Military of Ecuador on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
The Ecuadorian Armed Forces ( es, Fuerzas Armadas del Ecuador) is the national military force of
 The command is in charge of the administration and coordination of the four
The command is in charge of the administration and coordination of the four
 The Ecuadorian Army (''Ejército Ecuatoriano'') is the land component of the
The Ecuadorian Army (''Ejército Ecuatoriano'') is the land component of the
 The present day Ecuadorian Air Force (''Fuerza Aérea Ecuatoriana'') saw combat-action several times in 1981 and 1995 when it gained valuable experiences against the
The present day Ecuadorian Air Force (''Fuerza Aérea Ecuatoriana'') saw combat-action several times in 1981 and 1995 when it gained valuable experiences against the
 The present day Ecuadorian Navy or (''Armada del Ecuador'') is a compact, efficient and well-balanced force. However, limited funds hinder any major acquisitions and the chances of maintaining a strong force within the
The present day Ecuadorian Navy or (''Armada del Ecuador'') is a compact, efficient and well-balanced force. However, limited funds hinder any major acquisitions and the chances of maintaining a strong force within the
Official site of the Ministry of Defence
Official site of the National Security Council
Official site of the Ecuadorian Army
Official site of the Ecuadorian Air Force
Official site of the Ecuadorian Navy
Official Ecuadorian Coast Guard site
Official site of the Ecuadorian Marines
{{DEFAULTSORT:Military Of Ecuador Ecuadorian Armed Forces
Ecuador
Ecuador ( ; ; Quechua: ''Ikwayur''; Shuar: ''Ecuador'' or ''Ekuatur''), officially the Republic of Ecuador ( es, República del Ecuador, which literally translates as "Republic of the Equator"; Quechua: ''Ikwadur Ripuwlika''; Shuar: ' ...
. The commander-in-chief is the President of Ecuador
The president of Ecuador ( es, Presidente del Ecuador), officially called the Constitutional President of the Republic of Ecuador ( es, Presidente Constitucional de la República del Ecuador), serves as both the head of state and head of govern ...
, currently Guillermo Lasso
Guillermo Alberto Santiago Lasso Mendoza (; born 16 November 1955) is an Ecuadorian businessman, banker, writer and politician who has served as the 47th president of Ecuador since 24 May 2021. He is the country's first centre-right president ...
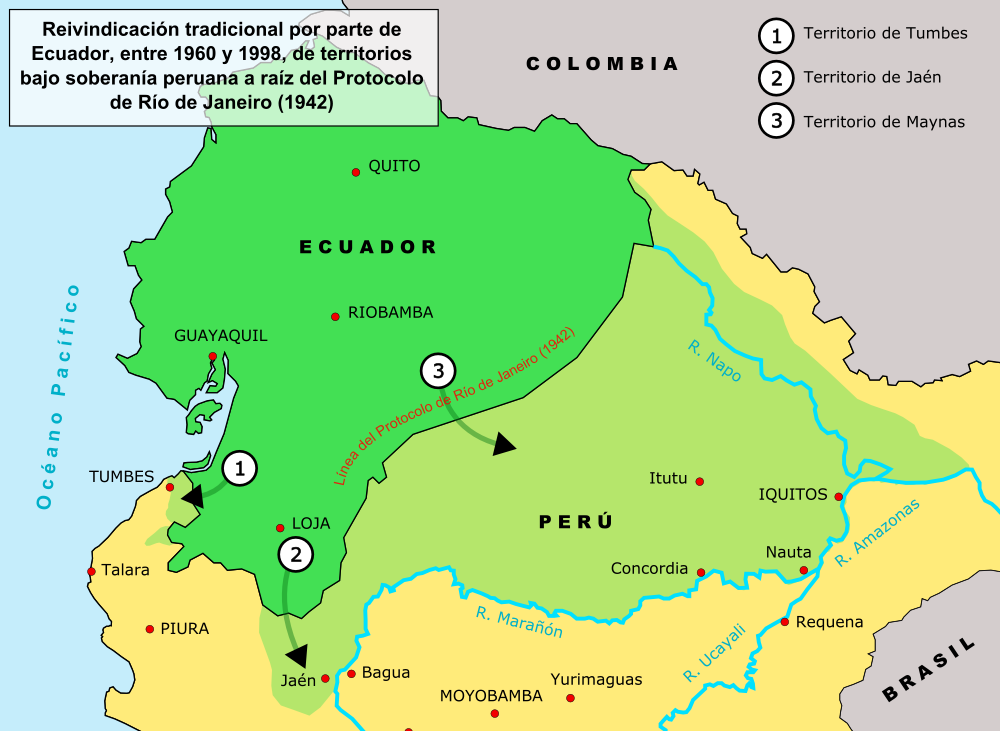
. The military is generally under civilian control, specifically the Ministry of National Defence. The Ecuadorian military of Ecuador has been involved in border disputes with Peru
, image_flag = Flag of Peru.svg
, image_coat = Escudo nacional del Perú.svg
, other_symbol = Great Seal of the State
, other_symbol_type = National seal
, national_motto = "Firm and Happy f ...
(Ecuadorian–Peruvian War (1857–1860)
The Ecuadorian–Peruvian War took place between 1857 and 1860. The conflict began when Ecuador attempted to sell Amazon basin land claimed by Peru in order to settle a debt with British creditors. When diplomatic relations between the two count ...
, Ecuadorian–Peruvian War, Paquisha War
The Paquisha War or Fake Paquisha War () was a military clash that took place between January and February 1981 between Ecuador and Peru over the control of three watchposts. While Peru felt that the matter was already decided in the Ecuadorian� ...
, Cenepa War
The Cenepa War (26 January – 28 February 1995), also known as the Alto Cenepa War, was a brief and localized military conflict between Ecuador and Peru, fought over control of an area in Peruvian territory (i.e. in the eastern side of the Cord ...
), and has provided military observers and troops to the United Nations
The United Nations (UN) is an intergovernmental organization whose stated purposes are to maintain international peace and security, develop friendly relations among nations, achieve international cooperation, and be a centre for harmoni ...
since 1948.
Mission
The armed forces are part of the public forces and have the stated mission of the preservation of the integrity and national sovereignty of the national territory. It also involves participation in the social andeconomic development
In the economics study of the public sector, economic and social development is the process by which the economic well-being and quality of life of a nation, region, local community, or an individual are improved according to targeted goals and ...
of the country and the provision of assistance in the maintenance of internal order. Tasks include fighting organised crime
Organized crime (or organised crime) is a category of transnational, national, or local groupings of highly centralized enterprises run by criminals to engage in illegal activity, most commonly for profit. While organized crime is generally th ...
, anti-narcotic operations and illegal immigration
Immigration is the international movement of people to a destination country of which they are not natives or where they do not possess citizenship in order to settle as permanent residents or naturalized citizens. Commuters, tourists, ...
. One social development programme applies the provision of teachers for rural schools through an accord with the Ministry of Education. Environmental protection is also a priority, several programmes were implemented: "National Forestation and Ornamentation", "Lonely Tree", "Green Surveillance", "Fire Plan", "Ecuador Forest" and "Arenillas Military Reserve". The Ecuadorian territory is divided into five "Joint Task Force Zones" or ''Fuerzas de Tarea Conjunta'', four on mainland Ecuador
Ecuador ( ; ; Quechua: ''Ikwayur''; Shuar: ''Ecuador'' or ''Ekuatur''), officially the Republic of Ecuador ( es, República del Ecuador, which literally translates as "Republic of the Equator"; Quechua: ''Ikwadur Ripuwlika''; Shuar: ' ...
, the fifth being the Naval-zone (including the Galápagos Islands
The Galápagos Islands ( Spanish: , , ) are an archipelago of volcanic islands. They are distributed on each side of the equator in the Pacific Ocean, surrounding the centre of the Western Hemisphere, and are part of the Republic of Ecuad ...
). Overseas territories include also the "Pedro Vicente Maldonado
Pedro Vicente Maldonado y Flores (November 24, 1704 in Riobamba, Royal Audience of Quito (today's Ecuador) – November 7, 1748 in London, England) was an Ecuadorian scientist who collaborated with the members of the French Geodesic Mission. As ...
" Naval Biological Research Station in the Antarctic
The Antarctic ( or , American English also or ; commonly ) is a polar region around Earth's South Pole, opposite the Arctic region around the North Pole. The Antarctic comprises the continent of Antarctica, the Kerguelen Plateau and othe ...
.
Geopolitical situation
Ecuador
Ecuador ( ; ; Quechua: ''Ikwayur''; Shuar: ''Ecuador'' or ''Ekuatur''), officially the Republic of Ecuador ( es, República del Ecuador, which literally translates as "Republic of the Equator"; Quechua: ''Ikwadur Ripuwlika''; Shuar: ' ...
shares a border with Peru
, image_flag = Flag of Peru.svg
, image_coat = Escudo nacional del Perú.svg
, other_symbol = Great Seal of the State
, other_symbol_type = National seal
, national_motto = "Firm and Happy f ...
. Although marked by many conflicts, relations have improved since the signing of a renewed Peace Treaty
A peace treaty is an agreement between two or more hostile parties, usually countries or governments, which formally ends a state of war between the parties. It is different from an armistice, which is an agreement to stop hostilities; a surre ...
in 1998. However, along the -long border with its neighbour Colombia
Colombia (, ; ), officially the Republic of Colombia, is a country in South America with insular regions in North America—near Nicaragua's Caribbean coast—as well as in the Pacific Ocean. The Colombian mainland is bordered by the ...
, relations have been strained mainly due to a cross-border raid by Colombian forces on FARC
The Revolutionary Armed Forces of Colombia – People's Army ( es, link=no, Fuerzas Armadas Revolucionarias de ColombiaEjército del Pueblo, FARC–EP or FARC) is a Marxist–Leninist guerrilla group involved in the continuing Colombian confl ...
guerrillas
Guerrilla warfare is a form of irregular warfare in which small groups of combatants, such as paramilitary personnel, armed civilians, or irregulars, use military tactics including ambushes, sabotage, raids, petty warfare, hit-and-run tacti ...
. The Armed Forces
A military, also known collectively as armed forces, is a heavily armed, highly organized force primarily intended for warfare. It is typically authorized and maintained by a sovereign state, with its members identifiable by their distinct ...
had logistical shortcomings and were caught off-guard. Their radar
Radar is a detection system that uses radio waves to determine the distance (''ranging''), angle, and radial velocity of objects relative to the site. It can be used to detect aircraft, Marine radar, ships, spacecraft, guided missiles, motor v ...
did not work, aviation was virtually non-existent and communications
Communication (from la, communicare, meaning "to share" or "to be in relation with") is usually defined as the transmission of information. The term may also refer to the message communicated through such transmissions or the field of inquir ...
were not fully operational. A diplomatic crisis {{Refimprove, date=December 2011
An international incident (or diplomatic incident) is a seemingly relatively small or limited action, incident or clash that results in a wider dispute between two or more nation-states. International incidents can ...
followed in 2008 which some attribute partially to the need for better equipment as well as a new national defence doctrine
Doctrine (from la, doctrina, meaning "teaching, instruction") is a codification of beliefs or a body of teachings or instructions, taught principles or positions, as the essence of teachings in a given branch of knowledge or in a belief syste ...
.
The new administration at the Defence Ministry launched a deep restructuring program under the name of "PATRIA I". It involves the modernisation of military
A military, also known collectively as armed forces, is a heavily armed, highly organized force primarily intended for warfare. It is typically authorized and maintained by a sovereign state, with its members identifiable by their distinct ...
equipment, improvement of planning and operations within the Ecuadorian territory. "PATRIA I" shall be completed by 2011. In 2009, the spending budget was increased by 25% and totaled $920 million.
History

Ecuador
Ecuador ( ; ; Quechua: ''Ikwayur''; Shuar: ''Ecuador'' or ''Ekuatur''), officially the Republic of Ecuador ( es, República del Ecuador, which literally translates as "Republic of the Equator"; Quechua: ''Ikwadur Ripuwlika''; Shuar: ' ...
's military
A military, also known collectively as armed forces, is a heavily armed, highly organized force primarily intended for warfare. It is typically authorized and maintained by a sovereign state, with its members identifiable by their distinct ...
history dates far back to its first attempt to secure freedom from Spain
, image_flag = Bandera de España.svg
, image_coat = Escudo de España (mazonado).svg
, national_motto = '' Plus ultra'' (Latin)(English: "Further Beyond")
, national_anthem = (English: "Royal March")
, ...
in 1811. In 1822 Ecuadorian troops, alongside other rebel forces, scored a decisive victory
A decisive victory is a military victory in battle that definitively resolves the objective being fought over, ending one stage of the conflict and beginning another stage. Until a decisive victory is achieved, conflict over the competing objecti ...
over the Spanish
Spanish might refer to:
* Items from or related to Spain:
**Spaniards are a nation and ethnic group indigenous to Spain
**Spanish language, spoken in Spain and many Latin American countries
**Spanish cuisine
Other places
* Spanish, Ontario, Can ...
royalist army
An army (from Old French ''armee'', itself derived from the Latin verb ''armāre'', meaning "to arm", and related to the Latin noun ''arma'', meaning "arms" or "weapons"), ground force or land force is a fighting force that fights primarily on ...
at the Battle of Pichincha. Although assisted by Peruvian troops, it would fight these only a few years later in 1828, as a member of the Confederation of Gran Colombia
Gran Colombia (, "Great Colombia"), or Greater Colombia, officially the Republic of Colombia ( Spanish: ''República de Colombia''), was a state that encompassed much of northern South America and part of southern Central America from 1819 to ...
. The troops of Gran Colombia (Less than half of its troops were Ecuadorians), is defeated in the Battle of Punta Malpelo and the combat of crosses, where the Peruvian navy blocks Guayaquil. Then the great Colombians in the land field defeat a division of Peruvian outpost, in the battle of Tarqui. This battle does not define war after the signing of the Giron agreement where it is indicated that it remains in a status quo before bellum. Eventually, Civil War would plunge the country and the army into disorder. In 1941 the Ecuadorian Military found itself weak and disorganized; the by now long-lasting territorial dispute with Peru
, image_flag = Flag of Peru.svg
, image_coat = Escudo nacional del Perú.svg
, other_symbol = Great Seal of the State
, other_symbol_type = National seal
, national_motto = "Firm and Happy f ...
escalated into a major conflict, the Ecuadorian–Peruvian War of 1941. A much larger and better equipped Peruvian force quickly overwhelmed the Ecuadorian forces, driving them back and invading the Ecuadorian territory. Ecuador had no choice but to accept Peru's territorial claims and signed Peace treaty
A peace treaty is an agreement between two or more hostile parties, usually countries or governments, which formally ends a state of war between the parties. It is different from an armistice, which is an agreement to stop hostilities; a surre ...
in 1942. However, the treaty of 1942 failed to settle the border dispute and occasional clashes occurred in a then still non-demarcated border area between the nations. These clashes flared into another outbreak of serious fighting in January 1981 called the Paquisha War
The Paquisha War or Fake Paquisha War () was a military clash that took place between January and February 1981 between Ecuador and Peru over the control of three watchposts. While Peru felt that the matter was already decided in the Ecuadorian� ...
where Ecuadorian troops infiltrated into Peruvian territory are expelled by the Peruvian army; similar incidents occurred in 1983 and again in 1984. The last military
A military, also known collectively as armed forces, is a heavily armed, highly organized force primarily intended for warfare. It is typically authorized and maintained by a sovereign state, with its members identifiable by their distinct ...
conflict with Peru occurred in 1995, during the Cenepa War
The Cenepa War (26 January – 28 February 1995), also known as the Alto Cenepa War, was a brief and localized military conflict between Ecuador and Peru, fought over control of an area in Peruvian territory (i.e. in the eastern side of the Cord ...
, in which both sides claimed to be fighting inside their own territory until the signing of a ceasefire and the eventual separation of forces. The longest-running source of armed international conflict in the Western Hemisphere had ended.
Local engagements
*Ecuadorian War of Independence
The Ecuadorian War of Independence was fought from 1820 to 1822 between several South American armies and Spain over control of the lands of the Royal Audience of Quito, a Spanish colonial administrative jurisdiction from which would eventuall ...
in 1820
* Battle of Pichincha in 1822
* Gran Colombia–Peru War in 1829
* Ecuadorian–Peruvian War (1857–1860)
The Ecuadorian–Peruvian War took place between 1857 and 1860. The conflict began when Ecuador attempted to sell Amazon basin land claimed by Peru in order to settle a debt with British creditors. When diplomatic relations between the two count ...
* Battle of Guayaquil
The Battle of Guayaquil was the final and pivotal armed confrontation in a struggle for political control of Ecuador. The battle was fought on the outskirts of the city of Guayaquil, Ecuador on September 22–24, 1860, among several factions cla ...
in 1860
* Ecuadorian-Colombian War in 1863
* Chincha Islands War
The Chincha Islands War, also known as Spanish–South American War ( es, Guerra hispano-sudamericana), was a series of coastal and naval battles between Spain and its former colonies of Peru, Chile, Ecuador, and Bolivia from 1865 to 1879. The ...
in 1864
* Ecuadorian–Peruvian War in 1941
* Paquisha War
The Paquisha War or Fake Paquisha War () was a military clash that took place between January and February 1981 between Ecuador and Peru over the control of three watchposts. While Peru felt that the matter was already decided in the Ecuadorian� ...
in 1981
* Cenepa War
The Cenepa War (26 January – 28 February 1995), also known as the Alto Cenepa War, was a brief and localized military conflict between Ecuador and Peru, fought over control of an area in Peruvian territory (i.e. in the eastern side of the Cord ...
in 1995
UN peacekeeping operations
The Ecuadorian Armed Forces has provided military observers and troops to theUnited Nations
The United Nations (UN) is an intergovernmental organization whose stated purposes are to maintain international peace and security, develop friendly relations among nations, achieve international cooperation, and be a centre for harmoni ...
since 1948. In November 2003, an Ecuadorian United Nations
The United Nations (UN) is an intergovernmental organization whose stated purposes are to maintain international peace and security, develop friendly relations among nations, achieve international cooperation, and be a centre for harmoni ...
Training Centre was established under the name of: (''La Unidad Escuela de Misiones de Paz "Ecuador
Ecuador ( ; ; Quechua: ''Ikwayur''; Shuar: ''Ecuador'' or ''Ekuatur''), officially the Republic of Ecuador ( es, República del Ecuador, which literally translates as "Republic of the Equator"; Quechua: ''Ikwadur Ripuwlika''; Shuar: ' ...
"''). In 2009, Ecuador
Ecuador ( ; ; Quechua: ''Ikwayur''; Shuar: ''Ecuador'' or ''Ekuatur''), officially the Republic of Ecuador ( es, República del Ecuador, which literally translates as "Republic of the Equator"; Quechua: ''Ikwadur Ripuwlika''; Shuar: ' ...
was deploying over 90 peacekeepers around the globe.
*1948 UNIMOGIP United Nations Military Observer Group in Pakistan
Pakistan ( ur, ), officially the Islamic Republic of Pakistan ( ur, , label=none), is a country in South Asia. It is the world's List of countries and dependencies by population, fifth-most populous country, with a population of almost 24 ...
.
*1948 UNIMOGIP United Nations Military Observer Group in India
India, officially the Republic of India (Hindi: ), is a country in South Asia. It is the List of countries and dependencies by area, seventh-largest country by area, the List of countries and dependencies by population, second-most populous ...
.
*1958 UNOGIL Peacekeeping mission in Lebanon
Lebanon ( , ar, لُبْنَان, translit=lubnān, ), officially the Republic of Lebanon () or the Lebanese Republic, is a country in Western Asia. It is located between Syria to the north and east and Israel to the south, while Cyprus lie ...
.
*1961 ONUC
The United Nations Operation in the Congo (french: Opération des Nations Unies au Congo, abbreviated to ONUC) was a United Nations peacekeeping force deployed in the Republic of the Congo in 1960 in response to the Congo Crisis. ONUC was th ...
Peacekeeping Force in Congo.
*1965 DOMREP Mission of the Representative of the Secretary-General in the Dominican Republic
The Dominican Republic ( ; es, República Dominicana, ) is a country located on the island of Hispaniola in the Greater Antilles archipelago of the Caribbean region. It occupies the eastern five-eighths of the island, which it shares with ...
.
*1990 ONUCA United Nations Observer Group in Central America
Central America ( es, América Central or ) is a subregion of the Americas. Its boundaries are defined as bordering the United States to the north, Colombia to the south, the Caribbean Sea to the east, and the Pacific Ocean to the west. ...
, Nicaragua
Nicaragua (; ), officially the Republic of Nicaragua (), is the largest country in Central America, bordered by Honduras to the north, the Caribbean to the east, Costa Rica to the south, and the Pacific Ocean to the west. Managua is the coun ...
.
*1991 ONUSAL
ONUCA and ONUSAL were two United Nations peacekeeping missions deployed in Central America during the late 1980s and early 1990s.
ONUCA
The United Nations Security Council formally created ONUCA ("United Nations Observer Group in Central Ame ...
United Nations Observer Group in El Salvador
El Salvador (; , meaning " The Saviour"), officially the Republic of El Salvador ( es, República de El Salvador), is a country in Central America. It is bordered on the northeast by Honduras, on the northwest by Guatemala, and on the south ...
.
*1994 MINUGUA United Nations Verification Mission in Guatemala
Guatemala ( ; ), officially the Republic of Guatemala ( es, República de Guatemala, links=no), is a country in Central America. It is bordered to the north and west by Mexico; to the northeast by Belize and the Caribbean; to the east by Hon ...
.
*2003 UNMIL
The United Nations Mission in Liberia (UNMIL) was a peacekeeping operation established in September 2003 to monitor a ceasefire agreement in Liberia following the resignation of President Charles Taylor and the conclusion of the Second Liberia ...
United Nations Observer Group in Liberia
Liberia (), officially the Republic of Liberia, is a country on the West African coast. It is bordered by Sierra Leone to Liberia–Sierra Leone border, its northwest, Guinea to Guinea–Liberia border, its north, Ivory Coast to Ivory Coast� ...
.
*2004 UNOCI Peacekeeping mission in Ivory Coast
Ivory Coast, also known as Côte d'Ivoire, officially the Republic of Côte d'Ivoire, is a country on the southern coast of West Africa. Its capital is Yamoussoukro, in the centre of the country, while its largest city and economic centre i ...
.
*2004 MINUSTAH
)
, leader_title = Head
, leader_name = Sandra Honoré (Special Representative of the Secretary-General)
, status = Replaced by MINUJUSTH
, formation = 1 June 2004
, websiteUN Peacekeeping: MINUSTAH
, United Nations Stabilization Mission in Haiti
Haiti (; ht, Ayiti ; French: ), officially the Republic of Haiti (); ) and formerly known as Hayti, is a country located on the island of Hispaniola in the Greater Antilles archipelago of the Caribbean Sea, east of Cuba and Jamaica, and s ...
.
*2005 UNMIS
The United Nations Mission in the Sudan (UNMIS) was established by the UN Security Council under Resolution 1590 of 24 March 2005, in response to the signing of the Comprehensive Peace Agreement between the government of the Sudan and the Suda ...
United Nations Mission in Sudan
Sudan ( or ; ar, السودان, as-Sūdān, officially the Republic of the Sudan ( ar, جمهورية السودان, link=no, Jumhūriyyat as-Sūdān), is a country in Northeast Africa. It shares borders with the Central African Republic t ...
.
*2007 UNMIN United Nations Mission in Nepal
Nepal (; ne, नेपाल ), formerly the Federal Democratic Republic of Nepal ( ne,
सङ्घीय लोकतान्त्रिक गणतन्त्र नेपाल ), is a landlocked country in South Asia. It is ma ...
.
*2008 MINURCAT
The United Nations Mission in the Central African Republic and Chad (MINURCAT) was a United Nations peacekeeping mission established by the United Nations Security Council on September 25, 2007 to provide a multidimensional presence of up to 350 po ...
United Nations Mission in Chad
Chad (; ar, تشاد , ; french: Tchad, ), officially the Republic of Chad, '; ) is a landlocked country at the crossroads of North and Central Africa. It is bordered by Libya to the north, Sudan to the east, the Central African Republic ...
.
*2008 MINURCAT
The United Nations Mission in the Central African Republic and Chad (MINURCAT) was a United Nations peacekeeping mission established by the United Nations Security Council on September 25, 2007 to provide a multidimensional presence of up to 350 po ...
Part of a Peacebuilding Commission in the Central African Republic
The Central African Republic (CAR; ; , RCA; , or , ) is a landlocked country in Central Africa. It is bordered by Chad to the north, Sudan to the northeast, South Sudan to the southeast, the DR Congo to the south, the Republic of th ...
.
*2010 UNAMID United Nations Mission and the African Union in Darfur
Darfur ( ; ar, دار فور, Dār Fūr, lit=Realm of the Fur) is a region of western Sudan. ''Dār'' is an Arabic word meaning "home f – the region was named Dardaju ( ar, دار داجو, Dār Dājū, links=no) while ruled by the Daju ...
.
Organization
The armed forces of Ecuador are under the authority of the President of the Republic through theMinistry of Defence
{{unsourced, date=February 2021
A ministry of defence or defense (see spelling differences), also known as a department of defence or defense, is an often-used name for the part of a government responsible for matters of defence, found in state ...
, coordinated by the Joint Command of the Armed Forces.
Command structure
*The Commander-in-Chief of the Armed Forces (''Comandante en Jefe de las Fuerzas Armadas'') is the President of the Republic. He exercises the political leadership of security and national defence and counts on the advice of the National Security Council. *The National Security Council (''El Consejo de Seguridad Nacional'') or N.S.C. is the superior body responsible for thenational defence
National security, or national defence, is the security and defence of a sovereign state, including its citizens, economy, and institutions, which is regarded as a duty of government. Originally conceived as protection against military attac ...
, in charge of issuing the strategic concept of national security
National security, or national defence, is the security and defence of a sovereign state, including its citizens, economy, and institutions, which is regarded as a duty of government. Originally conceived as protection against military att ...
, which in turn constitutes the essential instrument to start the planning and decision-making process. It is chaired by the President of the Republic, which is also the Commander-in-Chief of the Armed Forces
A military, also known collectively as armed forces, is a heavily armed, highly organized force primarily intended for warfare. It is typically authorized and maintained by a sovereign state, with its members identifiable by their distinct ...
. It includes the Presidents of the National Congress ''National Congress'' is a term used in the names of various political parties and legislatures .
Political parties
*Ethiopia: Oromo National Congress
*Guyana: People's National Congress (Guyana)
*India: Indian National Congress
*Iraq: Iraqi Nati ...
and the Supreme Court of Justice; the ministers in charge of National Defence
National security, or national defence, is the security and defence of a sovereign state, including its citizens, economy, and institutions, which is regarded as a duty of government. Originally conceived as protection against military attac ...
, Government
A government is the system or group of people governing an organized community, generally a state.
In the case of its broad associative definition, government normally consists of legislature, executive, and judiciary. Government i ...
and Police
The police are a Law enforcement organization, constituted body of Law enforcement officer, persons empowered by a State (polity), state, with the aim to law enforcement, enforce the law, to ensure the safety, health and possessions of citize ...
, Foreign Affairs
''Foreign Affairs'' is an American magazine of international relations and U.S. foreign policy published by the Council on Foreign Relations, a nonprofit, nonpartisan, membership organization and think tank specializing in U.S. foreign policy a ...
, and Economy and Finance; the Chief of the Joint Command, and the Chiefs of the three branches of the Armed Forces
A military, also known collectively as armed forces, is a heavily armed, highly organized force primarily intended for warfare. It is typically authorized and maintained by a sovereign state, with its members identifiable by their distinct ...
. It monitors the fulfillment of the defence policies and the strategic plans elaborated by the Joint Command of the Armed Forces
A military, also known collectively as armed forces, is a heavily armed, highly organized force primarily intended for warfare. It is typically authorized and maintained by a sovereign state, with its members identifiable by their distinct ...
, submitted by the Ministry of National Defence. The N.S.C. constitutes the highest ranking monitoring and crisis management body.
*The Ministry of Defense (''Ministerio de la Defensa National''), is the administrative body of the national defence. The Coordinating Minister of Internal and External Security accords the policies and actions that will be adopted by the following institutions as regards internal and external security: the Ministry of Government and Police
The police are a Law enforcement organization, constituted body of Law enforcement officer, persons empowered by a State (polity), state, with the aim to law enforcement, enforce the law, to ensure the safety, health and possessions of citize ...
, the Ministry of Foreign Affairs, the Ministry of Defence, and the Secretariat General for the Public administration
Public Administration (a form of governance) or Public Policy and Administration (an academic discipline) is the implementation of public policy, administration of government establishment ( public governance), management of non-profit es ...
.
*The Joint Armed Forces Command (''El Comando Conjunto de las Fuerzas Armadas''), is the highest planning, preparation and strategic body of military
A military, also known collectively as armed forces, is a heavily armed, highly organized force primarily intended for warfare. It is typically authorized and maintained by a sovereign state, with its members identifiable by their distinct ...
operations. It advises on national defence and is conformed by the Chief of the Joint Command of the Armed Forces
A military, also known collectively as armed forces, is a heavily armed, highly organized force primarily intended for warfare. It is typically authorized and maintained by a sovereign state, with its members identifiable by their distinct ...
and the Commander
Commander (commonly abbreviated as Cmdr.) is a common naval officer rank. Commander is also used as a rank or title in other formal organizations, including several police forces. In several countries this naval rank is termed frigate captain. ...
s of all three branches of the Ecuadorian Armed Forces
A military, also known collectively as armed forces, is a heavily armed, highly organized force primarily intended for warfare. It is typically authorized and maintained by a sovereign state, with its members identifiable by their distinct ...
: The Army
An army (from Old French ''armee'', itself derived from the Latin verb ''armāre'', meaning "to arm", and related to the Latin noun ''arma'', meaning "arms" or "weapons"), ground force or land force is a fighting force that fights primarily on ...
, Navy
A navy, naval force, or maritime force is the branch of a nation's armed forces principally designated for naval and amphibious warfare; namely, lake-borne, riverine, littoral, or ocean-borne combat operations and related functions. It in ...
and the Air Force
An air force – in the broadest sense – is the national military branch that primarily conducts aerial warfare. More specifically, it is the branch of a nation's armed services that is responsible for aerial warfare as distinct from an ...
.
Branches
Joint Command
 The command is in charge of the administration and coordination of the four
The command is in charge of the administration and coordination of the four military branch
Military branch (also service branch or armed service) is according to common standard a subdivision of the national armed forces of a sovereign nation or state.
Types of branches
Unified armed forces
The Canadian Armed Forces is the unif ...
es. The objectives of the command are to integrate the military branches with joint capabilities and interoperability, to address changes and new scenarios, which guarantee the peace, security, and well-being of the nation.
Through military strategic guidelines and guidelines, in the innovation, updating, development and implementation of the generation of military technology, through strategic study in the development of military capabilities, verification of the optimal installed military capacity, implementation of military technological development, in order to promote military operational growth to be the effective and efficient decisive force.
Army
Armed Forces
A military, also known collectively as armed forces, is a heavily armed, highly organized force primarily intended for warfare. It is typically authorized and maintained by a sovereign state, with its members identifiable by their distinct ...
. Its 52,538 soldiers are deployed in relation to its military doctrine
Military doctrine is the expression of how military forces contribute to campaigns, major operations, battles, and engagements.
It is a guide to action, rather than being hard and fast rules. Doctrine provides a common frame of reference acros ...
. The contemporary Ecuadorian Army
The Ecuadorian Army ( es, ''Ejército Ecuatoriano'', italic=unset) is the land component of the Ecuadorian Armed Forces. Its 160,500 soldiers are deployed in relation to its military doctrine. The contemporary Ecuadorian Army incorporates many jun ...
has a large component of jungle
A jungle is land covered with dense forest and tangled vegetation, usually in tropical climates. Application of the term has varied greatly during the past recent century.
Etymology
The word ''jungle'' originates from the Sanskrit word ''ja� ...
and special forces infantry units implemented within its structure. It operates around 236 tanks, 780 IFVs and 68 aircraft; their standard rifle is the Heckler & Koch HK33. Recently acquired material include:
* 30 4x4 vehicles
Four-wheel drive, also called 4×4 ("four by four") or 4WD, refers to a two-axled vehicle drivetrain capable of providing torque to all of its wheels simultaneously. It may be full-time or on-demand, and is typically linked via a transfer case ...
* 15 Hino trucks (donated by the USA)
* 2 4x4 vehicles
Four-wheel drive, also called 4×4 ("four by four") or 4WD, refers to a two-axled vehicle drivetrain capable of providing torque to all of its wheels simultaneously. It may be full-time or on-demand, and is typically linked via a transfer case ...
(Donated by Venezuela)
* 2 Mil Mi-17
The Mil Mi-17 (NATO reporting name: Hip) is a Soviet-designed Russian military helicopter family introduced in 1975 (Mi-8M), continuing in production at two factories, in Kazan and Ulan-Ude. It is known as the Mi-8M series in Russian service. ...
helicopters
* 107 Humvee
The High Mobility Multipurpose Wheeled Vehicle (HMMWV; colloquial: Humvee) is a family of light, four-wheel drive, military trucks and utility vehicles produced by AM General. It has largely supplanted the roles previously performed by the or ...
Air Force
Peruvian Air Force
The Peruvian Air Force ( es, link=no, Fuerza Aérea del Perú, FAP) is the branch of the Peruvian Armed Forces tasked with defending the nation and its interests through the use of air power. Additional missions include assistance in safeguardin ...
. Today the FAE has a personnel of 6,055 and focuses mainly on border control but also focuses on the war on drugs, guerrilla insurgencies, and humanitarian missions. Since 2009 the FAE has been undergoing major changes and modernisation plans are ongoing whilst new projects are considered to bolster the country's defence capacities. Recent and ongoing orders include:
* 18 Super Tucano
The Embraer EMB 314 Super Tucano (English: ''Super Toucan''), also named ALX or A-29, is a Brazilian turboprop light attack aircraft designed and built by Embraer as a development of the Embraer EMB 312 Tucano. The A-29 Super Tucano carries a wi ...
light combat aircraft
* 6 Mirage 5 (Donated by Venezuela)
* 12 Cheetah
The cheetah (''Acinonyx jubatus'') is a large cat native to Africa and central Iran. It is the fastest land animal, estimated to be capable of running at with the fastest reliably recorded speeds being , and as such has evolved specialized ...
supersonic
Supersonic speed is the speed of an object that exceeds the speed of sound ( Mach 1). For objects traveling in dry air of a temperature of 20 °C (68 °F) at sea level, this speed is approximately . Speeds greater than five times ...
fighter aircraft
Fighter aircraft are fixed-wing military aircraft designed primarily for air-to-air combat. In military conflict, the role of fighter aircraft is to establish air superiority of the battlespace. Domination of the airspace above a battlefield ...
* 8 HAL Dhruv
The HAL Dhruv is a utility helicopter designed and developed by Hindustan Aeronautics Limited (HAL) in November 1984. The helicopter first flew in 1992; however, its development was prolonged due to multiple factors including the Indian Army ...
helicopters from India
* 3D LANZA Radar low altitude radars
* 3 EADS CASA C-295
The CASA C-295 (now Airbus C295) is a medium tactical transport aircraft that was designed and initially manufactured by the Spanish aerospace company CASA.
Work on what would become the C-295 was started during the 1990s as a derivative of ...
Tactical military transport aircraft.
Navy
Pacific Ocean
The Pacific Ocean is the largest and deepest of Earth's five oceanic divisions. It extends from the Arctic Ocean in the north to the Southern Ocean (or, depending on definition, to Antarctica) in the south, and is bounded by the conti ...
. Since end 2009, the Navy's structure became simplified. The Ecuadorian Naval-Zone became one and measures, of the Pacific Coast
Pacific coast may be used to reference any coastline that borders the Pacific Ocean.
Geography Americas
Countries on the western side of the Americas have a Pacific coast as their western or southwestern border, except for Panama, where the Pac ...
and of the Pacific Ocean
The Pacific Ocean is the largest and deepest of Earth's five oceanic divisions. It extends from the Arctic Ocean in the north to the Southern Ocean (or, depending on definition, to Antarctica) in the south, and is bounded by the conti ...
, (including the Galápagos Islands
The Galápagos Islands ( Spanish: , , ) are an archipelago of volcanic islands. They are distributed on each side of the equator in the Pacific Ocean, surrounding the centre of the Western Hemisphere, and are part of the Republic of Ecuad ...
). Most sea-going assets are based at Guayaquil
, motto = Por Guayaquil Independiente en, For Independent Guayaquil
, image_map =
, map_caption =
, pushpin_map = Ecuador#South America
, pushpin_re ...
. The Navy focuses mainly on the border-control and illegal immigration. The Navy
A navy, naval force, or maritime force is the branch of a nation's armed forces principally designated for naval and amphibious warfare; namely, lake-borne, riverine, littoral, or ocean-borne combat operations and related functions. It in ...
operates around 20 major vessels (including two submarines) and 25 aircraft. It has a personnel of 7,258. To increase its operational capabilities it recently acquired:
* 2 Heron 1 unmanned aerial vehicles
An unmanned aerial vehicle (UAV), commonly known as a drone, is an aircraft without any human pilot, crew, or passengers on board. UAVs are a component of an unmanned aircraft system (UAS), which includes adding a ground-based controlle ...
* 4 Searcher MK II unmanned aerial vehicles
An unmanned aerial vehicle (UAV), commonly known as a drone, is an aircraft without any human pilot, crew, or passengers on board. UAVs are a component of an unmanned aircraft system (UAS), which includes adding a ground-based controlle ...
Cyber-Defense Operations Command
It is a body responsible for the planning and execution of actions related to cyberdefense in networks and information and telecommunications systems or others that it may have entrusted to, as well as contributing to the appropriate response in cyberspace to threats or aggressions that may affect National Defense, guaranteeing and providing security to strategic entities that are managed by computer systems. He is prepared to counter cyberattacks, cyberwarfare and espionage to "critical entities" that could be attacked "from anywhere in the world."Education
The training of army, navy and air force officers is the function of the Eloy Alfaro Military Higher School, the Rafael Morán Valverde Naval Higher School and the Cosme Rennella Barbatto Military Higher School, respectively.Equipment sources
Historically, Ecuador depended on a wide variety of foreign suppliers for virtually all of its equipment needs. Only in the 1980s did it begin to develop a modest domestic arms industry as the Directorate of Army Industries manufactured rifle ammunition, uniforms, boots, and other items. In the 1960s and 1970s,France
France (), officially the French Republic ( ), is a country primarily located in Western Europe. It also comprises of Overseas France, overseas regions and territories in the Americas and the Atlantic Ocean, Atlantic, Pacific Ocean, Pac ...
became a leading supplier and delivered AMX-13 tanks and various aircraft. Ecuador
Ecuador ( ; ; Quechua: ''Ikwayur''; Shuar: ''Ecuador'' or ''Ekuatur''), officially the Republic of Ecuador ( es, República del Ecuador, which literally translates as "Republic of the Equator"; Quechua: ''Ikwadur Ripuwlika''; Shuar: ' ...
also purchased Type 209 submarine
The Type 209 is a class of diesel-electric attack submarine developed exclusively for export by Howaldtswerke-Deutsche Werft of Germany. The original variant (Type 209/1100) was designed in the late 1960s. The class is exclusively designed for ...
s and Lürssen
Lürssen (or Lürssen Werft) is a German shipyard with headquarters in Bremen-Vegesack and shipbuilding facilities in Lemwerder, Berne and Bremen-Fähr-Lobbendorf.
Lürssen designs and constructs yachts, naval ships and special vessels. Tradi ...
-Seawolf TNC 45 patrol boats from West Germany
West Germany is the colloquial term used to indicate the Federal Republic of Germany (FRG; german: Bundesrepublik Deutschland , BRD) between its formation on 23 May 1949 and the German reunification through the accession of East Germany on 3 ...
. Various types of infantry
Infantry is a military specialization which engages in ground combat on foot. Infantry generally consists of light infantry, mountain infantry, motorized infantry & mechanized infantry, airborne infantry, air assault infantry, and mar ...
weapons were acquired from Belgium
Belgium, ; french: Belgique ; german: Belgien officially the Kingdom of Belgium, is a country in Northwestern Europe. The country is bordered by the Netherlands to the north, Germany to the east, Luxembourg to the southeast, France to ...
.
Ecuador became a substantial customer for Israel
Israel (; he, יִשְׂרָאֵל, ; ar, إِسْرَائِيل, ), officially the State of Israel ( he, מְדִינַת יִשְׂרָאֵל, label=none, translit=Medīnat Yīsrāʾēl; ), is a country in Western Asia. It is situated ...
i arms in the 1970s, purchasing Arava aircraft, Gabriel missiles for naval patrol craft, and Uzi submachine guns. Under technical assistance contracts, Israel serviced Israeli planes in the Ecuadorian Air Force
The Ecuadorian Air Force ( es, Fuerza Aérea Ecuatoriana, FAE) is the Air arm of the Military of Ecuador and responsible for the protection of the Ecuadorian airspace.
Mission
To develop the military air wing, in order to execute institutional ...
inventory as well as Boeing
The Boeing Company () is an American multinational corporation that designs, manufactures, and sells airplanes, rotorcraft, rockets, satellites, telecommunications equipment, and missiles worldwide. The company also provides leasing and ...
civilian aircraft flown by TAME
Tame may refer to:
*Taming, the act of training wild animals
*River Tame, Greater Manchester
*River Tame, West Midlands and the Tame Valley
*Tame, Arauca, a Colombian town and municipality
* "Tame" (song), a song by the Pixies from their 1989 alb ...
and ''Ecuatoriana Airlines''. Ecuador also reportedly employed Israeli security specialists as consultants in the fight against terrorism. In 1976 Ecuador became the first foreign country to order the Kfir, an advanced jet fighter equipped with the General Electric J-79 engine produced in Israel under license. The transaction, which required United States government approval because of the engine technology, was rejected by the administration of President Jimmy Carter
James Earl Carter Jr. (born October 1, 1924) is an American politician who served as the 39th president of the United States from 1977 to 1981. A member of the Democratic Party (United States), Democratic Party, he previously served as th ...
in order to discourage the proliferation of sophisticated military equipment in the Third World
The term "Third World" arose during the Cold War to define countries that remained non-aligned with either NATO or the Warsaw Pact. The United States, Canada, Japan, South Korea, Western European nations and their allies represented the " First ...
. The action caused an uproar in Israel where the sale was regarded as an important breakthrough in Israel's efforts to develop international markets for the Kfir. In 1981, after the inauguration of President Ronald Reagan
Ronald Wilson Reagan ( ; February 6, 1911June 5, 2004) was an American politician, actor, and union leader who served as the 40th president of the United States from 1981 to 1989. He also served as the 33rd governor of California from 1967 ...
, Washington
Washington commonly refers to:
* Washington (state), United States
* Washington, D.C., the capital of the United States
** A metonym for the federal government of the United States
** Washington metropolitan area, the metropolitan area centered o ...
removed its objection to the sale. Although the contract called for the purchase of 12 Kfirs and an option to purchase an additional 12, Ecuador acquired only the original group, at a price estimated at US$196 million.
Ecuador became a relatively heavy importer of arms in the late 1970s and early 1980s, averaging US$150 million annually and reaching a peak of US$280 million in 1982. These imports declined sharply to an average of US$50 million annually between 1985 and 1987, presumably as a result of a dramatic reduction in oil revenues and the precipitous drop in the value of the sucre
Sucre () is the capital of Bolivia, the capital of the Chuquisaca Department and the 6th most populated city in Bolivia. Located in the south-central part of the country, Sucre lies at an elevation of . This relatively high altitude gives the ...
, which made imported arms extremely expensive. Between 1983 and 1987, Ecuador imported an estimated US$460 million of arms, primarily from Italy
Italy ( it, Italia ), officially the Italian Republic, ) or the Republic of Italy, is a country in Southern Europe. It is located in the middle of the Mediterranean Sea, and its territory largely coincides with the homonymous geographical ...
, France, the United States, and Britain
Britain most often refers to:
* The United Kingdom, a sovereign state in Europe comprising the island of Great Britain, the north-eastern part of the island of Ireland and many smaller islands
* Great Britain, the largest island in the United King ...
. In 1995, during the Cenepa War
The Cenepa War (26 January – 28 February 1995), also known as the Alto Cenepa War, was a brief and localized military conflict between Ecuador and Peru, fought over control of an area in Peruvian territory (i.e. in the eastern side of the Cord ...
against Peru
, image_flag = Flag of Peru.svg
, image_coat = Escudo nacional del Perú.svg
, other_symbol = Great Seal of the State
, other_symbol_type = National seal
, national_motto = "Firm and Happy f ...
, Argentina
Argentina (), officially the Argentine Republic ( es, link=no, República Argentina), is a country in the southern half of South America. Argentina covers an area of , making it the List of South American countries by area, second-largest ...
gave to Ecuador 6,500 ton
Ton is the name of any one of several units of measure. It has a long history and has acquired several meanings and uses.
Mainly it describes units of weight. Confusion can arise because ''ton'' can mean
* the long ton, which is 2,240 pounds
...
s of rifle
A rifle is a long-barreled firearm designed for accurate shooting, with a barrel that has a helical pattern of grooves ( rifling) cut into the bore wall. In keeping with their focus on accuracy, rifles are typically designed to be held with ...
s, cannons, anti-tank rockets
Anti-tank warfare originated from the need to develop technology and tactics to destroy tanks during World War I. Since the Triple Entente deployed the first tanks in 1916, the German Empire developed the first anti-tank weapons. The first devel ...
, and ammunition in a controversial move.
Recent times saw changes in Ecuador's foreign policy, as it decided to look for alternative weapon suppliers. These included its long-term allies Chile
Chile, officially the Republic of Chile, is a country in the western part of South America. It is the southernmost country in the world, and the closest to Antarctica, occupying a long and narrow strip of land between the Andes to the eas ...
, which since 2008 has provided Leopard 1
The Leopard 1 (also styled Leopard I, before the Leopard 2 simply known as Leopard) is a main battle tank designed and produced by Porsche in West Germany that first entered service in 1965. Developed in an era when HEAT warheads were though ...
tanks and s. Israel delivered its unmanned aerial vehicles
An unmanned aerial vehicle (UAV), commonly known as a drone, is an aircraft without any human pilot, crew, or passengers on board. UAVs are a component of an unmanned aircraft system (UAS), which includes adding a ground-based controlle ...
in 2009, and Brazil
Brazil ( pt, Brasil; ), officially the Federative Republic of Brazil (Portuguese: ), is the largest country in both South America and Latin America. At and with over 217 million people, Brazil is the world's fifth-largest country by area ...
supplied additional military vehicles and Super Tucano
The Embraer EMB 314 Super Tucano (English: ''Super Toucan''), also named ALX or A-29, is a Brazilian turboprop light attack aircraft designed and built by Embraer as a development of the Embraer EMB 312 Tucano. The A-29 Super Tucano carries a wi ...
combat-aircraft. Countries like Russia
Russia (, , ), or the Russian Federation, is a transcontinental country spanning Eastern Europe and Northern Asia. It is the largest country in the world, with its internationally recognised territory covering , and encompassing one-ei ...
and China
China, officially the People's Republic of China (PRC), is a country in East Asia. It is the world's List of countries and dependencies by population, most populous country, with a Population of China, population exceeding 1.4 billion, slig ...
have delivered small quantities of military equipment in the past, but have gained importance in recent years. Since then, Chinese radars, anti-aircraft systems, and infantry weapons have been purchased. In 2009 two additional Mil Mi-17
The Mil Mi-17 (NATO reporting name: Hip) is a Soviet-designed Russian military helicopter family introduced in 1975 (Mi-8M), continuing in production at two factories, in Kazan and Ulan-Ude. It is known as the Mi-8M series in Russian service. ...
helicopters have been ordered from Russia
Russia (, , ), or the Russian Federation, is a transcontinental country spanning Eastern Europe and Northern Asia. It is the largest country in the world, with its internationally recognised territory covering , and encompassing one-ei ...
with further deals planned. India
India, officially the Republic of India (Hindi: ), is a country in South Asia. It is the List of countries and dependencies by area, seventh-largest country by area, the List of countries and dependencies by population, second-most populous ...
has delivered HAL Dhruv
The HAL Dhruv is a utility helicopter designed and developed by Hindustan Aeronautics Limited (HAL) in November 1984. The helicopter first flew in 1992; however, its development was prolonged due to multiple factors including the Indian Army ...
helicopters and South Africa
South Africa, officially the Republic of South Africa (RSA), is the southernmost country in Africa. It is bounded to the south by of coastline that stretch along the South Atlantic and Indian Oceans; to the north by the neighbouring coun ...
is about to deliver 12 Atlas Cheetah
The Atlas Cheetah is a South African fighter aircraft designed and produced by the aviation company Atlas Aircraft Corporation (later Denel Aeronautics). It was developed at the behest of, and principally operated by, the South African Air F ...
supersonic
Supersonic speed is the speed of an object that exceeds the speed of sound ( Mach 1). For objects traveling in dry air of a temperature of 20 °C (68 °F) at sea level, this speed is approximately . Speeds greater than five times ...
aircraft. Ecuador's political ally, Venezuela
Venezuela (; ), officially the Bolivarian Republic of Venezuela ( es, link=no, República Bolivariana de Venezuela), is a country on the northern coast of South America, consisting of a continental landmass and many islands and islets in th ...
, has donated military equipment including six Mirage 50 aircraft.
In 2010, the U.S. embassy in Ecuador announced that it had delivered $1.2 million of donated military equipment to the Ecuadorian military. The donations were intended to support operations countering drug smuggling and guerilla activity along the Colombia
Colombia (, ; ), officially the Republic of Colombia, is a country in South America with insular regions in North America—near Nicaragua's Caribbean coast—as well as in the Pacific Ocean. The Colombian mainland is bordered by the ...
n border. Although the U.S. has refused to renew their lease on the Manta military airbase, deliveries included trucks, patrol boats, GPS, night vision, and M4 carbine
The M4 carbine (officially Carbine, Caliber 5.56 mm, M4) is a 5.56×45mm NATO, gas-operated, magazine-fed carbine developed in the United States during the 1980s. It is a shortened version of the M16A2 assault rifle.
The M4 is extensive ...
rifles.
See also
*History of the Ecuadorian–Peruvian territorial dispute
History (derived ) is the systematic study and the documentation of the human activity. The time period of event before the invention of writing systems is considered prehistory. "History" is an umbrella term comprising past events as well ...
* Ecuadorian–Peruvian War (1857–1860)
The Ecuadorian–Peruvian War took place between 1857 and 1860. The conflict began when Ecuador attempted to sell Amazon basin land claimed by Peru in order to settle a debt with British creditors. When diplomatic relations between the two count ...
* Military Governments of Ecuador (1960-1979)
* 2008 Andean diplomatic crisis
* Ecuadorian–Peruvian War
* Military of Venezuela
The National Bolivarian Armed Forces ( es, Fuerza Armada Nacional Bolivariana - FANB) of Venezuela are controlled by the Commander-in-Chief (the President) and a civilian Minister of Defense. In addition to the army, navy, and air force there ...
* Military of Colombia
* Military of Peru
References
External links
Official site of the Ministry of Defence
Official site of the National Security Council
Official site of the Ecuadorian Army
Official site of the Ecuadorian Air Force
Official site of the Ecuadorian Navy
Official Ecuadorian Coast Guard site
Official site of the Ecuadorian Marines
{{DEFAULTSORT:Military Of Ecuador Ecuadorian Armed Forces