Mond Crucifixion on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
The ''Mond Crucifixion'' or ''Gavari Altarpiece'' is an oil on poplar panel dated to 1502–1503, making it one of the earliest works by Italian Renaissance artist
 The painting was influenced by
The painting was influenced by
File:Rafael - Milagre de Santo Eusébio de Cremona-1.jpg, ''Eusebius of Cremona raising Three Men from the Dead with Saint Jerome's Cloak'',
Raphael, The Mond Crucifixion
ColourLex
''The Mond Crucifixion'', Raphael
National Gallery, London * Henry, Tom
"Raphael's Altar-Piece Patrons in Città Di Castello"
''The Burlington Magazine'', vol. 144, no. 1190, 2002, pp. 268–278
Raphael
Raffaello Sanzio da Urbino, better known as Raphael (; or ; March 28 or April 6, 1483April 6, 1520), was an Italian painter and architect of the High Renaissance. His work is admired for its clarity of form, ease of composition, and visual a ...
, perhaps the second after the c.1499-1500 Baronci Altarpiece. It originally comprised four elements, of which three survive, now all separated: a main panel of the ''Crucified Christ with the Virgin Mary, Saints and Angels'' which was bequeathed to the National Gallery, London, by Ludwig Mond
Ludwig Mond FRS (7 March 1839 – 11 December 1909) was a German-born, British chemist and industrialist. He discovered an important, previously unknown, class of compounds called metal carbonyls.
Education and career
Ludwig Mond was born ...
, and a three-panel predella
In art a predella (plural predelle) is the lowest part of an altarpiece, sometimes forming a platform or step, and the painting or sculpture along it, at the bottom of an altarpiece, sometimes with a single much larger main scene above, but oft ...
from which one panel is lost; the two surviving panels are ''Eusebius of Cremona raising Three Men from the Dead with Saint Jerome's Cloak'' in the Museu Nacional de Arte Antiga
The Museu Nacional de Arte Antiga (; MNAA), also known in English as the National Museum of Ancient Art, is a Portuguese national art museum located in Lisbon. With over 40,000 items spanning a vast collection of painting, sculpture, goldware, fu ...
, in Lisbon, and ''Saint Jerome saving Silvanus and punishing the Heretic Sabinianus'' in the North Carolina Museum of Art
The North Carolina Museum of Art (NCMA) is an art museum in Raleigh, North Carolina. It opened in 1956 as the first major museum collection in the country to be formed by state legislation and funding. Since the initial 1947 appropriation that e ...
.
Background
This early work by Raphael was commissioned by the wool merchant Domenico Gavari as the altarpiece for his burial chapel in the south aisle of the church of San Domenico inCittà di Castello
Città di Castello (); "Castle Town") is a city and ''comune'' in the province of Perugia, in the northern part of Umbria. It is situated on a slope of the Apennines, on the flood plain along the upper part of the river Tiber. The city is north of ...
, in Umbria
it, Umbro (man) it, Umbra (woman)
, population_note =
, population_blank1_title =
, population_blank1 =
, demographics_type1 =
, demographics1_footnotes =
, demographics1_title1 =
, demographics1_info1 =
, ...
, near Raphael's home town of Urbino
Urbino ( ; ; Romagnol: ''Urbìn'') is a walled city in the Marche region of Italy, south-west of Pesaro, a World Heritage Site notable for a remarkable historical legacy of independent Renaissance culture, especially under the patronage of F ...
. The side chapel
A chapel is a Christian place of prayer and worship that is usually relatively small. The term has several meanings. Firstly, smaller spaces inside a church that have their own altar are often called chapels; the Lady chapel is a common type ...
was dedicated to Saint Jerome
Jerome (; la, Eusebius Sophronius Hieronymus; grc-gre, Εὐσέβιος Σωφρόνιος Ἱερώνυμος; – 30 September 420), also known as Jerome of Stridon, was a Christian priest, confessor, theologian, and historian; he is co ...
, where most of the painting's original ''pietra serena
Pietra serena is a blue-gray sandstone used extensively in Renaissance Florence for architectural details. It is also known as Macigno stone. The material obtained at Fiesole is considered the best and is also quarried at Arezzo, Cortona, and Volt ...
'' stone frame survives including the inscribed date 1503. Gavari was an associate of Andrea Baronci, for whom Raphael had already made the Baronci Altarpiece. Gavari's first son Girolamo (Jerome) died young.
Main panel
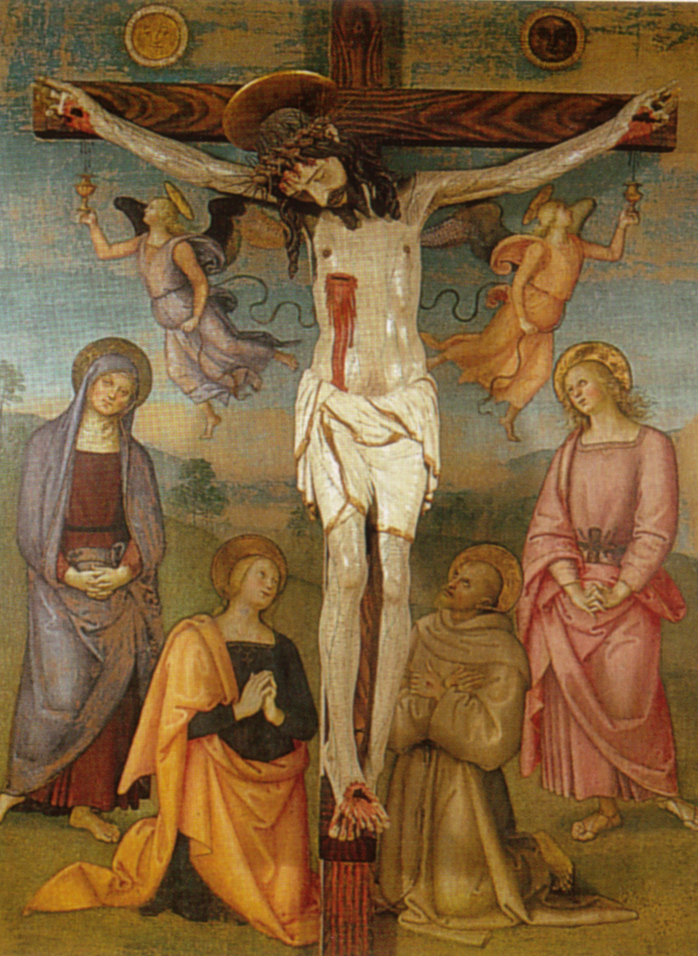
The main panel portrays theCrucifixion of Jesus
The crucifixion and death of Jesus occurred in 1st-century Judea, most likely in AD 30 or AD 33. It is described in the four canonical gospels, referred to in the New Testament epistles, attested to by other ancient sources, and consid ...
, against a background of hills in the Umbrian countryside, with a view of Città di Castello in the distance. Jesus
Jesus, likely from he, יֵשׁוּעַ, translit=Yēšūaʿ, label= Hebrew/ Aramaic ( AD 30 or 33), also referred to as Jesus Christ or Jesus of Nazareth (among other names and titles), was a first-century Jewish preacher and religiou ...
looks peaceful even as he is dying on the cross, crowned with thorns and clad only in a loincloth that has an unusual red colour. Above, a sun in gold leaf and moon in silver leaf appear together in the sky. Two angels with flowing robes and scrolling ribbons at their waists, one floating to either side of the cross, are using gold chalices similar to communion vessels to catch the blood dripping from Jesus' nail-pierced hands and spurting from the wound in his side. To the proper right (Jesus' left) kneels Mary Magdalene, with John the Evangelist
John the Evangelist ( grc-gre, Ἰωάννης, Iōánnēs; Aramaic: ܝܘܚܢܢ; Ge'ez: ዮሐንስ; ar, يوحنا الإنجيلي, la, Ioannes, he, יוחנן cop, ⲓⲱⲁⲛⲛⲏⲥ or ⲓⲱ̅ⲁ) is the name traditionally given ...
standing behind her. To the proper left (Jesus' right) his mother Mary
Mary may refer to:
People
* Mary (name), a feminine given name (includes a list of people with the name)
Religious contexts
* New Testament people named Mary, overview article linking to many of those below
* Mary, mother of Jesus, also calle ...
stands behind the kneeling Saint Jerome
Jerome (; la, Eusebius Sophronius Hieronymus; grc-gre, Εὐσέβιος Σωφρόνιος Ἱερώνυμος; – 30 September 420), also known as Jerome of Stridon, was a Christian priest, confessor, theologian, and historian; he is co ...
, who is holding a stone with which the hermit would piously beat his own chest.
The two kneeling figures are both reverently contemplating Jesus on the cross, while the two standing figures are wringing their hands while looking out at the viewer. A panel at the top of the cross bears the inscription "INRI
In the New Testament, Jesus is referred to as the King of the Jews, both at the beginning of his life and at the end. In the Koine Greek of the New Testament, e.g., in John 19:3, this is written as '' Basileus ton Ioudaion'' ().
Both uses of t ...
", while the foot of the cross bears a Latin inscription in silver letters: "RAPHAEL/ VRBIN / AS /.P. NXIT/small>" ("Raphael of Urbino painted this"). The work is lit from the left, consistent with the illumination of the altarpiece by the windows in the chapel.
The main panel measures and is now housed in a 19th-century frame. The geometrical precision of the composition suggest it was laid out using a grid, using a rule and compasses to copy from a preparatory drawings.
A drawing of a kneeling person, perhaps a study for the figure of Mary Magdalene, is held by the Ashmolean Museum in Oxford.
 The painting was influenced by
The painting was influenced by Perugino
Pietro Perugino (, ; – 1523), born Pietro Vannucci, was an Italian Renaissance painter of the Umbrian school, who developed some of the qualities that found classic expression in the High Renaissance. Raphael was his most famous pupil.
Ea ...
, whom Raphael knew while living in Perugia
Perugia (, , ; lat, Perusia) is the capital city of Umbria in central Italy, crossed by the River Tiber, and of the province of Perugia.
The city is located about north of Rome and southeast of Florence. It covers a high hilltop and pa ...
. It is similar to Perugino's c.1502 Monteripido Altarpiece, made the convent of San Francesco al Monte at Monteripido near Perugia, a similar crucifixion scene which has two similar angels with ribbons catching the blood of Jesus is chalices, accompanied by four figures, two standing and two kneeling, including the Virgin Mary, John the Evangelist, and Mary Magdalene, but the fourth is Francis of Assisi rather than Saint Jerome. In the Mond Crucifixion, Raphael has used Perugino's technique of cross-hatched shadows, but also used his fingers to smear and soften the wet paint in places, leaving some detectable fingerprints. Vasari
Giorgio Vasari (, also , ; 30 July 1511 – 27 June 1574) was an Italian Renaissance Master, who worked as a painter, architect, engineer, writer, and historian, who is best known for his work '' The Lives of the Most Excellent Painters, Sculp ...
later famously commented that no one would have believed it was painted by Raphael rather than Perugino if he had not signed it.
Predella
The two surviving panels of the predella each measure approximately and depict miracles from the life story of Saint Jerome from the ''Hierominianum'' ofGiovanni d'Andrea
Giovanni d'Andrea or Johannes Andreæ (1270 1275 – 1348) was an Italian expert in canon law, the most renowned and successful canonist of the later Middle Ages. His contemporaries referred to him as ''iuris canonici fons et ...
. Saint Jerome lived in the late 4th and early 5th century AD, so he could not have attended the crucifixion, but he is portrayed here as the patron saint of the chapel.
One of the surviving predella panels has been in the Museu Nacional de Arte Antiga
The Museu Nacional de Arte Antiga (; MNAA), also known in English as the National Museum of Ancient Art, is a Portuguese national art museum located in Lisbon. With over 40,000 items spanning a vast collection of painting, sculpture, goldware, fu ...
in Lisbon since 1866. It depicts ''Eusebius of Cremona raising Three Men from the Dead with Saint Jerome's Cloak''
Eusebius of Cremona Eusebius of Cremona was a 5th-century monk, pre-congregational saint, and disciple of Jerome.
Life
He was born in Cremona, Italy. As a young man he travelled to Rome where he became an associate of Jerome, who was a secretary for Pope Damascus. ...
was a close associate and active supporter of Jerome against the teachings of Origen
Origen of Alexandria, ''Ōrigénēs''; Origen's Greek name ''Ōrigénēs'' () probably means "child of Horus" (from , "Horus", and , "born"). ( 185 – 253), also known as Origen Adamantius, was an early Christian scholar, ascetic, and theo ...
.
The other surviving predella panel is in the North Carolina Museum of Art
The North Carolina Museum of Art (NCMA) is an art museum in Raleigh, North Carolina. It opened in 1956 as the first major museum collection in the country to be formed by state legislation and funding. Since the initial 1947 appropriation that e ...
in Raleigh, North Carolina
Raleigh (; ) is the capital city of the state of North Carolina and the seat of Wake County in the United States. It is the second-most populous city in North Carolina, after Charlotte. Raleigh is the tenth-most populous city in the Southe ...
. It depicts ''Saint Jerome saving Silvanus and punishing the Heretic Sabinianus''. Saint Jerome is holding back the arm of the executioner ready to behead bishop Silvanus, but the heretic Sabinianus has been miraculously decapitated instead.
Museu Nacional de Arte Antiga
The Museu Nacional de Arte Antiga (; MNAA), also known in English as the National Museum of Ancient Art, is a Portuguese national art museum located in Lisbon. With over 40,000 items spanning a vast collection of painting, sculpture, goldware, fu ...
, Lisbon
File:Raffaello Sanzio - St. Jerome Punishing the Heretic Sabinian.jpg, ''Saint Jerome saving Silvanus and punishing the Heretic Sabinianus'', North Carolina Museum of Art
The North Carolina Museum of Art (NCMA) is an art museum in Raleigh, North Carolina. It opened in 1956 as the first major museum collection in the country to be formed by state legislation and funding. Since the initial 1947 appropriation that e ...
, Raleigh, North Carolina
Raleigh (; ) is the capital city of the state of North Carolina and the seat of Wake County in the United States. It is the second-most populous city in North Carolina, after Charlotte. Raleigh is the tenth-most populous city in the Southe ...
Provenance
The main panel was bought by Cardinal Fesch in 1808 for 2500scudi
The ''scudo'' (pl. ''scudi'') was the name for a number of coins used in various states in the Italian peninsula until the 19th century. The name, like that of the French écu and the Spanish and Portuguese escudo, was derived from the Latin ''s ...
, and replaced in the chapel by a copy. At the Fesch sale in 1845, it was sold to the Principe di Canino, and quickly bought by Lord Ward
Lord is an appellation for a person or deity who has authority, control, or power over others, acting as a master, chief, or ruler. The appellation can also denote certain persons who hold a title of the peerage in the United Kingdom, or a ...
(later Earl of Dudley
Earl of Dudley, of Dudley Castle in the County of Stafford (now the West Midlands), is a title that has been created twice in the Peerage of the United Kingdom, both times for members of the Ward family.
History
Dudley was first used for a p ...
). It was then in several English collections, and eventually acquired by Ludwig Mond
Ludwig Mond FRS (7 March 1839 – 11 December 1909) was a German-born, British chemist and industrialist. He discovered an important, previously unknown, class of compounds called metal carbonyls.
Education and career
Ludwig Mond was born ...
in 1892, after whose death in 1909 it was acquired by the National Gallery in 1924.
The predella panels seem to have been removed in the 17th century, and given as gifts to a visiting cardinal. The panel in North Carolina was formerly in the collection of Sir Francis Cook at Doughty House, Richmond, London
Richmond is a town in south-west London,The London Government Act 1963 (c.33) (as amended) categorises the London Borough of Richmond upon Thames as an Outer London borough. Although it is on both sides of the River Thames, the Boundary Commis ...
.
Painting materials
The main panel was analyzed in the National Gallery London and the typicalpigments
A pigment is a colored material that is completely or nearly insoluble in water. In contrast, dyes are typically soluble, at least at some stage in their use. Generally dyes are often organic compounds whereas pigments are often inorganic compoun ...
of the Renaissance
The Renaissance ( , ) , from , with the same meanings. is a period in European history
The history of Europe is traditionally divided into four time periods: prehistoric Europe (prior to about 800 BC), classical antiquity (800 BC to AD ...
period were identified. He painted the Crucifixion among other pigments with natural ultramarine
Ultramarine is a deep blue color pigment which was originally made by grinding lapis lazuli into a powder. The name comes from the Latin ''ultramarinus'', literally 'beyond the sea', because the pigment was imported into Europe from mines in Afg ...
, lead-tin-yellow
Lead-tin-yellow is a yellow pigment, of historical importance in oil painting, sometimes called the "Yellow of the Old Masters" because of the frequency with which it was used by those famous painters.
Nomenclature
The name lead-tin yellow ...
, verdigris
Verdigris is the common name for blue-green, copper-based pigments that form a patina on copper, bronze, and brass. The technical literature is ambiguous as to its chemical composition. Some sources refer to "neutral verdigris" as copper(II) ...
, vermilion
Vermilion (sometimes vermillion) is a color, color family, and pigment most often made, since antiquity until the 19th century, from the powdered mineral cinnabar (a form of mercury sulfide, which is toxic) and its corresponding color. It i ...
and ochres
Ochre ( ; , ), or ocher in American English, is a natural clay earth pigment, a mixture of ferric oxide and varying amounts of clay and sand. It ranges in colour from yellow to deep orange or brown. It is also the name of the colours produced ...
.ColourLex
See also
*List of paintings by Raphael
The following is a list of paintings by Italian Renaissance painter Raphael. Together with Michelangelo and Leonardo da Vinci he forms the traditional trinity of great masters of that period. He was enormously prolific, despite his early death at ...
References
Sources
''The Mond Crucifixion'', Raphael
National Gallery, London * Henry, Tom
"Raphael's Altar-Piece Patrons in Città Di Castello"
''The Burlington Magazine'', vol. 144, no. 1190, 2002, pp. 268–278
External links
* {{Raphael Collections of the National Gallery, London Paintings by Raphael Paintings depicting the Crucifixion of JesusRaphael
Raffaello Sanzio da Urbino, better known as Raphael (; or ; March 28 or April 6, 1483April 6, 1520), was an Italian painter and architect of the High Renaissance. His work is admired for its clarity of form, ease of composition, and visual a ...
Raphael
Raffaello Sanzio da Urbino, better known as Raphael (; or ; March 28 or April 6, 1483April 6, 1520), was an Italian painter and architect of the High Renaissance. His work is admired for its clarity of form, ease of composition, and visual a ...
Angels in art
Raphael
Raffaello Sanzio da Urbino, better known as Raphael (; or ; March 28 or April 6, 1483April 6, 1520), was an Italian painter and architect of the High Renaissance. His work is admired for its clarity of form, ease of composition, and visual a ...
Altarpieces
Paintings in the collection of the National Museum of Ancient Art
Paintings in the collection of the North Carolina Museum of Art