Nacht und Nebel on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 ''Nacht und Nebel'' (
''Nacht und Nebel'' (
 Even before the
Even before the  Three months later Keitel further expanded on this principle in a February 1942 letter stating that any prisoners not executed within eight days were to be handed over to the Gestapo. and
Three months later Keitel further expanded on this principle in a February 1942 letter stating that any prisoners not executed within eight days were to be handed over to the Gestapo. and
 The ''Nacht und Nebel'' prisoners' hair was shaved and the women were given a convict costume of a thin cotton dress, wooden sandals and a triangular black headcloth. According to historian Wolfgang Sofsky,
The ''Nacht und Nebel'' prisoners' hair was shaved and the women were given a convict costume of a thin cotton dress, wooden sandals and a triangular black headcloth. According to historian Wolfgang Sofsky,
 Early in the war, the program caused the mass execution of political prisoners, especially
Early in the war, the program caused the mass execution of political prisoners, especially
United States Holocaust Memorial Museum. (2014). ''Holocaust Encyclopedia'', "Night and Fog Decree"
;Further reading * Harthoorn, Willem Lodewijk. ''Verboden te sterven'', Van Gruting, 2007, – A personal account of a person who survived as a "Night and Fog" prisoner four months in Gross-Rosen and a year in
Night and Fog Prisoners
'. {{DEFAULTSORT:Nacht Und Nebel Nazi war crimes Crimes against humanity Holocaust terminology Law in Nazi Germany Orders by Adolf Hitler December 1941 events 1941 in Germany 1941 documents German words and phrases Political quotes 1940s neologisms
 ''Nacht und Nebel'' (
''Nacht und Nebel'' (German
German(s) may refer to:
* Germany (of or related to)
**Germania (historical use)
* Germans, citizens of Germany, people of German ancestry, or native speakers of the German language
** For citizens of Germany, see also German nationality law
**Ge ...
: ), meaning Night and Fog, was a directive issued by Adolf Hitler
Adolf Hitler (; 20 April 188930 April 1945) was an Austrian-born German politician who was dictator of Germany from 1933 until his death in 1945. He rose to power as the leader of the Nazi Party, becoming the chancellor in 1933 and the ...
on 7 December 1941 targeting political activists and resistance "helpers" in the territories occupied by Nazi Germany during World War II
World War II or the Second World War, often abbreviated as WWII or WW2, was a world war that lasted from 1939 to 1945. It involved the World War II by country, vast majority of the world's countries—including all of the great power ...
, who were to be imprisoned, murdered, or made to disappear, while the family and the population remained uncertain as to the fate or whereabouts of the alleged offender against the Nazi occupation power. Victims who disappeared in these clandestine actions were never heard from again.
Name
The alliterative hendiadys ''Nacht und Nebel'' (German
German(s) may refer to:
* Germany (of or related to)
**Germania (historical use)
* Germans, citizens of Germany, people of German ancestry, or native speakers of the German language
** For citizens of Germany, see also German nationality law
**Ge ...
for "Night and Fog") is documented in German since the beginning of the 17th century. It was used by Wagner in ''Das Rheingold
''Das Rheingold'' (; ''The Rhinegold''), WWV 86A, is the first of the four music dramas that constitute Richard Wagner's '' Der Ring des Nibelungen'' (English: ''The Ring of the Nibelung''). It was performed, as a single opera, at the National ...
'' (1869) and has since been adopted into everyday German (e.g. it appears in Thomas Mann's ''Der Zauberberg
''The Magic Mountain'' (german: Der Zauberberg, links=no, ) is a novel by Thomas Mann, first published in German in November 1924. It is widely considered to be one of the most influential works of twentieth-century German literature.
Mann s ...
,'' or "The Magic Mountain
''The Magic Mountain'' (german: Der Zauberberg, links=no, ) is a novel by Thomas Mann, first published in German in November 1924. It is widely considered to be one of the most influential works of twentieth-century German literature.
Mann s ...
"). It is not clear whether the term ''Nacht-und-Nebel-Erlass'' ("Night and Fog directive") had been in wide circulation or used publicly before 1945. The designation "NN" was sometimes used, however, to refer to prisoners and deportees ("NN-Gefangener", "NN-Häftling", "NN-Sache") at the time. The abbreviation "NN" was otherwise well known in German to mean "nullus nomen" ("without name" for security reasons), similar to the English NN for "nomen nescio
''Nomen nescio'' (), abbreviated to ''N.N.'', is used to signify an anonymous or unnamed person. From Latin ''nomen'' – "name", and ''nescio'' – "I do not know", it literally means "I do not know the name". The generic name Numerius Negidius ...
".
Background
 Even before the
Even before the Holocaust
The Holocaust, also known as the Shoah, was the genocide of European Jews during World War II. Between 1941 and 1945, Nazi Germany and its collaborators systematically murdered some six million Jews across German-occupied Europe; ...
gained momentum, the Nazis had begun rounding up political prisoner
A political prisoner is someone imprisoned for their political activity. The political offense is not always the official reason for the prisoner's detention.
There is no internationally recognized legal definition of the concept, although nu ...
s from both Germany and occupied Europe
German-occupied Europe refers to the sovereign countries of Europe which were wholly or partly occupied and civil-occupied (including puppet governments) by the military forces and the government of Nazi Germany at various times between 1939 an ...
. Most of the early prisoners were of two sorts: they were either political prisoners of personal conviction or belief whom the Nazis deemed in need of "re-education" to Nazi ideals, or resistance leaders in occupied western Europe.
Up until the time of the ''Nacht und Nebel'' decree, prisoners from Western Europe were handled by German soldiers in approximately the same way as by other countries: according to international agreements and procedures such as the Geneva Convention
upright=1.15, Original document in single pages, 1864
The Geneva Conventions are four treaties, and three additional protocols, that establish international legal standards for humanitarian treatment in war. The singular term ''Geneva Conve ...
. Hitler and his upper-level staff, however, made a critical decision not to conform to what they considered unnecessary rules and in the process abandoned "all chivalry towards the opponent" and removed "every traditional restraint on warfare." During the Nuremberg Trial against the High Command of the Wehrmacht (OKW), the head of the legal department in the OKW, Ministerial Director and General, Dr. Rudolf Lehmann, testified that Hitler had literally demanded opponents of the regime, who could not be immediately given a short trial, should be brought across the border to Germany in the "Night and Fog" and remain isolated there.
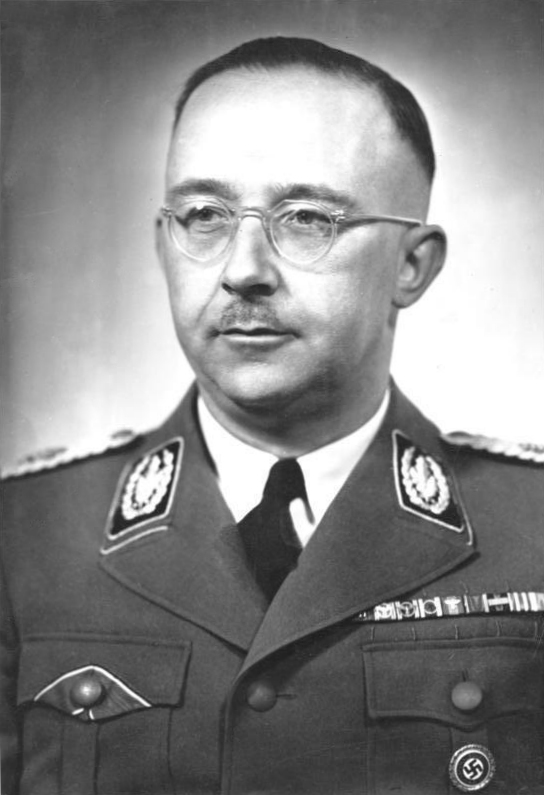
On 7 December 1941, ''Reichsführer-SS
(, ) was a special title and rank that existed between the years of 1925 and 1945 for the commander of the (SS). ''Reichsführer-SS'' was a title from 1925 to 1933, and from 1934 to 1945 it was the highest rank of the SS. The longest-servi ...
'' Heinrich Himmler
Heinrich Luitpold Himmler (; 7 October 1900 – 23 May 1945) was of the (Protection Squadron; SS), and a leading member of the Nazi Party of Germany. Himmler was one of the most powerful men in Nazi Germany and a main architect of th ...
issued the following instructions to the Gestapo
The (), abbreviated Gestapo (; ), was the official secret police of Nazi Germany and in German-occupied Europe.
The force was created by Hermann Göring in 1933 by combining the various political police agencies of Prussia into one orga ...
:
Armed Forces High Command Feldmarschall Wilhelm Keitel had also received a so-called "Führer's decree" from Hitler on 7 December 1941, and while this order was not documented in writing, Keitel immediately passed it on to the appropriate authorities in the form of "guidelines" and likewise issued a secret decree containing more detailed instructions for its implementation. Essentially, the decree was about how to more effectively combat the increasing resistance actions in the territories occupied by Germany in Western Europe after the beginning of the war against the Soviet Union; thereto, the "Night and Fog" decree originally concerned only nationals of France, Belgium, the Netherlands, Luxembourg and Norway. On 12 December, Keitel issued a directive explaining Hitler's orders:
 Three months later Keitel further expanded on this principle in a February 1942 letter stating that any prisoners not executed within eight days were to be handed over to the Gestapo. and
Three months later Keitel further expanded on this principle in a February 1942 letter stating that any prisoners not executed within eight days were to be handed over to the Gestapo. and
Reinhard Heydrich
Reinhard Tristan Eugen Heydrich ( ; ; 7 March 1904 – 4 June 1942) was a high-ranking German SS and police official during the Nazi era and a principal architect of the Holocaust.
He was chief of the Reich Security Main Office (inclu ...
's ''Sicherheitsdienst
' (, ''Security Service''), full title ' (Security Service of the '' Reichsführer-SS''), or SD, was the intelligence agency of the SS and the Nazi Party in Nazi Germany. Established in 1931, the SD was the first Nazi intelligence organization ...
'' (Security Service; SD) was given responsibility for over-seeing and carrying out the ''Nacht und Nebel'' decree. The SD was mainly an information-gathering agency, while the Gestapo was the main executive agency of the political police system. The decree was meant to intimidate local populations into submission, by denying friends and families of seized persons any knowledge of their whereabouts or their fate. The prisoners were secretly transported to Germany, and vanished without a trace. In 1945, abandoned SD records were found to include merely names and the initials "NN" (''Nacht und Nebel''); even the sites of graves were unrecorded. The Nazis even coined a new term for those who "vanished" in accordance with this decree; they were ''vernebelt''—"transformed into mist". To this day, it is not known how many people disappeared as a result of this decree. The International Military Tribunal at Nuremberg held that the disappearances committed as part of the ''Nacht und Nebel'' program were war crimes which violated both the Hague Conventions and customary international law
Customary international law is an aspect of international law involving the principle of custom. Along with general principles of law and treaties, custom is considered by the International Court of Justice, jurists, the United Nations, and its ...
.
Himmler immediately communicated Keitel's directive to various SS stations and within six months, the decree was sent to concentration camp commanders by Richard Glücks
Richard Glücks (; 22 April 1889 – 10 May 1945) was a high-ranking German Nazi official in the SS. From November 1939 until the end of World War II, he was Concentration Camps Inspector (CCI), which became ''Amt D: Konzentrationslagerwesen' ...
. The ''Nacht und Nebel'' prisoners were mostly from France
France (), officially the French Republic ( ), is a country primarily located in Western Europe. It also comprises of Overseas France, overseas regions and territories in the Americas and the Atlantic Ocean, Atlantic, Pacific Ocean, Pac ...
, Belgium
Belgium, ; french: Belgique ; german: Belgien officially the Kingdom of Belgium, is a country in Northwestern Europe. The country is bordered by the Netherlands to the north, Germany to the east, Luxembourg to the southeast, France to ...
, Luxembourg
Luxembourg ( ; lb, Lëtzebuerg ; french: link=no, Luxembourg; german: link=no, Luxemburg), officially the Grand Duchy of Luxembourg, ; french: link=no, Grand-Duché de Luxembourg ; german: link=no, Großherzogtum Luxemburg is a small lan ...
, Denmark
)
, song = ( en, "King Christian stood by the lofty mast")
, song_type = National and royal anthem
, image_map = EU-Denmark.svg
, map_caption =
, subdivision_type = Sovereign state
, subdivision_name = Kingdom of Denmark
, establish ...
, the Netherlands
)
, anthem = ( en, "William of Nassau")
, image_map =
, map_caption =
, subdivision_type = Sovereign state
, subdivision_name = Kingdom of the Netherlands
, established_title = Before independence
, established_date = Spanish Netherl ...
, and Norway
Norway, officially the Kingdom of Norway, is a Nordic countries, Nordic country in Northern Europe, the mainland territory of which comprises the western and northernmost portion of the Scandinavian Peninsula. The remote Arctic island of ...
. They were usually arrested in the middle of the night and quickly taken to prisons hundreds of kilometres away for questioning, eventually arriving at concentration camps such as Natzweiler
Natzwiller () is a commune in the Bas-Rhin department in Grand Est in northeastern France.
History
Built in spring 1941 on the territory of the commune, Natzweiler-Struthof concentration camp opened for prisoners in May 1941. It was the only N ...
, Esterwegen or Gross-Rosen, if they survived.
Natzweiler concentration camp in particular, became an isolation camp for political prisoners from northern and western Europe under the decree's mandate. Natzweiler was the most prominent concentration camp with NN prisoners and probably also the one in which most of them spent the longest time. When the concentration camps in the east and west of German-occupied Europe were dissolved in the face of the advancing Allied armies and their inmates evacuated, often on cruel death marches, centrally located camps such as Dachau and Mauthausen were filled with thousands of NN prisoners at the end of the war, whose special status was largely lost in the chaos of the last months before the liberation.
Up to 30 April 1944, at least 6,639 persons had been arrested under ''Nacht und Nebel'' orders. Some 340 of them may have been executed. The 1956 film ''Night and Fog
''Nacht und Nebel'' (German: ), meaning Night and Fog, was a directive issued by Adolf Hitler on 7 December 1941 targeting political activists and resistance "helpers" in the territories occupied by Nazi Germany during World War II, who were to ...
'', directed by Alain Resnais
Alain Resnais (; 3 June 19221 March 2014) was a French film director and screenwriter whose career extended over more than six decades. After training as a film editor in the mid-1940s, he went on to direct a number of short films which included ...
, uses the term to illustrate one aspect of the concentration camp system as it was transformed into a system of labour and death camps.
Text of the decrees
Rationale
The reasons for ''Nacht und Nebel'' were many. The policy, enforced inNazi-occupied countries
German-occupied Europe refers to the sovereign countries of Europe which were wholly or partly occupied and civil-occupied (including puppet governments) by the military forces and the government of Nazi Germany at various times between 1939 ...
, meant that whenever someone was arrested, the family would learn nothing about the person's fate. The people arrested, sometimes only suspected resisters, were secretly sent to Germany and perhaps to a concentration camp. Whether they lived or died, the Germans would give out no information to the families involved. This was done to keep the population in occupied countries quiet by promoting an atmosphere of mystery, fear and terror.
The program made it far more difficult for other governments or humanitarian organizations to accuse the German government of specific misconduct because it obscured whether or not internment or death had even occurred, let alone the cause of the person's disappearance. It thereby kept the Nazis from being held accountable. It allowed across-the-board, silent defiance of international treaties and conventions – one cannot apply the requirements for humane treatment in war if one cannot locate a victim or discern that victim's fate. Additionally, the policy lessened German subjects' moral qualms about the Nazi regime, as well as their desire to speak out against it, by keeping the general public ignorant of the regime's malfeasance and by creating extreme pressure for service members to remain silent.
Treatment of prisoners
 The ''Nacht und Nebel'' prisoners' hair was shaved and the women were given a convict costume of a thin cotton dress, wooden sandals and a triangular black headcloth. According to historian Wolfgang Sofsky,
The ''Nacht und Nebel'' prisoners' hair was shaved and the women were given a convict costume of a thin cotton dress, wooden sandals and a triangular black headcloth. According to historian Wolfgang Sofsky,
Prisoners of the ''Nacht und Nebel'' transports were marked by broad red bands; on their backs and both trouser legs was a cross, with the letters "NN" to its right. From these emblems, it was possible to recognize immediately what class a prisoner belonged to and how he or she was pigeonholed and evaluated by the SS.The prisoners were often moved apparently at random from prison to prison such as Fresnes Prison in Paris, Waldheim near
Dresden
Dresden (, ; Upper Saxon: ''Dräsdn''; wen, label= Upper Sorbian, Drježdźany) is the capital city of the German state of Saxony and its second most populous city, after Leipzig. It is the 12th most populous city of Germany, the fourth ...
, Leipzig
Leipzig ( , ; Upper Saxon: ) is the most populous city in the German state of Saxony. Leipzig's population of 605,407 inhabitants (1.1 million in the larger urban zone) as of 2021 places the city as Germany's eighth most populous, as ...
, Potsdam
Potsdam () is the capital and, with around 183,000 inhabitants, largest city of the German state of Brandenburg. It is part of the Berlin/Brandenburg Metropolitan Region. Potsdam sits on the River Havel, a tributary of the Elbe, downstream of ...
, Lübeck
Lübeck (; Low German also ), officially the Hanseatic City of Lübeck (german: Hansestadt Lübeck), is a city in Northern Germany. With around 217,000 inhabitants, Lübeck is the second-largest city on the German Baltic coast and in the state ...
and Stettin
Szczecin (, , german: Stettin ; sv, Stettin ; Latin: ''Sedinum'' or ''Stetinum'') is the capital and largest city of the West Pomeranian Voivodeship in northwestern Poland. Located near the Baltic Sea and the German border, it is a major s ...
. The deportees were sometimes herded 80 at a time with standing room only into slow moving, dirty cattle wagons with little or no food or water on journeys lasting up to five days to their next unknown destination.
At the camps, the prisoners were forced to stand for hours in freezing and wet conditions at 5:00 a.m. every morning, standing strictly to attention, before being sent to work a twelve-hour day with only a twenty-minute break for a scant meal. They were confined in cold and starving conditions; many had dysentery or other illnesses, and the weakest were often beaten to death, shot, guillotined, or hanged, while the others were subjected to torture by the Germans.Nichol, John and Rennell, Tony (2007). ''Escape from Nazi Europe'', Penguin Books.
When the inmates were totally exhausted or if they were too ill or too weak to work, they were then transferred to the Revier (''Krankenrevier'', sick barrack) or other places for extermination. If a camp did not have a gas chamber
A gas chamber is an apparatus for killing humans or other animals with gas, consisting of a sealed chamber into which a poisonous or asphyxiant gas is introduced. Poisonous agents used include hydrogen cyanide and carbon monoxide.
History
...
of its own, the so-called Muselmänner, or prisoners who were too sick to work, were often murdered or transferred to other concentration camps for extermination.
When the Allies
An alliance is a relationship among people, groups, or states that have joined together for mutual benefit or to achieve some common purpose, whether or not explicit agreement has been worked out among them. Members of an alliance are called ...
liberated Paris
Paris () is the capital and most populous city of France, with an estimated population of 2,165,423 residents in 2019 in an area of more than 105 km² (41 sq mi), making it the 30th most densely populated city in the world in 2020. Si ...
and Brussels
Brussels (french: Bruxelles or ; nl, Brussel ), officially the Brussels-Capital Region (All text and all but one graphic show the English name as Brussels-Capital Region.) (french: link=no, Région de Bruxelles-Capitale; nl, link=no, Bruss ...
, the SS transported many of its remaining ''Nacht und Nebel'' prisoners to concentration camps deeper in Nazi-controlled territory, such as Ravensbrück concentration camp
Ravensbrück () was a German concentration camp exclusively for women from 1939 to 1945, located in northern Germany, north of Berlin at a site near the village of Ravensbrück (part of Fürstenberg/Havel). The camp memorial's estimated figure ...
for women, Mauthausen-Gusen concentration camp
Mauthausen was a Nazi concentration camp on a hill above the market town of Mauthausen (roughly east of Linz), Upper Austria. It was the main camp of a group with nearly 100 further subcamps located throughout Austria and southern German ...
, Buchenwald concentration camp
Buchenwald (; literally 'beech forest') was a Nazi concentration camp established on hill near Weimar, Germany, in July 1937. It was one of the first and the largest of the concentration camps within Germany's 1937 borders. Many actual or su ...
, Schloss Hartheim
Schloss Hartheim, also known as Hartheim Castle, is a castle at Alkoven in Upper Austria, some from Linz, Austria. It was built by Jakob von Aspen in 1600, and it is a prominent Renaissance castle in the country. The building became notorious as ...
, or Flossenbürg concentration camp.
Results
 Early in the war, the program caused the mass execution of political prisoners, especially
Early in the war, the program caused the mass execution of political prisoners, especially Soviet
The Soviet Union,. officially the Union of Soviet Socialist Republics. (USSR),. was a List of former transcontinental countries#Since 1700, transcontinental country that spanned much of Eurasia from 1922 to 1991. A flagship communist state, ...
military prisoners, who in early 1942 outnumbered the Jews in number of deaths even at Auschwitz
Auschwitz concentration camp ( (); also or ) was a complex of over 40 Nazi concentration camps, concentration and extermination camps operated by Nazi Germany in Polish areas annexed by Nazi Germany, occupied Poland (in a portion annexed int ...
. As the transports grew and Hitler's troops moved across Europe, that ratio changed dramatically. The ''Nacht und Nebel'' decree was carried out surreptitiously, but it set the background for orders that would follow and established a "new dimension of fear". As the war continued, so did the openness of such decrees and orders.
It can be surmised from various writings that in the beginning the German public knew only a little of the plans Hitler had to enforce a "New European Order". As the years passed, despite the best attempts of Goebbels
Paul Joseph Goebbels (; 29 October 1897 – 1 May 1945) was a German Nazi politician who was the ''Gauleiter'' (district leader) of Berlin, chief propagandist for the Nazi Party, and then Reich Minister of Propaganda from 1933 to 19 ...
and the Propaganda Ministry with its formidable domestic information control, diaries and periodicals of the time show that information about the harshness and cruelty of the program became progressively known to the German public.
Soldiers brought back information, families on rare occasion heard from or about loved ones, and Allied news sources and the BBC were able to get past censorship sporadically. Although captured archives from the SD contain numerous orders stamped with "NN" (''Nacht und Nebel''), it has never been determined exactly how many people disappeared as a result of the decree.
Hesitant if not outright skeptical at first of reports coming in about the atrocities being committed by the Nazis, the Allies' doubts were pushed aside when the French entered the Natzweiler-Struthof camp (one of the ''Nacht und Nebel'' facilities) on 23 November 1944, and discovered a chamber where victims were hung by their wrists from hooks to accommodate the process of pumping poisonous Zyklon-B
Zyklon B (; translated Cyclone B) was the trade name of a cyanide-based pesticide invented in Germany in the early 1920s. It consisted of hydrogen cyanide (prussic acid), as well as a cautionary eye irritant and one of several adsorbents such ...
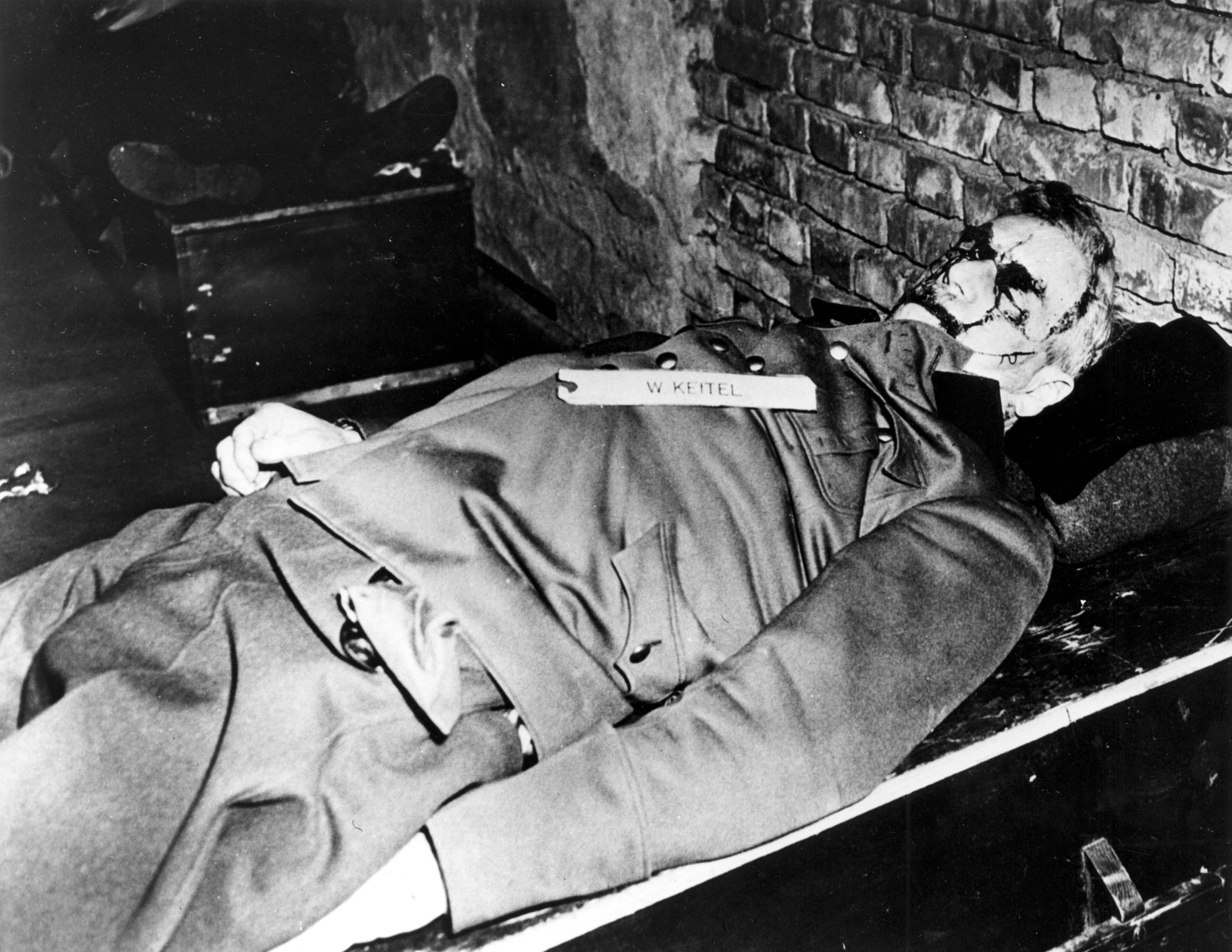
gas into the room. Keitel later testified at the Nuremberg Trials
The Nuremberg trials were held by the Allies of World War II, Allies against representatives of the defeated Nazi Germany, for plotting and carrying out invasions of other countries, and other crimes, in World War II.
Between 1939 and 1945 ...
that of all the illegal orders he had carried out, the ''Nacht und Nebel'' decree was "the worst of all".
Former Supreme Court Justice and chief prosecutor at the international Nuremberg trial, Robert H. Jackson
Robert Houghwout Jackson (February 13, 1892 – October 9, 1954) was an American lawyer, jurist, and politician who served as an Associate Justice of the U.S. Supreme Court from 1941 until his death in 1954. He had previously served as Unit ...
listed the "terrifying" ''Nacht und Nebel'' decree with the other crimes committed by the Nazis in his closing address. In part because of his role in carrying out this decree, Keitel was sentenced to death by hanging
Hanging is the suspension of a person by a noose or ligature around the neck.Oxford English Dictionary, 2nd ed. Hanging as method of execution is unknown, as method of suicide from 1325. The ''Oxford English Dictionary'' states that hanging ...
, despite his insistence on being shot instead due to his military service and rank. At 1:20 a.m. on 16 October 1946 Keitel defiantly shouted out, "'' Alles für Deutschland! Deutschland über alles!''" just before the trap door opened beneath his feet.Conot (2000). ''Justice at Nuremberg'', p. 506.
Notable prisoners
up Noor Inayat Khan, a British agent executed under the ''Nacht und Nebel'' program *Trygve Bratteli
(11 January 1910 – 20 November 1984) was a Norwegian newspaper editor and politician with the Norwegian Labour Party. He served as the 26th prime minister of Norway from 1971 to 1972 and again from 1973 to 1976. He was president of the ...
(Norwegian Resistance, later Prime Minister)
*Virginia d'Albert-Lake
Virginia d'Albert-Lake (born 4 June 1910, Dayton, Ohio – died 20 September 1997, Dinard, France) was a member of the anti-Nazi French Resistance during World War II. She worked with the Comet Escape Line. She and her husband Philippe helped ...
(American)
* Charles Delestraint (French Resistance)
*Andrée de Jongh
Countess Andrée Eugénie Adrienne de Jongh (30 November 1916 – 13 October 2007), called Dédée and Postman, was a member of the Belgian Resistance during the Second World War. She organised and led the Comet Line (''Le Réseau Comète'' ...
("Dédée") (Belgian Resistance)
*Noor Inayat Khan
Noor-un-Nisa Inayat Khan, GC (1 January 1914 – 13 September 1944), also known as Nora Inayat-Khan and Nora Baker, was a British resistance agent in France in World War II who served in the Special Operations Executive (SOE). The purpose of S ...
* Mary Lindell (Comtesse de Milleville)
*Henriette Bie Lorentzen
Henriette Bie Lorentzen (18 July 1911 – 23 August 2001), born Anna Henriette Wegner Haagaas, was a Norwegian journalist, humanist, peace activist, feminist, co-founder of the Nansen Academy, resistance member and concentration camp survivor dur ...
* Elsie Maréchal (Belgian Resistance)
* Henriette Roosenburg
* Xavier, Duke of Parma
See also
*Commando Order
The Commando Order () was issued by the OKW, the high command of the German armed forces, on 18 October 1942. This order stated that all Allied commandos captured in Europe and Africa should be summarily executed without trial, even if in pro ...
*Commissar Order
The Commissar Order (german: Kommissarbefehl) was an order issued by the German High Command ( OKW) on 6 June 1941 before Operation Barbarossa. Its official name was Guidelines for the Treatment of Political Commissars (''Richtlinien für die Be ...
*'' Le prisonnier politique'' - a 1949 sculpture
*Resistance during World War II
Resistance movements during World War II occurred in every occupied country by a variety of means, ranging from non-cooperation to propaganda, hiding crashed pilots and even to outright warfare and the recapturing of towns. In many countries, r ...
** Belgian Resistance
** Dutch Resistance
**French Resistance
The French Resistance (french: La Résistance) was a collection of organisations that fought the German occupation of France during World War II, Nazi occupation of France and the Collaborationism, collaborationist Vichy France, Vichy régim ...
**Norwegian resistance movement
The Norwegian resistance ( Norwegian: ''Motstandsbevegelsen'') to the occupation of Norway by Nazi Germany began after Operation Weserübung in 1940 and ended in 1945. It took several forms:
*Asserting the legitimacy of the exiled governme ...
* List of Nazi-German concentration camps
* Black jails (China)
*Extraordinary rendition
Extraordinary rendition is a euphemism for state-sponsored forcible abduction in another jurisdiction and transfer to a third state. The phrase usually refers to a United States-led program used during the War on Terror, which had the purpos ...
(US)
*Forced disappearance
An enforced disappearance (or forced disappearance) is the secret abduction or imprisonment of a person by a state or political organization, or by a third party with the authorization, support, or acquiescence of a state or political organi ...
*Ghost detainee
Ghost detainee is a term used in the executive branch of the United States government to designate a person held in a detention center, whose identity has been hidden by keeping them unregistered and therefore anonymous.National Defense Authorization Act
The National Defense Authorization Act (NDAA) is the name for each of a series of United States federal laws specifying the annual budget and expenditures of the U.S. Department of Defense. The first NDAA was passed in 1961. The U.S. Congress o ...
(US)
*Timeline of SOE's Prosper Network
The Prosper Network, also called the Physician Network, was the most important network in France of the Special Operations Executive (SOE) in 1943. SOE was a secret British organization in World War II. The objectives of SOE were to conduct espio ...
*Without the right of correspondence
"Without the right of correspondence" (WRC) (russian: Без права переписки, abbreviated as БПП in official documents) was a clause in a sentence of many political repressions victims of Stalinist Great Purges in Soviet Union ...
(USSR)
*'' The Walls Came Tumbling Down'' (1957 book)
* List of books about Nazi Germany
References
;NotesBibliography
* Barnett, Correlli, ed., (2003). ''Hitler's Generals''. New York: Grove Press. * * Browning, Christoper, and Jürgen Matthäus (2004). ''The Origins of the Final Solution: The Evolution of Nazi Jewish Policy, September 1939–March 1942''. Lincoln: University of Nebraska Press. * Conot, Robert E. (2000) 983 ''Justice at Nuremberg''. New York: Carroll & Graf Publishers. * Crankshaw, Edward (1990). ''Gestapo: Instrument of Tyranny''. London: Greenhill Books. * Dülffer, Jost (2009). ''Nazi Germany 1933-1945: Faith and Annihilation''. London: Bloomsbury. * Gellately, Robert (2001). ''Backing Hitler: Consent and Coercion in Nazi Germany''. New York: Oxford University Press. * Huhle, Rainer. "Nacht und Nebel – Mythos und Bedeutung." ''Zeitschrift für Menschenrechte'' 8, no. 1 (2014): 120–135. * Johnson, Eric (2006). ''What We Knew: Terror, Mass Murder, and Everyday Life in Nazi Germany''. New York: Basic Books. * Kaden, Helma, and Ludwig Nestler, eds., (1993). ''Dokumente des Verbrechens: Aus den Akten des Dritten Reiches''. 3 Bände. Vol i. Berlin: Dietz Verlag. * Kammer, Hilde and Elisabet Bartsch (1999). ''Lexikon Nationalsozialismus: Begriffe, Organisationen und Institutionen'' (Rororo-Sachbuch). Hamburg: Rowohlt Taschenbuch. * Kogon, Eugen (2006) 950 ''The Theory and Practice of Hell: The German Concentration Camps and the System behind Them''. New York: Farrar, Straus and Giroux. * Lowe Keith (2012). ''Savage Continent: Europe in the Aftermath of World War II''. New York: Picador. * Manchester, William (2003). ''The Arms of Krupp, 1587-1968: The Rise and Fall of the Industrial Dynasty that Armed Germany at War''. New York & Boston: Back Bay Books. * Mayer, Arno (2012)988
Year 988 ( CMLXXXVIII) was a leap year starting on Sunday (link will display the full calendar) of the Julian calendar.
Events
By place
Byzantine Empire
* Fall – Emperor Basil II, supported by a contingent of 6,000 Varangia ...
''Why Did the Heavens Not Darken?: The "Final Solution" in History''. London & New York: Verso Publishing.
* Overy, Richard (2006). ''The Dictators: Hitler's Germany, Stalin's Russia''. New York: W. W. Norton & Company.
* Shirer, William L. (1990). ''The Rise and Fall of the Third Reich''. New York: MJF Books. Originally published in 959 Drawing upon ''Nazi Conspiracy and Aggression'', part of the Nuremberg Documents, Vol. VII, pages 871-874, Nuremberg Document L-90.
* Sofsky, Wolfgang (1997). ''The Order of Terror: The Concentration Camp''. Translated by William Templer. Princeton, NJ: Princeton University Press.
* Spielvogel, Jackson (1992). ''Hitler and Nazi Germany: A History''. New York: Prentice Hall.
* Stackelberg, Roderick (2007). ''The Routledge Companion to Nazi Germany''. New York: Routledge.
* Taylor, James, and Warren Shaw (2002) ''Dictionary of the Third Reich''. New York: Penguin.
* Toland, John (1976). ''Adolf Hitler''. New York: Doubleday.
*
United States Holocaust Memorial Museum. (2014). ''Holocaust Encyclopedia'', "Night and Fog Decree"
;Further reading * Harthoorn, Willem Lodewijk. ''Verboden te sterven'', Van Gruting, 2007, – A personal account of a person who survived as a "Night and Fog" prisoner four months in Gross-Rosen and a year in
Natzweiler
Natzwiller () is a commune in the Bas-Rhin department in Grand Est in northeastern France.
History
Built in spring 1941 on the territory of the commune, Natzweiler-Struthof concentration camp opened for prisoners in May 1941. It was the only N ...
External links
Hassall, Peter D., (1997),Night and Fog Prisoners
'. {{DEFAULTSORT:Nacht Und Nebel Nazi war crimes Crimes against humanity Holocaust terminology Law in Nazi Germany Orders by Adolf Hitler December 1941 events 1941 in Germany 1941 documents German words and phrases Political quotes 1940s neologisms