Naples Zoo on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Naples (; it, Napoli ; nap, Napule ), from grc, Νεάπολις, Neápolis, lit=new city. is the regional capital of
Campania
(man), it, Campana (woman)
, population_note =
, population_blank1_title =
, population_blank1 =
, demographics_type1 =
, demographics1_footnotes =
, demographics1_title1 =
, demographics1_info1 =
, demog ...
and the third-largest city of
Italy
Italy ( it, Italia ), officially the Italian Republic, ) or the Republic of Italy, is a country in Southern Europe. It is located in the middle of the Mediterranean Sea, and its territory largely coincides with the homonymous geographical ...
, after
Rome
, established_title = Founded
, established_date = 753 BC
, founder = King Romulus (legendary)
, image_map = Map of comune of Rome (metropolitan city of Capital Rome, region Lazio, Italy).svg
, map_caption ...
and
Milan
Milan ( , , Lombard: ; it, Milano ) is a city in northern Italy, capital of Lombardy, and the second-most populous city proper in Italy after Rome. The city proper has a population of about 1.4 million, while its metropolitan city h ...
, with a population of 909,048 within the city's administrative limits as of 2022.
Its province-level municipality is the third-most populous
metropolitan city in Italy with a population of 3,115,320 residents, and
its metropolitan area stretches beyond the boundaries of the city wall for approximately 20 miles.
Founded by Greeks in the
first millennium
File:1st millennium montage.png, From top left, clockwise: Depiction of Jesus, the central figure in Christianity; The Colosseum, a landmark of the once-mighty Roman Empire; Kaaba, the Great Mosque of Mecca, the holiest site of Islam; Chess, ...
BC, Naples is one of the oldest continuously inhabited urban areas in the world. In the eighth century BC, a colony known as Parthenope ( grc, Παρθενόπη) was established on the Pizzofalcone hill. In the sixth century BC, it was refounded as Neápolis. The city was an important part of
Magna Graecia, played a major role in the merging of Greek and Roman society, and was a significant cultural centre under the Romans.
Naples served as the capital of the
Duchy of Naples (661–1139), subsequently as the capital of the
Kingdom of Naples (1282–1816), and finally as the capital of the
Kingdom of the Two Sicilies — until the
unification of Italy
The unification of Italy ( it, Unità d'Italia ), also known as the ''Risorgimento'' (, ; ), was the 19th-century political and social movement that resulted in the consolidation of different states of the Italian Peninsula into a single ...
in 1861. Naples is also considered a capital of the
Baroque, beginning with the artist
Caravaggio's career in the 17th century and the artistic revolution he inspired. It was also an important centre of
humanism
Humanism is a philosophy, philosophical stance that emphasizes the individual and social potential and Agency (philosophy), agency of Human, human beings. It considers human beings the starting point for serious moral and philosophical in ...
and
Enlightenment. The city has long been a global point of reference for classical music and opera through the
Neapolitan School
In music history, the Neapolitan School is a group, associated with opera, of 17th and 18th-century composers who studied or worked in Naples, Italy,Don Michael Randel (2003). ''The Harvard Dictionary of Music'', p. 549. . the best known of whom ...
. Between 1925 and 1936, Naples was expanded and upgraded by
Benito Mussolini's government. During the later years of
World War II
World War II or the Second World War, often abbreviated as WWII or WW2, was a world war that lasted from 1939 to 1945. It involved the vast majority of the world's countries—including all of the great powers—forming two opposing ...
, it sustained
severe damage from Allied bombing as they invaded the peninsula. The city received extensive post-1945 reconstruction work.
Since the late 20th century, Naples has had significant economic growth, helped by the construction of the
Centro Direzionale business district and an advanced transportation network, which includes the
Alta Velocità high-speed rail link to Rome and
Salerno and an expanded
subway network. Naples is the third-largest urban economy in Italy by
GDP
Gross domestic product (GDP) is a monetary measure of the market value of all the final goods and services produced and sold (not resold) in a specific time period by countries. Due to its complex and subjective nature this measure is ofte ...
, after
Milan
Milan ( , , Lombard: ; it, Milano ) is a city in northern Italy, capital of Lombardy, and the second-most populous city proper in Italy after Rome. The city proper has a population of about 1.4 million, while its metropolitan city h ...
and
Rome
, established_title = Founded
, established_date = 753 BC
, founder = King Romulus (legendary)
, image_map = Map of comune of Rome (metropolitan city of Capital Rome, region Lazio, Italy).svg
, map_caption ...
. The
Port of Naples is one of the most important in Europe. In addition to commercial activities, it is home to the
Allied Joint Force Command Naples
Allied Joint Force Command Naples (JFC Naples) is a NATO military command based in Lago Patria, in the Metropolitan City of Naples, Italy. It was activated on 15 March 2004, after effectively redesigning its predecessor command, Allied Forces So ...
, the NATO body that oversees
North Africa
North Africa, or Northern Africa is a region encompassing the northern portion of the African continent. There is no singularly accepted scope for the region, and it is sometimes defined as stretching from the Atlantic shores of Mauritania in ...
, the
Sahel, and the Middle East.
Naples' historic city centre is the largest in Europe and has been designated as a UNESCO
World Heritage Site
A World Heritage Site is a landmark or area with legal protection by an international convention administered by the United Nations Educational, Scientific and Cultural Organization (UNESCO). World Heritage Sites are designated by UNESCO for h ...
. A wide range of culturally and historically significant sites are nearby, including the
Palace of Caserta
The Royal Palace of Caserta ( it, Reggia di Caserta ) is a former royal residence in Caserta, southern Italy, constructed by the House of Bourbon-Two Sicilies as their main residence as kings of Naples. It is the largest palace erected in Euro ...
and the Roman ruins of
Pompeii and
Herculaneum. Naples is also known for its natural beauties, such as
Posillipo
Posillipo (; nap, Pusilleco ) is an affluent residential quarter of Naples, southern Italy, located along the northern coast of the Gulf of Naples.
From the 1st century BC the Bay of Naples witnessed the rise of villas constructed by elite Roma ...
,
Phlegraean Fields
The Phlegraean Fields ( it, Campi Flegrei ; nap, Campe Flegree, from Ancient Greek 'to burn') is a large region of supervolcanic calderas situated to the west of Naples, Italy. It was declared a regional park in 2003. The area of the calde ...
,
Nisida
Nisida is a volcanic islet of the Flegrean Islands archipelago, in southern Italy. It lies at a very short distance from Cape Posillipo, just north of Naples; it is now connected to the mainland by a stone bridge. The islet is almost circular, wi ...
and
Vesuvius
Mount Vesuvius ( ; it, Vesuvio ; nap, 'O Vesuvio , also or ; la, Vesuvius , also , or ) is a somma- stratovolcano located on the Gulf of Naples in Campania, Italy, about east of Naples and a short distance from the shore. It is one of ...
.
Neapolitan cuisine
Neapolitan cuisine has ancient historical roots that date back to the Greco-Roman period, which was enriched over the centuries by the influence of the different cultures that controlled Naples and its kingdoms, such as that of Aragon and France ...
is noted for its association with
pizza, which originated in the city, as well as numerous other local dishes. Restaurants in the Naples' area have earned the most stars from the
Michelin Guide
The Michelin Guides ( ) are a series of guide books that have been published by the French tyre company Michelin since 1900. The Guide awards up to three Michelin stars for excellence to a select few establishments. The acquisition or loss of ...
of any Italian province. Naples'
Centro Direzionale was built in 1994 as the first grouping of skyscrapers in Italy, remaining the only such grouping in Italy until 2009. The most widely-known sports team in Naples is the
Serie A
The Serie A (), also called Serie A TIM for national sponsorship with TIM, is a professional league competition for football clubs located at the top of the Italian football league system and the winner is awarded the Scudetto and the Cop ...
football club
S.S.C. Napoli
Società Sportiva Calcio Napoli, commonly referred to as Napoli (), is an Football in Italy, Italian professional Association football, football List of football clubs in Italy, club based in the city of Naples ( it, Napoli, nap, Napule), Camp ...
, two-time Italian champions who play at the
Stadio Diego Armando Maradona in the southwest of the city, in the
Fuorigrotta quarter.
History
Greek birth and Roman acquisition




Naples has been inhabited since the
Neolithic
The Neolithic period, or New Stone Age, is an Old World archaeological period and the final division of the Stone Age. It saw the Neolithic Revolution, a wide-ranging set of developments that appear to have arisen independently in several p ...
period. In the second millennium BC, a first Mycenaean settlement arose not far from the geographical position of the future city of Parthenope.
Sailors from the Greek island of
Rhodes
Rhodes (; el, Ρόδος , translit=Ródos ) is the largest and the historical capital of the Dodecanese islands of Greece. Administratively, the island forms a separate municipality within the Rhodes regional unit, which is part of the S ...
established probably a small commercial port called
Parthenope (, meaning "Pure Eyes", a Siren in
Greek mythology
A major branch of classical mythology, Greek mythology is the body of myths originally told by the ancient Greeks, and a genre of Ancient Greek folklore. These stories concern the origin and nature of the world, the lives and activities ...
) on the
island of Megaride in the ninth century BC. By the eighth century BC, the settlement was expanded by Cumans, as evidenced by the archaeological findings, to include Monte Echia. In the sixth century BC the city was refounded as Neápolis (), eventually becoming one of the foremost cities of Magna Graecia.
The city grew rapidly due to the influence of the powerful Greek
city-state
A city-state is an independent sovereign city which serves as the center of political, economic, and cultural life over its contiguous territory. They have existed in many parts of the world since the dawn of history, including cities such as ...
of
Syracuse,
and became an ally of the
Roman Republic
The Roman Republic ( la, Res publica Romana ) was a form of government of Rome and the era of the classical Roman civilization when it was run through public representation of the Roman people. Beginning with the overthrow of the Roman Ki ...
against
Carthage
Carthage was the capital city of Ancient Carthage, on the eastern side of the Lake of Tunis in what is now Tunisia. Carthage was one of the most important trading hubs of the Ancient Mediterranean and one of the most affluent cities of the cla ...
. During the
Samnite Wars
The First, Second, and Third Samnite Wars (343–341 BC, 326–304 BC, and 298–290 BC) were fought between the Roman Republic and the Samnites, who lived on a stretch of the Apennine Mountains south of Rome and north of the Lucanian tribe. ...
, the city, now a bustling centre of trade, was
captured by the
Samnites; however, the Romans soon captured the city from them and made it a
Roman colony
A Roman (plural ) was originally a Roman outpost established in conquered territory to secure it. Eventually, however, the term came to denote the highest status of a Roman city. It is also the origin of the modern term ''colony''.
Character ...
.
During the
Punic Wars, the strong walls surrounding Neápolis repelled the invading forces of the Carthaginian general
Hannibal.
The Romans greatly respected Naples as a paragon of
Hellenistic culture
In Classical antiquity, the Hellenistic period covers the time in Mediterranean history after Classical Greece, between the death of Alexander the Great in 323 BC and the emergence of the Roman Empire, as signified by the Battle of Actium in ...
. During the Roman era, the people of Naples maintained their
Greek language
Greek ( el, label= Modern Greek, Ελληνικά, Elliniká, ; grc, Ἑλληνική, Hellēnikḗ) is an independent branch of the Indo-European family of languages, native to Greece, Cyprus, southern Italy ( Calabria and Salento), southe ...
and customs. At the same time, the city was expanded with elegant Roman
villa
A villa is a type of house that was originally an ancient Roman upper class country house. Since its origins in the Roman villa, the idea and function of a villa have evolved considerably. After the fall of the Roman Republic, villas became s ...
s,
aqueducts
Aqueduct may refer to:
Structures
*Aqueduct (bridge), a bridge to convey water over an obstacle, such as a ravine or valley
*Navigable aqueduct, or water bridge, a structure to carry navigable waterway canals over other rivers, valleys, railw ...
, and
public baths
Public baths originated when most people in population centers did not have access to private bathing facilities. Though termed "public", they have often been restricted according to gender, religious affiliation, personal membership, and other cr ...
. Landmarks such as the
Temple of Dioscures were built, and many emperors chose to holiday in the city, including
Claudius and
Tiberius
Tiberius Julius Caesar Augustus (; 16 November 42 BC – 16 March AD 37) was the second Roman emperor. He reigned from AD 14 until 37, succeeding his stepfather, the first Roman emperor Augustus. Tiberius was born in Rome in 42 BC. His father ...
.
Virgil
Publius Vergilius Maro (; traditional dates 15 October 7021 September 19 BC), usually called Virgil or Vergil ( ) in English, was an ancient Roman poet of the Augustan period. He composed three of the most famous poems in Latin literature: th ...
, the author of Rome's
national epic, the ''
Aeneid
The ''Aeneid'' ( ; la, Aenē̆is or ) is a Latin epic poem, written by Virgil between 29 and 19 BC, that tells the legendary story of Aeneas, a Trojan who fled the fall of Troy and travelled to Italy, where he became the ancestor of th ...
'', received part of his education in the city, and later resided in its environs.
It was during this period that Christianity first arrived in Naples; the
apostles Peter
Peter may refer to:
People
* List of people named Peter, a list of people and fictional characters with the given name
* Peter (given name)
** Saint Peter (died 60s), apostle of Jesus, leader of the early Christian Church
* Peter (surname), a sur ...
and
Paul
Paul may refer to:
*Paul (given name), a given name (includes a list of people with that name)
* Paul (surname), a list of people
People
Christianity
*Paul the Apostle (AD c.5–c.64/65), also known as Saul of Tarsus or Saint Paul, early Chri ...
are said to have preached in the city.
Januarius
Januarius ( ; la, Ianuarius; Neapolitan and it, Gennaro), also known as , was Bishop of Benevento and is a martyr and saint of the Catholic Church and the Eastern Orthodox Church. While no contemporary sources on his life are preserved, later ...
, who would become Naples'
patron saint
A patron saint, patroness saint, patron hallow or heavenly protector is a saint who in Catholicism, Anglicanism, or Eastern Orthodoxy is regarded as the heavenly advocate of a nation, place, craft, activity, class, clan, family, or perso ...
, was martyred there in the fourth century AD.
The last emperor of the
Western Roman Empire
The Western Roman Empire comprised the western provinces of the Roman Empire at any time during which they were administered by a separate independent Imperial court; in particular, this term is used in historiography to describe the period ...
,
Romulus Augustulus
Romulus Augustus ( 465 – after 511), nicknamed Augustulus, was Roman emperor of the West from 31 October 475 until 4 September 476. Romulus was placed on the imperial throne by his father, the ''magister militum'' Orestes, and, at that time ...
, was
exiled to Naples by the Germanic king
Odoacer in the fifth century AD.
Duchy of Naples

Following the decline of the
Western Roman Empire
The Western Roman Empire comprised the western provinces of the Roman Empire at any time during which they were administered by a separate independent Imperial court; in particular, this term is used in historiography to describe the period ...
, Naples was captured by the
Ostrogoths
The Ostrogoths ( la, Ostrogothi, Austrogothi) were a Roman-era Germanic people. In the 5th century, they followed the Visigoths in creating one of the two great Gothic kingdoms within the Roman Empire, based upon the large Gothic populations who ...
, a
Germanic people
The Germanic peoples were historical groups of people that once occupied Central Europe and Scandinavia during antiquity and into the early Middle Ages. Since the 19th century, they have traditionally been defined by the use of ancient and ear ...
, and incorporated into the
Ostrogothic Kingdom
The Ostrogothic Kingdom, officially the Kingdom of Italy (), existed under the control of the Germanic Ostrogoths in Italy and neighbouring areas from 493 to 553.
In Italy, the Ostrogoths led by Theodoric the Great killed and replaced Odoacer, ...
.
However,
Belisarius
Belisarius (; el, Βελισάριος; The exact date of his birth is unknown. – 565) was a military commander of the Byzantine Empire under the emperor Justinian I. He was instrumental in the reconquest of much of the Mediterranean terr ...
of the
Byzantine Empire
The Byzantine Empire, also referred to as the Eastern Roman Empire or Byzantium, was the continuation of the Roman Empire primarily in its eastern provinces during Late Antiquity and the Middle Ages, when its capital city was Constantinopl ...
recaptured Naples in 536, after entering the city via an aqueduct.
In 543, during the
Gothic Wars
The Gothic Wars were a long series of conflicts between the Goths and the Roman Empire between the years 249 and 554. The main wars are detailed below.
Gothic War (249–253)
(Goths under Cniva against the Roman Empire)
The War was probably in ...
,
Totila
Totila, original name Baduila (died 1 July 552), was the penultimate King of the Ostrogoths, reigning from 541 to 552 AD. A skilled military and political leader, Totila reversed the tide of the Gothic War, recovering by 543 almost all the t ...
briefly took the city for the Ostrogoths, but the Byzantines seized control of the area following the
Battle of Mons Lactarius
The Battle of Mons Lactarius (also known as Battle of the Vesuvius) took place in 552 or 553 AD during the Gothic War waged on behalf of Justinian I against the Ostrogoths in Italy.
After the Battle of Taginae, in which the Ostrogoth king Toti ...
on the slopes of
Vesuvius
Mount Vesuvius ( ; it, Vesuvio ; nap, 'O Vesuvio , also or ; la, Vesuvius , also , or ) is a somma- stratovolcano located on the Gulf of Naples in Campania, Italy, about east of Naples and a short distance from the shore. It is one of ...
.
Naples was expected to keep in contact with the
Exarchate of Ravenna
The Exarchate of Ravenna ( la, Exarchatus Ravennatis; el, Εξαρχάτο της Ραβέννας) or of Italy was a lordship of the Eastern Roman Empire (Byzantine Empire) in Italy, from 584 to 751, when the last exarch was put to death by the ...
, which was the centre of Byzantine power on the
Italian Peninsula.
After the
exarchate fell, a
Duchy of Naples was created. Although Naples'
Greco-Roman culture endured, it eventually switched allegiance from
Constantinople
la, Constantinopolis ota, قسطنطينيه
, alternate_name = Byzantion (earlier Greek name), Nova Roma ("New Rome"), Miklagard/Miklagarth (Old Norse), Tsargrad ( Slavic), Qustantiniya ( Arabic), Basileuousa ("Queen of Cities"), Megalopolis ( ...
to Rome under Duke
Stephen II, putting it under
papal suzerainty by 763.
The years between 818 and 832 saw tumultuous relations with the
Byzantine Emperor
This is a list of the Byzantine emperors from the foundation of Constantinople in 330 AD, which marks the conventional start of the Byzantine Empire, Eastern Roman Empire, to Fall of Constantinople, its fall to the Ottoman Empire in 1453 AD. On ...
, with numerous local pretenders feuding for possession of the ducal throne.
was appointed without imperial approval; his appointment was later revoked and
Theodore II took his place. However, the disgruntled general populace chased him from the city and elected
Stephen III instead, a man who minted coins with his initials rather than those of the Byzantine Emperor. Naples gained complete independence by the early ninth century.
Naples allied with the Muslim
Saracens in 836 and asked for their support to repel the siege of
Lombard troops coming from the neighbouring
Duchy of Benevento
The Duchy of Benevento (after 774, Principality of Benevento) was the southernmost Lombard duchy in the Italian Peninsula that was centred on Benevento, a city in Southern Italy. Lombard dukes ruled Benevento from 571 to 1077, when it was conq ...
. However, during the 850s,
Muhammad I Abu 'l-Abbas led the Arab-
Muslim to sack the city.
The duchy was under the direct control of the
Lombards
The Lombards () or Langobards ( la, Langobardi) were a Germanic people who ruled most of the Italian Peninsula from 568 to 774.
The medieval Lombard historian Paul the Deacon wrote in the '' History of the Lombards'' (written between 787 an ...
for a brief period after the capture by
Pandulf IV of the
Principality of Capua
The Principality of Capua ( la, italic=yes, Principatus Capuae or ''Capue'', it, italic=yes, Principato di Capua) was a Lombard state centred on Capua in Southern Italy, usually ''de facto'' independent, but under the varying suzerainty of H ...
, a long-term rival of Naples; however, this regime lasted only three years before the Greco-Roman-influenced dukes were reinstated.
By the 11th century, Naples had begun to employ
Norman
Norman or Normans may refer to:
Ethnic and cultural identity
* The Normans, a people partly descended from Norse Vikings who settled in the territory of Normandy in France in the 10th and 11th centuries
** People or things connected with the Norm ...
mercenaries to battle their rivals; Duke
Sergius IV hired
Rainulf Drengot Rainulf Drengot (also Ranulph, Ranulf, or Rannulf; died June 1045) was a Norman adventurer and mercenary in southern Italy. In 1030 he became the first count of Aversa. He was a member of the Drengot family.
Early life and arrival in Italy
When ...
to wage war on Capua for him.
By 1137, the Normans had attained great influence in Italy, controlling previously independent principalities and duchies such as
Capua
Capua ( , ) is a city and ''comune'' in the province of Caserta, in the region of Campania, southern Italy, situated north of Naples, on the northeastern edge of the Campanian plain.
History
Ancient era
The name of Capua comes from the Etrus ...
,
Benevento,
Salerno,
Amalfi
Amalfi (, , ) is a town and ''comune'' in the province of Salerno, in the region of Campania, Italy, on the Gulf of Salerno. It lies at the mouth of a deep ravine, at the foot of Monte Cerreto (1,315 metres, 4,314 feet), surrounded by dramati ...
,
Sorrento
Sorrento (, ; nap, Surriento ; la, Surrentum) is a town overlooking the Bay of Naples in Southern Italy. A popular tourist destination, Sorrento is located on the Sorrentine Peninsula at the south-eastern terminus of the Circumvesuviana ra ...
and
Gaeta; it was in this year that Naples, the last independent duchy in the southern part of the peninsula, came under Norman control. The last ruling duke of the duchy,
Sergius VII
Sergius VII (died 30 October 1137) was the thirty-ninth and last duke
Duke is a male title either of a monarch ruling over a duchy, or of a member of royalty, or nobility. As rulers, dukes are ranked below emperors, kings, grand princes, ...
, was forced to surrender to
Roger II
Roger II ( it, Ruggero II; 22 December 1095 – 26 February 1154) was King of Sicily and Africa, son of Roger I of Sicily and successor to his brother Simon. He began his rule as Count of Sicily in 1105, became Duke of Apulia and Calabria in ...
, who had been proclaimed
King of Sicily by
Antipope Anacletus II seven years earlier. Naples thus joined the
Kingdom of Sicily, with
Palermo as the capital.
As part of the Kingdom of Sicily

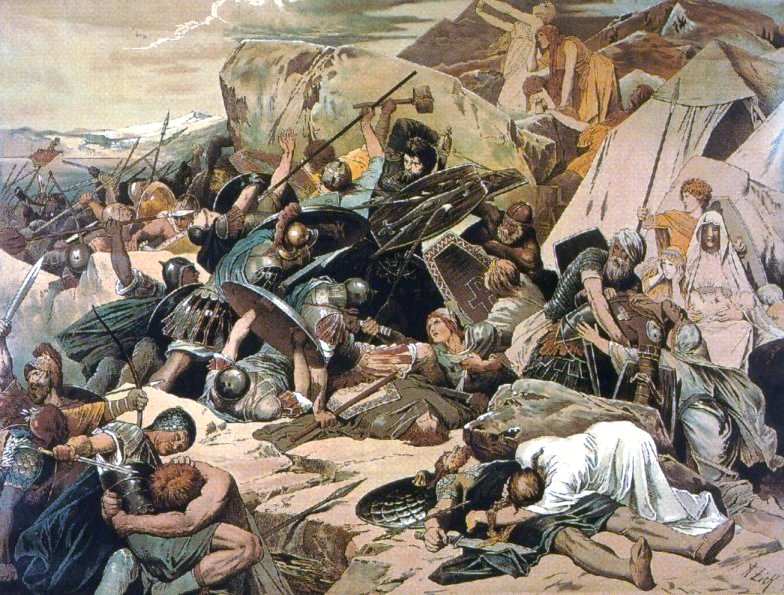
After a period of Norman rule, in 1189 the
Kingdom of Sicily was in a succession dispute between
Tancred, King of Sicily
Tancred ( it, Tancredi; 113820 February 1194) was King of Sicily from 1189 to 1194. He was born in Lecce an illegitimate son of Roger III, Duke of Apulia (the eldest son of King Roger II) by his mistress Emma, a daughter of Achard II, Count of ...
of an illegitimate birth and the
Hohenstaufens
The Hohenstaufen dynasty (, , ), also known as the Staufer, was a noble family of unclear origin that rose to rule the Duchy of Swabia from 1079, and to royal rule in the Holy Roman Empire during the Middle Ages from 1138 until 1254. The dynasty ...
, a Germanic
royal house, as its Prince Henry had married
Princess Constance the last legitimate heir to the Sicilian throne. In 1191 Henry invaded Sicily after being crowned as
Henry VI, Holy Roman Emperor, and many cities surrendered. Still, Naples resisted him from May to August under the leadership of
Richard, Count of Acerra
Richard, count of Acerra (died 30 November 1196) was an Italo-Norman nobleman, grandson of Robert of Medania, a Frenchman of Anjou. Brother of Sibylla, queen of Tancred of Sicily, Richard was the chief peninsular supporter of his brother-in-law ...
,
Nicholas of Ajello,
Aligerno Cottone and
Margaritus of Brindisi
Margaritus of Brindisi (also Margarito; Italian ''Margaritone'' or Greek ''Megareites'' or ''Margaritoni'' �αργαριτώνη c. 1149 – 1197), called "the new Neptune", was the last great '' ammiratus ammiratorum'' (Grand Admiral) of Sic ...
before the Germans suffered from disease and were forced to retreat.
Conrad II, Duke of Bohemia and
Philip I, Archbishop of Cologne
Philip I () (c. 1130 – 13 August 1191) was the Archbishop of Cologne and Archchancellor of Italy from 1167 to 1191.
He was the son of Count Goswin II of Heinsberg and Adelaide of Sommerschenburg. He received his ecclesiastic training in Colog ...
died of disease during
the siege. During his counterattack, Tancred captured Constance, now empress. He had the empress imprisoned at
Castel dell'Ovo
Castel dell'Ovo ("Egg Castle") is a seafront castle in Naples, located on the former island of Megaride, now a peninsula, on the Gulf of Naples in Italy. The castle's name comes from a legend about the Roman poet Virgil, who had a reputation in ...
at Naples before her release on May 1192 under the pressure of
Pope Celestine III. In 1194 Henry started his second campaign upon the death of Tancred, but this time Aligerno surrendered without resistance, and finally, Henry conquered Sicily, putting it under the rule of Hohenstaufens.
The
University of Naples
The University of Naples Federico II ( it, Università degli Studi di Napoli Federico II) is a public university in Naples, Italy. Founded in 1224, it is the oldest public non-sectarian university in the world, and is now organized into 26 depar ...
, the first university in Europe dedicated to training secular administrators, was founded by
Frederick II, making Naples the intellectual centre of the kingdom. Conflict between the Hohenstaufens and the
Papacy
The pope ( la, papa, from el, πάππας, translit=pappas, 'father'), also known as supreme pontiff ( or ), Roman pontiff () or sovereign pontiff, is the bishop of Rome (or historically the patriarch of Rome), head of the worldwide Cathol ...
led in 1266 to
Pope Innocent IV
Pope Innocent IV ( la, Innocentius IV; – 7 December 1254), born Sinibaldo Fieschi, was head of the Catholic Church and ruler of the Papal States from 25 June 1243 to his death in 1254.
Fieschi was born in Genoa and studied at the universitie ...
crowning the
Angevin
Angevin or House of Anjou may refer to:
*County of Anjou or Duchy of Anjou, a historical county, and later Duchy, in France
**Angevin (language), the traditional langue d'oïl spoken in Anjou
**Counts and Dukes of Anjou
* House of Ingelger, a Frank ...
duke
Charles I Charles I may refer to:
Kings and emperors
* Charlemagne (742–814), numbered Charles I in the lists of Holy Roman Emperors and French kings
* Charles I of Anjou (1226–1285), also king of Albania, Jerusalem, Naples and Sicily
* Charles I of ...
King of Sicily:
Charles officially moved the capital from Palermo to Naples, where he resided at the
Castel Nuovo. Having a great interest in architecture, Charles I imported French architects and workmen and was personally involved in several building projects in the city. Many examples of
Gothic architecture
Gothic architecture (or pointed architecture) is an architectural style that was prevalent in Europe from the late 12th to the 16th century, during the High and Late Middle Ages, surviving into the 17th and 18th centuries in some areas. It ...
sprang up around Naples, including the
Naples Cathedral
The Naples Cathedral ( it, Duomo di Napoli; nap, Viscuvato 'e Napule), or Cathedral of the Assumption of Mary ( it, Cattedrale di Santa Maria Assunta, links=no), is a Roman Catholic cathedral, the main church of Naples, southern Italy, and the s ...
, which remains the city's main church.
Kingdom of Naples

In 1282, after the
Sicilian Vespers
The Sicilian Vespers ( it, Vespri siciliani; scn, Vespiri siciliani) was a successful rebellion on the island of Sicily that broke out at Easter 1282 against the rule of the French-born king Charles I of Anjou, who had ruled the Kingdom of ...
, the Kingdom of Sicily was divided into two. The Angevin
Kingdom of Naples included the southern part of the Italian peninsula, while the island of
Sicily
(man) it, Siciliana (woman)
, population_note =
, population_blank1_title =
, population_blank1 =
, demographics_type1 = Ethnicity
, demographics1_footnotes =
, demographi ...
became the
Aragonese Kingdom of Sicily.
Wars between the competing dynasties continued until the
Peace of Caltabellotta
The Peace of Caltabellotta, signed on 31 August 1302, was the last of a series of treaties, including those of Tarascon and Anagni, designed to end the conflict between the Houses of Anjou and Barcelona for ascendancy in the Mediterranean and esp ...
in 1302, which saw
Frederick III recognised as king of Sicily, while
Charles II was recognised as king of Naples by
Pope Boniface VIII.
Despite the split, Naples grew in importance, attracting
Pisan and
Genoese merchants,
Tuscan bankers, and some of the most prominent
Renaissance
The Renaissance ( , ) , from , with the same meanings. is a period in European history
The history of Europe is traditionally divided into four time periods: prehistoric Europe (prior to about 800 BC), classical antiquity (800 BC to AD ...
artists of the time, such as
Boccaccio
Giovanni Boccaccio (, , ; 16 June 1313 – 21 December 1375) was an Italian writer, poet, correspondent of Petrarch, and an important Renaissance humanist. Born in the town of Certaldo, he became so well known as a writer that he was some ...
,
Petrarch
Francesco Petrarca (; 20 July 1304 – 18/19 July 1374), commonly anglicized as Petrarch (), was a scholar and poet of early Renaissance Italy, and one of the earliest humanists.
Petrarch's rediscovery of Cicero's letters is often credited ...
and
Giotto
Giotto di Bondone (; – January 8, 1337), known mononymously as Giotto ( , ) and Latinised as Giottus, was an Italian painter and architect from Florence during the Late Middle Ages. He worked during the Gothic/ Proto-Renaissance period. G ...
. During the 14th century, the
Hungarian Angevin king
Louis the Great
Louis I, also Louis the Great ( hu, Nagy Lajos; hr, Ludovik Veliki; sk, Ľudovít Veľký) or Louis the Hungarian ( pl, Ludwik Węgierski; 5 March 132610 September 1382), was King of Hungary and Croatia from 1342 and King of Poland from 1370. ...
captured the city several times. In 1442,
Alfonso I conquered Naples after his victory against the last
Angevin
Angevin or House of Anjou may refer to:
*County of Anjou or Duchy of Anjou, a historical county, and later Duchy, in France
**Angevin (language), the traditional langue d'oïl spoken in Anjou
**Counts and Dukes of Anjou
* House of Ingelger, a Frank ...
king,
René
René ('' born again'' or ''reborn'' in French) is a common first name in French-speaking, Spanish-speaking, and German-speaking countries. It derives from the Latin name Renatus.
René is the masculine form of the name ( Renée being the femin ...
, and Naples was unified with Sicily again for a brief period.
Aragonese and Spanish

Sicily and Naples were separated since 1282, but remained dependencies of
Aragon under
Ferdinand I. The new dynasty enhanced Naples' commercial standing by establishing relations with the
Iberian Peninsula
The Iberian Peninsula (),
**
* Aragonese and Occitan: ''Peninsula Iberica''
**
**
* french: Péninsule Ibérique
* mwl, Península Eibérica
* eu, Iberiar penintsula also known as Iberia, is a peninsula in southwestern Europe, def ...
. Naples also became a centre of the Renaissance, with artists such as
Laurana,
da Messina,
Sannazzaro and
Poliziano
Agnolo (Angelo) Ambrogini (14 July 1454 – 24 September 1494), commonly known by his nickname Poliziano (; anglicized as Politian; Latin: '' Politianus''), was an Italian classical scholar and poet of the Florentine Renaissance. His scho ...
arriving in the city. In 1501, Naples came under direct rule from
France
France (), officially the French Republic ( ), is a country primarily located in Western Europe. It also comprises of overseas regions and territories in the Americas and the Atlantic, Pacific and Indian Oceans. Its metropolitan area ...
under
Louis XII
Louis XII (27 June 14621 January 1515), was King of France from 1498 to 1515 and King of Naples from 1501 to 1504. The son of Charles, Duke of Orléans, and Maria of Cleves, he succeeded his 2nd cousin once removed and brother in law at the tim ...
, with the Neapolitan king
Frederick Frederick may refer to:
People
* Frederick (given name), the name
Nobility
Anhalt-Harzgerode
*Frederick, Prince of Anhalt-Harzgerode (1613–1670)
Austria
* Frederick I, Duke of Austria (Babenberg), Duke of Austria from 1195 to 1198
* Frederick ...
being taken as a prisoner to France; however, this state of affairs did not last long, as Spain won Naples from the French at the
Battle of Garigliano
The Battle of Garigliano was fought in 915 between Christian forces and the Saracens. Pope John X personally led the Christian forces into battle. The aim was to destroy the Arab fortress on the Garigliano River, which had threatened central Ita ...
in 1503.

Following the Spanish victory, Naples became part of the
Spanish Empire
The Spanish Empire ( es, link=no, Imperio español), also known as the Hispanic Monarchy ( es, link=no, Monarquía Hispánica) or the Catholic Monarchy ( es, link=no, Monarquía Católica) was a colonial empire governed by Spain and its prede ...
, and remained so throughout the
Spanish Habsburg
Habsburg Spain is a contemporary historiographical term referring to the huge extent of territories (including modern-day Spain, a piece of south-east France, eventually Portugal, and many other lands outside of the Iberian Peninsula) ruled bet ...
period.
The Spanish sent
viceroy
A viceroy () is an official who reigns over a polity in the name of and as the representative of the monarch of the territory. The term derives from the Latin prefix ''vice-'', meaning "in the place of" and the French word ''roy'', meaning " ...
s
to Naples to directly deal with local issues: the most important of these viceroys was
Pedro Álvarez de Toledo
Pedro is a masculine given name. Pedro is the Spanish, Portuguese, and Galician name for ''Peter''. Its French equivalent is Pierre while its English and Germanic form is Peter.
The counterpart patronymic surname of the name Pedro, meaning " ...
, who was responsible for considerable social, economic and urban reforms in the city; he also tried to introduce the
Inquisition
The Inquisition was a group of institutions within the Catholic Church whose aim was to combat heresy, conducting trials of suspected heretics. Studies of the records have found that the overwhelming majority of sentences consisted of penances, ...
. In 1544, around 7,000 people were taken as
slaves by
Barbary pirates and brought to the
Barbary Coast of North Africa (see
Sack of Naples).
By the 17th century, Naples had become Europe's second-largest city – second only to Paris – and the largest European Mediterranean city, with around 250,000 inhabitants. The city was a major cultural centre during the
Baroque era, being home to artists such as
Caravaggio,
Salvator Rosa and
Bernini, philosophers such as
Bernardino Telesio
Bernardino Telesio (; 7 November 1509 – 2 October 1588) was an Italian philosopher and natural scientist. While his natural theories were later disproven, his emphasis on observation made him the "first of the moderns" who eventually deve ...
,
Giordano Bruno,
Tommaso Campanella
Tommaso Campanella (; 5 September 1568 – 21 May 1639), baptized Giovanni Domenico Campanella, was an Italian Dominican friar, philosopher, theologian, astrologer, and poet.
He was prosecuted by the Roman Inquisition for heresy in 1594 an ...
and
Giambattista Vico
Giambattista Vico (born Giovan Battista Vico ; ; 23 June 1668 – 23 January 1744) was an Italian philosopher, rhetorician, historian, and jurist during the Italian Enlightenment. He criticized the expansion and development of modern rationali ...
, and writers such as
Giambattista Marino
Giovanni Battista was a common Italian given name (see Battista for those with the surname) in the 16th-18th centuries. It refers to "John the Baptist" in English, the French equivalent is "Jean-Baptiste". Common nicknames include Giambattista, Gi ...
. A revolution led by the local fisherman
Masaniello saw the creation of a brief independent
Neapolitan Republic in 1647. However, this lasted only a few months before Spanish rule was reasserted.
In 1656, an outbreak of
bubonic plague killed about half of Naples' 300,000 inhabitants.

In 1714, Spanish rule over Naples came to an end as a result of the
War of the Spanish Succession
The War of the Spanish Succession was a European great power conflict that took place from 1701 to 1714. The death of childless Charles II of Spain in November 1700 led to a struggle for control of the Spanish Empire between his heirs, Phil ...
; the Austrian
Charles VI ruled the city from
Vienna
en, Viennese
, iso_code = AT-9
, registration_plate = W
, postal_code_type = Postal code
, postal_code =
, timezone = CET
, utc_offset = +1
, timezone_DST ...
through viceroys of his own. However, the
War of the Polish Succession
The War of the Polish Succession ( pl, Wojna o sukcesję polską; 1733–35) was a major European conflict sparked by a Polish civil war over the succession to Augustus II of Poland, which the other European powers widened in pursuit of thei ...
saw the Spanish regain Sicily and Naples as part of a
personal union
A personal union is the combination of two or more states that have the same monarch while their boundaries, laws, and interests remain distinct. A real union, by contrast, would involve the constituent states being to some extent interlink ...
, with the 1738
Treaty of Vienna recognising the two polities as independent under a cadet branch of the Spanish
Bourbons
The House of Bourbon (, also ; ) is a European dynasty of French origin, a branch of the Capetian dynasty, the royal House of France. Bourbon kings first ruled France and Navarre in the 16th century. By the 18th century, members of the Spani ...
.
In 1755, the Duke of Noja commissioned an accurate topographic map of Naples, later known as the
Map of the Duke of Nojo, employing rigorous surveying accuracy and becoming an essential urban planning tool for Naples.
During the time of
Ferdinand IV, the effects of the
French Revolution
The French Revolution ( ) was a period of radical political and societal change in France that began with the Estates General of 1789 and ended with the formation of the French Consulate in coup of 18 Brumaire, November 1799. Many of its ...
were felt in Naples:
Horatio Nelson, an ally of the Bourbons, arrived in the city in 1798 to warn against the French republicans. Ferdinand was forced to retreat and fled to
Palermo, where he was protected by a
British fleet.
However, Naples'
lower class ''
lazzaroni'' were strongly
pious and
royalist
A royalist supports a particular monarch as head of state for a particular kingdom, or of a particular dynastic claim. In the abstract, this position is royalism. It is distinct from monarchism, which advocates a monarchical system of governm ...
, favouring the Bourbons; in the mêlée that followed, they fought the Neapolitan pro-
Republican
Republican can refer to:
Political ideology
* An advocate of a republic, a type of government that is not a monarchy or dictatorship, and is usually associated with the rule of law.
** Republicanism, the ideology in support of republics or agains ...
aristocracy, causing a civil war.
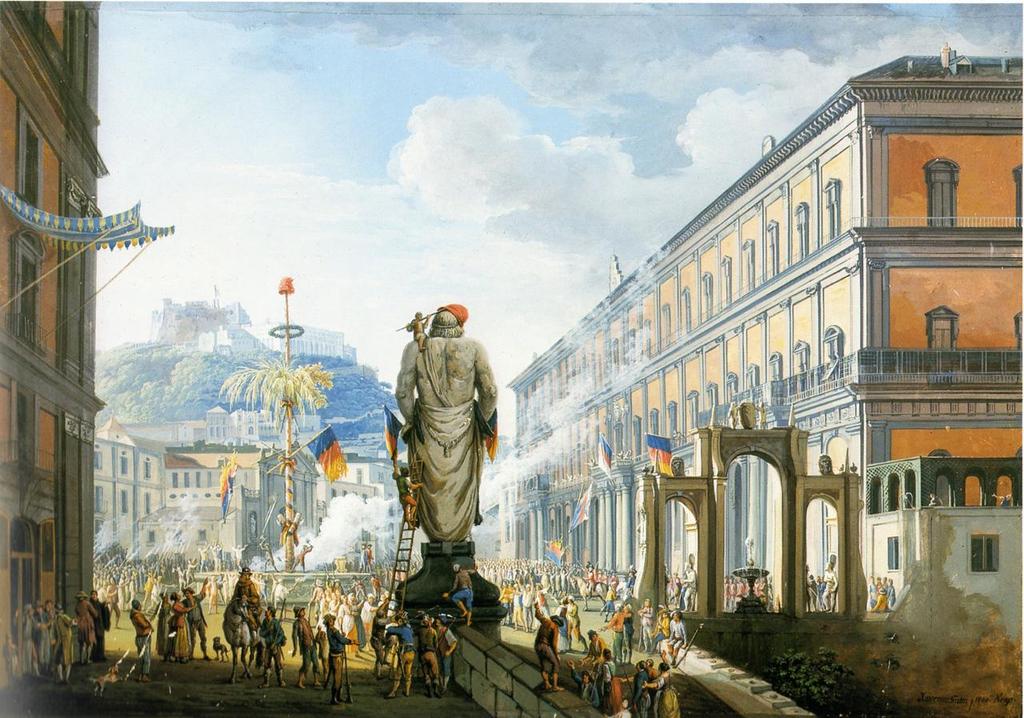

Eventually, the Republicans conquered
Castel Sant'Elmo
Castel Sant'Elmo is a medieval fortress located on Vomero Hill adjacent to the Certosa di San Martino, overlooking Naples, Italy. The name "Sant'Elmo" derives from a former 10th-century church dedicated to Sant'Erasmo, shortened to "Ermo" and, ...
and proclaimed a
Parthenopaean Republic
The Parthenopean Republic ( it, Repubblica Partenopea, french: République Parthénopéenne) or Neapolitan Republic (''Repubblica Napoletana'') was a short-lived, semi-autonomous republic located within the Kingdom of Naples and supported by th ...
, secured by the
French Army
The French Army, officially known as the Land Army (french: Armée de Terre, ), is the land-based and largest component of the French Armed Forces. It is responsible to the Government of France, along with the other components of the Armed Force ...
.
A
counter-revolutionary
A counter-revolutionary or an anti-revolutionary is anyone who opposes or resists a revolution, particularly one who acts after a revolution in order to try to overturn it or reverse its course, in full or in part. The adjective "counter-revolut ...
religious army of ''lazzaroni'' known as the ''
sanfedisti'' under Cardinal
Fabrizio Ruffo
Fabrizio Dionigi Ruffo (16 September 1744 – 13 December 1827) was an Italian cardinal and politician, who led the popular anti-republican ''Sanfedismo'' movement (whose members were known as the ''Sanfedisti'').
Biography
Ruffo was born at ...
was raised; they met with great success, and the French were forced to surrender the Neapolitan castles, with their fleet sailing back to
Toulon
Toulon (, , ; oc, label= Provençal, Tolon , , ) is a city on the French Riviera and a large port on the Mediterranean coast, with a major naval base. Located in the Provence-Alpes-Côte d'Azur region, and the Provence province, Toulon is th ...
.
Ferdinand IV was restored as king; however, after only seven years,
Napoleon
Napoleon Bonaparte ; it, Napoleone Bonaparte, ; co, Napulione Buonaparte. (born Napoleone Buonaparte; 15 August 1769 – 5 May 1821), later known by his regnal name Napoleon I, was a French military commander and political leader who ...
conquered the kingdom and installed
Bonapartist
Bonapartism (french: Bonapartisme) is the political ideology supervening from Napoleon Bonaparte and his followers and successors. The term was used to refer to people who hoped to restore the House of Bonaparte and its style of government. In thi ...
kings, including his brother
Joseph Bonaparte
it, Giuseppe-Napoleone Buonaparte es, José Napoleón Bonaparte
, house = Bonaparte
, father = Carlo Buonaparte
, mother = Letizia Ramolino
, birth_date = 7 January 1768
, birth_place = Corte, Corsica, Republic of ...
(King of Spain).
With the help of the
Austrian Empire
The Austrian Empire (german: link=no, Kaiserthum Oesterreich, modern spelling , ) was a Central-Eastern European multinational great power from 1804 to 1867, created by proclamation out of the realms of the Habsburgs. During its existence ...
and its allies, the Bonapartists were defeated in the
Neapolitan War. Ferdinand IV once again regained the throne and the kingdom.
Independent Two Sicilies
The
Congress of Vienna
The Congress of Vienna (, ) of 1814–1815 was a series of international diplomatic meetings to discuss and agree upon a possible new layout of the European political and constitutional order after the downfall of the French Emperor Napoleon B ...
in 1815 saw the kingdoms of Naples and Sicily combine to form the
Kingdom of the Two Sicilies,
with Naples as the capital city. In 1839, Naples became the first city on the Italian peninsula to have a railway, with the construction of the
Naples–Portici railway
The Naples–Portici railway ( it, ferrovia Napoli–Portici) was the first Italian railway line, built by the Bayard Company and opened in 1839. It now forms part of the Naples–Salerno railway line, Naples–Salerno line.
Geography
The initia ...
.
Italian unification to the present day
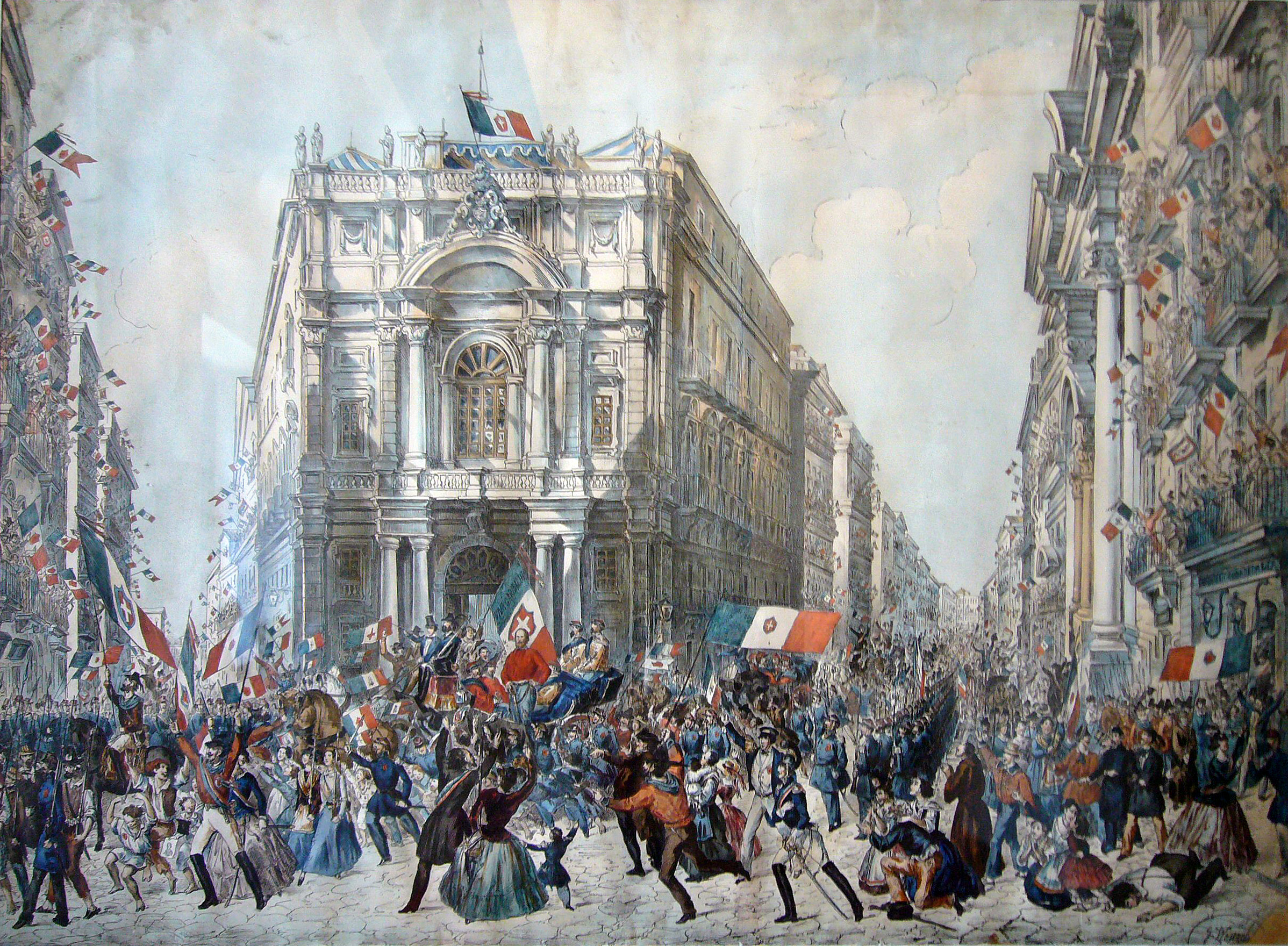

After the
Expedition of the Thousand
The Expedition of the Thousand ( it, Spedizione dei Mille) was an event of the Italian Risorgimento that took place in 1860. A corps of volunteers led by Giuseppe Garibaldi sailed from Quarto, near Genoa (now Quarto dei Mille) and landed in Mars ...
led by
Giuseppe Garibaldi, which culminated in the controversial
Siege of Gaeta, Naples became part of the
Kingdom of Italy
The Kingdom of Italy ( it, Regno d'Italia) was a state that existed from 1861, when Victor Emmanuel II of Sardinia was proclaimed King of Italy, until 1946, when civil discontent led to an institutional referendum to abandon the monarchy and f ...
in 1861 as part of the
Italian unification, ending the era of Bourbon rule. The economy of the area formerly known as the Two Sicilies declined, leading to an unprecedented
wave of emigration,
with an estimated 4 million people emigrating from the Naples area between 1876 and 1913. In the forty years following unification, the population of Naples grew by only 26%, vs. 63% for Turin and 103% for Milan; however, by 1884, Naples was still the largest city in Italy with 496,499 inhabitants, or roughly 64,000 per square kilometre (more than twice the population density of Paris).
Public health conditions in certain areas of the city were poor, with twelve epidemics of
cholera and
typhoid fever
Typhoid fever, also known as typhoid, is a disease caused by '' Salmonella'' serotype Typhi bacteria. Symptoms vary from mild to severe, and usually begin six to 30 days after exposure. Often there is a gradual onset of a high fever over several ...
claiming some 48,000 people between 1834 and 1884. A
death rate
Mortality rate, or death rate, is a measure of the number of deaths (in general, or due to a specific cause) in a particular population, scaled to the size of that population, per unit of time. Mortality rate is typically expressed in units of de ...
31.84 per thousand, high even for the time, insisted in the absence of epidemics between 1878 and 1883. Then in 1884, Naples fell victim to a major
cholera epidemic, caused largely by the city's poor
sewerage infrastructure. In response to these problems, in 1852, the government prompted a radical transformation of the city called ''risanamento'' to improve the sewerage infrastructure and replace the most clustered areas, considered the main cause of insalubrity, with large and airy avenues. The project proved difficult to accomplish politically and economically due to corruption, as shown in the
Saredo Inquiry, land speculation and extremely long bureaucracy. This led to the project to massive delays with contrasting results. The most notable transformations made were the construction of Via Caracciolo in place of the beach along the promenade, the creation of
Galleria Umberto I
Galleria Umberto I is a public shopping gallery in Naples, southern Italy. It is located directly across from the San Carlo opera house. It was built between 1887–1890, and was the cornerstone in the decades-long rebuilding of Naples—called t ...
and
Galleria Principe and the construction of Corso Umberto.
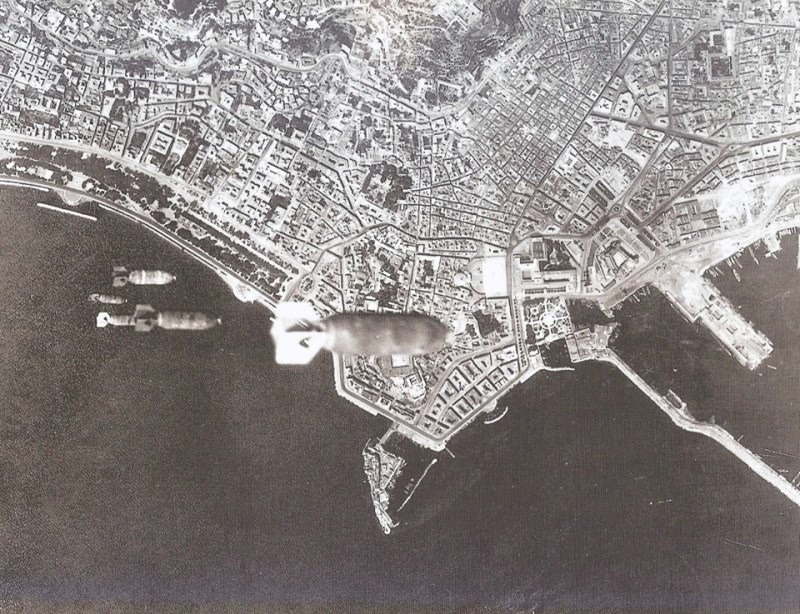

Naples was the
most-bombed Italian city during
World War II
World War II or the Second World War, often abbreviated as WWII or WW2, was a world war that lasted from 1939 to 1945. It involved the vast majority of the world's countries—including all of the great powers—forming two opposing ...
.
Though Neapolitans did not rebel under
Italian Fascism, Naples was the first Italian city to
rise up against German
German(s) may refer to:
* Germany (of or related to)
** Germania (historical use)
* Germans, citizens of Germany, people of German ancestry, or native speakers of the German language
** For citizens of Germany, see also German nationality law
**Ge ...
military occupation
Military occupation, also known as belligerent occupation or simply occupation, is the effective military control by a ruling power over a territory that is outside of that power's sovereign territory.Eyāl Benveniśtî. The international law ...
; the city was completely freed by 1 October 1943, when British and American forces entered the city. Departing Germans
burned the library of
the university, as well as the Italian Royal Society. They also destroyed the city archives. Time bombs planted throughout the city continued to explode into November. The symbol of the rebirth of Naples was the rebuilding of the church of
Santa Chiara, which had been destroyed in a
United States Army Air Corps
The United States Army Air Corps (USAAC) was the aerial warfare service component of the United States Army between 1926 and 1941. After World War I, as early aviation became an increasingly important part of modern warfare, a philosophical r ...
bombing raid.
Special funding from the Italian government's
Fund for the South was provided from 1950 to 1984, helping the Neapolitan economy to improve somewhat, with city landmarks such as the
Piazza del Plebiscito
Piazza del Plebiscito (; nap, Chiazza d''o Plebbiscito) is a large public town square, square in central Naples, Italy.
History
Named after the plebiscite taken on October 21, 1860, that brought Naples into the unified Italian unification#Creat ...
being renovated. However, high unemployment continues to affect Naples.
Italian media attributed the past city's
waste disposal issues to the activity of the
Camorra organised crime
Organized crime (or organised crime) is a category of transnational, national, or local groupings of highly centralized enterprises run by criminals to engage in illegal activity, most commonly for profit. While organized crime is generally th ...
network. Due to this event, environmental contamination and increased health risks are also prevalent.
In 2007,
Silvio Berlusconi
Silvio Berlusconi ( ; ; born 29 September 1936) is an Italian media tycoon and politician who served as Prime Minister of Italy in four governments from 1994 to 1995, 2001 to 2006 and 2008 to 2011. He was a member of the Chamber of Deputies f ...
's government held senior meetings in Naples to demonstrate their intention to solve these problems. However, the
late-2000s recession had a severe impact on the city, intensifying its waste-management and unemployment problems. By August 2011, the number of unemployed in the Naples area had risen to 250,000, sparking public protests against the economic situation. In June 2012, allegations of blackmail, extortion, and illicit contract tendering emerged concerning the city's waste management issues.
["Cricca veneta sui rifiuti di Napoli: arrestati i fratelli Gavioli" (in Italian)]
. ''Il Mattino''. 20 June 2012. Retrieved 11 July 2012.
. ''Il Mattino di Padova''. 21 June 2012. Retrieved 14 July 2012.
Naples hosted the sixth
World Urban Forum in September 2012 and the 63rd
International Astronautical Congress
Every year, the International Astronautical Federation with the support of the International Academy of Astronautics and the International Institute of Space Law (IISL), holds the International Astronautical Congress (IAC) which is hosted by ...
in October 2012. In 2013, it was the host of the
Universal Forum of Cultures and the host for the
2019 Summer Universiade
)
, Nations participating = 118
, Athletes participating = 5,971
, Events = 220
, Sports = 18
, Opening ceremony = 3 July
, Closing ceremony = 14 July
, Officially opened by = President Se ...
.
Architecture
UNESCO World Heritage Site

Naples' 2,800-year history has left it with a wealth of historical buildings and monuments, from medieval castles to classical ruins, and a wide range of culturally and historically significant sites nearby, including the
Palace of Caserta
The Royal Palace of Caserta ( it, Reggia di Caserta ) is a former royal residence in Caserta, southern Italy, constructed by the House of Bourbon-Two Sicilies as their main residence as kings of Naples. It is the largest palace erected in Euro ...
and the Roman ruins of
Pompeii and
Herculaneum. In
2017
File:2017 Events Collage V2.png, From top left, clockwise: The War Against ISIS at the Battle of Mosul (2016-2017); aftermath of the Manchester Arena bombing; The Solar eclipse of August 21, 2017 ("Great American Eclipse"); North Korea tests a s ...
the
BBC #REDIRECT BBC #REDIRECT BBC
Here i going to introduce about the best teacher of my life b BALAJI sir. He is the precious gift that I got befor 2yrs . How has helped and thought all the concept and made my success in the 10th board exam. ...
...
defined Naples as «the Italian city with too much history to handle».
The most prominent forms of architecture visible in present-day Naples are the
Medieval
In the history of Europe, the Middle Ages or medieval period lasted approximately from the late 5th to the late 15th centuries, similar to the post-classical period of global history. It began with the fall of the Western Roman Empire ...
,
Renaissance
The Renaissance ( , ) , from , with the same meanings. is a period in European history
The history of Europe is traditionally divided into four time periods: prehistoric Europe (prior to about 800 BC), classical antiquity (800 BC to AD ...
and
Baroque styles. Naples has a total of 448 historical churches (1000 in total), making it one of the most Catholic cities in the world in terms of the number of places of worship.
In 1995, the historic centre of Naples was listed by
UNESCO
The United Nations Educational, Scientific and Cultural Organization is a specialized agency of the United Nations (UN) aimed at promoting world peace and security through international cooperation in education, arts, sciences and culture. It ...
as a
World Heritage Site
A World Heritage Site is a landmark or area with legal protection by an international convention administered by the United Nations Educational, Scientific and Cultural Organization (UNESCO). World Heritage Sites are designated by UNESCO for h ...
, a United Nations programme which aims to catalogue and conserve sites of outstanding cultural or natural importance to the
common heritage of mankind
Common heritage of humanity (also termed the common heritage of mankind, common heritage of humankind or common heritage principle) is a principle of international law that holds the defined territorial areas and elements of humanity's common heri ...
.
Piazzas, palaces and castles

The main city square or ''
piazza
A town square (or square, plaza, public square, city square, urban square, or ''piazza'') is an open public space, commonly found in the heart of a traditional town but not necessarily a true geometric square, used for community gatherings. ...
'' of the city is the
Piazza del Plebiscito
Piazza del Plebiscito (; nap, Chiazza d''o Plebbiscito) is a large public town square, square in central Naples, Italy.
History
Named after the plebiscite taken on October 21, 1860, that brought Naples into the unified Italian unification#Creat ...
. Its construction was begun by the Bonapartist king
Joachim Murat
Joachim Murat ( , also , ; it, Gioacchino Murati; 25 March 1767 – 13 October 1815) was a French military commander and statesman who served during the French Revolutionary Wars and Napoleonic Wars. Under the French Empire he received the ...
and finished by the Bourbon king
Ferdinand IV. The piazza is bounded on the east by the
Royal Palace and on the west by the church of
San Francesco di Paola, with the colonnades extending on both sides. Nearby is the
Teatro di San Carlo
The Real Teatro di San Carlo ("Royal Theatre of Saint Charles"), as originally named by the Bourbon monarchy but today known simply as the Teatro (di) San Carlo, is an opera house in Naples, Italy, connected to the Royal Palace and adjacent ...
, which is the oldest
opera house
An opera house is a theatre building used for performances of opera. It usually includes a stage, an orchestra pit, audience seating, and backstage facilities for costumes and building sets.
While some venues are constructed specifically fo ...
in Italy. Directly across San Carlo is
Galleria Umberto.
Naples is well known for its castles: The most ancient is
Castel dell'Ovo
Castel dell'Ovo ("Egg Castle") is a seafront castle in Naples, located on the former island of Megaride, now a peninsula, on the Gulf of Naples in Italy. The castle's name comes from a legend about the Roman poet Virgil, who had a reputation in ...
("Egg Castle"), which was built on the tiny
islet
An islet is a very small, often unnamed island. Most definitions are not precise, but some suggest that an islet has little or no vegetation and cannot support human habitation. It may be made of rock, sand and/or hard coral; may be permanen ...
of Megarides, where the original
Cumae
Cumae ( grc, Κύμη, (Kumē) or or ; it, Cuma) was the first ancient Greek colony on the mainland of Italy, founded by settlers from Euboea in the 8th century BC and soon becoming one of the strongest colonies. It later became a rich Ro ...
an colonists had founded the city. In Roman times the islet became part of
Lucullus
Lucius Licinius Lucullus (; 118–57/56 BC) was a Roman general and statesman, closely connected with Lucius Cornelius Sulla. In culmination of over 20 years of almost continuous military and government service, he conquered the eastern kingd ...
's villa, later hosting
Romulus Augustulus
Romulus Augustus ( 465 – after 511), nicknamed Augustulus, was Roman emperor of the West from 31 October 475 until 4 September 476. Romulus was placed on the imperial throne by his father, the ''magister militum'' Orestes, and, at that time ...
, the exiled last western Roman emperor. It had also been the prison for
Empress Constance between 1191 and 1192 after her being captured by Sicilians, and
Conradin
Conrad III (25 March 1252 – 29 October 1268), called ''the Younger'' or ''the Boy'', but usually known by the diminutive Conradin (german: link=no, Konradin, it, Corradino), was the last direct heir of the House of Hohenstaufen. He was Duk ...
and
Giovanna I of Naples
Joanna I, also known as Johanna I ( it, Giovanna I; December 1325 – 27 July 1382), was Queen of Naples, and Countess of Provence and Forcalquier from 1343 to 1382; she was also Princess of Achaea from 1373 to 1381.
Joanna was the eldest dau ...
before their executions.
Castel Nuovo, also known as ''Maschio
Angioino'', is one of the city's top landmarks; it was built during the time of
Charles I Charles I may refer to:
Kings and emperors
* Charlemagne (742–814), numbered Charles I in the lists of Holy Roman Emperors and French kings
* Charles I of Anjou (1226–1285), also king of Albania, Jerusalem, Naples and Sicily
* Charles I of ...
, the first
king of Naples
The following is a list of rulers of the Kingdom of Naples, from its first separation from the Kingdom of Sicily to its merger with the same into the Kingdom of the Two Sicilies.
Kingdom of Naples (1282–1501)
House of Anjou
In 1382, the Kin ...
. Castel Nuovo has seen many notable historical events: for example, in 1294,
Pope Celestine V resigned as pope in a hall of the castle, and following this
Pope Boniface VIII was elected pope by the cardinal
collegium
A (plural ), or college, was any association in ancient Rome that acted as a legal entity. Following the passage of the ''Lex Julia'' during the reign of Julius Caesar as Consul and Dictator of the Roman Republic (49–44 BC), and their rea ...
, before moving to Rome.
Castel Capuano
Castel Capuano is a castle in Naples, southern Italy. It takes its name from the fact that it was at that point in the city walls where the road led out to the city of Capua. The castle is at the southwest end of via dei Tribunali, and until re ...
was built in the 12th century by
William I
William I; ang, WillelmI (Bates ''William the Conqueror'' p. 33– 9 September 1087), usually known as William the Conqueror and sometimes William the Bastard, was the first Norman king of England, reigning from 1066 until his death in 10 ...
, the son of
Roger II of Sicily, the first monarch of the
Kingdom of Naples. It was expanded by
Frederick II and became one of his royal palaces. The castle was the residence of many kings and queens throughout its history. In the 16th century, it became the Hall of Justice.
Another Neapolitan castle is
Castel Sant'Elmo
Castel Sant'Elmo is a medieval fortress located on Vomero Hill adjacent to the Certosa di San Martino, overlooking Naples, Italy. The name "Sant'Elmo" derives from a former 10th-century church dedicated to Sant'Erasmo, shortened to "Ermo" and, ...
, which was completed in 1329 and is built in the shape of a
star. Its strategic position overlooking the entire city made it a target of various invaders. During the uprising of
Masaniello in 1647, the Spanish took refuge in Sant'Elmo to escape the revolutionaries.
The
Carmine Castle, built in 1392 and highly modified in the 16th century by the Spanish, was demolished in 1906 to make room for the Via Marina, although two of the castle's towers remain as a monument. The Vigliena Fort, built in 1702, was destroyed in 1799 during the royalist war against the Parthenopean Republic and is now abandoned and in ruin.
Museums


Naples is widely known for its wealth of historical museums. The
Naples National Archaeological Museum is one of the city's main museums, with one of the most extensive collections of
artefacts of the
Roman Empire
The Roman Empire ( la, Imperium Romanum ; grc-gre, Βασιλεία τῶν Ῥωμαίων, Basileía tôn Rhōmaíōn) was the post- Republican period of ancient Rome. As a polity, it included large territorial holdings around the Mediter ...
in the world.
It also houses many of the antiques unearthed at
Pompeii and
Herculaneum, as well as some artefacts from the
Greek
Greek may refer to:
Greece
Anything of, from, or related to Greece, a country in Southern Europe:
*Greeks, an ethnic group.
*Greek language, a branch of the Indo-European language family.
**Proto-Greek language, the assumed last common ancestor ...
and
Renaissance
The Renaissance ( , ) , from , with the same meanings. is a period in European history
The history of Europe is traditionally divided into four time periods: prehistoric Europe (prior to about 800 BC), classical antiquity (800 BC to AD ...
periods.
Previously a Bourbon palace, now a museum and art gallery, the
Museo di Capodimonte
Museo di Capodimonte is an art museum located in the Palace of Capodimonte, a grand Bourbon palazzo in Naples, Italy. The museum is the prime repository of Neapolitan painting and decorative art, with several important works from other Italia ...
is another museum of note. The
gallery features paintings from the 13th to the 18th centuries, including major works by
Simone Martini
Simone Martini ( – 1344) was an Italian painter born in Siena.
He was a major figure in the development of early Italian painting and greatly influenced the development of the International Gothic style.
It is thought that Martini was a pupil ...
,
Raphael
Raffaello Sanzio da Urbino, better known as Raphael (; or ; March 28 or April 6, 1483April 6, 1520), was an Italian painter and architect of the High Renaissance. His work is admired for its clarity of form, ease of composition, and visual a ...
,
Titian
Tiziano Vecelli or Vecellio (; 27 August 1576), known in English as Titian ( ), was an Italian (Venetian) painter of the Renaissance, considered the most important member of the 16th-century Venetian school. He was born in Pieve di Cadore, nea ...
,
Caravaggio,
El Greco,
Jusepe de Ribera
Jusepe de Ribera (1591 – 1652) was a painter and printmaker, who along with Francisco de Zurbarán, Bartolomé Esteban Murillo, and the singular Diego Velázquez, are regarded as the major artists of Spanish Baroque painting. Referring ...
and
Luca Giordano
Luca Giordano (18 October 1634 – 3 January 1705) was an Italian late-Baroque painter and printmaker in etching. Fluent and decorative, he worked successfully in Naples and Rome, Florence, and Venice, before spending a decade in Spain.
Earl ...
. The royal apartments are furnished with antique 18th-century furniture and a collection of
porcelain
Porcelain () is a ceramic material made by heating substances, generally including materials such as kaolinite, in a kiln to temperatures between . The strength and translucence of porcelain, relative to other types of pottery, arises main ...
and
majolica
In different periods of time and in different countries, the term ''majolica'' has been used for two distinct types of pottery.
Firstly, from the mid-15th century onwards, was ''maiolica'', a type of pottery reaching Italy from Spain, Majorca a ...
from the various royal residences: the famous
Capodimonte Porcelain Factory once stood just adjacent to the palace.
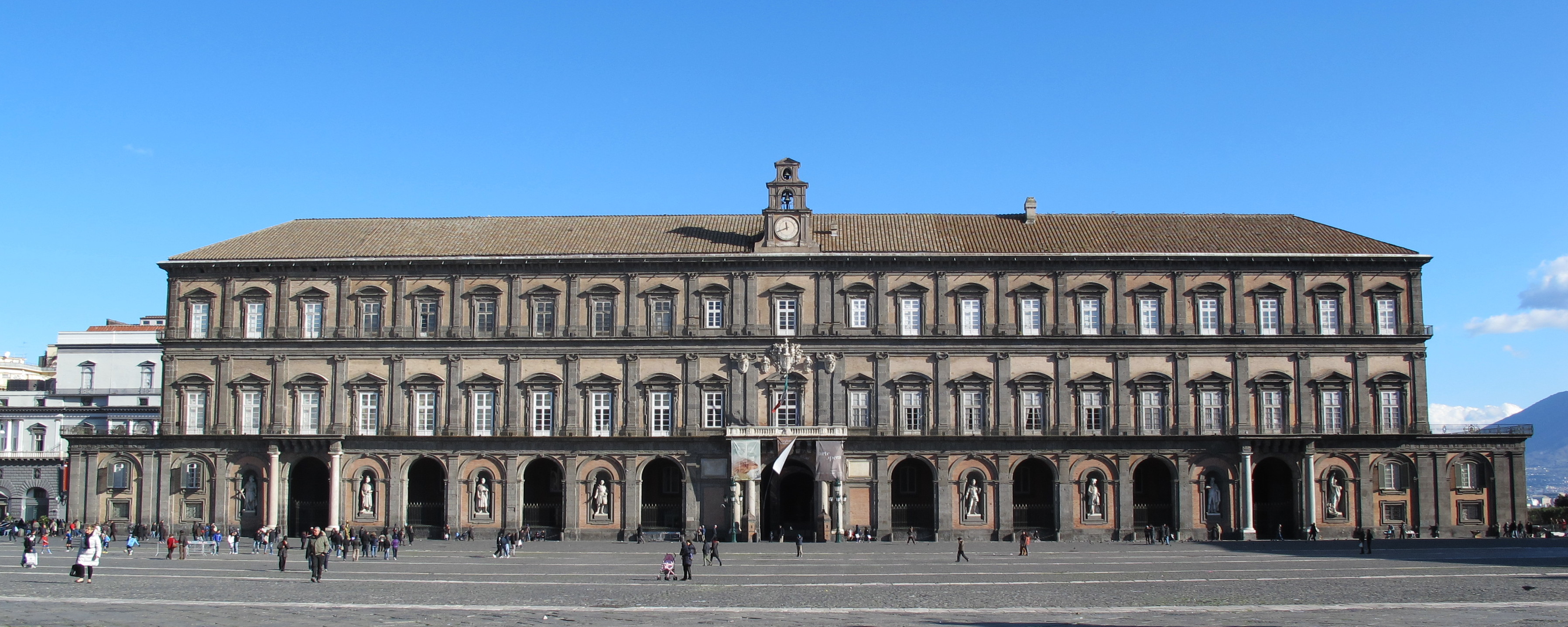
In front of the
Royal Palace of Naples
The Royal Palace of Naples ( it, Palazzo Reale di Napoli, italic=no, nap, Palazzo Riale ‘e Napule) is a palace, museum, and historical tourist destination located in central Naples, southern Italy.
It was one of the four residences near Napl ...
stands the
Galleria Umberto I
Galleria Umberto I is a public shopping gallery in Naples, southern Italy. It is located directly across from the San Carlo opera house. It was built between 1887–1890, and was the cornerstone in the decades-long rebuilding of Naples—called t ...
, which contains the
Coral Jewellery Museum
The Museo del Corallo is a small private museum of coral jewellery in Naples, in Campania in southern Italy. It also holds some cameos and jewellery in ivory
Ivory is a hard, white material from the tusks (traditionally from elephants) an ...
. Occupying a 19th-century palazzo renovated by the Portuguese architect
Álvaro Siza, the Museo d'Arte Contemporanea Donnaregina (MADRE) features an
enfilade
Enfilade and defilade are concepts in military tactics used to describe a military formation's exposure to enemy fire. A formation or position is "in enfilade" if weapon fire can be directed along its longest axis. A unit or position is "in de ...
procession of permanent installations by artists such as
Francesco Clemente
Francesco Clemente (born 23 March 1952) is an Italian contemporary artist. He has lived at various times in Italy, India and New York City. Some of his work is influenced by the traditional art and culture of India. He has worked in various art ...
,
Richard Serra
Richard Serra (born November 2, 1938) is an American artist known for his large-scale sculptures made for site-specific landscape, Urban area, urban, and Architecture, architectural settings. Serra's sculptures are notable for their material q ...
, and
Rebecca Horn
Rebecca Horn (born 24 March 1944, in Michelstadt, Hesse) is a German visual artist, who is best known for her installation art, film directing, and her body modifications such a''Einhorn'' (Unicorn) a body-suit with a very large horn projecting ve ...
. The 16th-century palace of Roccella hosts the Palazzo delle Arti Napoli, which contains the civic collections of art belonging to the City of Naples, and features temporary exhibits of art and culture. Palazzo Como, which dates from the 15th century, hosts the Museo Filangieri of
plastic arts, created in 1883 by Gaetano Filangieri.
Churches and other religious structures




Naples is the seat of the
Archdiocese of Naples
The Roman Catholic Archdiocese of Naples ( it, Arcidiocesi di Napoli; la, Archidioecesis Neapolitana) is a Roman Catholic Archdiocese in southern Italy, the see being in Naples. A Christian community was founded there in the 1st century AD a ...
; there are hundreds of churches in the city.
The
Cathedral of Naples is the city's premier place of worship; each year on 19 September, it hosts the longstanding Miracle of
Saint Januarius
Januarius ( ; la, Ianuarius; Neapolitan and it, Gennaro), also known as , was Bishop of Benevento and is a martyr and saint of the Catholic Church and the Eastern Orthodox Church. While no contemporary sources on his life are preserved, later ...
, the city's
patron saint
A patron saint, patroness saint, patron hallow or heavenly protector is a saint who in Catholicism, Anglicanism, or Eastern Orthodoxy is regarded as the heavenly advocate of a nation, place, craft, activity, class, clan, family, or perso ...
.
During the miracle, which thousands of Neapolitans flock to witness, the dried blood of Januarius is said to turn to liquid when brought close to holy
relics said to be of his body.
Below is a selective list of Naples' major churches, chapels, and monastery complexes:
*
Certosa di San Martino
The (" Charterhouse of St. Martin") is a former monastery complex, now a museum, in Naples, southern Italy. Along with Castel Sant'Elmo that stands beside it, this is the most visible landmark of the city, perched atop the Vomero hill that comman ...
*
Naples Cathedral
The Naples Cathedral ( it, Duomo di Napoli; nap, Viscuvato 'e Napule), or Cathedral of the Assumption of Mary ( it, Cattedrale di Santa Maria Assunta, links=no), is a Roman Catholic cathedral, the main church of Naples, southern Italy, and the s ...
*
San Francesco di Paola
*
Gesù Nuovo
*
Girolamini
*
San Domenico Maggiore
San Domenico Maggiore is a Gothic, Roman Catholic church and monastery, founded by the friars of the Dominican Order, and located in the square of the same name in the historic center of Naples.
History
The square is bordered by a street/alle ...
*
Santa Chiara
*
San Paolo Maggiore
San Paolo Maggiore is a basilica church in Naples, southern Italy, and the burial place of Gaetano Thiene, known as Saint Cajetan, founder of the Order of Clerics Regular (or Theatines). It is located on Piazza Gaetano, about 1-2 blocks north of V ...
*
Santa Maria della Sanità, Naples
*
Santa Maria del Carmine
*
Sant'Agostino alla Zecca
*
Madre del Buon Consiglio
*
Santa Maria Donna Regina Nuova
*
San Lorenzo Maggiore
San Lorenzo Maggiore is a town and ''comune'' in the province of Benevento, in the Campania region of southern Italy. It is a member of the Titerno Local Action Group.
Geography
San Lorenzo Maggiore covers 16.17 square kilometers of hilly land ...
*
Santa Maria Donna Regina Vecchia
*
Santa Caterina a Formiello
Santa Caterina a Formiello is a church in Naples, in southern Italy, located at the extreme eastern end of the old historic center of the city, on Via Carbonara and Piazza Enrico de Nicola, near the gate called Porta Capuana. The term ''Formiello' ...
*
Santissima Annunziata Maggiore
*
San Gregorio Armeno
*
San Giovanni a Carbonara
*
Santa Maria La Nova
Santa Maria la Nova is a Renaissance architecture, Renaissance style, now-deconsecrated, Roman Catholic church and monastery in central Naples. The church is located at the beginning of a side street directly across from the east side of the ma ...
*
Sant'Anna dei Lombardi
Sant'Anna dei Lombardi, ( it, St. Anne of the Lombards), and also known as Santa Maria di Monte Oliveto, is an ancient church and convent located in ''piazza Monteoliveto'' in central Naples, Italy. Across Monteoliveto street from the Fountain in ...
*
Sant'Eligio Maggiore
*
Santa Restituta
Santa Restituta is a church in Naples, southern Italy, dedicated to Saint Restituta. The foundation of the basilica is attributed to the Emperor Constantine the Great in the 4th century and is mentioned in a passage from the life of Pope Sylves ...
*
Sansevero Chapel
The Cappella Sansevero (also known as the Cappella Sansevero de' Sangri or Pietatella) is a chapel located on Via Francesco de Sanctis 19, just northwest of the church of San Domenico Maggiore, in the historic center of Naples, Italy. The chapel ...
*
San Pietro a Maiella
*
San Gennaro extra Moenia
San Gennaro Extra moenia, extra Moenia ("San Gennaro Beyond the Walls") is a church in Naples, Italy. It is located in the Rione Sanita on the large road that leads up to the Museo Nazionale di Capodimonte, Capodimonte museum and is an example of s ...
*
San Ferdinando
*
Pio Monte della Misericordia
The Pio Monte della Misericordia is a church in the historic center of Naples, southern Italy. It is famous for its art works, including Caravaggio's ''The Seven Works of Mercy''.
A charity brotherhood (''Pio Monte della Misericordia'' meaning ...
*
Santa Maria di Montesanto
*
Sant'Antonio Abate
Sant'Antonio Abate ( nap, Sant'Antuono) is a ''commune'' (municipality) in the Metropolitan City of Naples in the Italian region Campania, located about 30 km southeast of Naples.
Sant'Antonio Abate borders the following municipalities: A ...
*
Santa Caterina a Chiaia
*
San Pietro Martire
*
Hermitage of Camaldoli
The Hermitage of Camaldoli, in Italian Complesso dell'Eremo dei Camaldoli, is a hermitage in Naples, Campania, Italy — also known in Italian as ''Eremo Santissimo Salvatore Camaldoli.'' Originally intended as an actual hermitage, a place ...
*
Archbishop's Palace
Other features
Aside from the Piazza del Plebiscito, Naples has two other major public squares: the
Piazza Dante and the
Piazza dei Martiri. The latter originally had only a memorial to religious
martyr
A martyr (, ''mártys'', "witness", or , ''marturia'', stem , ''martyr-'') is someone who suffers persecution and death for advocating, renouncing, or refusing to renounce or advocate, a religious belief or other cause as demanded by an externa ...
s, but in 1866, after the
Italian unification, four lions were added, representing the four rebellions against the Bourbons.
The
San Gennaro dei Poveri is a Renaissance-era hospital for the poor, erected by the Spanish in 1667. It was the forerunner of a much more ambitious project, the
Bourbon Hospice for the Poor started by
Charles III
Charles III (Charles Philip Arthur George; born 14 November 1948) is King of the United Kingdom and the 14 other Commonwealth realms. He was the longest-serving heir apparent and Prince of Wales and, at age 73, became the oldest person t ...
. This was for the destitute and ill of the city; it also provided a self-sufficient community where the poor would live and work. Though a notable landmark, it is no longer a functioning hospital.
Subterranean Naples
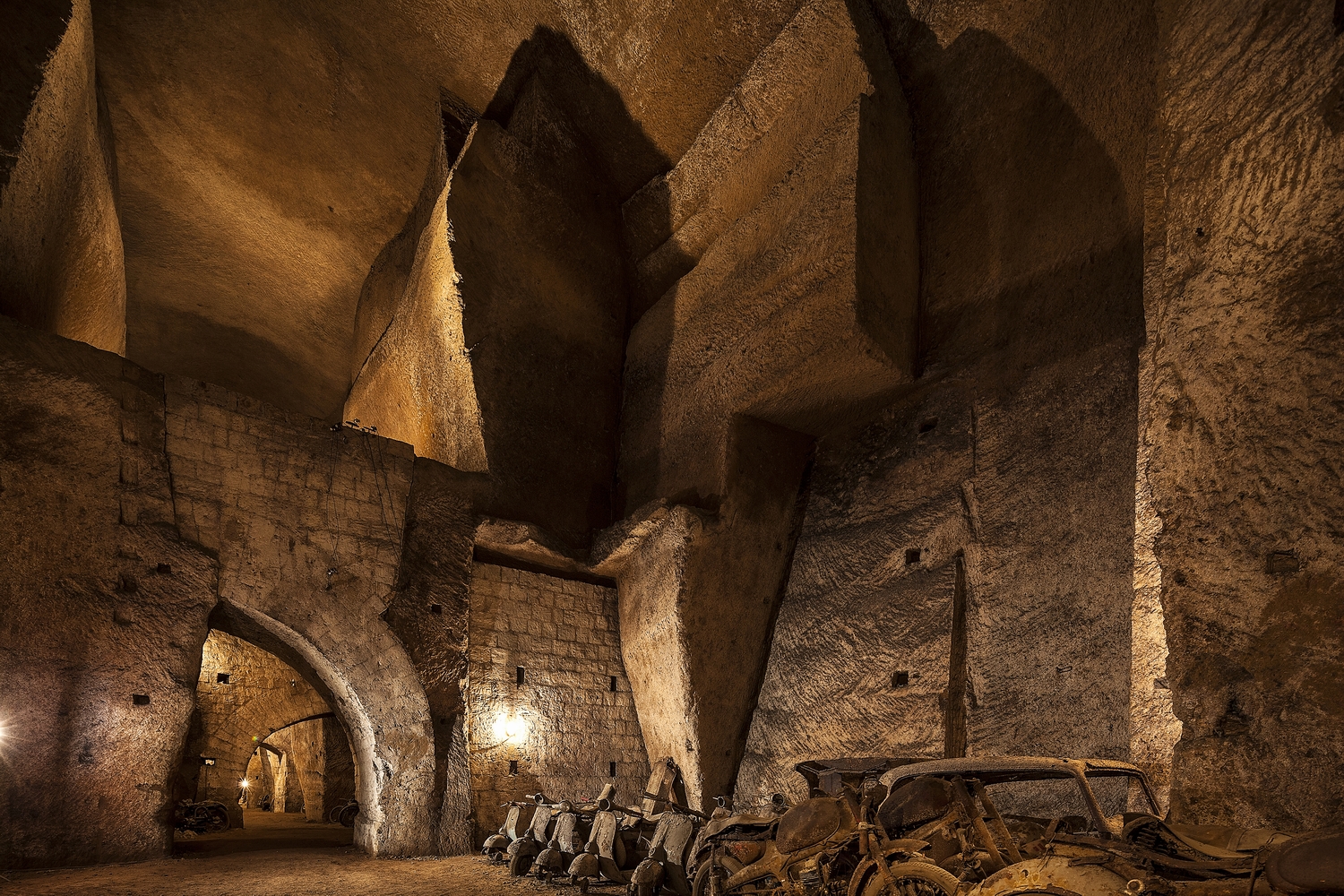 Underneath Naples
Underneath Naples lies a series of caves and structures created by centuries of mining, and the city rests atop a major
geothermal zone. There are also several ancient
Greco-Roman reservoirs dug out from the soft
tufo stone on which, and from which, much of the city is built. Approximately of the many kilometres of tunnels under the city can be visited from the
Napoli Sotteranea, situated in the historic centre of the city in
Via dei Tribunali. This system of tunnels and cisterns underlies most of the city and lies approximately below ground level. During
World War II
World War II or the Second World War, often abbreviated as WWII or WW2, was a world war that lasted from 1939 to 1945. It involved the vast majority of the world's countries—including all of the great powers—forming two opposing ...
, these tunnels were used as
air-raid shelters, and there are inscriptions on the walls depicting the suffering endured by the refugees of that era.
There are large
catacombs in and around the city, and other landmarks such as the
Piscina Mirabilis
The Piscina Mirabilis (Latin "wondrous pool") is an ancient Roman cistern on the Bacoli hill at the western end of the Gulf of Naples, southern Italy. It was one of the largest ancient cisterns. It was built under Augustus as suggested by the b ...
, the main cistern serving the
Bay of Naples during Roman times.
Several archeological excavations are also present; they revealed in
San Lorenzo Maggiore
San Lorenzo Maggiore is a town and ''comune'' in the province of Benevento, in the Campania region of southern Italy. It is a member of the Titerno Local Action Group.
Geography
San Lorenzo Maggiore covers 16.17 square kilometers of hilly land ...
the
macellum of Naples
The Macellum of Naples was the macellum or market building of the Ancient Rome, Roman city of Neapolis, now known as Naples. Due to the rise of the ground level the macellum is now located beneath the church of San Lorenzo Maggiore (Naples), San L ...
, and in
Santa Chiara, the biggest thermal complex of the city in Roman times.
Parks, gardens, villas, fountains and stairways
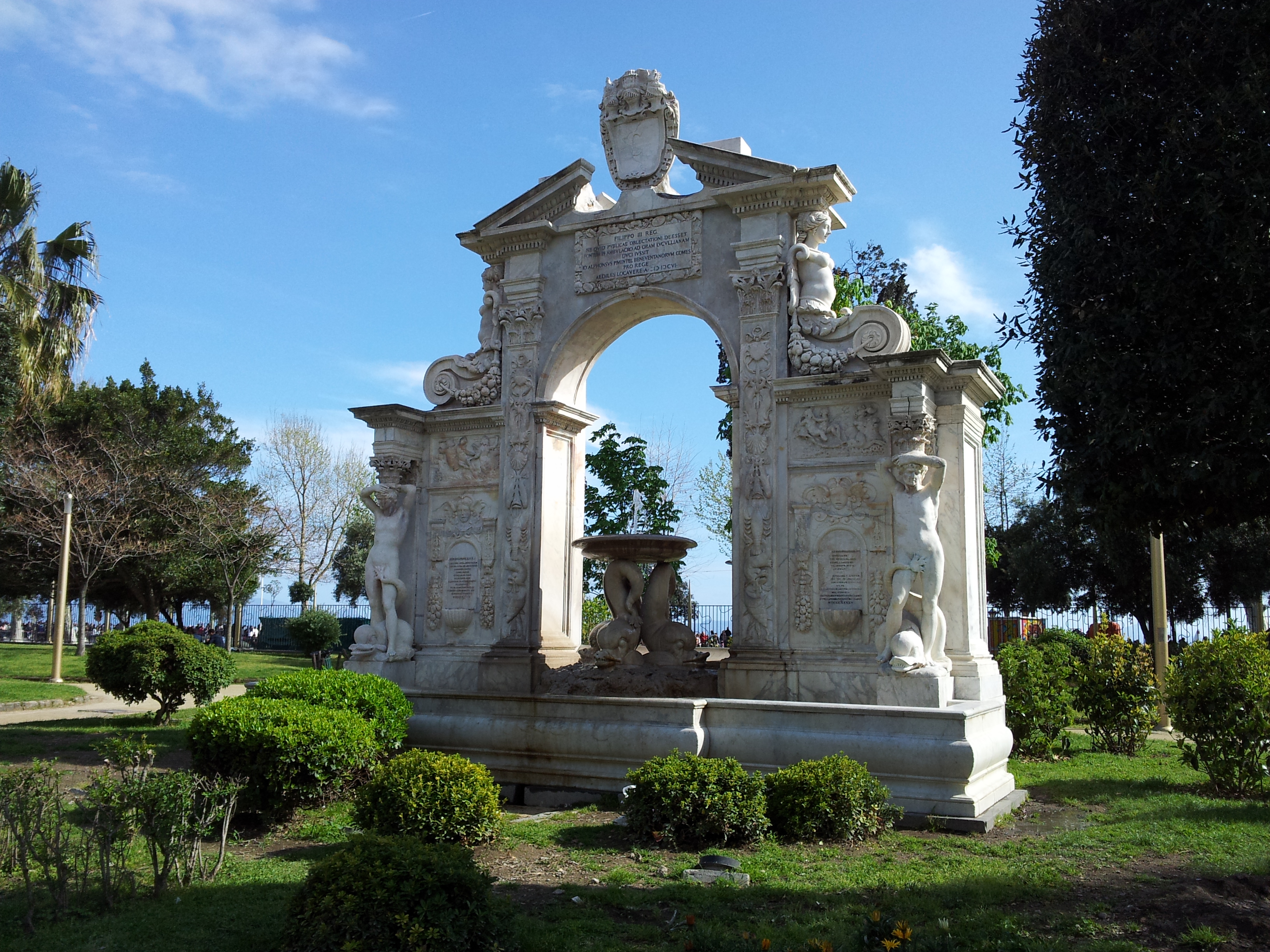

Of the various
public parks in Naples, the most prominent are the
Villa Comunale
The Villa Comunale is a park in Naples, southern Italy. It was built in the 1780s by King Ferdinand IV (later known as Ferdinand I of the Two Sicilies) on land reclaimed along the coast between the main body of the city and the small port of M ...
, which was built by the Bourbon king
Ferdinand IV in the 1780s; the park was originally a "Royal Garden", reserved for members of the royal family, but open to the public on special holidays. The Bosco di Capodimonte, the city's largest green space, served as a royal hunting reserve. The Park has 16 additional historical buildings, including residences, lodges, churches, fountains, statues, orchards and woods.
Another important park is the
Parco Virgiliano, which looks towards the tiny volcanic islet of
Nisida
Nisida is a volcanic islet of the Flegrean Islands archipelago, in southern Italy. It lies at a very short distance from Cape Posillipo, just north of Naples; it is now connected to the mainland by a stone bridge. The islet is almost circular, wi ...
; beyond Nisida lie
Procida
Procida (; nap, Proceta ) is one of the Flegrean Islands off the coast of Naples in southern Italy. The island is between Cape Miseno and the island of Ischia. With its tiny satellite island of Vivara, it is a ''comune'' of the Metropolitan Ci ...
and
Ischia
Ischia ( , , ) is a volcanic island in the Tyrrhenian Sea. It lies at the northern end of the Gulf of Naples, about from Naples. It is the largest of the Phlegrean Islands. Roughly trapezoidal in shape, it measures approximately east to west ...
.
was named after
Virgil
Publius Vergilius Maro (; traditional dates 15 October 7021 September 19 BC), usually called Virgil or Vergil ( ) in English, was an ancient Roman poet of the Augustan period. He composed three of the most famous poems in Latin literature: th ...
, the classical Roman poet and Latin writer who is thought to be
entombed nearby.
Naples is noted for its numerous stately
villa
A villa is a type of house that was originally an ancient Roman upper class country house. Since its origins in the Roman villa, the idea and function of a villa have evolved considerably. After the fall of the Roman Republic, villas became s ...
s, fountains and stairways, such as the
Neoclassical Villa Floridiana
The Villa Floridiana is a monumental house located amid a large park in the Vomero quarter in Naples, southern Italy. It overlooks the western Neapolitan suburbs of Chiaia and Mergellina.
History
Construction of a villa at the site was begun by ...
, the
Fountain of Neptune and the
Pedamentina stairways.
Neo-Gothic, ''Liberty Napoletano'' and modern architecture


Various buildings inspired by the
Gothic Revival are extant in Naples, due to the influence that this movement had on the Scottish-Indian architect
Lamont Young
Lamont H. Young (1851–1880) was an Australian assistant geological surveyor for the New South Wales Mines Department. He mysteriously disappeared while on field-work at Bermagui, New South Wales.
Disappearance
Young was inspecting the new g ...
, one of the most active Neapolitan architects of the late 19th and early 20th centuries. Young left a significant footprint in the cityscape and designed many urban projects, such as the city's first subway.
In the first years of the 20th century, a local version of the
Art Nouveau phenomenon, known as "Liberty Napoletano", developed in the city, creating many buildings which still stand today. In 1935, the Rationalist architect Luigi Cosenza designed a new fish market for the city. During the
Benito Mussolini era, the first structures of the city's "service center" were built, all in a Rationalist-Functionalist style, including the Palazzo delle Poste and the Pretura buildings. The
Centro Direzionale di Napoli
The Centro direzionale is a business district in Naples, Italy, close to the station of Napoli Centrale, they constitute an entire citadel. Designed by the Japanese architect Kenzō Tange, the entire complex was completed in 1995. It is the first ...
is the only adjacent cluster of skyscrapers in southern Europe.
Geography

The city is situated on the
Gulf of Naples
The Gulf of Naples (), also called the Bay of Naples, is a roughly 15-kilometer-wide (9.3 mi) gulf located along the south-western coast of Italy (province of Naples, Campania region). It opens to the west into the Mediterranean Sea. It i ...
, on the western coast of
southern Italy; it rises from sea level to an elevation of . The small rivers that formerly crossed the city's centre have since been covered by construction. It lies between two notable
volcanic
A volcano is a rupture in the crust of a planetary-mass object, such as Earth, that allows hot lava, volcanic ash, and gases to escape from a magma chamber below the surface.
On Earth, volcanoes are most often found where tectonic plates a ...
regions,
Mount Vesuvius
Mount Vesuvius ( ; it, Vesuvio ; nap, 'O Vesuvio , also or ; la, Vesuvius , also , or ) is a somma-stratovolcano located on the Gulf of Naples in Campania, Italy, about east of Naples and a short distance from the shore. It is one of ...
and the
Campi Flegrei
The Phlegraean Fields ( it, Campi Flegrei ; nap, Campe Flegree, from Ancient Greek 'to burn') is a large region of supervolcanic calderas situated to the west of Naples, Italy. It was declared a regional park in 2003. The area of the calde ...
( en, Phlegraean Fields). The islands of
Procida
Procida (; nap, Proceta ) is one of the Flegrean Islands off the coast of Naples in southern Italy. The island is between Cape Miseno and the island of Ischia. With its tiny satellite island of Vivara, it is a ''comune'' of the Metropolitan Ci ...
,
Capri and
Ischia
Ischia ( , , ) is a volcanic island in the Tyrrhenian Sea. It lies at the northern end of the Gulf of Naples, about from Naples. It is the largest of the Phlegrean Islands. Roughly trapezoidal in shape, it measures approximately east to west ...
can all be reached from Naples by
hydrofoils and ferries.
Sorrento
Sorrento (, ; nap, Surriento ; la, Surrentum) is a town overlooking the Bay of Naples in Southern Italy. A popular tourist destination, Sorrento is located on the Sorrentine Peninsula at the south-eastern terminus of the Circumvesuviana ra ...
and the
Amalfi Coast
The Amalfi Coast ( it, Costiera amalfitana) is a stretch of coastline in southern Italy overlooking the Tyrrhenian Sea and the Gulf of Salerno. It is located south of the Sorrentine Peninsula and north of the Cilentan Coast.
Celebrated worldw ...
are situated south of the city. At the same time, the Roman ruins of
Pompeii,
Herculaneum,
Oplontis
Oplontis is an ancient Roman archaeological site located in the town of Torre Annunziata, south of Naples in the Campania region of southern Italy. The excavated site comprises two Roman villas, the best-known of which is Villa A, the so-called ...
and
Stabiae, which were destroyed in the eruption of Vesuvius in 79 AD, are also visible nearby. The port towns of
Pozzuoli
Pozzuoli (; ; ) is a city and ''comune'' of the Metropolitan City of Naples, in the Italian region of Campania. It is the main city of the Phlegrean Peninsula.
History
Pozzuoli began as the Greek colony of ''Dicaearchia'' ( el, Δικα ...
and
Baia
Baia (german: Baja, Stadt Molde, or Moldenmarkt; hu, Moldvabánya; lat, Civitas Moldaviae) is a commune in Suceava County, in the historical region of Western Moldavia, northeastern Romania with a population of 6,793 (2002 census).[Portus Julius
(alternatively spelled in the Latin ) was the first harbour specifically constructed to be a base for the Roman western naval fleet, the ; the eastern fleet was based in the Port of Ravenna. The port was located at Misenum on a peninsula at th ...]
, lie to the west of the city.
Quarters
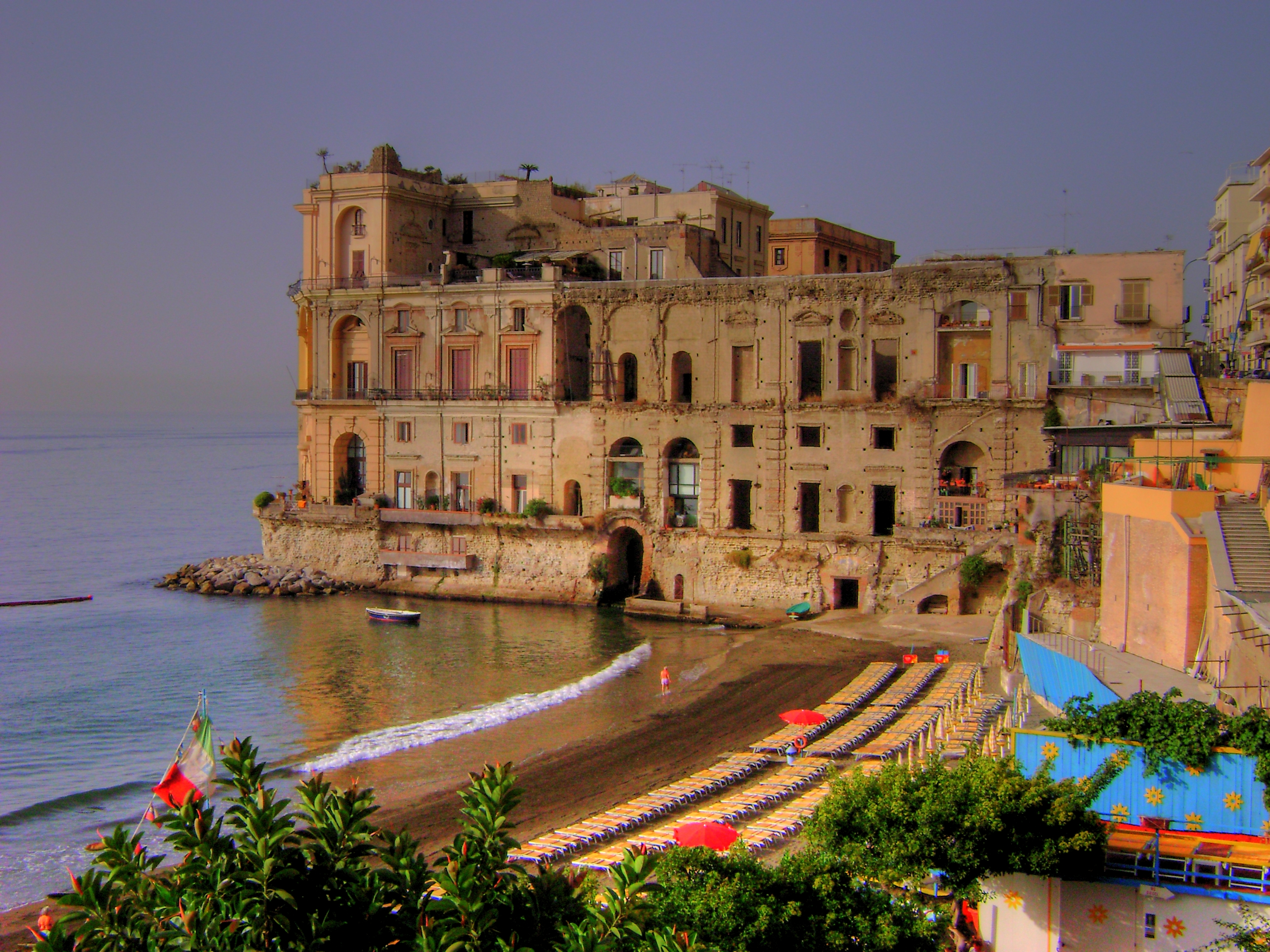

The thirty quarters (''
quartieri'') of Naples are listed below. For administrative purposes, these thirty districts are grouped together into ten governmental community boards.
Climate
Naples has a
Mediterranean climate
A Mediterranean climate (also called a dry summer temperate climate ''Cs'') is a temperate climate sub-type, generally characterized by warm, dry summers and mild, fairly wet winters; these weather conditions are typically experienced in the ...
(''Csa'') in the
Köppen climate classification
The Köppen climate classification is one of the most widely used climate classification systems. It was first published by German-Russian climatologist Wladimir Köppen (1846–1940) in 1884, with several later modifications by Köppen, notabl ...
. The climate and fertility of the
Gulf of Naples
The Gulf of Naples (), also called the Bay of Naples, is a roughly 15-kilometer-wide (9.3 mi) gulf located along the south-western coast of Italy (province of Naples, Campania region). It opens to the west into the Mediterranean Sea. It i ...
made the region famous during Roman times, when emperors such as
Claudius and
Tiberius
Tiberius Julius Caesar Augustus (; 16 November 42 BC – 16 March AD 37) was the second Roman emperor. He reigned from AD 14 until 37, succeeding his stepfather, the first Roman emperor Augustus. Tiberius was born in Rome in 42 BC. His father ...
holidayed near the city.
The climate is a crossover between maritime and continental features, as typical of peninsular Italy. Maritime features mitigate the winters but occasionally cause heavy rainfall, particularly in the autumn and winter. Summers feature high temperatures and humidity. The continental influence still ensures summer highs averaging near , and Naples falls within the
subtropical climate range with summer daily-mean above with hot days, warm nights and occasional summer thunderstorms.
Winters are mild, and snow is rare in the city area but frequent on Mount Vesuvius.
November is the wettest month in Naples, while July is the driest.
Demographics

, the population of the ''comune di Napoli'' totals around 910,000. Naples' wider
metropolitan area, sometimes known as Greater Naples, has a population of approximately 4.4 million.
The
demographic profile
Demographic profiling is a form of demographic analysis used by marketers so that they may be as efficient as possible with advertising products or services and identifying any possible gaps in their marketing strategy. Demographic profiling can e ...
for the Neapolitan province in general is relatively young: 19% are under the age of 14, while 13% are over 65, compared to the national average of 14% and 19%, respectively.
Naples has a higher percentage of females (52.5%) than males (47.5%).
[‘City’ population (i.e. that of the '']comune
The (; plural: ) is a local administrative division of Italy, roughly equivalent to a township or municipality. It is the third-level administrative division of Italy, after regions ('' regioni'') and provinces (''province''). The can also ...
'' or municipality)
City of Naples
. Comuni-italiani.it. 2012. Retrieved 11 April 2012. Naples currently has a higher
birth rate
The birth rate for a given period is the total number of live human births per 1,000 population divided by the length of the period in years. The number of live births is normally taken from a universal registration system for births; populati ...
than other parts of Italy, with 10.46 births per 1,000 inhabitants, compared to the Italian average of 9.45 births.
Naples's population rose from 621,000 in 1901 to 1,226,000 in 1971, declining to 910,000 in 2022 as city dwellers moved to the suburbs. According to different sources, Naples'
metropolitan area is either the
second-most-populated metropolitan area in Italy after
Milan
Milan ( , , Lombard: ; it, Milano ) is a city in northern Italy, capital of Lombardy, and the second-most populous city proper in Italy after Rome. The city proper has a population of about 1.4 million, while its metropolitan city h ...
(with 4,434,136 inhabitants according to Svimez Data) or the third (with 3.5 million inhabitants according to the
OECD
The Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development (OECD; french: Organisation de coopération et de développement économiques, ''OCDE'') is an intergovernmental organisation with 38 member countries, founded in 1961 to stimulate e ...
).
In addition, Naples is Italy's most densely populated major city, with approximately 8,182 people per square kilometre;
however, it has seen a notable decline in population density since 2003, when the figure was over 9,000 people per square kilometre.
In contrast to many northern Italian cities, there are relatively few foreign immigrants in Naples; 94.3% of the city's inhabitants are
Italian nationals. In 2017, there were a total of 58,203 foreigners in the city of Naples; the majority of these are mostly from
Sri Lanka, China, Ukraine, Pakistan and Romania.
Statistics show that, in the past, the vast majority of immigrants in Naples were female; this happened because male immigrants in Italy tended to head to the wealthier north.
Education
Naples is noted for its numerous higher education institutes and research centres. Naples hosts what is thought to be the oldest state university in the world, in the form of the
University of Naples Federico II
The University of Naples Federico II ( it, Università degli Studi di Napoli Federico II) is a public university in Naples, Italy. Founded in 1224, it is the oldest public non-sectarian university in the world, and is now organized into 26 depar ...
, which was founded by
Frederick II in 1224. The university is among the most prominent in Italy, with around 100,000 students and over 3,000 professors in 2007. It is host to the
Botanical Garden of Naples, which was opened in 1807 by
Joseph Bonaparte
it, Giuseppe-Napoleone Buonaparte es, José Napoleón Bonaparte
, house = Bonaparte
, father = Carlo Buonaparte
, mother = Letizia Ramolino
, birth_date = 7 January 1768
, birth_place = Corte, Corsica, Republic of ...
, using plans drawn up under the Bourbon king
Ferdinand IV. The garden's 15 hectares feature around 25,000 samples of over 10,000 species.
Naples is also served by the "
Second University" (today named
University of Campania Luigi Vanvitelli), a modern university which opened in 1989, and which has strong links to the nearby
province of Caserta
The Province of Caserta ( it, Provincia di Caserta) is a province in the Campania region of southern Italy. Its capital is the city of Caserta, situated about by road north of Naples. The province has an area of , and had a total population of ...
. Another notable centre of education is the
Istituto Universitario Orientale, which specialises in
Eastern culture, and was founded by the
Jesuit missionary Matteo Ripa in 1732, after he returned from the court of
Kangxi
The Kangxi Emperor (4 May 1654– 20 December 1722), also known by his temple name Emperor Shengzu of Qing, born Xuanye, was the third emperor of the Qing dynasty, and the second Qing emperor to rule over China proper, reigning from 1661 to 1 ...
, the
Emperor
An emperor (from la, imperator, via fro, empereor) is a monarch, and usually the sovereignty, sovereign ruler of an empire or another type of imperial realm. Empress, the female equivalent, may indicate an emperor's wife (empress consort), ...
of the
Manchu Qing Dynasty
The Qing dynasty ( ), officially the Great Qing,, was a Manchu-led imperial dynasty of China and the last orthodox dynasty in Chinese history. It emerged from the Later Jin dynasty founded by the Jianzhou Jurchens, a Tungusic-spea ...
of China.
Other prominent universities in Naples include the
Parthenope University of Naples, the private
Istituto Universitario Suor Orsola Benincasa, and the
Jesuit Theological Seminary of Southern Italy. The
San Pietro a Maiella music conservatory is the city's foremost institution of musical education; the earliest Neapolitan music conservatories were founded in the 16th century under the Spanish. The
Academy of Fine Arts
The following is a list of notable art schools.
Accredited non-profit art and design colleges
* Adelaide Central School of Art
* Alberta College of Art and Design
* Art Academy of Cincinnati
* Art Center College of Design
* The Art Institute ...
located on the Via Santa Maria di Costantinopoli is the city's foremost art school and one of the oldest in Italy.
Naples hosts also the
Astronomical Observatory of Capodimonte
The Astronomical Observatory of Capodimonte ( it, Osservatorio Astronomico di Capodimonte, italic=no) is the Neapolitan department of Istituto Nazionale di Astrofisica (National Institute for Astrophysics, INAF), the most important Italian instit ...
, established in 1812 by the king
Joachim Murat
Joachim Murat ( , also , ; it, Gioacchino Murati; 25 March 1767 – 13 October 1815) was a French military commander and statesman who served during the French Revolutionary Wars and Napoleonic Wars. Under the French Empire he received the ...
and the astronomer Federigo Zuccari, the oldest
marine zoological study station in the world,
Stazione Zoologica
The Stazione Zoologica Anton Dohrn is a research institute in Naples, Italy, devoted to basic research in biology. Research is largely interdisciplinary involving the fields of evolution, biochemistry, molecular biology, neurobiology, cell bio ...
Anton Dohrn, created in 1872 by German scientist
Anton Dohrn
Felix Anton Dohrn FRS FRSE (29 December 1840 – 26 September 1909) was a prominent German Darwinist and the founder and first director of the first zoological research station in the world, the Stazione Zoologica in Naples, Italy. He worked ...
, and the world's oldest permanent volcano observatory, the
Vesuvius Observatory, founded in 1841. The Observatory lies on the slopes of Mount Vesuvius, near the city of
Ercolano
Ercolano () is a town and ''comune'' in the Metropolitan City of Naples, Campania of Southern Italy. It lies at the western foot of Mount Vesuvius, on the Bay of Naples, just southeast of the city of Naples. The medieval town of Resina () was bu ...
, and is now a permanent specialised institute of the
Italian National Institute of Geophysics.
Politics


Governance
Each of the 7,904 ''
comune
The (; plural: ) is a local administrative division of Italy, roughly equivalent to a township or municipality. It is the third-level administrative division of Italy, after regions ('' regioni'') and provinces (''province''). The can also ...
'' in Italy is today represented locally by a
city council
A municipal council is the legislative body of a municipality or local government area. Depending on the location and classification of the municipality it may be known as a city council, town council, town board, community council, rural counc ...
headed by an elected mayor, known as a ''sindaco'' and informally called the first citizen (''primo cittadino''). This system, or one very similar to it, has been in place since the invasion of Italy by
Napoleonic
Napoleon Bonaparte ; it, Napoleone Bonaparte, ; co, Napulione Buonaparte. (born Napoleone Buonaparte; 15 August 1769 – 5 May 1821), later known by his regnal name Napoleon I, was a French military commander and political leader wh ...
forces in 1808. When the
Kingdom of the Two Sicilies was restored, the system was kept in place with members of the nobility filling mayoral roles. By the end of the 19th century,
party politics
A political party is an organization that coordinates candidates to compete in a particular country's elections. It is common for the members of a party to hold similar ideas about politics, and parties may promote specific political ideology ...
had begun to emerge; during the
fascist era, each commune was represented by a ''podestà''. Since
World War II
World War II or the Second World War, often abbreviated as WWII or WW2, was a world war that lasted from 1939 to 1945. It involved the vast majority of the world's countries—including all of the great powers—forming two opposing ...
, the political landscape of Naples has been neither strongly
right-wing nor
left-wing
Left-wing politics describes the range of political ideologies that support and seek to achieve social equality and egalitarianism, often in opposition to social hierarchy. Left-wing politics typically involve a concern for those in soci ...
– both
Christian democrats
__NOTOC__
Christian democratic parties are political parties that seek to apply Christian principles to public policy. The underlying Christian democracy movement emerged in 19th-century Europe, largely under the influence of Catholic social ...
and
democratic socialists
Democratic socialism is a left-wing political philosophy that supports political democracy and some form of a socially owned economy, with a particular emphasis on economic democracy, workplace democracy, and workers' self-management within ...
have governed the city at different times, with roughly equal frequency. Currently, the mayor of Naples is
Gaetano Manfredi
Gaetano Manfredi ( Ottaviano, 4 January 1964) is an Italian university professor and politician. He has been mayor of Naples since 2021, and has served as the Minister of University and Research in the second government of Giuseppe Conte from ...
, an
independent politician
An independent or non-partisan politician is a politician not affiliated with any political party or bureaucratic association. There are numerous reasons why someone may stand for office as an independent.
Some politicians have political views th ...
, former
minister of university and research in the
second Conte government, and former rector of the
University of Naples Federico II
The University of Naples Federico II ( it, Università degli Studi di Napoli Federico II) is a public university in Naples, Italy. Founded in 1224, it is the oldest public non-sectarian university in the world, and is now organized into 26 depar ...
.
Administrative subdivisions
Economy


Naples, within its administrative limits, is Italy's fourth-largest economy after
Milan
Milan ( , , Lombard: ; it, Milano ) is a city in northern Italy, capital of Lombardy, and the second-most populous city proper in Italy after Rome. The city proper has a population of about 1.4 million, while its metropolitan city h ...
, Rome and
Turin
Turin ( , Piedmontese: ; it, Torino ) is a city and an important business and cultural centre in Northern Italy. It is the capital city of Piedmont and of the Metropolitan City of Turin, and was the first Italian capital from 1861 to 1865. The ...
, and is the world's
103rd-largest urban economy by
purchasing power
Purchasing power is the amount of goods and services that can be purchased with a unit of currency. For example, if one had taken one unit of currency to a store in the 1950s, it would have been possible to buy a greater number of items than would ...
, with an estimated 2011 GDP of US$83.6 billion, equivalent to $28,749 per capita.
["Which are the largest city economies in the world and how might this change by 2025?"](_blank)
PricewaterhouseCoopers
PricewaterhouseCoopers is an international professional services brand of firms, operating as partnerships under the PwC brand. It is the second-largest professional services network in the world and is considered one of the Big Four accounti ...
. November 2009. Retrieved 23 April 2012.
Naples is a major
cargo terminal
A container port or container terminal is a facility where cargo containers are transshipped between different transport vehicles, for onward transportation. The transshipment may be between container ships and land vehicles, for example train ...
, and the
port of Naples is one of the Mediterranean's largest and busiest. The city has experienced significant economic growth since World War II, but joblessness remains a major problem, and the city is characterised by high levels of political corruption and
organised crime
Organized crime (or organised crime) is a category of transnational, national, or local groupings of highly centralized enterprises run by criminals to engage in illegal activity, most commonly for profit. While organized crime is generally th ...
, as well as in other cities of the country.
Naples is a major national, and international tourist destination, one of Italy's and Europe's top tourist cities. Tourists began visiting Naples in the 18th century during the
Grand Tour
The Grand Tour was the principally 17th- to early 19th-century custom of a traditional trip through Europe, with Italy as a key destination, undertaken by upper-class young European men of sufficient means and rank (typically accompanied by a tut ...
.
In the last decades, there has been a move away from a traditional agriculture-based economy in the province of Naples to one based on
service industries
Service industries are those not directly concerned with the production of physical goods (such as agriculture and manufacturing).
Some service industries, including transportation, wholesale trade and retail trade are part of the supply chain de ...
. The service sector employs the majority of Neapolitans, although more than half of these are small enterprises with fewer than 20 workers; about 70 companies are said to be medium-sized with more than 200 workers, and about 15 have more than 500 workers.
Tourism
Naples is, with
Florence
Florence ( ; it, Firenze ) is a city in Central Italy and the capital city of the Tuscany Regions of Italy, region. It is the most populated city in Tuscany, with 383,083 inhabitants in 2016, and over 1,520,000 in its metropolitan area.Bilan ...
,
Rome
, established_title = Founded
, established_date = 753 BC
, founder = King Romulus (legendary)
, image_map = Map of comune of Rome (metropolitan city of Capital Rome, region Lazio, Italy).svg
, map_caption ...
,
Venice
Venice ( ; it, Venezia ; vec, Venesia or ) is a city in northeastern Italy and the capital of the Veneto region. It is built on a group of 118 small islands that are separated by canals and linked by over 400 bridges. The isla ...
and
Milan
Milan ( , , Lombard: ; it, Milano ) is a city in northern Italy, capital of Lombardy, and the second-most populous city proper in Italy after Rome. The city proper has a population of about 1.4 million, while its metropolitan city h ...
, one of the main Italian tourist destinations. With 3,700,000 visitors in 2018, the city has completely emerged from the strong tourist depression of past decades (due primarily to the unilateral destination of an industrial city but also to the damage to image caused by the Italian media, from the
1980 Irpinia earthquake
The 1980 Irpinia earthquake ( it, Terremoto dell'Irpinia) took place in Italy on 23 November 1980, with a moment magnitude of 6.9 and a maximum Mercalli intensity of X (''Extreme''). It left at least 2,483 people dead, at least 7,700 injured, an ...
and the
waste crisis, in favor of the coastal centers of its
metropolitan area). To adequately assess the phenomenon, however, it must be considered that a large slice of tourists visit Naples per year, staying in the numerous localities in its surroundings, connected to the city with both private and public direct lines. Daily visits to Naples are carried out by various Roman tour operators and by all the main tourist resorts of
Campania
(man), it, Campana (woman)
, population_note =
, population_blank1_title =
, population_blank1 =
, demographics_type1 =
, demographics1_footnotes =
, demographics1_title1 =
, demographics1_info1 =
, demog ...
: as of 2019, Naples is the tenth most visited
municipality in Italy and the first in the
South.
The sector is constantly growing and the prospect of reaching the art cities of its level is once again expected in a relatively short time; tourism is increasingly assuming a decisive weight for the city's economy, which is why, exactly as happened for example in the case of Venice or Florence, the risk of gentrification of the
historic center is now high.
Transport



Naples is served by several major motorways (
it: ''
autostrade''). The
Autostrada A1, the longest
motorway in Italy, links Naples to
Milan
Milan ( , , Lombard: ; it, Milano ) is a city in northern Italy, capital of Lombardy, and the second-most populous city proper in Italy after Rome. The city proper has a population of about 1.4 million, while its metropolitan city h ...
. The
A3 runs southwards from Naples to
Salerno, where the
motorway to Reggio Calabria begins, while the A16 runs east to
Canosa. The A16 is nicknamed the ''autostrada dei Due Mari'' ("Motorway of the Two Seas") because it connects the
Tyrrhenian Sea
The Tyrrhenian Sea (; it, Mar Tirreno , french: Mer Tyrrhénienne , sc, Mare Tirrenu, co, Mari Tirrenu, scn, Mari Tirrenu, nap, Mare Tirreno) is part of the Mediterranean Sea off the western coast of Italy. It is named for the Tyrrhenian pe ...
to the
Adriatic Sea
The Adriatic Sea () is a body of water separating the Italian Peninsula from the Balkan Peninsula. The Adriatic is the northernmost arm of the Mediterranean Sea, extending from the Strait of Otranto (where it connects to the Ionian Sea) to t ...
.
Suburban rail services are provided by
Trenitalia
Trenitalia is the primary train operator in Italy. A subsidiary of Ferrovie dello Stato Italiane, itself owned by the Italian government, the company was established in 2000 following a European Union directive on the deregulation of rail tra ...
,
Circumvesuviana
Circumvesuviana () is a railway network in the east of the Naples metropolitan area, previously run by a company of the same name, now operated by Ente Autonomo Volturno. Electrically powered throughout, the system uses the narrow gauge of ...
,
Ferrovia Cumana and
Metronapoli
Metronapoli SpA was an Italian company responsible for the provision of public transport in the city of Naples, and its primary function was the operation and maintenance of the Naples Metro system. It was founded on 26 July 2000 and became operat ...
.
The city's main railway station is
Napoli Centrale, which is located in Piazza Garibaldi; other significant stations include the
Napoli Campi Flegrei and
Napoli Mergellina.
Napoli Afragola serves high-speed trains that do not start or finish at Napoli Centrale. Naples' streets are famously narrow (it was the first city in the world to set up a pedestrian one-way street), so the general public commonly use compact
hatchback cars and
scooters for personal transit. Since 2007 trains running at have connected Naples with Rome with a journey time of under an hour, and direct high speed services also operate to Florence, Bologna, Milan, Turin and Salerno. Direct sleeper 'boat train' services operate nightly to cities in Sicily.
The port of Naples runs several ferry,
hydrofoil, and
SWATH
A small waterplane area twin hull, better known by the acronym SWATH, is a catamaran design that minimizes hull cross section area at the sea's surface. Minimizing the ship's volume near the surface area of the sea, where wave energy is located ...
catamaran lines to
Capri,
Ischia
Ischia ( , , ) is a volcanic island in the Tyrrhenian Sea. It lies at the northern end of the Gulf of Naples, about from Naples. It is the largest of the Phlegrean Islands. Roughly trapezoidal in shape, it measures approximately east to west ...
and
Sorrento
Sorrento (, ; nap, Surriento ; la, Surrentum) is a town overlooking the Bay of Naples in Southern Italy. A popular tourist destination, Sorrento is located on the Sorrentine Peninsula at the south-eastern terminus of the Circumvesuviana ra ...
,
Salerno,
Positano
Positano (Campanian: ) is a village and ''comune'' on the Amalfi Coast (Province of Salerno), in Campania, Italy, mainly in an enclave in the hills leading down to the coast.
Climate
The climate of Positano is very mild, of the Mediterranean ...
and
Amalfi
Amalfi (, , ) is a town and ''comune'' in the province of Salerno, in the region of Campania, Italy, on the Gulf of Salerno. It lies at the mouth of a deep ravine, at the foot of Monte Cerreto (1,315 metres, 4,314 feet), surrounded by dramati ...
.
Services are also available to
Sicily
(man) it, Siciliana (woman)
, population_note =
, population_blank1_title =
, population_blank1 =
, demographics_type1 = Ethnicity
, demographics1_footnotes =
, demographi ...
, Sardinia,
Ponza
Ponza (Italian: ''isola di Ponza'' ) is the largest island of the Italian Pontine Islands archipelago, located south of Cape Circeo in the Tyrrhenian Sea. It is also the name of the commune of the island, a part of the province of Latina in th ...
and the
Aeolian Islands.
The port serves over 6 million local passengers annually,
plus a further 1 million international
cruise ship
Cruise ships are large passenger ships used mainly for vacationing. Unlike ocean liners, which are used for transport, cruise ships typically embark on round-trip voyages to various ports-of-call, where passengers may go on tours known as ...
passengers.
A regional hydrofoil transport service, the "Metropolitana del Mare", runs annually from July to September, maintained by a consortium of shipowners and local administrations.
The
Naples International Airport is located in the suburb of
San Pietro a Patierno
San Pietro a Patierno is a suburb of Naples, the chief city in Campania, Italy.
Geography
It is one of the largest suburbs of Naples and is relatively lightly populated compared to surrounding areas, with around 20,000 residents. The district of ...
. It is the largest airport in southern Italy, with around 250 national and international flights arriving or departing daily.
The average commute with public transit in Naples on a weekday is 77 minutes. Nineteen per cent of public transit commuters ride for more than 2 hours every day. The average time people wait at a stop or station for public transit is 27 minutes, while 56% of riders wait for over 20 minutes. The average distance people usually ride in a single trip with public transit is , while 11% travel for over in a single direction.
Urban public transport
Naples has an extensive public transport network, including
trams
A tram (called a streetcar or trolley in North America) is a rail vehicle that travels on tramway tracks on public urban streets; some include segments on segregated right-of-way. The tramlines or networks operated as public transport ar ...
, buses and
trolleybus
A trolleybus (also known as trolley bus, trolley coach, trackless trolley, trackless tramin the 1910s and 1920sJoyce, J.; King, J. S.; and Newman, A. G. (1986). ''British Trolleybus Systems'', pp. 9, 12. London: Ian Allan Publishing. .or trol ...
es,
most of which are operated by the municipally owned company
Azienda Napoletana Mobilità (ANM).
The city furthermore operates the ''
Metropolitana di Napoli'', the
Naples Metro
The Naples Metro ( it, Metropolitana di Napoli; nap, Metrupulitana 'e Napule) is the rapid transit system serving the city of Naples, Italy. The system comprises three underground rapid transit lines ( Line 1, Line 6 and the Naples-Aversa Me ...
, an underground
rapid transit
Rapid transit or mass rapid transit (MRT), also known as heavy rail or metro, is a type of high-capacity public transport generally found in urban areas. A rapid transit system that primarily or traditionally runs below the surface may be ...
railway system which integrates both surface railway lines and the city's
metro stations,
many of which are noted for their decorative architecture and
public art
Public art is art in any media whose form, function and meaning are created for the general public through a public process. It is a specific art genre with its own professional and critical discourse. Public art is visually and physically acce ...
. In fact, the station of Via Toledo is often in the top spots of the rankings of the most beautiful metro stations in the world.
There are also four
funicular
A funicular (, , ) is a type of cable railway system that connects points along a railway track laid on a steep slope. The system is characterized by two counterbalanced carriages (also called cars or trains) permanently attached to opposite e ...
s in the city (operated by ANM):
''Centrale'',
''Chiaia'',
''Montesanto'' and
''Mergellina''. Four public
elevator
An elevator or lift is a cable-assisted, hydraulic cylinder-assisted, or roller-track assisted machine that vertically transports people or freight between floors, levels, or decks of a building, vessel, or other structure. They a ...
s are in operation in the city: within the bridge of
Chiaia, in via Acton, near the Sanità Bridge, and in the Ventaglieri Park, accompanied by two public
escalator
An escalator is a moving staircase which carries people between floors of a building or structure. It consists of a motor-driven chain of individually linked steps on a track which cycle on a pair of tracks which keep the step tread horizo ...
s.
Culture
Art
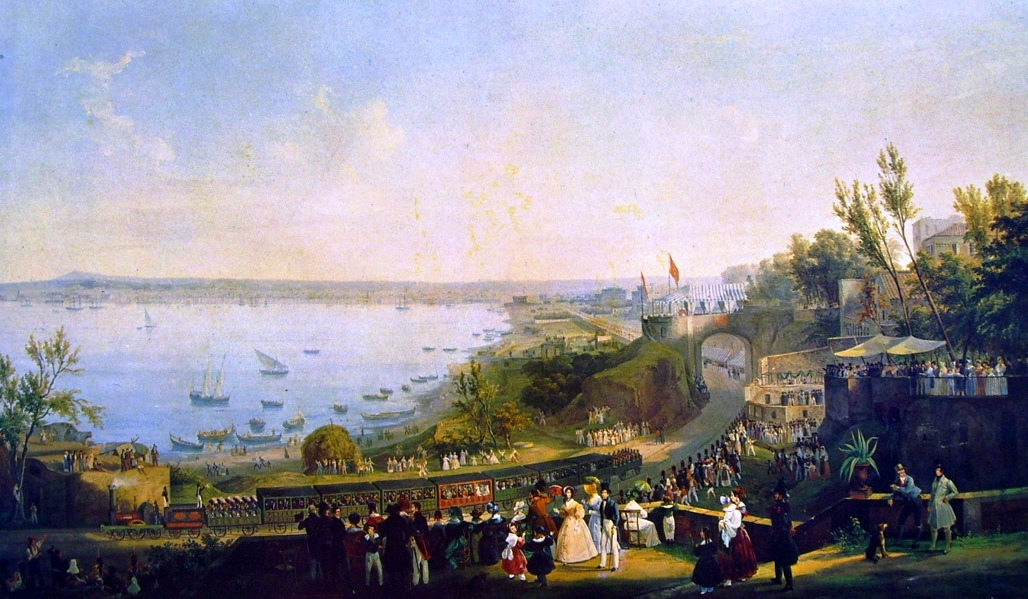
Naples has long been a centre of art and architecture, dotted with Medieval-, Baroque- and Renaissance-era churches, castles and palaces. A critical factor in the development of the Neapolitan school of painting was Caravaggio's arrival in Naples in 1606. In the 18th century, Naples went through a period of
neoclassicism, following the discovery of the remarkably intact Roman ruins of
Herculaneum and
Pompeii.
The
Neapolitan Academy of Fine Arts, founded by
Charles III of Bourbon in 1752 as the Real Accademia di Disegno (
en: ''Royal Academy of Design''), was the centre of the artistic School of
Posillipo
Posillipo (; nap, Pusilleco ) is an affluent residential quarter of Naples, southern Italy, located along the northern coast of the Gulf of Naples.
From the 1st century BC the Bay of Naples witnessed the rise of villas constructed by elite Roma ...
in the 19th century. Artists such as
Domenico Morelli
Domenico Morelli (4 August 182313 August 1901) was an Italian painter, who mainly produced historical and religious works. Morelli was immensely influential in the arts of the second half of the 19th century, both as director of the Accademia di ...
,
Giacomo Di Chirico,
Francesco Saverio Altamura and
Gioacchino Toma
Gioacchino Toma (24 January 1836 12 January 1891) was an Italian art instructor and painter, noted primarily for historic, realistic and genre subjects in a Romantic style.
Toward the end of his life, Toma authored his autobiography, ''Memorie ...
worked in Naples during this period, and many of their works are now exhibited in the academy's art collection. The modern Academy offers courses in painting,
decorating, sculpture, design,
restoration, and urban planning. Naples is also known for its theatres, which are among the oldest in Europe: the
Teatro di San Carlo
The Real Teatro di San Carlo ("Royal Theatre of Saint Charles"), as originally named by the Bourbon monarchy but today known simply as the Teatro (di) San Carlo, is an opera house in Naples, Italy, connected to the Royal Palace and adjacent ...
opera house
An opera house is a theatre building used for performances of opera. It usually includes a stage, an orchestra pit, audience seating, and backstage facilities for costumes and building sets.
While some venues are constructed specifically fo ...
dates back to the 18th century.
Naples is also the home of the artistic tradition of
Capodimonte porcelain. In 1743, Charles of Bourbon founded the Royal Factory of Capodimonte, many of whose artworks are now on display in the
Museum of Capodimonte
Museo di Capodimonte is an art museum located in the Palace of Capodimonte, a grand Bourbon palazzo in Naples, Italy. The museum is the prime repository of Neapolitan painting and decorative art, with several important works from other Italia ...
. Several of Naples' mid-19th-century porcelain factories remain active today.
Cuisine


Naples is internationally famous for its
cuisine and wine; it draws culinary influences from the numerous cultures which have inhabited it throughout its history, including the
Greeks
The Greeks or Hellenes (; el, Έλληνες, ''Éllines'' ) are an ethnic group and nation indigenous to the Eastern Mediterranean and the Black Sea regions, namely Greece, Cyprus, Albania, Italy, Turkey, Egypt, and, to a lesser extent, oth ...
, Spanish and French. Neapolitan cuisine emerged as a distinct form in the 18th century. The ingredients are typically rich in taste while remaining affordable to the general populace.
Naples is traditionally credited as the home of
pizza.
This originated as a meal of the poor, but under
Ferdinand IV it became popular among the upper classes: famously, the
Margherita pizza was named after Queen
Margherita of Savoy
Margherita of Savoy (''Margherita Maria Teresa Giovanna''; 20 November 1851 – 4 January 1926) was Queen of Italy by marriage to Umberto I.
Life
Early life
Margherita was born to Prince Ferdinand of Savoy, Duke of Genoa and Princess Elisabe ...
after her visit to the city.
Cooked traditionally in a wood-burning
oven, the ingredients of Neapolitan pizza have been strictly regulated by law since 2004, and must include wheat flour type "00" with the addition of flour type "0"
yeast
Yeasts are eukaryotic, single-celled microorganisms classified as members of the fungus kingdom. The first yeast originated hundreds of millions of years ago, and at least 1,500 species are currently recognized. They are estimated to constit ...
, natural mineral water, peeled tomatoes or fresh
cherry tomato
The cherry tomato is a type of small round tomato believed to be an intermediate genetic admixture between wild currant-type tomatoes and domesticated garden tomatoes. Cherry tomatoes range in size from a thumbtip up to the size of a golf bal ...
es,
mozzarella
Mozzarella (, ; nap, muzzarella ) is a southern Italian cheese traditionally made from Italian buffalo's milk by the pasta filata method.
Fresh mozzarella is generally white but when seasoned it turns to a light yellow depending on the anim ...
,
sea salt
Sea salt is salt that is produced by the evaporation of seawater. It is used as a seasoning in foods, cooking, cosmetics and for preserving food. It is also called bay salt, solar salt, or simply salt. Like mined rock salt, production of sea sa ...
and extra virgin
olive oil.
["Proposal of recognition of the Specialita' Traditionale Garantita 'Pizza Napoletana'"]
. Forno Bravo. 24 May 2004. Retrieved 27 November 2011.
Spaghetti
Spaghetti () is a long, thin, solid, cylindrical pasta.[spaghetti](_blank)
Dictionary.com. Dictionary.com Unabridg ...
is also associated with the city and is commonly eaten with clams ''
vongole or lupini di mare'': a popular Neapolitan
folkloric
Folklore is shared by a particular group of people; it encompasses the traditions common to that culture, subculture or group. This includes oral traditions such as tales, legends, proverbs and jokes. They include material culture, ranging fro ...
symbol is the comic figure
Pulcinella
Pulcinella (; nap, Pulecenella) is a classical character that originated in of the 17th century and became a stock character in Neapolitan puppetry. Pulcinella's versatility in status and attitude has captivated audiences worldwide and kept t ...
eating a plate of spaghetti. Other dishes popular in Naples include ''
Parmigiana
Parmigiana (, ), also called parmigiana di melanzane , melanzane alla parmigiana , or eggplant parmesan, is an Italian dish made with fried, sliced eggplant layered with cheese and tomato sauce, then baked. The origin of the dish is claimed by ...
di melanzane'', ''spaghetti alle vongole'' and ''
casatiello
Casatiello ( nap, casatiéllo, it, casatello) is a leavened savory bread Neapolitan cuisine, originating from Naples prepared during the Easter period.
Its basic ingredients are flour, lard, cheese, salami, cracklings, eggs and black pepper. ...
''. As a coastal city, Naples is furthermore known for numerous seafood dishes, including ''impepata di cozze'' (peppered
mussels), ''purpetiello affogato'' (
octopus poached in broth), ''alici marinate'' (marinated
anchovies
An anchovy is a small, common forage fish of the family Engraulidae. Most species are found in marine waters, but several will enter brackish water, and some in South America are restricted to fresh water.
More than 140 species are placed in 1 ...
), ''baccalà alla napoletana'' (salt
cod
Cod is the common name for the demersal fish genus '' Gadus'', belonging to the family Gadidae. Cod is also used as part of the common name for a number of other fish species, and one species that belongs to genus ''Gadus'' is commonly not call ...
) and ''baccalà fritto'' (fried cod), a dish commonly eaten during the
Christmas
Christmas is an annual festival commemorating the birth of Jesus Christ, observed primarily on December 25 as a religious and cultural celebration among billions of people around the world. A feast central to the Christian liturgical year ...
period.
Naples is well known for its sweet dishes, including colourful
gelato, which is similar to
ice cream
Ice cream is a sweetened frozen food typically eaten as a snack or dessert. It may be made from milk or cream and is flavoured with a sweetener, either sugar or an alternative, and a spice, such as cocoa or vanilla, or with fruit such as ...
, though more fruit-based. Popular Neapolitan pastry dishes include ''
zeppole
A zeppola (; plural: zeppole; sometimes called frittelle, and in Sardinia the italianized ''zippole'' or ''zeppole sarde'' from the original Sardinian ) is an Italian pastry consisting of a deep-fried dough ball of varying size but typically ...
'' (more commonly called "'a Pasta Cresciuta" and "'e fFritt' 'e Viento") ''
babà'', ''
sfogliatelle
A sfogliatella (, plural: sfogliatelle; nap, sfugliatella), sometimes called a lobster tail in the US, is a shell-shaped filled Italian pastry originating from Campania. ''Sfogliatella'' means "small, thin leaf/layer", as the pastry's texture res ...
'' and ''
pastiera'', the latter of which is prepared specially for Easter celebrations. Another seasonal sweet is ''
struffoli
Struffoli also known as Honey Balls (; nap, struffule ) is a Neapolitan dish made of deep fried balls of sweet dough. The dough is used in many Italian sweet treats such as chiacchiere. For struffoli, the dough is formed in to balls about the s ...
'', a sweet-tasting
honey
Honey is a sweet and viscous substance made by several bees, the best-known of which are honey bees. Honey is made and stored to nourish bee colonies. Bees produce honey by gathering and then refining the sugary secretions of plants (primar ...
dough decorated and eaten around Christmas. Neapolitan coffee is also widely acclaimed. The traditional
Neapolitan flip coffee pot
The Neapolitan flip coffee pot ( it, napoletana or ''caffettiera napoletana'', ; nap, cuccumella, ) is a drip brew coffeemaker for the stove top that was very popular in Italy until last century. Unlike a moka express, a ''napoletana'' does not u ...
, known as the ''cuccuma'' or ''cuccumella'', was the basis for the invention of the
espresso machine
An espresso machine brews coffee by forcing pressurized water near boiling point through a "puck" of ground coffee and a filter in order to produce a thick, concentrated coffee called espresso. The first machine for making espresso was built in ...
, and also inspired the
Moka pot
The moka pot is a stove-top or electric coffee maker that brews coffee by passing boiling water pressurized by steam through ground coffee. Named after the Yemeni city of Mocha, it was invented by Italian engineer Alfonso Bialetti in 1933 and ...
.
Wineries
A winery is a building or property that produces wine, or a business involved in the production of wine, such as a wine company. Some wine companies own many wineries. Besides wine making equipment, larger wineries may also feature warehouses, b ...
in the Vesuvius area produce wines such as the ''
Lacryma Christi'' ("tears of Christ") and ''Terzigno''. Naples is also the home of ''
limoncello'', a popular
lemon liqueur.
Festivals
The cultural significance of Naples is often represented through a series of festivals held in the city. The following is a list of several festivals that take place in Naples (note: some festivals are not held on an annual basis).

* ''Festa di Piedigrotta'' ("Piedigrotta Festival") – A musical event typically held in September in memory of the famous Madonna of Piedigrotta. Throughout the month, a series of musical workshops, concerts, religious events and children's events are held to entertain the citizens of Naples and surrounding areas.
* ''Pizzafest'' – As Naples is famous for being home to pizza, the city hosts an eleven-day festival dedicated to this iconic dish. This is a key event for Neapolitans and tourists alike, as various stations are open for tasting a wide range of true Neapolitan pizza. In addition to pizza tasting, a variety of entertainment shows are displayed.
* ''Maggio dei Monumenti'' ("May of Monuments") – A cultural event where the city hosts a variety of special events dedicated to the birth of King Charles of Bourbon. It festival features art and music of the 18th century, and many buildings which may normally be closed throughout the year are opened for visitors to view.
* ''Il Ritorno della festa di San Gennaro'' ("The Return of the
Feast of San Gennaro
The Feast of San Gennaro (in Italian: ''Festa di San Gennaro''), also known as San Gennaro Festival, is a Neapolitan and Italian-American patronal festival dedicated to Saint Januarius, patron saint of Naples and Little Italy, New York.
His feas ...
") – An annual celebration and feast of faith held over three days, commemorating Saint
Gennaro. Throughout the festival, parades, religious processions and musical entertainment are featured. An annual celebration is also held in "
Little Italy
Little Italy is a general name for an ethnic enclave populated primarily by Italians or people of Italian ancestry, usually in an urban neighborhood. The concept of "Little Italy" holds many different aspects of the Italian culture. There are ...
" in Manhattan.
Language
The
Naples language, considered to be a distinct language and mainly spoken in the city, is also found in the region of
Campania
(man), it, Campana (woman)
, population_note =
, population_blank1_title =
, population_blank1 =
, demographics_type1 =
, demographics1_footnotes =
, demographics1_title1 =
, demographics1_info1 =
, demog ...
and has been diffused into other areas of
Southern Italy by Neapolitan migrants, and in many different places in the world.
On 14 October 2008, a regional law was enacted by Campania which has the effect that the use of the Neapolitan language is protected.
The term "Neapolitan language" is often used to describe the language of all of
Campania
(man), it, Campana (woman)
, population_note =
, population_blank1_title =
, population_blank1 =
, demographics_type1 =
, demographics1_footnotes =
, demographics1_title1 =
, demographics1_info1 =
, demog ...
(except
Cilento), and is sometimes applied to the entire
South Italian language; ''
Ethnologue'' refers to the latter as ''Napoletano-Calabrese''.
This linguistic group is spoken throughout most of southern continental Italy, including the
Gaeta and
Sora district of southern
Lazio
it, Laziale
, population_note =
, population_blank1_title =
, population_blank1 =
, demographics_type1 =
, demographics1_footnotes =
, demographics1_title1 =
, demographics1_info1 =
, demographics1_title2 ...
, the southern part of
Marche and
Abruzzo, Molise,
Basilicata, northern
Calabria, and northern and central
Apulia. In 1976, there were an estimated 7,047,399
native speakers
A first language, native tongue, native language, mother tongue or L1 is the first language or dialect that a person has been exposed to from birth or within the critical period. In some countries, the term ''native language'' or ''mother tongu ...
of this group of dialects.
Literature and philosophy

Naples is one of the leading centres of Italian literature. The history of the Neapolitan language was deeply entwined with that of the
Tuscan dialect
Tuscan ( it, dialetto toscano ; it, vernacolo, label=locally) is a set of Italo-Dalmatian varieties of Romance mainly spoken in Tuscany, Italy.
Standard Italian is based on Tuscan, specifically on its Florentine dialect, and it became the ...
, which then became the current Italian language. The first written testimonies of the Italian language are the
Placiti Cassinensi legal documents, dated 960 A.D., preserved in the
Monte Cassino
Monte Cassino (today usually spelled Montecassino) is a rocky hill about southeast of Rome, in the Latin Valley, Italy, west of Cassino and at an elevation of . Site of the Roman town of Casinum, it is widely known for its abbey, the first ho ...
Abbey, which are, in fact, evidence of a language spoken in a southern dialect. The Tuscan poet
Boccaccio
Giovanni Boccaccio (, , ; 16 June 1313 – 21 December 1375) was an Italian writer, poet, correspondent of Petrarch, and an important Renaissance humanist. Born in the town of Certaldo, he became so well known as a writer that he was some ...
lived for many years at the court of King
Robert the Wise
Robert of Anjou ( it, Roberto d'Angiò), known as Robert the Wise ( it, Roberto il Saggio; 1276 – 20 January 1343), was King of Naples, titular King of Jerusalem and Count of Provence and Forcalquier from 1309 to 1343, the central figure of I ...
and his successor
Joanna of Naples, using Naples as a setting for ''
The Decameron
''The Decameron'' (; it, label= Italian, Decameron or ''Decamerone'' ), subtitled ''Prince Galehaut'' (Old it, Prencipe Galeotto, links=no ) and sometimes nicknamed ''l'Umana commedia'' ("the Human comedy", as it was Boccaccio that dubbed Da ...
'' and a number of his later novels. His works contain some words that are taken from Neapolitan instead of the corresponding Italian, e.g. "testo" (neap.: "testa"), which in Naples indicates a large terracotta jar used to cultivate shrubs and little trees. King
Alfonso V of Aragon stated in 1442 that the Neapolitan language was to be used instead of
Latin
Latin (, or , ) is a classical language belonging to the Italic branch of the Indo-European languages. Latin was originally a dialect spoken in the lower Tiber area (then known as Latium) around present-day Rome, but through the power of the ...
in official documents.

Later Neapolitan was replaced by Italian in the first half of the 16th century, during Spanish domination. In 1458 the ''
Accademia Pontaniana
The Accademia Pontaniana was the first academy in the modern sense, as a learned society for scholars and humanists and guided by a formal statute. Patronized by Alfonso V of Aragon, it was founded by the poet Antonio Beccadelli in Naples during ...
'', one of the first academies in Italy, was established in Naples as a free initiative by men of letters, science and literature. In 1480 the writer and poet
Jacopo Sannazzaro wrote the first pastoral romance, ''Arcadia'', which influenced Italian literature. In 1634
Giambattista Basile
Giambattista Basile (February 1566 – February 1632) was an Italian poet, courtier, and fairy tale collector. His collections include the oldest recorded forms of many well-known (and more obscure) European fairy tales. He is chiefly remembere ...
collected ''
Lo Cunto de li Cunti'' five books of ancient tales written in the Neapolitan dialect rather than Italian. Philosopher
Giordano Bruno, who theorised the existence of infinite solar systems and the infinity of the entire universe, completed his studies at the University of Naples. Due to philosophers such as
Giambattista Vico
Giambattista Vico (born Giovan Battista Vico ; ; 23 June 1668 – 23 January 1744) was an Italian philosopher, rhetorician, historian, and jurist during the Italian Enlightenment. He criticized the expansion and development of modern rationali ...
, Naples became one of the centres of the Italian peninsula for historical and
philosophy of history studies.
Jurisprudence
Jurisprudence, or legal theory, is the theoretical study of the propriety of law. Scholars of jurisprudence seek to explain the nature of law in its most general form and they also seek to achieve a deeper understanding of legal reasoning a ...
studies were enhanced in Naples thanks to eminent personalities of jurists like
Bernardo Tanucci
Bernardo Tanucci (20 February 1698 – 29 April 1783) was an Italian statesman, who brought an enlightened absolutism style of government to the Kingdom of the Two Sicilies for Charles III and his son Ferdinand IV.
Biography
Born of a poor fami ...
,
Gaetano Filangieri
Gaetano Filangieri (22 August 1753 – 21 July 1788) was an Italian jurist and philosopher.
Filangieri was born in San Sebastiano al Vesuvio, in the province of Naples, Italy. He was born the third son of a sibship of the noble family of Fila ...
and
Antonio Genovesi. In the 18th century Naples, together with
Milan
Milan ( , , Lombard: ; it, Milano ) is a city in northern Italy, capital of Lombardy, and the second-most populous city proper in Italy after Rome. The city proper has a population of about 1.4 million, while its metropolitan city h ...
, became one of the most important sites from which the
Enlightenment penetrated Italy. Poet and philosopher
Giacomo Leopardi
Count Giacomo Taldegardo Francesco di Sales Saverio Pietro Leopardi (, ; 29 June 1798 – 14 June 1837) was an Italian philosopher, poet, essayist, and philologist. He is considered the greatest Italian poet of the nineteenth century and one of ...
visited the city in 1837 and died there. His works influenced
Francesco de Sanctis, who studied in Naples and eventually became Minister of Instruction during the Italian kingdom. De Sanctis was one of the first literary critics to discover, study and diffuse the poems and literary works of the great poet from
Recanati
Recanati () is a town and ''comune'' in the Province of Macerata, in the Marche region of Italy. Recanati was founded around 1150 AD from three pre-existing castles. In 1290 it proclaimed itself an independent republic and, in the 15th century, ...
.
Writer and journalist
Matilde Serao
200px, Matilde Serao, by "Rossi"
Matilde Serao (; gr, Ματθίλδη Σεράο; 7 March 1856 – 25 July 1927) was an Italian journalist and novelist. She was the first woman called to edit an Italian newspaper, Il ''Corriere di Roma'' an ...
co-founded the newspaper
Il Mattino with her husband
Edoardo Scarfoglio
Edoardo Scarfoglio (September 26, 1860 – October 6, 1917) was an Italian author and journalist, one of the early practitioners in Italian fiction of realism, a style of writing that embraced direct, colloquial language and rejected the more o ...
in 1892. Serao was an acclaimed novelist and writer during her day. Poet
Salvatore Di Giacomo
Salvatore Di Giacomo (12 March 1860 – 5 April 1934) was an Italian poet, songwriter, playwright and fascist, one of the signatories to the Manifesto of the Fascist Intellectuals.
Di Giacomo is credited as being one of those responsible for ...
was one of the most famous writers in the Neapolitan dialect, and many of his poems were adapted to music, becoming famous Neapolitan songs. In the 20th century, philosophers like
Benedetto Croce pursued the long tradition of philosophy studies in Naples, and personalities like jurists and lawyer
Enrico De Nicola
Enrico De Nicola, (; 9 November 1877 – 1 October 1959) was an Italian jurist, journalist, politician, and provisional head of state of republican Italy from 1946 to 1948. Afterwards, he became the first president of Italy on 1 January 1948 ...
pursued legal and constitutional studies. De Nicola later helped to draft the modern Constitution of the Italian Republic and was eventually elected to the office of President of the Italian Republic. Other noted Neapolitan writers and journalists include
Antonio De Curtis,
Curzio Malaparte
Curzio Malaparte (; 9 June 1898 – 19 July 1957), born Kurt Erich Suckert, was an Italian writer, filmmaker, war correspondent and diplomat. Malaparte is best known outside Italy due to his works ''Kaputt'' (1944) and ''La pelle'' (1949). The f ...
,
Giancarlo Siani,
Roberto Saviano
Roberto Saviano (; born 22 September 1979) is an Italian writer, essayist, journalist, and screenwriter. In his writings, including articles and his book '' Gomorrah'', he uses literature and investigative reporting to tell of the economic reali ...
and
Elena Ferrante
Elena Ferrante () is a pseudonymous Italian novelist. Ferrante's books, originally published in Italian, have been translated into many languages. Her four-book series of ''Neapolitan Novels'' are her most widely known works.
''Time'' magazine ...
.
Theatre

Naples was one of the centres of the peninsula from which originated the modern theatre genre as nowadays intended, evolving from 16th century "
comedy of art".
The masked character of
Pulcinella
Pulcinella (; nap, Pulecenella) is a classical character that originated in of the 17th century and became a stock character in Neapolitan puppetry. Pulcinella's versatility in status and attitude has captivated audiences worldwide and kept t ...
is a worldwide famous figure either as a theatrical character or
puppetry character.
The music Opera genre of
opera buffa
''Opera buffa'' (; "comic opera", plural: ''opere buffe'') is a genre of opera. It was first used as an informal description of Italian comic operas variously classified by their authors as ''commedia in musica'', ''commedia per musica'', ''dramm ...
was created in Naples in the 18th century and then spread to Rome and northern Italy. In the period of
Belle Époque, Naples rivalled Paris for its
Café-chantants, and many famous Neapolitan songs were originally created to entertain the public in the cafès of Naples. Perhaps the most well-known song is "Ninì Tirabusciò". The history of how this song was born was dramatised in the eponymous comedy movie "
Ninì Tirabusciò: la donna che inventò la mossa" starring
Monica Vitti
Monica Vitti (born Maria Luisa Ceciarelli; 3 November 1931 – 2 February 2022) was an Italian actress who starred in several award-winning films directed by Michelangelo Antonioni during the 1960s. After working with Antonioni, Vitti changed fo ...
.
The Neapolitan popular genre of "
Sceneggiata" is an important genre of modern folk theatre worldwide, dramatising common canon themes of thwarted love stories, comedies, tearjerker stories, commonly about honest people becoming
camorra outlaws due to unfortunate events. The Sceneggiata became very popular amongst Neapolitans and eventually one of the best-known genres of Italian cinematography thanks to actors and singers like
Mario Merola and
Nino D'Angelo
Gaetano "Nino" D'Angelo (born 21 June 1957) is an Italian singer, songwriter, actor, television personality, film director, screenwriter and author.
He was born to a poor family in San Pietro a Patierno, a suburb of Naples, and dropped out of ...
. Many writers and playwrights, such as
Raffaele Viviani
Raffaele Viviani (10 January 1888 in Castellammare di Stabia, Province of Naples – 22 March 1950) was an Italian author, playwright, actor and musician. Viviani belongs to the turn-of-the-century school of realism in Italian literature, a ...
, wrote comedies and dramas for this genre. Actors and comedians like
Eduardo Scarpetta and then his sons
Eduardo De Filippo
Eduardo De Filippo (; 24 May 1900 – 31 October 1984), also known simply as ''Eduardo'', was an Italian actor, director, screenwriter and playwright, best known for his Neapolitan works ''Filumena Marturano'' and '' Napoli Milionaria''. Consid ...
,
Peppino De Filippo and
Titina De Filippo
Titina De Filippo (born Annunziata De Filippo; 27 March 1898 – 26 December 1963) was an Italian actress and playwright.[Filumena Marturano
''Filumena Marturano'' (, ), sometime performed in English as ''The Best House in Naples'', is a play written in 1946 by Italian playwright, actor and poet Eduardo De Filippo. It is the basis for the 1950 Spanish language Argentine musical film ...]
" and "
Napoli Milionaria", are well-known.
Music

Naples has played an important role in the history of
Western European art music for more than four centuries. The first
music conservatories were established in the city under Spanish rule in the 16th century. The San Pietro a Majella music conservatory, founded in 1826 by
Francesco I of Bourbon, continues to operate today as both a prestigious centre of musical education and a musical museum.
During the late
Baroque period
The Baroque (, ; ) is a style of architecture, music, dance, painting, sculpture, poetry, and other arts that flourished in Europe from the early 17th century until the 1750s. In the territories of the Spanish and Portuguese empires including t ...
,
Alessandro Scarlatti, the father of
Domenico Scarlatti, established the Neapolitan school of opera; this was in the form of ''
opera seria'', which was a new development for its time. Another form of opera originating in Naples is ''
opera buffa
''Opera buffa'' (; "comic opera", plural: ''opere buffe'') is a genre of opera. It was first used as an informal description of Italian comic operas variously classified by their authors as ''commedia in musica'', ''commedia per musica'', ''dramm ...
'', a style of
comic opera
Comic opera, sometimes known as light opera, is a sung dramatic work of a light or comic nature, usually with a happy ending and often including spoken dialogue.
Forms of comic opera first developed in late 17th-century Italy. By the 1730s, a ne ...
strongly linked to
Battista Pergolesi and
Piccinni; later contributors to the genre included
Rossini and
Wolfgang Amadeus Mozart
Wolfgang Amadeus Mozart (27 January 17565 December 1791), baptised as Joannes Chrysostomus Wolfgangus Theophilus Mozart, was a prolific and influential composer of the Classical period. Despite his short life, his rapid pace of composition r ...
. The
Teatro di San Carlo
The Real Teatro di San Carlo ("Royal Theatre of Saint Charles"), as originally named by the Bourbon monarchy but today known simply as the Teatro (di) San Carlo, is an opera house in Naples, Italy, connected to the Royal Palace and adjacent ...
, built in 1737, is the oldest working theatre in Europe, and remains the operatic centre of Naples.


The earliest six-string guitar was created by the Neapolitan Gaetano Vinaccia in 1779; the instrument is now referred to as the
romantic guitar. The Vinaccia family also developed the
mandolin. Influenced by the Spanish, Neapolitans became pioneers of classical guitar music, with
Ferdinando Carulli and
Mauro Giuliani
Mauro Giuseppe Sergio Pantaleo Giuliani (27 July 1781 – 8 May 1829) was an Italian guitarist, cellist, singer, and composer. He was a leading guitar virtuoso of the early 19th century.
Biography
Although born in Bisceglie, Giuliani's cent ...
being prominent exponents. Giuliani, who was actually from
Apulia but lived and worked in Naples, is widely considered to be one of the greatest
guitar players and composers of the 19th century, along with his
Catalan contemporary
Fernando Sor. Another Neapolitan musician of note was
opera singer
Opera is a form of theatre in which music is a fundamental component and dramatic roles are taken by singers. Such a "work" (the literal translation of the Italian word "opera") is typically a collaboration between a composer and a libretti ...
Enrico Caruso, one of the most prominent opera
tenor
A tenor is a type of classical male singing voice whose vocal range lies between the countertenor and baritone voice types. It is the highest male chest voice type. The tenor's vocal range extends up to C5. The low extreme for tenors is wide ...
s of all time: he was considered a man of the people in Naples, hailing from a working-class background.
A popular traditional dance in
Southern Italy and Naples is the
Tarantella
() is a group of various southern Italian folk dances originating in the regions of Calabria, Campania and Puglia. It is characterized by a fast upbeat tempo, usually in time (sometimes or ), accompanied by tambourines. It is among the mo ...
, which originated in
Apulia and spread throughout the
Kingdom of the Two Sicilies. The Neapolitan tarantella is a
courtship dance
A courtship display is a set of display behaviors in which an animal, usually a male, attempts to attract a mate; the mate exercises choice, so sexual selection acts on the display. These behaviors often include ritualized movement ("dances"), ...
performed by couples whose "rhythms, melodies, gestures, and accompanying songs are quite distinct", featuring faster, more cheerful music.
A notable element of popular Neapolitan music is the ''
Canzone Napoletana
Canzone napoletana (), sometimes referred to as Neapolitan song ( nap, canzona napulitana ), is a generic term for a traditional form of music sung in the Neapolitan language, ordinarily for the male voice singing solo, although well represented b ...
'' style, essentially the
traditional music
Folk music is a music genre that includes traditional folk music and the contemporary genre that evolved from the former during the 20th-century folk revival. Some types of folk music may be called world music. Traditional folk music has ...
of the city, with a repertoire of hundreds of
folk
Folk or Folks may refer to:
Sociology
*Nation
*People
* Folklore
** Folk art
** Folk dance
** Folk hero
** Folk music
*** Folk metal
*** Folk punk
*** Folk rock
** Folk religion
* Folk taxonomy
Arts, entertainment, and media
* Folk Plus or Fo ...
songs, some of which can be traced back to the 13th century.
The genre became a formal institution in 1835, after the introduction of the annual Festival of
Piedigrotta
Piedigrotta (; nap, Piererotta ; "at the foot of the grotto") is a section of the Chiaia quarter of Naples, Italy, so-called for the presence of the Church of the Madonna of Piedigrotta near the entrance to the Crypta Neapolitana. The area wa ...
songwriting competition.
Some of the best-known recording artists in this field include Roberto Murolo,
Sergio Bruni and
Renato Carosone
Renato Carosone (; born Renato Carusone; 3 January 1920 – 20 May 2001) was an Italian musician.
He was a prominent figure of the Italian music scene in the second half of the 20th century. He was also a modern performer of the so-called ' ...
. There are furthermore various forms of music popular in Naples but not well known outside it, such as ''cantautore'' ("singer-songwriter") and ''sceneggiata'', which has been described as a musical soap opera; the most well-known exponent of this style is
Mario Merola.
Cinema and television

Naples has had a significant influence on Italian cinema. Because of the city's relevance, many films and television shows are set (entirely or partially) in Naples. In addition to serving as the backdrop for several movies and shows, many talented celebrities (actors, actresses, directors, and producers) are originally from Naples.
Naples was the location for several early Italian cinema masterpieces. ''
Assunta Spina'' (1915) was a silent film adapted from a theatrical drama by Neapolitan writer
Salvatore Di Giacomo
Salvatore Di Giacomo (12 March 1860 – 5 April 1934) was an Italian poet, songwriter, playwright and fascist, one of the signatories to the Manifesto of the Fascist Intellectuals.
Di Giacomo is credited as being one of those responsible for ...
. The film was directed by Neapolitan
Gustavo Serena
Gustavo Serena (5 October 1881 – 16 April 1970) was an Italian actor and film director. He appeared in 107 films between 1909 and 1961. He also directed 33 films between 1912 and 1932. He was born in Naples and died in Rome.
Selected fil ...
. Serena also starred in the 1912 film ''Romeo and Juliet''.
A list of some well-known films that take place (fully or partially) in Naples includes:
* ''
Shoeshine'' (1946), directed by Neapolitan,
Vittorio De Sica
Vittorio De Sica ( , ; 7 July 1901 – 13 November 1974) was an Italian film director and actor, a leading figure in the neorealist movement.
Four of the films he directed won Academy Awards: ''Sciuscià'' and ''Bicycle Thieves'' (honorary) ...
* ''
Hands over the City'' (1963), directed by Neapolitan,
Francesco Rosi
Francesco Rosi (; 15 November 1922 – 10 January 2015) was an Italian film director. His film '' The Mattei Affair'' won the Palme d'Or at the 1972 Cannes Film Festival. Rosi's films, especially those of the 1960s and 1970s, often appeared to ha ...
* ''
Journey to Italy'' (1954), directed by
Roberto Rossellini
Roberto Gastone Zeffiro Rossellini (8 May 1906 – 3 June 1977) was an Italian film director, producer, and screenwriter. He was one of the most prominent directors of the Italian neorealist cinema, contributing to the movement with films such ...
* ''
Marriage Italian Style'' (1964), directed by Neapolitan,
Vittorio De Sica
Vittorio De Sica ( , ; 7 July 1901 – 13 November 1974) was an Italian film director and actor, a leading figure in the neorealist movement.
Four of the films he directed won Academy Awards: ''Sciuscià'' and ''Bicycle Thieves'' (honorary) ...
* ''
It Started in Naples
''It Started in Naples'' is a 1960 American romantic comedy film directed by Melville Shavelson and produced by Jack Rose from a screenplay by Suso Cecchi d'Amico, based on the story by Michael Pertwee and Jack Davies. The Technicolor cinematog ...
'' (1960), Directed by
Melville Shavelson
Melville Shavelson (April 1, 1917 – August 8, 2007) was an American film director, producer, screenwriter, and author. He was President of the Writers Guild of America, West (WGAw) from 1969 to 1971, 1979 to 1981, and 1985 to 1987.
Biog ...
* ''
The Hand of God (film)'' (2021), Directed by
Paolo Sorrentino
Paolo Sorrentino (; born 31 May 1970) is an Italian film director, screenwriter, and writer. His 2013 film ''The Great Beauty'' won the Academy Awards, Academy Award, the Golden Globe Awards, Golden Globe, and the British Academy of Film and Te ...
Naples is home to one of the first Italian colour films, ''
Toto in Color'' (1952), starring
Totò
Antonio Griffo Focas Flavio Angelo Ducas Comneno Porfirogenito Gagliardi de Curtis di Bisanzio (15 February 1898 – 15 April 1967), best known by his stage name Totò (), or simply as Antonio de Curtis, and nicknamed ''il Principe della risata ...
(Antonio de Curtis), a famous comedic actor born in Naples.
Some notable comedies set in Naples include ''Ieri, Oggi e Domani'' (
Yesterday, Today and Tomorrow
''Yesterday, Today and Tomorrow'' ( it, Ieri, oggi, domani) is a 1963 comedy anthology film by Italian director Vittorio De Sica. It stars Sophia Loren and Marcello Mastroianni. The film consists of three short stories about couples in differ ...
), by Vittorio De Sica, starring Sophia Loren and
Marcello Mastroianni, ''Adelina of Naples'' (Academy Award-winning movie), ''
It Started in Naples
''It Started in Naples'' is a 1960 American romantic comedy film directed by Melville Shavelson and produced by Jack Rose from a screenplay by Suso Cecchi d'Amico, based on the story by Michael Pertwee and Jack Davies. The Technicolor cinematog ...
'', ''
L'oro di Napoli'' again by Vittorio De Sica, dramatic movies like
Dino Risi
Dino Risi (23 December 1916 – 7 June 2008) was an Italian film director. With Mario Monicelli, Luigi Comencini, Nanni Loy and Ettore Scola, he was one of the masters of ''commedia all'italiana''.
Biography
Risi was born in Milan. He had an o ...
's ''
Scent of a Woman'', war movies like ''
The Four Days of Naples'' by Sardinian director
Nanni Loy
Nanni Loy (born Giovanni Loi; 23 October 1925 – 21 August 1995) was an Italian film, theatre and TV director. Specifically, Nanni Loy was Sardinian, and one of several notable Sardinian film makers, including Franco Solinas.
Biography
Lo ...
, music and Sceneggiata movies like ''
Zappatore
''Zappatore'' is an Italian drama film directed by Alfonso Brescia and starring Mario Merola. The film was released in Italy on 5 December 1980.
It is the "cine-scripted" which received the highest grossing theaters, ranking the 60th place of t ...
'', from the eponymous song by
Libero Bovio
Libero Bovio (9 June 1883 – 26 May 1942) was a Neapolitan lyricist and dialect poet.
Bovio was one of those responsible for the rejuvenation of Neapolitan
dialect in plays, poetry and song at the beginning of the twentieth
century. He took ...
, starring singer and actor
Mario Merola, crime movies like ''
Il Camorrista'' with
Ben Gazzara
Biagio Anthony Gazzara (August 28, 1930 – February 3, 2012) was an American actor and director of film, stage, and television. He received numerous accolades, including a Primetime Emmy Award and a Drama Desk Award, in addition to nominatio ...
playing the part of infamous camorra boss
Raffaele Cutolo
Raffaele Cutolo (; 4 November 1941 – 17 February 2021) was an Italian crime boss, leader of the Nuova Camorra Organizzata (NCO), an organisation he built to renew the Camorra. Cutolo had a variety of nicknames including o Vangelo'' ("the gosp ...
, and historical or costume movies like ''
That Hamilton Woman
''That Hamilton Woman'', also known as ''Lady Hamilton'', is a 1941 black-and-white historical film drama produced and directed by Alexander Korda for his British company during his exile in the United States. Set during the Napoleonic Wars, th ...
'' starring
Vivien Leigh and
Laurence Olivier.
More modern Neapolitan films include ''
Ricomincio da tre'', which depicts the misadventures of a young emigrant in the late 20th century. The 2008 film ''
Gomorrah'', based on the book by
Roberto Saviano
Roberto Saviano (; born 22 September 1979) is an Italian writer, essayist, journalist, and screenwriter. In his writings, including articles and his book '' Gomorrah'', he uses literature and investigative reporting to tell of the economic reali ...
, explores the dark underbelly of the city of Naples through five intertwining stories about the powerful
Neapolitan crime syndicate, as well as the
TV series of the same name.
The Japanese series ''
JoJo's Bizarre Adventure
is a Japanese manga series written and illustrated by Hirohiko Araki. It was originally serialized in Shueisha's ''shōnen'' manga magazine ''Weekly Shōnen Jump'' from 1987 to 2004, and was transferred to the monthly ''seinen'' manga ...
''s Part 5,
Vento Aureo, takes place in the city.
Several episodes of the animated series ''
Tom and Jerry
''Tom and Jerry'' is an American Animated cartoon, animated media franchise and series of comedy short films created in 1940 by William Hanna and Joseph Barbera. Best known for its 161 theatrical short films by Metro-Goldwyn-Mayer, the series c ...
'' also have references/influences from Naples. The song "
Santa Lucia" played by Tom Cat in ''
Cat and Dupli-cat'' has its origins in Naples.
Neapolitan Mouse takes place in the same city.
Naples has appeared in episodes of TV serials such as ''
The Sopranos
''The Sopranos'' is an American crime drama television series created by David Chase. The story revolves around Tony Soprano (James Gandolfini), a New Jersey-based Italian-American mobster, portraying his difficulties as he tries to balance ...
'' and the 1998 version of ''
The Count of Monte Cristo'', starring
Gérard Depardieu.
Sports
 Football
Football is by far the most popular sport in Naples. Brought to the city by the British during the early 20th century,
the sport is deeply embedded in local culture: it is popular at every level of society, from the ''scugnizzi'' (
street children) to wealthy professionals. The city's best known
football club is
SSC Napoli, which plays its home games at the
Stadio San Paolo
Stadio Diego Armando Maradona (formerly known as Stadio San Paolo) is a stadium in the western Fuorigrotta suburb of Naples, Italy. It is the third largest football stadium in Italy, after Milan's San Siro and Rome's Stadio Olimpico, as well as ...
in
Fuorigrotta. The club's stadium was renamed Stadio Diego Armando Maradona in honour of the Argentinian attacking midfielder who played for them for seven years. The team plays in the
Serie A
The Serie A (), also called Serie A TIM for national sponsorship with TIM, is a professional league competition for football clubs located at the top of the Italian football league system and the winner is awarded the Scudetto and the Cop ...
league and has won the ''
Scudetto'' twice, the
Coppa Italia
The ("Italy Cup") is an annual knockout cup competition in Italian football organized by the FIGC until the 2009–10 season and the Lega Serie A ever since.
History
The beginning of the tournament was turbulent, due to the complexity of ...
six times and the
Supercoppa Italiana twice. The team has also won the
UEFA Cup
A cup is an open-top used to hold hot or cold liquids for pouring or drinking; while mainly used for drinking, it also can be used to store solids for pouring (e.g., sugar, flour, grains, salt). Cups may be made of glass, metal, china, clay ...
,
and once named
FIFA Player of the Century
FIFA Player of the Century was a one-off award created by FIFA to decide the greatest football player of the 20th century, announced at the annual FIFA World gala, held in Rome on 11 December 2000. Diego Maradona and Pelé were joint winners of ...
Diego Maradona
Diego Armando Maradona (; 30 October 196025 November 2020) was an Argentine professional football player and manager. Widely regarded as one of the greatest players in the history of the sport, he was one of the two joint winners of the F ...
among its players. Naples is the birthplace of numerous prominent professional footballers, including
Ciro Ferrara
Ciro Ferrara (; born 11 February 1967) is an Italian former footballer and manager. His most recent position was as manager of Wuhan Zall. He had also previously coached Juventus and the Italy national under-21 team. As an assistant coach to M ...
and
Fabio Cannavaro. Cannavaro was
captain of Italy's national team until 2010 and led the team to victory in the
2006 World Cup
The 2006 FIFA World Cup, also branded as Germany 2006, was the 18th FIFA World Cup, the quadrennial international football world championship tournament. It was held from 9 June to 9 July 2006 in Germany, which had won the right to host the ...
. He was consequently named
World Player of the Year.
Some of the city's smaller clubs include
Sporting Neapolis and
Internapoli, which play at the
Stadio Arturo Collana. The city also has teams in a variety of other sports:
Eldo Napoli represents the city in basketball's
Serie A
The Serie A (), also called Serie A TIM for national sponsorship with TIM, is a professional league competition for football clubs located at the top of the Italian football league system and the winner is awarded the Scudetto and the Cop ...
and plays in the city of
Bagnoli. The city co-hosted the
EuroBasket 1969
The 1969 FIBA European Championship, commonly called FIBA EuroBasket 1969, was the sixteenth FIBA EuroBasket regional basketball championship, held by FIBA Europe.
First round Group A – Caserta
Group B – Naples
Knockout stage Pla ...
. Partenope Rugby is the city's best-known
rugby union
Rugby union, commonly known simply as rugby, is a close-contact team sport that originated at Rugby School in the first half of the 19th century. One of the two codes of rugby football, it is based on running with the ball in hand. In it ...
side: the team has won the rugby union
Serie A
The Serie A (), also called Serie A TIM for national sponsorship with TIM, is a professional league competition for football clubs located at the top of the Italian football league system and the winner is awarded the Scudetto and the Cop ...
twice. Other popular local sports include
water polo
Water polo is a competitive sport, competitive team sport played in water between two teams of seven players each. The game consists of four quarters in which the teams attempt to score goals by throwing the water polo ball, ball into the oppo ...
,
horse racing, sailing, fencing,
boxing
Boxing (also known as "Western boxing" or "pugilism") is a combat sport in which two people, usually wearing protective gloves and other protective equipment such as hand wraps and mouthguards, throw punches at each other for a predetermine ...
and martial arts. The Accademia Nazionale di Scherma (National Academy and Fencing School of Naples) is the only place in Italy where the titles "Master of Sword" and "Master of
Kendo" can be obtained.
Tailoring
Neapolitan tailoring was born as an attempt to loosen up the stiffness of English tailoring, which didn't suit the Neapolitan lifestyle.
Characteristics of Neapolitan tailoring:
* The Shoulders: the Neapolitan jacket has no shoulder padding. Neapolitan tailors removed the shoulder padding from their jackets to provide more movement freedom. For this reason, the Neapolitan shoulder on informal jackets is sewn like a shirt sleeve ("spalla a camicia"), and it follows the natural curve of the human body rather than giving it shape. This type of sleeve is cut about 10 cm larger than the armhole, and it can be finished with the "repecchia" – that shirring the tailor creates with the extra fabric. This little flair is known as "manica a mappina" and gives the jacket a "rugged" appearance. For formal occasions, the Neapolitan shoulder features a "rollino" – a little roll of padding that raises the sleeve head to drape more cleanly.
* The Sleeves: the Neapolitan sleeve is shorter than that found on other jackets, as Neapolitans like shirt cuffs to show right above their wrists, especially when adorned with cufflinks. The sleeves are cut closer to the arms to avoid extra fabric hanging when these are raised.
* The Pockets: the pockets of a Neapolitan jackets are curved and applied as patches; the breast pocket is called "a barchetta", which means "little boat",
due to the higher top corner of the pocket, which, along with the rounded bottom, gives it the shape of a stylized boat. The side pockets are equally curved, and their shape recalls that of a pot; hence the name "a pignata". Neither feature has any practical functionality, but they are particular to Neapolitan tailoring and contribute to the look of a jacket made in Naples. Double-hand finished stitching may also run throughout the sides of the patch pockets – a recurring feature in informal Neapolitan tailoring.
* The Lining: lining is considered an unnecessary burden, and the Neapolitan tailors keep it as minimal as possible. Usually, the jacket is unlined or only half lined; even the sleeves are entirely unlined, as they're meant to fit closely. Additionally, the lining is often left open ("volante," literally "flying") so that people can admire the fine details and construction of the jacket.
* The Lapels: Neapolitan jackets are famous for their wide
lapels, which are often peaked ("a punta") for double-breasted jackets, formal jackets, and coats. The "risvolto dentellato" (the "classic" style of lapels – not peaked) is wider in Neapolitan jackets: they can be as wide as 4 inches (compared to the 3 inches of a regular lapel width). Just as is the case for the pockets, the Neapolitan lapel features double stitching running along the sides – a peculiar detail of a Neapolitan creation – although reserved for the less formal pieces. The "scollo a martiello" (literally "hammer neck") is the opening of the jacket over the shirt, which in Neapolitan tailoring is parallel to the lapels. The cran is the space that separates the lapel and the neck, and it is usually higher in Neapolitan tailoring to create the illusion of a more slender figure.
* The Body: Neapolitan jackets tend to be shorter in the back; in Neapolitan dialect, they say the jacket "zompa arrèto," which roughly translates as "it jumps in the back". This characteristic allows the jacket to "slide" gracefully along the body. The vents on the sides are pretty deep in Neapolitan jackets – up to 12 inches. The
darts
Darts or dart-throwing is a competitive sport in which two or more players bare-handedly throw small sharp-pointed missiles known as darts at a round target known as a dartboard.
Points can be scored by hitting specific marked areas of the bo ...
in the front goes all the way down to help the fabric follow the shape of the body and create elegant quarters.
* Buttons and Buttonholes: the three-roll-two construction features a lapel that hides the third button to provide extra freedom of movement thanks to a longer opening in the front. The buttonhole on the lapel is called "occhiello" in Italian, and it means "little eye" to its elongated almond shape. There isn't a tradition for a specific type of
buttonhole in Naples, but there is a tendency of Neapolitan tailors to prefer slightly shorter and thicker buttonholes that resemble those of a shirt, while "regular" buttonholes of English tradition are more elongated and slender. Some tailors add a slight teardrop shape at the end of the buttonhole, an aesthetic choice that does not refer to a particular tradition. The buttons on the sleeves are always working and overlapping buttons.
Neapolitans
Honorary citizens
People awarded
honorary citizenship
Honorary citizenship is a status bestowed by a city or other government on a foreign or native individual whom it considers to be especially admirable or otherwise worthy of the distinction. The honour usually is symbolic and does not confer an ...
of Naples include:
International relations
Twin towns and sister cities
Naples is
twinned with:
*
Gafsa
Gafsa ( aeb, ڨفصة '; ar, قفصة qafṣah), originally called Capsa in Latin, is the capital of Gafsa Governorate of Tunisia. It lends its Latin name to the Mesolithic Capsian culture. With a population of 111,170, Gafsa is the ninth-la ...
, Tunisia
*
Kragujevac, Serbia
*
Palma de Mallorca, Spain
*
Athens
Athens ( ; el, Αθήνα, Athína ; grc, Ἀθῆναι, Athênai (pl.) ) is both the capital and largest city of Greece. With a population close to four million, it is also the seventh largest city in the European Union. Athens dominates ...
, Greece
*
Santiago de Cuba
Santiago de Cuba is the second-largest city in Cuba and the capital city of Santiago de Cuba Province. It lies in the southeastern area of the island, some southeast of the Cuban capital of Havana.
The municipality extends over , and contains ...
, Cuba
*
Santiago de Cuba Province
Santiago de Cuba Province is the second most populated province in the island of Cuba. The largest city Santiago de Cuba is the main administrative center. Other large cities include Palma Soriano, Contramaestre, San Luis and Songo-la Maya.
Hi ...
, Cuba
*
Nosy Be
Nosy Be (formerly Nossi-bé and Nosse Be) is an island off the northwest coast of Madagascar. Nosy Be is Madagascar's largest and busiest tourist resort. It has an area of , and its population was 109,465 according to the provisional results of ...
, Madagascar
*
Nablus, Palestine
*
Sassari, Italy
Partnerships
*
Sighetu Marmației
Sighetu Marmației (, also spelled ''Sighetul Marmației''; german: Marmaroschsiget or ''Siget''; hu, Máramarossziget, ; uk, Сигіт, Syhit; yi, סיגעט, Siget), until 1960 Sighet, is a city (municipality) in Maramureș County near the ...
, Romania
[
* ]Călărași
Călărași (), the capital of Călărași County in the Muntenia region, is situated in south-east Romania, on the banks of the Danube's Borcea branch, at about from the Bulgarian border and from Bucharest.
The city is an industrial centre f ...
, Romania[
* ]Budapest
Budapest (, ; ) is the capital and most populous city of Hungary. It is the ninth-largest city in the European Union by population within city limits and the second-largest city on the Danube river; the city has an estimated population ...
, Hungary[
* ]Kagoshima
, abbreviated to , is the capital city of Kagoshima Prefecture, Japan. Located at the southwestern tip of the island of Kyushu, Kagoshima is the largest city in the prefecture by some margin. It has been nicknamed the "Naples of the Eastern wor ...
, JapanKolkata
Kolkata (, or , ; also known as Calcutta , the official name until 2001) is the capital of the Indian state of West Bengal, on the eastern bank of the Hooghly River west of the border with Bangladesh. It is the primary business, comme ...
, IndiaSarajevo
Sarajevo ( ; cyrl, Сарајево, ; ''see names in other languages'') is the capital and largest city of Bosnia and Herzegovina, with a population of 275,524 in its administrative limits. The Sarajevo metropolitan area including Sarajevo ...
, Bosnia and Herzegovina (since 1964)[Fraternity cities on Sarajevo Official Web Site](_blank)
. City of Sarajevo. 2008. Retrieved 9 November 2008.
See also
* Neapolitan Mastiff
The Neapolitan Mastiff or is an Italian breed of large dog of mastiff type. It descends from the traditional guard dogs of central Italy. It was recognised as a breed by the Ente Nazionale della Cinofilia Italiana in 1949, and accepted by the ...
Notes
References
Bibliography
* Acton, Harold (1956). ''The Bourbons of Naples (1734–1825)''. London: Methuen.
* Acton, Harold (1961). ''The Last Bourbons of Naples (1825–1861)''. London: Methuen.
*
* Chaney, Edward (2000). "Inigo Jones in Naples" in ''The Evolution of the Grand Tour''. London: Routledge
Routledge () is a British multinational publisher. It was founded in 1836 by George Routledge, and specialises in providing academic books, journals and online resources in the fields of the humanities, behavioural science, education, law ...
.
* De Grand, Alexander J. (2001).
The hunchback's tailor: Giovanni Giolitti and liberal Italy from the challenge of mass politics to the rise of fascism, 1882–1922
', Wesport/London: Praeger,
*
* Snowden, Frank M. (1995)
Naples in the Time of Cholera, 1884–1911
', Cambridge: Cambridge University Press,
External links
*
{{Authority control
Cities and towns in Campania
Coastal towns in Campania
Cumaean colonies
Colonies of Magna Graecia
Capitals of former nations
Mediterranean port cities and towns in Italy
Populated places established in the 7th century BC
World Heritage Sites in Italy
Burial sites of the House of Dampierre


 Naples has been inhabited since the
Naples has been inhabited since the  Following the decline of the
Following the decline of the  After a period of Norman rule, in 1189 the Kingdom of Sicily was in a succession dispute between
After a period of Norman rule, in 1189 the Kingdom of Sicily was in a succession dispute between  Sicily and Naples were separated since 1282, but remained dependencies of Aragon under Ferdinand I. The new dynasty enhanced Naples' commercial standing by establishing relations with the
Sicily and Naples were separated since 1282, but remained dependencies of Aragon under Ferdinand I. The new dynasty enhanced Naples' commercial standing by establishing relations with the  Following the Spanish victory, Naples became part of the
Following the Spanish victory, Naples became part of the  In 1714, Spanish rule over Naples came to an end as a result of the
In 1714, Spanish rule over Naples came to an end as a result of the  Eventually, the Republicans conquered
Eventually, the Republicans conquered  After the
After the  Naples was the most-bombed Italian city during
Naples was the most-bombed Italian city during  Naples' 2,800-year history has left it with a wealth of historical buildings and monuments, from medieval castles to classical ruins, and a wide range of culturally and historically significant sites nearby, including the
Naples' 2,800-year history has left it with a wealth of historical buildings and monuments, from medieval castles to classical ruins, and a wide range of culturally and historically significant sites nearby, including the  The main city square or ''
The main city square or ''
 Naples is widely known for its wealth of historical museums. The Naples National Archaeological Museum is one of the city's main museums, with one of the most extensive collections of artefacts of the
Naples is widely known for its wealth of historical museums. The Naples National Archaeological Museum is one of the city's main museums, with one of the most extensive collections of artefacts of the 


 Naples is the seat of the
Naples is the seat of the  Underneath Naples lies a series of caves and structures created by centuries of mining, and the city rests atop a major geothermal zone. There are also several ancient Greco-Roman reservoirs dug out from the soft tufo stone on which, and from which, much of the city is built. Approximately of the many kilometres of tunnels under the city can be visited from the Napoli Sotteranea, situated in the historic centre of the city in Via dei Tribunali. This system of tunnels and cisterns underlies most of the city and lies approximately below ground level. During
Underneath Naples lies a series of caves and structures created by centuries of mining, and the city rests atop a major geothermal zone. There are also several ancient Greco-Roman reservoirs dug out from the soft tufo stone on which, and from which, much of the city is built. Approximately of the many kilometres of tunnels under the city can be visited from the Napoli Sotteranea, situated in the historic centre of the city in Via dei Tribunali. This system of tunnels and cisterns underlies most of the city and lies approximately below ground level. During  Of the various public parks in Naples, the most prominent are the
Of the various public parks in Naples, the most prominent are the 
 Various buildings inspired by the Gothic Revival are extant in Naples, due to the influence that this movement had on the Scottish-Indian architect
Various buildings inspired by the Gothic Revival are extant in Naples, due to the influence that this movement had on the Scottish-Indian architect  The city is situated on the
The city is situated on the  The thirty quarters ('' quartieri'') of Naples are listed below. For administrative purposes, these thirty districts are grouped together into ten governmental community boards.
The thirty quarters ('' quartieri'') of Naples are listed below. For administrative purposes, these thirty districts are grouped together into ten governmental community boards.
 , the population of the ''comune di Napoli'' totals around 910,000. Naples' wider metropolitan area, sometimes known as Greater Naples, has a population of approximately 4.4 million. The
, the population of the ''comune di Napoli'' totals around 910,000. Naples' wider metropolitan area, sometimes known as Greater Naples, has a population of approximately 4.4 million. The 


 Naples, within its administrative limits, is Italy's fourth-largest economy after
Naples, within its administrative limits, is Italy's fourth-largest economy after 

 Naples is served by several major motorways ( it: '' autostrade''). The Autostrada A1, the longest motorway in Italy, links Naples to
Naples is served by several major motorways ( it: '' autostrade''). The Autostrada A1, the longest motorway in Italy, links Naples to 
 Naples is internationally famous for its cuisine and wine; it draws culinary influences from the numerous cultures which have inhabited it throughout its history, including the
Naples is internationally famous for its cuisine and wine; it draws culinary influences from the numerous cultures which have inhabited it throughout its history, including the  * ''Festa di Piedigrotta'' ("Piedigrotta Festival") – A musical event typically held in September in memory of the famous Madonna of Piedigrotta. Throughout the month, a series of musical workshops, concerts, religious events and children's events are held to entertain the citizens of Naples and surrounding areas.
* ''Pizzafest'' – As Naples is famous for being home to pizza, the city hosts an eleven-day festival dedicated to this iconic dish. This is a key event for Neapolitans and tourists alike, as various stations are open for tasting a wide range of true Neapolitan pizza. In addition to pizza tasting, a variety of entertainment shows are displayed.
* ''Maggio dei Monumenti'' ("May of Monuments") – A cultural event where the city hosts a variety of special events dedicated to the birth of King Charles of Bourbon. It festival features art and music of the 18th century, and many buildings which may normally be closed throughout the year are opened for visitors to view.
* ''Il Ritorno della festa di San Gennaro'' ("The Return of the
* ''Festa di Piedigrotta'' ("Piedigrotta Festival") – A musical event typically held in September in memory of the famous Madonna of Piedigrotta. Throughout the month, a series of musical workshops, concerts, religious events and children's events are held to entertain the citizens of Naples and surrounding areas.
* ''Pizzafest'' – As Naples is famous for being home to pizza, the city hosts an eleven-day festival dedicated to this iconic dish. This is a key event for Neapolitans and tourists alike, as various stations are open for tasting a wide range of true Neapolitan pizza. In addition to pizza tasting, a variety of entertainment shows are displayed.
* ''Maggio dei Monumenti'' ("May of Monuments") – A cultural event where the city hosts a variety of special events dedicated to the birth of King Charles of Bourbon. It festival features art and music of the 18th century, and many buildings which may normally be closed throughout the year are opened for visitors to view.
* ''Il Ritorno della festa di San Gennaro'' ("The Return of the  Naples is one of the leading centres of Italian literature. The history of the Neapolitan language was deeply entwined with that of the
Naples is one of the leading centres of Italian literature. The history of the Neapolitan language was deeply entwined with that of the  Naples was one of the centres of the peninsula from which originated the modern theatre genre as nowadays intended, evolving from 16th century " comedy of art".
The masked character of
Naples was one of the centres of the peninsula from which originated the modern theatre genre as nowadays intended, evolving from 16th century " comedy of art".
The masked character of  Naples has played an important role in the history of Western European art music for more than four centuries. The first music conservatories were established in the city under Spanish rule in the 16th century. The San Pietro a Majella music conservatory, founded in 1826 by Francesco I of Bourbon, continues to operate today as both a prestigious centre of musical education and a musical museum.
During the late
Naples has played an important role in the history of Western European art music for more than four centuries. The first music conservatories were established in the city under Spanish rule in the 16th century. The San Pietro a Majella music conservatory, founded in 1826 by Francesco I of Bourbon, continues to operate today as both a prestigious centre of musical education and a musical museum.
During the late 
 The earliest six-string guitar was created by the Neapolitan Gaetano Vinaccia in 1779; the instrument is now referred to as the romantic guitar. The Vinaccia family also developed the mandolin. Influenced by the Spanish, Neapolitans became pioneers of classical guitar music, with Ferdinando Carulli and
The earliest six-string guitar was created by the Neapolitan Gaetano Vinaccia in 1779; the instrument is now referred to as the romantic guitar. The Vinaccia family also developed the mandolin. Influenced by the Spanish, Neapolitans became pioneers of classical guitar music, with Ferdinando Carulli and  Naples has had a significant influence on Italian cinema. Because of the city's relevance, many films and television shows are set (entirely or partially) in Naples. In addition to serving as the backdrop for several movies and shows, many talented celebrities (actors, actresses, directors, and producers) are originally from Naples.
Naples was the location for several early Italian cinema masterpieces. '' Assunta Spina'' (1915) was a silent film adapted from a theatrical drama by Neapolitan writer
Naples has had a significant influence on Italian cinema. Because of the city's relevance, many films and television shows are set (entirely or partially) in Naples. In addition to serving as the backdrop for several movies and shows, many talented celebrities (actors, actresses, directors, and producers) are originally from Naples.
Naples was the location for several early Italian cinema masterpieces. '' Assunta Spina'' (1915) was a silent film adapted from a theatrical drama by Neapolitan writer  Football is by far the most popular sport in Naples. Brought to the city by the British during the early 20th century, the sport is deeply embedded in local culture: it is popular at every level of society, from the ''scugnizzi'' ( street children) to wealthy professionals. The city's best known football club is SSC Napoli, which plays its home games at the
Football is by far the most popular sport in Naples. Brought to the city by the British during the early 20th century, the sport is deeply embedded in local culture: it is popular at every level of society, from the ''scugnizzi'' ( street children) to wealthy professionals. The city's best known football club is SSC Napoli, which plays its home games at the