NQ Vulpeculae on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 NQ Vulpeculae also known as Nova Vulpeculae 1976, was a
NQ Vulpeculae also known as Nova Vulpeculae 1976, was a
 NQ Vulpeculae also known as Nova Vulpeculae 1976, was a
NQ Vulpeculae also known as Nova Vulpeculae 1976, was a nova
A nova (plural novae or novas) is a transient astronomical event that causes the sudden appearance of a bright, apparently "new" star (hence the name "nova", which is Latin for "new") that slowly fades over weeks or months. Causes of the dramati ...
that appeared in the constellation Vulpecula
Vulpecula is a faint constellation in the northern sky. Its name is Latin for "little fox", although it is commonly known simply as the fox. It was identified in the seventeenth century, and is located in the middle of the Summer Triangle (an ...
in 1976. It was discovered visually at 18:20 UT on October 21, 1976 by English amateur astronomer George Alcock
George Eric Deacon Alcock, MBE (28 August 1912, in Peterborough, Northamptonshire – 15 December 2000) was an English astronomer. He was one of the most successful visual discoverers of novae and comets.
George’s interest in astronomy wa ...
. Its apparent magnitude
Apparent magnitude () is a measure of the brightness of a star or other astronomical object observed from Earth. An object's apparent magnitude depends on its intrinsic luminosity, its distance from Earth, and any extinction of the object's li ...
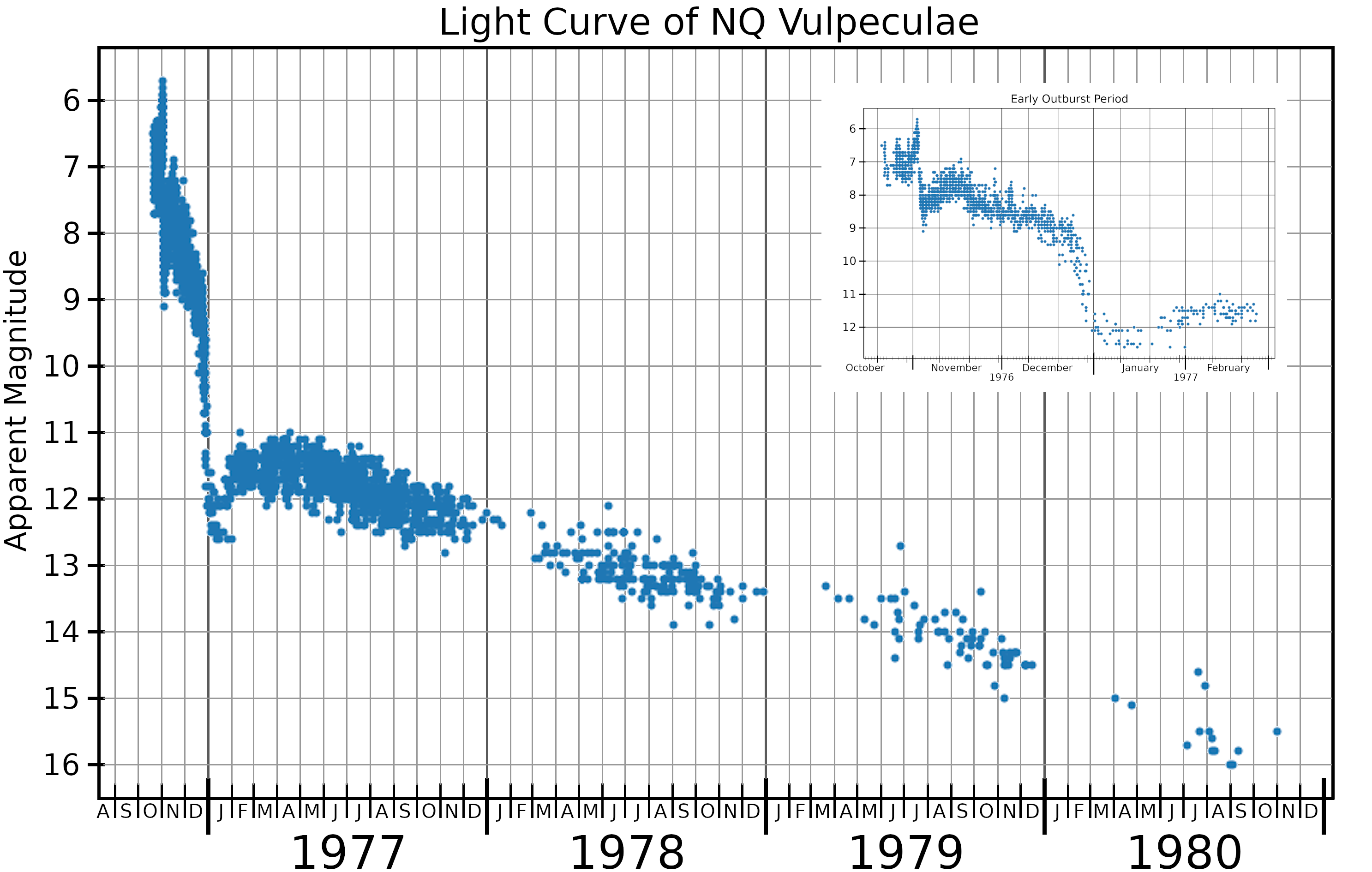
at the time of discovery was 6.5 It reached its maximum brightness of magnitude 6.0 thirteen days after its discovery, at which point it may have been faintly visible to the naked eye. A few days after maximum brightness, it had faded to magnitude 8.3.
NQ Vulpeculae faded by 3 magnitudes from peak brightness in 65 days, which makes it a "moderate speed" nova. It was one of the first novae to be closely monitored near peak brightness in the infrared. The visual light curve went through a local minimum in January 1977 (resulting in its classification as a DQ Herculis
DQ Herculis, or Nova Herculis 1934, was a slow, bright nova occurring in the northern constellation of Hercules in December 1934. This cataclysmic variable star was discovered on 13 December 1934 by J. P. M. Prentice from Stowmarket, ...
-type nova), and at the same time near infrared (3.5 micron) emission peaked, signalling the formation of a dust shell around the nova. The IRAS
The Infrared Astronomical Satellite (Dutch: ''Infrarood Astronomische Satelliet'') (IRAS) was the first space telescope to perform a survey of the entire night sky at infrared wavelengths. Launched on 25 January 1983, its mission lasted ten mo ...
satellite was launched a little more than six years after NQ Vulpeculae's outburst, and IRAS detected the nova in the 25, 60 and 100 micron bands.
4.9 GHz radio emission was detected in 1984 at the Very Large Array
The Karl G. Jansky Very Large Array (VLA) is a centimeter-wavelength radio astronomy observatory located in central New Mexico on the Plains of San Agustin, between the towns of Magdalena and Datil, ~ west of Socorro. The VLA comprises twen ...
.
All novae are binary stars, with a "donor" star orbiting a white dwarf
A white dwarf is a stellar core remnant composed mostly of electron-degenerate matter. A white dwarf is very dense: its mass is comparable to the Sun's, while its volume is comparable to the Earth's. A white dwarf's faint luminosity comes fro ...
. The two stars are so close to each other that material is transferred from the donor to the white dwarf. Modelling by Shara ''et al.'' in 2018 gave an estimated mass for the white dwarf of 1.10 , and a mass transfer rate of . The orbital period of NQ Vulpeculae is 0.146501 days, or approximately 3 hours and 31 minutes.
In 1993 a small nearly circular nova remnant
A nova remnant is made up of the material either left behind by a sudden explosive fusion eruption by classical novae, or from multiple ejections by recurrent novae. Over their short lifetimes, nova shells show expansion velocities of around 1000& ...
was imaged in Hα
H-alpha (Hα) is a specific deep-red visible spectral line in the Balmer series with a wavelength of 656.28 nm in air and 656.46 nm in vacuum; it occurs when a hydrogen electron falls from its third to second lowest energy level. H-alpha ...
line emission with the William Herschel Telescope
The William Herschel Telescope (WHT) is a optical/near-infrared reflecting telescope located at the Roque de los Muchachos Observatory on the island of La Palma in the Canary Islands, Spain. The telescope, which is named after William Herschel, ...
. On the raw image its radius was about 4 arc seconds, but deconvolution
In mathematics, deconvolution is the operation inverse to convolution. Both operations are used in signal processing and image processing. For example, it may be possible to recover the original signal after a filter (convolution) by using a deco ...
resulted in a ring-like image with a radius of 1.5 arc seconds, and a width of 0.5 arc seconds.
References
* * *External links
* https://web.archive.org/web/20100401152223/http://www.tsm.toyama.toyama.jp/curators/aroom/var/nova/1970.htm * http://www.aavso.org/vstar/vsots/nqvul.shtml {{DEFAULTSORT:NQ Vulpeculae Novae Vulpecula 1976 in science Vulpeculae, NQ