A national championship in the highest level of
college football in the United States, currently the
NCAA Division I Football Bowl Subdivision (FBS), is a designation awarded annually by various organizations to their selection of the best college football team. Division I FBS football is the only
National Collegiate Athletic Association
The National Collegiate Athletic Association (NCAA) is a nonprofit organization that regulates student athletics among about 1,100 schools in the United States, Canada, and Puerto Rico. It also organizes the athletic programs of colleges ...
(NCAA) sport for which the NCAA does not sanction a yearly championship event. As such, it is sometimes unofficially referred to as a "
mythical national championship".
Due to the lack of an official NCAA title, determining the nation's top college football team has often engendered controversy.
A championship team is independently declared by multiple individuals and organizations, often referred to as "selectors".
These choices are not always unanimous.
In 1969 even President of the United States
Richard Nixon
Richard Milhous Nixon (January 9, 1913April 22, 1994) was the 37th president of the United States, serving from 1969 to 1974. A member of the Republican Party, he previously served as a representative and senator from California and was ...
made a selection by announcing, ahead of the season-ending
"game of the century" between No. 1
Texas
Texas (, ; Spanish: ''Texas'', ''Tejas'') is a state in the South Central region of the United States. At 268,596 square miles (695,662 km2), and with more than 29.1 million residents in 2020, it is the second-largest U.S. state by ...
and No. 2
Arkansas
Arkansas ( ) is a landlocked state in the South Central United States. It is bordered by Missouri to the north, Tennessee and Mississippi to the east, Louisiana to the south, and Texas and Oklahoma to the west. Its name is from the O ...
, that the winner would receive a presidential plaque commemorating them as national champions.
Texas went on to win, 15–14.
While the NCAA has never officially endorsed a championship team, it has documented the choices of some selectors in its official ''NCAA Football Bowl Subdivision Records'' publication.
In addition, various analysts have independently published their own choices for each season. These opinions can often diverge with others as well as individual schools' claims to national titles, which may or may not correlate to the selections published elsewhere. Currently, two of the most widely recognized national champion selectors are the
Associated Press
The Associated Press (AP) is an American non-profit news agency headquartered in New York City. Founded in 1846, it operates as a cooperative, unincorporated association. It produces news reports that are distributed to its members, U.S. ne ...
(AP), which conducts a
poll of sportswriters, and the
Coaches Poll
The Coaches Poll is a weekly ranking of the top 25 NCAA Division I Football Bowl Subdivision (FBS) college football, Division I college basketball, and Division I college baseball teams. The football version of the poll has been known officiall ...
, a survey of active members of the
American Football Coaches Association
The American Football Coaches Association (AFCA) is an association of over 11,000 American football coaches and staff on all levels. According to its constitution, some of the main goals of the American Football Coaches Association are to "mainta ...
(AFCA).
Since 1992, various consortia of major
bowl game
In North America, a bowl game is one of a number of post-season college football games that are primarily played by teams belonging to the NCAA's Division I Football Bowl Subdivision (FBS). For most of its history, the Division I Bowl Subdivi ...
s have aimed to invite the top two teams at the end of the regular season (as determined by internal rankings, or aggregates of the major polls and other statistics) to compete in what is intended to be the ''de facto'' national championship game. The current iteration of this practice, the
College Football Playoff
The College Football Playoff (CFP) is an annual postseason knockout invitational tournament to determine a national champion for the National Collegiate Athletic Association (NCAA) Division I Football Bowl Subdivision (FBS), the highest level ...
, selects four teams to participate in national semi-finals hosted by two of six partner bowl games, with their winners advancing to the
College Football Playoff National Championship
The College Football Playoff National Championship is a post-season college football bowl game, used to determine a national champion of the NCAA Division I Football Bowl Subdivision (FBS), which began play in the 2014 college football season. ...
.
History
The concept of a national championship in college football dates to the early years of the sport in the late 19th century, and the earliest contemporaneous polls can be traced to
Caspar Whitney
Caspar William Whitney (September 2, 1864 – January 18, 1929) was an American author, editor, explorer, outdoorsman and war correspondent. He originated the concept of the All-American team in college football in 1889 when he worked for '' Harp ...
, Charles Patterson, and ''
The Sun'' in 1901.
Therefore, the concept of polls and national champions predated mathematical ranking systems, but it was
Frank Dickinson's math system that was one of the first to be widely popularized. His system named 10–0
Stanford the national champion of 1926, prior to their tie with
Alabama
(We dare defend our rights)
, anthem = "Alabama"
, image_map = Alabama in United States.svg
, seat = Montgomery
, LargestCity = Huntsville
, LargestCounty = Baldwin County
, LargestMetro = Greater Birmingham
, area_total_km2 = 135,765 ...
in the
Rose Bowl. A curious
Knute Rockne, then coach of
Notre Dame, had Dickinson backdate two seasons, which produced
Notre Dame as the 1924 national champion and
Dartmouth in 1925.
A number of other mathematical systems were born in the 1920s and 1930s and were the only organized methods selecting national champions until the
Associated Press
The Associated Press (AP) is an American non-profit news agency headquartered in New York City. Founded in 1846, it operates as a cooperative, unincorporated association. It produces news reports that are distributed to its members, U.S. ne ...
began
polling
Poll, polled, or polling may refer to:
Figurative head counts
* Poll, a formal election
** Election verification exit poll, a survey taken to verify election counts
** Polling, voting to make decisions or determine opinions
** Polling places o ...
sportswriters in 1936 to obtain rankings.
Alan J. Gould, the creator of the AP Poll, named
Minnesota
Minnesota () is a state in the upper midwestern region of the United States. It is the 12th largest U.S. state in area and the 22nd most populous, with over 5.75 million residents. Minnesota is home to western prairies, now given over to ...
,
Princeton
Princeton University is a private research university in Princeton, New Jersey. Founded in 1746 in Elizabeth as the College of New Jersey, Princeton is the fourth-oldest institution of higher education in the United States and one of the ni ...
, and
SMU co-champions in 1935, and polled writers the following year, which resulted in a national championship for
Minnesota
Minnesota () is a state in the upper midwestern region of the United States. It is the 12th largest U.S. state in area and the 22nd most populous, with over 5.75 million residents. Minnesota is home to western prairies, now given over to ...
.
The AP's main competition,
United Press
United Press International (UPI) is an American international news agency whose newswires, photo, news film, and audio services provided news material to thousands of newspapers, magazines, radio and television stations for most of the 20t ...
, created the first
Coaches Poll
The Coaches Poll is a weekly ranking of the top 25 NCAA Division I Football Bowl Subdivision (FBS) college football, Division I college basketball, and Division I college baseball teams. The football version of the poll has been known officiall ...
in 1950. For that year and the next three, the AP and UP agreed on the national champion. The first "split" championship occurred in 1954, when the writers selected
Ohio State
The Ohio State University, commonly called Ohio State or OSU, is a public land-grant research university in Columbus, Ohio. A member of the University System of Ohio, it has been ranked by major institutional rankings among the best public ...
and the coaches chose
UCLA
The University of California, Los Angeles (UCLA) is a public land-grant research university in Los Angeles, California. UCLA's academic roots were established in 1881 as a teachers college then known as the southern branch of the California ...
.
The two polls also disagreed in 1957, 1965, 1970, 1973, 1974, 1978, 1990, 1991, 1997, and 2003.
Though some of the math systems selected champions after the
bowl game
In North America, a bowl game is one of a number of post-season college football games that are primarily played by teams belonging to the NCAA's Division I Football Bowl Subdivision (FBS). For most of its history, the Division I Bowl Subdivi ...
s, both of the major polls released their rankings after the end of the regular season until the AP polled writers after the bowls in 1965, resulting in what was perceived at the time as a better championship selection (
Alabama
(We dare defend our rights)
, anthem = "Alabama"
, image_map = Alabama in United States.svg
, seat = Montgomery
, LargestCity = Huntsville
, LargestCounty = Baldwin County
, LargestMetro = Greater Birmingham
, area_total_km2 = 135,765 ...
) than UPI's (
Michigan State).
After 1965, the AP again voted before the bowls for two years, before permanently returning to a post-bowl vote in 1968. The coaches did not conduct a vote after the bowls until 1974, in the wake of awarding their 1973 championship to
Alabama
(We dare defend our rights)
, anthem = "Alabama"
, image_map = Alabama in United States.svg
, seat = Montgomery
, LargestCity = Huntsville
, LargestCounty = Baldwin County
, LargestMetro = Greater Birmingham
, area_total_km2 = 135,765 ...
, who lost to the AP champion, undefeated
Notre Dame, in the
Sugar Bowl.
The AP and Coaches polls remain the major rankings to this day.
From the 1930s to the advent of the College Football Playoff, each top team played a single postseason bowl game per season. The process of selecting a national champion during this period was complicated by the fact that the champions of major conferences were tied to specific bowls (for example, the Big 8 champion was tied to the Orange Bowl), and the top two teams in the nation often played in different bowls. A few bowls over the years featured a #1 vs. #2 matchup; one example was the 1987 Fiesta Bowl, played January 2 following the 1986 season.
Two attempts to annually crown a champion on the field were the
Bowl Coalition (1992–1994) and
Bowl Alliance (1995–1997). However, their effort to host a national championship was hampered by the lack of participation of the Pac-10 and Big Ten champions, who had a contractual obligation to play in the Rose Bowl.
The
Bowl Championship Series, famous for its use of math, was the successor of the Coalition and Alliance. Besides the many adjustments it underwent during its tenure, including a large overhaul following the
2004 season that included the replacement of the AP Poll with the
Harris poll
The Harris Poll (legal name: Harris Insights and Analytics) is an American market research and analytics company that has been tracking the sentiment, behaviors and motivations of American adults since 1963. In addition to the traditional consulti ...
, the BCS remained a mixture of math systems and human polls since its inception in 1998, with the goal of matching the best two teams in the nation in a national championship bowl game which rotated yearly between the
Sugar,
Fiesta,
Rose
A rose is either a woody perennial flowering plant of the genus ''Rosa'' (), in the family Rosaceae (), or the flower it bears. There are over three hundred species and tens of thousands of cultivars. They form a group of plants that can be ...
, and
Orange
Orange most often refers to:
*Orange (fruit), the fruit of the tree species '' Citrus'' × ''sinensis''
** Orange blossom, its fragrant flower
*Orange (colour), from the color of an orange, occurs between red and yellow in the visible spectrum
* ...
Bowls from 1998 to 2005, and later a standalone game titled the
BCS National Championship Game
The BCS National Championship Game, or BCS National Championship, was a postseason college football bowl game, used to determine a national champion of the NCAA Division I Football Bowl Subdivision (FBS), first played in the 1998 college fo ...
(2006 to 2013).
The winner of the BCS Championship Game was awarded the national championship of the Coaches Poll thus winning the
AFCA National Championship Trophy. The BCS winner also received the
MacArthur Bowl from the
National Football Foundation
The National Football Foundation (NFF) is a non-profit organization to promote and develop amateur American football on all levels throughout the United States and "developing the qualities of leadership, sportsmanship, competitive zeal and the dr ...
.
Neither the AP Poll, nor other current selectors, had contractual obligations to select the BCS champion as their national champion. The BCS resulted in a number of
controversies
Controversy is a state of prolonged public dispute or debate, usually concerning a matter of conflicting opinion or point of view. The word was coined from the Latin ''controversia'', as a composite of ''controversus'' – "turned in an opposite d ...
, most notably after the 2003 season, when the BCS championship game did not include eventual AP champion
USC, the only time the two championships have diverged since the advent of the BCS. After many seasons of controversy, the BCS was replaced with the
College Football Playoff
The College Football Playoff (CFP) is an annual postseason knockout invitational tournament to determine a national champion for the National Collegiate Athletic Association (NCAA) Division I Football Bowl Subdivision (FBS), the highest level ...
, a
Plus-One system
The plus-one system, also known as a 4-team playoff, is the system used to determine the National Champion in the Football Bowl Subdivision (formerly called Division I-A) of NCAA football in the United States. The format is of a 4-team playoff, whe ...
aimed at reducing the controversy involved in which teams get to play in a championship game through use of a tournament.
NCAA records book
Although the
National Collegiate Athletic Association
The National Collegiate Athletic Association (NCAA) is a nonprofit organization that regulates student athletics among about 1,100 schools in the United States, Canada, and Puerto Rico. It also organizes the athletic programs of colleges ...
(NCAA) has never bestowed national championships in college football at the topmost level, it does maintain an official records book for the sport. The records book, with consultation from various college football historians, contains a list of "major selectors"
of national championships from throughout the history of college football, along with their championship selections.
Major selectors
While many people and organizations have named national champions throughout the years, the selectors below are listed in the official NCAA ''Football Bowl Subdivision Records'' book as being "major selectors" of national championships. The criterion for the NCAA's designation is that the poll or selector be "national in scope, either through distribution in newspaper, television, radio and/or computer online".
Former selectors, deemed instrumental in the sport of college football, and selectors that were included for the calculation of the BCS standing, are listed together.
The NCAA records book divides its major selectors into three categories: those determined by mathematical formula, human polls, and historical research. The
BCS is additionally categorized as a hybrid between math and polls, and the
CFP as a playoff system.
Math
The mathematical system is the oldest systematic selector of college football national champions. Many of the math selectors were created during the "championship rush" of the 1920s and 1930s, beginning with Frank Dickinson's
system, or during the dawn of the
computer age in the 1990s. Selectors are listed below with years selected retroactively in ''italics''.
aThe NCAA Football Bowl Subdivision Records book shows Anderson & Hester listed as "Seattle Times."
bThe Billingsley Report also provides an alternate selection that uses margin-of-victory in its calculation. The NCAA Football Bowl Subdivision Records book notes both selections in years where they disagree.COVID-19 pandemic
The COVID-19 pandemic, also known as the coronavirus pandemic, is an ongoing global pandemic of coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) caused by severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2). The novel virus was first identi ...
.
Poll
The poll has been the dominant national champion selection method since the inception of the
AP Poll
The Associated Press poll (AP poll) provides weekly rankings of the top 25 NCAA teams in one of three Division I college sports: football, men's basketball and women's basketball. The rankings are compiled by polling 62 sportswriters and broad ...
in 1936. The
National Football Foundation
The National Football Foundation (NFF) is a non-profit organization to promote and develop amateur American football on all levels throughout the United States and "developing the qualities of leadership, sportsmanship, competitive zeal and the dr ...
merged its poll with
UPI
United Press International (UPI) is an American international news agency whose newswires, photo, news film, and audio services provided news material to thousands of newspapers, magazines, radio and television stations for most of the 20th c ...
from 1991 to 1992, with ''
USA Today
''USA Today'' (stylized in all uppercase) is an American daily middle-market newspaper and news broadcasting company. Founded by Al Neuharth on September 15, 1982, the newspaper operates from Gannett's corporate headquarters in Tysons, Virgi ...
'' from 1993 to 1996, and with the
FWAA since 2014.
For many years, the national champions of various polls were selected before the annual bowl games were played, by AP (1936–1964 and 1966–1967), Coaches Poll (1950–1973), FWAA (1954), and NFF (1959–1970). In all other latter-day polls, champions were selected after bowl games.
During the BCS era, the winner of the BCS Championship Game was automatically awarded the national championship of the
Coaches Poll
The Coaches Poll is a weekly ranking of the top 25 NCAA Division I Football Bowl Subdivision (FBS) college football, Division I college basketball, and Division I college baseball teams. The football version of the poll has been known officiall ...
and the National Football Foundation.
Selectors are listed below with years selected retroactively in ''italics''.
aAt the request of several schools, the AFCA established a "Blue Ribbon Commission" in 2016 to begin retroactively selecting Coaches' Trophy winners from 1922 through 1949.
Research
College football historian
Parke H. Davis is the only selector considered by the
NCAA
The National Collegiate Athletic Association (NCAA) is a nonprofit organization that regulates student athletics among about 1,100 schools in the United States, Canada, and Puerto Rico. It also organizes the athletic programs of colleges an ...
to have primarily used research in his selections.
Davis published his work in the 1934 edition of ''Spalding's Foot Ball Guide'',
naming retroactive national champions for the years 1869 to 1932 while naming
Michigan
Michigan () is a U.S. state, state in the Great Lakes region, Great Lakes region of the Upper Midwest, upper Midwestern United States. With a population of nearly 10.12 million and an area of nearly , Michigan is the List of U.S. states and ...
and
Princeton
Princeton University is a private research university in Princeton, New Jersey. Founded in 1746 in Elizabeth as the College of New Jersey, Princeton is the fourth-oldest institution of higher education in the United States and one of the ni ...
(his
alma mater) contemporary co-champions for the 1933 season. In all, he selected 94 teams over 61 seasons as "National Champion Foot Ball Teams".
For 21 of these teams (at 12 schools), he was the only major selector to choose them. Their schools use 17 of Davis' singular selections to claim national titles. His work has been criticized for having a heavy Eastern bias, with little regard for the South and the West Coast.
Hybrid
The
Bowl Championship Series used a mathematical system that combined polls (Coaches and AP/Harris) and multiple computer rankings (including some individual selectors listed above) to determine a season ending matchup between its top two ranked teams in the BCS Championship Game. The champion of that game was contractually awarded the Coaches Poll and National Football Foundation championships.
Playoff
Unlike all selectors prior to 2014, the
College Football Playoff
The College Football Playoff (CFP) is an annual postseason knockout invitational tournament to determine a national champion for the National Collegiate Athletic Association (NCAA) Division I Football Bowl Subdivision (FBS), the highest level ...
does not use math, polls or research to select the participants. Rather, a 13-member committee selects and seeds the teams. The playoff system marked the first time any championship selector arranged a bracket competition to determine whom it would declare to be its champion.
Yearly national championship selections from major selectors
Below is a list of the national champions of college football since 1869 chosen by
NCAA
The National Collegiate Athletic Association (NCAA) is a nonprofit organization that regulates student athletics among about 1,100 schools in the United States, Canada, and Puerto Rico. It also organizes the athletic programs of colleges an ...
-designated "major selectors" listed in the official ''Football Bowl Subdivision Records'' publication.
Many teams did not have coaches as late as 1899. The first contemporaneous poll to include teams across the country and selection of a national champions can be traced to
Caspar Whitney
Caspar William Whitney (September 2, 1864 – January 18, 1929) was an American author, editor, explorer, outdoorsman and war correspondent. He originated the concept of the All-American team in college football in 1889 when he worked for '' Harp ...
in 1901.
The last retroactive selection in the list is Clyde Berryman's choice of
Notre Dame for 1989. The
tie was removed from college football in 1995 and the last consensus champion with a tie in its record was
Georgia Tech
The Georgia Institute of Technology, commonly referred to as Georgia Tech or, in the state of Georgia, as Tech or The Institute, is a public research university and institute of technology in Atlanta, Georgia. Established in 1885, it is part of ...
in 1990.
As designated by the official NCAA ''Football Bowl Subdivision Records'' publication:
* Champions included in this table are exclusively those named by an NCAA-designated "major selector" for the given year.
* Teams listed in ''italics'' indicate retroactively-applied championships.
* Teams listed in bold reflect the NCAA's designation as "Consensus National Champions" by virtue of their selection from 1950 onward by one or more of the following selectors:
Associated Press
The Associated Press (AP) is an American non-profit news agency headquartered in New York City. Founded in 1846, it operates as a cooperative, unincorporated association. It produces news reports that are distributed to its members, U.S. ne ...
,
United Press/UPI,
Football Writers Association of America,
National Football Foundation
The National Football Foundation (NFF) is a non-profit organization to promote and develop amateur American football on all levels throughout the United States and "developing the qualities of leadership, sportsmanship, competitive zeal and the dr ...
, and
USA Today
''USA Today'' (stylized in all uppercase) is an American daily middle-market newspaper and news broadcasting company. Founded by Al Neuharth on September 15, 1982, the newspaper operates from Gannett's corporate headquarters in Tysons, Virgi ...
.
A letter next to any season, team, record, coach or selector indicates a footnote that appears at the bottom of the table.
aParke H. Davis' selection for 1901, as published in the 1934 edition of ''Spalding's Foot Ball Guide'', was Harvard.
Total championship selections from major selectors by school
The national title count listed below is a culmination of all championship awarded since 1869, regardless of "consensus"
or non-consensus status, as listed in the table above according to the selectors deemed to be "major"
as listed in the official ''NCAA Football Bowl Subdivision Records''.
The totals can be said to be disputed. Individual schools may claim national championships not accounted for by the ''NCAA Football Bowl Subdivision Records'' or may not claim national championship selections that do appear in the official NCAA Football Bowl Subdivision Records (see
National championship claims by school below).
Poll era (1936–present)
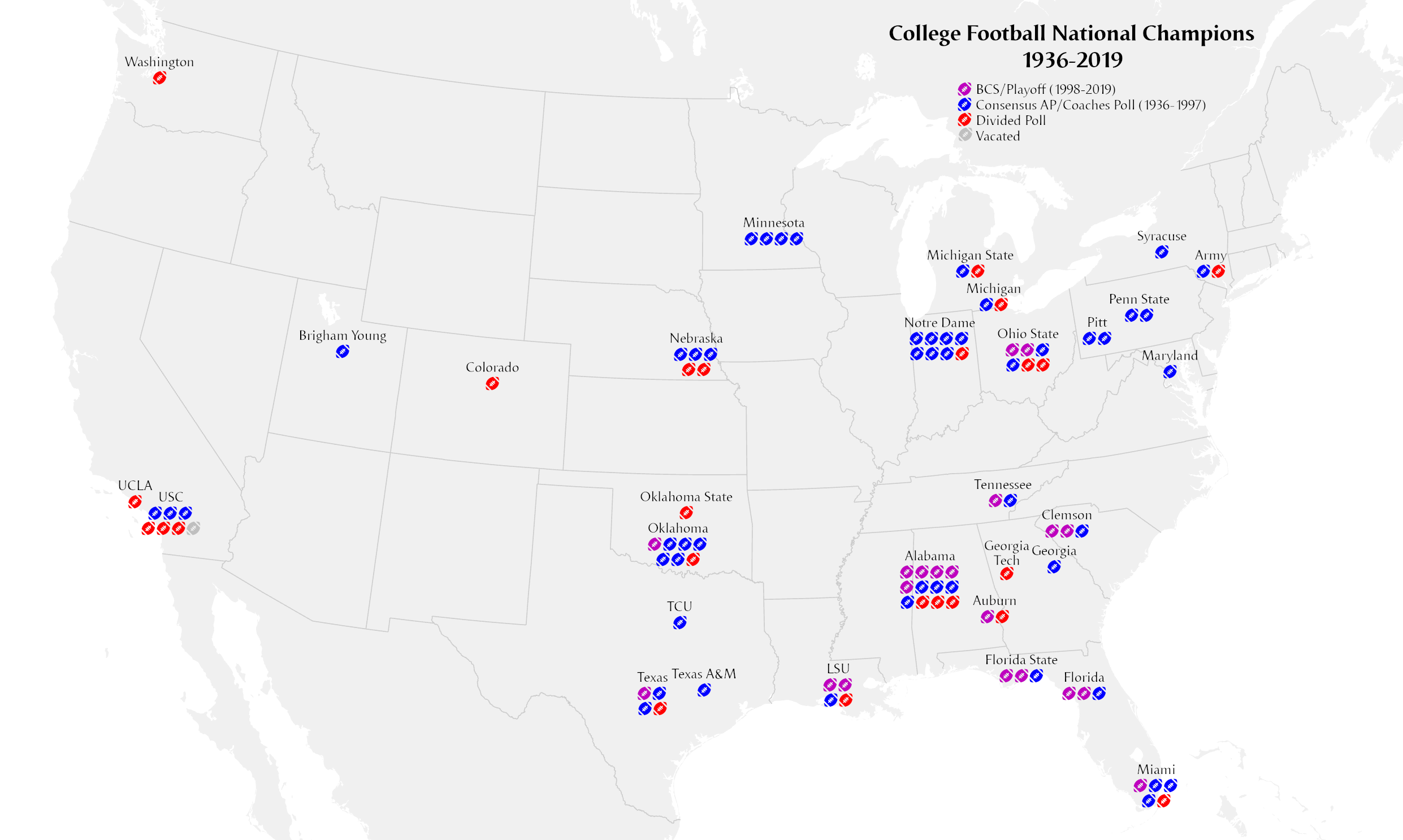
National championship selectors came to be dominated by two competing
news agencies
A news agency is an organization that gathers news reports and sells them to subscribing news organizations, such as newspapers, magazines and radio and television broadcasters. A news agency may also be referred to as a wire service, newswire, ...
in the later half of the 20th century: the
Associated Press
The Associated Press (AP) is an American non-profit news agency headquartered in New York City. Founded in 1846, it operates as a cooperative, unincorporated association. It produces news reports that are distributed to its members, U.S. ne ...
(AP) and
United Press International
United Press International (UPI) is an American international news agency whose newswires, photo, news film, and audio services provided news material to thousands of newspapers, magazines, radio and television stations for most of the 20t ...
(UPI).
These
wire services
A news agency is an organization that gathers news reports and sells them to subscribing news organizations, such as newspapers, magazines and radio and television broadcasters. A news agency may also be referred to as a wire service, newswire, ...
began ranking college football teams in weekly polls, which were then promptly published in the sports sections of each agency's subscribing newspapers across the country. The team ranking No. 1 in each agency's final poll of the season was awarded that agency's national championship.
National championships are often popularly considered to be "consensus" when both of these polls are in agreement with their national championship selections, although other selectors exist and do make alternative selections.
AP Poll
The
AP college football poll has a long history. The
news media
The news media or news industry are forms of mass media that focus on delivering news to the general public or a target public. These include news agencies, print media (newspapers, news magazines), broadcast news (radio and television), and ...
began running their own polls of
sports writer
Sports journalism is a form of writing that reports on matters pertaining to sporting topics and competitions. Sports journalism started in the early 1800s when it was targeted to the social elite and transitioned into an integral part of the n ...
s to determine who was, by popular opinion, the best football team in the country at the end of the season. One of the earliest such polls was the AP College Football Poll, first run in 1934 (compiled and organized by Charles Woodroof, former
SEC Assistant Director of Media Relations, but not recognized in the official ''NCAA Football Bowl Subdivision Records'') and then continuously from 1936. The first major nationwide poll for ranking college football teams, the Associated Press is probably the most well-known and widely circulated among all of history’s polls. Due to the long-standing historical ties between individual college football conferences and high-paying
bowl game
In North America, a bowl game is one of a number of post-season college football games that are primarily played by teams belonging to the NCAA's Division I Football Bowl Subdivision (FBS). For most of its history, the Division I Bowl Subdivi ...
s like the
Rose Bowl and
Orange Bowl
The Orange Bowl is an annual American college football bowl game played in the Miami metropolitan area. It has been played annually since January 1, 1935, making it, along with the Sugar Bowl and the Sun Bowl, the second-oldest bowl game ...
, the
NCAA
The National Collegiate Athletic Association (NCAA) is a nonprofit organization that regulates student athletics among about 1,100 schools in the United States, Canada, and Puerto Rico. It also organizes the athletic programs of colleges an ...
has never held a tournament or championship game to determine the champion of what is now the highest division,
NCAA Division I
NCAA Division I (D-I) is the highest level of intercollegiate athletics sanctioned by the National Collegiate Athletic Association (NCAA) in the United States, which accepts players globally. D-I schools include the major collegiate athletic ...
,
Football Bowl Subdivision
The NCAA Division I Football Bowl Subdivision (FBS), formerly known as Division I-A, is the highest level of college football in the United States. The FBS consists of the largest schools in the National Collegiate Athletic Association (NCAA). As ...
(the Division I,
Football Championship Subdivision and lower divisions do hold championship tournaments). As a result, the public and the media began to take the leading vote-getter in the final AP Poll as the national champion for that season.

In the AP Poll's early years, the final poll of sportswriters was taken prior to any
bowl games
In North America, a bowl game is one of a number of post-season college football games that are primarily played by teams belonging to the National Collegiate Athletic Association, NCAA's NCAA Division I Football Bowl Subdivision, Division I Fo ...
and sometimes even prior to the top teams' final games of the regular season.
In
1938, the poll was extended for one week
after
Notre Dame, No. 1 in the scheduled "final" poll,
subsequently lost to rival
USC.
Following the
1947 season the AP held a special post-bowl poll
with only two teams on the ballot,
Notre Dame and
Michigan
Michigan () is a U.S. state, state in the Great Lakes region, Great Lakes region of the Upper Midwest, upper Midwestern United States. With a population of nearly 10.12 million and an area of nearly , Michigan is the List of U.S. states and ...
, but stated that the result would not supersede that of the final poll conducted following the end of the regular season.
The
rivals
A rivalry is the state of two people or groups engaging in a lasting competitive relationship. Rivalry is the "against each other" spirit between two competing sides. The relationship itself may also be called "a rivalry", and each participant ...
, both unbeaten and untied, had been ranked No. 1 and No. 2 respectively in the final poll. January voters were impressed by Michigan's 49–0 win over common opponent
USC in the
Rose Bowl and elevated the Wolverines above the Irish in the special post-bowl poll.
In
1965 the AP decided to delay the season's final poll until after
New Year's Day, citing the proliferation of
bowl games
In North America, a bowl game is one of a number of post-season college football games that are primarily played by teams belonging to the National Collegiate Athletic Association, NCAA's NCAA Division I Football Bowl Subdivision, Division I Fo ...
and the involvement of eight of the poll's current top ten teams in post-season play.
In the next season,
1966, neither of the top two teams were attending bowl games so no post-bowl poll was taken,
even after two-time defending AP national champion No. 3
Alabama
(We dare defend our rights)
, anthem = "Alabama"
, image_map = Alabama in United States.svg
, seat = Montgomery
, LargestCity = Huntsville
, LargestCounty = Baldwin County
, LargestMetro = Greater Birmingham
, area_total_km2 = 135,765 ...
won the
Sugar Bowl and finished the season unbeaten and untied. In
1967
Events
January
* January 1 – Canada begins a year-long celebration of the 100th anniversary of Confederation, featuring the Expo 67 World's Fair.
* January 5
** Spain and Romania sign an agreement in Paris, establishing full consular and ...
the final poll crowning
USC national champion was taken before No. 2
Tennessee
Tennessee ( , ), officially the State of Tennessee, is a landlocked state in the Southeastern region of the United States. Tennessee is the 36th-largest by area and the 15th-most populous of the 50 states. It is bordered by Kentucky to th ...
or No. 3
Oklahoma had even played their final games of the regular season,
and well before those two teams met in the
Orange Bowl
The Orange Bowl is an annual American college football bowl game played in the Miami metropolitan area. It has been played annually since January 1, 1935, making it, along with the Sugar Bowl and the Sun Bowl, the second-oldest bowl game ...
.
In
1968
The year was highlighted by protests and other unrests that occurred worldwide.
Events January–February
* January 5 – " Prague Spring": Alexander Dubček is chosen as leader of the Communist Party of Czechoslovakia.
* Janu ...
the final poll was again delayed until after the bowl games so that No. 1
Ohio State
The Ohio State University, commonly called Ohio State or OSU, is a public land-grant research university in Columbus, Ohio. A member of the University System of Ohio, it has been ranked by major institutional rankings among the best public ...
could meet No. 2
USC in a "dream match" in the
Rose Bowl.
Every subsequent season's final AP Poll would be released after the bowl games going forward. The UPI did not follow suit with the Coaches Poll until the
1974 season.
Until the
1968 NCAA University Division football season
In the 1968 NCAA University Division football season, the system of "polls and bowls" changed. The Associated Press returned to its pre-1961 system of ranking the Top 20 rather than the Top 10, and voted on the national champion after the bowl ga ...
, the final AP Poll of the season was released following the end of the regular season, with the exception of the
1965 season. In 1964,
Alabama
(We dare defend our rights)
, anthem = "Alabama"
, image_map = Alabama in United States.svg
, seat = Montgomery
, LargestCity = Huntsville
, LargestCounty = Baldwin County
, LargestMetro = Greater Birmingham
, area_total_km2 = 135,765 ...
was named the national champion in the final AP Poll following the completion of the regular season, but lost in the
Orange Bowl
The Orange Bowl is an annual American college football bowl game played in the Miami metropolitan area. It has been played annually since January 1, 1935, making it, along with the Sugar Bowl and the Sun Bowl, the second-oldest bowl game ...
to
Texas
Texas (, ; Spanish: ''Texas'', ''Tejas'') is a state in the South Central region of the United States. At 268,596 square miles (695,662 km2), and with more than 29.1 million residents in 2020, it is the second-largest U.S. state by ...
, leaving
Arkansas
Arkansas ( ) is a landlocked state in the South Central United States. It is bordered by Missouri to the north, Tennessee and Mississippi to the east, Louisiana to the south, and Texas and Oklahoma to the west. Its name is from the O ...
as the only undefeated, untied team after the Razorbacks defeated
Nebraska
Nebraska () is a state in the Midwestern region of the United States. It is bordered by South Dakota to the north; Iowa to the east and Missouri to the southeast, both across the Missouri River; Kansas to the south; Colorado to the sout ...
in the
Cotton Bowl Classic
The Cotton Bowl Classic (also known as the Cotton Bowl) is an American college football bowl game that has been held annually in the Dallas–Fort Worth metroplex since January 1, 1937. The game was originally played at its namesake stadium i ...
. In 1965, the AP's decision to wait to crown its champion paid off, as top-ranked
Michigan State lost to
UCLA
The University of California, Los Angeles (UCLA) is a public land-grant research university in Los Angeles, California. UCLA's academic roots were established in 1881 as a teachers college then known as the southern branch of the California ...
in the
Rose Bowl, number two
Arkansas
Arkansas ( ) is a landlocked state in the South Central United States. It is bordered by Missouri to the north, Tennessee and Mississippi to the east, Louisiana to the south, and Texas and Oklahoma to the west. Its name is from the O ...
lost to
LSU in the
Cotton Bowl Classic
The Cotton Bowl Classic (also known as the Cotton Bowl) is an American college football bowl game that has been held annually in the Dallas–Fort Worth metroplex since January 1, 1937. The game was originally played at its namesake stadium i ...
, and fourth-ranked
Alabama
(We dare defend our rights)
, anthem = "Alabama"
, image_map = Alabama in United States.svg
, seat = Montgomery
, LargestCity = Huntsville
, LargestCounty = Baldwin County
, LargestMetro = Greater Birmingham
, area_total_km2 = 135,765 ...
defeated third-ranked
Nebraska
Nebraska () is a state in the Midwestern region of the United States. It is bordered by South Dakota to the north; Iowa to the east and Missouri to the southeast, both across the Missouri River; Kansas to the south; Colorado to the sout ...
in the
Orange Bowl
The Orange Bowl is an annual American college football bowl game played in the Miami metropolitan area. It has been played annually since January 1, 1935, making it, along with the Sugar Bowl and the Sun Bowl, the second-oldest bowl game ...
, vaulting the Crimson Tide to the top of the AP's final poll. Michigan State was named national champion in the final
United Press International
United Press International (UPI) is an American international news agency whose newswires, photo, news film, and audio services provided news material to thousands of newspapers, magazines, radio and television stations for most of the 20t ...
poll of coaches, which did not conduct a post-bowl poll.
The AP Poll was used as a component of the
Bowl Championship Series computer ranking formula starting in 1998, but without any formal agreement in place like the contract made between the BCS and the Coaches Poll.
For the 2003 season the AP Poll caused a split national title and
BCS controversy when it awarded its national championship to No. 1
USC instead of BCS champion
LSU.
In December 2004 the AP opted out of the BCS formula, requesting that the BCS "discontinue its unauthorized use of the AP poll as a component of BCS rankings", in response to three AP voters from Texas elevating
Texas
Texas (, ; Spanish: ''Texas'', ''Tejas'') is a state in the South Central region of the United States. At 268,596 square miles (695,662 km2), and with more than 29.1 million residents in 2020, it is the second-largest U.S. state by ...
above
California
California is a state in the Western United States, located along the Pacific Coast. With nearly 39.2million residents across a total area of approximately , it is the most populous U.S. state and the 3rd largest by area. It is also the m ...
into the
Rose Bowl in the last regular season AP Poll.
Coaches Poll
News agency
United Press
United Press International (UPI) is an American international news agency whose newswires, photo, news film, and audio services provided news material to thousands of newspapers, magazines, radio and television stations for most of the 20t ...
(UP), the main competitor to the
Associated Press
The Associated Press (AP) is an American non-profit news agency headquartered in New York City. Founded in 1846, it operates as a cooperative, unincorporated association. It produces news reports that are distributed to its members, U.S. ne ...
, began conducting its own college football ratings during the
1950 season.
The
wire service
A news agency is an organization that gathers news reports and sells them to subscribing news organizations, such as newspapers, magazines and radio and television broadcasters. A news agency may also be referred to as a wire service, newswire, ...
came to be known as United Press International (UPI) following a merger with
International News Service
The International News Service (INS) was a U.S.-based news agency (newswire) founded by newspaper publisher William Randolph Hearst in 1909. in 1958.
The weekly ranking was a joint polling effort between the news agency and the
American Football Coaches Association
The American Football Coaches Association (AFCA) is an association of over 11,000 American football coaches and staff on all levels. According to its constitution, some of the main goals of the American Football Coaches Association are to "mainta ...
(AFCA), with UP/UPI sports writers gathering and tabulating the coaches' votes and publishing the results in newspapers across the nation.
The UP/UPI rankings were originally conducted by polling 35 of the nation's college football coaches.
The coaches were chosen to represent every major football conference, with 5 coaches from each of 7 regions, in an apparent effort to combat the perceived
East Coast bias East Coast bias is the perceived tendency for sports broadcasting and journalism in the United States to give greater weight and attention to teams and athletes on the East Coast than those on the West Coast. In Canada, a similar bias is perceived ...
of the rival AP Poll's constituent
sports writers.
Each season's final Coaches Poll was initially published following the regular season and did not take
bowl game
In North America, a bowl game is one of a number of post-season college football games that are primarily played by teams belonging to the NCAA's Division I Football Bowl Subdivision (FBS). For most of its history, the Division I Bowl Subdivi ...
results into account; the UP/UPI national champion lost its bowl game 8 times between 1950 and 1973. Since the 1974 season the poll has awarded its national championship following the postseason bowls.
That same year the AFCA voted to thereafter not rank any team currently under NCAA or conference-sanctioned probation.
Following the
decline of UPI in the 1980s, the AFCA ended their 42-year relationship with the wire service in 1991.
The Coaches Poll continued, with new sponsorship and distribution partners, as the
USA Today
''USA Today'' (stylized in all uppercase) is an American daily middle-market newspaper and news broadcasting company. Founded by Al Neuharth on September 15, 1982, the newspaper operates from Gannett's corporate headquarters in Tysons, Virgi ...
/
CNN
CNN (Cable News Network) is a multinational cable news channel headquartered in Atlanta, Georgia, U.S. Founded in 1980 by American media proprietor Ted Turner and Reese Schonfeld as a 24-hour cable news channel, and presently owned by ...
poll (1991–1996), USA Today/
ESPN
ESPN (originally an initialism for Entertainment and Sports Programming Network) is an American international basic cable sports channel owned by ESPN Inc., owned jointly by The Walt Disney Company (80%) and Hearst Communications (20%). Th ...
poll (1997–2004), USA Today poll (2005–2014), and USA Today/
Amway
Amway (short for "American Way") is an American multi-level marketing (MLM) company that sells health, beauty, and home care products. The company was founded in 1959 by Jay Van Andel and Richard DeVos and is based in Ada, Michigan. Amway and it ...
poll (2014–present).
The
Bowl Championship Series included the Coaches Poll as a major factor in its ranking formula.
In return, voting AFCA members were contractually obligated to award their Coaches Poll national championship selections to the winner of the
BCS National Championship Game
The BCS National Championship Game, or BCS National Championship, was a postseason college football bowl game, used to determine a national champion of the NCAA Division I Football Bowl Subdivision (FBS), first played in the 1998 college fo ...
. Lacking its own dedicated trophy, the BCS champion was awarded
The Coaches' Trophy on the field immediately following the game.
Poll era national championships by school (1936–present)
The following table contains the national championships that have been recognized by the final AP or Coaches Poll. Originally both the AP and Coaches poll champions were crowned after the regular season, but since 1968 and 1974 respectively, both polls crown their champions after the bowl games are completed (with the exception of the 1965 season). The BCS champion was automatically awarded the Coaches Poll championship. Of the current 120+
Football Bowl Subdivision
The NCAA Division I Football Bowl Subdivision (FBS), formerly known as Division I-A, is the highest level of college football in the United States. The FBS consists of the largest schools in the National Collegiate Athletic Association (NCAA). As ...
(FBS, formerly Division I-A) schools, only 30 have won at least a share of a national title by the AP or Coaches poll. Of these 30 teams, only 20 teams have won multiple titles. Of the 20 teams, only 7 have won five or more national titles:
Alabama
(We dare defend our rights)
, anthem = "Alabama"
, image_map = Alabama in United States.svg
, seat = Montgomery
, LargestCity = Huntsville
, LargestCounty = Baldwin County
, LargestMetro = Greater Birmingham
, area_total_km2 = 135,765 ...
,
Notre Dame,
Oklahoma,
USC,
Miami (FL)
Miami ( ), officially the City of Miami, known as "the 305", "The Magic City", and "Gateway to the Americas", is a coastal metropolis and the county seat of Miami-Dade County in South Florida, United States. With a population of 442,241 at the ...
,
Nebraska
Nebraska () is a state in the Midwestern region of the United States. It is bordered by South Dakota to the north; Iowa to the east and Missouri to the southeast, both across the Missouri River; Kansas to the south; Colorado to the sout ...
, and
Ohio State
The Ohio State University, commonly called Ohio State or OSU, is a public land-grant research university in Columbus, Ohio. A member of the University System of Ohio, it has been ranked by major institutional rankings among the best public ...
. The years listed in the table below indicate a national championship selection by the AP or Coaches Poll. The selections are noted with (AP) or (Coaches) when a national champion selection differed between the two polls for that particular season, which has occurred in twelve different seasons (including 2004, for which the coaches selection was rescinded) since the polls first came to coexist in 1950.
† USC's 2004 BCS National Championship was vacated by the BCS and the AFCA Coaches Trophy returned.
Split national championships
The
AP Poll
The Associated Press poll (AP poll) provides weekly rankings of the top 25 NCAA teams in one of three Division I college sports: football, men's basketball and women's basketball. The rankings are compiled by polling 62 sportswriters and broad ...
and
Coaches Poll
The Coaches Poll is a weekly ranking of the top 25 NCAA Division I Football Bowl Subdivision (FBS) college football, Division I college basketball, and Division I college baseball teams. The football version of the poll has been known officiall ...
have picked different final national poll leaders at the end of 11 different seasons since their first concurrent polls in 1950. This situation is referred to as a
"split" national championship.
National championship games
College football fans and administrators have long sought to match the No. 1 vs. No. 2 teams in an end-of-season national championship game to determine an undisputed national champion on the gridiron.
Historic occurrences
Throughout most of the 20th century,
bowl game
In North America, a bowl game is one of a number of post-season college football games that are primarily played by teams belonging to the NCAA's Division I Football Bowl Subdivision (FBS). For most of its history, the Division I Bowl Subdivi ...
conference tie-ins made it impossible to automatically schedule the two top teams for a single post-season game.
Through luck and fortuitous scheduling, a "national championship game" was occasionally able to settle the matter on the field.
Bowl Coalition (1992–1994)
Following back-to-back years of split AP and Coaches Poll national champions in
1990
File:1990 Events Collage.png, From left, clockwise: The 1990 FIFA World Cup is played in Italy; The Human Genome Project is launched; Voyager I takes the famous Pale Blue Dot image- speaking on the fragility of humanity on Earth, astrophysicist ...
:
Colorado
Colorado (, other variants) is a state in the Mountain states, Mountain West subregion of the Western United States. It encompasses most of the Southern Rocky Mountains, as well as the northeastern portion of the Colorado Plateau and the wes ...
(AP),
Georgia Tech
The Georgia Institute of Technology, commonly referred to as Georgia Tech or, in the state of Georgia, as Tech or The Institute, is a public research university and institute of technology in Atlanta, Georgia. Established in 1885, it is part of ...
(Coaches); and
1991
File:1991 Events Collage.png, From left, clockwise: Boris Yeltsin, elected as Russia's first president, waves the new flag of Russia after the 1991 Soviet coup d'état attempt, orchestrated by Soviet hardliners; Mount Pinatubo erupts in the Phi ...
:
Miami (FL)
Miami ( ), officially the City of Miami, known as "the 305", "The Magic City", and "Gateway to the Americas", is a coastal metropolis and the county seat of Miami-Dade County in South Florida, United States. With a population of 442,241 at the ...
(AP),
Washington
Washington commonly refers to:
* Washington (state), United States
* Washington, D.C., the capital of the United States
** A metonym for the federal government of the United States
** Washington metropolitan area, the metropolitan area centered o ...
(Coaches), the
Bowl Coalition was formed in
1992 to increase the probability of a No. 1 vs. No. 2 national championship game matchup in one of the Coalition's participating bowls.
The Coalition's rules retained traditional
bowl game
In North America, a bowl game is one of a number of post-season college football games that are primarily played by teams belonging to the NCAA's Division I Football Bowl Subdivision (FBS). For most of its history, the Division I Bowl Subdivi ...
conference tie-ins but provided some flexibility for scheduling a No. 1 vs. No. 2 matchup between two teams selected from among the champions of the
ACC,
Big East
The Big East Conference is a collegiate athletic conference that competes in NCAA Division I in ten men's sports and twelve women's sports. Headquartered in New York City, the eleven full-member schools are primarily located in Northeast and ...
,
Big Eight,
SEC, and
SWC conferences, or independent
Notre Dame, in the
Cotton Bowl,
Fiesta Bowl
The Fiesta Bowl is an American college football bowl game played annually in the Phoenix metropolitan area. From its beginning in 1971 until 2006, the game was hosted at the Sun Devil Stadium in Tempe, Arizona. Since 2007, the game has been pla ...
,
Orange Bowl
The Orange Bowl is an annual American college football bowl game played in the Miami metropolitan area. It has been played annually since January 1, 1935, making it, along with the Sugar Bowl and the Sun Bowl, the second-oldest bowl game ...
, or
Sugar Bowl.
The
Big Ten
The Big Ten Conference (stylized B1G, formerly the Western Conference and the Big Nine Conference) is the oldest Division I collegiate athletic conference in the United States. Founded as the Intercollegiate Conference of Faculty Representati ...
and
Pac-10 conferences were notably not members of the Bowl Coalition, with their champions retaining their traditional and contractual matchup in the
Rose Bowl. Likewise,
mid-major
Mid-major is a term used in American NCAA Division I college sports, particularly men's basketball, to refer to athletic conferences that are not among the "Power Five conferences" (the ACC, Big 10, Big 12, Pac-12, and SEC), which are alternativ ...
teams had no route to the Bowl Coalition National Championship Game.
Bowl Alliance (1995–1997)
In
1995
File:1995 Events Collage V2.png, From left, clockwise: O.J. Simpson is acquitted of the murders of Nicole Brown Simpson and Ronald Goldman from the year prior in "The Trial of the Century" in the United States; The Great Hanshin earthquake str ...
the
Bowl Alliance replaced the Bowl Coalition.
Going further than the Coalition, the Alliance guaranteed a postseason matchup of the No. 1 and No. 2 ranked teams of its same five conference champions plus Notre Dame. Beginning in
1996, the
Big 12
The Big 12 Conference is a college athletic conference headquartered in Irving, Texas, USA. It consists of ten full-member universities. It is a member of Division I of the National Collegiate Athletic Association (NCAA) for all sports. Its f ...
champion joined the Alliance in place of the champions of the disbanded
Big Eight and
Southwest
The points of the compass are a set of horizontal, radially arrayed compass directions (or azimuths) used in navigation and cartography. A compass rose is primarily composed of four cardinal directions—north, east, south, and west—each sepa ...
conferences.
Unlike the Coalition, the Alliance eliminated traditional conference tie-ins to its associated bowls. The Bowl Alliance national championship game would be rotated amongst the Fiesta Bowl, Sugar Bowl, and Orange Bowl, with the Cotton Bowl dropped from the slate. The Bowl Alliance also awarded
its own trophy to the winner of its national championship game.
The Rose Bowl remained independent of the Alliance, leaving open the possibility of a national title going to the Big Ten or Pac-10 Rose Bowl champion rather than the Alliance's champion.
This occurred in
1997
File:1997 Events Collage.png, From left, clockwise: The movie set of ''Titanic'', the highest-grossing movie in history at the time; '' Harry Potter and the Philosopher's Stone'', is published; Comet Hale-Bopp passes by Earth and becomes one of ...
, when No. 1
Michigan
Michigan () is a U.S. state, state in the Great Lakes region, Great Lakes region of the Upper Midwest, upper Midwestern United States. With a population of nearly 10.12 million and an area of nearly , Michigan is the List of U.S. states and ...
won the
Rose Bowl and retained their top ranking in the
AP Poll
The Associated Press poll (AP poll) provides weekly rankings of the top 25 NCAA teams in one of three Division I college sports: football, men's basketball and women's basketball. The rankings are compiled by polling 62 sportswriters and broad ...
.
The Bowl Alliance National Championship Game
winner
Nebraska
Nebraska () is a state in the Midwestern region of the United States. It is bordered by South Dakota to the north; Iowa to the east and Missouri to the southeast, both across the Missouri River; Kansas to the south; Colorado to the sout ...
split the championship when they passed Michigan in the final
Coaches Poll
The Coaches Poll is a weekly ranking of the top 25 NCAA Division I Football Bowl Subdivision (FBS) college football, Division I college basketball, and Division I college baseball teams. The football version of the poll has been known officiall ...
(a result denied by the Coaches Poll to Penn State three years earlier in the same situation).
Bowl Championship Series (1998–2013)
The
Bowl Championship Series (BCS), starting in
1998
1998 was designated as the ''International Year of the Ocean''.
Events January
* January 6 – The ''Lunar Prospector'' spacecraft is launched into orbit around the Moon, and later finds evidence for frozen water, in soil in permanently s ...
, finally succeeded in bringing the Big Ten and Pac-10 conferences together with the former Coalition and Alliance members for a combined national championship game.
Following the regular season, the BCS paired its No. 1 and No. 2 ranked teams to play for the title in the
BCS National Championship Game
The BCS National Championship Game, or BCS National Championship, was a postseason college football bowl game, used to determine a national champion of the NCAA Division I Football Bowl Subdivision (FBS), first played in the 1998 college fo ...
. This designation initially rotated in order between four BCS Bowls: the
Fiesta Bowl
The Fiesta Bowl is an American college football bowl game played annually in the Phoenix metropolitan area. From its beginning in 1971 until 2006, the game was hosted at the Sun Devil Stadium in Tempe, Arizona. Since 2007, the game has been pla ...
,
Sugar Bowl,
Orange Bowl
The Orange Bowl is an annual American college football bowl game played in the Miami metropolitan area. It has been played annually since January 1, 1935, making it, along with the Sugar Bowl and the Sun Bowl, the second-oldest bowl game ...
, and
Rose Bowl. For the
2006 season onward the BCS National Championship Game became its own separate contest, played one week later at the site of the bowl in the same rotation.
The BCS formula varied over the years, with the final version relying on a combination of the Coaches and
Harris
Harris may refer to:
Places Canada
* Harris, Ontario
* Northland Pyrite Mine (also known as Harris Mine)
* Harris, Saskatchewan
* Rural Municipality of Harris No. 316, Saskatchewan
Scotland
* Harris, Outer Hebrides (sometimes called the Isle of ...
polls and an average of various computer rankings to determine relative team rankings.
The winners of the BCS National Championship Game were crowned the Coaches Poll national champions and were awarded the
Coaches' Trophy on the field following the game. They were also awarded the
MacArthur Bowl by the
National Football Foundation
The National Football Foundation (NFF) is a non-profit organization to promote and develop amateur American football on all levels throughout the United States and "developing the qualities of leadership, sportsmanship, competitive zeal and the dr ...
.
BCS National Championships by school
† USC's victory in the
2005 Orange Bowl and subsequent 2004–05 BCS National Championship was vacated by the BCS.
College Football Playoff (2014–present)
The
College Football Playoff
The College Football Playoff (CFP) is an annual postseason knockout invitational tournament to determine a national champion for the National Collegiate Athletic Association (NCAA) Division I Football Bowl Subdivision (FBS), the highest level ...
(CFP) was designed as a replacement for the BCS. While the NCAA still does not officially sanction the event, organizers sought to bring a playoff system similar to all other levels of NCAA football to the Football Bowl Subdivision.
The College Football Playoff relies on a 13-member selection committee to choose the top four teams to play in a two-round single-elimination playoff bracket. The winner of the final game is awarded the
College Football Playoff National Championship Trophy
The College Football Playoff National Championship Trophy is the trophy awarded to the winner of the College Football Playoff (CFP), the postseason tournament in American college football that determines a national champion for the NCAA Division ...
.
CFP National Championships by school
National championship claims

The following tables list schools' known national championship claims at the highest level of play in college football. Some of these schools no longer compete at the highest level, which is currently
NCAA Division I FBS
The NCAA Division I Football Bowl Subdivision (FBS), formerly known as Division I-A, is the highest level of college football in the United States. The FBS consists of the largest schools in the National Collegiate Athletic Association (NCAA). As ...
, but nonetheless maintain claims to titles from when they did compete at the highest level.
Because there is no one governing or official body that regulates, recognizes, or awards national championships in college football, and because many independent selectors of championships exist, many of the claims by the schools listed below are shared, contradict each other, or are controversial.
In addition, because there is no one body overseeing national championships, no standardized requirements exist in order for a school to make a claim on a national championship, as any particular institution is free to make any declaration it deems to be fit.
The majority of these claims, but not all, are based on championships awarded from selectors listed as "major" in the official ''NCAA Football Bowl Subdivision Records''.
Not all championships awarded by third party selectors, nor those listed in the official NCAA Football Bowl Subdivision Records, are necessarily claimed by each school. Therefore, these claims represent how each individual school sees their own history on the subject of national championships. For the pre-poll era from 1901 through 1935, 41 major selections of teams from 20 schools have not been used to make national title claims.
The tables below include only national championship claims originating from each particular school and therefore represent the point-of-view of each individual institution. Each total number of championships, and the years for which they are claimed, are documented by the particular school on its official website, in its football media guide, on a prominent stadium sign, or in other official publications or literature (see Source). If a championship is not mentioned by a school for any particular season, regardless of whether it was awarded by a selector or listed in a third-party publication such as the official NCAA Football Bowl Subdivision Records, it is not considered to be claimed by that institution.
[All National Championships listed in the official ''NCAA Football Bowl Subdivision Records'' were checked for claims by the applicable schools. Although every care was taken to be thorough and accurate, it can not be assumed that there are no missing or misrepresented claims due to potential limitations of the available source material for any one institution.]
Claims by school
aUSC's January 4, 2005 win over Oklahoma in the BCS Championship Game was vacated as mandated by the NCAA, its 2004 BCS National Championship vacated by the BCS, and its AFCA Coaches' Trophy returned. NCAA sanctions mandate that "any reference to the vacated results, including championships, shall be removed." USC still retains the 2004 Associated Press National Championship and has not abandoned its claim to a 2004 national championship.Billingsley Report The Billingsley Report is a college football rating system developed in the late 1960s to determine a national champion. Billingsley has actively rated college football teams on a current basis since 1970. Beginning in 1999, Billingsley's ratings ...
named the 1907 team National Champions,
website notes to five titles
that appear in the NCAA Record Book, while not claiming three of them (1913, 1983, and 1993).
fNo major selectors chose Boston College for 1940.
gNo major selectors chose Yale for 1901. The original source for Parke H. Davis' "National Champion Foot Ball Teams" states "1901 Harvard".
Claims by year
Other selectors
In addition to the NCAA-designated "major selectors" listed above, various other people and organizations have selected national champions in college football. Selections from such notable selectors are listed below.
Unique championship selections from non-major selectors
Teams in the following table were selected by notable national championship selectors not listed as a "major selector "in the NCAA ''Football Bowl Subdivision Records'' book.
In the interest of brevity, this table contains only teams that were ''not'' also selected by any NCAA-designated major selector for the given year.
* Teams listed in ''italics'' indicate retroactively-applied championships.
See also
*
List of NCAA college football rankings
The AP Poll and Coaches Poll are the two major polls used annually within the highest level of college football to determine the national championship. Division I FBS football is the only National Collegiate Athletic Association (NCAA) sport for ...
*
List of NCAA Division I FBS football programs
This is a list of the 131 schools in the Division I Football Bowl Subdivision (FBS) of the National Collegiate Athletic Association (NCAA) in the United States.https://web3.ncaa.org/directory/memberList?type=12&division=I-FBS&sportCode=MFB By ...
Notes
References
External links
*
{{DEFAULTSORT:NCAA Division I Fbs National Football Championship
National Championship
A national championship(s) is the top achievement for any sport or contest within a league of a particular nation or nation state. The title is usually awarded by contests, ranking systems, stature, ability, etc. This determines the best team, indi ...
Lists of sports championships
Football
NCAA Division I FBS football
D1 Fbs
 National championship selectors came to be dominated by two competing
National championship selectors came to be dominated by two competing  In the AP Poll's early years, the final poll of sportswriters was taken prior to any
In the AP Poll's early years, the final poll of sportswriters was taken prior to any  The following tables list schools' known national championship claims at the highest level of play in college football. Some of these schools no longer compete at the highest level, which is currently
The following tables list schools' known national championship claims at the highest level of play in college football. Some of these schools no longer compete at the highest level, which is currently