2010 census, there are 19,338 Hopi in the country. The Hopi Tribe is a sovereign nation within the United ...
and Zuni may have retained more of the original elements.
Indigenous cuisine of North America
Country food
Country food, in Canada, refers to thetraditional diet
In nutrition, diet is the sum of food consumed by a person or other organism.
The word diet often implies the use of specific intake of nutrition for health or weight-management reasons (with the two often being related). Although humans are o ...
s of the Indigenous peoples in Canada
In Canada, Indigenous groups comprise the First Nations, Inuit and Métis. Although ''Indian'' is a term still commonly used in legal documents, the descriptors ''Indian'' and '' Eskimo'' have fallen into disuse in Canada, and most consider th ...
(known in Canada as First Nations
First Nations or first peoples may refer to:
* Indigenous peoples, for ethnic groups who are the earliest known inhabitants of an area.
Indigenous groups
*First Nations is commonly used to describe some Indigenous groups including:
**First Natio ...
, Metis
Metis or Métis may refer to:
Ethnic groups
* Métis, recognized Indigenous communities in Canada and America whose distinct culture and language emerged after early intermarriage between First Nations peoples and early European settlers, primar ...
, and Inuit
Inuit (; iu, ᐃᓄᐃᑦ 'the people', singular: Inuk, , dual: Inuuk, ) are a group of culturally similar indigenous peoples inhabiting the Arctic and subarctic regions of Greenland, Labrador, Quebec, Nunavut, the Northwest Territorie ...
), especially in remote northern regions where Western food is an expensive import, and traditional food
Traditional foods are foods and dishes that are passed on through generations or which have been consumed for many generations. Traditional foods and dishes are traditional in nature, and may have a historic precedent in a national dish, regio ...
s are still relied upon.
The Government of the Northwest Territories
The Northwest Territories (abbreviated ''NT'' or ''NWT''; french: Territoires du Nord-Ouest, formerly ''North-Western Territory'' and ''North-West Territories'' and namely shortened as ''Northwest Territory'') is a federal territory of Canada. ...
estimated in 2015 that nearly half of Northwest Territories residents in smaller communities relied on country food for 75% of their meat and fish intake; in larger communities the percentage was lower, with the lowest percentage relying on country foods (4%) being in Yellowknife
Yellowknife (; Dogrib: ) is the capital, largest community, and only city in the Northwest Territories, Canada. It is on the northern shore of Great Slave Lake, about south of the Arctic Circle, on the west side of Yellowknife Bay near the ...
, the capital and only "large community".
The most common country foods in the Northwest Territories' area include mammals and birds (caribou, moose, ducks, geese, seals, hare, grouse, ptarmigan), fish (lake trout, char, inconnu (coney), whitefish, pike, burbot) and berries (blueberries, cranberries, blackberries, cloudberries).
In the eastern Canadian Arctic
Northern Canada, colloquially the North or the Territories, is the vast northernmost region of Canada variously defined by geography and politics. Politically, the term refers to the three territories of Canada: Yukon, Northwest Territories and ...
, Inuit consume a diet of foods that are fished, hunted, and gathered locally. This may include caribou
Reindeer (in North American English, known as caribou if wild and ''reindeer'' if domesticated) are deer in the genus ''Rangifer''. For the last few decades, reindeer were assigned to one species, ''Rangifer tarandus'', with about 10 subspe ...
, walrus
The walrus (''Odobenus rosmarus'') is a large flippered marine mammal with a discontinuous distribution about the North Pole in the Arctic Ocean and subarctic seas of the Northern Hemisphere. The walrus is the only living species in the fami ...
, ringed seal
The ringed seal (''Pusa hispida'') is an earless seal inhabiting the Arctic and sub-Arctic regions. The ringed seal is a relatively small seal, rarely greater than 1.5 m in length, with a distinctive patterning of dark spots surrounded by light ...
, bearded seal
The bearded seal (''Erignathus barbatus''), also called the square flipper seal, is a medium-sized pinniped that is found in and near to the Arctic Ocean. It gets its generic name from two Greek words (''eri'' and ''gnathos'') that refer to its ...
, beluga whale
The beluga whale () (''Delphinapterus leucas'') is an Arctic and sub-Arctic cetacean. It is one of two members of the family Monodontidae, along with the narwhal, and the only member of the genus ''Delphinapterus''. It is also known as the ...
, polar bear
The polar bear (''Ursus maritimus'') is a hypercarnivorous bear whose native range lies largely within the Arctic Circle, encompassing the Arctic Ocean, its surrounding seas and surrounding land masses. It is the largest extant bear spec ...
, berries
A berry is a small, pulpy, and often edible fruit. Typically, berries are juicy, rounded, brightly colored, sweet, sour or tart, and do not have a stone or pit, although many pips or seeds may be present. Common examples are strawberries, ras ...
, and fireweed
''Chamaenerion angustifolium'' is a perennial herbaceous flowering plant in the willowherb family Onagraceae. It is known in North America as fireweed, in some parts of Canada as great willowherb, in Britain and Ireland as rosebay willowherb. ...
.
The cultural value attached to certain game species, and certain parts, varies. For example, in the James Bay
James Bay (french: Baie James; cr, ᐐᓂᐯᒄ, Wînipekw, dirty water) is a large body of water located on the southern end of Hudson Bay in Canada. Both bodies of water extend from the Arctic Ocean, of which James Bay is the southernmost p ...
region, a 1982 study found that beluga whale meat was principally used as dog food, whereas the blubber, or muktuk
Muktuk (transliterated in various ways, see below) is a traditional food of the peoples of the Arctic, consisting of whale skin and blubber. It is most often made from the bowhead whale, although the beluga and the narwhal are also used. It is ...
was a "valued delicacy". Value also varies by age, with Inuit preferring younger ring seals, and often using the older ones for dog food.
Contaminants in country foods are a public health concern in Northern Canada; volunteers are tested to track the spread of industrial chemicals from emitters (usually in the South) into the northern food web via the air and water.
In 2017, the Government of the Northwest Territories committed to using country foods in the soon-to-open Stanton Territorial Hospital, despite the challenges of obtaining, inspecting, and preparing sufficient quantities of wild game and plants.
In Southern Canada
The list of regions of Canada is a summary of geographical areas on a hierarchy that ranges from national (groups of provinces and territories) at the top to local regions and sub-regions of provinces at the bottom. Administrative regions that ran ...
, wild foods (especially meats) are relatively rare in restaurants, due to wildlife conservation
Wildlife conservation refers to the practice of protecting wild species and their habitats in order to maintain healthy wildlife species or populations and to restore, protect or enhance natural ecosystems. Major threats to wildlife include habita ...
rules against selling hunted meat, as well as strict meat inspection rules. There is a cultural divide
A cultural divide is "a boundary in society that separates communities whose social economic structures, opportunities for success, conventions, styles, are so different that they have substantially different psychologies". A cultural divide is th ...
between rural and remote communities that rely on wild foods, and urban Canadians (the majority), who have little or no experience with them.
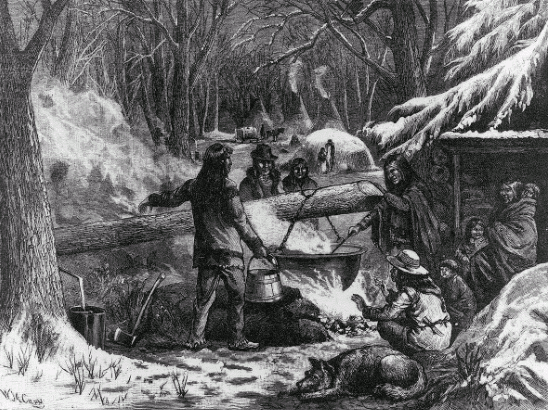
Eastern Native American cuisine
The essential staple foods of theIndigenous peoples of the Eastern Woodlands
The Eastern Woodlands is a cultural area of the indigenous people of North America. The Eastern Woodlands extended roughly from the Atlantic Ocean to the eastern Great Plains, and from the Great Lakes region to the Gulf of Mexico, which is now pa ...
have traditionally been corn (also known as maize), bean
A bean is the seed of several plants in the family Fabaceae, which are used as vegetables for human or animal food. They can be cooked in many different ways, including boiling, frying, and baking, and are used in many traditional dishes th ...
s, and squash
Squash may refer to:
Sports
* Squash (sport), the high-speed racquet sport also known as squash racquets
* Squash (professional wrestling), an extremely one-sided match in professional wrestling
* Squash tennis, a game similar to squash but pla ...
, known as " The Three Sisters" because they were planted interdependently: the beans grew up the tall stalks of the corn, while the squash spread out at the base of the three plants and provided protection and support for the root systems.
Maple syrup
Maple syrup is a syrup made from the sap of maple trees. In cold climates, these trees store starch in their trunks and roots before winter; the starch is then converted to sugar that rises in the sap in late winter and early spring. Maple tr ...
is another essential food staple of the Eastern Woodlands peoples. Tree sap is collected from sugar maple trees during the beginning of springtime when the nights are still cold. Birch bark containers are used in the process of making maple syrup, maple cakes, maple sugar, and maple taffy. When the sap is boiled to a certain temperature, the different variations of maple food products are created. When the sap starts to thicken, it can be poured into the snow to make taffy.
Since the first colonists of New England
New England is a region comprising six states in the Northeastern United States: Connecticut, Maine, Massachusetts, New Hampshire, Rhode Island, and Vermont. It is bordered by the state of New York to the west and by the Canadian provinces ...
had to adapt their foods to the local crops and resources, the Native influences of Southern New England Algonquian cuisine Southern New England Algonquian cuisine comprises the shared foods and preparation methods of the indigenous Algonquian peoples of the southern half of New England, which consists of Massachusetts, Connecticut, Rhode Island, but also included po ...
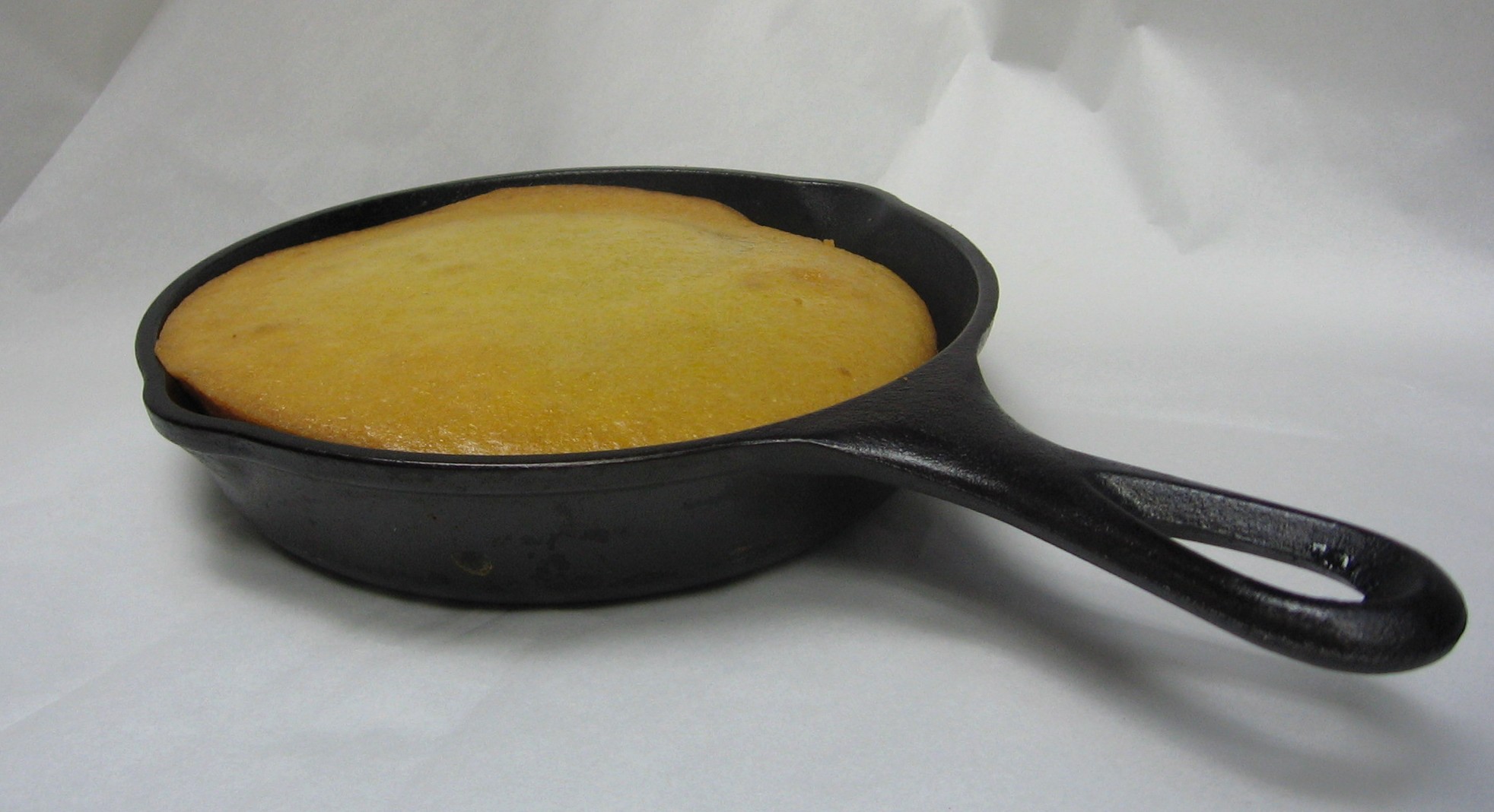
form a significant part of New England cuisine with dishes such as cornbread
Cornbread is a quick bread made with cornmeal, associated with the cuisine of the Southern United States, with origins in Native American cuisine. It is an example of batter bread. Dumplings and pancakes made with finely ground cornmeal are ...
, succotash
Succotash (from Narragansett ''sahquttahhash'', "broken corn kernels") is a vegetable dish consisting primarily of sweet corn with lima beans or other shell beans.
Other ingredients may be added, such as onions, potatoes, turnips, tomatoes, b ...
and Johnnycakes and ingredients such as corn
Maize ( ; ''Zea mays'' subsp. ''mays'', from es, maíz after tnq, mahiz), also known as corn (North American and Australian English), is a cereal grain first domesticated by indigenous peoples in southern Mexico about 10,000 years ago. The ...
, cranberries
Cranberries are a group of evergreen dwarf shrubs or trailing vines in the subgenus ''Oxycoccus'' of the genus ''Vaccinium''. In Britain, cranberry may refer to the native species ''Vaccinium oxycoccos'', while in North America, cranberry m ...
and local species of clam
Clam is a common name for several kinds of bivalve molluscs. The word is often applied only to those that are edible and live as infauna, spending most of their lives halfway buried in the sand of the seafloor or riverbeds. Clams have two shel ...
still enjoyed in the region today.
The Wabanaki tribal nations and other eastern woodlands peoples have made nut milk and infant formula
Infant formula, baby formula, or simply formula (American English); or baby milk, infant milk or first milk (British English), is a manufactured food designed and marketed for feeding to babies and infants under 12 months of age, usually prepar ...
made from nuts and cornmeal, while the Cherokee nation made Kanuchi soup from hickory nuts.
Southeastern Native American cuisine
Southeastern Native American culture has formed the cornerstone ofSouthern cuisine
The cuisine of the Southern United States encompasses diverse food traditions of several regions, including Tidewater, Appalachian, Lowcountry, Cajun, Creole, and Floribbean cuisine. In recent history, elements of Southern cuisine have spread t ...
from its origins through the present day. From Southeastern Native American culture came one of the main staples of the Southern diet: corn
Maize ( ; ''Zea mays'' subsp. ''mays'', from es, maíz after tnq, mahiz), also known as corn (North American and Australian English), is a cereal grain first domesticated by indigenous peoples in southern Mexico about 10,000 years ago. The ...
(maize), either ground into meal or limed with an alkaline salt to make hominy
Hominy (Spanish: maíz molido; literally meaning "milled corn") is a food produced from dried maize (corn) kernels that have been treated with an alkali, in a process called nixtamalization ( is the Nahuatl word for "hominy"). "Lye hominy" is a ...
, using a Native American technique known as nixtamalization
Nixtamalization () is a process for the preparation of corn, or other grain, in which the grain is soaked and cooked in an alkaline solution, usually limewater (but sometimes aqueous alkali metal carbonates), washed, and then hulled. The ter ...
. Corn is used to make all kinds of dishes from the familiar cornbread
Cornbread is a quick bread made with cornmeal, associated with the cuisine of the Southern United States, with origins in Native American cuisine. It is an example of batter bread. Dumplings and pancakes made with finely ground cornmeal are ...
and grits.
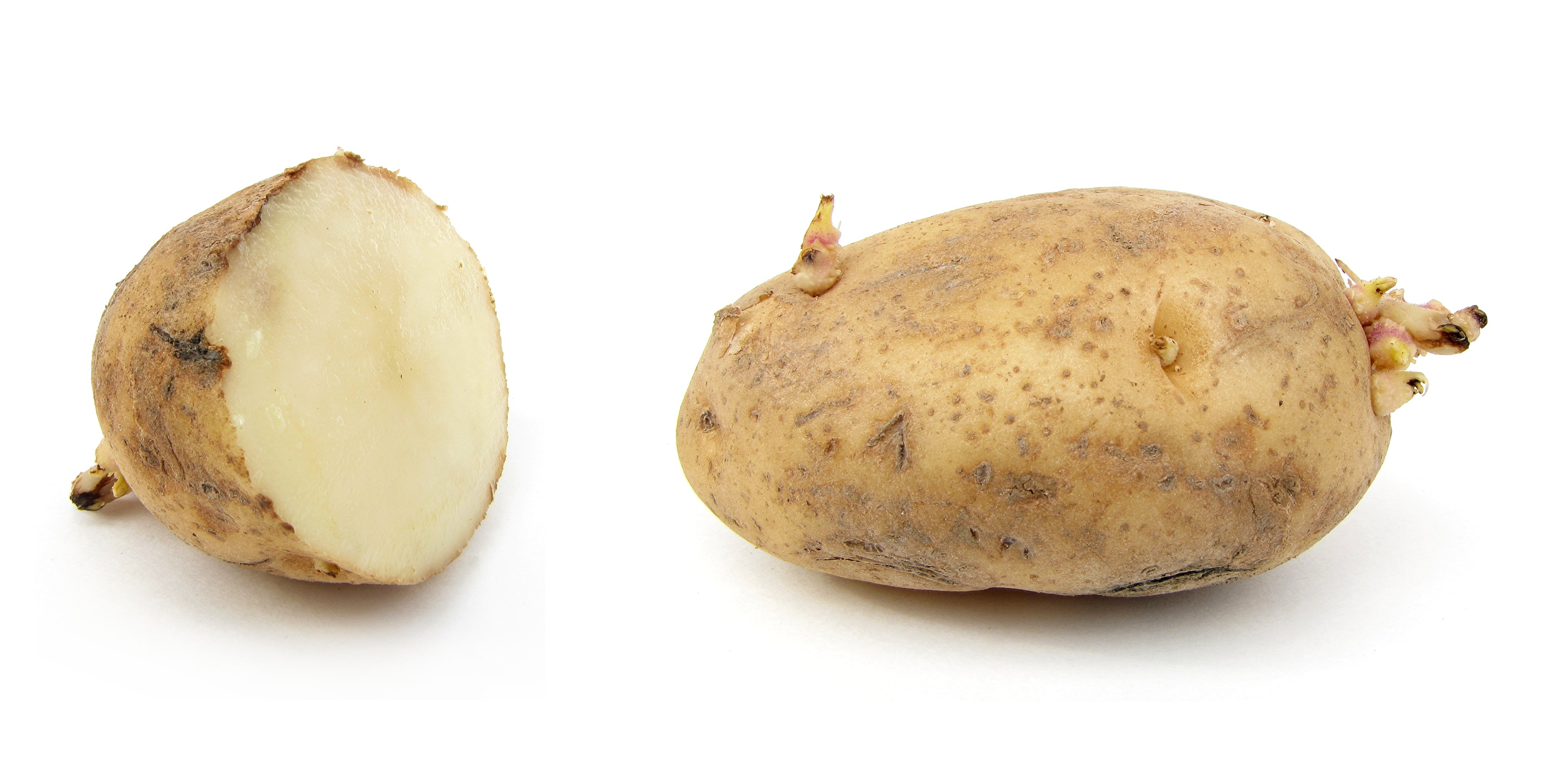
Though a less important staple, potato
The potato is a starchy food, a tuber of the plant ''Solanum tuberosum'' and is a root vegetable native to the Americas. The plant is a perennial in the nightshade family Solanaceae.
Wild potato species can be found from the southern Uni ...
es were also adopted from Native American cuisine and have been used in many ways similar to corn. Native Americans introduced the first non-Native American Southerners to many other vegetables still familiar on southern tables. Squash
Squash may refer to:
Sports
* Squash (sport), the high-speed racquet sport also known as squash racquets
* Squash (professional wrestling), an extremely one-sided match in professional wrestling
* Squash tennis, a game similar to squash but pla ...
, pumpkin
A pumpkin is a vernacular term for mature winter squash of species and varieties in the genus ''Cucurbita'' that has culinary and cultural significance but no agreed upon botanical or scientific meaning. The term ''pumpkin'' is sometimes use ...
, many types of bean
A bean is the seed of several plants in the family Fabaceae, which are used as vegetables for human or animal food. They can be cooked in many different ways, including boiling, frying, and baking, and are used in many traditional dishes th ...
s, tomato
The tomato is the edible berry of the plant ''Solanum lycopersicum'', commonly known as the tomato plant. The species originated in western South America, Mexico, and Central America. The Mexican Nahuatl word gave rise to the Spanish word ...
es, many types of pepper
Pepper or peppers may refer to:
Food and spice
* Piperaceae or the pepper family, a large family of flowering plant
** Black pepper
* ''Capsicum'' or pepper, a genus of flowering plants in the nightshade family Solanaceae
** Bell pepper
** Chili ...
s, and sassafras
''Sassafras'' is a genus of three extant and one extinct species of deciduous trees in the family Lauraceae, native to eastern North America and eastern Asia.Wolfe, Jack A. & Wehr, Wesley C. 1987. The sassafras is an ornamental tree. "Middle ...
all came to the settlers via Indigenous peoples. The Virginia Algonquian word ''pawcohiccora'' means hickory
Hickory is a common name for trees composing the genus ''Carya'', which includes around 18 species. Five or six species are native to China, Indochina, and India (Assam), as many as twelve are native to the United States, four are found in Mex ...
-nut meat or a nut milk drink made from it.
Many fruit
In botany, a fruit is the seed-bearing structure in flowering plants that is formed from the ovary after flowering.
Fruits are the means by which flowering plants (also known as angiosperms) disseminate their seeds. Edible fruits in partic ...
s are available in this region. Muscadine
''Vitis rotundifolia'', or muscadine, is a grapevine species native to the southeastern and south-central United States. The growth range extends from Florida to New Jersey coast, and west to eastern Texas and Oklahoma. It has been extensive ...
s, blackberries
The blackberry is an edible fruit produced by many species in the genus ''Rubus'' in the family (biology), family Rosaceae, hybrids among these species within the subgenus ''Rubus'', and hybrids between the subgenera ''Rubus'' and ''Idaeobatus' ...
, raspberries
The raspberry is the edible fruit of a multitude of plant species in the genus ''Rubus'' of the rose family, most of which are in the subgenus '' Idaeobatus''. The name also applies to these plants themselves. Raspberries are perennial with ...
, and many other wild berries were part of Southern Native Americans' diet.
Southeastern Native Americans traditionally supplement their diets with meats derived from the hunting of native game. Venison
Venison originally meant the meat of a game animal but now refers primarily to the meat of antlered ungulates such as elk or deer (or antelope in South Africa). Venison can be used to refer to any part of the animal, so long as it is edibl ...
has always been an important meat staple, due to the abundance of white-tailed deer
The white-tailed deer (''Odocoileus virginianus''), also known as the whitetail or Virginia deer, is a medium-sized deer native to North America, Central America, and South America as far south as Peru and Bolivia. It has also been introduced t ...
in the area. Rabbit
Rabbits, also known as bunnies or bunny rabbits, are small mammals in the family Leporidae (which also contains the hares) of the order Lagomorpha (which also contains the pikas). ''Oryctolagus cuniculus'' includes the European rabbit sp ...
s, squirrel
Squirrels are members of the family Sciuridae, a family that includes small or medium-size rodents. The squirrel family includes tree squirrels, ground squirrels (including chipmunks and prairie dogs, among others), and flying squirrels. ...
s, opossum
Opossums () are members of the marsupial order Didelphimorphia () endemic to the Americas. The largest order of marsupials in the Western Hemisphere, it comprises 93 species in 18 genera. Opossums originated in South America and entered No ...
s, and raccoon
The raccoon ( or , ''Procyon lotor''), sometimes called the common raccoon to distinguish it from other species, is a mammal native to North America. It is the largest of the procyonid family, having a body length of , and a body weight of ...
s are also common.
Livestock
Livestock are the domesticated animals raised in an agricultural setting to provide labor and produce diversified products for consumption such as meat, eggs, milk, fur, leather, and wool. The term is sometimes used to refer solely to ani ...
, adopted from Europeans, in the form of hogs and cattle
Cattle (''Bos taurus'') are large, domesticated, cloven-hooved, herbivores. They are a prominent modern member of the subfamily Bovinae and the most widespread species of the genus '' Bos''. Adult females are referred to as cows and adult ...
, are also kept. Aside from the more commonly consumed parts of the animal, it is traditional to also eat organ meats such as liver
The liver is a major organ only found in vertebrates which performs many essential biological functions such as detoxification of the organism, and the synthesis of proteins and biochemicals necessary for digestion and growth. In humans, it i ...
, brain
A brain is an organ (biology), organ that serves as the center of the nervous system in all vertebrate and most invertebrate animals. It is located in the head, usually close to the sensory organs for senses such as Visual perception, vision. I ...
s, and intestine
The gastrointestinal tract (GI tract, digestive tract, alimentary canal) is the tract or passageway of the digestive system that leads from the mouth to the anus. The GI tract contains all the major organs of the digestive system, in humans an ...
s. This tradition remains today in hallmark dishes like chitterlings
Chitterlings (), sometimes spelled chitlins or chittlins, are the small intestines of domestic animals. They are usually made from pigs' intestines. They may also be filled with a forcemeat to make sausage.''Oxford English Dictionary'', 1st edit ...
, commonly called chitlins, which are the fried large intestine
The gastrointestinal tract (GI tract, digestive tract, alimentary canal) is the tract or passageway of the digestive system that leads from the mouth to the anus. The GI tract contains all the major organs of the digestive system, in humans an ...
s of hogs; livermush, a common dish in the Carolinas made from hog liver; and pork brains and eggs. The fat of the animals, particularly of hogs, is traditionally rendered and used for cooking and frying. Many of the early settlers were taught Southeastern Native American cooking methods.
Selected dishes
* Chitterling ( Chitlin), usually made from the large intestines of a hog *Cornbread
Cornbread is a quick bread made with cornmeal, associated with the cuisine of the Southern United States, with origins in Native American cuisine. It is an example of batter bread. Dumplings and pancakes made with finely ground cornmeal are ...
* Hominy
Hominy (Spanish: maíz molido; literally meaning "milled corn") is a food produced from dried maize (corn) kernels that have been treated with an alkali, in a process called nixtamalization ( is the Nahuatl word for "hominy"). "Lye hominy" is a ...
, coarsely ground corn used to make grits
* Hush puppy
A hush puppy (or hushpuppy) is a small, savory, deep-fried round ball made from cornmeal-based batter. Hushpuppies are frequently served as a side dish with seafood and other deep-fried foods.
History
The use of ground maize (corn) in cooking ...
, small, savory, deep-fried round ball made from cornmeal-based batter
* Indian fritter
* Kanuchi, soup made from ground hickory nuts
* Livermush, pig liver, parts of pig heads, cornmeal and spices
* Sofkee, corn soup or drink, sour
Great Plains Native American cuisine
Indigenous peoples of the Great Plains and Canadian Prairies orPlains Indians
Plains Indians or Indigenous peoples of the Great Plains and Canadian Prairies are the Native American tribes and First Nation band governments who have historically lived on the Interior Plains (the Great Plains and Canadian Prairies) of ...
have historically relied heavily on American bison
The American bison (''Bison bison'') is a species of bison native to North America. Sometimes colloquially referred to as American buffalo or simply buffalo (a different clade of bovine), it is one of two extant species of bison, alongside the ...
(American buffalo) as a staple food source. One traditional method of preparation is to cut the meat into thin slices then dry it, either over a slow fire or in the hot sun, until it is hard and brittle. In this form it can last for months, making it a main ingredient to be combined with other foods, or eaten on its own.
One such use could be pemmican
Pemmican (also pemican in older sources) is a mixture of tallow, dried meat, and sometimes dried berries. A calorie-rich food, it can be used as a key component in prepared meals or eaten raw. Historically, it was an important part of indigenou ...
, a concentrated mixture of fat and protein, and fruits such as cranberries
Cranberries are a group of evergreen dwarf shrubs or trailing vines in the subgenus ''Oxycoccus'' of the genus ''Vaccinium''. In Britain, cranberry may refer to the native species ''Vaccinium oxycoccos'', while in North America, cranberry m ...
, Saskatoon berries, blueberries
Blueberries are a widely distributed and widespread group of perennial flowering plants with blue or purple berries. They are classified in the section ''Cyanococcus'' within the genus ''Vaccinium''. ''Vaccinium'' also includes cranberries, bi ...
, cherries
A cherry is the fruit of many plants of the genus '' Prunus'', and is a fleshy drupe (stone fruit).
Commercial cherries are obtained from cultivars of several species, such as the sweet ''Prunus avium'' and the sour ''Prunus cerasus''. The ...
, chokecherries
''Prunus virginiana'', commonly called bitter-berry, chokecherry, Virginia bird cherry, and western chokecherry (also black chokecherry for ''P. virginiana'' var. ''demissa''), is a species of bird cherry (''Prunus'' subgenus ''Padus'') nat ...
, and currants are sometimes added. Many parts of the bison were utilized and prepared in numerous ways, including: "boiled meat, tripe soup perhaps thickened with brains, roasted intestines, jerked/smoked meat, and raw kidneys, liver, tongue sprinkled with gall or bile were eaten immediately after a kill."
The animals that Great Plains Indians consumed, like bison, deer, and antelope, were grazing animals. Due to this, they were high in omega-3 fatty acids, an essential acid that many diets lack.
When asked to state traditional staple foods, a group of Plains elders identified prairie turnips (''Psoralea esculenta
''Psoralea esculenta'', common name prairie turnip or timpsula, is an herbaceous perennial plant native to prairies and dry woodlands of central North America, which bears a starchy tuberous root edible as a root vegetable. The plant is also kn ...
''), called timpsula or Tin'psila in the Lakota language group; fruits (chokecherries
''Prunus virginiana'', commonly called bitter-berry, chokecherry, Virginia bird cherry, and western chokecherry (also black chokecherry for ''P. virginiana'' var. ''demissa''), is a species of bird cherry (''Prunus'' subgenus ''Padus'') nat ...
, June berries, plums
A plum is a fruit of some species in ''Prunus'' subg. ''Prunus'.'' Dried plums are called prunes.
History
Plums may have been one of the first fruits domesticated by humans. Three of the most abundantly cultivated species are not found i ...
, blueberries
Blueberries are a widely distributed and widespread group of perennial flowering plants with blue or purple berries. They are classified in the section ''Cyanococcus'' within the genus ''Vaccinium''. ''Vaccinium'' also includes cranberries, bi ...
, cranberries
Cranberries are a group of evergreen dwarf shrubs or trailing vines in the subgenus ''Oxycoccus'' of the genus ''Vaccinium''. In Britain, cranberry may refer to the native species ''Vaccinium oxycoccos'', while in North America, cranberry m ...
, strawberries
The garden strawberry (or simply strawberry; ''Fragaria × ananassa'') is a widely grown hybrid species of the genus '' Fragaria'', collectively known as the strawberries, which are cultivated worldwide for their fruit. The fruit is widely ap ...
, buffalo berries, gooseberries); potato
The potato is a starchy food, a tuber of the plant ''Solanum tuberosum'' and is a root vegetable native to the Americas. The plant is a perennial in the nightshade family Solanaceae.
Wild potato species can be found from the southern Uni ...
es; squash
Squash may refer to:
Sports
* Squash (sport), the high-speed racquet sport also known as squash racquets
* Squash (professional wrestling), an extremely one-sided match in professional wrestling
* Squash tennis, a game similar to squash but pla ...
; dried meats (venison
Venison originally meant the meat of a game animal but now refers primarily to the meat of antlered ungulates such as elk or deer (or antelope in South Africa). Venison can be used to refer to any part of the animal, so long as it is edibl ...
, buffalo, jack rabbit
Hares and jackrabbits are mammals belonging to the genus ''Lepus''. They are herbivores, and live Solitary animal, solitarily or in pairs. They nest in slight depressions called forms, and their young are precociality, able to fend for themselves ...
, pheasant
Pheasants ( ) are birds of several genera within the family Phasianidae in the order Galliformes. Although they can be found all over the world in introduced (and captive) populations, the pheasant genera native range is restricted to Eurasia ...
, and prairie chicken); and wild rice
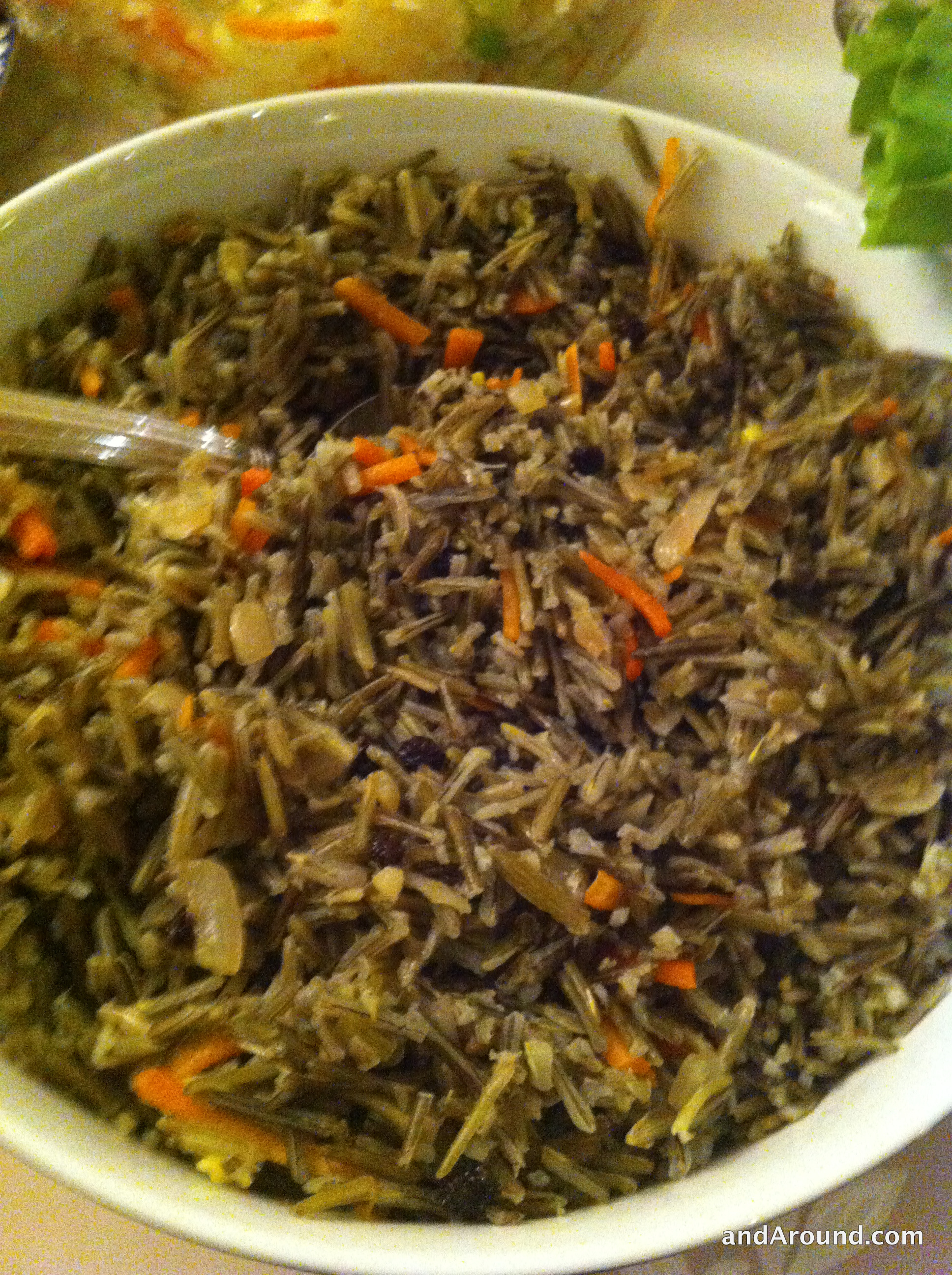
Wild rice, also called manoomin, Canada rice, Indian rice, or water oats, is any of four species of grasses that form the genus ''Zizania'', and the grain that can be harvested from them. The grain was historically gathered and eaten in both ...
as being these staple foods.
"We landed at a Watlala village 200 men of Flatheads of 25 houses 50 canoes built of Straw, we were treated verry kindly by them, they gave us round root near the size of a hens egg roasted which they call Wap-to (wapato) to eate . . . . which they roasted in the embers until they became Soft"
—William Clark, Lewis and Clark Expedition
Wapato (''Sagittaria latifolia
''Sagittaria latifolia'' is a plant found in shallow wetlands and is sometimes known as broadleaf arrowhead, duck-potato, Indian potato, katniss, or wapato. This plant produces edible tubers that have traditionally been extensively used by Nati ...
'') has a number of varieties and is found growing in damp marsh area around ponds, lakes, rivers, and streams. The edible rhizomes were gathered and could be roasted in the embers of a fire, or dried, ground and the meal pressed into a cake which "served well as bread" as noted by Meriwether Lewis of the Lewis and Clark Expedition. They are known today as broadleaf arrowhead, arrowhead, duckroot, or duck-potato.
Western Indigenous cuisine
In thePacific Northwest
The Pacific Northwest (sometimes Cascadia, or simply abbreviated as PNW) is a geographic region in western North America bounded by its coastal waters of the Pacific Ocean to the west and, loosely, by the Rocky Mountains to the east. Thou ...
, traditional diets include salmon and other fish, seafood, mushrooms, berries, and meats such as deer, duck, and rabbit.
In contrast to the Easterners, the Northwestern peoples are traditionally hunter-gatherers, primarily. The generally mild climate led to the development of an economy based on year-round abundant food supplies, rather than having to rely upon seasonal agriculture.
In what is now California, acorn
The acorn, or oaknut, is the nut of the oaks and their close relatives (genera '' Quercus'' and '' Lithocarpus'', in the family Fagaceae). It usually contains one seed (occasionally
two seeds), enclosed in a tough, leathery shell, and b ...
s can be ground into a flour that has at times served as the principal foodstuff for about 75 percent of the population, and dried meats can be prepared during the dry season.
Southwestern Indigenous cuisine
Ancestral Puebloans
The Ancestral Puebloans, also known as the Anasazi, were an ancient Native American culture that spanned the present-day Four Corners region of the United States, comprising southeastern Utah, northeastern Arizona, northwestern New Mexico, a ...
of the present-day Four Corners region of the United States, comprising Arizona
Arizona ( ; nv, Hoozdo Hahoodzo ; ood, Alĭ ṣonak ) is a state in the Southwestern United States. It is the 6th largest and the 14th most populous of the 50 states. Its capital and largest city is Phoenix. Arizona is part of the Fou ...
, Colorado
Colorado (, other variants) is a state in the Mountain West subregion of the Western United States. It encompasses most of the Southern Rocky Mountains, as well as the northeastern portion of the Colorado Plateau and the western edge of the ...
, New Mexico
)
, population_demonym = New Mexican ( es, Neomexicano, Neomejicano, Nuevo Mexicano)
, seat = Santa Fe, New Mexico, Santa Fe
, LargestCity = Albuquerque, New Mexico, Albuquerque
, LargestMetro = Albuquerque metropolitan area, Tiguex
, Offi ...
, and Utah
Utah ( , ) is a state in the Mountain West subregion of the Western United States. Utah is a landlocked U.S. state bordered to its east by Colorado, to its northeast by Wyoming, to its north by Idaho, to its south by Arizona, and to its ...
, initially practiced subsistence agriculture by cultivating maize
Maize ( ; ''Zea mays'' subsp. ''mays'', from es, maíz after tnq, mahiz), also known as corn (North American English, North American and Australian English), is a cereal grain first domesticated by indigenous peoples of Mexico, indigenous ...
, beans
A bean is the seed of several plants in the family Fabaceae, which are used as vegetables for human or animal food. They can be cooked in many different ways, including boiling, frying, and baking, and are used in many traditional dishes thr ...
, squash
Squash may refer to:
Sports
* Squash (sport), the high-speed racquet sport also known as squash racquets
* Squash (professional wrestling), an extremely one-sided match in professional wrestling
* Squash tennis, a game similar to squash but pla ...
, sunflower seed
The sunflower seed is the seed of the sunflower (''Helianthus annuus''). There are three types of commonly used sunflower seeds: linoleic (most common), high oleic, and sunflower oil seeds. Each variety has its own unique levels of monounsat ...
s, and pine nuts
Pine nuts, also called piñón (), pinoli (), pignoli or chilgoza (), are the edible seeds of pines (family Pinaceae, genus ''Pinus''). According to the Food and Agriculture Organization, only 29 species provide edible nuts, while 20 are trade ...
from the pinyon pine
The pinyon or piñon pine group grows in southwestern North America, especially in New Mexico, Arizona, and Utah. The trees yield edible nuts, which are a staple food of Native Americans, and widely eaten as a snack and as an ingredient in ...
, and game meat including venison
Venison originally meant the meat of a game animal but now refers primarily to the meat of antlered ungulates such as elk or deer (or antelope in South Africa). Venison can be used to refer to any part of the animal, so long as it is edibl ...
and cuniculture
Cuniculture is the agricultural practice of breeding and raising domestic rabbits as livestock for their meat, fur, or wool. Cuniculture is also employed by rabbit fanciers and hobbyists in the development and betterment of rabbit breeds and the ...
, and freshwater fish such as Rio Grande cutthroat trout
The Rio Grande cutthroat trout (''Oncorhynchus clarki virginalis''), a member of the family Salmonidae, is found in northern New Mexico and southern Colorado in tributaries of the Rio Grande.
It is one of 14 subspecies of cutthroat trout native ...
and rainbow trout
The rainbow trout (''Oncorhynchus mykiss'') is a species of trout native to cold-water tributaries of the Pacific Ocean in Asia and North America. The steelhead (sometimes called "steelhead trout") is an anadromous (sea-run) form of the coast ...
are also traditional foods in the region.
Ancestral Puebloans are also known for their basketry and pottery, indicating both an agricultural surplus that needed to be carried and stored, and clay pot cooking. Grinding stones have been used to grind maize into meal for cooking. Archaeological digs indicate a very early domestication of turkeys for food.
New Mexican cuisine is heavily rooted in both Pueblo
In the Southwestern United States, Pueblo (capitalized) refers to the Native tribes of Puebloans having fixed-location communities with permanent buildings which also are called pueblos (lowercased). The Spanish explorers of northern New Spain ...
and Hispano food traditions, and is a prevalent cuisine in the American Southwest, especially in New Mexico
)
, population_demonym = New Mexican ( es, Neomexicano, Neomejicano, Nuevo Mexicano)
, seat = Santa Fe, New Mexico, Santa Fe
, LargestCity = Albuquerque, New Mexico, Albuquerque
, LargestMetro = Albuquerque metropolitan area, Tiguex
, Offi ...
.
The 2002 ''Foods of the Southwest Indian Nations
''Foods of the Southwest Indian Nations'' is a 2002 cookbook by Lois Ellen Frank, food historian, cookbook author, photographer, and culinary anthropologist. The book won a 2003 James Beard award, the first Native American cuisine cookbook so hon ...
'' won a James Beard Award
The James Beard Foundation Awards are annual awards presented by the James Beard Foundation to recognize chefs, restaurateurs, authors and journalists in the United States. They are scheduled around James Beard's May 5 birthday. The media awa ...
, the first Native American cookbook so honored. Publishers had told the author, Lois Ellen Frank, that there was no such thing as Native American cuisine.
Alaska Native cuisine
Alaska Native
Alaska Natives (also known as Alaskan Natives, Native Alaskans, Indigenous Alaskans, Aboriginal Alaskans or First Alaskans) are the indigenous peoples of Alaska and include Iñupiat, Yupik, Aleut, Eyak, Tlingit, Haida, Tsimshian, and a num ...
cuisine consists of nutrient-dense foods such as seal, fish (salmon), and moose. Along with these, berries (huckleberries) and bird eggs are traditionally consumed by Alaska Natives.
Seal, walruses, and polar bear are the large game that Alaska Natives hunt. Smaller game includes whitefish, Arctic char
The Arctic char or Arctic charr (''Salvelinus alpinus'') is a cold-water fish in the family Salmonidae, native to alpine lakes and arctic and subarctic coastal waters. Its distribution is Circumpolar North. It spawns
Spawn is the eggs a ...
, Arctic hare
The Arctic hare (''Lepus arcticus'') is a species of hare highly adapted to living in the Arctic tundra and other icy biomes. The Arctic hare survives with shortened ears and limbs, a small nose, fat that makes up close to 20% of its body, and a ...
, and ptarmigan.
Due to weather, edible plants like berries are only available to be consumed in the summer, so the people have a diet very high in fat and protein, but low in carbohydrates.
The game that is hunted is also used for clothing. The intestines of large mammals are used to make waterproof clothing and caribou fur is used to make warm clothing.
Dishes


 *
*Acorn
The acorn, or oaknut, is the nut of the oaks and their close relatives (genera '' Quercus'' and '' Lithocarpus'', in the family Fagaceae). It usually contains one seed (occasionally
two seeds), enclosed in a tough, leathery shell, and b ...
bread
* Acorn mush, from the Miwok
The Miwok (also spelled Miwuk, Mi-Wuk, or Me-Wuk) are members of four linguistically related Native American groups indigenous to what is now Northern California, who traditionally spoke one of the Miwok languages in the Utian family. The word ...
people
*Akutaq
Alaskan ice cream (also known as Alaskan Indian ice cream, Inuit ice cream, Indian ice cream or Native ice cream, and Inuit-Yupik varieties of which are known as ''akutaq'' or ''akutuq'') is a dessert made by Alaskan Athabaskans and other Alaska N ...
, also called "Eskimo ice cream", made from caribou or moose tallow and meat, berries, seal oil, and sometimes fish, whipped together with snow or water
* Bannock, a bread of European origin, cooked over an open fire
* Bean bread, made with corn meal and beans, popular among the Cherokee
The Cherokee (; chr, ᎠᏂᏴᏫᏯᎢ, translit=Aniyvwiyaʔi or Anigiduwagi, or chr, ᏣᎳᎩ, links=no, translit=Tsalagi) are one of the indigenous peoples of the Southeastern Woodlands of the United States. Prior to the 18th century, th ...
*Bird brain stew, from the Cree
The Cree ( cr, néhinaw, script=Latn, , etc.; french: link=no, Cri) are a North American Indigenous people. They live primarily in Canada, where they form one of the country's largest First Nations.
In Canada, over 350,000 people are Cree o ...
nation
*Black drink
Black drink is a name for several kinds of ritual beverages brewed by Native Americans in the Southeastern United States. Traditional ceremonial people of the Yuchi, Caddo, Chickasaw, Cherokee, Choctaw, Muscogee and some other Indigenous pe ...
or ''asi'', a Southeastern ceremonial drink made from the yaupon holly
''Ilex vomitoria'', commonly known as yaupon () or yaupon holly, is a species of holly that is native to southeastern North America. The word ''yaupon'' was derived from the Catawban ''yą́pą'', from ''yą-'' tree + ''pą'' leaf. Another commo ...
*Buffalo stew, from the Lakota and Cherokee people, also called ''tanka-me-a-lo''
* Chinook olives, a type of cured acorn eaten by the aboriginal people of the Columbia River Valley
*Cornbread
Cornbread is a quick bread made with cornmeal, associated with the cuisine of the Southern United States, with origins in Native American cuisine. It is an example of batter bread. Dumplings and pancakes made with finely ground cornmeal are ...
and corn pone
Cornbread is a quick bread made with cornmeal, associated with the cuisine of the Southern United States, with origins in Native American cuisine. It is an example of batter bread. Dumplings and pancakes made with finely ground cornmeal are st ...
—the word ''pone'' derives from the word for 'bread' in some Eastern Algonquian languages
The Eastern Algonquian languages constitute a subgroup of the Algonquian languages. Prior to European contact, Eastern Algonquian consisted of at least 17 languages, whose speakers collectively occupied the Atlantic coast of North America and ad ...
, such as Powhatan
The Powhatan people (; also spelled Powatan) may refer to any of the indigenous Algonquian people that are traditionally from eastern Virginia. All of the Powhatan groups descend from the Powhatan Confederacy. In some instances, The Powhatan ...
''apon'' and Lenape
The Lenape (, , or Lenape , del, Lënapeyok) also called the Leni Lenape, Lenni Lenape and Delaware people, are an indigenous peoples of the Northeastern Woodlands, who live in the United States and Canada. Their historical territory inclu ...
''ahpòn''
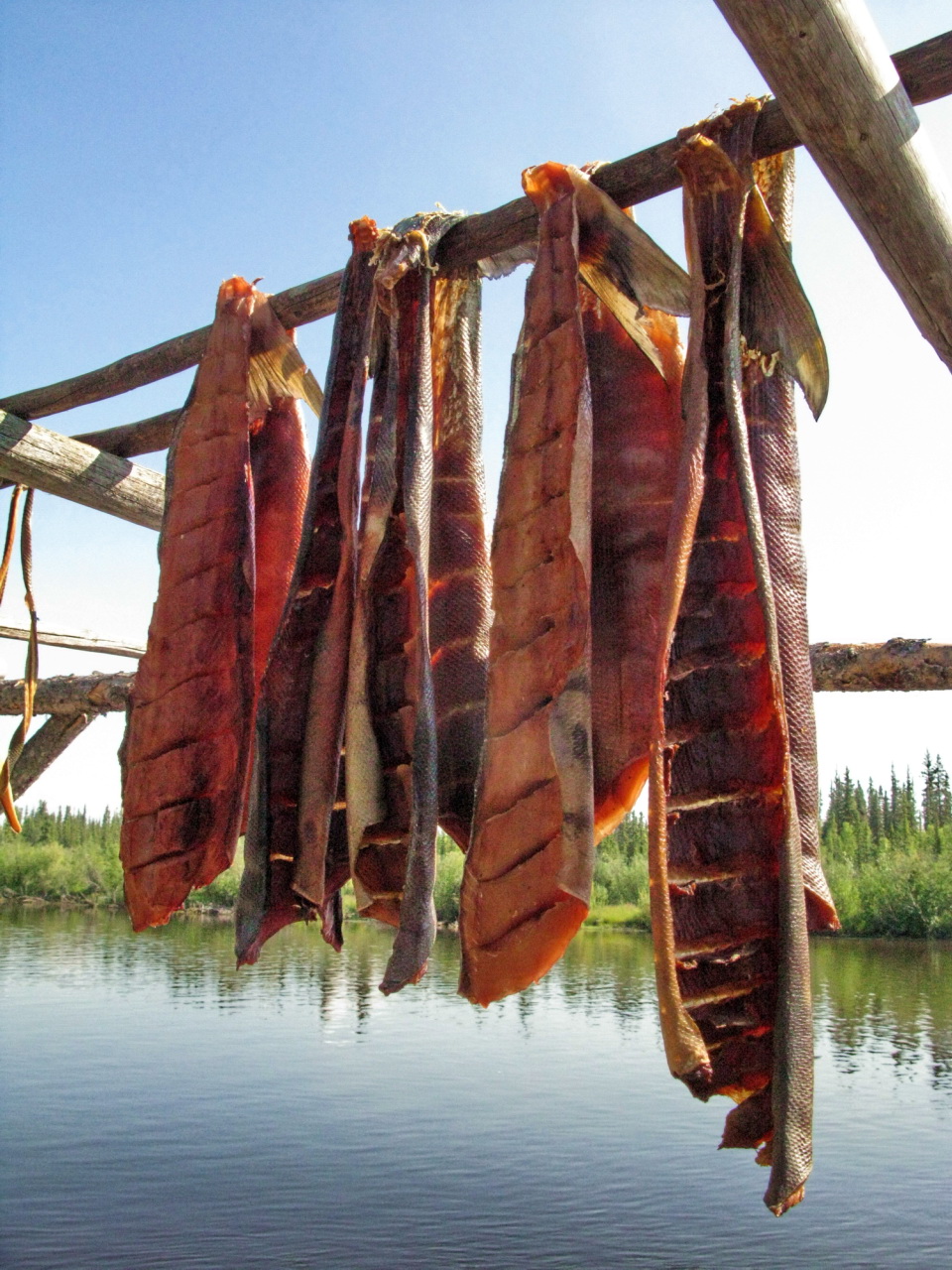
*Dried meat
Dried meat is a feature of many cuisines around the world. Examples include:
*Kulen Slanina Pečenica
*Aliya, sun-dried meat from Kenya
* Bakkwa or rougan, Chinese salty-sweet dried meat sheets.
* Biltong, a cured meat that originated in Sout ...
s like jerky
Jerky is lean trimmed meat cut into strips and dried (dehydrated) to prevent spoilage. Normally, this drying includes the addition of salt to prevent bacteria growth before the meat has finished the dehydrating process. The word "jerky" derive ...
and smoked salmon
Salmon () is the common name for several commercially important species of euryhaline ray-finned fish from the family Salmonidae, which are native to tributaries of the North Atlantic (genus '' Salmo'') and North Pacific (genus '' Onco ...
strips
* Filé powder, made from sassafras leaves, used by the Choctaw
The Choctaw (in the Choctaw language, Chahta) are a Native American people originally based in the Southeastern Woodlands, in what is now Alabama and Mississippi. Their Choctaw language is a Western Muskogean language. Today, Choctaw people are ...
for flavoring and thickening soups and stews as well as for herbal medicine
* Frybread, a dish made from ingredients distributed to Native Americans living on reservations
* Green chili stew
* Hopi tea, an herbal tea
Herbal teas, also known as herbal infusions and less commonly called tisanes (UK and US , US also ), are beverages made from the infusion or decoction of herbs, spices, or other plant material in hot water. Oftentimes herb tea, or the plain term ...
made from ''Thelesperma megapotamicum
''Thelesperma megapotamicum'' is a perennial species of flowering plant in the aster family known by the common name wild tea and rayless greenthread. It is native to sections of the Americas, including the central United States, where it grows i ...
''
*Mutton stew, from the Navajo people
*''Nokake'', Algonquian hoecakes, made of cornmeal
* Nut milk, from the Wabanaki
*Pemmican
Pemmican (also pemican in older sources) is a mixture of tallow, dried meat, and sometimes dried berries. A calorie-rich food, it can be used as a key component in prepared meals or eaten raw. Historically, it was an important part of indigenou ...
, a concentrated food consisting of dried pulverized meat, dried berries, and rendered fat.
 * Piki bread, from the
* Piki bread, from the Hopi
The Hopi are a Native American ethnic group who primarily live on the Hopi Reservation in northeastern Arizona, United States. As of the 2010 census, there are 19,338 Hopi in the country. The Hopi Tribe is a sovereign nation within the United ...
people
*''Psindamoakan'', a Lenape
The Lenape (, , or Lenape , del, Lënapeyok) also called the Leni Lenape, Lenni Lenape and Delaware people, are an indigenous peoples of the Northeastern Woodlands, who live in the United States and Canada. Their historical territory inclu ...
hunter's food made of parched cornmeal mixed with maple sugar
*Pueblo bread
* Salted salmon, an Inuit dish of brined salmon
Salmon () is the common name for several commercially important species of euryhaline ray-finned fish from the family Salmonidae, which are native to tributaries of the North Atlantic (genus '' Salmo'') and North Pacific (genus '' Onco ...
in a heavy concentration of salt water, left for months to soak up salts
*''Sapan'' (), cornmeal mush
Mush is a type of cornmeal pudding (or porridge) which is usually boiled in water or milk. It is often allowed to set, or gel into a semisolid, then cut into flat squares or rectangles, and pan fried. Usage is especially common in the Eastern U ...
, a staple of Lenape cuisine
*Stink fish, an Inuit dish of dried fish, kept underground until ripe, for later consumption; also done with fish heads
*Succotash
Succotash (from Narragansett ''sahquttahhash'', "broken corn kernels") is a vegetable dish consisting primarily of sweet corn with lima beans or other shell beans.
Other ingredients may be added, such as onions, potatoes, turnips, tomatoes, b ...
, a dish of beans and corn
*Sumac lemonade, a Native American beverage made from sumac
Sumac ( or ), also spelled sumach, is any of about 35 species of flowering plants in the genus ''Rhus'' and related genera in the cashew family (Anacardiaceae). Sumacs grow in subtropical and temperate regions throughout the world, including Eas ...
berries
*'' Tiswin'', a term used for several fermented beverage
This is a list of fermented foods, which are foods produced or preserved by the action of microorganisms. In this context, fermentation typically refers to the fermentation of sugar to alcohol using yeast, but other fermentation processes involv ...
s in the Southwest, including a corn or fruit beer of the Apache
The Apache () are a group of culturally related Native American tribes in the Southwestern United States, which include the Chiricahua, Jicarilla, Lipan, Mescalero, Mimbreño, Ndendahe (Bedonkohe or Mogollon and Nednhi or Carrizaleño a ...
and a saguaro
The saguaro (, ) (''Carnegiea gigantea'') is a tree-like cactus species in the monotypic genus ''Carnegiea'' that can grow to be over tall. It is native to the Sonoran Desert in Arizona, the Mexican state of Sonora, and the Whipple Mountai ...
fruit beer of the Tohono O'odham
*Walrus flipper soup, an Inuit dish made from walrus
The walrus (''Odobenus rosmarus'') is a large flippered marine mammal with a discontinuous distribution about the North Pole in the Arctic Ocean and subarctic seas of the Northern Hemisphere. The walrus is the only living species in the fami ...
flippers
*'' Wojapi'', a Plains Indian
Plains Indians or Indigenous peoples of the Great Plains and Canadian Prairies are the Native American tribes and First Nation band governments who have historically lived on the Interior Plains (the Great Plains and Canadian Prairies) of ...
pudding of mashed, cooked berries
Restaurants
Indigenous cuisine of the Circum-Caribbean
 This region comprises the cultures of the
This region comprises the cultures of the Arawaks
The Arawak are a group of indigenous peoples of northern South America and of the Caribbean. Specifically, the term "Arawak" has been applied at various times to the Lokono of South America and the Taíno, who historically lived in the Greater ...
, the Caribs, and the Ciboney
The Ciboney, or Siboney, were a Taíno people of western Cuba, Jamaica, and the Tiburon Peninsula of Haiti. A Western Taíno group living in central Cuba during the 15th and 16th centuries, they had a dialect and culture distinct from the Classi ...
. The Taíno
The Taíno were a historic Indigenous peoples of the Caribbean, indigenous people of the Caribbean whose culture has been continued today by Taíno descendant communities and Taíno revivalist communities. At the time of European contact in the ...
of the Greater Antilles
The Greater Antilles ( es, Grandes Antillas or Antillas Mayores; french: Grandes Antilles; ht, Gwo Zantiy; jam, Grieta hAntiliiz) is a grouping of the larger islands in the Caribbean Sea, including Cuba, Hispaniola, Puerto Rico, Jamaica, a ...
were the first New World
The term ''New World'' is often used to mean the majority of Earth's Western Hemisphere, specifically the Americas."America." ''The Oxford Companion to the English Language'' (). McArthur, Tom, ed., 1992. New York: Oxford University Press, p. ...
people to encounter Columbus. Prior to European contact, these groups foraged, hunted, and fished. The Taíno cultivated cassava
''Manihot esculenta'', commonly called cassava (), manioc, or yuca (among numerous regional names), is a woody shrub of the spurge family, Euphorbiaceae, native to South America. Although a perennial plant, cassava is extensively cultivated ...
, sweet potato
The sweet potato or sweetpotato ('' Ipomoea batatas'') is a dicotyledonous plant that belongs to the bindweed or morning glory family, Convolvulaceae. Its large, starchy, sweet-tasting tuberous roots are used as a root vegetable. The young ...
, maize
Maize ( ; ''Zea mays'' subsp. ''mays'', from es, maíz after tnq, mahiz), also known as corn (North American English, North American and Australian English), is a cereal grain first domesticated by indigenous peoples of Mexico, indigenous ...
, bean
A bean is the seed of several plants in the family Fabaceae, which are used as vegetables for human or animal food. They can be cooked in many different ways, including boiling, frying, and baking, and are used in many traditional dishes th ...
s, squash
Squash may refer to:
Sports
* Squash (sport), the high-speed racquet sport also known as squash racquets
* Squash (professional wrestling), an extremely one-sided match in professional wrestling
* Squash tennis, a game similar to squash but pla ...
, pineapple
The pineapple (''Ananas comosus'') is a tropical plant with an edible fruit; it is the most economically significant plant in the family Bromeliaceae. The pineapple is indigenous to South America, where it has been cultivated for many centuri ...
, peanut
The peanut (''Arachis hypogaea''), also known as the groundnut, goober (US), pindar (US) or monkey nut (UK), is a legume crop grown mainly for its edible seeds. It is widely grown in the tropics and subtropics, important to both small an ...
, and peppers
Pepper or peppers may refer to:
Food and spice
* Piperaceae or the pepper family, a large family of flowering plant
** Black pepper
* ''Capsicum'' or pepper, a genus of flowering plants in the nightshade family Solanaceae
** Bell pepper
** Chili ...
. Today these cultural groups have mostly assimilated into the surrounding population, but their culinary legacy lives on.
*''Ajiaco
Ajiaco () is a soup common to Colombia, Cuba, and Peru.Clark, Melissa (October 28, 2011)"From Colombia, the Ultimate One-Pot Meal" ''The New York Times''. Accessed April 2016. Scholars have debated the origin of the dish. The dish is especially p ...
'', same as pepperpot, a soup believed to have originated in Cuba before Columbus' arrival. The soup mixes a variety of meats, tubers, and peppers.
*''Barbacoa
Barbacoa () is a form of cooking meat that originated in the Caribbean with the Taíno people, who called it by the Arawak word ''barbaca'', from which the term "barbacoa" derives, and ultimately, the word 'barbecue". In contemporary Mexico, ...
'', the origin of the English word barbecue
Barbecue or barbeque (informally BBQ in the UK, US, and Canada, barbie in Australia and braai in South Africa) is a term used with significant regional and national variations to describe various cooking methods that use live fire and smoke ...
, a method of slow-grilling meat over a fire pit.
* Jerk, a style of cooking meat that originated with the Taíno of Jamaica
Jamaica (; ) is an island country situated in the Caribbean Sea. Spanning in area, it is the third-largest island of the Greater Antilles and the Caribbean (after Cuba and Hispaniola). Jamaica lies about south of Cuba, and west of Hispa ...
. Meat was applied with a dry rub of allspice
Allspice, also known as Jamaica pepper, myrtle pepper, pimenta, or pimento, is the dried unripe berry of ''Pimenta dioica'', a midcanopy tree native to the Greater Antilles, southern Mexico, and Central America, now cultivated in many warm par ...
, Scotch bonnet pepper
Scotch bonnet (also known as Bonney peppers, or Caribbean red peppers) is a variety of chili pepper named for its supposed resemblance to a Scottish tam o' shanter bonnet. It is ubiquitous in West Africa as well as the Caribbean. Like the clos ...
, and perhaps additional spices, before being smoked over fire or wood charcoal.
*'' Casabe'', a crispy, thin flatbread made from cassava root widespread in the Pre-Columbian Caribbean and Amazonia.
*Bammy
Bammy is a traditional Jamaican cassava flatbread descended from the simple flatbread eaten by the Arawaks, Jamaica's original inhabitants. Today, it is produced in many rural communities and sold in stores and by street vendors in Jamaica and ab ...
, a Jamaican bread made from cassava and water, today this bread is fried and made with coconut milk.
*''Guanime
Guanimes are a prepared food that can be traced back to the pre-Columbian era in Puerto Rico.
Origin
Guanimes are related to tamales and hallacas. Cornmeal masa is wrapped in corn husk stuffed with meat, nuts, fish, beans, or nothing at all. They ...
'', a Puerto Rican food similar to the tamale
A tamale, in Spanish tamal, is a traditional Mesoamerican dish made of masa, a dough made from nixtamalized corn, which is steamed in a corn husk or banana leaf. The wrapping can either be discarded prior to eating or used as a plate. Tam ...
; made with cornmeal or cornmeal and mashed cassave together.
*''Pasteles
''Pasteles'' (; singular ''pastel''), also pastelles in the English-speaking Caribbean, are a traditional dish in several Latin American and Caribbean countries. In Puerto Rico, the Dominican Republic, Venezuela, Panama, Trinidad and Tobago, ...
'', a dish that may have also been called ''hallaca
Hallaca (, ; alt. spelling, ''hayaca'' and ''ayaca'') is a traditional dish from Venezuela that looks like a tamal, though different in flavour, texture, ingredients and cultural significance. It consists of corn dough stuffed with a stew of bee ...
'' and originated from Puerto Rico. ''Pasteles'' were once made with cassava and taro
Taro () (''Colocasia esculenta)'' is a root vegetable. It is the most widely cultivated species of several plants in the family Araceae that are used as vegetables for their corms, leaves, and petioles. Taro corms are a food staple in Afri ...
mashed into a ''masa
''Masa'' (or ''masa de maíz'') (; ) is a maize dough that comes from ground nixtamalized corn. It is used for making corn tortillas, '' gorditas'', ''tamales'', '' pupusas'', and many other Latin American dishes. It is dried and powdered into ...
'' onto a taro leaf. They are then stuffed with meat and wrapped.
*'' Funche'' or ''fungi'', a cornmeal mush.
*''Cassareep
Cassareep is a thick black liquid made from cassava root, often with additional spices, which is used as a base for many sauces and especially in Guyanese pepperpot. Besides use as a flavoring and browning agent, it is commonly regarded as a food p ...
'', a sauce, condiment, or thickening agent made by boiling down the extracted juices of bitter cassava root.
* Mama Juana, a tea made in Hispaniola
Hispaniola (, also ; es, La Española; Latin and french: Hispaniola; ht, Ispayola; tnq, Ayiti or Quisqueya) is an island in the Caribbean that is part of the Greater Antilles. Hispaniola is the most populous island in the West Indies, and th ...
(Dominican Republic and Haiti).
* Pepperpot, a spicy stew of Taíno origin based on meat, vegetables, chili peppers, and boiled-down cassava juice, with a legacy stretching from Cuba
Cuba ( , ), officially the Republic of Cuba ( es, República de Cuba, links=no ), is an island country comprising the island of Cuba, as well as Isla de la Juventud and several minor archipelagos. Cuba is located where the northern Caribb ...
, Colombia
Colombia (, ; ), officially the Republic of Colombia, is a country in South America with insular regions in North America—near Nicaragua's Caribbean coast—as well as in the Pacific Ocean. The Colombian mainland is bordered by the ...
coast and to Guyana.
*Bush teas, popular as herbal remedies in the Virgin Islands and other parts of the Caribbean, often derived from indigenous sources, such as ginger thomas, soursop, inflammation bush, ''Spanish lime, kenip,'' wormgrass, worry wine, and many other leaves, barks, and herbs.
*''Ouicou'', a fermented, cassava-based beer brewed by the Caribs of the Lesser Antilles.
*Tomalley, Taumali or taumalin, a Carib sauce made from the green liver meat of lobsters, chile pepper, and lime juice.
Indigenous cuisine of Mesoamerica

 The pre-Spanish colonization of the Americas, conquest cuisine of the Indigenous peoples of the Americas, Indigenous peoples of Mesoamerica made a major contribution to shaping modern-day
The pre-Spanish colonization of the Americas, conquest cuisine of the Indigenous peoples of the Americas, Indigenous peoples of Mesoamerica made a major contribution to shaping modern-day Mexican cuisine
Mexican cuisine consists of the cooking cuisines and traditions of the modern country of Mexico. Its earliest roots lie in Mesoamerican cuisine. Its ingredients and methods begin with the first agricultural communities such as the Olmec and ...
, Salvadoran cuisine, Honduran cuisine, Guatemalan cuisine. The cultures involved included the Aztec, Maya civilization, Maya, Olmec, Pipil people, Pipil and many more (see the List of pre-Columbian civilizations).
Some known dishes
*''Amaranth, Alegría'', a candy made from puffed amaranth and boiled-down honey or Agave americana, maguey sap, in ancient times formed into the shapes of Aztec gods *''Balché'', Mayan fermented honey drink *''Champurrado'', a chocolate drink *Chili pepper, Chili *Corn tortillas *Guacamole *''Huarache (food), Huarache'' *''Mezcal'' *''Mole (sauce), Mole'' *''Pejelagarto'', a fish with an alligator-like head seasoned with amashito chile and lime *Pozole *''Pulque'' or ''octli'', an alcoholic beverage of fermented Agave americana, maguey juice *Pupusas, thick cornmeal flatbread from the Pipil people, Pipil culture of El Salvador *Salsa (sauce), Salsa *Tacos *Tamales *''Tepache'', pineapple beer *''Tlacoyos'' (''gordita'') *''Words of Nahuatl origin#Words from Nahuatl, Xocolātl''Indigenous cuisine of South America



Andean cultures
This currently includes recipes known from the Quechua people, Quechua, Aymara people, Aymara and Nazca culture, Nazca of the Andes. *guinea pig, Grilled guinea pig, a native to most of the Andes region, this small rodent has been cultivated for at least 4000 years. *Fried green tomatoes (food), Fried green tomatoes, a nightshade relative native to Peru. *Chicha, ''Saraiaka'', a corn liquor. *''Chicha'', a generic name for any number of Indigenous beers found in South America. Though ''chichas'' made from various types of corn are the most common in the Andes, ''chicha'' in the Amazon Basin frequently use manioc. Variations found throughout the continent can be based on amaranth, quinoa,peanut
The peanut (''Arachis hypogaea''), also known as the groundnut, goober (US), pindar (US) or monkey nut (UK), is a legume crop grown mainly for its edible seeds. It is widely grown in the tropics and subtropics, important to both small an ...
, potato
The potato is a starchy food, a tuber of the plant ''Solanum tuberosum'' and is a root vegetable native to the Americas. The plant is a perennial in the nightshade family Solanaceae.
Wild potato species can be found from the southern Uni ...
, coca, and many other ingredients.
*''Chicha morada'', a Peruvian, sweet, unfermented drink made from purple corn, fruits, and spices.
*''Colada morada'', a thickened, spiced fruit drink based on the Rubus glaucus, Andean blackberry, traditional to the Day of the Dead ceremonies held in Ecuador, it is typically served with ''guagua de pan'', a bread shaped like a swaddled infant (formerly made from cornmeal in Pre-Columbian times), though other shapes can be found in various regions.
*Quinoa porridge.
*Charqui, ''Ch'arki'', a type of dried meat.
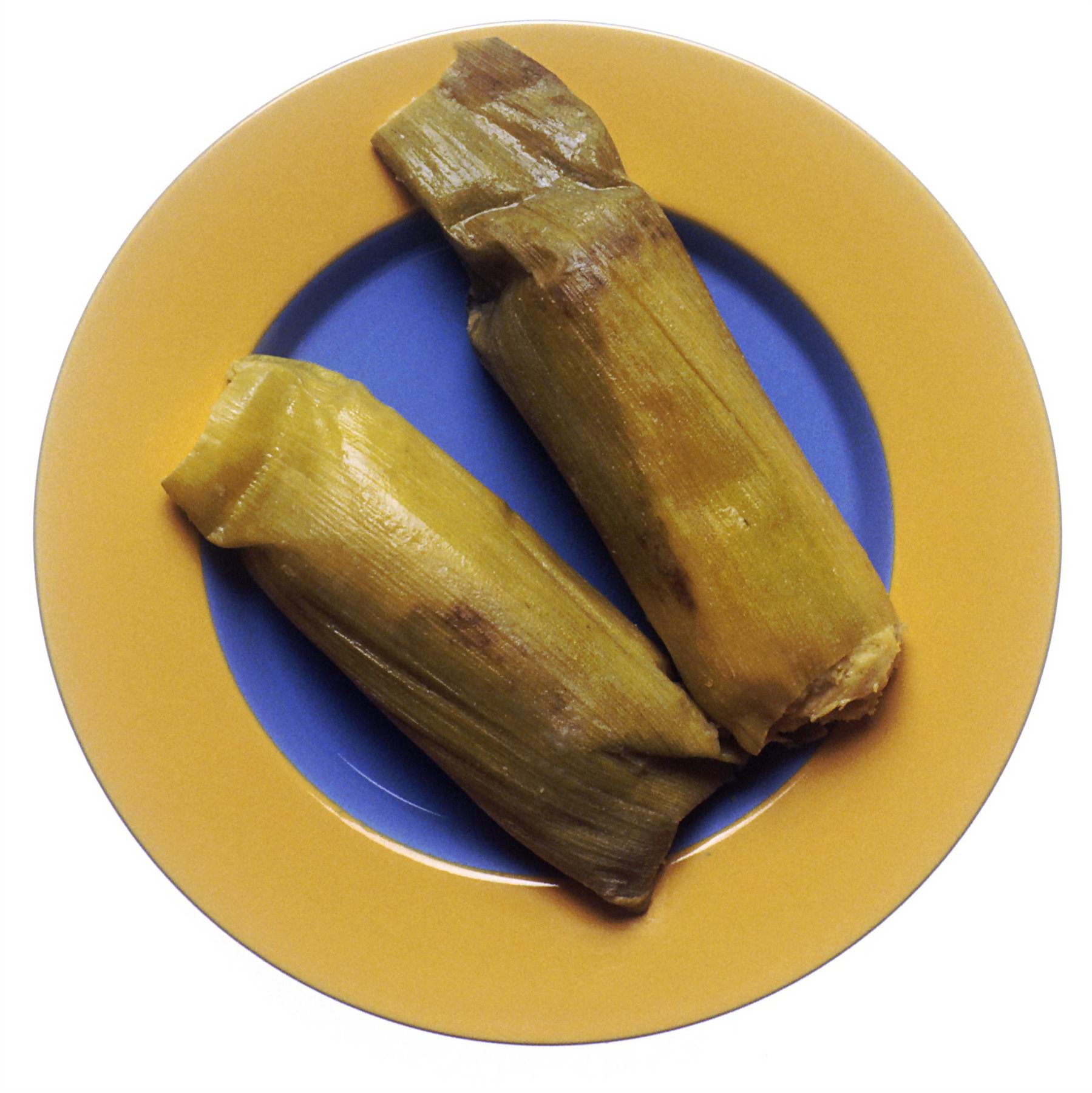
*Humita, ''Humitas'', similar to modern-day ''tamales'', a thick mixture of corn, herbs and onion, cooked in a corn-leaf wrapping. The name is modern, meaning bow-tie, because of the shape in which it's wrapped.
*''Locro'' (from the Quechua ''ruqru'') is a hearty thick stew popular along the Andes mountain range. It one of the national dishes of Argentina and Bolivia.
*''Mazamorra morada'', a thick, sweet pudding made from ground purple corn and fruit. Sold in mix form in Peru.
*''Mate de coca'', a Peruvian tea made from steeped coca leaves. It is commonly sipped by Indigenous people living at high altitudes in the Andes to prevent elevation illnesses.
*''Pachamanca'', stew cooked in a ''hautía'' oven.
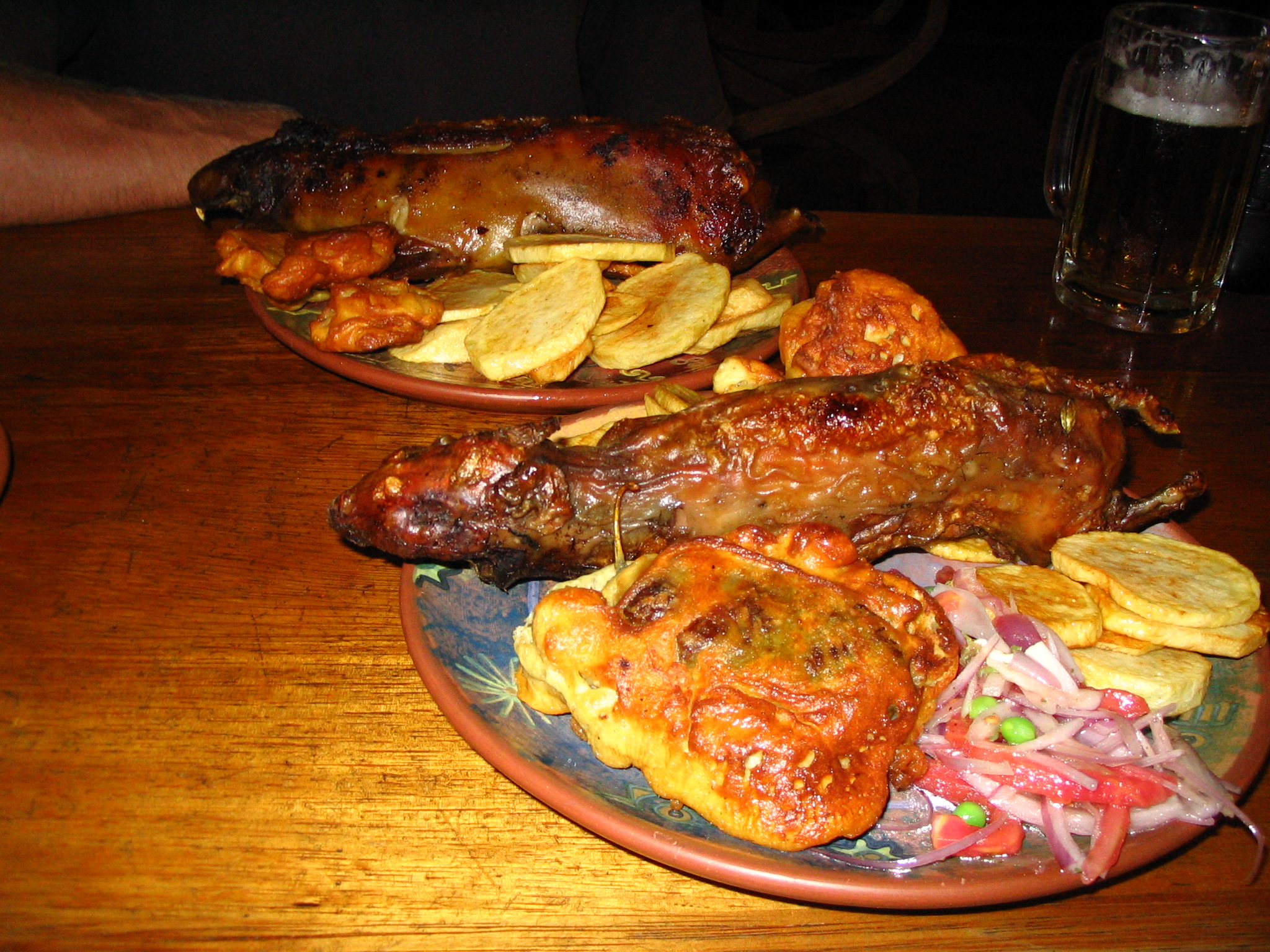
*Papa a la huancaína, ''Papa a la Huancaína'', Peruvian potatoes covered in a spicy, peanut-based sauce called ''Huancaína'' (Wan-ka-EE-na) sauce.
*''Patasca'', spicy stew made from boiled maize, potatoes, and dried meat.
*''Ceviche'', raw fish marinated in lime juice. One of Peru's national dishes.
*''Cancha'' or Tostada (tortilla), ''tostada'', fried golden hominy
Hominy (Spanish: maíz molido; literally meaning "milled corn") is a food produced from dried maize (corn) kernels that have been treated with an alkali, in a process called nixtamalization ( is the Nahuatl word for "hominy"). "Lye hominy" is a ...
.
*''Llajwa'', Salsa (sauce), salsa of Bolivia.
*Llapingacho, ''Llapingachos'', mashed-potato cakes from Ecuador.
*''Tocosh'' (''togosh''), a traditional Quechua food prepared from fermented potato pulp.
Other South American cultures
*Polenta, ''Angu'', an Indigenous Brazilian type of corn mush. *''Arepa'', a maize-based bread originating from the Indigenous peoples ofColombia
Colombia (, ; ), officially the Republic of Colombia, is a country in South America with insular regions in North America—near Nicaragua's Caribbean coast—as well as in the Pacific Ocean. The Colombian mainland is bordered by the ...
and Venezuela.
*''Vori vori'', a Paraguayan soup with cornmeal dumplings.
*''Cauim'', a fermented beverage based on maize or manioc broken down by the enzymes of human saliva, traditional to the Tupinambá people, Tupinambá and other iIdigenous peoples of Brazil.
*''Chipa'', a wide variety of corn flour or manioc-based breads traditional to Paraguay.
*''Curanto'', a Chilean cuisine, Chilean stew cooked in an earthen oven originally from the Chono people, Chono people of Chiloé Island.
*Mazamorra, ''Kaguyjy'', a Guarani-derived ''locro'' corn mush that become part of the national Paraguayan cuisine.
*''Kiveve'', a sweet or savory dish from Paraguay consisting of puréed pumpkin and other ingredients cooked over a fire.
*''Lampreado'' or ''payaguá mascada'', a starchy, manioc-based fried cake from Paraguay and the northeast of Argentina.
*''Lapacho'' or ''taheebo'', a medicinal tree-bark infusion.
*''Maniçoba'', dish of boiled manioc leaves and smoked meat indigenous to the Brazilian Amazon Basin, Amazon.
*Mate (beverage), ''Mate'' (beverage).
*''Mbeju'', a pan-cooked cake utilizing manioc starch.
*''Merken'', an ''ají'' powder from the Mapuche of Patagonia.
*''Mocotó'', a Brazilian cuisine, Brazilian stew with cow's feet, beans, and vegetables.
*''Moqueca'', a Brazilian seafood stew.
*''Paçoca'', from the Tupi "to crumble," describes two different dishes of pulverized ingredients: one with peanuts and sugar, and the other with dried meat, ground manioc, and onion.
*''Pamonha'', a Brazilian ''tamale
A tamale, in Spanish tamal, is a traditional Mesoamerican dish made of masa, a dough made from nixtamalized corn, which is steamed in a corn husk or banana leaf. The wrapping can either be discarded prior to eating or used as a plate. Tam ...
''.
*''Pira caldo'', Paraguayan fish soup.
*''Sopa paraguaya'', a corn-flour casserole esteemed as the national dish of Paraguay, related to ''chipa guasu.''
*''Soyo'', shortened from the Guarani name ''so’o josopy'', a Paraguayan soup based on meat crushed in a mortar.
*''Tacacá'', a Brazilian stew of ''tucupi'', paracress, ''jambu'' leaves, and shrimp, typically served in a dried gourd.
*''Tereré'' or ''ka'ay'', a cold-brewed version of ''yerba mate''.
*''Tucupi'', manioc-based broth used in Brazilian dishes such as ''pato no tucupi'' and ''tacacá''.
*''Yerba mate'', a tea made from the holly of the same name, derived from Guarani language, Guaraní.
Cooking utensils
 The earliest utensils, including bowls, knives, spoons, grinders, and griddles, were made from all kinds of materials, such as rock and animal bone. Gourds were also initially cultivated, hollowed, and dried to be used as bowls, spoons, ladles, and storage containers.
Many Indigenous cultures also developed elaborate ceramics for making bowls and cooking pots, and basketry for making containers. Nobility in the Andean and Mesoamerican civilizations were even known to have utensils and vessels smelted from gold, silver, copper, or other minerals.
*Batan (stone), ''Batan'', an Andean grinding slab used in conjunction with a small stone ''uña''
*''Burén'', a clay griddle used by the
The earliest utensils, including bowls, knives, spoons, grinders, and griddles, were made from all kinds of materials, such as rock and animal bone. Gourds were also initially cultivated, hollowed, and dried to be used as bowls, spoons, ladles, and storage containers.
Many Indigenous cultures also developed elaborate ceramics for making bowls and cooking pots, and basketry for making containers. Nobility in the Andean and Mesoamerican civilizations were even known to have utensils and vessels smelted from gold, silver, copper, or other minerals.
*Batan (stone), ''Batan'', an Andean grinding slab used in conjunction with a small stone ''uña''
*''Burén'', a clay griddle used by the Taíno
The Taíno were a historic Indigenous peoples of the Caribbean, indigenous people of the Caribbean whose culture has been continued today by Taíno descendant communities and Taíno revivalist communities. At the time of European contact in the ...
.
*Comal (cookware), ''Comal'', a griddle used since Pre-Columbian times in Mexico and Central America for a variety of purposes, especially to cook tortillas.
*''Cuia'', a gourd used for drinking mate in South America.
*''Metate'', a stone grinding slab used with a stone ''mano'' or ''metlapil'' to process meal in Mesoamerica and one of the most notable Pre-Columbian artifacts in Costa Rica.
*molinillo (whisk), ''Molinillo'', a device used by Mesoamerican royalty for frothing cacao drinks.
*''Molcajete'', a basalt stone bowl, used with a ''tejolote'' to grind ingredients as a Mesoamerican form of mortar and pestle.
*''Paila'', an Andean earthenware bowl.
*Cooking baskets were woven from a variety of local fibers and sometimes coated with clay to improve durability. The notable thing about basket cooking and some native clay pot cooking is that the heat source, i.e. hot stones or charcoal, is used inside the utensil rather than outside. (Also see Cookware and bakeware.)
Crops and ingredients





Non-animal foods
*Acorn
The acorn, or oaknut, is the nut of the oaks and their close relatives (genera '' Quercus'' and '' Lithocarpus'', in the family Fagaceae). It usually contains one seed (occasionally
two seeds), enclosed in a tough, leathery shell, and b ...
—used to make flour and fertilizers for plants
*Canna indica, ''Achira''—edible tubercule
*''Achiote''—annatto seed, a seasoning
*''Acuyo''—a seasoning
*''Agarita''—berries
*Agave nectar—a sweetener
*Allspice—a seasoning
*Amaranth
*American chestnut
*''Eugenia stipitata, Arazá''
*Nelumbo lutea, American lotus—seeds & root, leaves for baking coverings
*''Amole'' - can include Chlorogalum and Agave schottii
*Aspen—inner bark and sap (both used as sweetener)
*Avocado
*Barbados cherry or acerola
*Beans—throughout the Americas
*Bear grass
*Callicarpa, Beautyberry
*Beech, Beech nuts
*Birch bark
*Birch syrup—sweetener
*Bitterroot
*Blackberry, Blackberries
*Achyrachaena, Blow wife seeds
*Blueberry, Blueberries
*Maclura pomifera, Bodark seeds—also called Osage orange, hedge apple, monkeybrain
*Andromeda polifolia, Bog rosemary—poisonous, but leaves can be brewed into tea regardless
*Acer negundo, Box elder—inner bark (used as sweetener)
*Aesculus flava, Buckeye—(same rules apply as acorn)
*Butia odorata, Butia—palm fruits from South America
*Cucurbita foetidissima, Buffalo gourd—(wild ancestor of all squash/ pumpkin)
*Sicyos angulatus, Bur cucumber
*Cocoa mass, Cacao
*Cactus (various species)—fruits and young pads (see nopales)
*Eschscholzia californica, California poppy seeds—(There are eastern American poppies also, but they are believed to have always been so rare, inclusion in the human diet is highly unlikely)
*Camassia, Camas root
*Canellaceae, Canella winterana—white cinnamon (used as a seasoning before cinnamon)
*Cashew nuts
*Cassava—primarily South America
*Cattails—rootstocks
*Century plant (Agave parryi, mescal or agave)—crowns (tuberous base portion) and shoots
*Chia seed
*Chicle—chewing gum
*Chili peppers (including bell peppers)—seasoning
*Cherimoya
*Chokecherry, Chokecherries
*Cylindropuntia, Cholla fruits
*Coca—South and Central America
*Heracleum maximum, Cow parsnip root
*Cranberry, Cranberries
*Empetrum nigrum, Crowberry
*Culantro—used as a seasoning before cilantro
*Ribes, Currants
*Custard-apple
*Taraxacum, Dandelion
*Datil pepper, Datil—fruit and flowers
*Proboscidea (plant), Devil's claw
*Dewberry
*Dropseed grasses (various varieties)—seeds
*Plantago, Dwarf plantain
*Cercis canadensis, Eastern redbud—flowers as spice, fruit
*Aquilegia canadensis, Eastern red columbine—nectar only
*Elderberry, Elderberries
*Emory oak—acorns
*Epazote—a seasoning
*Feijoa—fruit from South America
* Ferns (various edible species, such as Fiddlehead fern, fiddleheads)
*Gaylussacia baccata, Gaylussacias or black huckleberry—grows near wild blueberries, tastes similar, but unrelated
*Goji or wolf berry
*Goldenberry
*Gooseberry, Gooseberries
*Physalis virginiana, Groundcherry—multiple species from North and South America
*Guarana
*Guava
*Myrcianthes pungens, ''Guaviyú''
*Celtis, Hackberries
*Crataegus, Hawthorn—fruit
*Hazelnut or filbert
*Aloysia citrodora, ''Hierba Luisa''
*Cymbopetalum penduliflorum, ''Hueinacaztli'', or ear-flower
*Hickory nuts
*Amphicarpaea bracteata, Hogpeanut
*Holly
*Hops
*Monarda, Horsemint
*Chenopodium berlandieri, ''Huazontle''
*Huckleberry, Huckleberries
*Medeola, Indian cucumber
*Apios americana, Indian potato or ''hopniss'', ''openowag'', cinnamon vine, groundnut (cultivated in Japan as ''hodoimo'', edible root bulbs and beans, dried flowers as spice)
*Amorpha, Indigo bush—sources disagree whether edible, but presumably fruit?
*Arisaema triphyllum, Jack in the pulpit root
*Paracress, ''Jambú''
*Jerusalem artichoke
*Jicama
*Juniper berry, Juniper berries
*Kaniwa
*Kentucky coffeetree
*Amaranthus caudatus, Kiwicha
*Chenopodium, Lamb's-quarters—leaves and seeds
*Lapacho
*Brachygastra lecheguana, ''Lechehuana'' honey
*Lemon-verbena—lemon-flavoring herb
*Lichen (certain species)
*Nymphaeaceae, Lilypad root
*Honey locust, Locust—blossoms and pods
*''Lúcuma''
*''Maca''
*Maize—throughout the Americas, probably domesticated in or near Mexico, including the blue corn variety
*Pouteria sapota, ''Mamey''
*Manzanita
*Maple syrup
Maple syrup is a syrup made from the sap of maple trees. In cold climates, these trees store starch in their trunks and roots before winter; the starch is then converted to sugar that rises in the sap in late winter and early spring. Maple tr ...
and sugar, used as the primary sweetener and seasoning in Northern America
*Mesquite—bean pods, flour/meal
*Mexican oregano
*Asclepias, Milkweed
* Mint, various species—Mentha arvensis, American mint is best known in eastern woodlands region
*Highbush cranberry, Mooseberry—called highbush cranberry in Eastern US—actually a type of ''Viburnum''
*Mulberry, Mulberries
*Nopales—cactus
*Okra
*Onions
*Mahonia aquifolium, Oregon grape—(not a real grape)
*Sabal palmetto, Palmetto
*Surinam cherry
*Papaya
*Passionfruit
*Carica papaya, Pawpaw
*Peanuts (thought to be native to West Africa)
*Pecans
*Hedeoma pulegioides, Pennyroyal—American false variety
*Persimmon
*Amaranthus palmeri, Pigweed —seeds
*Pine (including western white pine and ''Pinus ponderosa'')—inner bark (used as sweetener), sap as chewing gum ingredient, tips for jelly, cuttings for tea, and Pine nut, pinenuts
*Pineapples—South America
*Pinyon pine, Pinyon—nuts
*Piñonero—nuts
*Chimaphila umbellata, ''Pipsissewa''
*Prunus hortulana, Plum
*Popcorn flower—herb
*Potatoes—North and South America
*opuntia, Prickly pears
*Prairie turnips
*Pumpkins
*Portulaca oleracea, Purslane—leaves
*Quinoa—South America, Central America, and Eastern North America
*Allium tricoccum, Ramps—wild onion
*Raspberry, Raspberries
*Rice—imported by the Spanish
*Boechera laevigata, rock cress
*Rose pepper
*Leucophyllum, Sage
*Saguaro cactus—fruits and seeds
*Salt
*''Croton lechleri, Sangre de drago''
*''Sapote''
*Sassafras
*Prosopis pubescens, Screwbean—fruit
*Cyperaceae, Sedge—tubers
*Coccoloba uvifera, Sea grape or ''uva de playa''
*Amelanchier, Serviceberry—also juneberry, saskatoon
*Shepherd's purse—leaves
*Polygonatum biflorum, Solomon's seal
*Sotol—crowns
*Soursop or ''guanábana''
*Yucca schidigera, Spanish bayonet—fruit
*Spanish lime or ''mamoncillo''
*Common spicebush—a seasoning
*Aralia nudicaulis, Spikenard—berries and roots for tea, some tribes ate roots (this is a select species, of which there are many in the America's and not all species are edible, though Natives had wide medicinal and practical uses)
*Squash
Squash may refer to:
Sports
* Squash (sport), the high-speed racquet sport also known as squash racquets
* Squash (professional wrestling), an extremely one-sided match in professional wrestling
* Squash tennis, a game similar to squash but pla ...
—throughout the Americas
*Stevia—sweetener
*Strawberry, Strawberries
*Sumac—berries
*Sunflower seeds
*Osmorhiza longistylis, Sweet anise
*Sweet potato—South America (misleading name: not a potato)
*Sweetsop or sugar-apple
*Tamarillo
*Eastern teaberry, Teaberry or wintergreen
*Tobacco
*Tomatillo
*Tomato
*Diospyros texana, Texas persimmons or sugar plum
*Peltandra virginica, Tuckahoe
*Tulip poplar—syrup made from bark
*Tule—rhizomes
*Tumbleweed—seeds
*Banana passionfruit, ''Tumbo'' or ''taxo''
*Vanilla—a seasoning
*Vetch—pods
*Sagittaria latifolia, Wapato root
*White evening primrose—fruit
*Juglans cinerea, White walnuts or butternuts
* Wild Erigenia, carrot—also harbinger of spring, salt and pepper
*Wild celery
*Wild cherries
A cherry is the fruit of many plants of the genus '' Prunus'', and is a fleshy drupe (stone fruit).
Commercial cherries are obtained from cultivars of several species, such as the sweet ''Prunus avium'' and the sour ''Prunus cerasus''. The ...
*Vitis, Wild grapes—fruit
*Honey, Wild honey
*Allium, Wild onion
*Wild pea—pods
*Rosa acicularis, Wild roses
*Ipomoea pandurata, Wild sweet potato—(misleading name: not a potato)
*Wood sorrel—leaves
*''Yacón''—nectar
*Yaupon holly—leaves
*''Yerba buena''
*''Yerba mate''
*Yucca—blossoms, fruit, and stalks
*''Zamia''—nuts
Hunted or livestock

 *Pronghorn, Antelope
*Armadillo
*Badger
*Bear
*Beaver
*Bighorn sheep
*American bison, Bison—originally found throughout most of the North American plains
*Burro—European import
*Camel—extinct in the Americas
*Capybara
*Cattle—European import
*Chipmunk
*Deer
*Dove
*Duck
*Elk
*Ants
*Geese
*Ground hog
*Grouse
*''Guanaco''—hunted in South America by hunter-gatherer societies, for ex. in Patagonia until the 19th century
*Guinea pig—domesticated in the Andes
*Hog (swine), Hog—important European import
*Mexican honey wasp, Honey wasp—''Brachygastra mellifica'', ''Brachygastra lecheguana'', and ''Polybia occidentalis'', a source of honey found from the Southwestern United States to Argentina
*Horse—although imported by Europeans, the horse was still very important to Indigenous cultures throughout the Americas (famously on the North American Plains) in the historic era
*''Hutia''
*Iguana
*
*Pronghorn, Antelope
*Armadillo
*Badger
*Bear
*Beaver
*Bighorn sheep
*American bison, Bison—originally found throughout most of the North American plains
*Burro—European import
*Camel—extinct in the Americas
*Capybara
*Cattle—European import
*Chipmunk
*Deer
*Dove
*Duck
*Elk
*Ants
*Geese
*Ground hog
*Grouse
*''Guanaco''—hunted in South America by hunter-gatherer societies, for ex. in Patagonia until the 19th century
*Guinea pig—domesticated in the Andes
*Hog (swine), Hog—important European import
*Mexican honey wasp, Honey wasp—''Brachygastra mellifica'', ''Brachygastra lecheguana'', and ''Polybia occidentalis'', a source of honey found from the Southwestern United States to Argentina
*Horse—although imported by Europeans, the horse was still very important to Indigenous cultures throughout the Americas (famously on the North American Plains) in the historic era
*''Hutia''
*Iguana
*Livestock
Livestock are the domesticated animals raised in an agricultural setting to provide labor and produce diversified products for consumption such as meat, eggs, milk, fur, leather, and wool. The term is sometimes used to refer solely to ani ...
*Llama—domesticated in the Andes
*Locust (cicada)
*Manatee
*Mastodon—extinct
*Moose
*Mourning dove
*Mule—European import
*Muscovy duck—domesticated in Mesoamerica
*Opossum
*Otter
*Passenger pigeon—extinct
*Peccary, Peccaries
*Pheasant
*Porcupine
*Prairie dog
*Pronghorn (antelope)
*New World quail, Quail
*Rabbit
Rabbits, also known as bunnies or bunny rabbits, are small mammals in the family Leporidae (which also contains the hares) of the order Lagomorpha (which also contains the pikas). ''Oryctolagus cuniculus'' includes the European rabbit sp ...
*Raccoon
*Sheep—important European import
*Skunk
*Sloth
*Stingless bee—''Melipona beecheii'' and ''M. yucatanica'', Mayan source of honey
*Squirrel
*Turkey (bird), Turkey
*Turtle
*Yacare caiman
*Wood rat
*Woolly mammoth—extinct
Notable chefs and food writers
* Lois Ellen Frank * Sean ShermanSee also
* * House dish * Hunter gatherer * Locavores * Tlingit cuisine * Wild onion festival * Inuit diet * List of First Nations peoples * Aboriginal food security in Canada * Peasant food * Staple food * Soul food * Bush meat (Africa) * Bushfood (Australia) * Game (food)References
Bibliography
* * *External links
Traditional Chiricahua recipes
American Indian Health and Diet Project
{{DEFAULTSORT:Indigenous Cuisine of the Americas Indigenous cuisine of the Americas, Indigenous culture of the Americas, Cuisine Native American culture, Cuisine Native American cuisine, Latin American cuisine North American cuisine First Nations culture