Nam Kỳ on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
French Cochinchina (sometimes spelled ''Cochin-China''; french: Cochinchine française; vi, Xứ thuộc địa Nam Kỳ, Hán tự: ) was a colony of French Indochina, encompassing the whole region of Lower Cochinchina or Southern Vietnam from 1862 to 1946. The French operated a plantation economy whose primary strategic product was rubber.
After the end of Japanese occupation (1941–45) and the expulsion from Saigon of
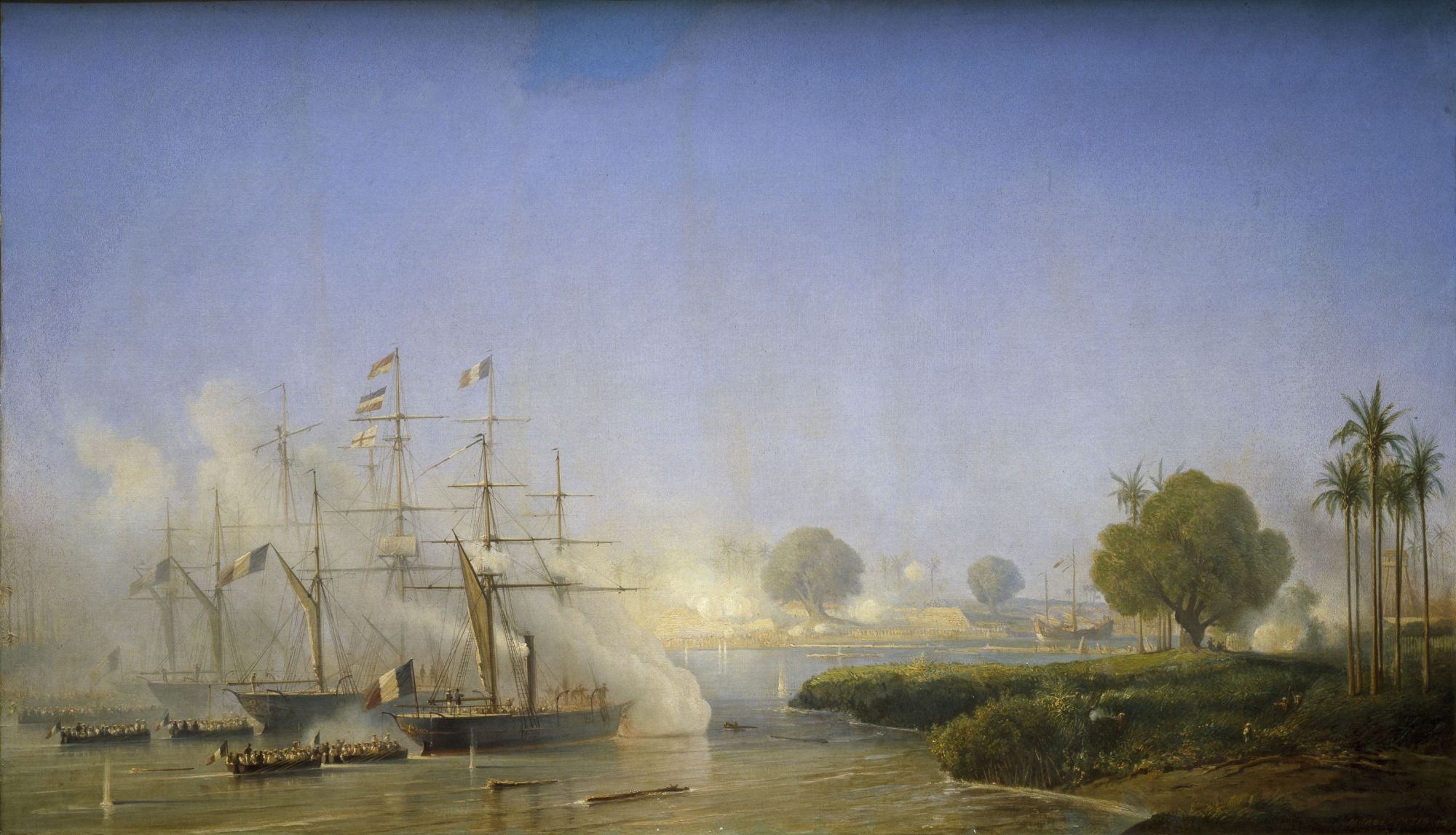 In 1858, under the pretext of protecting the work of French Catholic missionaries, which the imperial Vietnamese
In 1858, under the pretext of protecting the work of French Catholic missionaries, which the imperial Vietnamese
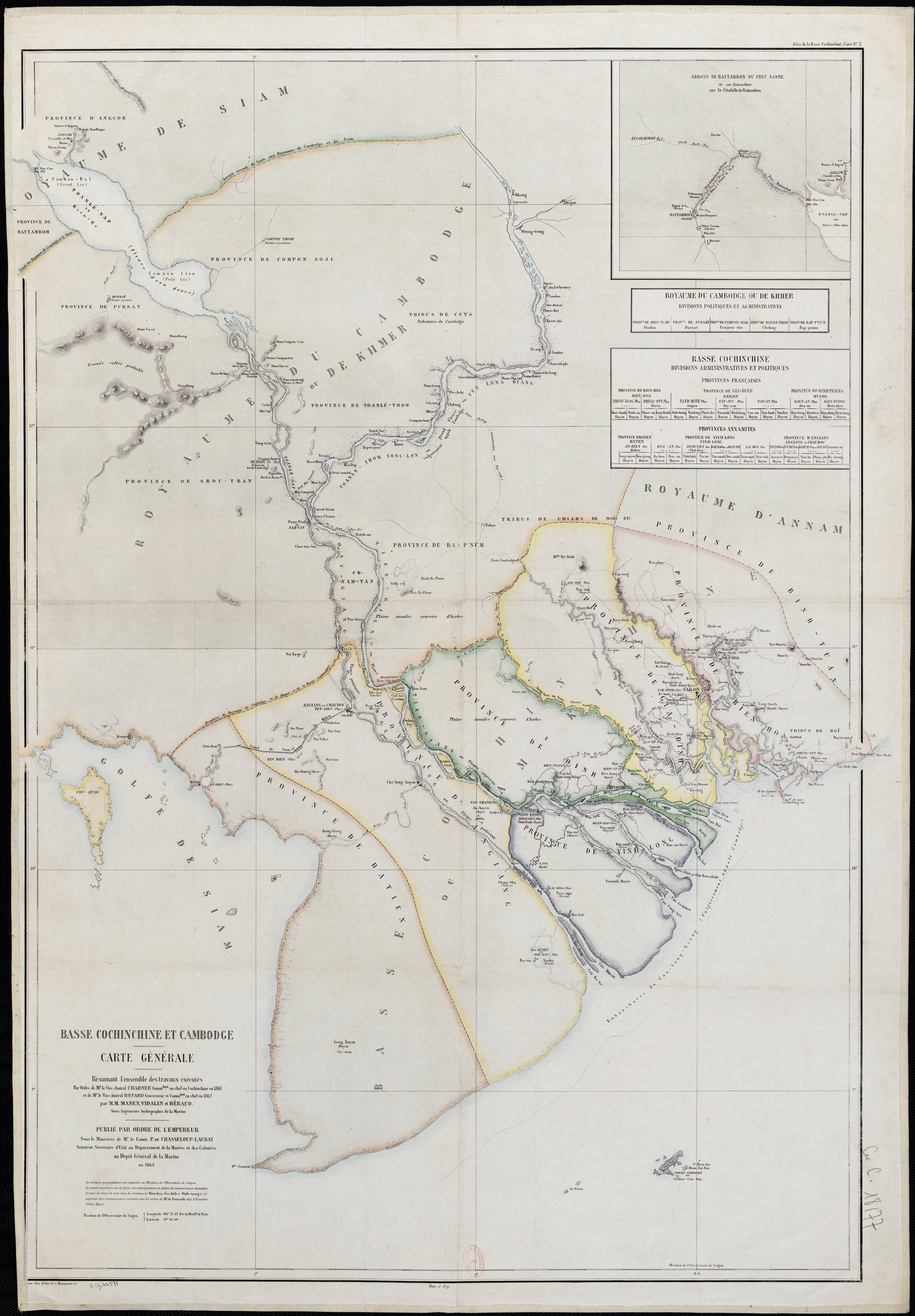 In 1871 all the territories ceded to the French in southern Vietnam were incorporated as colony of Cochinchina, with Admiral Dupré as its first governor.
In 1887, the colony became a confederal member of the Union of French Indochina. Unlike the protectorates of Annam (central Vietnam) and Tonkin (northern Vietnam), Cochinchina was ruled directly by the French, both ''de jure'' and ''de facto'', and was represented by a deputy in the National Assembly in Paris.
Within Indochina, Cochinchina was the territory with the greatest European presence. At its height, in 1940, it was estimated at 16,550 people, the vast majority living in Saigon.
In 1871 all the territories ceded to the French in southern Vietnam were incorporated as colony of Cochinchina, with Admiral Dupré as its first governor.
In 1887, the colony became a confederal member of the Union of French Indochina. Unlike the protectorates of Annam (central Vietnam) and Tonkin (northern Vietnam), Cochinchina was ruled directly by the French, both ''de jure'' and ''de facto'', and was represented by a deputy in the National Assembly in Paris.
Within Indochina, Cochinchina was the territory with the greatest European presence. At its height, in 1940, it was estimated at 16,550 people, the vast majority living in Saigon.
File:NamKy1829.jpg, Cochinchina in 1829 under Nguyễn Dynasty
File:Cochinchine-map-03.jpg, Cochinchina in 1876
File:NamKy1878.jpg, Cochinchina in 1878
File:Cochinchine 1882.jpg, Cochinchina in 1882
File:NamKy1906.png, Cochinchina in 1906
File:Atlas colonial français Colonies Protectorats (...)Pollacchi Paul bpt6k1100182m (1).jpg, Cochinchina in 1929
ArtHanoi Vietnamese money in historical context
{{coord missing, Vietnam French Indochina Former countries in Vietnamese history Former colonies in Asia Former French colonies French colonisation in Asia Former countries in Southeast Asia States and territories established in 1862 States and territories established in 1945 States and territories disestablished in 1945 States and territories disestablished in 1949 1862 establishments in Vietnam 1945 establishments in Vietnam 1945 disestablishments in Vietnam 1949 disestablishments in Vietnam 1862 establishments in the French colonial empire 1945 establishments in the French colonial empire 1945 disestablishments in French Indochina 1949 disestablishments in French Indochina History of South Vietnam
Communist
Communism (from Latin la, communis, lit=common, universal, label=none) is a far-left sociopolitical, philosophical, and economic ideology and current within the socialist movement whose goal is the establishment of a communist society, a s ...
-led nationalist Viet Minh in 1946, the territory was established by the French as the ''Autonomous Republic of Cochinchina'', a controversial decision that helped trigger the First Indochina War. In a further move to deny the claims of the Democratic Republic of Vietnam declared in Hanoi by the Viet Minh in 1949, Cochinchina was formally united with Annam and Tonkin in the State of Vietnam
The State of Vietnam ( vi, Quốc gia Việt Nam; Chữ Nôm: 國家越南; french: État du Viêt-Nam) was a governmental entity in Southeast Asia that existed from 1949 until 1955, first as a member of the French Union and later as a country ...
within the French Union.
''Nam Kỳ'' originated from the reign of Minh Mạng
Minh Mạng () or Minh Mệnh (, vi-hantu, 明 命, lit. "the bright favour of Heaven"; 25 May 1791 – 20 January 1841; born Nguyễn Phúc Đảm, also known as Nguyễn Phúc Kiểu) was the second emperor of the Nguyễn dynasty of V ...
of the Nguyễn dynasty
The Nguyễn dynasty (chữ Nôm: 茹阮, vi, Nhà Nguyễn; chữ Hán: 阮朝, vi, Nguyễn triều) was the last Vietnamese dynasty, which ruled the unified Vietnamese state largely independently from 1802 to 1883. During its existence, ...
, but became a name associated with the French colonial period and so Vietnamese, especially nationalists, prefer the term ''Nam Phần'' to refer to Southern Vietnam.
History
French conquest
 In 1858, under the pretext of protecting the work of French Catholic missionaries, which the imperial Vietnamese
In 1858, under the pretext of protecting the work of French Catholic missionaries, which the imperial Vietnamese Nguyễn dynasty
The Nguyễn dynasty (chữ Nôm: 茹阮, vi, Nhà Nguyễn; chữ Hán: 阮朝, vi, Nguyễn triều) was the last Vietnamese dynasty, which ruled the unified Vietnamese state largely independently from 1802 to 1883. During its existence, ...
increasingly regarded as a political threat, French Admiral Charles Rigault de Genouilly, with the assistance of Spanish forces from the Philippines, attacked Tourane (present day Da Nang
Nang or DanangSee also Danang Dragons ( ; vi, Đà Nẵng, ) is a class-1 municipality and the fifth-largest city in Vietnam by municipal population. It lies on the coast of the East Sea of Vietnam at the mouth of the Hàn River, and is one ...
) in Annam. Early in 1859 he followed this up with an attack on Saigon, but as in Tourane was unable to seize territory outside of the defensive perimeter of the city. The Vietnamese Siege of Saigon
The siege of Saigon, a two-year siege of the city by the Vietnamese after its capture on February 17, 1859 by a Franco-Spanish flotilla under the command of the French admiral Charles Rigault de Genouilly, was one of the major events of the Conq ...
was not lifted until 1861 when additional French forces were able to advance across the Mekong Delta
The Mekong Delta ( vi, Đồng bằng Sông Cửu Long, lit=Nine Dragon River Delta or simply vi, Đồng Bằng Sông Mê Kông, lit=Mekong River Delta, label=none), also known as the Western Region ( vi, Miền Tây, links=no) or South-weste ...
.
The Vietnamese conceded in 1862 and signed the Treaty of Saigon Treaty of Saigon may refer to:
*Treaty of Saigon (1862), between France and Vietnam
*Treaty of Saigon (1874)
The Treaty of Saigon was signed on 15 March 1874 by the Third French Republic and the Nguyễn dynasty of Vietnam. Vietnam made economic a ...
. This ensured the free practice of the Catholic religion; opened the Mekong Delta (and three ports in the north, in Tonkin) to trade; and ceded to France the provinces of Biên Hòa, Gia Định
''Gia'' is a 1998 American biographical drama television film about the life and times of one of the first supermodels, Gia Carangi. The film stars Angelina Jolie as Gia and Faye Dunaway as Wilhelmina Cooper, with Mercedes Ruehl and Elizabeth ...
and Định Tường along with the islands of Poulo Condore. In 1867, French Admiral Pierre de la Grandière forced the Vietnamese to surrender three additional provinces, Châu Đốc, Hà Tiên
Hà Tiên is a Provincial city in Kiên Giang Province, Mekong Delta in Vietnam. Its area is and the population as of 2019 is 81,576. The city borders Cambodia to the west. Hà Tiên is a tourist site of the region thanks to its beaches and la ...
and Vĩnh Long
Vĩnh Long () is a city and the capital of Vĩnh Long Province in Vietnam's Mekong Delta. Vĩnh Long covers and has a population of 147,039 (as of 2009). The name was spelled 永 隆 ("eternal prosperity") in the former Hán Nôm writing syst ...
. With these three additions all of southern Vietnam and the Mekong Delta fell under French control.
Consolidation of power
 In 1871 all the territories ceded to the French in southern Vietnam were incorporated as colony of Cochinchina, with Admiral Dupré as its first governor.
In 1887, the colony became a confederal member of the Union of French Indochina. Unlike the protectorates of Annam (central Vietnam) and Tonkin (northern Vietnam), Cochinchina was ruled directly by the French, both ''de jure'' and ''de facto'', and was represented by a deputy in the National Assembly in Paris.
Within Indochina, Cochinchina was the territory with the greatest European presence. At its height, in 1940, it was estimated at 16,550 people, the vast majority living in Saigon.
In 1871 all the territories ceded to the French in southern Vietnam were incorporated as colony of Cochinchina, with Admiral Dupré as its first governor.
In 1887, the colony became a confederal member of the Union of French Indochina. Unlike the protectorates of Annam (central Vietnam) and Tonkin (northern Vietnam), Cochinchina was ruled directly by the French, both ''de jure'' and ''de facto'', and was represented by a deputy in the National Assembly in Paris.
Within Indochina, Cochinchina was the territory with the greatest European presence. At its height, in 1940, it was estimated at 16,550 people, the vast majority living in Saigon.
Plantation economy
The French authorities dispossessed Vietnamese landowners and peasants to ensure European control of the expansion of rice and rubber production. The French began rubber production in Cochinchina in 1907 seeking a share of the monopoly profits that the British were earning from their plantations inMalaya
Malaya refers to a number of historical and current political entities related to what is currently Peninsular Malaysia in Southeast Asia:
Political entities
* British Malaya (1826–1957), a loose collection of the British colony of the Straits ...
. Investment from metropolitan France was encouraged by large land grants allowing for rubber cultivation on an industrial scale. Virgin rainforests in eastern Cochinchina, the highly fertile 'red lands', were cleared for the new export crop.
These developments contributed to the 1916 Cochinchina uprising
The 1916 Cochinchina uprising was a series of defiant protests and attempted revolts in February against the French authority of southern Vietnam, which had been the colony of Cochinchina since 1862.
The organization and motivation of the upris ...
. Insurgents attempted to storm Saigon central prison, and maintained a prolonged resistance in the Mekong Delta. 51 were hanged.
As they expanded in response to the increased rubber demand after the First World War, the European plantations recruited, as indentured labour, workers from "the overcrowded villages of the Red River Delta in Tonkin and the coastal lowlands of Annam". These migrants, despite '' Sûreté'' efforts at political screening, brought south the influence of the Communist Party of Nguyen Ai Quoc ( Ho Chi Minh), and of other underground nationalist parties (the ''Tan Viet'' and ''Việt Nam Quốc Dân Đảng
The Việt Nam Quốc Dân Đảng (; chữ Hán: ; ), abbreviated VNQDĐ or Việt Quốc, was a nationalist and democratic socialist political party that sought independence from French colonial rule in Vietnam during the early 20th century. ...
''—VNQDD). At the same time, the local peasantry were driven into debt servitude, and into plantation labour, by land and poll taxes. By 1930, 80% of riceland was owned by 25% of landowners, and 57% of the rural population were landless peasants working on large estates. This combination led to widespread and recurring unrest and to strikes. Of these the most significant, leading to armed confrontations, was the refusal of work by labourers Phu Rieng Do, a sprawling 5,500 hectares Michelin
Michelin (; ; full name: ) is a French multinational tyre manufacturing company based in Clermont-Ferrand in the Auvergne-Rhône-Alpes ''région'' of France. It is the second largest tyre manufacturer in the world behind Bridgestone and la ...
rubber plantation in 1930.
In response to rural unrest and to growing labour militancy in Saigon, between 1930 and 1932 the French authorities detained more than 12,000 political prisoners, of whom 88 were guillotined, and almost 7000 sentenced to prison or to hard labour in penal colonies.
Popular Front promise of reform
In 1936 the formation in France of the Popular Front government led byLeon Blum
Leon, Léon (French) or León (Spanish) may refer to:
Places
Europe
* León, Spain, capital city of the Province of León
* Province of León, Spain
* Kingdom of León, an independent state in the Iberian Peninsula from 910 to 1230 and again fro ...
was accompanied by promises of colonial reform. In Cochinchina the new governor-general of Indochina Jules Brévié
Joseph-Jules Brévié (12 March 1880 – 28 July 1964) was a French colonial administrator who became governor-general of French West Africa from 1930 to 1936, and then governor-general of French Indochina from 1937 to 1939. He promoted liberal an ...
, sought to defuse the tense and expectant political situation by amnestying political prisoners, and by easing restrictions on the press, political parties, and trade unions.
Saigon witnessed further unrest culminating in the summer of 1937 in general dock and transport strikes. In April of that year the Communist Party and their Trotskyist left opposition
Trotskyism is the political ideology and branch of Marxism developed by Ukrainian-Russian revolutionary Leon Trotsky and some other members of the Left Opposition and Fourth International. Trotsky self-identified as an orthodox Marxist, a r ...
ran a common slate for the municipal elections with both their respective leaders Nguyễn Văn Tạo and Tạ Thu Thâu
Tạ Thu Thâu (1906–1945) in the 1930s was the principal representative of Trotskyism in Vietnam and, in colonial Cochinchina, of left opposition to the Indochinese Communist Party (PCI) of Nguyen Ai Quoc (Ho Chi Minh). He joined to Left Oppos ...
winning seats. The exceptional anti-colonial unity of the left, however, was split by the lengthening shadow of the Moscow Trials
The Moscow trials were a series of show trials held by the Soviet Union between 1936 and 1938 at the instigation of Joseph Stalin. They were nominally directed against "Trotskyists" and members of "Right Opposition" of the Communist Party of th ...
and by growing protest over the failure of the Communist-supported Popular Front to deliver constitutional reform. Colonial Minister Marius Moutet
Marius Moutet (19 April 1876 – 29 October 1968) was a French Socialist diplomat and colonial adviser. An expert in colonial issues, he served as Minister of the Colonies for four terms in the 1930s and 1940s and was president of the Gener ...
, a Socialist commented that he had sought "a wide consultation with all elements of the popular ill ILL may refer to:
* ''I Love Lucy'', a landmark American television sitcom
* Illorsuit Heliport (location identifier: ILL), a heliport in Illorsuit, Greenland
* Institut Laue–Langevin, an internationally financed scientific facility
* Interlibrar ...
" but with "Trotskyist-Communists intervening in the villages to menace and intimidate the peasant part of the population, taking all authority from the public officials," the necessary "formula" had not been found.
War and the Insurrection of 1940
In April 1939 Cochinchina Council elections Tạ Thu Thâu led a "Workers' and Peasants' Slate" into victory over both the moderate Constitutionalists and the Communists' Democratic Front. Key to their success was popular opposition to the war taxes ("national defence levy") that the Communist Party, in the spirit of Franco-Soviet accord, had felt obliged to support. Brévié set the election results aside and wrote to Colonial Minister Georges Mandel: "the Trotskyists under the leadership of Ta Thu Thau, want to take advantage of a possible war in order to win total liberation." The Stalinists, on the other hand, are "following the position of the Communist Party in France" and "will thus be loyal if war breaks out." With the Hitler-Stalin Pact of 23 August 1939, the local Communists were ordered by Moscow to return to direct confrontation with the French. Under the slogan "Land to the Tillers, Freedom for the workers and independence for Vietnam", in November 1940 the Party in Cochinchina instigated a widespread insurrection. The revolt did not penetrate Saigon (an attempted uprising in the city was quelled in a day). In the Mekong Delta fighting continued until the end of the year.Japanese occupation
After a brief cross-border confrontation with French forces in September 1940, Japanese forces occupied Tonkin. On 9 December 1940, an agreement was reached with the Vichy government whereby French sovereignty over its army and administrative affairs was confirmed, while Japanese forces were free to fight the war against the Allies from Indochinese soil. A large scale movement of troops did not occur until after theNazi invasion of the Soviet Union
Operation Barbarossa (german: link=no, Unternehmen Barbarossa; ) was the invasion of the Soviet Union by Nazi Germany and many of its Axis allies, starting on Sunday, 22 June 1941, during World War II, the Second World War. The operation, code ...
in late June 1941. With the Soviets tied down, the high command concluded that a " strike south" would solve the problems posed for Japan by the American-led oil embargo. To prepare for an invasion of the oil-rich Dutch East Indies, some 140,000 Japanese troops occupied southern French Indochina on 28 July 1941.Namba, Chizuru. (2019). “The French Colonization and Japanese Occupation of Indochina during the Second World War: Encounters of the French, Japanese, and Vietnamese.” ''Cross-Currents: East Asian History and Culture Review'' 32: 74–96.
French troops and the civil administration were allowed to remain, albeit under Japanese supervision. While the Japanese government’s policy of “maintaining peace” in Indochina limited interactions between the Japanese and Vietnamese, the contradiction of mutual coexistence between France, as the “missionary of civilization,” and Japan, as the “liberator of Asia” from Western colonialism, could not be concealed. The tensions contributed to nationalist, anti-colonial feeling. Drawing on the local Coadaist sect, the Japanese began to encourage nationalist groups in Cohinchina from 1943.
Following the liberation of Paris
The liberation of Paris (french: Libération de Paris) was a military battle that took place during World War II from 19 August 1944 until the German garrison surrendered the French capital on 25 August 1944. Paris had been occupied by Nazi Germ ...
in 1944, Japan increasingly suspected that the French authorities would assist Allied
An alliance is a relationship among people, groups, or states that have joined together for mutual benefit or to achieve some common purpose, whether or not explicit agreement has been worked out among them. Members of an alliance are called ...
operations. In March 1945, a Japanese coup d'état in French Indochina took the Europeans into custody and imposed their direct authority. The coup had, in the words of diplomat Jean Sainteny, "wrecked a colonial enterprise that had been in existence for 80 years." In August 1945, as they faced defeat, the Japanese belatedly created a puppet state, incorporating Cochinchina in the Empire of Vietnam
The Empire of Vietnam (; Literary Chinese and Contemporary Japanese: ; Modern Japanese: ja, ベトナム帝国, Betonamu Teikoku, label=none) was a short-lived puppet state of Imperial Japan governing the former French protectorates of Annam ...
under the nominal authority of the Bảo Đại.
The August Revolution and the return of French rule
On 2 September 1945, in Hanoi, Ho Chi Minh and his new Front for the Independence of Vietnam, the Viet Minh, proclaimed the Democratic Republic of Vietnam. Already on 24 August the Viet Minh had declared a provisional government (a Southern Administrative Committee) in Saigon. When, for the declared purpose of disarming the Japanese, the Viet-Minh accommodated the landing and strategic positioning of their wartime "democratic allies", the British, rival political groups turned out in force including the syncreticHoa Hao
The Hoa people (Vietnamese: ''Người Hoa'', or ) are citizens of Vietnam of full or partial Chinese origin. Chinese migration into Vietnam dates back millennia but most Hoa today derive their recent ancestral Chinese heritage from the 18th ...
and Cao Dai
Caodaism ( vi, Đạo Cao Đài, Chữ Hán: ) is a monotheistic syncretic new religious movement officially established in the city of Tây Ninh in southern Vietnam in 1926. The full name of the religion is (The Great Faith or theThird Univ ...
sects. On 7 and 8 September 1945, in the delta city of Cần Thơ the Committee had to rely on the ''Jeunesse d'Avant-Garde/Thanh Niên Tiền Phong'' ( Vanguard Youth), who had contributed to civil defence and policing under Japanese. They fired upon crowds demanding arms against the French.
In Saigon, the violence of a French restoration assisted by British and surrendered Japanese troops, triggered a general uprising on 23 September. In the course of what became known as the Southern Resistance War (Nam Bộ kháng chiến) the Viet Minh defeated rival resistance forces, executing their leading cadres, but, by the end of 1945, had been pushed out of Saigon and major urban centres into the countryside.
Incorporation into the State of Vietnam
On 1 June 1946, while the Viet Minh leadership was in France for negotiations, at the initiative of High Commissioner d'Argenlieu and in violation of the 6 March Ho–Sainteny agreement, a local territorial assembly proclaimed an "Autonomous Republic". War between France and the Viet Minh followed (1946–54).Nguyễn Văn Thinh
Nguyễn Văn Thinh (1888 – 10 November 1946, Saigon) was the first President of Cochinchina. Thinh was a French citizen and joined the Constitutionalist Party in 1926. He founded the Cochinchinese Democratic Party in 1937. He became chief ...
, the first head of its government, died in an apparent suicide in November of the same year. He was succeeded by Lê Văn Hoạch
Lê Văn Hoạch (1898 – 1978) was a Vietnamese politician who served as president of Cochinchina from 1946 to 1947.
Hoạch took over the premiership on 26 November 1946 after the death of Nguyen Van Thinh.''Vietnamese Royal Exile in Japa ...
, a member of the caodaist
Caodaism ( vi, Đạo Cao Đài, Chữ Hán: ) is a monotheistic syncretic new religious movement officially established in the city of Tây Ninh in southern Vietnam in 1926. The full name of the religion is (The Great Faith or theThird Uni ...
sect. In 1947, Nguyễn Văn Xuân replaced Lê and renamed the "Provisional Government of the Autonomous Republic of Cochinchina" as the "Provisional Government of Southern Vietnam", suggesting that his aim was to reunite the whole country.
The next year, the Provisional Central Government of Vietnam
The Provisional Central Government of Vietnam was an entity proclaimed in Vietnam during the First Indochina War. It was created as a transitional government replacing the protectorates of Tonkin (Northern Vietnam) and Annam (Central Vietnam), u ...
was proclaimed with the merger of Annam and Tonkin: Xuân became its Prime minister and left office in Cochichina, where he was replaced by Trần Văn Hữu. Xuân and the French had agreed to reunite Vietnam, but Cochinchina posed a problem because of its ill-defined legal status. The reunification was opposed by the French colonists, who were still influential in the Cochinchinese council, and by Southern Vietnamese autonomists: they delayed the process of reunification by arguing that Cochinchina was still legally a colony – as its new status as a Republic
A republic () is a "state in which power rests with the people or their representatives; specifically a state without a monarchy" and also a "government, or system of government, of such a state." Previously, especially in the 17th and 18th c ...
had never been ratified by the French National Assembly
The National Assembly (french: link=no, italics=set, Assemblée nationale; ) is the lower house of the bicameral French Parliament under the Fifth Republic, the upper house being the Senate (). The National Assembly's legislators are known a ...
– and that any territorial change therefore required the approval of the French parliament. Xuân issued a by-law reuniting Cochinchina with the rest of Vietnam, but it was overruled by the Cochinchinese council.Philippe Franchini, ''Les Guerres d'Indochine'', vol. I, Pygmalion – Gérard Watelet, Paris, 1988, pp. 399–406
Cochinchina remained separated from the rest of Vietnam for over a year, while former Emperor Bảo Đại – whom the French wanted to bring back to power as a political alternative to Ho Chi Minh – refused to return to Vietnam and take office as head of state until the country was fully reunited. On 14 March 1949, the French National Assembly voted a law permitting the creation of a Territorial Assembly of Cochinchina. This new Cochinchinese parliament was elected on 10 April 1949, with the Vietnamese representatives then becoming a majority. On 23 April, the Territorial Assembly approved the merger of the Provisional Government of Southern Vietnam with the Provisional Central Government of Vietnam. The decision was in turn approved by the French National Assembly on 20 May, and the merger was effective on 4 June. The State of Vietnam
The State of Vietnam ( vi, Quốc gia Việt Nam; Chữ Nôm: 國家越南; french: État du Viêt-Nam) was a governmental entity in Southeast Asia that existed from 1949 until 1955, first as a member of the French Union and later as a country ...
was then be proclaimed, with Bảo Đại as head of state.
Administration
Government
Following the French colonial invasion, Vietnamese mandarins withdrew from Cochinchina, forcing the French to adopt a policy of direct rule. The highest office in the government of French Cochinchina was theGovernor of Cochinchina
List of administrators of the French colony of Cochinchina
(Dates in italics indicate ''de facto ''continuation of office)
See also
* History of Vietnam
*Cochinchina
* Cochinchina Campaign
*French colonial empire
*Notre-Dame Cathedral Basilica ...
(統督南圻, ''Thống đốc Nam Kỳ''), who after 1887 reported directly to the Governor-General of French Indochina
European (as well as Japanese and Chinese) colonial administrators had historically been responsible for the territory of French Indochina, an area equivalent to modern-day Vietnam, Laos, Cambodia, and the Chinese city of Zhanjiang.
List o ...
. As French Cochinchina was a directly-ruled colony the French colonial apparatus operated at every level of government including at the provincial, district, and communal levels.
Each Cochinchinese province was headed by French official with the title of "Chủ tỉnh" (主省) or "Tỉnh trưởng" (省長), these French officials had similar roles and responsibilities as the equivalent French "Công sứ" (公使) had in the provinces of the Nguyễn dynasty. The provinces of French Cochinchina was further divided into districts
A district is a type of administrative division that, in some countries, is managed by the local government. Across the world, areas known as "districts" vary greatly in size, spanning regions or counties, several municipalities, subdivisions o ...
known as "Tong" headed by a "Chanh tong", which were further divided into communes known as "xã" (社), which were headed by a "Huong ca". Both the district and commune chiefs were salaried employees of the French colonial administration.
Laws
During the early periods of French rule in Cochinchina both French laws and Nguyễn dynasty laws applied and offenders of both faced trial in French courts. Initially French people were tried using French laws and Vietnamese people (then known as "Annamese people") were tried using the Nguyễn dynasty's laws alongside a new set of provisions that the French had introduced for their colonial subjects. The French courts applied their rulings based on the two different legal systems. After their consolidation of power the Nguyễn's laws were completely abolished in French Cochinchina and only French laws applied to everyone in the colony. On 6 January 1903, the Governor-General of French Indochina Jean Baptiste Paul Beau issued a decree that stated that offences for both French and indigenous laws would go to French courts and that offenders would only be tried against French Cochinchina's penal code. During this period the Governor-General of French Indochina also issued a decree that introduced new laws to fine people for a number of common offences outside of the French penal code.Gallery
See also
* Cochinchina * French Indochina ** Protectorate of Annam ** Protectorate of Tonkin *List of administrators of the French colony of Cochinchina
List of administrators of the French colony of Cochinchina
(Dates in italics indicate ''de facto ''continuation of office)
See also
*History of Vietnam
*Cochinchina
* Cochinchina Campaign
*French colonial empire
*Notre-Dame Cathedral Basilica ...
* List of French possessions and colonies
* State of Vietnam
The State of Vietnam ( vi, Quốc gia Việt Nam; Chữ Nôm: 國家越南; french: État du Viêt-Nam) was a governmental entity in Southeast Asia that existed from 1949 until 1955, first as a member of the French Union and later as a country ...
Notes
References
Further reading
* Encyclopedia of Asian History, Volume 4 (Vietnam) 1988. Charles Scribner's Sons, New York. * ''Vietnam – A Long History'' by Nguyễn Khắc Viện (1999). Hanoi, Thế Giới PublishersArtHanoi Vietnamese money in historical context
{{coord missing, Vietnam French Indochina Former countries in Vietnamese history Former colonies in Asia Former French colonies French colonisation in Asia Former countries in Southeast Asia States and territories established in 1862 States and territories established in 1945 States and territories disestablished in 1945 States and territories disestablished in 1949 1862 establishments in Vietnam 1945 establishments in Vietnam 1945 disestablishments in Vietnam 1949 disestablishments in Vietnam 1862 establishments in the French colonial empire 1945 establishments in the French colonial empire 1945 disestablishments in French Indochina 1949 disestablishments in French Indochina History of South Vietnam