Mount Fuji sign on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Pneumocephalus is the presence of air or gas within the

cranial cavity
The cranial cavity, also known as intracranial space, is the space within the skull that accommodates the brain. The skull minus the mandible is called the ''cranium''. The cavity is formed by eight cranial bones known as the neurocranium that in ...
. It is usually associated with disruption of the skull
The skull is a bone protective cavity for the brain. The skull is composed of four types of bone i.e., cranial bones, facial bones, ear ossicles and hyoid bone. However two parts are more prominent: the cranium and the mandible. In humans, the ...
: after head
A head is the part of an organism which usually includes the ears, brain, forehead, cheeks, chin, eyes, nose, and mouth, each of which aid in various sensory functions such as sight, hearing, smell, and taste. Some very simple animals may ...
and facial trauma
Facial trauma, also called maxillofacial trauma, is any physical trauma to the face. Facial trauma can involve soft tissue injuries such as burns, lacerations and bruises, or fractures of the facial bones such as nasal fractures and fractures ...
, tumors of the skull base, after neurosurgery
Neurosurgery or neurological surgery, known in common parlance as brain surgery, is the medical specialty concerned with the surgical treatment of disorders which affect any portion of the nervous system including the brain, spinal cord and peri ...
or otorhinolaryngology
Otorhinolaryngology ( , abbreviated ORL and also known as otolaryngology, otolaryngology–head and neck surgery (ORL–H&N or OHNS), or ear, nose, and throat (ENT)) is a surgical subspeciality within medicine that deals with the surgical a ...
, and rarely, spontaneously. Pneumocephalus can occur in scuba diving, but is very rare in this context.
If there is a valve mechanism which allows air to enter the skull but prevents it from escaping, a tension pneumocephalus can occur (similar to what can happen in a tension pneumothorax
A pneumothorax is an abnormal collection of air in the pleural space between the lung and the chest wall. Symptoms typically include sudden onset of sharp, one-sided chest pain and shortness of breath. In a minority of cases, a one-way valve is ...
).
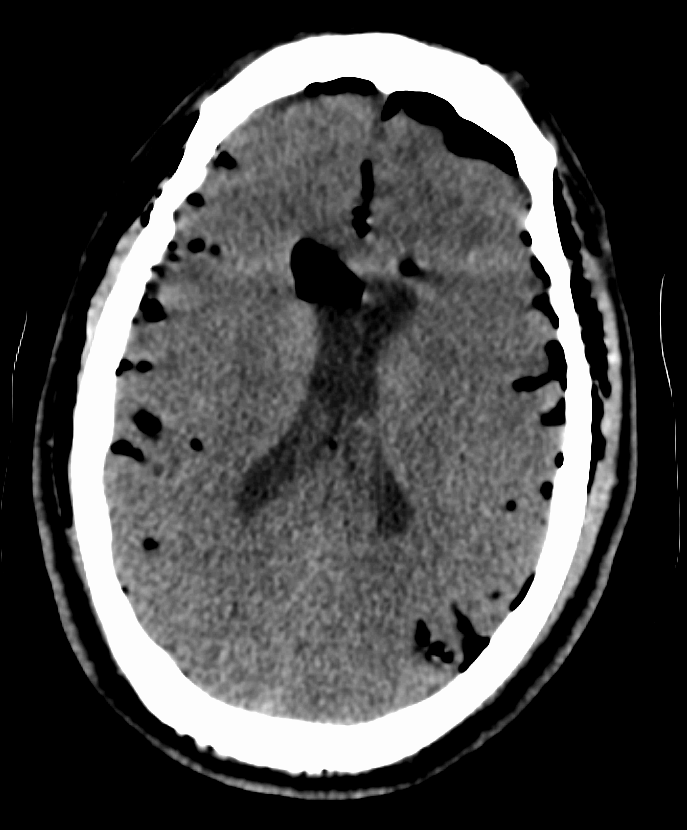
CT scan
A computed tomography scan (CT scan; formerly called computed axial tomography scan or CAT scan) is a medical imaging technique used to obtain detailed internal images of the body. The personnel that perform CT scans are called radiographers ...
s of patients with a tension pneumocephalus typically show air that compresses the frontal lobes of the brain, which results in a tented appearance of the brain in the skull known as the Mount Fuji sign.
The name is derived from the resemblance of the brain to Mount Fuji
, or Fugaku, located on the island of Honshū, is the highest mountain in Japan, with a summit elevation of . It is the second-highest volcano located on an island in Asia (after Mount Kerinci on the island of Sumatra), and seventh-highest p ...
in Japan
Japan ( ja, 日本, or , and formally , ''Nihonkoku'') is an island country in East Asia. It is situated in the northwest Pacific Ocean, and is bordered on the west by the Sea of Japan, while extending from the Sea of Okhotsk in the north ...
, a volcano known for its symmetrical cone. In typical cases, there is a symmetrical depression near the midline (such as the crater of a volcano), due to intact bridging veins Bridging veins are veins in the subarachnoid space that puncture the dura mater and empty into the dural venous sinuses. A rupture of a bridging vein causes a subdural hematoma
A subdural hematoma (SDH) is a type of bleeding in which a Hematoma, ...
. Its occurrence seems to be limited to tension pneumocephalus (not occurring in pneumocephalus without tension). The sign was first described by a team of Japanese neurosurgeons.
Pneumocephalus has also been shown to follow neurosurgical procedures such as deep brain stimulation and hematoma evacuation (e.g., chronic subdural hematoma), where while seemingly innocuous to the patient, may cause brain shift, subsequent stereotactic inaccuracy, and even another surgical intervention. Regarding chronic subdural hematoma (CSDH) surgery, a postoperative volume of pneumocephalus greater than 15mL puts a patient at increased risk of CSDH recurrence; in fact, for every milliliter of air entering the cranial cavity after CSDH evacuation, the recurrence risk increases by 4%. Efforts are made by neurosurgeons to reduce pneumocephalus volume during surgery, and thus, subsequent brain shift.
Additional images


Footnotes
External links
Neurological disorders {{Med-sign-stub