Music of Hungary on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 Unlike most Western European peoples, the Hungarian people,
Unlike most Western European peoples, the Hungarian people,
 The earliest documentation of Hungarian music dates from the introduction of
The earliest documentation of Hungarian music dates from the introduction of  During the 18th century, some of the students at colleges such as those in S├Īrospatak and Sz├®kelyudvarhely were minor nobles from rural areas who brought with them their regional styles of music. Whilst the choirs in these colleges adopted a more polyphonic style, the students' songbooks indicate a growth in the popularity of homophonic songs. Their notation, however, was relatively crude and no extensive collection appeared until the publication of ├üd├Īm P├Īl├│czi Horv├ĪthŌĆÖs '' ├¢t├Čdf├®lsz├Īz ├ēnekek'' in 1853. These songs indicate that during the mid to late 18th century the previous Hungarian song styles died out and musicians looked more to other (Western) European styles for influence.
The 18th century also saw the rise of verbunkos, a form of music initially used by army recruiters. Like much Hungarian music of the time, melody was treated as more important than lyrics, although this balance changed as verbunkos became more established.
During the 18th century, some of the students at colleges such as those in S├Īrospatak and Sz├®kelyudvarhely were minor nobles from rural areas who brought with them their regional styles of music. Whilst the choirs in these colleges adopted a more polyphonic style, the students' songbooks indicate a growth in the popularity of homophonic songs. Their notation, however, was relatively crude and no extensive collection appeared until the publication of ├üd├Īm P├Īl├│czi Horv├ĪthŌĆÖs '' ├¢t├Čdf├®lsz├Īz ├ēnekek'' in 1853. These songs indicate that during the mid to late 18th century the previous Hungarian song styles died out and musicians looked more to other (Western) European styles for influence.
The 18th century also saw the rise of verbunkos, a form of music initially used by army recruiters. Like much Hungarian music of the time, melody was treated as more important than lyrics, although this balance changed as verbunkos became more established.
 In the 19th century, verbunkos was the most popular style in Hungary. This consisted of a slow dance followed by a faster dance; this dichotomy, between the slower and faster dances, has been seen as the "two contrasting aspects of the Hungarian character". The rhythmic patterns and embellishments of the verbunkos are distinctively Hungarian in nature, and draw heavily upon the folk music composed in the early part of the century by Antal Csermak,
In the 19th century, verbunkos was the most popular style in Hungary. This consisted of a slow dance followed by a faster dance; this dichotomy, between the slower and faster dances, has been seen as the "two contrasting aspects of the Hungarian character". The rhythmic patterns and embellishments of the verbunkos are distinctively Hungarian in nature, and draw heavily upon the folk music composed in the early part of the century by Antal Csermak,
 Hungary has also produced
Hungary has also produced
 Several musical festivals have been launched since the early 1990s propelled by increasing demand of the developing youth culture. Aside from country-wide events like
Several musical festivals have been launched since the early 1990s propelled by increasing demand of the developing youth culture. Aside from country-wide events like
Audio clips: Traditional music of Hungary.
Hungarian music
summarized at the administrative website of Hungary
Hungarian Folk Music Collection
N├®pdalok and Magyar N├│ta (5000 melodies).
:Urban Hungarian music or Magyar N├│ta
YouTube playlists {{Music of Europe Central European music
Hungary
Hungary ( hu, Magyarorsz├Īg ) is a landlocked country in Central Europe. Spanning of the Carpathian Basin, it is bordered by Slovakia to the north, Ukraine to the northeast, Romania to the east and southeast, Serbia to the south, Cr ...
has made many contributions to the fields of folk, popular
Popularity or social status is the quality of being well liked, admired or well known to a particular group.
Popular may also refer to:
In sociology
* Popular culture
* Popular fiction
* Popular music
* Popular science
* Populace, the total ...
and classical music
Classical music generally refers to the art music of the Western world, considered to be distinct from Western folk music or popular music traditions. It is sometimes distinguished as Western classical music, as the term "classical music" al ...
. Hungarian folk music is a prominent part of the national identity and continues to play a major part in Hungarian music. It is also strong in the Szabolcs-Szatm├Īr area and in the southwest part of Transdanubia
Transdanubia ( hu, Dun├Īnt├║l; german: Transdanubien, hr, Prekodunavlje or ', sk, Zadunajsko :sk:Zadunajsko) is a traditional region of Hungary. It is also referred to as Hungarian Pannonia, or Pannonian Hungary.
Administrative divisions Trad ...
. The Bus├│j├Īr├Īs carnival in Moh├Īcs
Moh├Īcs (; Croatian and Bunjevac: ''Moha─Ź''; german: Mohatsch; sr, ą£ąŠčģą░čć; tr, Moha├¦) is a town in Baranya County, Hungary, on the right bank of the Danube.
Etymology
The name probably comes from the Slavic ''*MčŖcha─Źčī'',''*Moch├Ī─Ź'': ...
is a major Hungarian folk music event, formerly featuring the long-established and well-regarded Bogyiszl├│ orchestra.Broughton, p. 159-167
Hungarian classical music
Classical music generally refers to the art music of the Western world, considered to be distinct from Western folk music or popular music traditions. It is sometimes distinguished as Western classical music, as the term "classical music" al ...
has long been an "experiment, made from Hungarian antedecents and on Hungarian soil, to create a conscious musical culture sing themusical world of the folk song". Although the Hungarian upper class has long had cultural and political connections with the rest of Europe, leading to an influx of European musical ideas, the rural peasants maintained their own traditions such that by the end of the 19th century Hungarian composers could draw on rural peasant music to (re)create a Hungarian classical style. For example, B├®la Bart├│k
B├®la Viktor J├Īnos Bart├│k (; ; 25 March 1881 ŌĆō 26 September 1945) was a Hungarian composer, pianist, and ethnomusicologist. He is considered one of the most important composers of the 20th century; he and Franz Liszt are regarded as Hu ...
and Zolt├Īn Kod├Īly
Zolt├Īn Kod├Īly (; hu, Kod├Īly Zolt├Īn, ; 16 December 1882 ŌĆō 6 March 1967) was a Hungarian composer, ethnomusicologist, pedagogue, linguist, and philosopher. He is well known internationally as the creator of the Kod├Īly method of music edu ...
, two of Hungary's most famous composers, are known for using folk themes in their music. Bart├│k collected folk songs from across Central and Eastern Europe
Central and Eastern Europe is a term encompassing the countries in the Baltics, Central Europe, Eastern Europe and Southeast Europe (mostly the Balkans), usually meaning former communist states from the Eastern Bloc and Warsaw Pact in Europ ...
, including the Czech Republic, Poland, Romania and Slovakia, whilst Kod├Īly was more interested in creating a distinctively Hungarian musical style.
During the era of Communist rule in Hungary (1949–1989) a Song Committee scoured and censored popular music for traces of subversion and ideological impurity. Since then, however, the Hungarian music industry has begun to recover, producing successful performers in the fields of jazz
Jazz is a music genre that originated in the African-American communities of New Orleans, Louisiana in the late 19th and early 20th centuries, with its roots in blues and ragtime. Since the 1920s Jazz Age, it has been recognized as a m ...
such as trumpeter Rudolf Tomsits
Rudolf Tomsits (12 May 1946 - 11 June 2003) was a Hungarian jazz musician who played the trumpet and the flugelhorn.
Biography
After a year in Sweden where he worked with Arne Domnerus, Jan Johansson und Egil Johansen, Tomsits became soloist, ...
, pianist-composer K├Īroly Binder
K├Īroly Binder (born 2 April 1956) is a Hungarian jazz pianist, composer and educator.
Early life
Binder was born in Budapest on 2 April 1956. He was five years old when he started playing the piano and studied jazz in Budapest at the B├®la Bart ...
and, in a modernized form of Hungarian folk, Ferenc Sebő
Ferenc Seb┼æ (born February 10, 1947, in Szeksz├Īrd) is a Hungarian folklorist
Folklore studies, less often known as folkloristics, and occasionally tradition studies or folk life studies in the United Kingdom, is the branch of anthropology d ...
and M├Īrta Sebesty├®n. The three giants of Hungarian rock, Ill├®s, Metr├│ and Omega
Omega (; capital: ╬®, lowercase: Žē; Ancient Greek ßĮ”, later ßĮ” ╬╝╬Ł╬│╬▒, Modern Greek Žē╬╝╬Ł╬│╬▒) is the twenty-fourth and final letter in the Greek alphabet. In the Greek numeric system/ isopsephy ( gematria), it has a value of 800. The ...
, remain very popular, especially Omega, which has followings in Germany and beyond as well as in Hungary. Older veteran underground bands such as Beatrice from the 1980s also remain popular.
Characteristics
 Unlike most Western European peoples, the Hungarian people,
Unlike most Western European peoples, the Hungarian people, Magyars
Hungarians, also known as Magyars ( ; hu, magyarok ), are a nation and┬Āethnic group native to Hungary () and historical Hungarian lands who share a common culture, history, ancestry, and language. The Hungarian language belongs to the Uralic ...
, emerged from the intermingling of Ugric and Eastern Turkish peoples during the fifth to eighth centuries CE. This makes the origins of their traditional music unique in Europe. According to author Simon Broughton, the composer and song collector Kod├Īly identified songs that "apparently date back 2,500 years" in common with the Mari people
The Mari ( chm, ą╝ą░čĆąĖ; russian: ą╝ą░čĆąĖą╣čåčŗ, mariytsy) are a Finnic people, who have traditionally lived along the Volga and Kama rivers in Russia. Almost half of Maris today live in the Mari El republic, with significant populations in ...
of Russia;Broughton, pp. 159 - 167 and, as well as the Mari, the ethnomusicologist
Ethnomusicology is the study of music from the cultural and social aspects of the people who make it. It encompasses distinct theoretical and methodical approaches that emphasize cultural, social, material, cognitive, biological, and other dim ...
Bruno Nettl
Bruno Nettl (14 March 1930 ŌĆō 15 January 2020) was an ethnomusicologist who was central in defining ethnomusicology as a discipline. His research focused on folk and traditional music, specifically Native American music the music of Iran an ...
indicates similarities in traditional Hungarian music with Mongolian and Native American music
Indigenous music of North America, which includes American Indian music or Native American music, is the
music that is used, created or performed by Indigenous peoples of North America, including Native Americans in the United States and Abor ...
al styles.Nettl Bence Szabolcsi
Bence Szabolcsi (2 August 1899 ŌĆō 21 January 1973) was a Hungarian music historian. Along with Ervin Major, "he can be considered the founder of scholarly study of the history of Hungarian music, and he was primarily responsible for creating an ...
, however, claims that the Finno-Ugric and Turkish-Mongolian elements are present but "cannot be attached to certain, definite national or linguistic groups". Nonetheless, Szabolcsi claims links between Hungarian musical traditions and those of the Mari, Kalmyk, Ostyak, northwest Chinese, Tatar
The Tatars ()Tatar
in the Collins English Dictionary is an umbrella term for different
, in the Collins English Dictionary is an umbrella term for different
Vogul
The Mansi (Mansi language, Mansi: ą£─üąĮčīčüąĖ / ą£─üąĮčīčüąĖ ą╝─üčģčāą╝, ''M─ü┼äsi / M─ü┼äsi m─ühum'', ) are a Ob-Ugric languages, Ugric indigenous people living in Khanty-Mansi Autonomous Okrug, KhantyŌĆōMansia, an Autonomous okrugs of Russi ...
, Anatolian Turkish, Bashkirian
The Bashkirian is in the ICS geologic timescale the lowest stage or oldest age of the Pennsylvanian. The Bashkirian age lasted from to Ma, is preceded by the Serpukhovian and is followed by the Moscovian.
The Bashkirian overlaps with the ...
, Mongol
The Mongols ( mn, ą£ąŠąĮą│ąŠą╗čćčāčāą┤, , , ; ; russian: ą£ąŠąĮą│ąŠą╗čŗ) are an East Asian ethnic group native to Mongolia, Inner Mongolia in China and the Buryatia Republic of the Russian Federation. The Mongols are the principal member ...
and Chuvash musics. These, he claims, are evidence that "Asia
Asia (, ) is one of the world's most notable geographical regions, which is either considered a continent in its own right or a subcontinent of Eurasia, which shares the continental landmass of Afro-Eurasia with Africa. Asia covers an are ...
n memories slumber in the depths of Hungarian folk music and that this folk music is the last Western
Western may refer to:
Places
*Western, Nebraska, a village in the US
*Western, New York, a town in the US
*Western Creek, Tasmania, a locality in Australia
*Western Junction, Tasmania, a locality in Australia
*Western world, countries that id ...
link in the chain of ancient Eastern cultural relations".
According to Broughton, traditional Hungarian music is "highly distinctive" like the Hungarian language
Hungarian () is an Uralic language spoken in Hungary and parts of several neighbouring countries. It is the official language of Hungary and one of the 24 official languages of the European Union. Outside Hungary, it is also spoken by Hungar ...
, which invariably is stressed on the first syllable, lending a strongly accented dactylic rhythm
Rhythm (from Greek , ''rhythmos'', "any regular recurring motion, symmetry") generally means a " movement marked by the regulated succession of strong and weak elements, or of opposite or different conditions". This general meaning of regular re ...
to the music". Nettl identifies two "essential features" of Hungarian folk music to be the use of "pentatonic scale
A pentatonic scale is a musical scale with five notes per octave, in contrast to the heptatonic scale, which has seven notes per octave (such as the major scale and minor scale).
Pentatonic scales were developed independently by many an ...
s composed of major second
In Western music theory, a major second (sometimes also called whole tone or a whole step) is a second spanning two semitones (). A second is a musical interval encompassing two adjacent staff positions (see Interval number for more de ...
s and minor third
In music theory, a minor third is a musical interval that encompasses three half steps, or semitones. Staff notation represents the minor third as encompassing three staff positions (see: interval number). The minor third is one of two com ...
s" (or "gapped scales") and "the practice of transposing a bit of melody
A melody (from Greek ╬╝╬Ą╬╗ß┐│╬┤╬»╬▒, ''mel┼Źid├Ła'', "singing, chanting"), also tune, voice or line, is a linear succession of musical tones that the listener perceives as a single entity. In its most literal sense, a melody is a combina ...
several times to create the essence of a song". These transpositions are "usually up or down a fifth", a fundamental interval in the series of overtones and an indication perhaps of the "influence of Chinese musical theory in which the fifth is significant".
According to Szabolcsi, these 'Hungarian transpositions', along with "some melodic, rhythmical and ornamental peculiarities, clearly show on the map of Eurasia
Eurasia (, ) is the largest continental area on Earth, comprising all of Europe and Asia. Primarily in the Northern and Eastern Hemispheres, it spans from the British Isles and the Iberian Peninsula in the west to the Japanese archipelag ...
the movements of Turkish people from the East to the West". The subsequent influence on neighbouring countries' music is seen in the music of Slovakia, Poland
Poland, officially the Republic of Poland, is a country in Central Europe. It is divided into 16 administrative provinces called voivodeships, covering an area of . Poland has a population of over 38 million and is the fifth-most populou ...
, and, with intervals of the third
Third or 3rd may refer to:
Numbers
* 3rd, the ordinal form of the cardinal number 3
* , a fraction of one third
* 1Ōüä60 of a ''second'', or 1Ōüä3600 of a ''minute''
Places
* 3rd Street (disambiguation)
* Third Avenue (disambiguation)
* Hi ...
or second
The second (symbol: s) is the unit of time in the International System of Units (SI), historically defined as of a day ŌĆō this factor derived from the division of the day first into 24 hours, then to 60 minutes and finally to 60 seconds ea ...
, in the music of the Czech Republic
Music of the Czech Republic comprises the musical traditions of that state or the historical entities of which it is compound, i.e. the Czech lands (Bohemia, Moravia, Czech Silesia). Czech music also constitutes a substantial part of the music c ...
. Hungarian and Finnoic musical traditions are also characterised by the use of an ABBA binary musical form
In music, ''form'' refers to the structure of a musical composition or performance. In his book, ''Worlds of Music'', Jeff Todd Titon suggests that a number of organizational elements may determine the formal structure of a piece of music, such ...
, with Hungary itself especially known for the A A' A' A variant, where the B sections are the A sections transposed up or down a fifth (A'). Modern Hungarian folk music evolved in the 19th century, and is contrasted with previous styles through the use of arched melodic lines as opposed to the more archaic descending lines.
Music history
 The earliest documentation of Hungarian music dates from the introduction of
The earliest documentation of Hungarian music dates from the introduction of Gregorian chant
Gregorian chant is the central tradition of Western plainchant, a form of monophonic, unaccompanied sacred song in Latin (and occasionally Greek) of the Roman Catholic Church. Gregorian chant developed mainly in western and central Europe dur ...
in the 11th century. By that time, Hungary had begun to enter the European cultural establishment with the country's conversion to Christianity and the musically important importation of plainsong
Plainsong or plainchant (calque from the French ''plain-chant''; la, cantus planus) is a body of chants used in the liturgies of the Western Church. When referring to the term plainsong, it is those sacred pieces that are composed in Latin text ...
, a form of Christian chant. Though Hungary's early religious musical history is relatively well documented, secular music remains mostly unknown, though it was apparently a common feature of community festivals and other events. The earliest documented instrumentation in Hungary dates back to the whistle
A whistle is an instrument which produces sound from a stream of gas, most commonly air. It may be mouth-operated, or powered by air pressure, steam, or other means. Whistles vary in size from a small slide whistle or nose flute type to a lar ...
in 1222, the Koboz around 1237-1325, the bugle
The bugle is one of the simplest brass instruments, normally having no valves or other pitch-altering devices. All pitch control is done by varying the player's embouchure.
History
The bugle developed from early musical or communication ...
in 1355, the fiddle
A fiddle is a bowed string musical instrument, most often a violin. It is a colloquial term for the violin, used by players in all genres, including classical music. Although in many cases violins and fiddles are essentially synonymous, the ...
in 1358, the bagpipe
Bagpipes are a woodwind instrument using enclosed reeds fed from a constant reservoir of air in the form of a bag. The Great Highland bagpipes are well known, but people have played bagpipes for centuries throughout large parts of Europe, ...
in 1402, the lute
A lute ( or ) is any plucked string instrument with a neck and a deep round back enclosing a hollow cavity, usually with a sound hole or opening in the body. It may be either fretted or unfretted.
More specifically, the term "lute" can ref ...
in 1427 and the trumpet
The trumpet is a brass instrument commonly used in classical and jazz ensembles. The trumpet group ranges from the piccolo trumpetŌĆöwith the highest register in the brass familyŌĆöto the bass trumpet, pitched one octave below the standard ...
in 1428. Thereafter the organ came to play a major role.
The 16th century saw the rise of Transylvania
Transylvania ( ro, Ardeal or ; hu, Erd├®ly; german: Siebenb├╝rgen) is a historical and cultural region in Central Europe, encompassing central Romania. To the east and south its natural border is the Carpathian Mountains, and to the west the A ...
(a region inhabited by Hungarians, never occupied by the Turks) as a centre for Hungarian music. It also saw the first publication of music in Hungary, in Krak├│w
Krak├│w (), or Cracow, is the second-largest and one of the oldest cities in Poland. Situated on the Vistula, Vistula River in Lesser Poland Voivodeship, the city dates back to the seventh century. Krak├│w was the official capital of Poland un ...
. At this time Hungarian instrumental music was well known in Europe; the lutenist and composer B├Īlint Bakfark
B├Īlint Bakfark (; in contemporary sources Valentin Bakfark or (from 1565 onward) Valentin Greff alias Bakfark, his name is variously spelled as ''Bacfarc'', ''Bakfarc'', ''Bakfarkh'', ''Bakffark'', ''Backuart'') (1526ŌĆō30 ŌĆō 15 or 22 August 1 ...
, for example, was famed as a virtuoso player. His compositions pioneered a new style of writing for the lute based on vocal polyphony. The lutenist brothers Melchior and Konrad Neusiedler were also noted, as was Stephan Monetarius, the author of an important early work in music theory, the '' Epithoma utriusque musices''.
During the 16th century, Hungary was divided into three parts: an area controlled by the Turks; an area controlled by the Habsburg
The House of Habsburg (), alternatively spelled Hapsburg in Englishgerman: Haus Habsburg, ; es, Casa de Habsburgo; hu, Habsburg csal├Īd, it, Casa di Asburgo, nl, Huis van Habsburg, pl, dom Habsburg├│w, pt, Casa de Habsburgo, la, Domus Hab ...
s; and Transylvania. Historic songs declined in popularity and were replaced by lyrical poetry, whilst minstrels were replaced by court musicians. Many courts or households maintained large ensembles of musicians who played the trumpet, whistle, cimbalom
The cimbalom (; ) or concert cimbalom is a type of chordophone composed of a large, trapezoidal box on legs with metal strings stretched across its top and a damping pedal underneath. It was designed and created by V. Josef Schunda in 1874 in ...
, violin or bagpipes. Some of these ensemble musicians were German, Polish, French or Italian; the court of G├Ībor Bethlen
Gabriel Bethlen ( hu, Bethlen G├Ībor; 15 November 1580 ŌĆō 15 November 1629) was Prince of Transylvania from 1613 to 1629 and Duke of Opole from 1622 to 1625. He was also King-elect of Hungary from 1620 to 1621, but he never took control of ...
, Prince of Transylvania, included a Spanish guitarist. Little detail about the music played during this era survives, however. Musical life in the areas controlled by the Ottoman Turks declined precipitously, with even the formerly widespread and entrenched plainsong style disappearing by the end of the 17th century. Outside of the Ottoman area, however, plainsong flourished after the establishment of Protestant missions in around 1540, while a similarly styled form of folk song called verse chronicles also arose.
 During the 18th century, some of the students at colleges such as those in S├Īrospatak and Sz├®kelyudvarhely were minor nobles from rural areas who brought with them their regional styles of music. Whilst the choirs in these colleges adopted a more polyphonic style, the students' songbooks indicate a growth in the popularity of homophonic songs. Their notation, however, was relatively crude and no extensive collection appeared until the publication of ├üd├Īm P├Īl├│czi Horv├ĪthŌĆÖs '' ├¢t├Čdf├®lsz├Īz ├ēnekek'' in 1853. These songs indicate that during the mid to late 18th century the previous Hungarian song styles died out and musicians looked more to other (Western) European styles for influence.
The 18th century also saw the rise of verbunkos, a form of music initially used by army recruiters. Like much Hungarian music of the time, melody was treated as more important than lyrics, although this balance changed as verbunkos became more established.
During the 18th century, some of the students at colleges such as those in S├Īrospatak and Sz├®kelyudvarhely were minor nobles from rural areas who brought with them their regional styles of music. Whilst the choirs in these colleges adopted a more polyphonic style, the students' songbooks indicate a growth in the popularity of homophonic songs. Their notation, however, was relatively crude and no extensive collection appeared until the publication of ├üd├Īm P├Īl├│czi Horv├ĪthŌĆÖs '' ├¢t├Čdf├®lsz├Īz ├ēnekek'' in 1853. These songs indicate that during the mid to late 18th century the previous Hungarian song styles died out and musicians looked more to other (Western) European styles for influence.
The 18th century also saw the rise of verbunkos, a form of music initially used by army recruiters. Like much Hungarian music of the time, melody was treated as more important than lyrics, although this balance changed as verbunkos became more established.
Folk music
Hungarian folk music changed greatly beginning in the 19th century, evolving into a new style that had little in common with the music that came before it. Modern Hungarian music was characterised by an "arched melodic line, strict composition, long phrases and extended register", in contrast to the older styles which always utilize a "descending melodic line". left, Old Hungarian war song created some time between 1878 and 1914 and sung by ├Üjv├Īry K├Īroly (1856-1918). Modern Hungarian folk music was first recorded in 1895 by B├®la Vik├Īr, setting the stage for the pioneering work ofB├®la Bart├│k
B├®la Viktor J├Īnos Bart├│k (; ; 25 March 1881 ŌĆō 26 September 1945) was a Hungarian composer, pianist, and ethnomusicologist. He is considered one of the most important composers of the 20th century; he and Franz Liszt are regarded as Hu ...
, Zolt├Īn Kod├Īly
Zolt├Īn Kod├Īly (; hu, Kod├Īly Zolt├Īn, ; 16 December 1882 ŌĆō 6 March 1967) was a Hungarian composer, ethnomusicologist, pedagogue, linguist, and philosopher. He is well known internationally as the creator of the Kod├Īly method of music edu ...
and L├Īszl├│ Lajtha
L├Īszl├│ Lajtha (; 30 June 1892 ŌĆō 16 February 1963) was a Hungarian composer, ethnomusicologist and conductor.
Career
Born to Ida Wiesel, a Transsylvanian-Hungarian and P├Īl Lajtha, an owner of a leather factory. The father P├Īl had ambitio ...
in musicological collecting. Modern Hungarian folk music began its history with the Habsburg
The House of Habsburg (), alternatively spelled Hapsburg in Englishgerman: Haus Habsburg, ; es, Casa de Habsburgo; hu, Habsburg csal├Īd, it, Casa di Asburgo, nl, Huis van Habsburg, pl, dom Habsburg├│w, pt, Casa de Habsburgo, la, Domus Hab ...
Empire in the 18th century, when central Europe
Europe is a large peninsula conventionally considered a continent in its own right because of its great physical size and the weight of its history and traditions. Europe is also considered a Continent#Subcontinents, subcontinent of Eurasia ...
an influences became paramount, including a "regular metric structure for dancing and marching instead of the free speech rhythms of the old style. Folk music at that time consisting of village bagpipe
Bagpipes are a woodwind instrument using enclosed reeds fed from a constant reservoir of air in the form of a bag. The Great Highland bagpipes are well known, but people have played bagpipes for centuries throughout large parts of Europe, ...
rs who were replaced by string-based orchestras of the Gypsy, or Roma people.
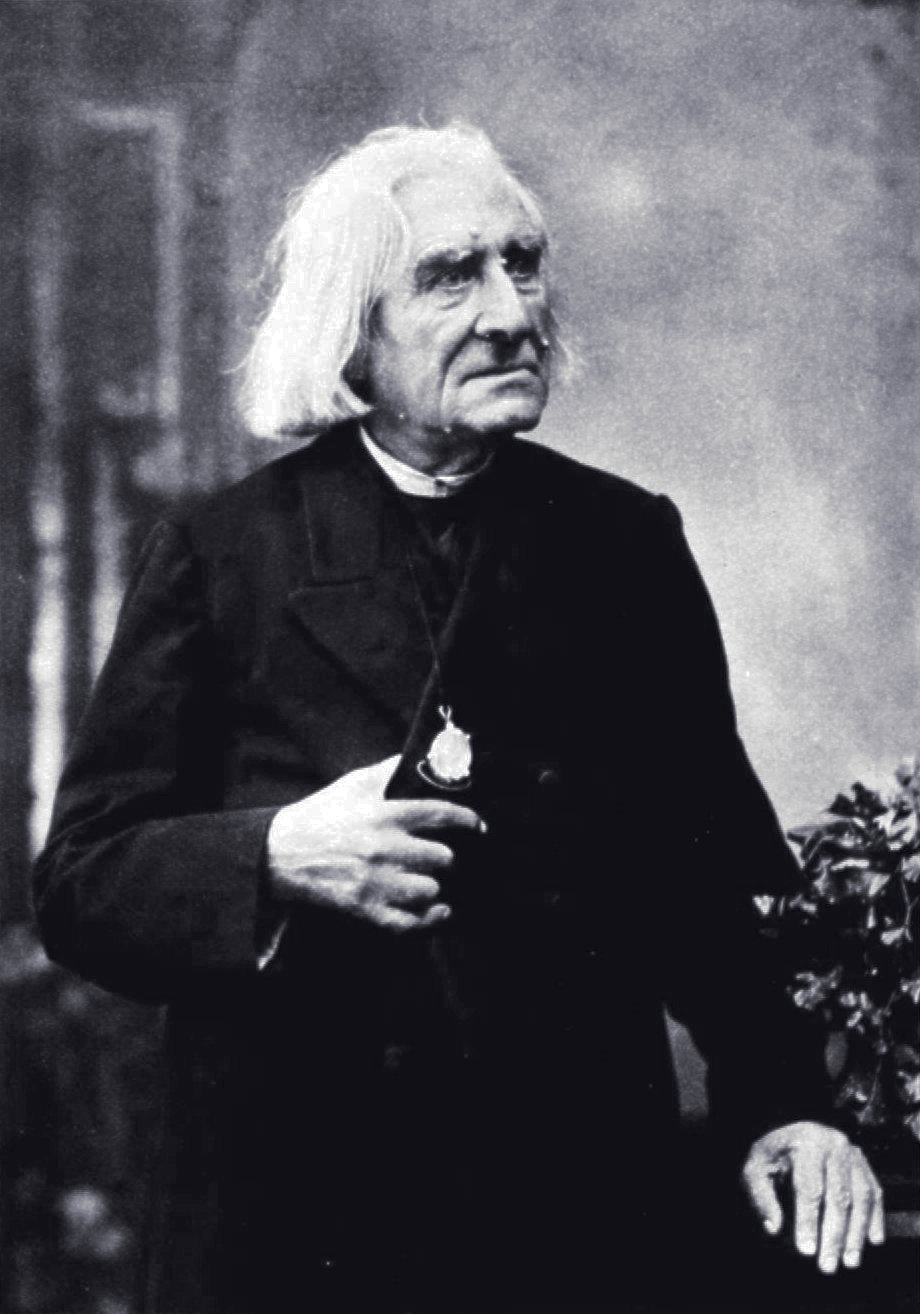
In the 19th century, Roma orchestras became very well known throughout Europe, and were frequently thought of as the primary musical heritage of Hungary, as in Franz Liszt
Franz Liszt, in modern usage ''Liszt Ferenc'' . Liszt's Hungarian passport spelled his given name as "Ferencz". An orthographic reform of the Hungarian language in 1922 (which was 36 years after Liszt's death) changed the letter "cz" to simpl ...
's '' Hungarian Dances'' and ''Rhapsodies
Rhapsody may refer to:
* A work of epic poetry, or part of one, that is suitable for recitation at one time
** Rhapsode, a classical Greek professional performer of epic poetry
Computer software
* Rhapsody (online music service), an online m ...
'', which used Hungarian Roma music as representative of Hungarian folk music Hungarian Romani
Romani may refer to:
Ethnicities
* Romani people, an ethnic group of Northern Indian origin, living dispersed in Europe, the Americas and Asia
** Romani genocide, under Nazi rule
* Romani language, any of several Indo-Aryan languages of the Roma ...
music is often represented as the only music of the Roma, though multiple forms of Roma music are common throughout Europe and are often dissimilar to Hungarian forms. In the Hungarian language
Hungarian () is an Uralic language spoken in Hungary and parts of several neighbouring countries. It is the official language of Hungary and one of the 24 official languages of the European Union. Outside Hungary, it is also spoken by Hungar ...
, 19th-century folk styles like the csardas and the verbunkos, are collectively referred to as ''cig├Īnyzene'', which translates literally as ''Gypsy music''.
Hungarian nationalist composers, like Bart├│k, rejected the conflation of Hungarian and Roma music, studying the rural peasant songs of Hungary which, according to music historian Bruno Nettl, "has little in common with" Roma music, a position that is held to by some modern writers, such as the Hungarian author B├Īlint S├Īrosi. Simon Broughton, however, has claimed that Roma music is "no less Hungarian and... has more in common with peasant music than the folklorists like to admit", and authors Marian Cotton and Adelaide Bradburn claimed that Hungarian-Roma music was "perhaps... originally Hungarian in character, but (the Roma have made so many changes that) it is difficult to tell what is Hungarian and what is" the authentic music of the Roma.Cotton
The ethnic Cs├Īng├│ Hungarians of Moldavia
Moldavia ( ro, Moldova, or , literally "The Country of Moldavia"; in Romanian Cyrillic: or ; chu, ąŚąĄą╝ą╗č¦ ą£ąŠą╗ą┤ą░ą▓čüą║ą░č¦; el, ß╝®╬│╬Ą╬╝╬┐╬Į╬»╬▒ Žäß┐åŽé ╬£╬┐╬╗╬┤╬▒╬▓╬»╬▒Žé) is a historical region and former principality in Centr ...
's Seret Valley have moved in large numbers to Budapest
Budapest (, ; ) is the capital and most populous city of Hungary. It is the ninth-largest city in the European Union by population within city limits and the second-largest city on the Danube river; the city has an estimated population o ...
, and become a staple of the local folk scene with their distinctive instrumentation using flutes, fiddles, drums and the lute.
Prominent folk ensembles, such as the Hungaria Folk Orchestra, the Danube Folk Ensemble and the Hungarian State Folk Ensemble have regular performances in Budapest
Budapest (, ; ) is the capital and most populous city of Hungary. It is the ninth-largest city in the European Union by population within city limits and the second-largest city on the Danube river; the city has an estimated population o ...
and are a popular attraction for visitors.
Verbunkos
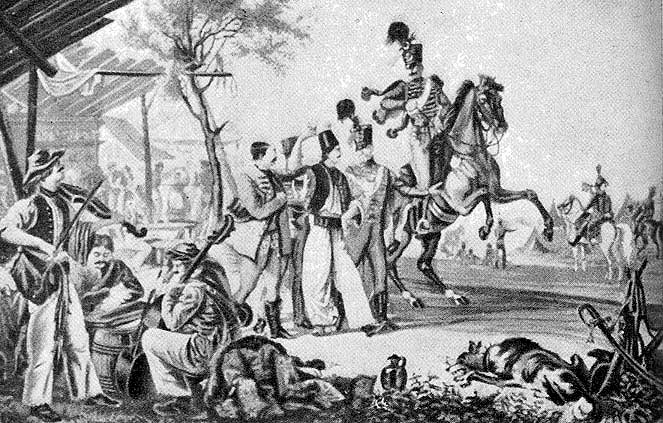
 In the 19th century, verbunkos was the most popular style in Hungary. This consisted of a slow dance followed by a faster dance; this dichotomy, between the slower and faster dances, has been seen as the "two contrasting aspects of the Hungarian character". The rhythmic patterns and embellishments of the verbunkos are distinctively Hungarian in nature, and draw heavily upon the folk music composed in the early part of the century by Antal Csermak,
In the 19th century, verbunkos was the most popular style in Hungary. This consisted of a slow dance followed by a faster dance; this dichotomy, between the slower and faster dances, has been seen as the "two contrasting aspects of the Hungarian character". The rhythmic patterns and embellishments of the verbunkos are distinctively Hungarian in nature, and draw heavily upon the folk music composed in the early part of the century by Antal Csermak, Ferdinand Kauer
Ferdinand August Kauer (18 January 1751 ŌĆō 13 April 1831) was an Austrian composer and pianist.
Biography
Kauer was born in Klein-Thaya (today Dyj├Īkovi─Źky) near Znojmo in South Moravia). He studied in Znojmo, Tyrnau, and Vienna, and later set ...
, Janos Lavotta and others.
Verbunkos was originally played at recruitment ceremonies to convince young men to join the army, and was performed, as in so much of Hungarian music, by Roma bands. One verbunkos tune, the " R├Īk├│czi March" became a march that was a prominent part of compositions by both Liszt
Franz Liszt, in modern usage ''Liszt Ferenc'' . Liszt's Hungarian passport spelled his given name as "Ferencz". An orthographic reform of the Hungarian language in 1922 (which was 36 years after Liszt's death) changed the letter "cz" to simpl ...
and Hector Berlioz
In Greek mythology, Hector (; grc, ß╝Ø╬║ŽäŽēŽü, Hekt┼Źr, label=none, ) is a character in Homer's Iliad. He was a Trojan prince and the greatest warrior for Troy during the Trojan War. Hector led the Trojans and their allies in the defense o ...
. The 18th-century origins of verbunkos are not well known, but probably include old dances like the swine-herd dance and the Hajduk dance, as well as elements of Balkan, Slavic and Levantine music, and the cultured music of Italy and Vienna, all filtered through the Roma performers. Verbunkos became wildly popular, not just among the poor peasantry, but also among the upper-class aristocratics, who saw verbunkos as the authentic music of the Hungarian nation. Characteristics of verbunkos include the bok├Īz├│ (''clicking of heels'') cadence
In Western musical theory, a cadence (Latin ''cadentia'', "a falling") is the end of a phrase in which the melody or harmony creates a sense of full or partial resolution, especially in music of the 16th century onwards.Don Michael Randel (199 ...
-pattern, the use of the interval of the augmented second, garlands of triplets, widely arched, free melodies without words, and alternately swift and slow tempi. By the end of the 18th century, verbunkos was in use in opera, chamber
Chamber or the chamber may refer to:
In government and organizations
*Chamber of commerce, an organization of business owners to promote commercial interests
*Legislative chamber, in politics
*Debate chamber, the space or room that houses deliber ...
and piano
The piano is a stringed keyboard instrument in which the strings are struck by wooden hammers that are coated with a softer material (modern hammers are covered with dense wool felt; some early pianos used leather). It is played using a keyboa ...
music, and in song literature, and was regarded as "the continuation, the resurrection of ancient Hungarian dance and music, and its success signified the triumph of the people's art".
The violin
The violin, sometimes known as a '' fiddle'', is a wooden chordophone ( string instrument) in the violin family. Most violins have a hollow wooden body. It is the smallest and thus highest-pitched instrument ( soprano) in the family in regu ...
ist Panna Czinka was among the most celebrated musicians of the 19th century, as was the Roma bandleader J├Īnos Bihari
J├Īnos Bihari (21 October 1764 – 26 April 1827) was an influential Hungarian Romani violinist. He is one of the founders of Romani academic music and the musical genre verbunkos.
By the middle of the nineteenth century, "Gypsy music" w ...
, known as the "Napoleon of the fiddle". Bihari, Antal Cserm├Īk and other composers helped make verbunkos the "most important expression of the Hungarian musical Romanticism
Romanticism (also known as the Romantic movement or Romantic era) was an artistic, literary, musical, and intellectual movement that originated in Europe towards the end of the 18th century, and in most areas was at its peak in the approximate ...
" and have it "the role of national music". Bihari was especially important in popularizing and innovating the verbunkos; he was the "incarnation of the musical demon of fiery imagination". Bihari and others after his death helped invent n├│ta, a popular form written by composers like L├│r├Īnd Fr├Īter, ├ürp├Īd Bal├Īzs, Pista Dank├│, B├®ni Egressy
B├®ni Egressy (; born Galambos Benj├Īmin; 21 April 1814 ŌĆō 17 July 1851 in Saj├│kazinc) was a Hungarian composer, librettist, translator and actor. He created a number of popular melodic compositions, including the one to Mih├Īly V├Čr├Čsmart ...
, M├Īrk R├│zsav├Člgyi and Imre Farkas. Many of the biggest names in modern Hungarian music are the verbunkos-playing Lakatos family, including S├Īndor Lakatos and Roby Lakatos
Roby Lakatos (born 1965) is a violinist from Hungary who combines jazz, classical, and Hungarian Romani music
Romani music (often referred to as gypsy or gipsy music, which is sometimes considered a derogatory term) is the music of the Roman ...
.
Roma music
Though the Roma are primarily known as the performers of Hungarian styles like verbunkos, they have their own form of folk music that is largely without instrumentation, in spite of their reputation in that field outside of the Roma community. Roma music tends to take on characteristics of whatever music the people are around, however, embellished with "twists and turns, trills and runs", making a very new, and distinctively Roma style. Though without instruments, Roma folk musicians use sticks, tapped on the ground, rhythmic grunts and a technique called oral-bassing which vocally imitates the sound of instruments. Some modern Roma musicians, like Ando Drom, Romano Drom, Romani Rota and Kalyi Jag have added modern instruments likeguitar
The guitar is a fretted musical instrument that typically has six strings. It is usually held flat against the player's body and played by strumming or plucking the strings with the dominant hand, while simultaneously pressing selected string ...
s to the Roma style, while Gyula Babos
Gyula Babos (June 26, 1949 in Budapest - April 12, 2018 ibid) was a Hungary, Hungarian jazz guitarist.
Biography
Babos was a part of the bands Kex, R├Īkfog├│ and Saturnus, and won the Jazz Competition of the Hungarian Radio in 1966. Since 1977 ...
' Project Romani has used elements of avant-garde jazz
Avant-garde jazz (also known as avant-jazz and experimental jazz) is a style of music and improvisation that combines avant-garde art music and composition with jazz. It originated in the early 1950s and developed through to the late 1960s. Ori ...
.
Hungarian music abroad
Ethnic Hungarians live in parts of theCzech Republic
The Czech Republic, or simply Czechia, is a landlocked country in Central Europe. Historically known as Bohemia, it is bordered by Austria to the south, Germany to the west, Poland to the northeast, and Slovakia to the southeast. The ...
, Poland
Poland, officially the Republic of Poland, is a country in Central Europe. It is divided into 16 administrative provinces called voivodeships, covering an area of . Poland has a population of over 38 million and is the fifth-most populou ...
, Romania
Romania ( ; ro, România ) is a country located at the crossroads of Central Europe, Central, Eastern Europe, Eastern, and Southeast Europe, Southeastern Europe. It borders Bulgaria to the south, Ukraine to the north, Hungary to the west, S ...
, Slovakia
Slovakia (; sk, Slovensko ), officially the Slovak Republic ( sk, Slovensk├Ī republika, links=no ), is a landlocked country in Central Europe. It is bordered by Poland to the north, Ukraine to the east, Hungary to the south, Austria to the ...
, Serbia
Serbia (, ; Serbian: , , ), officially the Republic of Serbia ( Serbian: , , ), is a landlocked country in Southeastern and Central Europe, situated at the crossroads of the Pannonian Basin and the Balkans. It shares land borders with Hu ...
, Slovenia
Slovenia ( ; sl, Slovenija ), officially the Republic of Slovenia (Slovene: , abbr.: ''RS''), is a country in Central Europe. It is bordered by Italy to the west, Austria to the north, Hungary to the northeast, Croatia to the southeast, and ...
, and elsewhere. Of these, the Hungarian population of Romania (both in the region of Transylvania and among the Cs├Īng├│ people) - being the more rural, outer rims of the kingdom of Hungary - has had the most musical impact on Hungarian folk music. The Hungarian community in Slovakia has produced the roots revival
A roots revival (folk revival) is a trend which includes young performers popularizing the traditional musical styles of their ancestors. Often, roots revivals include an addition of newly composed songs with socially and politically aware ly ...
band Ghymes, who play in the t├Īnch├Īz tradition. The Serbian region of Vojvodina
Vojvodina ( sr-Cyrl, ąÆąŠčśą▓ąŠą┤ąĖąĮą░}), officially the Autonomous Province of Vojvodina, is an autonomous province that occupies the northernmost part of Serbia. It lies within the Pannonian Basin, bordered to the south by the national capital ...
is home to a large Hungarian minority
Transylvanian folk music remains vital part of life in modern Transylvania. Bart├│k and Kod├Īly found Transylvania to be a fertile area for folk song collecting. Folk bands are usually a string trio, consisting of a violin, viola and double bass, occasionally with a cimbalom
The cimbalom (; ) or concert cimbalom is a type of chordophone composed of a large, trapezoidal box on legs with metal strings stretched across its top and a damping pedal underneath. It was designed and created by V. Josef Schunda in 1874 in ...
; the first violin, or ''prim├Īs'', plays the melody, with the others accompanying and providing the rhythm. Transylvania is also the original home of the t├Īnch├Īz tradition, which has since spread throughout Hungary.
T├Īnch├Īz
T├Īnch├Īz
T├Īnch├Īz (, literally "dance house") is a "casual" Hungarian folk dance event (as opposed to stage performances). It is an aspect of the Hungarian roots revival of traditional culture which began in the early 1970s, and remains an active part of ...
(literally "dance house") is a dance music
Dance music is music composed specifically to facilitate or accompany dancing. It can be either a whole musical piece or part of a larger musical arrangement. In terms of performance, the major categories are live dance music and recorded da ...
movement which first appeared in the 1970s as a reaction against state-supported homogenised and sanitised folk music. They have been described as a "cross between a barn dance
A barn dance is any kind of dance involving traditional or folk music with traditional dancing, occasionally held in a barn, but, these days, much more likely to be in any suitable building.
The term ŌĆ£barn danceŌĆØ is usually associated ...
and folk club", and generally begin with a slow tempo ''verbunkos'' (recruiting dance), followed by swifter ''cs├Īrd├Īs
Cs├Īrd├Īs (, ; ), often seen as Cz├Īrd├Īs, is a traditional Hungarian folk dance, the name derived from ' (old Hungarian term for roadside tavern and restaurant). It originated in Hungary and was popularized by bands in Hungary and neighboring l ...
'' dances. Cs├Īrd├Īs is a very popular Hungarian folk dance that comes in many regional varieties, and is characterized by changes in tempo
In musical terminology, tempo ( Italian, 'time'; plural ''tempos'', or ''tempi'' from the Italian plural) is the speed or pace of a given piece. In classical music, tempo is typically indicated with an instruction at the start of a piece (ofte ...
. T├Īnch├Īz began with the folk song collecting of musicians like B├®la Halmos and Ferenc Seb┼æ
Ferenc Seb┼æ (born February 10, 1947, in Szeksz├Īrd) is a Hungarian folklorist
Folklore studies, less often known as folkloristics, and occasionally tradition studies or folk life studies in the United Kingdom, is the branch of anthropology d ...
, who collected rural instrumental and dance music for popular, urban consumption, along with the dance collectors Gy├Črgy Martin and S├Īndor Tim├Īr. The most important rural source of these songs was Transylvania
Transylvania ( ro, Ardeal or ; hu, Erd├®ly; german: Siebenb├╝rgen) is a historical and cultural region in Central Europe, encompassing central Romania. To the east and south its natural border is the Carpathian Mountains, and to the west the A ...
, which is actually in Romania
Romania ( ; ro, România ) is a country located at the crossroads of Central Europe, Central, Eastern Europe, Eastern, and Southeast Europe, Southeastern Europe. It borders Bulgaria to the south, Ukraine to the north, Hungary to the west, S ...
but has a large ethnic Hungarian minority. The instrumentation of these bands, based on Transylvanian and sometimes the southern Slovak Hungarian communities, included a fiddle
A fiddle is a bowed string musical instrument, most often a violin. It is a colloquial term for the violin, used by players in all genres, including classical music. Although in many cases violins and fiddles are essentially synonymous, the ...
on lead with violin
The violin, sometimes known as a '' fiddle'', is a wooden chordophone ( string instrument) in the violin family. Most violins have a hollow wooden body. It is the smallest and thus highest-pitched instrument ( soprano) in the family in regu ...
, a kontra (a 3-string viola also called a ''br├Īcsa''), and bowed double bass, and sometimes a cimbalom
The cimbalom (; ) or concert cimbalom is a type of chordophone composed of a large, trapezoidal box on legs with metal strings stretched across its top and a damping pedal underneath. It was designed and created by V. Josef Schunda in 1874 in ...
as well.
Many of the biggest names in modern Hungarian music emerged from the t├Īnch├Īz scene, including Muzsik├Īs and M├Īrta Sebesty├®n. Other bands include Vujicsics, J├Īnosi, T├®ka and Kalamajka, while singers include ├ēva F├Ībi├Īn and Andr├Īs Berecz. Famous instrumentalists include fiddlers Csaba ├¢kr├Čs and Bal├Īzs Vizeli, cimbalomist K├Īlm├Īn Balogh
K├Īlm├Īn Balogh (born 18 January 1959) is a Hungarian cimbalom player and leader of Kalman Balogh's Gypsy Cimbalom Band.
History
Balogh is a Hungarian cimbalom player part of a lineage of Hungarian Gypsy musicians. A graduate of Franz Liszt ...
, violinist F├®lix Lajk├│
F├®lix Lajk├│ ( sr, ążąĄą╗ąĖą║čü ąøą░čśą║ąŠ, ''Feliks Lajko''; born 17 December 1974 in Ba─Źka Topola, SR Serbia, SFR Yugoslavia) is a Hungarian violinist, zither player and composer. He plays a variety of musical styles: folk music (tradition ...
(from Subotica
Subotica ( sr-cyrl, ąĪčāą▒ąŠčéąĖčåą░, ; hu, Szabadka) is a city and the administrative center of the North Ba─Źka District in the autonomous province of Vojvodina, Serbia. Formerly the largest city of Vojvodina region, contemporary Subotica i ...
in Serbia) and multi-instrumentalist Mih├Īly Dresch
Mih├Īly Dresch (born 1955) is a Hungarian saxophone player. He plays a combination of American free jazz and traditional Hungarian folk music.
Dresch was studying to become an engineer when he turned to jazz. He was a member of the K├Īroly Bind ...
.
left, Cs├Īrd├Īs, composed around 1904 by Vittorio Monti.
Classical music
Hungary's most important contribution to the worldwide field ofEuropean classical music
Classical music generally refers to the art music of the Western world, considered to be distinct from Western folk music or popular music traditions. It is sometimes distinguished as Western classical music, as the term "classical music" als ...
is probably Franz Liszt
Franz Liszt, in modern usage ''Liszt Ferenc'' . Liszt's Hungarian passport spelled his given name as "Ferencz". An orthographic reform of the Hungarian language in 1922 (which was 36 years after Liszt's death) changed the letter "cz" to simpl ...
, a renowned pianist in his own time and a well-regarded composer of 19 ''Hungarian Rhapsodies
The Hungarian Rhapsodies, S.244, R.106 (french: Rhapsodies hongroises, german: Ungarische Rhapsodien, hu, Magyar rapsz├│di├Īk), is a set of 19 piano pieces based on Hungarian folk themes, composed by Franz Liszt during 1846ŌĆō1853, and late ...
'' and a number of symphonic poems such as ''Les pr├®ludes
' ("Preludes" or "The Beginnings"), S.97, is the third of Franz Liszt's thirteen symphonic poems. The music was composed between 1845ŌĆō54, and began as an overture to Liszt's choral cycle ' (The Four Elements), then revised as a stand-alone co ...
''. Liszt was among the major composers during the late 19th century, a time when modern Hungarian classical music was in its formative stage. Along with Liszt and his French Romantic tendencies, Ferenc Erkel
Ferenc Erkel ( hu, Erkel Ferenc , german: link=no, Franz Erkel; November 7, 1810June 15, 1893) was a Hungarian composer, conductor and pianist. He was the father of Hungarian grand opera, written mainly on historical themes, which are still o ...
's Italian and French-style operas, with Hungarian words, and Mih├Īly Mosonyi's German classical style, helped set the stage for future music, and their influence is "unsurpassed even by their successors, because in addition to their individual abilities they bring about an unprecedented artistic intensification of the Romantic musical idiom, which is practically consumed by this extreme passion". Elements of Hungarian folk music, especially verbunkos, became important elements of many composers, both Hungarians like Kalman Simonffy and foreign composers like Johannes Brahms
Johannes Brahms (; 7 May 1833 ŌĆō 3 April 1897) was a German composer, pianist, and conductor of the mid-Romantic period. Born in Hamburg into a Lutheran family, he spent much of his professional life in Vienna. He is sometimes grouped wit ...
and Ludwig van Beethoven
Ludwig van Beethoven (baptised 17 December 177026 March 1827) was a German composer and pianist. Beethoven remains one of the most admired composers in the history of Western music; his works rank amongst the most performed of the classic ...
.
 Hungary has also produced
Hungary has also produced Karl Goldmark
Karl Goldmark (born K├Īroly Goldmark, Keszthely, 18 May 1830 ŌĆō Vienna, 2 January 1915) was a Hungarian-born Viennese composer.Peter Revers, Michael Cherlin, Halina Filipowicz, Richard L. Rudolph The Great Tradition and Its Legacy 2004; , p. ...
, composer of the ''Rustic Wedding Symphony
''Rustic Wedding Symphony'', Op. 26 (''L├żndliche Hochzeit'') is a symphony in E flat major by Karl Goldmark, written in 1875, a year before his renowned Violin Concerto No. 1.
The symphony was premiered in Vienna on 5 March 1876, conducted by H ...
'', composer and pianist Ern┼æ Dohn├Īnyi
Ernő or Erno is a Finnish and Hungarian masculine given name. Notable people with the name include:
* Ernő Balogh (1897-1989), Hungarian pianist, composer, editor, and educator
* Ern┼æ B├Īnk (1883-1962), Hungarian painter and teacher
* Ernő B ...
, composer and ethnomusicologist L├Īszl├│ Lajtha
L├Īszl├│ Lajtha (; 30 June 1892 ŌĆō 16 February 1963) was a Hungarian composer, ethnomusicologist and conductor.
Career
Born to Ida Wiesel, a Transsylvanian-Hungarian and P├Īl Lajtha, an owner of a leather factory. The father P├Īl had ambitio ...
, and the piano composer Stephen Heller
Stephen Heller (15 May 1813 ŌĆō 14 January 1888) was a Hungarian pianist, teacher, and composer whose career spanned the period from Schumann to Bizet. Heller was an influence for later Romantic composers. He outlived his reputation, and was ...
. A number of violinists from Hungary have also achieved international renown, especially Joseph Joachim
Joseph Joachim (28 June 1831 ŌĆō 15 August 1907) was a Hungarian violinist, conductor, composer and teacher who made an international career, based in Hanover and Berlin. A close collaborator of Johannes Brahms, he is widely regarded as one of t ...
, Jen┼æ Hubay, Edward Rem├®nyi, S├Īndor V├®gh S├Īndor V├®gh (17 May 19126 January 1997) was a Hungarian, later French, violinist and conductor. He was best known as one of the great chamber music violinists of the twentieth century.
Education
S├Īndor V├®gh was born in 1912 in Kolozsv├Īr, T ...
, Franz von Vecsey, Ede Zathureczky
Ede Zathureczky (Igl├│, 24 August 1903 ŌĆō Bloomington, 31 May 1959) was a Hungarian violin virtuoso and pedagogue.
Life and career
Ede Zathureczky was born in Igl├│, Kingdom of Hungary (now Spi┼Īsk├Ī Nov├Ī Ves in Slovakia). His teacher was the ...
, Emil Telm├Īnyi, Tibor Varga and Leopold Auer
Leopold von Auer ( hu, Auer Lip├│t; June 7, 1845July 15, 1930) was a Hungarian violinist, academic, conductor, composer, and instructor. Many of his students went on to become prominent concert performers and teachers.
Early life and career
Au ...
. Hungarian-born conductors include Antal Dor├Īti
Antal Dor├Īti (, , ; 9 April 1906 ŌĆō 13 November 1988) was a Hungarian-born conductor and composer who became a naturalized American citizen in 1943.
Biography
Antal Dor├Īti was born in Budapest, where his father Alexander Dor├Īti was a vi ...
; ; Eugene Ormandy
Eugene Ormandy (born Jen┼æ Blau; November 18, 1899 ŌĆō March 12, 1985) was a Hungarian-born American conductor and violinist, best known for his association with the Philadelphia Orchestra, as its music director. His 44-year association with ...
; Fritz Reiner
Frederick Martin "Fritz" Reiner (December 19, 1888 ŌĆō November 15, 1963) was a prominent conductor of opera and symphonic music in the twentieth century. Hungarian born and trained, he emigrated to the United States in 1922, where he rose to ...
; George Szell
George Szell (; June 7, 1897 – July 30, 1970), originally Gy├Črgy Sz├®ll, Gy├Črgy Endre Sz├®l, or Georg Szell, was a Hungarian-born American conductor and composer. He is widely considered one of the twentieth century's greatest condu ...
and Georg Solti
Sir Georg Solti ( , ; born Gy├Črgy Stern; 21 October 1912 ŌĆō 5 September 1997) was a Hungarian-British orchestral and operatic conductor, known for his appearances with opera companies in Munich, Frankfurt and London, and as a long-servin ...
, ├üd├Īm Fischer
├üd├Īm Fischer (born 9 September 1949 in Budapest) is a Hungarian conductor. He is the general music director of the Austro-Hungarian Haydn Orchestra, chief conductor of the Danish Chamber Orchestra, and chief conductor of the D├╝sseldorfer Sy ...
and Iv├Īn Fischer
Iv├Īn Fischer (born 20 January 1951) is a Hungarian conductor and composer.
Born in Budapest into a musical family of Jewish heritage, Fischer initially studied piano, violin, cello and composition in Budapest. His older brother, ├üd├Īm Fisc ...
, as well as Gregory Vajda
Gregory Vajda (born Gergely Vajda; August 13, 1973) is a Hungarian clarinetist, composer and conductor.
Early life and education
He was born in Budapest in 1973 to bassoonist J├│zsef Vajda (1947-2016) and operatic soprano Veronika Kincses. Vaj ...
.
Pianists of international renown: G├®za Anda, Tam├Īs V├Īs├Īry
Tam├Īs V├Īs├Īry (; born 11 August 1933) is a Hungarian concert pianist and conductor.
Biography and career
V├Īs├Īry was born in Debrecen, Hungary, and made his stage debut at the age of 8, performing Mozart's Piano Concerto in D major, K.10 ...
, Georges Cziffra, Annie Fischer
Annie Fischer (July 5, 1914April 10, 1995) was a Hungarian
classical pianist.
Biography
Fischer was born into a Jewish family in Budapest and studied at the Franz Liszt Academy of Music with Ern┼æ Dohn├Īnyi and Arnold Szekely. She began he ...
, Zolt├Īn Kocsis, Dezs┼æ R├Īnki
Dezs┼æ R├Īnki (born 8 September 1951) is a Hungarian virtuoso concert pianist with a broad repertoire and a significant discography of solo, duo and concerto works.
Life and career
Born in Budapest, he began taking piano lessons at the Budapes ...
, Andr├Īs Schiff
Sir Andr├Īs Schiff (; born 21 December 1953) is a Hungarian-born British classical pianist and conductor, who has received numerous major awards and honours, including the Grammy Award, Gramophone Award, Mozart Medal, and Royal Academy of Mus ...
and Jenő Jandó
Jenő Jandó (; born 1 February 1952) is a Hungarian pianist and Professor of the Franz Liszt Academy of Music in Budapest, Hungary.
Background and education
Jand├│ studied piano at the Liszt Academy with Katalin Nemes and P├Īl Kadosa, la ...
Hungarian opera
The origins of Hungarian opera can be traced to the late 18th century, with the rise of imported opera and other concert styles in cities likePozsony
Bratislava (, also ; ; german: Pre├¤burg/Pressburg ; hu, Pozsony) is the capital and largest city of Slovakia. Officially, the population of the city is about 475,000; however, it is estimated to be more than 660,000 ŌĆö approximately 140% of ...
, Kismarton
Eisenstadt (; hu, Kismarton; hr, ┼Įeljezni grad; ; sl, ┼Įelezno, Austro-Bavarian: ''Eisnstod'') is a city in Austria, the state capital of Burgenland. It had a recorded population on 29 April 2021 of 15,074.
In the Habsburg Empire's Kingdom ...
, Nagyszeben and Budapest
Budapest (, ; ) is the capital and most populous city of Hungary. It is the ninth-largest city in the European Union by population within city limits and the second-largest city on the Danube river; the city has an estimated population o ...
. Operas at the time were in either the German
German(s) may refer to:
* Germany (of or related to)
**Germania (historical use)
* Germans, citizens of Germany, people of German ancestry, or native speakers of the German language
** For citizens of Germany, see also German nationality law
**Ge ...
or Italian style. The field Hungarian opera began with school dramas and interpolations of German operas, which began at the end of the 18th century. School dramas in places like the Pauline School in S├Ītoralja├║jhely, the Calvinist School in Csurg├│
) in Csurg├│
, image_shield = HUN_Csurg├│_C├Łmer.svg
, image_flag = Flag of Csurg├│.svg
, map =
, pushpin_map = Hungary
, pushpin_label_position =
, pushpin_map_caption = Location of C ...
and the Piarist School in Beszterce.
Pozsony produced the first music drama experiments in the country, though the work of G├Īsp├Īr Pacha and J├│zsef Chudy; it was the latter's 1793 ''Prince Pikk├│ and Jutka Perzsi'' that is generally considered the first opera in a distinctively Hungarian style. The text of that piece was translated from ''Prinz Schnudi und Prinzessin Evakathel'' by Philipp Hafner. This style was still strongly informed by the Viennese Zauberposse
This is a glossary list of opera genres, giving alternative names.
" Opera" is an Italian word (short for "opera in musica"); it was not at first ''commonly'' used in Italy (or in other countries) to refer to the genre of particular works. Most ...
style of comedic play, and remained thus throughout the 19th century. Though these operas used foreign styles, the "idyllic, lyric and heroic" parts of the story were always based on verbunkos, which was becoming a symbol of the Hungarian nation during this time. It was not until the middle of the 19th century that Ferenc Erkel wrote the first Hungarian language opera, using French and Italian models, thus launching the field of Hungarian opera.
Bart├│k and Kod├Īly
At the end of the 19th century, Hungarian music was dominated by compositions in the German classical style, while Viennese-styleoperetta
Operetta is a form of theatre and a genre of light opera. It includes spoken dialogue, songs, and dances. It is lighter than opera in terms of its music, orchestral size, length of the work, and at face value, subject matter. Apart from its ...
s gained immensely in popularity. This ended beginning in about 1905, when Endre Ady
Endre Ady (Hungarian: ''di├│sadi Ady Andr├Īs Endre,'' archaic English: Andrew Ady, 22 November 1877 ŌĆō 27 January 1919) was a turn-of-the-century Hungarian poet and journalist. Regarded by many as the greatest Hungarian poet of the 20th century ...
's poems were published, composer B├®la Bart├│k was published for the first time, and Zolt├Īn Kod├Īly began collecting folk songs. Bart├│k and Kod├Īly were two exceptional composers who created a distinctively Hungarian style. Bart├│k collected songs across Eastern Europe, though much of his activity was in Hungary, and he used their elements in his music. He was interested in all forms of folk music, while Kod├Īly was more specifically Hungarian in his outlook. In contrast to previous composers who worked with Hungarian popular musical idioms, Kod├Īly and Bart├│k drew a sharp line between the popular music played by Roma (also known as "magyarn├│ta", or Hungarian music or Gypsy music) and the music of farmers. Their work was a watershed that incorporated "every great tradition of the Hungarian people" and influenced all the later composers of the country.
Later 20th century
For the first half of the 20th century, Bart├│k and Kod├Īly were potent symbols for a generation of composers, especially Kod├Īly. Starting in about 1947, a revival in folk choir music began, ended as an honest force by 1950, when state-run art became dominant with the rise ofCommunism
Communism (from Latin la, communis, lit=common, universal, label=none) is a far-left sociopolitical, philosophical, and economic ideology and current within the socialist movement whose goal is the establishment of a communist society, ...
. Under Communism, "(c)ommitment and ideological affiliation (were) measured by the musical style of a composer; the ignominious adjectives 'formalistic' and 'cosmopolitan' gain currency ... (and the proper Hungarian style was) identified with the major mode, the classical aria
In music, an aria ( Italian: ; plural: ''arie'' , or ''arias'' in common usage, diminutive form arietta , plural ariette, or in English simply air) is a self-contained piece for one voice, with or without instrumental or orchestral accompa ...
, rondo
The rondo is an instrumental musical form introduced in the Classical period.
Etymology
The English word ''rondo'' comes from the Italian form of the French ''rondeau'', which means "a little round".
Despite the common etymological root, rondo ...
or sonata form
Sonata form (also ''sonata-allegro form'' or ''first movement form'') is a musical structure generally consisting of three main sections: an exposition, a development, and a recapitulation. It has been used widely since the middle of the 18th c ...
, the chord sequences distilled" from Kod├Īly's works. Music was uniformly festive and optimistic, with every deviation arousing suspicion; this simplicity led to a lack of popular support from the public, who did not identify with the sterile approved styles. The most prominent composers of this period were Endre Szerv├Īnszky, Ferenc Szab├│ and Lajos B├Īrdos
Lajos B├Īrdos (1 October 1899 ŌĆō 18 November 1986) was a composer, conductor, music theorist, and professor of music at the Franz Liszt Academy of Music, in Budapest, Hungary, where he had previously studied under Albert Sikl├│s and Zolt├Īn K ...
.
Beginning in about 1955, a new wave of composers appeared, inspired by Bart├│k and breathing new life into Hungarian music. Composers from this era included Andr├Īs Mih├Īly
Andr├Īs Mih├Īly ł╔Ændra╦É╩ā ╦łmiha╦Éj(6 November 1917 ŌĆō 19 September 1993) was a Hungarian cellist, composer and academic teacher.
Life
Mih├Īly was born in Budapest. He studied there at the Franz Liszt Academy: cello with Adolf Schiffer, ch ...
, Endre Szerv├Īnszky, P├Īl Kadosa, Ferenc Farkas and Gy├Črgy R├Īnki. These composers both brought back old techniques of Hungarian music, as well as adapting imported avant-garde
The avant-garde (; In 'advance guard' or ' vanguard', literally 'fore-guard') is a person or work that is experimental, radical, or unorthodox with respect to art, culture, or society.John Picchione, The New Avant-garde in Italy: Theoretica ...
and modernist elements of Western classical music. Gy├Črgy Ligeti
Gy├Črgy S├Īndor Ligeti (; ; 28 May 1923 ŌĆō 12 June 2006) was a Hungarian-Austrian composer of contemporary classical music. He has been described as "one of the most important avant-garde composers in the latter half of the twentieth century ...
and Gy├Črgy Kurt├Īg are often mentioned in the same sentence. They were born near each other in Transylvania and studied in Budapest
Budapest (, ; ) is the capital and most populous city of Hungary. It is the ninth-largest city in the European Union by population within city limits and the second-largest city on the Danube river; the city has an estimated population o ...
in the 1940s. Both were influenced by Stockhausen. Kurt├Īg's modernism borrowed many influences from the past. By contrast Ligeti invented a new language with chromatic tone clusters and elements of parody. Both were multi-lingual and became exiles. This is reflected in the texts for their works. The foundation of the New Music Studio in 1970 helped further modernise Hungarian classical music though promoting composers that felt audience education was as important a consideration as artistic merit in composition and performance; these Studio's well-known composers include L├Īszl├│ Vidovszky, L├Īszl├│ S├Īry
L├Īszl├│ S├Īry (born Gy┼ærasszonyfa, Hungary
Hungary ( hu, Magyarorsz├Īg ) is a landlocked country in Central Europe. Spanning of the Carpathian Basin, it is bordered by Slovakia to the north, Ukraine to the northeast, Romania to ...
and Zolt├Īn Jeney
Zolt├Īn Jeney (4 March 1943 ŌĆō 28 October 2019) was a Hungarian composer.
Jeney was born in Szolnok Hungary. He first studied piano and attended Pongr├Īcz's composition classes at the Debrecen Secondary Music School, later continuing compositi ...
. Mikl├│s R├│zsa
Mikl├│s R├│zsa (; April 18, 1907 ŌĆō July 27, 1995) was a Hungarian-American composer trained in Germany (1925ŌĆō1931) and active in France (1931ŌĆō1935), the United Kingdom (1935ŌĆō1940), and the United States (1940ŌĆō1995), with extensi ...
, who studied in Germany and eventually settled in the United States, achieved international recognition for his Hollywood film scores as well as his concert music.
Popular music
Hungarian popular music in the early 20th century consisted of lightoperetta
Operetta is a form of theatre and a genre of light opera. It includes spoken dialogue, songs, and dances. It is lighter than opera in terms of its music, orchestral size, length of the work, and at face value, subject matter. Apart from its ...
s and the Roma music of various styles. Nagymező utca, the "Broadway
Broadway may refer to:
Theatre
* Broadway Theatre (disambiguation)
* Broadway theatre, theatrical productions in professional theatres near Broadway, Manhattan, New York City, U.S.
** Broadway (Manhattan), the street
**Broadway Theatre (53rd Stree ...
of Budapest
Budapest (, ; ) is the capital and most populous city of Hungary. It is the ninth-largest city in the European Union by population within city limits and the second-largest city on the Danube river; the city has an estimated population o ...
", was a major centre for popular music, and boasted enough nightclubs and theatres to earn its nickname. In 1945, however, this era abruptly ended and popular music was mostly synonymous with the patriotic songs imposed by the Russian Communists. Some operettas were still performed, though infrequently, and any music with Western influences was seen as harmful and dangerous. In 1956, however, liberalisation began with the "three Ts" ("''tilt├Īs, t┼▒r├®s, t├Īmogat├Īs"'', meaning "prohibition, toleration, support''"''), and a long period of cultural struggle began, starting with a battle over African American
African Americans (also referred to as Black Americans and Afro-Americans) are an ethnic group consisting of Americans with partial or total ancestry from sub-Saharan Africa. The term "African American" generally denotes descendants of ens ...
jazz
Jazz is a music genre that originated in the African-American communities of New Orleans, Louisiana in the late 19th and early 20th centuries, with its roots in blues and ragtime. Since the 1920s Jazz Age, it has been recognized as a m ...
. Jazz became a part of Hungarian music in the early 20th century, and although common place in Budapest's venues such as the Tabarin, the Astoria and Central Cafe which set up its own coffee jazz band, it has not achieved widespread renown until the 1970s, when Hungary began producing internationally known performers like the Benk├│ Dixieland Band and B├®la Szakcsi Lakatos. Other renowned performers from the younger generation are the Hot Jazz Band and the Boh├®m Ragtime Jazz Band.
Rock
In the early 1960s, Hungarian youths began listening to rock in droves, in spite of condemnation from the authorities. Three bands dominated the scene by the beginning of the 1970s, Ill├®s, Metr├│ andOmega
Omega (; capital: ╬®, lowercase: Žē; Ancient Greek ßĮ”, later ßĮ” ╬╝╬Ł╬│╬▒, Modern Greek Žē╬╝╬Ł╬│╬▒) is the twenty-fourth and final letter in the Greek alphabet. In the Greek numeric system/ isopsephy ( gematria), it has a value of 800. The ...
, all three of which had released at least one album. A few other bands recorded a few singles, but the Record-Producing Company, a state-run record label
A record label, or record company, is a brand or trademark of music recordings and music videos, or the company that owns it. Sometimes, a record label is also a publishing company that manages such brands and trademarks, coordinates the pr ...
, did not promote or support these bands, which quickly disappeared.
In 1968, the New Economic Mechanism was introduced, intending on revitalising the Hungarian economy, while the band Ill├®s won almost every prize at the prestigious T├Īncdalfesztiv├Īl. In the 1970s, however, the hard-liners of the Communist party cracked down on dissidence in Hungary, and rock was a major target. The band Ill├®s was banned from performing and recording, while Metr├│ and Omega left. Some of the members of these bands formed a supergroup, Locomotiv GT, that quickly became very famous. The remaining members of Omega, meanwhile, succeeded in achieving stardom in Germany, and remained very popular for a time.
Rock bands in the late 1970s had to conform to the Record Company's demands and ensure that all songs passed the inspection of the Song Committee, who scoured all songs looking for hidden political messages. LGT was the most prominent band of a classic rock
Classic rock is a US radio format which developed from the album-oriented rock (AOR) format in the early 1980s. In the United States, the classic rock format comprises rock music ranging generally from the mid-1960s through the mid 1990s, prim ...
style that was very popular, along with Ill├®s, Bergendy and Zor├Īn, while there were other bands like The Sweet
The Sweet (often shortened to just Sweet), are a British glam rock band that rose to prominence in the 1970s. Their best known line-up consisted of lead vocalist Brian Connolly, bass player Steve Priest, guitarist Andy Scott, and drummer M ...
and Middle of the Road who catered to the desires of the Song Committee, producing rock-based pop music
Pop music is a genre of popular music that originated in its modern form during the mid-1950s in the United States and the United Kingdom. The terms ''popular music'' and ''pop music'' are often used interchangeably, although the former descri ...
without a hint of subversion. Meanwhile, the disco
Disco is a genre of dance music and a subculture that emerged in the 1970s from the United States' urban nightlife scene. Its sound is typified by four-on-the-floor beats, syncopated basslines, string sections, brass and horns, electric p ...
style of electronic music
Electronic music is a genre of music that employs electronic musical instruments, digital instruments, or circuitry-based music technology in its creation. It includes both music made using electronic and electromechanical means ( electro ...
produced such performers as the expensively produced and managed Neoton Familia, Beatrice and Sz┼▒cs Judit, while the more critically acclaimed progressive rock
Progressive rock (shortened as prog rock or simply prog; sometimes conflated with art rock) is a broad genre of rock music that developed in the United Kingdom and United States through the mid- to late 1960s, peaking in the early 1970s. I ...
scene produced bands like East
East or Orient is one of the four cardinal directions or points of the compass. It is the opposite direction from west and is the direction from which the Sun rises on the Earth.
Etymology
As in other languages, the word is formed from the fac ...
, V73, Color
Color (American English) or colour (British English) is the visual perceptual property deriving from the spectrum of light interacting with the photoreceptor cells of the eyes. Color categories and physical specifications of color are associ ...
and Panta Rhei.
In the early 1980s, economic depression wracked Hungary, leading to a wave of politically disillusioned and alienated yet vibrant youth culture, a crucial part of which were hard rock, punk, new wave and art rock. Major bands from this era included Beatrice, who had moved from disco to punk and folk-influenced rock and were known for their splashy, uncensored and theatrical performances, P. Mobil, Bikini
A bikini is a two-piece swimsuit primarily worn by women that features two triangles of fabric on top that cover the breasts, and two triangles of fabric on the bottom: the front covering the pelvis but exposing the navel, and the back coverin ...
, Hobo Blues Band, A. E. Bizotts├Īg, Eur├│pa Kiad├│, Szi├Īmi and Edda m┼▒vek. The first major prison sentences for rock-related subversion were given out, with the members of the punk band CPg sentenced to two years for political incitement.
As the communist system was falling apart, the Hungarian Record Company (MHV) was privatized and smaller independent labels such as Bahia and Human Telex were formed. Major multinational companies such as EMI established headquarters in Budapest. Hungarian popular music became incorporated into the global music industry.
Electronic music
Clubbing and electronic dance music started gaining popularity in Hungary following the change of regime in 1989 and corresponding toElectronic music
Electronic music is a genre of music that employs electronic musical instruments, digital instruments, or circuitry-based music technology in its creation. It includes both music made using electronic and electromechanical means ( electro ...
's increasing popularity in the worldwide musical mainstream. The political freedom and cultural boom of western culture opened the way for the clubbing scene, with several venues starting all around the country, especially in Budapest
Budapest (, ; ) is the capital and most populous city of Hungary. It is the ninth-largest city in the European Union by population within city limits and the second-largest city on the Danube river; the city has an estimated population o ...
and around Lake Balaton
Lake Balaton () is a freshwater lake in the Transdanubian region of Hungary. It is the largest lake in Central Europe, and one of the region's foremost tourist destinations. The Zala River provides the largest inflow of water to the lake, and ...
.
The 1990s also marked the creation of several dance formations, notably Soho Party, Splash, N├Īksi & Brunner and also rave formations such as Emergency House and Kozmix. Notable techno and house DJ-s are Sterbinszky, Budai
Budai ( zh, c=ÕĖāĶóŗ, p=B├╣d├Āi; ko, ĒżļīĆ, Podae; ja, ÕĖāĶóŗ, Hotei; vi, Bß╗æ ─Éß║Īi) was a Chinese monk who is often identified with and venerated as Maitreya Buddha in Chan Buddhism. With the spread of Chan Buddhism, he also came to b ...
, and Newl. The workings of the scene culminated in events like Budapest Parade, the largest such street festival in Hungary, that was held yearly from 2000 to 2006, attracting more than half million visitors. The history of Electronic Dance Music and Techno culture in Hungary is documented in Ferenc K├Čml┼ædy's book "F├®nykatedr├Īlis", (1999 in Hungarian).
A thriving underground scene was marked by the start of Tilos R├Īdi├│
Tilos R├Īdi├│ is a community, non-profit, listener supported radio station in Budapest, Hungary. History
Tilos R├Īdi├│ was the first community radio station in Hungary, established as a pirate broadcaster in 1991. The station's programmers have ...
in 1991, the first free independent community station, starting out as a pirate radio
Pirate radio or a pirate radio station is a radio station that broadcasts without a valid license.
In some cases, radio stations are considered legal where the signal is transmitted, but illegal where the signals are received—especially ...
. The station soon developed strong ties with the first alternative electronic formations, and inspired to start many others. Bands like Korai ├¢r├Čm and M├Īsf├®l (also check Myster Mobius) started, playing ambient, psychedelic music. Anima Sound System, one of the most influential bands on the scene, was created in 1993 playing dub and trip-hop influenced by acid jazz and ethnic music. Several other bands and formations followed, like Colorstar and Neo
Neo or NEO may refer to:
Arts and entertainment Fictional entities
* Neo (''The Matrix''), the alias of Thomas Anderson, a hacker and the protagonist of the Matrix film series
* Neo (''Marvel Comics'' species), a fictional race of superhumans
* ...
. Neo has won a worldwide reputation for their unique electro-pop style and the "Mozart of pop music" award (Cannes, 2004) they received for their soundtrack album called "Control". Apart from Anima, ethnic and folk influenced the scene in many ways, exemplified by formations like Balkan Fanatik, or Mitsoura. One of the most successful Hungarian electronic musician is Yonderboi
L├Īszl├│ Fogarasi Jr. (born September 14, 1980), known by his stage name Yonderboi, is a Hungarian composer, music producer and visual artist. His debut album, Shallow and Profound, released in 2000, brought Eastern European music to the Wester ...
, who recently co-created ┼Įagar, gaining wide reputation in the country. In the past few years, dubstep
Dubstep is a genre of electronic dance music that originated in South London in the early 2000s. The style emerged as a UK garage offshoot that blended 2-step rhythms and sparse dub production, as well as incorporating elements of broken be ...
has gained popular attention as well, nationwide.
Experimental and minimal scene is in its early age, although several crews and DJs are working, organising numerous events. Notable performers include c0p, Cadik, Ferenc Vasp├Čeri and Isu.
Hip hop
Hip hop and rap have been developing in Hungary with two scenes, underground and mainstream, which is mostly popular among young people in Hungary. Underground rappers condemn the mainstream for "selling" their music and usually provide deeper message. Mainstream hip hop is dominated by the pioneer of Gangsta rap in Hungary, Ganxsta Zolee, and there are also other famous ones including FankaDeli, Sub Bass Monster, Dope Man, and LL Junior. Mainstream hip-hop is extremely popular among theRomani
Romani may refer to:
Ethnicities
* Romani people, an ethnic group of Northern Indian origin, living dispersed in Europe, the Americas and Asia
** Romani genocide, under Nazi rule
* Romani language, any of several Indo-Aryan languages of the Roma ...
youth.
B├½lga started as an offshoot hiphop project at Tilos R├Īdi├│
Tilos R├Īdi├│ is a community, non-profit, listener supported radio station in Budapest, Hungary. History
Tilos R├Īdi├│ was the first community radio station in Hungary, established as a pirate broadcaster in 1991. The station's programmers have ...
. As lyrical innovators and phenomenal parodists, they gained wide popularity for an extremely explicit criticism of Budapest
Budapest (, ; ) is the capital and most populous city of Hungary. It is the ninth-largest city in the European Union by population within city limits and the second-largest city on the Danube river; the city has an estimated population o ...
public transport company BKV, as well as hilarious wordplays and self-irony. Their lyrics are significant beyond the hip-hop scope as a cultural documentation of turn-of-the-millennia Culture of Hungary.
Hungarian Slam sessions are rare and few, and still a novelty for the mainstream, but are gaining popularity with literary performers, emcees and audiences alike.
Hardcore, metal
Despite being unknown among most Hungarian people, hardcore andmetal
A metal (from ancient Greek, Greek ╬╝╬ŁŽä╬▒╬╗╬╗╬┐╬Į ''m├®tallon'', "mine, quarry, metal") is a material that, when freshly prepared, polished, or fractured, shows a lustrous appearance, and conducts electrical resistivity and conductivity, e ...
are flourishing styles of music in Hungary. Metal bands are formed all over the country. Dominant styles are death metal
Death metal is an extreme subgenre of heavy metal music. It typically employs heavily distorted and low-tuned guitars, played with techniques such as palm muting and tremolo picking; deep growling vocals; aggressive, powerful drumming, fe ...
, black metal
Black metal is an extreme subgenre of heavy metal music. Common traits include fast tempos, a shrieking vocal style, heavily distorted guitars played with tremolo picking, raw (lo-fi) recording, unconventional song structures, and an em ...
and thrash
Thrash may refer to:
*Thrashing (computer science), where increasing resources are used to do a decreasing amount of work
*Thrash (surname)
* Thrash, mascot of the Atlanta Thrashers
*'' Thrash Rally'', a top-down perspective rally racing video gam ...
. There are also power metal
Power metal is a subgenre of heavy metal combining characteristics of traditional heavy metal with speed metal, often within symphonic context. Generally, power metal is characterized by a faster, lighter, and more uplifting sound, in contra ...
, folk metal
Folk metal is a fusion genre of heavy metal music and traditional folk music that developed in Europe during the 1990s. It is characterised by the widespread use of folk instruments and, to a lesser extent, traditional singing styles (for exam ...
and heavy metal groups, including Dalriada and Thy Catafalque.
Hardcore and metalcore
Metalcore (also known as metallic hardcore) is a fusion music genre that combines elements of extreme metal and hardcore punk. As with other styles blending metal and hardcore, such as crust punk and grindcore, metalcore is noted for its use ...
are most common in Budapest and Western Hungary, in towns like Győr
Gy┼ær ( , ; german: Raab, links=no; names in other languages) is the main city of northwest Hungary, the capital of Gy┼ær-Moson-Sopron County and Western Transdanubia region, and ŌĆō halfway between Budapest and Vienna ŌĆō situated on one of ...
, Csorna, Szombathely
Szombathely (; german: Steinamanger, ; see also other alternative names) is the 10th largest city in Hungary. It is the administrative centre of Vas county in the west of the country, located near the border with Austria. Szombathely lies by t ...
and Veszpr├®m, but Eastern Hungary and Debrecen
Debrecen ( , is Hungary's second-largest city, after Budapest, the regional centre of the Northern Great Plain region and the seat of Hajd├║-Bihar County. A city with county rights, it was the largest Hungarian city in the 18th century and ...
is getting into a more and more important place in the hardcore scene. The first Hungarian acts that tagged themselves Hardcore like AMD, Leuk├®mia, Marina revue emerged in the late 1980s, and were followed by a number of acts, constituting a scene that flourishes since the early 1990s. Notable bands were Dawncore and Newborn
An infant or baby is the very young offspring of human beings. ''Infant'' (from the Latin word ''infans'', meaning 'unable to speak' or 'speechless') is a formal or specialised synonym for the common term ''baby''. The terms may also be used to ...
of the late 1990s gaining also some international success. Members of these bands went on to form Bridge to Solace and The Idoru. Other important, active bands: Hold X True, Fallenintoashes, Embers, Suicide Pride, Subscribe, Road
A road is a linear way for the conveyance of traffic that mostly has an improved surface for use by vehicles (motorized and non-motorized) and pedestrians. Unlike streets, the main function of roads is transportation.
There are many types o ...
, Shell Beach, Hatred Solution, Blind Myself, Superbutt
Superbutt is a Hungarian rock and heavy metal band. The Budapest-based act started up in 2000, and has released five full-length albums in English, as well as a 4 track EP and a bonus disc for their latest album with 4 new songs in Hungarian. S ...
, Stillborn (Hatebreed tribute). An internationally known band is Ektomorf
Ektomorf is a heavy metal band from Hungary.
Biography
Ektomorf was founded in 1993 in Mez┼ækov├Īcsh├Īza, Hungary, a small city near the Romanian border, by Zolt├Īn "Zoli/Zotya" Farkas. In the actual line-up Zoli/Zotya ŌĆō songwriter and l ...
, infusing heavy ethnic content with harsh vocals, One of North America's most popular metal band with record sales over two million albums; Five Finger Death Punch
Five Finger Death Punch, also abbreviated as 5FDP or FFDP, is an American heavy metal band from Las Vegas, Nevada, formed in 2005. The band originally consisted of vocalist and keyboardist Ivan Moody, rhythm guitarist Zoltan Bathory, lead g ...
was formed by the Hungarian born, Golden God Shredder Award winning guitarist Zoltan Bathory
Zoltan Bathory (born in 1978) is a Hungarian-American musician and martial artist. He is the founder and rhythm guitarist of Las Vegas-based heavy metal band Five Finger Death Punch. In 2010, he was named Golden God's "Best Shredder" by ''Meta ...
Extreme hardcorepunk and grindcore bands from Hungary include Jack (crustgrind), Human Error(crustcore), Step On It (allschool hardcore), Another Way (fastcore), Gyal├Īzat (crustpunk).
Indie
The origins of the Hungarian indie music scene go back to the early 1980s when Eur├│pa Kiad├│, Sziami and Balaton released their records. The first revival took place in the mid-1990s when bands like Sexepil gained international success, followed by Heaven Street Seven. The second and most notable revival of the indie-alternative scene took place in the mid-2000s when bands like Amber Smith,The Moog
The Moog were a Hungarian indie rock band based in Budapest, Hungary formed in 2004. The group is noted for being the first in the region to be signed to an American record label. The band consists of members Tam├Īs Szab├│ (vocals, keyboard), ...
signed to international labels. Other notable bands include EZ Basic
EZ Basic is a guitar-pop, indie-rock project based in Budapest, Hungary formed in 2004. It started out as an experimental bedroom project in the early 00s and is noted for being one of the most eclectic bands of the Budapest indie music scene.
Hi ...
, The KOLIN
The KOLIN are a Hungarian indie-pop band best known for their hit song ''San Francisco''. The band was formed in 2007 in Budapest. Their music style is synthpop influenced with indie rock and new rave sounds. The band consists of M├Īrk├│ Lincz├®ny ...
and Dawnstar
Dawnstar is a superheroine appearing in comic books published by DC Comics, primarily as a member of the Legion of Super-Heroes in the 30th and 31st centuries. She was created by Paul Levitz and Mike Grell, and first appeared in ''Superboy and ...
. The Hungarian indie scene is closely intertwined with electronic music therefore artists like Yonderboi
L├Īszl├│ Fogarasi Jr. (born September 14, 1980), known by his stage name Yonderboi, is a Hungarian composer, music producer and visual artist. His debut album, Shallow and Profound, released in 2000, brought Eastern European music to the Wester ...
and ┼Įagar are often considered part of the indie scene.
The Hungarian indie music has its special, Hungarian languaged line. It is based rather on 1980s bands like Eur├│pa Kiad├│ or Neurotic. The most notable bands and artists are Kisp├Īl ├®s a borz (the lead singer and songwriter Andr├Īs Lovasi was honored by the Kossuth Prize
The Kossuth Prize ( hu, Kossuth-d├Łj) is a state-sponsored award in Hungary, named after the Hungarian politician and revolutionist Lajos Kossuth. The Prize was established in 1948 (on occasion of the centenary of the March 15th revolution, the ...
), Hiperkarma ( R├│bert B├®rczesi made alone the first album), and Quimby (most notable member is Tibor Kiss).
Punk
The origins of the Hungarian punk movement go back to the early eighties, when a handful of bands like ''ETA'', ''QSS'', ''CPG'', and ''Aur├│ra'' emerged as angry young men playing fast and raw punk rock music. Like many other musicians of their age, they often criticised the communist government. They were a part of the national movement to reject the oppressiveness, and particularly the censorship, of the communist regime. As their music was on the verge of acceptance both by the public and the authorities, concerts were held under tight police control, and often caused moral outrage. With band members often living under constant surveillance, prison was a serious possibility. Two members of the band ''CPG'' were found guilty and sent to prison for two years for allegedly unmoral lyrics. After their release, they had to leave Hungary, as did ''Aur├│ra''ŌĆÖs lead singer. The change of regime in 1989 brought a new situation, and bands now revolted against corruption and the Americanisation of the country. They felt that the new system retained the bad things from the previous one, but lacked that good things that many expected. In lyrics, they often mention the newly appearing organised crime, and the still low standard of living. Today the Hungarian punk scene is low profile, but vibrant with several active bands, often touring the country and beyond. Summer brings a slew of punk and alternative festivals where they can all be sampled. Top venues playing punk music around Budapest include V├Čr├Čs Yuk, Borg├Čd├Čr, ''Music Factory'' and A38 Haj├│. Major bands include Aur├│ra, the oldest Hungarian punk band with twenty-five years of history, come from the northwest Hungarian town ofGy┼ær
Gy┼ær ( , ; german: Raab, links=no; names in other languages) is the main city of northwest Hungary, the capital of Gy┼ær-Moson-Sopron County and Western Transdanubia region, and ŌĆō halfway between Budapest and Vienna ŌĆō situated on one of ...
and their originally street punk music has been recently updated with a ska-punk flavor, H├®tk├ČznaPI CSAl├│d├Īsok (also called PICSA), a simplistic but powerful punk band, most popular in the end of the 1990s. They, similarly to ''Junkies'', ''F├╝rger├│kal├Ībak'', and ''Prosectura'', are part of the new wave of punk bands that had risen in the mid-late 1990s in Hungary. Out of the newer bands, two northeast Hungarian bands are the most known, both playing California punk: Alvin ├®s a m├│kusok come from Ny├Łregyh├Īza
Ny├Łregyh├Īza (, sk, N├Łre─Åh├Īza) is a city with county rights in northeastern Hungary and the county capital of Szabolcs-Szatm├Īr-Bereg. With a population of 118,001, it is the seventh-largest city in Hungary and the second largest in ...
, while Macskanadr├Īg are from Salg├│tarj├Īn
Salg├│tarj├Īn (; sk, ┼Āalgotarj├Īn) is city with county rights in Hungary, the capital of N├│gr├Īd county, north-eastern Hungary, making it the third smallest county capital based on population. The nearby Salg├│ castle is a well-known tourist ...
.
Festivals, venues and other institutions
Folk and classical music
Budapest
Budapest (, ; ) is the capital and most populous city of Hungary. It is the ninth-largest city in the European Union by population within city limits and the second-largest city on the Danube river; the city has an estimated population o ...
, the capital and music centre of Hungary, is one of the best places to go in Hungary to hear "really good folk music", says world music author Simon Broughton. The city is home to an annual folk festival called T├Īnch├Īztal├Īlkoz├│ ("Meeting of the T├Īnch├Īzak", literally "dance houses"), which is a major part of the modern music scene. The Budapest Spring Festival along with the Budapest Autumn Festival
Budapest (, ; ) is the capital and most populous city of Hungary. It is the ninth-largest city in the European Union by population within city limits and the second-largest city on the Danube river; the city has an estimated population of ...
are large scale cultural events every year. The Budapesti Fesztiv├Īl Zenekar (Budapest Festival Orchestra) has recently been awarded the Editor's Choice Gramophone Award
The Gramophone Classical Music Awards, launched in 1977, are one of the most significant honours bestowed on recordings in the classical record industry. They are often viewed as equivalent to or surpassing the American Grammy award, and refe ...
. Long-standing venues in Budapest include the Philharmonic Society (founded 1853), the Opera House of Budapest (founded 1884) the Academy of Music, which opened in 1875 with President Franz Liszt and Director Ferenc Erkel and which has remained the centre for music education in the country since.
Popular music festivals
 Several musical festivals have been launched since the early 1990s propelled by increasing demand of the developing youth culture. Aside from country-wide events like
Several musical festivals have been launched since the early 1990s propelled by increasing demand of the developing youth culture. Aside from country-wide events like Sziget Festival
The Sziget Festival ( hu, Sziget Fesztiv├Īl, ; "Sziget" for "Island") is one of the largest music and cultural festivals in Europe. It is held every August in northern Budapest, Hungary, on ├ōbudai-sziget ("Old Buda Island"), a leafy 108-hect ...
or Hegyalja Festival, local festivals started to emerge since the first half of the first decade of the new millennium, with the aim to showcase known bands in all regions of Hungary.
Growing out of a low-profile student meeting in 1993, Sziget Festival became one of the largest open-air festival in the world, taking place each summer in the heart of Budapest, the 108 hectare ├ōbudai island. Visited by hundreds of thousands from all over Europe, it is the largest cultural event in Hungary, inviting world-class performers from all genres.
Also having a history from 1993, VOLT Festival is the second-largest music festival in the country, held each year in Sopron
Sopron (; german: ├¢denburg, ; sl, ┼Āopron) is a city in Hungary on the Austrian border, near Lake Neusiedl/Lake Fert┼æ.
History
Ancient times-13th century
When the area that is today Western Hungary was a province of the Roman Empire, a ...
. With a colorful mix of musical styles, and popularity increasing each year, is considered to be the "cheaper version" of Sziget. Also founded by the Sziget management, Balaton Sound is a festival of mainly electronic music, held yearly in Zam├Īrdi
, timezone = CET
, utc_offset = +1
, timezone_DST = CEST
, utc_offset_DST = +2
, subdivision_type = Country
, subdivision_name =
, subdivision_type1 = County
, subdivision_nam ...
, next to Lake Balaton
Lake Balaton () is a freshwater lake in the Transdanubian region of Hungary. It is the largest lake in Central Europe, and one of the region's foremost tourist destinations. The Zala River provides the largest inflow of water to the lake, and ...
. With prestigious performers and exclusive surroundings, it tries to position itself as a high-standard event.
Hegyalja Festival, held in Tokaj
Tokaj () is a historical town in Borsod-Aba├║j-Zempl├®n county, Northern Hungary, 54 kilometers from county capital Miskolc. It is the centre of the Tokaj-Hegyalja wine district where Tokaji wine is produced.
History
The wine-growing are ...
, the historic wine-region of the country, is the largest such event in the Northern part. Visited by 50.000 guests each year, it showcases mainly hard rock and rock formations, but many more genres are present. BalaTone, another major event near lake Balaton is held in Z├Īnka. Magyar Sziget, held in Ver┼æce, has a nationalist theme, with mainly right-wing performers, bands representing the recently emerged nationalistic rock, folk and folk-rock.
As a tradition, each larger University (or more precisely, its students' union
A students' union, also known by many other names, is a student organization present in many colleges, universities, and high schools. In higher education, the students' union is often accorded its own building on the campus, dedicated to ...
) holds a periodical music festival, "University Days", of various size, the largest one is PEN (of the University of P├®cs
The University of P├®cs (UP; Hungarian language, Hungarian: ''P├®csi Tudom├Īnyegyetem''; PTE) is an institution of higher education in Hungary. The modern university was established in 1912 but has its roots in the medieval university founded ...
). Examples of smaller, local festivals are SZIN held in Szeged
Szeged ( , ; see also other alternative names) is the third largest city of Hungary, the largest city and regional centre of the Southern Great Plain and the county seat of Csongr├Īd-Csan├Īd county. The University of Szeged is one of the m ...
, the free Utcazene Fesztiv├Īl held on the streets of Veszpr├®m, Pann├│nia Fesztiv├Īl in V├Īrpalota
V├Īrpalota (; German: Burgschlo├¤) is a town in Western Hungary, in the Transdanubian county of Veszpr├®m. It was a mining town during the Socialist era, but the mines have been closed. Most of the citizens work in the nearby cities, Veszpr├®m or ...
, or the recently (2008) started Fishing on Orf┼▒, held on the beach of the Orf┼▒ lake.
Funding
The HungarianMinistry of Culture Ministry of Culture may refer to:
*Ministry of Tourism, Cultural Affairs, Youth and Sports (Albania)
* Ministry of Culture (Algeria)
*Ministry of Culture (Argentina)
*Minister for the Arts (Australia)
*Ministry of Culture (Azerbaijan)
* Ministry of ...
helps to fund some forms of music, as does the government-run National Cultural Fund. Non-profit organisations in Hungary include the Hungarian Jazz Alliance and the Hungarian Music Council.
See also
* Kontra *Hungary in the Eurovision Song Contest
Hungary has participated in the Eurovision Song Contest 17 times since making its debut in . Hungary attempted to participate in but failed to qualify from ''Kvalifikacija za Millstreet'', a special qualifying competition set up for seven form ...
References
* * * * * * * * * * * * *Notes
Further reading
* * * * * * *External links
*Audio clips: Traditional music of Hungary.
Mus├®e d'ethnographie de Gen├©ve
The ' ("Geneva Ethnography Museum") is one of the most important ethnographic museums in Switzerland.
History
The MEG, or Geneva Museum of Ethnography, was founded on 25 September 1901, on the initiative of Professor Eug├©ne Pittard (1867-1962), ...
. Accessed November 25, 2010.Hungarian music
summarized at the administrative website of Hungary
Hungarian Folk Music Collection
N├®pdalok and Magyar N├│ta (5000 melodies).
:Urban Hungarian music or Magyar N├│ta
YouTube playlists {{Music of Europe Central European music