Nasal polyp on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Nasal polyps (NP) are noncancerous growths within the

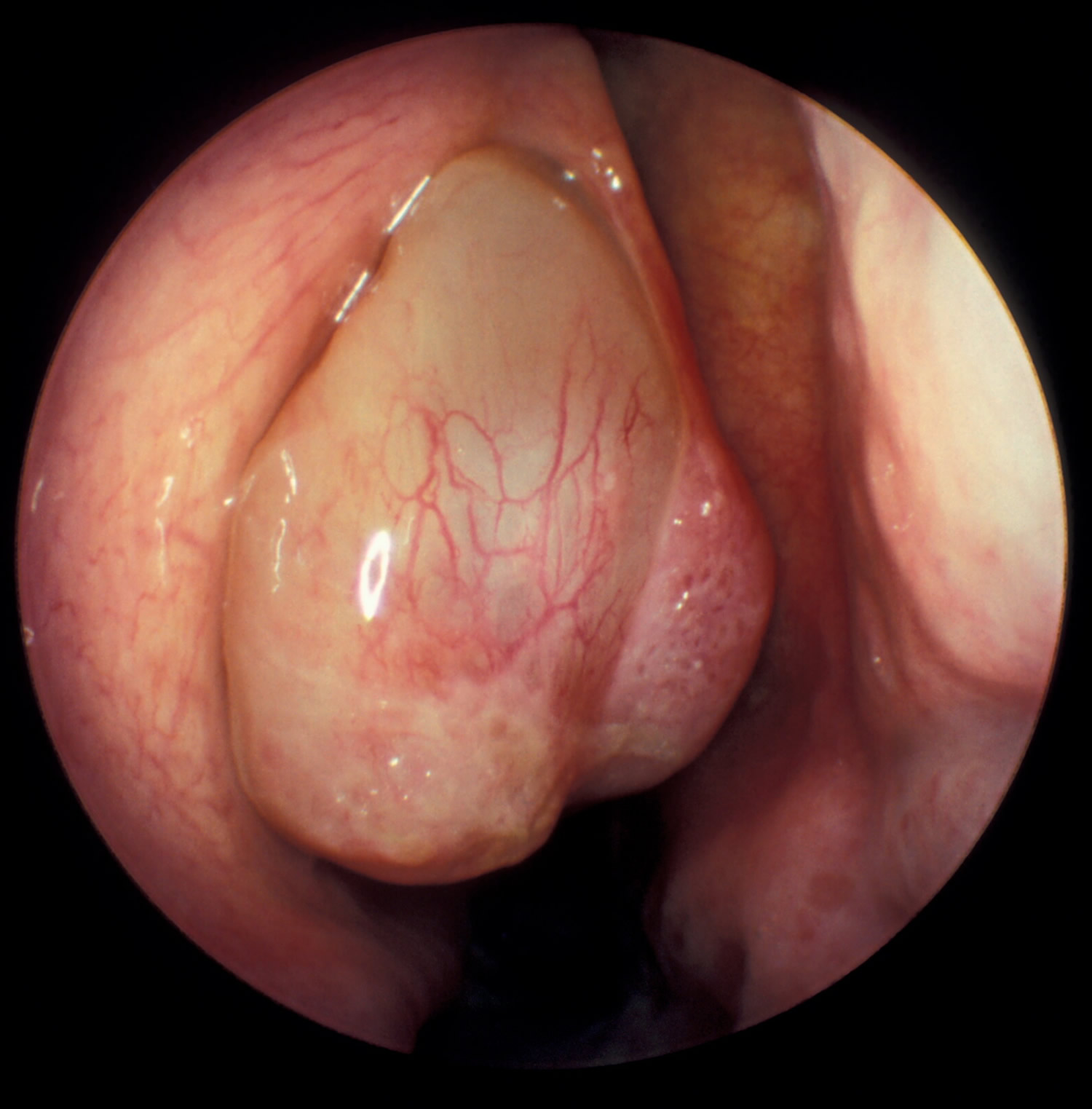 Nasal polyps can be seen on physical examination inside of the nose and are often detected during the evaluation of symptoms. On examination, a polyp will appear as a visible mass in the nostril. Some polyps may be seen with anterior rhinoscopy (looking in the nose with a nasal speculum and a light), but frequently, they are farther back in the nose and must be seen by nasal
Nasal polyps can be seen on physical examination inside of the nose and are often detected during the evaluation of symptoms. On examination, a polyp will appear as a visible mass in the nostril. Some polyps may be seen with anterior rhinoscopy (looking in the nose with a nasal speculum and a light), but frequently, they are farther back in the nose and must be seen by nasal
File:Histopathology of sinonasal inflammatory polyp with mixed inflammation, annotated.jpg, Benign mixed inflammation of an inflammatory nasal polyp.
File:Histopathology of extranodal NK-T cell lymphoma, nasal type.png, Extranodal NK/T cell lymphoma, nasal type for comparison. These lymphoma cells are typically monotonous, with folded nuclei, indistinct nucleoli and moderate amount of cytoplasm.
 ]
Functional endoscopic sinus surgery, Endoscopic sinus surgery, advocated and popularized by Professor Stammberger, is often very effective for most people, providing rapid symptom relief. Endoscopic sinus surgery is minimally-invasive and is done entirely through the nostril with the help of a camera. Surgery should be considered for those with complete nasal obstruction, uncontrolled runny nose, nasal deformity caused by polyps or continued symptoms despite medical management. Surgery serves to remove the polyps as well as the surrounding inflamed mucosa, open obstructed nasal passages, and clear the sinuses. This not only removes the obstruction caused by the polyps themselves, but allows medications such as saline irrigations and topical steroids to become more effective. It has been suggested that one of the main objectives in sinus surgery for polyps is to allow delivery of the steroids into those areas of the sinuses where polyps develop, namely, the ethmoid sinuses. Specially designed long nozzles had been developed to use postoperatively to deliver steroids into those areas after sinus surgery for polyps.
Surgery lasts approximately 45 minutes to 1 hour and can be done under general or local anesthesia. Most people tolerate the surgery without much pain, though this can vary from person to person. The person should expect some discomfort, congestion, and drainage from the nose in the first few days after surgery, but this should be mild. Complications from endoscopic sinus surgery are rare, but can include bleeding and damage to other structures in the area including the eye or brain.
Many physicians recommend a course of oral steroids prior to surgery to reduce mucosal inflammation, decrease bleeding during surgery, and help with visualization of the polyps. Nasal steroid sprays should be used preventatively after surgery to delay or prevent recurrence. People often have recurrence of polyps even following surgery. Therefore, continued follow up with a combination of medical and surgical management is preferred for the treatment of nasal polyps.
]
Functional endoscopic sinus surgery, Endoscopic sinus surgery, advocated and popularized by Professor Stammberger, is often very effective for most people, providing rapid symptom relief. Endoscopic sinus surgery is minimally-invasive and is done entirely through the nostril with the help of a camera. Surgery should be considered for those with complete nasal obstruction, uncontrolled runny nose, nasal deformity caused by polyps or continued symptoms despite medical management. Surgery serves to remove the polyps as well as the surrounding inflamed mucosa, open obstructed nasal passages, and clear the sinuses. This not only removes the obstruction caused by the polyps themselves, but allows medications such as saline irrigations and topical steroids to become more effective. It has been suggested that one of the main objectives in sinus surgery for polyps is to allow delivery of the steroids into those areas of the sinuses where polyps develop, namely, the ethmoid sinuses. Specially designed long nozzles had been developed to use postoperatively to deliver steroids into those areas after sinus surgery for polyps.
Surgery lasts approximately 45 minutes to 1 hour and can be done under general or local anesthesia. Most people tolerate the surgery without much pain, though this can vary from person to person. The person should expect some discomfort, congestion, and drainage from the nose in the first few days after surgery, but this should be mild. Complications from endoscopic sinus surgery are rare, but can include bleeding and damage to other structures in the area including the eye or brain.
Many physicians recommend a course of oral steroids prior to surgery to reduce mucosal inflammation, decrease bleeding during surgery, and help with visualization of the polyps. Nasal steroid sprays should be used preventatively after surgery to delay or prevent recurrence. People often have recurrence of polyps even following surgery. Therefore, continued follow up with a combination of medical and surgical management is preferred for the treatment of nasal polyps.

nose
A nose is a protuberance in vertebrates that houses the nostrils, or nares, which receive and expel air for respiration alongside the mouth. Behind the nose are the olfactory mucosa and the sinuses. Behind the nasal cavity, air next passe ...
or sinuses
Paranasal sinuses are a group of four paired air-filled spaces that surround the nasal cavity. The maxillary sinuses are located under the eyes; the frontal sinuses are above the eyes; the ethmoidal sinuses are between the eyes and the spheno ...
. Symptoms include trouble breathing through the nose, loss of smell
Anosmia, also known as smell blindness, is the loss of the ability to detect one or more smells. Anosmia may be temporary or permanent. It differs from hyposmia, which is a decreased sensitivity to some or all smells.
Anosmia can be due to a num ...
, decreased taste, post nasal drip
Post-nasal drip (PND), also known as upper airway cough syndrome (UACS), occurs when excessive mucus is produced by the nasal mucosa. The excess mucus accumulates in the back of the nose, and eventually in the throat once it drips down the back ...
, and a runny nose
Rhinorrhea, rhinorrhoea, or informally runny nose is the free discharge of a thin mucus fluid from the nose; it is a common condition. It is a common symptom of allergies ( hay fever) or certain viral infections, such as the common cold or COV ...
. The growths are sac-like, movable, and nontender, though face pain may occasionally occur. They typically occur in both nostrils in those who are affected. Complications may include sinusitis
Sinusitis, also known as rhinosinusitis, is inflammation of the mucous membranes that line the sinuses resulting in symptoms that may include thick nasal mucus, a plugged nose, and facial pain. Other signs and symptoms may include fever, head ...
and broadening of the nose.
The exact cause is unclear. They may be related to chronic inflammation
Inflammation (from la, inflammatio) is part of the complex biological response of body tissues to harmful stimuli, such as pathogens, damaged cells, or irritants, and is a protective response involving immune cells, blood vessels, and molec ...
of the lining of the sinuses. They occur more commonly among people who have allergies
Allergies, also known as allergic diseases, refer a number of conditions caused by the hypersensitivity of the immune system to typically harmless substances in the environment. These diseases include hay fever, food allergies, atopic dermat ...
, cystic fibrosis
Cystic fibrosis (CF) is a rare genetic disorder that affects mostly the lungs, but also the pancreas, liver, kidneys, and intestine. Long-term issues include difficulty breathing and coughing up mucus as a result of frequent lung infections. Ot ...
, aspirin sensitivity
Salicylate sensitivity is any adverse effect that occurs when a usual amount of salicylate is ingested. People with salicylate intolerance are unable to consume a normal amount of salicylate without adverse effects.
Salicylate sensitivity diffe ...
, or certain infections. The polyp itself represents an overgrowth of the mucous membranes. Diagnosis may be accomplished by looking up the nose. A CT scan may be used to determine the number of polyps and help plan surgery.
Treatment is typically with steroids
A steroid is a biologically active organic compound with four rings arranged in a specific molecular configuration. Steroids have two principal biological functions: as important components of cell membranes that alter membrane fluidity; and ...
, often in the form of a nasal spray
Nasal sprays are used to deliver medications locally in the nasal cavities or systemically. They are used locally for conditions such as nasal congestion and allergic rhinitis. In some situations, the nasal delivery route is preferred for syst ...
. If this is not effective, surgery
Surgery ''cheirourgikē'' (composed of χείρ, "hand", and ἔργον, "work"), via la, chirurgiae, meaning "hand work". is a medical specialty that uses operative manual and instrumental techniques on a person to investigate or treat a pa ...
may be considered. The condition often recurs following surgery; thus, continued use of a steroid nasal spray is often recommended. Antihistamine
Antihistamines are drugs which treat allergic rhinitis, common cold, influenza, and other allergies. Typically, people take antihistamines as an inexpensive, generic (not patented) drug that can be bought without a prescription and provide ...
s may help with symptoms but do not change the underlying disease. Antibiotics
An antibiotic is a type of antimicrobial substance active against bacteria. It is the most important type of antibacterial agent for fighting bacterial infections, and antibiotic medications are widely used in the treatment and preventio ...
are not required for treatment unless an infection occurs.
About 4% of people currently have nasal polyps while up to 40% of people develop them at some point in their life. They most often occur after the age of 20 and are more frequent in males than females. Nasal polyps have been described since the time of the Ancient Egyptians.
Signs and symptoms
Symptoms of polyps includenasal congestion
Nasal congestion is the blockage of nasal breathing usually due to membranes lining the nose becoming swollen from inflamed blood vessels.
Background
In about 85% of cases, nasal congestion leads to mouth breathing rather than nasal breathin ...
, sinusitis
Sinusitis, also known as rhinosinusitis, is inflammation of the mucous membranes that line the sinuses resulting in symptoms that may include thick nasal mucus, a plugged nose, and facial pain. Other signs and symptoms may include fever, head ...
, loss of smell
Anosmia, also known as smell blindness, is the loss of the ability to detect one or more smells. Anosmia may be temporary or permanent. It differs from hyposmia, which is a decreased sensitivity to some or all smells.
Anosmia can be due to a num ...
, thick nasal discharge, facial pressure, nasal speech, and mouth breathing. Recurrent sinusitis
Sinusitis, also known as rhinosinusitis, is inflammation of the mucous membranes that line the sinuses resulting in symptoms that may include thick nasal mucus, a plugged nose, and facial pain. Other signs and symptoms may include fever, head ...
can result from polyps. Long-term, nasal polyps can cause destruction of the nasal bones and widening of the nose.
As polyps grow larger, they eventually prolapse into the nasal cavity
The nasal cavity is a large, air-filled space above and behind the nose in the middle of the face. The nasal septum divides the cavity into two cavities, also known as fossae. Each cavity is the continuation of one of the two nostrils. The nasal ...
, resulting in symptoms. The most prominent symptoms of nasal polyps is blockage of the nasal passage. People with nasal polyps due to aspirin intolerance often have symptoms known as Samter's triad, which consists of asthma worse with aspirin, a skin rash caused by aspirin, and chronic nasal polyps.
Causes
The exact cause of nasal polyps is unclear. They are, however, commonly associated with conditions that cause long terminflammation
Inflammation (from la, inflammatio) is part of the complex biological response of body tissues to harmful stimuli, such as pathogens, damaged cells, or irritants, and is a protective response involving immune cells, blood vessels, and molec ...
of the sinuses. This includes chronic rhinosinusitis, asthma
Asthma is a long-term inflammatory disease of the airways of the lungs. It is characterized by variable and recurring symptoms, reversible airflow obstruction, and easily triggered bronchospasms. Symptoms include episodes of wheezing, co ...
, aspirin
Aspirin, also known as acetylsalicylic acid (ASA), is a nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug (NSAID) used to reduce pain, fever, and/or inflammation, and as an antithrombotic. Specific inflammatory conditions which aspirin is used to treat inc ...
sensitivity, and cystic fibrosis
Cystic fibrosis (CF) is a rare genetic disorder that affects mostly the lungs, but also the pancreas, liver, kidneys, and intestine. Long-term issues include difficulty breathing and coughing up mucus as a result of frequent lung infections. Ot ...
.
Various additional diseases associated with polyp formation include:
Chronic rhinosinusitis is a common medical condition characterized by symptoms of sinus inflammation lasting at least 12 weeks. The cause is unknown and the role of microorganisms remains unclear. It can be classified as either with or without nasal polyposis.
Cystic fibrosis
Cystic fibrosis (CF) is a rare genetic disorder that affects mostly the lungs, but also the pancreas, liver, kidneys, and intestine. Long-term issues include difficulty breathing and coughing up mucus as a result of frequent lung infections. Ot ...
(CF) is the most common cause of nasal polyps in children. Therefore, any child under 12 to 20 years old with nasal polyps should be tested for CF. Half of people with CF will experience extensive polyps leading to nasal obstruction and requiring aggressive management.
Pathophysiology
The true cause of nasal polyps is unknown, but they are thought to be due to recurrent infection or inflammation. Polyps arise from the lining of the sinuses. Nasal mucosa, particularly in the region ofmiddle meatus
In anatomy, the term nasal meatus can refer to any of the three meatuses (passages) through the skulls nasal cavity: the superior meatus (''meatus nasi superior''), middle meatus (''meatus nasi medius''), and inferior meatus (''meatus nasi inferi ...
becomes swollen due to collection of extracellular fluid. This extracellular fluid collection causes polyp formation and protrusion into the nasal cavity or sinuses. Polyps which are sessile in the beginning become pedunculated due to gravity.
In people with nasal polyps due to aspirin
Aspirin, also known as acetylsalicylic acid (ASA), is a nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug (NSAID) used to reduce pain, fever, and/or inflammation, and as an antithrombotic. Specific inflammatory conditions which aspirin is used to treat inc ...
or NSAID
Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAID) are members of a therapeutic drug class which reduces pain, decreases inflammation, decreases fever, and prevents blood clots. Side effects depend on the specific drug, its dose and duration of ...
sensitivity, the underlying mechanism is due to disorders in the metabolism of arachidonic acid
Arachidonic acid (AA, sometimes ARA) is a polyunsaturated omega-6 fatty acid 20:4(ω-6), or 20:4(5,8,11,14). It is structurally related to the saturated arachidic acid found in cupuaçu butter. Its name derives from the New Latin word ''ara ...
. Exposure to cycloxygenase inhibitors
Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAID) are members of a therapeutic drug class which reduces pain, decreases inflammation, decreases fever, and prevents blood clots. Side effects depend on the specific drug, its dose and duration of ...
such as aspirin and NSAIDs leads to shunting of products through the lipoxygenase pathway leading to an increased production of products that cause inflammation. In the airway, these inflammatory products lead to symptoms of asthma such as wheezing as well as nasal polyp formation.
Diagnosis
 Nasal polyps can be seen on physical examination inside of the nose and are often detected during the evaluation of symptoms. On examination, a polyp will appear as a visible mass in the nostril. Some polyps may be seen with anterior rhinoscopy (looking in the nose with a nasal speculum and a light), but frequently, they are farther back in the nose and must be seen by nasal
Nasal polyps can be seen on physical examination inside of the nose and are often detected during the evaluation of symptoms. On examination, a polyp will appear as a visible mass in the nostril. Some polyps may be seen with anterior rhinoscopy (looking in the nose with a nasal speculum and a light), but frequently, they are farther back in the nose and must be seen by nasal endoscopy
An endoscopy is a procedure used in medicine to look inside the body. The endoscopy procedure uses an endoscope to examine the interior of a hollow organ or cavity of the body. Unlike many other medical imaging techniques, endoscopes are inse ...
. Nasal endoscopy involves passing a small, rigid camera with a light source into the nose. An image is projected onto a screen in the office so the doctor can examine the nasal passages and sinuses in greater detail. The procedure is not generally painful, but the person can be given a spray decongestant and local anesthetic to minimize discomfort.
Attempts have been made to develop scoring systems to determine the severity of nasal polyps. Proposed staging systems take into account the extent of polyps seen on endoscopic exam and the number of sinuses affected on CT imaging. This staging system is only partially validated, but in the future, may be useful for communicating the severity of disease, assessing treatment response, and planning treatment.
Types
There are two primary types of nasal polyps: ethmoidal and antrochoanal. Ethmoidal polyps arise from theethmoid sinuses
The ethmoid sinuses or ethmoid air cells of the ethmoid bone are one of the four paired paranasal sinuses. The cells are variable in both size and number in the lateral mass of each of the ethmoid bones and cannot be palpated during an extraoral ...
and extend through the middle meatus
In anatomy, the term nasal meatus can refer to any of the three meatuses (passages) through the skulls nasal cavity: the superior meatus (''meatus nasi superior''), middle meatus (''meatus nasi medius''), and inferior meatus (''meatus nasi inferi ...
into the nasal cavity. Antrochoanal polyps usually arise in the maxillary sinus
The pyramid-shaped maxillary sinus (or antrum of Highmore) is the largest of the paranasal sinuses, and drains into the middle meatus of the nose through the osteomeatal complex.Human Anatomy, Jacobs, Elsevier, 2008, page 209-210
Structure
It i ...
and extend into the nasopharynx and represent only 4–6% of all nasal polyps.
However, antrochoanal polyps are more common in children comprising one-third of all polyps in this population. Ethmoidal polyps are usually smaller and multiple while antrochoanal polyps are usually single and larger.
CT scan
CT scan can show the full extent of the polyp, which may not be fully appreciated with physical examination alone. Imaging is also required for planning surgical treatment. On a CT scan, a nasal polyp generally has an attenuation of 10–18 Hounsfield units, which is similar to that ofmucus
Mucus ( ) is a slippery aqueous secretion produced by, and covering, mucous membranes. It is typically produced from cells found in mucous glands, although it may also originate from mixed glands, which contain both serous and mucous cells. It ...
. Nasal polyps may have calcification
Calcification is the accumulation of calcium salts in a body tissue. It normally occurs in the formation of bone, but calcium can be deposited abnormally in soft tissue,Miller, J. D. Cardiovascular calcification: Orbicular origins. ''Nature M ...
.
Histology
On histologic examination, nasal polyps consist of hyperplastic edematous (excess fluid)connective tissue
Connective tissue is one of the four primary types of animal tissue, along with epithelial tissue, muscle tissue, and nervous tissue. It develops from the mesenchyme derived from the mesoderm the middle embryonic germ layer. Connective tiss ...
with some seromucous glands and cells representing inflammation (mostly neutrophil
Neutrophils (also known as neutrocytes or heterophils) are the most abundant type of granulocytes and make up 40% to 70% of all white blood cells in humans. They form an essential part of the innate immune system, with their functions varying ...
s and eosinophil
Eosinophils, sometimes called eosinophiles or, less commonly, acidophils, are a variety of white blood cells (WBCs) and one of the immune system components responsible for combating multicellular parasites and certain infections in vertebrates. A ...
s). Polyps have virtually no neurons. Therefore, the tissue that makes up the polyp does not have any tissue sensation and the polyp itself will not be painful. In early stages, the surface of the nasal polyp is covered by normal respiratory epithelium, but later it undergoes metaplastic change to squamous type epithelium with the constant irritation and inflammation. The submucosa shows large intercellular spaces filled with serous fluid.
Differential diagnosis
Other disorders can mimic the appearance of nasal polyps and should be considered if a mass is seen on exam. Examples include encephalocele,glioma
A glioma is a type of tumor that starts in the glial cells of the brain or the spine. Gliomas comprise about 30 percent of all brain tumors and central nervous system tumours, and 80 percent of all malignant brain tumours.
Signs and symptoms
...
, inverted papilloma
An inverted papilloma, also known as Ringertz tumour, is a type of tumor in which surface epithelial cells grow downward into the underlying supportive tissue. It may occur in the nose and/or sinuses or in the urinary tract (bladder, renal pel ...
, and cancer. Early biopsy is recommended for unilateral nasal polyps to rule out more serious conditions such as cancer, inverted papilloma
An inverted papilloma, also known as Ringertz tumour, is a type of tumor in which surface epithelial cells grow downward into the underlying supportive tissue. It may occur in the nose and/or sinuses or in the urinary tract (bladder, renal pel ...
, or fungal sinusitis
Fungal sinusitis is the inflammation of the lining mucosa of the paranasal sinuses due to fungal infection. It occurs in people with reduced immunity. The maxillary sinus is the most commonly involved. Fungi responsible for fungal sinusitis ar ...
.
Treatment
The first line of treatment for nasal polyps is topicalsteroid
A steroid is a biologically active organic compound with four rings arranged in a specific molecular configuration. Steroids have two principal biological functions: as important components of cell membranes that alter membrane fluidity; and ...
s. Steroids decrease the inflammation of the sinus mucosa to decrease the size of the polyps and improve symptoms. Topical preparations are preferred in the form of a nasal spray but are often ineffective for people with many polyps. Steroids by mouth often provide drastic symptom relief, but should not be taken for long periods of time due to their side effects. Because steroids only shrink the size and swelling of the polyp, people often have recurrence of symptoms once the steroids are stopped. Decongestants do not shrink the polyps, but can decrease swelling and provide some relief. Antibiotics are only recommended if the person has a co-occurring bacterial infection
Pathogenic bacteria are bacteria that can cause disease. This article focuses on the bacteria that are pathogenic to humans. Most species of bacteria are harmless and are often beneficial but others can cause infectious diseases. The number ...
.
In people with nasal polyps caused by aspirin or NSAIDs, avoidance of these medications will help with symptoms. Aspirin desensitization has also been shown to be beneficial.
Surgery
 ]
Functional endoscopic sinus surgery, Endoscopic sinus surgery, advocated and popularized by Professor Stammberger, is often very effective for most people, providing rapid symptom relief. Endoscopic sinus surgery is minimally-invasive and is done entirely through the nostril with the help of a camera. Surgery should be considered for those with complete nasal obstruction, uncontrolled runny nose, nasal deformity caused by polyps or continued symptoms despite medical management. Surgery serves to remove the polyps as well as the surrounding inflamed mucosa, open obstructed nasal passages, and clear the sinuses. This not only removes the obstruction caused by the polyps themselves, but allows medications such as saline irrigations and topical steroids to become more effective. It has been suggested that one of the main objectives in sinus surgery for polyps is to allow delivery of the steroids into those areas of the sinuses where polyps develop, namely, the ethmoid sinuses. Specially designed long nozzles had been developed to use postoperatively to deliver steroids into those areas after sinus surgery for polyps.
Surgery lasts approximately 45 minutes to 1 hour and can be done under general or local anesthesia. Most people tolerate the surgery without much pain, though this can vary from person to person. The person should expect some discomfort, congestion, and drainage from the nose in the first few days after surgery, but this should be mild. Complications from endoscopic sinus surgery are rare, but can include bleeding and damage to other structures in the area including the eye or brain.
Many physicians recommend a course of oral steroids prior to surgery to reduce mucosal inflammation, decrease bleeding during surgery, and help with visualization of the polyps. Nasal steroid sprays should be used preventatively after surgery to delay or prevent recurrence. People often have recurrence of polyps even following surgery. Therefore, continued follow up with a combination of medical and surgical management is preferred for the treatment of nasal polyps.
]
Functional endoscopic sinus surgery, Endoscopic sinus surgery, advocated and popularized by Professor Stammberger, is often very effective for most people, providing rapid symptom relief. Endoscopic sinus surgery is minimally-invasive and is done entirely through the nostril with the help of a camera. Surgery should be considered for those with complete nasal obstruction, uncontrolled runny nose, nasal deformity caused by polyps or continued symptoms despite medical management. Surgery serves to remove the polyps as well as the surrounding inflamed mucosa, open obstructed nasal passages, and clear the sinuses. This not only removes the obstruction caused by the polyps themselves, but allows medications such as saline irrigations and topical steroids to become more effective. It has been suggested that one of the main objectives in sinus surgery for polyps is to allow delivery of the steroids into those areas of the sinuses where polyps develop, namely, the ethmoid sinuses. Specially designed long nozzles had been developed to use postoperatively to deliver steroids into those areas after sinus surgery for polyps.
Surgery lasts approximately 45 minutes to 1 hour and can be done under general or local anesthesia. Most people tolerate the surgery without much pain, though this can vary from person to person. The person should expect some discomfort, congestion, and drainage from the nose in the first few days after surgery, but this should be mild. Complications from endoscopic sinus surgery are rare, but can include bleeding and damage to other structures in the area including the eye or brain.
Many physicians recommend a course of oral steroids prior to surgery to reduce mucosal inflammation, decrease bleeding during surgery, and help with visualization of the polyps. Nasal steroid sprays should be used preventatively after surgery to delay or prevent recurrence. People often have recurrence of polyps even following surgery. Therefore, continued follow up with a combination of medical and surgical management is preferred for the treatment of nasal polyps.

Epidemiology
Nasal polyps resulting from chronic rhinosinusitis affect approximately 4.3% of the population. Nasal polyps occur more frequently in men than women and are more common as people get older, increasing drastically after the age of 40. Of people with chronic rhinosinusitis, 10% to 54% also have allergies. An estimated 40% to 80% of people with sensitivity to aspirin will develop nasal polyposis. In people with cystic fibrosis, nasal polyps are noted in 37% to 48%.References
External links
{{Medicine Nose disorders Wikipedia medicine articles ready to translate Wikipedia neurology articles ready to translate