The predecessors to the contemporary
Army of India were many: the
sepoy regiment
A regiment is a military unit. Its role and size varies markedly, depending on the country, service and/or a specialisation.
In Medieval Europe, the term "regiment" denoted any large body of front-line soldiers, recruited or conscript ...
s, native cavalry, irregular horse and
Indian sapper and miner companies raised by the three
British presidencies. The Army of India was raised under the
British Raj
The British Raj (; from Hindi ''rāj'': kingdom, realm, state, or empire) was the rule of the British Crown on the Indian subcontinent;
*
* it is also called Crown rule in India,
*
*
*
*
or Direct rule in India,
* Quote: "Mill, who was him ...
in the 19th century by taking the erstwhile presidency armies, merging them, and bringing them under the Crown. The British Indian Army fought in both World Wars.
The armed forces succeeded the
military of British India
The British Indian Army, commonly referred to as the Indian Army, was the main military of the British Raj before its dissolution in 1947. It was responsible for the defence of the British Indian Empire, including the princely states, which cou ...
following India's independence in 1947. After
World War II
World War II or the Second World War, often abbreviated as WWII or WW2, was a world war that lasted from 1939 to 1945. It involved the vast majority of the world's countries—including all of the great powers—forming two opposing ...
, many of the wartime troops were discharged and units disbanded. The reduced armed forces were partitioned between India and
Pakistan
Pakistan ( ur, ), officially the Islamic Republic of Pakistan ( ur, , label=none), is a country in South Asia. It is the world's fifth-most populous country, with a population of almost 243 million people, and has the world's second-lar ...
. The Indian armed forces fought
in all fours wars against Pakistan and two wars against
People's Republic of China
China, officially the People's Republic of China (PRC), is a country in East Asia. It is the world's most populous country, with a population exceeding 1.4 billion, slightly ahead of India. China spans the equivalent of five time zones and ...
in
1962
Events January
* January 1 – Western Samoa becomes independent from New Zealand.
* January 3 – Pope John XXIII excommunicates Fidel Castro for preaching communism.
* January 8 – Harmelen train disaster: 93 die in the wor ...
and
1967
Events
January
* January 1 – Canada begins a year-long celebration of the 100th anniversary of Confederation, featuring the Expo 67 World's Fair.
* January 5
** Spain and Romania sign an agreement in Paris, establishing full consular and ...
. India also fought in the
Kargil War
The Kargil War, also known as the Kargil conflict, was fought between India and Pakistan from May to July 1999 in the Kargil district of Jammu and Kashmir and elsewhere along the Line of Control (LoC). In India, the conflict is also referr ...
with Pakistan in 1999, the
highest altitude mountain warfare
Mountain warfare (also known as alpine warfare) is warfare in mountains or similarly rough terrain. Mountain ranges are of strategic importance since they often act as a natural border, and may also be the origin of a water source (for example, ...
in history. The Indian Armed Forces have participated in several
United Nations
The United Nations (UN) is an intergovernmental organization whose stated purposes are to maintain international peace and security, develop friendly relations among nations, achieve international cooperation, and be a centre for harmoniz ...
peacekeeping operations and are presently the second largest contributor of troops to the peacekeeping force.
Indus Valley Civilisation
Fortified towns have been excavated from
Indus Valley civilisation
The Indus Valley Civilisation (IVC), also known as the Indus Civilisation was a Bronze Age civilisation in the northwestern regions of South Asia, lasting from 3300 BCE to 1300 BCE, and in its mature form 2600 BCE to 1900& ...
with thick and tall walls.
Banawali
Banawali (Devanagari: बनावली) is an archaeological site belonging to Indus Valley civilization period in fatehabad district, Haryana, India and is located about 120 km northeast of Kalibangan and 16 km from Fatehabad. Ban ...
is among the earliest sites in the world where moats have been discovered. These forts also feature square and round bastion and contain a citadel constructed at an elevated height. Sites such as
Mohenjo Daro
Mohenjo-daro (; sd, موئن جو دڙو'', ''meaning 'Mound of the Dead Men';[Dholavira
Dholavira ( gu, ધોળાવીરા) is an archaeological site at Khadirbet in Bhachau Taluka of Kutch District, in the state of Gujarat in western India, which has taken its name from a modern-day village south of it. This village is ...]
exhibit some outstanding examples of
Bronze Age India
The Bronze Age in the Indian subcontinent begins around 3000 BCE, and in the end gives rise to the Indus Valley Civilisation, which had its (mature) period between 2600 BCE and 1900 BCE. It continues into the Rigvedic period, the early part of the ...
n fortifications with their thick tall walls, with the walls made of burned bricks at some places solid mud-brick embankment have been discovered which run for twenty five feet (7.5 meters) without reaching the bottom. Sites such as
Desalpar, Dholavira's have yielded massive stone fortifications and the acropolis is extensively fortified with tall standing walls and furnished with ramparts and gateways.
An excavation at
Sinauli
Sinauli is an archaeological site in western Uttar Pradesh, India, at the Ganga-Yamuna Doab. The site gained attention for its Bronze Age solid-disk wheel carts, found in 2018, which were interpreted by some as horse-pulled "chariots".
The e ...
's necropolis has yielded copper swords, helmets and chariots, dating from 2000 to 1800 BC, which suggests the presence of a warrior class of people in the region during the Copper-Bronze Age (3300 BC–1200 BC).
An Indus seal depicting a soldier firing a
composite bow
A composite bow is a traditional bow made from horn, wood, and sinew laminated together, a form of laminated bow. The horn is on the belly, facing the archer, and sinew on the outer side of a wooden core. When the bow is drawn, the sinew (stre ...
was unearthed in
Shortugai
Shortugai (Shortughai), in Darqad District of northern Afghanistan, was a trading colony of the Indus Valley civilization (or Harappan Civilization) established around 2000 BC on the Oxus river (Amu Darya) near the lapis lazuli mines. It is co ...
,
Afghanistan
Afghanistan, officially the Islamic Emirate of Afghanistan,; prs, امارت اسلامی افغانستان is a landlocked country located at the crossroads of Central Asia and South Asia. Referred to as the Heart of Asia, it is bordere ...
, which indicates that Indus people were already familiar with it long before they were depicted in ancient Indian reliefs. Another copper seal from Mohenjo Daro shows a horned hunter holding a composite bow.
Dholavira gujarat.jpg, Defensive wall of Dholavira
Dholavira ( gu, ધોળાવીરા) is an archaeological site at Khadirbet in Bhachau Taluka of Kutch District, in the state of Gujarat in western India, which has taken its name from a modern-day village south of it. This village is ...
, Gujarat, India
Gujarat (, ) is a state along the western coast of India. Its coastline of about is the longest in the country, most of which lies on the Kathiawar peninsula. Gujarat is the fifth-largest Indian state by area, covering some ; and the ninth ...
, 2650 BCE.
Kalibangan.jpg, Kalibangan
Kalibangān is a town located at on the left or southern banks of the Ghaggar (Ghaggar-Hakra River) in Tehsil Pilibangān, between Suratgarh and Hanumangarh in Hanumangarh District, Rajasthan, India 205 km. from Bikaner. It is also identi ...
Fortification wall and square bastions, Rajasthan, India
Rajasthan (; lit. 'Land of Kings') is a state in northern India. It covers or 10.4 per cent of India's total geographical area. It is the largest Indian state by area and the seventh largest by population. It is on India's northwestern si ...
, 2500 BCE.
The Vedic and Mahajanapada period

The
Rigvedic tribes
This is a list of ancient Indo-Aryan peoples and tribes that are mentioned in the literature of Indic religions.
From the second or first millennium BCE, ancient Indo-Aryan peoples and tribes turned into most of the population in the northern ...
of
Indo-Aryans
Indo-Aryan peoples are a diverse collection of Indo-European peoples speaking Indo-Aryan languages in the Indian subcontinent. Historically, Aryan were the Indo-European pastoralists who migrated from Central Asia into South Asia and intr ...
were led by their kings (''
raja
''Raja'' (; from , IAST ') is a royal title used for South Asian monarchs. The title is equivalent to king or princely ruler in South Asia and Southeast Asia.
The title has a long history in South Asia and Southeast Asia, being attested f ...
'') and engaged in wars with each other and other tribes. They used
bronze weapons and
horse
The horse (''Equus ferus caballus'') is a domesticated, one-toed, hoofed mammal. It belongs to the taxonomic family Equidae and is one of two extant subspecies of ''Equus ferus''. The horse has evolved over the past 45 to 55 million yea ...
-drawn spoke-wheeled
chariots described prominently in the
Rigveda
The ''Rigveda'' or ''Rig Veda'' ( ', from ' "praise" and ' "knowledge") is an ancient Indian collection of Vedic Sanskrit hymns (''sūktas''). It is one of the four sacred canonical Hindu texts ('' śruti'') known as the Vedas. Only one ...
. The main share from the booty obtained during
cattle raid
Cattle raiding is the act of stealing cattle. In Australia, such stealing is often referred to as duffing, and the perpetrator as a duffer.Baker, Sidney John (1945) ''The Australian language : an examination of the English language and English ...
s and battles went to the chief of the tribe. The warriors belonged to the
Kshatriya
Kshatriya ( hi, क्षत्रिय) (from Sanskrit ''kṣatra'', "rule, authority") is one of the four varna (social orders) of Hindu society, associated with warrior aristocracy. The Sanskrit term ''kṣatriyaḥ'' is used in the con ...
varna. The earliest of such battles is noted in
Rigveda
The ''Rigveda'' or ''Rig Veda'' ( ', from ' "praise" and ' "knowledge") is an ancient Indian collection of Vedic Sanskrit hymns (''sūktas''). It is one of the four sacred canonical Hindu texts ('' śruti'') known as the Vedas. Only one ...
as the
Battle of the Ten Kings.
The
Vedas
upright=1.2, The Vedas are ancient Sanskrit texts of Hinduism. Above: A page from the '' Atharvaveda''.
The Vedas (, , ) are a large body of religious texts originating in ancient India. Composed in Vedic Sanskrit, the texts constitute th ...
and other associated texts dating to the post-Rigvedic (
Iron Age
The Iron Age is the final epoch of the three-age division of the prehistory and protohistory of humanity. It was preceded by the Stone Age ( Paleolithic, Mesolithic, Neolithic) and the Bronze Age ( Chalcolithic). The concept has been mostl ...
)
Vedic period
The Vedic period, or the Vedic age (), is the period in the late Bronze Age and early Iron Age of the history of India when the Vedic literature, including the Vedas (ca. 1300–900 BCE), was composed in the northern Indian subcontinent, betwe ...
(ca. 1100–500 BC) contain the earliest written references to armies in India. The earliest known application of
war elephant
A war elephant was an elephant that was trained and guided by humans for combat. The war elephant's main use was to charge the enemy, break their ranks and instill terror and fear. Elephantry is a term for specific military units using elepha ...
s dates to this period; the animals are mentioned in several
Vedic Sanskrit
Vedic Sanskrit was an ancient language of the Indo-Aryan subgroup of the Indo-European language family. It is attested in the Vedas and related literature compiled over the period of the mid- 2nd to mid-1st millennium BCE. It was orally preser ...
hymns.
The two great epics of
Hinduism
Hinduism () is an Indian religion or '' dharma'', a religious and universal order or way of life by which followers abide. As a religion, it is the world's third-largest, with over 1.2–1.35 billion followers, or 15–16% of the global p ...
, the
Ramayana
The ''Rāmāyana'' (; sa, रामायणम्, ) is a Sanskrit literature, Sanskrit Indian epic poetry, epic composed over a period of nearly a millennium, with scholars' estimates for the earliest stage of the text ranging from the 8th ...
and the
Mahabharata
The ''Mahābhārata'' ( ; sa, महाभारतम्, ', ) is one of the two major Sanskrit literature, Sanskrit Indian epic poetry, epics of ancient India in Hinduism, the other being the ''Ramayana, Rāmāyaṇa''. It narrates the s ...
, center on conflicts between the emerging
Mahajanapadas and refer to military formations, theories of warfare and esoteric weaponry. They discuss standing armies that used in war
chariots, war elephants and even mythical
flying machines
Flying machines s.r.o. is a Czech manufacturer of light aircraft based in Rasošky. The company was established in 2004 and specializes in kit aircraft for amateur construction and ultralight trike
An ultralight trike is a type of powere ...
. The Ramayana describes in great detail the fortifications of
Ayodhya
Ayodhya (; ) is a city situated on the banks of holy river Saryu in the Indian state of Uttar Pradesh.
Ayodhya, also known as Saketa, is an ancient city of India, the birthplace of Rama and setting of the great epic Ramayana. Ayodhya wa ...
. The
Mahabharata
The ''Mahābhārata'' ( ; sa, महाभारतम्, ', ) is one of the two major Sanskrit literature, Sanskrit Indian epic poetry, epics of ancient India in Hinduism, the other being the ''Ramayana, Rāmāyaṇa''. It narrates the s ...
describes various military techniques such as
Chakravyuha used in the
Kurukshetra War.
The Indian dynasties
Shaishunaga dynasty
The
expansionist
Expansionism refers to states obtaining greater territory through military empire-building or colonialism.
In the classical age of conquest moral justification for territorial expansion at the direct expense of another established polity (who of ...
King
Bimbisara
Bimbisāra (in Buddhist tradition) or Shrenika () and Seniya () in the Jain histories (c. 558 – c. 491 BCE or during the late 5th century BCE) was a King of Magadha (V. K. Agnihotri (ed.), ''Indian History''. Allied Publishers, New Delhi ...
conquered
Anga
Anga (Sanskrit: ) was an ancient Indo-Aryan tribe of eastern South Asia whose existence is attested during the Iron Age. The members of the Aṅga tribe were called the Āṅgeyas.
Counted among the "sixteen great nations" in Buddhist texts ...
in what is now
West Bengal
West Bengal (, Bengali: ''Poshchim Bongo'', , abbr. WB) is a state in the eastern portion of India. It is situated along the Bay of Bengal, along with a population of over 91 million inhabitants within an area of . West Bengal is the fou ...
and strengthened the military of
Magadh
Magadha was a region and one of the sixteen sa, script=Latn, Mahajanapadas, label=none, lit=Great Kingdoms of the Second Urbanization (600–200 BCE) in what is now south Bihar (before expansion) at the eastern Ganges Plain. Magadha was ruled ...
's capital,
Rajagriha
Rajgir, meaning "The City of Kings," is a historic town in the district of Nalanda in Bihar, India. As the ancient seat and capital of the Haryanka dynasty, the Pradyota dynasty, the Brihadratha dynasty and the Mauryan Empire, as well as the ...
.
Ajatashatru
Ajatasattu (Pāli ) or Ajatashatru (Sanskrit ) in Buddhist tradition, or Kunika () and Kuniya () in the Jain histories, (c. 492 to 460 BCE or early 5th century BCE) was one of the most important kings of the Haryanka dynasty of Magadha in East ...
built a new fort at
Pataliputra
Pataliputra ( IAST: ), adjacent to modern-day Patna, was a city in ancient India, originally built by Magadha ruler Ajatashatru in 490 BCE as a small fort () near the Ganges river.. Udayin laid the foundation of the city of Pataliputra at the ...
, Magadh's new capital, to launch an attack on
Licchavis across the
Ganges River.
Jain
Jainism ( ), also known as Jain Dharma, is an Indian religion. Jainism traces its spiritual ideas and history through the succession of twenty-four tirthankaras (supreme preachers of ''Dharma''), with the first in the current time cycle being ...
texts tell that he used two new weapons;
catapults and a covered
chariot with swinging
mace that has been compared to modern
tank
A tank is an armoured fighting vehicle intended as a primary offensive weapon in front-line ground combat. Tank designs are a balance of heavy firepower, strong armour, and good battlefield mobility provided by tracks and a powerful engi ...
s.
Nanda dynasty
The
Nanda dynasty
The Nanda dynasty ruled in the northern part of the Indian subcontinent during the fourth century BCE, and possibly during the fifth century BCE. The Nandas overthrew the Shaishunaga dynasty in the Magadha region of eastern India, and expanded ...
originated from the region of Magadha in ancient India during the 4th century BC. At its greatest extent, the empire ruled by the Nanda dynasty extended from Bengal in the east, to Punjab in the west and as far south as the Vindhya Range.
In 327 BC
Alexander the Great
Alexander III of Macedon ( grc, Ἀλέξανδρος, Alexandros; 20/21 July 356 BC – 10/11 June 323 BC), commonly known as Alexander the Great, was a king of the ancient Greek kingdom of Macedon. He succeeded his father Philip II to ...
began his foray into Punjab. King Ambhi, ruler of Taxila, surrendered the city to Alexander. Alexander fought an epic battle against the Indian king Porus in the
Battle of Hydaspes (326). Despite winning, Alexander decided to turn back and end his campaign due to pressure from his generals and troops who were tired and fatigued because of constant battle.
Maurya Empire
According to
Megasthenes
Megasthenes ( ; grc, Μεγασθένης, c. 350 BCE– c. 290 BCE) was an ancient Greek historian, diplomat and Indian ethnographer and explorer in the Hellenistic period. He described India in his book '' Indica'', which is now lost, but ha ...
, who served as an ambassador from the
Seleucid Empire,
Chandragupta Maurya built an army consisting of 30,000
cavalry, 9,000
war elephant
A war elephant was an elephant that was trained and guided by humans for combat. The war elephant's main use was to charge the enemy, break their ranks and instill terror and fear. Elephantry is a term for specific military units using elepha ...
s, and 600,000
infantry
Infantry is a military specialization which engages in ground combat on foot. Infantry generally consists of light infantry, mountain infantry, motorized infantry & mechanized infantry, airborne infantry, air assault infantry, and mar ...
. Chandragupta conquered much of Indian subcontinent, establishing an empire from the
Arabian Sea
The Arabian Sea ( ar, اَلْبَحرْ ٱلْعَرَبِيُّ, Al-Bahr al-ˁArabī) is a region of the northern Indian Ocean bounded on the north by Pakistan, Iran and the Gulf of Oman, on the west by the Gulf of Aden, Guardafui Channel ...
to the
Bay of Bengal
The Bay of Bengal is the northeastern part of the Indian Ocean, bounded on the west and northwest by India, on the north by Bangladesh, and on the east by Myanmar and the Andaman and Nicobar Islands of India. Its southern limit is a line betwee ...
. He then defeated the Hellenistic
Seleucid Empire under
Seleucus I Nicator
Seleucus I Nicator (; ; grc-gre, Σέλευκος Νικάτωρ , ) was a Macedonian Greek general who was an officer and successor ( ''diadochus'') of Alexander the Great. Seleucus was the founder of the eponymous Seleucid Empire. In the po ...
to conquer the regions to the west of the
Indus River. He then turned south, taking over much of what is now Central India. His military was administered by six chairs, one for each of the four arms of the army (infantry, cavalry, elephants, and chariots), one chair for the navy, and one for logistics and supply.
Infantry at this time was most commonly armed with a
longbow
A longbow (known as warbow in its time, in contrast to a hunting bow) is a type of tall bow that makes a fairly long draw possible. A longbow is not significantly recurved. Its limbs are relatively narrow and are circular or D-shaped in cross ...
made of
bamboo
Bamboos are a diverse group of evergreen perennial flowering plants making up the subfamily Bambusoideae of the grass family Poaceae. Giant bamboos are the largest members of the grass family. The origin of the word "bamboo" is uncertain, ...
and a single- or double-handed broadsword probably similar to the
khanda
Khanda may refer to:
Places
* Khanda, Sonipat, a very big and historical village in Sonipat district of Haryana, India
* Khanda, Jind, a village in Jind district of Haryana, India
* Khanda Kheri, a village in Hansi Tehsil of Hisar district of ...
. Other foot soldiers could be armed with a large animal hide tower shield and a spear or javelins. Cavalry carried spears. Elephants were mounted, sometimes allegedly with howdahs, which may be an Indian invention by archers or javelin throwers, with a
mahout
A mahout is an elephant rider, trainer, or keeper. Mahouts were used since antiquity for both civilian and military use. Traditionally, mahouts came from ethnic groups with generations of elephant keeping experience, with a mahout retaining h ...
around the animal's neck. Chariots by this time were in definite decline, but remained in the army due to their prestige.
In 185 BCE, the last
Maurya
The Maurya Empire, or the Mauryan Empire, was a geographically extensive Iron Age historical power in the Indian subcontinent based in Magadha, having been founded by Chandragupta Maurya in 322 BCE, and existing in loose-knit fashion until 1 ...
n ruler was assassinated by
Pushyamitra Shunga, the Commander-in-Chief of the Mauryan armed forces.
Shunga Empire

War and conflict characterized the Shunga period. They are known to have warred with the Kalingas, Satavahanas, the Indo-Greeks, and possibly the Panchalas and Mathuras.
Extent of the Shunga Empire's wars with the Indo-Greek Kingdom figure greatly in the history of this period. From around 180 BCE the
Indo-Greek
The Indo-Greek Kingdom, or Graeco-Indian Kingdom, also known historically as the Yavana Kingdom (Yavanarajya), was a Hellenistic-era Greek kingdom covering various parts of Afghanistan and the northwestern regions of the Indian subcontinent ( ...
ruler
Demetrius I of Bactria
Demetrius I Anicetus ( grc, Δημήτριος Ἀνίκητος, Dēmētrios Anikētos, "the unconquered"), also called Damaytra was a Greco-Bactrian and later Indo-Greek king (Yona in Pali language, "Yavana" in Sanskrit) (reigned c. 200–167 ...
conquered the Kabul Valley and is theorized to have advanced into the trans-Indus. The Indo-Greek
Menander I
Menander I Soter ( grc, Μένανδρος Σωτήρ, Ménandros Sōtḗr, Menander the Saviour; pi, मिलिन्दो, Milinda), was a Greco-Bactrian and later Indo-Greek King (reigned c.165/155Bopearachchi (1998) and (1991), respectivel ...
is credited with either joining or leading a campaign to Pataliputra with other Indian rulers; however, very little is known about the exact nature and success of the campaign. The net result of these wars remains uncertain.
Pushyamitra is recorded to have performed two Ashvamedha Yagnas and Shunga imperial inscriptions have extended as far as Jalandhar. Scriptures such as the Divyavadhana note that his rule extended even farther to Sialkot, in the Punjab. Moreover, if it was lost, Mathura was regained by the Shungas around 100 BCE (or by other indigenous rulers: the Arjunayanas (area of Mathura) and Yaudheyas mention military victories on their coins ("Victory of the Arjunayanas", "Victory of the Yaudheyas"), and during the 1st century BCE, the Trigartas, Audumbaras and finally the Kunindas also started to mint their own coins). Accounts of battles between the Greeks and the Shunga in Northwestern India are also found in the Mālavikāgnimitram, a play by Kālidāsa which describes a battle between Greek cavalrymen and Vasumitra, the grandson of Pushyamitra, on the Indus river, in which the Indians defeated the Greeks and Pushyamitra successfully completed the Ashvamedha Yagna.
The Indo-Greeks and the Shungas seem to have reconciled and exchanged diplomatic missions around 110 BCE, as indicated by the Heliodorus pillar, which records the dispatch of a Greek ambassador named Heliodorus, from the court of the Indo-Greek king Antialcidas, to the court of the Shunga emperor Bhagabhadra at the site of Vidisha in central India.
The Golden age
Classical Indian texts on archery in particular and
martial arts in general are known as
Dhanurveda. Several classics of the genre date from this period.
Satavahana dynasty

According to some interpretations of the
Puranas, the
Satavahana
The Satavahanas (''Sādavāhana'' or ''Sātavāhana'', IAST: ), also referred to as the Andhras in the Puranas, were an ancient Indian dynasty based in the Deccan region. Most modern scholars believe that the Satavahana rule began in the la ...
family belonged to the Andhra-jati ("tribe") and was the first
Deccanese dynasty to build an empire in daksinapatha (southern region). The Satavahanas (also called Andhra and Shalivahan) rose to power in modern
Telangana
Telangana (; , ) is a state in India situated on the south-central stretch of the Indian peninsula on the high Deccan Plateau. It is the eleventh-largest state and the twelfth-most populated state in India with a geographical area of and 3 ...
,
Andhra Pradesh
Andhra Pradesh (, abbr. AP) is a state in the south-eastern coastal region of India. It is the seventh-largest state by area covering an area of and tenth-most populous state with 49,386,799 inhabitants. It is bordered by Telangana to the ...
and
Maharashtra around 200 BCE and remained in power for about 400 years. Almost the whole of present-day
Telangana
Telangana (; , ) is a state in India situated on the south-central stretch of the Indian peninsula on the high Deccan Plateau. It is the eleventh-largest state and the twelfth-most populated state in India with a geographical area of and 3 ...
, Maharashtra,
Madhya Pradesh
Madhya Pradesh (, ; meaning 'central province') is a state in central India. Its capital is Bhopal, and the largest city is Indore, with Jabalpur, Ujjain, Gwalior, Sagar, and Rewa being the other major cities. Madhya Pradesh is the seco ...
,
Chhattisgarh,
Odisha
Odisha (English: , ), formerly Orissa ( the official name until 2011), is an Indian state located in Eastern India. It is the 8th largest state by area, and the 11th largest by population. The state has the third largest population of ...
,
Goa
Goa () is a state on the southwestern coast of India within the Konkan region, geographically separated from the Deccan highlands by the Western Ghats. It is located between the Indian states of Maharashtra to the north and Karnataka to the ...
,
Karnataka
Karnataka (; ISO: , , also known as Karunāḍu) is a state in the southwestern region of India. It was formed on 1 November 1956, with the passage of the States Reorganisation Act. Originally known as Mysore State , it was renamed ''Karnat ...
, and
Andhra Pradesh
Andhra Pradesh (, abbr. AP) is a state in the south-eastern coastal region of India. It is the seventh-largest state by area covering an area of and tenth-most populous state with 49,386,799 inhabitants. It is bordered by Telangana to the ...
came under Satavahana rule. Their first capital was
Koti Lingala
Kotilingala is a Hindu pilgrimage site in Jagtial district of the Indian state of Telangana. It is situated in Velagatoor mandal of the district, on the Godavari river. It is located on the bank of the Godavari River, and has a traditional ...
, as well as
Paithan
Paithan pəɪ.ʈʰaɳ(), historically Pratiṣṭhāna ɾə'tɪʂʈʰana is a town with municipal council in Aurangabad district, Maharashtra, India. Paithan is located south of present-day Aurangabad on the Godavari River.
It was the cap ...
, then called Pratishthan.
Simuka
Simuka ( Dhamma lipi𑀲𑀺𑀫𑀼𑀓, ''Si-mu-ka'') was an Indian king belonging to the Satavahana dynasty. He is mentioned as the first king in a list of royals in a Satavahana inscription at Nanaghat. In the Puranas, the name of the first A ...
, the dynasty's founder, conquered
Maharashtra,
Malwa
Malwa is a historical region of west-central India occupying a plateau of volcanic origin. Geologically, the Malwa Plateau generally refers to the volcanic upland north of the Vindhya Range. Politically and administratively, it is also syn ...
and part of
Madhya Pradesh
Madhya Pradesh (, ; meaning 'central province') is a state in central India. Its capital is Bhopal, and the largest city is Indore, with Jabalpur, Ujjain, Gwalior, Sagar, and Rewa being the other major cities. Madhya Pradesh is the seco ...
. His successor and brother
Kanha (or Krishna) further extended his kingdom to the west and the south. He was succeeded by Satakarni I, who defeated the
Shunga dynasty of North India. His successor,
Gautamiputra Satakarni
Gautamiputra Satakarni (Brahmi: 𑀕𑁄𑀢𑀫𑀺𑀧𑀼𑀢 𑀲𑀸𑀢𑀓𑀡𑀺, ''Gotamiputa Sātakaṇi'', IAST: ) was a ruler of the Satavahana Empire in present-day Deccan region of India. He was mentioned as the important an ...
, defeated the invading
Indo-Scythians
Indo-Scythians (also called Indo-Sakas) were a group of nomadic Iranian peoples of Scythian origin who migrated from Central Asia southward into modern day Pakistan and Northwestern India from the middle of the 2nd century BCE to the 4th centu ...
,
Indo-Parthians
The Indo-Parthian Kingdom was a Parthian kingdom founded by Gondophares, and active from 19 CE to c. 226 CE. At their zenith, they ruled an area covering parts of eastern Iran, various parts of Afghanistan and the northwest regions of the India ...
and
Indo-Greeks
The Indo-Greek Kingdom, or Graeco-Indian Kingdom, also known historically as the Yavana Kingdom (Yavanarajya), was a Hellenistic period, Hellenistic-era Ancient Greece, Greek kingdom covering various parts of Afghanistan and the northwestern r ...
. His empire extended up to Banavasi in the south, and included Maharashtra,
Konkan
The Konkan ( kok, कोंकण) or Kokan () is a stretch of land by the western coast of India, running from Damaon in the north to Karwar in the south; with the Arabian Sea to the west and the Deccan plateau in the east. The hinterland ...
,
Saurashtra,
Malwa
Malwa is a historical region of west-central India occupying a plateau of volcanic origin. Geologically, the Malwa Plateau generally refers to the volcanic upland north of the Vindhya Range. Politically and administratively, it is also syn ...
, west
Rajasthan
Rajasthan (; lit. 'Land of Kings') is a state in northern India. It covers or 10.4 per cent of India's total geographical area. It is the largest Indian state by area and the seventh largest by population. It is on India's northwestern s ...
and Vidharbha. Later, Satavahana rulers lost some of these territories. Satavahana power revived briefly under
Yajna Sri Satakarni
Yajna Sri Satakarni (Brahmi: 𑀲𑀺𑀭𑀺 𑀬𑀜 𑀲𑀸𑀢𑀓𑀡𑀺 ''Siri Yaña Sātakaṇi''), also known as Gautamiputra Yajna Sri, was an Indian ruler of the Satavahana dynasty. He was the brother of Vashishtiputra Satakarni. Hi ...
but declined after his death.
Mahameghavahana dynasty
The
Mahameghavahana dynasty
The Mahameghavahana dynasty (, 2nd or 1st century BC to early 4th century CE) was an ancient ruling dynasty of Kalinga after the decline of the Maurya Empire. In the first century B.C., Mahameghavahana, a king of Chedirastra (or Cetarattha, i. ...
was an ancient ruling dynasty of Kalinga after the decline of the Mauryan Empire. The third ruler of the dynasty,
Khārabēḷa, conquered much of India in a series of campaigns at the beginning of the common era. Kaḷingan military might was reinstated by Khārabēḷa. Under Khārabēḷa's generalship, the Kaḷinga state had a formidable maritime reach with trade routes linking it to the then-Simhala (Sri Lanka), Burma (Myanmar), Siam (Thailand), Vietnam, Kamboja (Cambodia), Borneo, Bali, Samudra (Sumatra) and Yawadvipa (Java). Khārabēḷa led many successful campaigns against states of Magadha, Anga, Satavahanas and the South Indian regions of Pandyan Empire and expanded Kaḷinga as far as the Ganges and the Kaveri.
The Kharavelan state had a formidable maritime empire with trading routes linking it to Sri Lanka, Burma, Thailand, Vietnam, Cambodia, Borneo, Bali, Sumatra and Java. Colonists from Kalinga settled in Sri Lanka, Burma, as well as the Maldives and Maritime Southeast Asia. Even today Indians are referred to as Keling in Malaysia because of this.
The main source of information about Khārabeḷa is his famous seventeen line rock-cut Hātigumphā inscription in a cave in the Udayagiri hills near Bhubaneswar, Odisha. According to the inscription, he attacked Rajagriha in Magadha, thus defeating the
Indo-Greek
The Indo-Greek Kingdom, or Graeco-Indian Kingdom, also known historically as the Yavana Kingdom (Yavanarajya), was a Hellenistic-era Greek kingdom covering various parts of Afghanistan and the northwestern regions of the Indian subcontinent ( ...
king
Demetrius I of Bactria
Demetrius I Anicetus ( grc, Δημήτριος Ἀνίκητος, Dēmētrios Anikētos, "the unconquered"), also called Damaytra was a Greco-Bactrian and later Indo-Greek king (Yona in Pali language, "Yavana" in Sanskrit) (reigned c. 200–167 ...
to retreat to Mathura.
Gupta dynasty
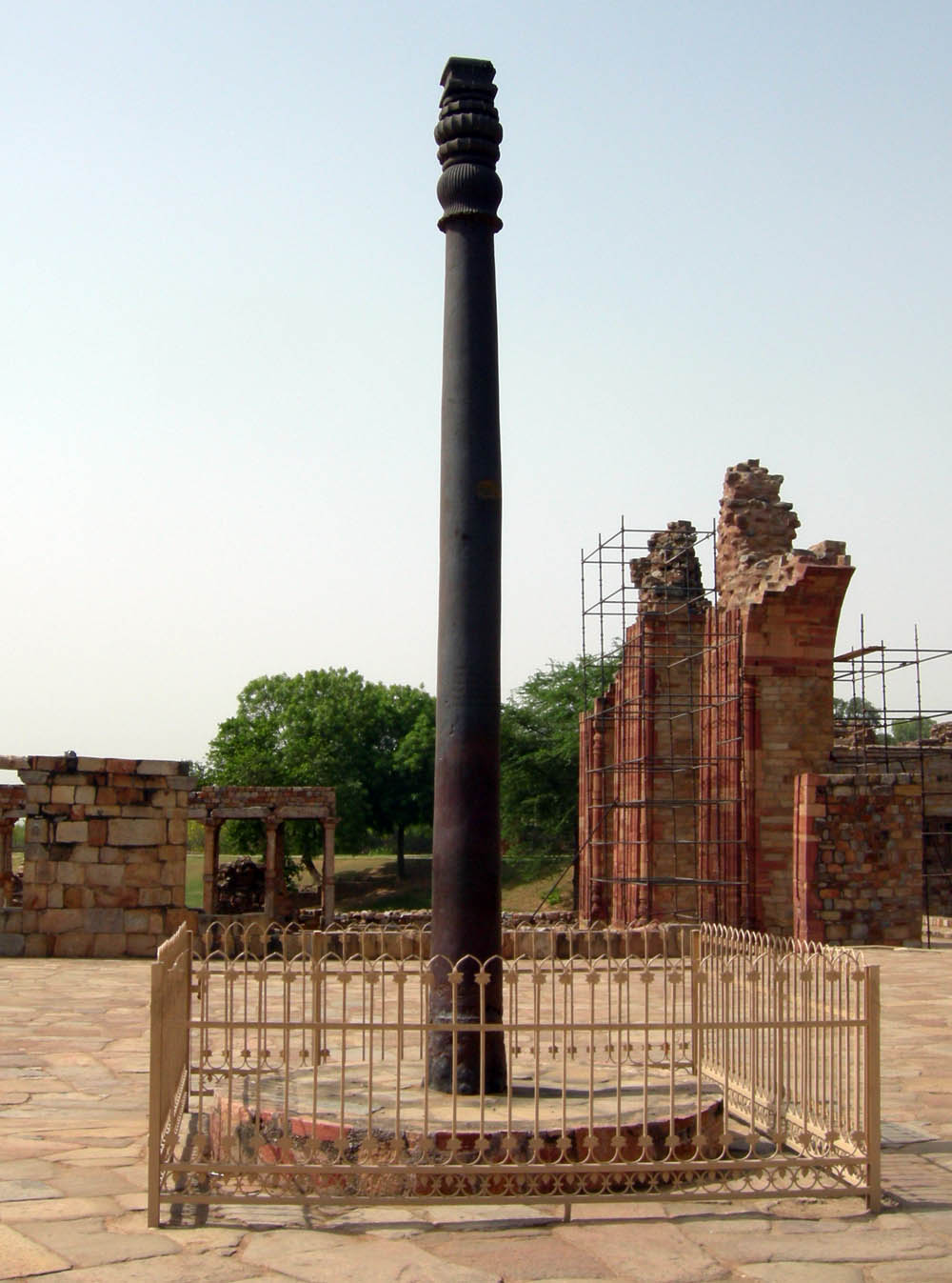


''Siva-Dhanur-veda'' discusses the military of the
Gupta Empire
The Gupta Empire was an ancient Indian empire which existed from the early 4th century CE to late 6th century CE. At its zenith, from approximately 319 to 467 CE, it covered much of the Indian subcontinent. This period is considered as the Gold ...
. The Guptas relied less on armoured war elephants compared to previous south Asian empires. The use of
chariots had declined heavily by the time of the Guptas, as they had not proved very useful against the
Greeks
The Greeks or Hellenes (; el, Έλληνες, ''Éllines'' ) are an ethnic group and nation indigenous to the Eastern Mediterranean and the Black Sea regions, namely Greece, Cyprus, Albania, Italy, Turkey, Egypt, and, to a lesser extent, oth ...
,
Scythians
The Scythians or Scyths, and sometimes also referred to as the Classical Scythians and the Pontic Scythians, were an ancient Eastern
* : "In modern scholarship the name 'Sakas' is reserved for the ancient tribes of northern and eastern Centra ...
, and other invaders. Guptas utilised famously used cavalry archers, and it became the prestige arm of the military as evidenced by coinage. heavy
cavalry clad in mail armour and equipped with
maces and lances, who would have used shock action to break the enemy line.
They also employed
infantry
Infantry is a military specialization which engages in ground combat on foot. Infantry generally consists of light infantry, mountain infantry, motorized infantry & mechanized infantry, airborne infantry, air assault infantry, and mar ...
similar to previous periods: Archers with a longbow composed of bamboo or metal and fired a long bamboo cane arrow with a metal head; iron shafts were used against armoured elephants. They also sometimes used fire arrows. Archers were frequently protected by infantry equipped with shields, javelins, and longswords. The Guptas also maintained a
navy
A navy, naval force, or maritime force is the branch of a nation's armed forces principally designated for naval and amphibious warfare; namely, lake-borne, riverine, littoral, or ocean-borne combat operations and related functions. It in ...
, allowing them to control regional waters.
Samudragupta
Samudragupta (Gupta script: ''Sa-mu-dra-gu-pta'', (c. 335–375 CE) was the second emperor of the Gupta Empire of ancient India, and is regarded among the greatest rulers of the dynasty. As a son of the Gupta emperor Chandragupta I and the ...
seized the kingdoms of
Ahichchhatra and
Padmavati early in his reign. Later, he took the Kota kingdom and attacked the tribes in
Malvas, the
Yaudheya
Yaudheya (Brahmi script: 𑀬𑁅𑀥𑁂𑀬) or Yoddheya Gana (Yoddheya Republic) was an ancient militant confederation. The word Yaudheya is a derivative of the word from yodha meaning warriors.“Yaudheyas.” Ancient Communities of the Hima ...
s, the
Arjunayana
Arjunayana, Arjunavana, Arjunavayana or Arjunayanaka was an ancient republican people located in Punjab or north-eastern Rajasthan. They emerged as a political power during the Shunga period (). In the Allahabad Pillar Inscription of Samudragupta ...
s, the
Madura
Madura Island is an Indonesian island off the northeastern coast of Java. The island comprises an area of approximately (administratively 5,379.33 km2 including various smaller islands to the east, southeast and north that are administrati ...
s and the
Abhira
The Abhira tribe is mentioned in the ancient Indian epic Mahabharata. A historical people of the same name are mentioned in the ''Periplus of the Erythraean Sea''. They are thought to be people who moved in from eastern Iran in the aftermath of ...
s. He also subjugated the remnants of the
Kushan Empire. By his death in 380, he had conquered over twenty kingdoms.
4th century CE Sanskrit poet Kalidasa, credits
Chandragupta II with having conquered about twenty one kingdoms, both in and outside India. After finishing his campaign in the East and West India, he proceeded northwards, subjugated the Parasikas, then the
Hunas
Hunas or Huna (Middle Brahmi script: ''Hūṇā'') was the name given by the ancient Indians to a group of Central Asian tribes who, via the Khyber Pass, entered the Indian subcontinent at the end of the 5th or early 6th century. The Huna Kin ...
and the
Kambojas
Kamboja ( sa, कम्बोज) was a kingdom of Iron Age India that spanned parts of South and Central Asia, frequently mentioned in Sanskrit and Pali literature. Eponymous with the kingdom name, the Kambojas were an Indo-Iranian people o ...
tribes located in the west and east Oxus valleys respectively. of the
Indian subcontinent
The Indian subcontinent is a list of the physiographic regions of the world, physiographical region in United Nations geoscheme for Asia#Southern Asia, Southern Asia. It is situated on the Indian Plate, projecting southwards into the Indian O ...
; the Gupta empire was the most powerful empire in the world during his reign, at a time when the Roman Empire in the west was in decline.
Skandagupta
Skandagupta ( Gupta script: ''Ska-nda-gu-pta'', r. c. 455-467) was a Gupta Emperor of India. His Bhitari pillar inscription suggests that he restored the Gupta power by defeating his enemies, who may have been rebels or foreign invaders. He ...
faced with invading
Indo-Hephthalites
The Hephthalites ( xbc, ηβοδαλο, translit= Ebodalo), sometimes called the White Huns (also known as the White Hunas, in Iranian as the ''Spet Xyon'' and in Sanskrit as the ''Sveta-huna''), were a people who lived in Central Asia during th ...
or
White Huns, from the northwest. Skandagupta had warred against the Huns during the reign of his father, and was celebrated throughout the empire as a great warrior. He crushed the Huns invasion in 455, and managed to keep them at bay; however, the expense of the wars drained the empire's resources and contributed to its decline
The Classical age
Empire of Harsha
Emperor
Harsha
Harshavardhana ( IAST Harṣa-vardhana; c. 590–647 CE) was a Pushyabhuti emperor who ruled northern India from 606 to 647 CE. He was the son of Prabhakaravardhana who had defeated the Alchon Huna invaders, and the younger brother of Rajy ...
(606–647) ruled the
Empire of Harsha
Harshavardhana (IAST Harṣa-vardhana; c. 590–647 CE) was a Pushyabhuti emperor who ruled northern India from 606 to 647 CE. He was the son of Prabhakaravardhana who had defeated the Alchon Huna invaders, and the younger brother of Rajyava ...
covering northern India for over forty years. His father, a king of
Thaneswar
Thanesar city or old Kurukshetra city is a historic town and an important Hindu pilgrimage centre in Kurukshetra district of the state of Haryana in northern India. It is located in Kurukshetra district, approximately 160 km northwest of D ...
, had gained prominence by successful wars against the
Huns
The Huns were a nomadic people who lived in Central Asia, the Caucasus, and Eastern Europe between the 4th and 6th century AD. According to European tradition, they were first reported living east of the Volga River, in an area that was part ...
. Harsha had plans to conquer the whole of India, and carried on wars for thirty years with considerable success. By 612 he had built up a vast army with which he conquered nearly all
North India
North India is a loosely defined region consisting of the northern part of India. The dominant geographical features of North India are the Indo-Gangetic Plain and the Himalayas, which demarcate the region from the Tibetan Plateau and Central ...
up to the
Narmada river. In 620 he invaded the
Deccan Plateau
The large Deccan Plateau in southern India is located between the Western Ghats and the Eastern Ghats, and is loosely defined as the peninsular region between these ranges that is south of the Narmada river. To the north, it is bounded by th ...
but was repelled by
Pulakeshin II.
The Chalukyas and Pallavas

In
South India
South India, also known as Dakshina Bharata or Peninsular India, consists of the peninsular southern part of India. It encompasses the Indian states of Andhra Pradesh, Karnataka, Kerala, Tamil Nadu, and Telangana, as well as the union territ ...
, the
Chalukyas
The Chalukya dynasty () was a Classical Indian dynasty that ruled large parts of southern and central India between the 6th and the 12th centuries. During this period, they ruled as three related yet individual dynasties. The earliest dynas ...
and the
Pallavas
The Pallava dynasty existed from 275 CE to 897 CE, ruling a significant portion of the Deccan, also known as Tondaimandalam. The dynasty rose to prominence after the downfall of the Satavahana dynasty, with whom they had formerly served as f ...
gained prominence. The
Chalukya
The Chalukya dynasty () was a Classical Indian dynasty that ruled large parts of southern and central India between the 6th and the 12th centuries. During this period, they ruled as three related yet individual dynasties. The earliest dynasty ...
ruler Pulakeshin II's expansionism started with minor campaigns against the
Alupas
The Alupa dynasty (ಅಳುಪೆರ್, ಆಳ್ವೆರ್) (circa 2nd century C.E to 15th century C.E) was an ancient ruling dynasty of India. The kingdom they ruled was known as ''Alvakheda Arusasira'' and its territory spanned the coa ...
,
Gangas
The Ganges ( ) (in India: Ganga ( ); in Bangladesh: Padma ( )). "The Ganges Basin, known in India as the Ganga and in Bangladesh as the Padma, is an international river to which India, Bangladesh, Nepal and China are the riparian states." is ...
and others. He defeated the Pallava king
Mahendravarman and conquered the
Cheras and the
Pandyas. His greatest military success, the defeat of Harshavardhana (also known as Harsha), depleted his treasury, forcing him to end his expansionist campaigns.
The Pallava king
Narasimhavarman vowed to avenge Mahendravarman's defeat by Pulakeshin II. He invaded
Vatapi
Badami, formerly known as Vatapi, is a town and headquarters of a taluk by the same name, in the Bagalkot district of Karnataka, India. It was the regal capital of the Badami Chalukyas from CE 540 to 757. It is famous for its rock cut monuments ...
with an army headed by his general Paranjothi. He defeated the Chalukyas, killing Pulakeshin II in 642. Clashes between the Chalukyas and the Pallavas continued for a century, until the Chalukya king
Vikramaditya II
Vikramaditya II (reigned 733 – 744 CE) was the son of King Vijayaditya and ascended the Badami Chalukya throne following the death of his father. This information comes from the Lakshmeshwar inscriptions in Kannada dated 13 January 735 A.D ...
won a decisive victory against the Pallavas in 740. The
Rashtrakutas
Rashtrakuta ( IAST: ') (r. 753-982 CE) was a royal Indian dynasty ruling large parts of the Indian subcontinent between the sixth and 10th centuries. The earliest known Rashtrakuta inscription is a 7th-century copper plate grant detailing the ...
overthrew the Chalukya empire in 750. During the 970s,
Tailapa II
Tailapa II (r. c. 973-997), also known as Taila II and by his title ''Ahavamalla'', was the founder of the Western Chalukya dynasty in southern India. Tailapa claimed descent from the earlier Chalukyas of Vatapi, and initially ruled as a Rashtr ...
overthrew the
Rashtrakutas and recovered most of the
Chalukya Empire, except for
Gujarat
Gujarat (, ) is a state along the western coast of India. Its coastline of about is the longest in the country, most of which lies on the Kathiawar peninsula. Gujarat is the fifth-largest Indian state by area, covering some ; and the ninth ...
. The Chalukyas of this period are known as the Kalyani Chalukyas, as
Kalyani was their capital. They clashed intermittently with the
Cholas.
The Chola Empire
The
Cholas were the first rulers of the Indian subcontinent to maintain a navy and use it to expand their dominion overseas.
Vijayalaya Chola
Vijayalaya Chola ( Tamil: விஜயாலய சோழன்) was a king of South India () who founded the imperial Chola Empire. He ruled over the region to the north of the river Kaveri.
Dark age of Cholas
The ancient Chola kingdom once ...
defeated the Pallavas and captured
Thanjavur
Thanjavur (), also Tanjore, Pletcher 2010, p. 195 is a city in the Indian state of Tamil Nadu. Thanjavur is the 11th biggest city in Tamil Nadu. Thanjavur is an important center of South Indian religion, art, and architecture. Most of the Gr ...
. In the early 10th century the Chola king
Parantaka I
Parantaka Chola I (Tamil : பராந்தக சோழன் I) (873 CE–955 CE) was a Chola emperor who ruled for forty-eight years, annexing Pandya by defeating Rajasimhan II. The best part of his reign was marked by increasing success ...
defeated the
Pandyan king
Maravarman Rajasimha II
Maravarman Rajasimha II (''r. c.'' 900–915 AD) was the last major king of the early medieval Pandya kingdom (6th–10th century AD) of south India. He was the son and successor of Parantaka Viranarayana (''r. c.'' 880–900 AD).Sastri, K. A. ...
and invaded
Sri Lanka. The
Rashtrakuta ruler
Krishna III
Krishna III whose Kannada name was Kannara (r. 939 – 967 C.E.) was the last great warrior and able monarch of the Rashtrakuta dynasty of Manyakheta. He was a shrewd administrator and skillful military campaigner. He waged many wars to bring b ...
defeated and killed Parantaka I's son
Rajaditya
Rajaditya Chola (''fl.'' mid-10th century AD) was a Chola prince, son of king Parantaka I (r. 907–955) and a Chera/Kerala princess ( the Ko Kizhan AdigalNarayanan, M. G. S. ''Perumāḷs of Kerala.'' Thrissur (Kerala): CosmoBooks, 2013. 96- ...
in about 949.
Uttama Chola
Uttama was a Chola Emperor who ruled from 973 CE to 985 CE in present-day Tamil Nadu, India. According to Tiruvalangadu plates of Rajendra Chola, Madurantaka Uttama Chola's reign is placed after Aditya II. The latter may have been a co-regent ...
reigned 970–85. Inscriptions tell that at least from his time, Chola warriors wore waist coats of armour. Hence, one regiment was called ''Niyayam-Uttama-Chola-tterinda-andalakattalar''. Paluvettaraiyar Maravan Kandanar served as a general under Uttama and his predecessor,
Sundara.
Rajaraja Chola
Rajaraja I (947 CE – 1014 CE), born Arunmozhi Varman or Arulmozhi Varman and often described as Raja Raja the Great or Raja Raja Chozhan was a Chola emperor who reigned from 985 CE to 1014 CE. He was the most powerful Tamil king in South ...
began his military career with the conquest of the Cheras in the
Kandalur War
The battle of Kandalur salai (c. 988 CE), also spelled Kanthaloor salai, was a naval engagement of the Cholas under Rajaraja I (985—1014 CE) against the "salai" at Kandalur in Trivandrum Kerala.Noburu Karashmia (ed.), ''A Concise History of S ...
. He captured the Pandya ruler Amara Bhujanga, the town of
Vizhinjam
Vizhinjam is a region located in the city of Thiruvananthapuram, the capital of the state of Kerala in India. It is located 16 km south west from the city centre and 17 km south of Trivandrum International Airport along NH66. Adani Por ...
, and a part of Sri Lanka. In the 14th year of his reign (998–999) he conquered the
Gangas
The Ganges ( ) (in India: Ganga ( ); in Bangladesh: Padma ( )). "The Ganges Basin, known in India as the Ganga and in Bangladesh as the Padma, is an international river to which India, Bangladesh, Nepal and China are the riparian states." is ...
of
Mysore
Mysore (), officially Mysuru (), is a city in the southern part of the state of Karnataka, India. Mysore city is geographically located between 12° 18′ 26″ north latitude and 76° 38′ 59″ east longitude. It is located at an altitude of ...
, the
Nolambas of
Bellary
Bellary, officially Ballari, in the eponymous Bellary district, is a city in the state of Karnataka, India.
History
Bellary was a part of Rayalaseema (Ceded Districts) which was part of Madras Presidency till 1 November 1956.
The Ballari ...
and Eastern Mysore, Tadigaipadi,
Vengi
Vengi (or Venginadu) is a delta region spread over the Krishna and Godavari River, (also called Godavari and Krishna districts), the region is also known as Godavari Delta, that used to house world famous diamond mines in the Medieval period ...
,
Coorg, the Pandyas and the Chalukyas of the Deccan. During the next three years, he subdued
Quilon
Kollam (), also known by its former name Quilon , is an ancient seaport and city on the Malabar Coast of India bordering the Laccadive Sea, which is a part of the Arabian Sea. It is north of the state capital Thiruvananthapuram. The city ...
and the northern kingdom of
Kalinga Kalinga may refer to:
Geography, linguistics and/or ethnology
* Kalinga (historical region), a historical region of India
** Kalinga (Mahabharata), an apocryphal kingdom mentioned in classical Indian literature
** Kalinga script, an ancient writ ...
with the help of his son
Rajendra Chola I
Rajendra Chola I (; Middle Tamil: Rājēntira Cōḻaṉ; Classical Sanskrit: Rājēndradēva Cōla; Old Malay: ''Raja Suran''; c. 971 CE – 1044 CE), often referred to as Rajendra the Great, and also known as Gangaikonda Chola (Middle Tamil ...
. Rajendra later completed the conquest of Sri Lanka, crossed the
Ganges
The Ganges ( ) (in India: Ganga ( ); in Bangladesh: Padma ( )). "The Ganges Basin, known in India as the Ganga and in Bangladesh as the Padma, is an international river to which India, Bangladesh, Nepal and China are the riparian states." is ...
, and marched across
Kalinga Kalinga may refer to:
Geography, linguistics and/or ethnology
* Kalinga (historical region), a historical region of India
** Kalinga (Mahabharata), an apocryphal kingdom mentioned in classical Indian literature
** Kalinga script, an ancient writ ...
to
Bengal
Bengal ( ; bn, বাংলা/বঙ্গ, translit=Bānglā/Bôngô, ) is a geopolitical, cultural and historical region in South Asia, specifically in the eastern part of the Indian subcontinent at the apex of the Bay of Bengal, predom ...
. He sent out
a great naval expedition that occupied parts of
Java
Java (; id, Jawa, ; jv, ꦗꦮ; su, ) is one of the Greater Sunda Islands in Indonesia. It is bordered by the Indian Ocean to the south and the Java Sea to the north. With a population of 151.6 million people, Java is the world's mos ...
,
Malaya, and
Sumatra. The Cholas were brought down by the
Hoysalas
The Hoysala Empire was a Kannadiga power originating from the Indian subcontinent that ruled most of what is now Karnataka between the 10th and the 14th centuries. The capital of the Hoysalas was initially located at Belur, but was later moved ...
from the west and Pandyas from the south.
The Gurjar-Pratiharas, Palas and Rashtrakutas
The Arab scholar Sulaiman described the emperor of the
Rashtrakuta dynasty
Rashtrakuta ( IAST: ') (r. 753-982 CE) was a royal Indian dynasty ruling large parts of the Indian subcontinent between the sixth and 10th centuries. The earliest known Rashtrakuta inscription is a 7th-century copper plate grant detailing thei ...
as one of the four great kings of the world in the 9th century. In middle of 9th century, the
Palas
A ''palas'' () is a German term for the imposing or prestigious building of a medieval ''Pfalz'' or castle that contained the great hall. Such buildings appeared during the Romanesque period (11th to 13th century) and, according to Thompson ...
under
Devapala attacked the
Gurjara-Pratihara
The Gurjara-Pratihara was a dynasty that ruled much of Northern India from the mid-8th to the 11th century. They ruled first at Ujjain and later at Kannauj.
The Gurjara-Pratiharas were instrumental in containing Arab armies moving east of th ...
s. Led by
Mihir Bhoja, the Pratiharas and their allies defeated
Narayan Pala.
There were many battles between the Gurjar Pratiharas under Bhoj and the
Rashtrakutas
Rashtrakuta ( IAST: ') (r. 753-982 CE) was a royal Indian dynasty ruling large parts of the Indian subcontinent between the sixth and 10th centuries. The earliest known Rashtrakuta inscription is a 7th-century copper plate grant detailing the ...
under
Krishna II
Krishna II (reigned 878–914 CE) was king of the Rashtrakuta empire. He throne after the demise of his father Amoghavarsha I Nrupatunga. His Kannada name was Kannara.Reu (1933), p75 His queen was a Haihaya princess of Chedi called Mahadevi. ...
with mixed results. When the Rashtrakuta king
Indra III
Indra III (reigned 914–929 CE) was the grandson of Rashtrakuta Krishna II and son of Chedi princess Lakshmi. He became the ruler of the empire due to the early demise of his father Jagattunga.From the Sangli, Karhad, Deoli and Bagumra inscri ...
attacked
Kanauj
Kannauj ( Hindustani pronunciation: ənːɔːd͡ʒ is a city, administrative headquarters and a municipal board or Nagar Palika Parishad in Kannauj district in the Indian state of Uttar Pradesh. The city's name is a corrupted form of the cl ...
,
Mahipala I
Mahipala I (913–944) ascended the throne of Pratihara dynasty after his step brother Bhoja II. He was a son of Queen Mahidevi. Mahipala I was also known by the names: ''Ksitipala'', ''Vinayakapala'', ''Herambapala'' and ''Uttarapatha Swami ...
, Mihir Bhoj's successor, fled; he later returned.
Al-Masudi
Al-Mas'udi ( ar, أَبُو ٱلْحَسَن عَلِيّ ٱبْن ٱلْحُسَيْن ٱبْن عَلِيّ ٱلْمَسْعُودِيّ, '; –956) was an Arab historian, geographer and traveler. He is sometimes referred to as the "Herodotus ...
wrote that in 915, during Mahipala's rule, the Pratiharas were at war with the Muslims in the west and the Rashtrakutas in the south, and that the Gurjar Pratiharas had four armies of about 80,000 men each.
Arab conquest of Sindh
In 712, an Arab general, named Muhammad bin Qasim Al-Thaqafi (Arabic: محمد بن قاسم) (c. 31 December 695 – 18 July 715), attacked and conquered
Sindh kingdom which is mainly situated in Indus valley area (after partition, now in modern-day
Pakistan
Pakistan ( ur, ), officially the Islamic Republic of Pakistan ( ur, , label=none), is a country in South Asia. It is the world's fifth-most populous country, with a population of almost 243 million people, and has the world's second-lar ...
); by the time
Sindh was ruled by
Raja Dahir
Raja Dahiraud (; ''Raja Dahiraud ''; 663 – 712 CE) was the last Hindu ruler of Sindh in present-day Pakistan. In 711 CE his kingdom was invaded by the Umayyad Caliphate led by Muhammad bin Qasim where Dahiraud died while defending his ki ...
of the
Rai dynasty
The Rai dynasty (c. 489–632 CE) was a polity of ancient Sindh.
Scholarship
Pre-Islamic Sindh has been the subject of voluminous scholarship concerning the eve of Arab conquests; otherwise, the paucity of source materials remains a severe hi ...
, and this dynasty was at war with Arabs. Though they defeated several
Arab invasions before 712 CE, this time being deprived of local Buddhist people's support, Sindh was captured and the first step of Islamic foundation in India was created.
Chach Nama
''Chach Nama'' ( sd, چچ نامو; ur, چچ نامہ; "Story of the Chach"), also known as the ''Fateh nama Sindh'' ( sd, فتح نامه سنڌ; "Story of the conquest of Sindh"), and as ''Tareekh al-Hind wa a's-Sind'' ( ar, تاريخ اله� ...
( sd, چچ نامو), written by Kàzí Ismáíl briefly discusses the events. However, the South Indian emperor
Vikramaditya II
Vikramaditya II (reigned 733 – 744 CE) was the son of King Vijayaditya and ascended the Badami Chalukya throne following the death of his father. This information comes from the Lakshmeshwar inscriptions in Kannada dated 13 January 735 A.D ...
of the
Chalukya dynasty and the Pratiharas defeated the Arabs during the
Caliphate campaigns in India
In the first half of the 8th century CE, a series of battles took place between the Umayyad Caliphate and kingdoms to the east of the Indus river, in the Indian subcontinent.
Subsequent to the Arab conquest of Sindh in present-day Pakistan i ...
(738 CE) when they tried to move eastward.
Indian inscriptions confirm this invasion but record the Arab success only against the smaller states in
Gujarat
Gujarat (, ) is a state along the western coast of India. Its coastline of about is the longest in the country, most of which lies on the Kathiawar peninsula. Gujarat is the fifth-largest Indian state by area, covering some ; and the ninth ...
. They also record the defeat of the Arabs at two places. The southern army moving south into Gujarat was defeated at Navsari by the south Indian Emperor
Vikramaditya II
Vikramaditya II (reigned 733 – 744 CE) was the son of King Vijayaditya and ascended the Badami Chalukya throne following the death of his father. This information comes from the Lakshmeshwar inscriptions in Kannada dated 13 January 735 A.D ...
of the
Chalukya
The Chalukya dynasty () was a Classical Indian dynasty that ruled large parts of southern and central India between the 6th and the 12th centuries. During this period, they ruled as three related yet individual dynasties. The earliest dynasty ...
dynasty who sent his general
Pulakeshin to defeat the Arabs. The army that went east, reached Avanti whose ruler
Nagabhata I
Nagabhata I (r. c. 730 – 760 CE) was a king who founded the imperial Gurjara Pratihara dynasty of northern India. He ruled the Avanti (or Malava) region in present-day Madhya Pradesh, from his capital at Ujjain. He may have extended his con ...
of
Gurjara Pratihara
The Gurjara-Pratihara was a dynasty that ruled much of Northern India from the mid-8th to the 11th century. They ruled first at Ujjain and later at Kannauj.
The Gurjara-Pratiharas were instrumental in containing Arab armies moving east of the ...
utterly defeated the invaders. Arab forces failed to make any substantial gains in India and in the
Caliphate campaigns in India
In the first half of the 8th century CE, a series of battles took place between the Umayyad Caliphate and kingdoms to the east of the Indus river, in the Indian subcontinent.
Subsequent to the Arab conquest of Sindh in present-day Pakistan i ...
(730 CE), their army was severely defeated by the Indian kings. As a result, Arabs' territory got restricted to
Sindh in modern
Pakistan
Pakistan ( ur, ), officially the Islamic Republic of Pakistan ( ur, , label=none), is a country in South Asia. It is the world's fifth-most populous country, with a population of almost 243 million people, and has the world's second-lar ...
.
Ghaznavid invasion
In the early 11th century,
Mahmud of Ghazni conquered the Rajput Hindu Shahi kingdom in the North-west frontier in Afghanistan and Pakistan, and his raids into northern India weakened the
Pratihara
The Gurjara-Pratihara was a dynasty that ruled much of Northern India from the mid-8th to the 11th century. They ruled first at Ujjain and later at Kannauj.
The Gurjara-Pratiharas were instrumental in containing Arab armies moving east of the ...
kingdom, which was drastically reduced in size and came under the control of the
Chandelas
The Chandelas of Jejakabhukti was an Indian dynasty in Central India. The Chandelas ruled much of the Bundelkhand region (then called ''Jejakabhukti'') between the 9th and the 13th centuries. They belonged to the Chandel clan of the Rajputs.
T ...
. Mahmud sacked some temples across northern India, including the temple at Somnath in Gujarat, but his permanent conquests were limited to the Punjab. The early 11th century also saw the reign of the
polymath
A polymath ( el, πολυμαθής, , "having learned much"; la, homo universalis, "universal human") is an individual whose knowledge spans a substantial number of subjects, known to draw on complex bodies of knowledge to solve specific pro ...
king
Raja Bhoj
Bhoja (reigned c. 1010–1055 CE) was an Indian king from the Paramara dynasty. His kingdom was centered around the Malwa region in central India, where his capital Dhara-nagara (modern Dhar) was located. Bhoja fought wars with nearly all h ...
, the Paramara ruler of
Malwa
Malwa is a historical region of west-central India occupying a plateau of volcanic origin. Geologically, the Malwa Plateau generally refers to the volcanic upland north of the Vindhya Range. Politically and administratively, it is also syn ...
.
[John Merci, Kim Smith; James Leuck (1922). "Muslim conquest and the Rajputs". The Medieval History of India pg 67–115]
The Medieval era
Delhi Sultanate
The
Delhi Sultanate, under the
Khalji dynasty, repelled several invasions by the
Mongol Empire.
Zafar Khan, a general serving
Alauddin Khalji
Alaud-Dīn Khaljī, also called Alauddin Khilji or Alauddin Ghilji (), born Ali Gurshasp, was an emperor of the Khalji dynasty that ruled the Delhi Sultanate in the Indian subcontinent. Alauddin instituted a number of significant administrativ ...
, defeated the Mongols near
Jalandhar
Jalandhar is the third most-populous city in the Indian state of Punjab and the largest city in Doaba region. Jalandhar lies alongside the Grand Trunk Road and is a well-connected rail and road junction. Jalandhar is northwest of the state ...
in 1297. In 1299, Zafar Khan fought back a Mongol army of 200,000 soldiers but was killed in the process. Its last
sultan,
Ibrahim Lodi, died fighting the forces of
Babur in the
first battle of Panipat in 1526, ending the sultanate and paving the way for the foundation of the Mughal Empire.
The Rajputs
After Babur's victory over Ibrahim Lodi, the
Mewar ruler
Rana Sanga led a combined Rajput army of 20,000 intending to defeat
Babur and capture
Delhi
Delhi, officially the National Capital Territory (NCT) of Delhi, is a city and a union territory of India containing New Delhi, the capital of India. Straddling the Yamuna river, primarily its western or right bank, Delhi shares borders ...
. The Rajput army defeated the combined armies of Mughals and Afghans in
Battle of Bayana
The Battle of Bayana or the Siege of Bayana was a military conflict between the Rajput Confederacy under Rana Sanga on one side and Afghans of Bayana under Nizam Khan and Mughal advance guard, led by Abdul Aziz on other side.
Background
Babur' ...
. The Mughals had superior
artillery
Artillery is a class of heavy military ranged weapons that launch munitions far beyond the range and power of infantry firearms. Early artillery development focused on the ability to breach defensive walls and fortifications during siege ...
, which prevailed against the Rajput
cavalry yet Mughals won only when
Tomar
Tomar (), also known in English as Thomar (the ancient name of Tomar), is a city and a municipality in the Santarém district of Portugal. The town proper has a population of about 20,000. The municipality population in 2011 was 40,677, in an a ...
general betrayed Rana Sanga, resulting in his defeat by Babur at the
Battle of Khanua
The Battle of Khanwa was fought at Khanwa on March 16, 1527. It was fought between the invading Timurid forces of Babur and the Rajput confederacy led by Rana Sanga for suprermacy of Northern India. The battle was a major event in Medieva ...
(16 March 1527). During the reign Rana Sanga's son Rana Udai Singh II, Babur's grandson
Akbar conquered
Chittor
Chittorgarh (also Chittor or Chittaurgarh) is a major city in Rajasthan state of western India. It lies on the Berach River, a tributary of the Banas, and is the administrative headquarters of Chittorgarh District. It was a major stronghold ...
, the capital of
Mewar.
In the
Battle of Haldighati (21 June 1576) between Akbar and
Rana Pratap Singh, the Mughal army of 80,000 was headed by a Rajput,
Raja Man Singh
Man Singh I, popularly known as Mirza Raja Man Singh (21 December 1550 – 6 July 1614) was the 29th Kachwaha Rajput Raja of Amer, later known as Jaipur state, in Rajputana. He was the most powerful and trusted general of the Mughal empe ...
, and Akbar's son
Salim
Salim, Saleem or Selim may refer to:
People
*Salim (name), or Saleem or Salem or Selim, a name of Arabic origin
* Salim (poet) (1800–1866)
* Saleem (playwright) (fl. 1996)
*Selim I, Selim II and Selim III, Ottoman Sultans
* Selim people, an e ...
. The Rajput army's strength was 20,000. Rana Pratap reluctantly retreated with the help of his estranged brother Shakti Singh. His legendary horse
Chetak was killed in the battle. Later, Rana Pratap organized a small army of
Bhil
Bhil or Bheel is an ethnic group in western India. They speak the Bhil languages, a subgroup of the Western Zone of the Indo-Aryan languages. As of 2013, Bhils were the largest tribal group in India.
Bhils are listed as tribal people of t ...
tribals funded by a Jain businessman called Bhamashah and started a
guerrilla war
Guerrilla warfare is a form of irregular warfare in which small groups of combatants, such as paramilitary personnel, armed civilians, or irregulars, use military tactics including ambushes, sabotage, raids, petty warfare, hit-and-run tactics ...
against Akbar and won
Battle of Dewair (1582)
Pratap Singh I, popularly known as Maharana Pratap (c. 9 May 1540 – 19 January 1597), was a king of Mewar from the Sisodia dynasty. Pratap became a folk hero for his military resistance against the expansionism of the Mughal Empire under ...
. He retook large parts of Mewar but could not retake Chittor.
Muzaffarid dynasty

Sultan Muzaffar Shah I, the governor of
Gujarat
Gujarat (, ) is a state along the western coast of India. Its coastline of about is the longest in the country, most of which lies on the Kathiawar peninsula. Gujarat is the fifth-largest Indian state by area, covering some ; and the ninth ...
, established the
Muzaffarid dynasty in 1391. It expanded rapidly and peaked under
Sultan Mahmud I, who lost the
Battle of Diu to the Portuguese in 1509.
Calicut
Ruled by the
Zamorin
The Samoothiri (Anglicised as Zamorin; Malayalam: , Arabic: ''Sāmuri'', Portuguese: ''Samorim'', Dutch: ''Samorijn'', Chinese: ''Shamitihsi''Ma Huan's Ying-yai Sheng-lan: 'The Overall Survey of the Ocean's Shores' 433 Translated and Edited b ...
, the small
Hindu
Hindus (; ) are people who religiously adhere to Hinduism. Jeffery D. Long (2007), A Vision for Hinduism, IB Tauris, , pages 35–37 Historically, the term has also been used as a geographical, cultural, and later religious identifier for ...
Nair
The Nair , also known as Nayar, are a group of Indian Hindu castes, described by anthropologist Kathleen Gough as "not a unitary group but a named category of castes". The Nair include several castes and many subdivisions, not all of whom histo ...
kingdom of
Calicut
Kozhikode (), also known in English as Calicut, is a city along the Malabar Coast in the state of Kerala in India. It has a corporation limit population of 609,224 and a metropolitan population of more than 2 million, making it the second l ...
(
Malabar) welcomed the
Portuguese
Portuguese may refer to:
* anything of, from, or related to the country and nation of Portugal
** Portuguese cuisine, traditional foods
** Portuguese language, a Romance language
*** Portuguese dialects, variants of the Portuguese language
** Portu ...
in 1498 as traders but then fought several naval wars with Portugal in the 16th century. The office of Muslim naval chief in
Calicut
Kozhikode (), also known in English as Calicut, is a city along the Malabar Coast in the state of Kerala in India. It has a corporation limit population of 609,224 and a metropolitan population of more than 2 million, making it the second l ...
was known as the
Kunhali Marakkar
Kunjali Marakkar (alternatively spelled Kunhali Marakkar) was the title inherited by the Admiral of the fleet of the Samoothiri / Zamorin, the king of Kozhikode / Calicut, in present-day Kerala, India. There were four Marakkars whose war tacti ...
.
Vijayanagara Empire

The Italian traveler Niccolo de Conti wrote of the Emperor of the
Vijayanagara Empire
The Vijayanagara Empire, also called the Karnata Kingdom, was a Hindu empire based in the region of South India, which consisted the modern states of Karnataka, Andhra Pradesh, Tamil Nadu, Kerala, Goa and some parts of Telangana and Mahar ...
as the most powerful ruler of India in the 15th century. In 1509, the
Bahamani
The Bahmani Sultanate, or Deccan, was a Persianate Sunni Muslim Indian Kingdom located in the Deccan region. It was the first independent Muslim kingdom of the Deccan, Sultan declared
war
War is an intense armed conflict between states, governments, societies, or paramilitary groups such as mercenaries, insurgents, and militias. It is generally characterized by extreme violence, destruction, and mortality, using regular o ...
against the
Vijayanagara Empire
The Vijayanagara Empire, also called the Karnata Kingdom, was a Hindu empire based in the region of South India, which consisted the modern states of Karnataka, Andhra Pradesh, Tamil Nadu, Kerala, Goa and some parts of Telangana and Mahar ...
. His large coalition army was defeated by
Krishnadevaraya in a battle in which the Sultan was wounded. In 1510, Krishnadevaraya launched a counteroffensive against the Sultan at Kovelaconda; Yusuf Adil Shahi of
Bijapur died in the battle. In 1512, Krishnadevaraya captured
Raichur
Raichur (formerly Raichore) is a city and municipality in the district of Raichur in the Indian state of Karnataka. Raichur, located between Krishna and Tungabhadra rivers, is the headquarters of Raichur district. It is located 409 km fr ...
and
Gulbarga after defeating Barid-i-Mamalik, the titular head of the
Bahmani Sultanate, who escaped to
Bidar
Bidar (/ biːd̪ər/) is a city in the north-eastern part of Karnataka state in India. It is the headquarters of Bidar district, which borders Maharashtra and Telangana. It is a rapidly urbanising city in the wider ''Bidar Metropolitan area ...
. Later, Bidar also fell to Krishnadevaraya, who restored the Bahmani Sultan to his throne under the terms of their peace treaty.
Between 1512 and 1514, Krishnadevaraya subjugated the Palaigar of
Ummattur, who had rebelled against his brother. During this campaign, the
Gajapati of
Odisha
Odisha (English: , ), formerly Orissa ( the official name until 2011), is an Indian state located in Eastern India. It is the 8th largest state by area, and the 11th largest by population. The state has the third largest population of ...
attacked Vijayanagara and occupied two northeast provinces:
Udayagiri and
Kondavidu. Krishnadevaraya recaptured these lands between 1513 and 1518.
On 26 January 1565, the neighboring kingdoms of
Ahmednagar,
Berar Berar may refer to:
*Vidarbha, the eastern region of Maharashtra Province, India, historically known as Berar
*Berar Sultanate (1490–1596), one of the Deccan sultanates
*Berar Subah (1596–1724), a Subah of the Mughal Empire
*Berar Province (1724 ...
,
Bidar
Bidar (/ biːd̪ər/) is a city in the north-eastern part of Karnataka state in India. It is the headquarters of Bidar district, which borders Maharashtra and Telangana. It is a rapidly urbanising city in the wider ''Bidar Metropolitan area ...
,
Bijapur and
Golconda came together to treacherously defeat the Vijayanagar decisively in the
Battle of Talikota
The Battle of Talikota (23 January 1565) was a watershed battle fought between the Vijayanagara Empire and an alliance of the Deccan sultanates. The battle resulted in the defeat of Aliya Rama Raya which led to the eventual collapse of the poli ...
. The surviving Vijaynagar forces fled with a large treasury to re-establish their headquarters at
Vellore Fort
Vellore Fort is a large 16th-century fort situated in heart of the Vellore city, in the States and territories of India, state of Tamil Nadu, India built by Vijayanagara Empire, Vijayanagara kings. The fort was at one time the headquarters of ...
in
Tamil Nadu
Tamil Nadu (; , TN) is a state in southern India. It is the tenth largest Indian state by area and the sixth largest by population. Its capital and largest city is Chennai. Tamil Nadu is the home of the Tamil people, whose Tamil language ...
and
Chandragiri
Chandragiri is a suburb and neighbourhood of Tirupati and located in Tirupati district of the Indian state of Andhra Pradesh. It is a part of Tirupati urban agglomeration and a major growing residential area in Tirupati It is the mandal headqua ...
(
Andhra Pradesh
Andhra Pradesh (, abbr. AP) is a state in the south-eastern coastal region of India. It is the seventh-largest state by area covering an area of and tenth-most populous state with 49,386,799 inhabitants. It is bordered by Telangana to the ...
) near
Tirupathi. It would be here that the British would seek a land grant to establish the
English East India Company Fort St. George in
Madras.
Later, the Vijayanagara's southern Telugu governors, in present-day
Tamil Nadu
Tamil Nadu (; , TN) is a state in southern India. It is the tenth largest Indian state by area and the sixth largest by population. Its capital and largest city is Chennai. Tamil Nadu is the home of the Tamil people, whose Tamil language ...
, became independent. They became the
Gingee Nayaks in
Gingee Fort
Gingee Fort or Senji Fort (also known as Chenji, Chanchi, Jinji or Senchi) in Tamil Nadu, India is one of the surviving forts in Tamil Nadu, India. It lies in Villupuram District, from the state capital, Chennai, and is close to the Union Terr ...
, the
Tanjore Nayaks
The Thanjavur Nayak kingdom or Thanjavur Nayak dynasty were the rulers of Thanjavur in the 15th and 17th centuries. The Nayaks of the Balija social group, were originally appointed as provincial governors by the Vijayanagara Emperor in the 15t ...
, and the
Nayaks of Madurai.
Ahom Kingdom
Ahom Kingdom (1228–1826) was a kingdom and tribe which rose to prominence in present-day
Assam
Assam (; ) is a state in northeastern India, south of the eastern Himalayas along the Brahmaputra and Barak River valleys. Assam covers an area of . The state is bordered by Bhutan and Arunachal Pradesh to the north; Nagaland and Manipur ...
early in the thirteenth century. They ruled much of Assam from the 13th century until the establishment of British rule in 1838.
The Ahoms brought with them a tribal religion and a language of their own, however they later merged with the
Hindu
Hindus (; ) are people who religiously adhere to Hinduism. Jeffery D. Long (2007), A Vision for Hinduism, IB Tauris, , pages 35–37 Historically, the term has also been used as a geographical, cultural, and later religious identifier for ...
religion.
From thirteenth until seventeenth century, repeated attempts were made by the Muslim rulers of Delhi to invade and subdue Ahoms, however the Ahoms managed to maintain their independence and ruled themselves for nearly 600 years.
Mughal Empire

The
Mughal Empire
The Mughal Empire was an early-modern empire that controlled much of South Asia between the 16th and 19th centuries. Quote: "Although the first two Timurid emperors and many of their noblemen were recent migrants to the subcontinent, the d ...
, one of the states
Age of the Islamic Gunpowders
The gunpowder empires, or Islamic gunpowder empires, is a collective term coined by Marshall G. S. Hodgson and William H. McNeill at the University of Chicago, referring to three Muslim empires: the Ottoman Empire, Safavid Empire and the Mugha ...
began in 1526 with the overthrow of Ibrahim Lodi and encompassed most of South Asia by the late 17th and early 18th centuries. Allied with the local rulers, it extended from
Bengal
Bengal ( ; bn, বাংলা/বঙ্গ, translit=Bānglā/Bôngô, ) is a geopolitical, cultural and historical region in South Asia, specifically in the eastern part of the Indian subcontinent at the apex of the Bay of Bengal, predom ...
in the east to
Kabul
Kabul (; ps, , ; , ) is the capital and largest city of Afghanistan. Located in the eastern half of the country, it is also a municipality, forming part of the Kabul Province; it is administratively divided into 22 municipal districts. Acco ...
in the west,
Kashmir in the north to the
Kaveri
The Kaveri (also known as Cauvery, the anglicized name) is one of the major Indian rivers flowing through the states of Karnataka and Tamil Nadu. The Kaveri river rises at Talakaveri in the Brahmagiri (hill), Karnataka, Brahmagiri range in th ...
basin in the south, a territory of over at its height. Its population at that time has been estimated at between 110 and 130 million. In the year 1540, then
Mughal Emperor
The Mughal emperors ( fa, , Pādishāhān) were the supreme heads of state of the Mughal Empire on the Indian subcontinent, mainly corresponding to the modern countries of India, Pakistan, Afghanistan and Bangladesh. The Mughal rulers styled t ...
Humayun
Nasir-ud-Din Muhammad ( fa, ) (; 6 March 1508 – 27 January 1556), better known by his regnal name, Humāyūn; (), was the second emperor of the Mughal Empire, who ruled over territory in what is now Eastern Afghanistan, Pakistan, Northe ...
was defeated by
Sher Shah Suri
Sher Shah Suri ( ps, شیرشاه سوری)
(1472, or 1486 – 22 May 1545), born Farīd Khān ( ps, فرید خان)
, was the founder of the Sur Empire in India, with its capital in Sasaram in modern-day Bihar. He standardized the silver coin ...
, and forced to retreat to
Kabul
Kabul (; ps, , ; , ) is the capital and largest city of Afghanistan. Located in the eastern half of the country, it is also a municipality, forming part of the Kabul Province; it is administratively divided into 22 municipal districts. Acco ...
. Suris and their adviser, the Hindu emperor
Hem Chandra Vikramaditya
Hemu (; also known as Hemu Vikramaditya and Hemchandra Vikramaditya; died 5 November 1556) was an Indian emperor who previously served as a general and Wazir of Adil Shah Suri of Sur Empire during a period in Indian history when Mughals and ...
, also called Hemu, ruled North India from 1540 to 1556. Hemu established a 'Hindu' empire briefly from Delhi in 1556.
The "classic period" of the empire started in 1556 with the accession of
Akbar the Great and ended with the death of Emperor
Aurangzeb in 1707, although the dynasty continued for another 150 years. During this period, the empire was marked by centralized administration and active culture. Following 1725 the empire declined rapidly, weakened by wars of succession; famine and local revolts fueled by it; the growth of religious intolerance; the rise of the
Maratha Empire
The Maratha Empire, also referred to as the Maratha Confederacy, was an early modern Indian confederation that came to dominate much of the Indian subcontinent in the 18th century. Maratha rule formally began in 1674 with the coronation of Sh ...
; and finally
British colonialism
The British Empire was composed of the dominions, colonies, protectorates, mandates, and other territories ruled or administered by the United Kingdom and its predecessor states. It began with the overseas possessions and trading posts est ...
. The last Mughal emperor,
Bahadur Shah II, whose rule was restricted to the city of
Delhi
Delhi, officially the National Capital Territory (NCT) of Delhi, is a city and a union territory of India containing New Delhi, the capital of India. Straddling the Yamuna river, primarily its western or right bank, Delhi shares borders ...
, was imprisoned and exiled by the British after the
Indian Rebellion of 1857
The Indian Rebellion of 1857 was a major uprising in India in 1857–58 against the rule of the British East India Company, which functioned as a sovereign power on behalf of the British Crown. The rebellion began on 10 May 1857 in the fo ...
.
The Marathas
In 1674,
Shivaji Bhosale carved an independent Maratha zone around
Pune
Pune (; ; also known as Poona, ( the official name from 1818 until 1978) is one of the most important industrial and educational hubs of India, with an estimated population of 7.4 million As of 2021, Pune Metropolitan Region is the largest i ...
, Maharashtra, from the
Bijapur Sultanate
The Adil Shahi or Adilshahi, was a Shia,Salma Ahmed Farooqui, ''A Comprehensive History of Medieval India: From Twelfth to the Mid-Eighteenth Century'', (Dorling Kindersley Pvt Ltd., 2011), 174. and later Sunni Muslim,Muhammad Qasim Firishta's T ...
and, with that began the emergence of the Marathas as the most important power in India that filled the vacuum created by the decline of the Mughal Empire. Shivaji established an effective civil and military administration. After a lifetime of conquest and
guerrilla warfare with the Mughal emperor
Aurangzeb, Shivaji died in 1680, leaving behind a kingdom of great but ill-defined extent. This was followed by a period of instability ending with Aurangzeb's death.
Shivaji was the second king in Indian history to maintain an active navy.
Kanhoji Angre
Kanhoji Angre (Marathi: कान्होजी आंग्रे, anʱod͡ʒiː aːŋɡɾe, also known as Conajee Angria or Sarkhel Angré (August 1669 – 4 July 1729) was a chief of the Maratha Navy in present-day India. Kanhoji became k ...
, the first Maratha naval chief under Shivaji's grandson
Shahuji
Chhatrapati Shahu Bhosale I (Pronunciation: �aːɦuː CE) was the fifth Chhatrapati of the Maratha Empire founded by his grandfather, Chhatrapati Shivaji Maharaj. Born into the Bhonsle family, he was the son of Chhatrapati Sambhaji Mahar ...
, controlled illegal entries into Maratha territory by
Dutch
Dutch commonly refers to:
* Something of, from, or related to the Netherlands
* Dutch people ()
* Dutch language ()
Dutch may also refer to:
Places
* Dutch, West Virginia, a community in the United States
* Pennsylvania Dutch Country
People E ...
,
English
English usually refers to:
* English language
* English people
English may also refer to:
Peoples, culture, and language
* ''English'', an adjective for something of, from, or related to England
** English national ide ...
and
Portuguese
Portuguese may refer to:
* anything of, from, or related to the country and nation of Portugal
** Portuguese cuisine, traditional foods
** Portuguese language, a Romance language
*** Portuguese dialects, variants of the Portuguese language
** Portu ...
commercial ships on the Western coast of India in the early 18th century. He remained undefeated until his death in 1729.
Although the descendants of Shivaji continued to rule, the office of the
Peshwa
The Peshwa (Pronunciation: e(ː)ʃʋaː was the appointed (later becoming hereditary) prime minister of the Maratha Empire of the Indian subcontinent. Originally, the Peshwas served as subordinates to the Chhatrapati (the Maratha king); later ...
, or the
prime minister
A prime minister, premier or chief of cabinet is the head of the cabinet and the leader of the ministers in the executive branch of government, often in a parliamentary or semi-presidential system. Under those systems, a prime minister i ...
, became the focus of Maratha power and patronage. The Peshwas were the effective rulers of the Maratha state and oversaw the period of greatest Maratha expansion, brought to an end by the Maratha's defeat by an
Afghan
Afghan may refer to:
*Something of or related to Afghanistan, a country in Southern-Central Asia
*Afghans, people or citizens of Afghanistan, typically of any ethnicity
** Afghan (ethnonym), the historic term applied strictly to people of the Pas ...
army at the
Third Battle of Panipat in 1761. The Marathas recovered their position as the dominant power in India by 1772 until the last Peshwa,
Baji Rao II
Shrimant Peshwa Baji Rao II (10 January 1775 – 28 January 1851) was the 13th and the last Peshwa of the Maratha Empire. He governed from 1795 to 1818. He was installed as a puppet ruler by the Maratha nobles, whose growing power prompted ...
, was defeated by the British in the
Third Anglo-Maratha War
The Third Anglo-Maratha War (1817–1819) was the final and decisive conflict between the English East India Company and the Maratha Empire in India. The war left the Company in control of most of India. It began with an invasion of Maratha ter ...
. With the defeat of the
Marathas
The Marathi people ( Marathi: मराठी लोक) or Marathis are an Indo-Aryan ethnolinguistic group who are indigenous to Maharashtra in western India. They natively speak Marathi, an Indo-Aryan language. Maharashtra was formed as a ...
, no native power represented a threat for the British any longer.
The end of the last Anglo-Maratha War marked the era of British paramountcy over India.
The Marathas also developed a potent ''
Navy
A navy, naval force, or maritime force is the branch of a nation's armed forces principally designated for naval and amphibious warfare; namely, lake-borne, riverine, littoral, or ocean-borne combat operations and related functions. It in ...
'' circa 1660s, which at its peak, dominated the territorial waters of the western coast of India from
Mumbai
Mumbai (, ; also known as Bombay — List of renamed Indian cities and states#Maharashtra, the official name until 1995) is the capital city of the Indian States and union territories of India, state of Maharashtra and the ''de facto'' fin ...
to
Savantwadi
Sawantwadi is a taluka (a unit of administration) in the Sindhudurg district in the Indian state of Maharashtra. The taluka headquarters is Sawantwadi which has a municipal council, which is a local civic body. Sawantwadi was formerly the capita ...
. It would engage in attacking the
British
British may refer to:
Peoples, culture, and language
* British people, nationals or natives of the United Kingdom, British Overseas Territories, and Crown Dependencies.
** Britishness, the British identity and common culture
* British English, ...
,
Portuguese
Portuguese may refer to:
* anything of, from, or related to the country and nation of Portugal
** Portuguese cuisine, traditional foods
** Portuguese language, a Romance language
*** Portuguese dialects, variants of the Portuguese language
** Portu ...
,
Dutch
Dutch commonly refers to:
* Something of, from, or related to the Netherlands
* Dutch people ()
* Dutch language ()
Dutch may also refer to:
Places
* Dutch, West Virginia, a community in the United States
* Pennsylvania Dutch Country
People E ...
, and
Siddi Naval ships and kept a check on their naval ambitions. The
Maratha Navy
The Maratha Navy was the naval wing of the armed forces of the Maratha Empire, which existed from around mid-17th century to mid-18th century in India.
Formative years
Historian Sir Jadunath Sarkar noted:
In medieval India, the Muslim rul ...
dominated until around the 1730s, was in a state of decline by 1770s, and ceased to exist by 1818.
The Jats
The
Kingdom of Bharatpur was founded by
Jats in northern India in 1680 AD. The formation of the
Kingdom of Bharatpur was a result of revolts by the
Jats living in the region around
Delhi
Delhi, officially the National Capital Territory (NCT) of Delhi, is a city and a union territory of India containing New Delhi, the capital of India. Straddling the Yamuna river, primarily its western or right bank, Delhi shares borders ...
,
Agra
Agra (, ) is a city on the banks of the Yamuna river in the Indian state of Uttar Pradesh, about south-east of the national capital New Delhi and 330 km west of the state capital Lucknow. With a population of roughly 1.6 million, Agra i ...
, and
Mathura
Mathura () is a city and the administrative headquarters of Mathura district in the Indian state of Uttar Pradesh. It is located approximately north of Agra, and south-east of Delhi; about from the town of Vrindavan, and from Govardhan. ...
against the imperial
Mughals
The Mughal Empire was an early-modern empire that controlled much of South Asia between the 16th and 19th centuries. Quote: "Although the first two Timurid emperors and many of their noblemen were recent migrants to the subcontinent, the d ...
.
Gokula
Gokula Singh (also known as Veer Gokula, or Gokal or Gokul Singh Jat; died on 1 January 1670 AD) was a Jat zamindar of Tilpat, belonging to Haga(Agre/Agha) gotra, in what is now the state of Haryana, India. The second of four sons born to Madu ...
, a local Jat
zamindar
A zamindar ( Hindustani: Devanagari: , ; Persian: , ) in the Indian subcontinent was an autonomous or semiautonomous ruler of a province. The term itself came into use during the reign of Mughals and later the British had begun using it as ...
of Mathura, lead the first of such revolts in 1669. Even though the
Jats were defeated and Gokula was executed, the movement was not completely crushed and discontent continued to simmer. Under
Maharaja Suraj Mal
Suraj Mal (13 February 1707 – 25 December 1763) was a Jat ruler of Bharatpur in present-day state of Rajasthan. Under him, the Jat rule covered the present-day districts of Agra, Aligarh, Bharatpur, Dholpur, Etawa, Hathras, Mainpuri, ...
, the
Kingdom of Bharatpur expanded to the present-day districts of
Agra
Agra (, ) is a city on the banks of the Yamuna river in the Indian state of Uttar Pradesh, about south-east of the national capital New Delhi and 330 km west of the state capital Lucknow. With a population of roughly 1.6 million, Agra i ...
,
Aligarh
Aligarh (; formerly known as Allygarh, and Kol) is a city in the state of Uttar Pradesh in India. It is the administrative headquarters of Aligarh district, and lies northwest of state capital Lucknow and approximately southeast of the cap ...
,
Bharatpur,
Dholpur
Dholpur is a city in the Dholpur district in Rajasthan state of India. It is situated on the left bank of the famous Chambal river. The city is the administrative headquarters of Dholpur District and was formerly seat of the Dholpur prin ...
,
Etawa,
Gurgaon,
Hathras,
Mainpuri
Mainpuri is a city in Mainpuri district in the Indian state of Uttar Pradesh. It is the administrative headquarters of Mainpuri district and is situated to the north-east of Agra and is 270 km from New Delhi. Mainpuri forms part of the an ...
,
Mathura
Mathura () is a city and the administrative headquarters of Mathura district in the Indian state of Uttar Pradesh. It is located approximately north of Agra, and south-east of Delhi; about from the town of Vrindavan, and from Govardhan. ...
,
Mewat,
Meerut
Meerut (, IAST: ''Meraṭh'') is a city in Meerut district of the western part of the Indian state of Uttar Pradesh. The city lies northeast of the national capital New Delhi, within the National Capital Region and west of the state capital ...
,
Rewari, and
Rohtak
Rohtak () is a city and the administrative headquarters of the Rohtak district in the Indian state of Haryana. It lies north-west of New Delhi and south of the state capital Chandigarh on NH 9(old NH 10). Rohtak forms a part of the National ...
.
Travancore Kingdom

King
Marthanda Varma
Anizham Thirunal Marthanda Varma (Malayalam: ) was the founding monarch of the southern Indian Kingdom of Travancore (previously Venadu) from 1729 until his death in 1758. He was succeeded by Rama Varma ("Dharma Raja") (1758–98).Subrahman ...
inherited the small feudal state of
Venad
Venad was a medieval kingdom lying between the Western Ghat mountains and the Arabian Sea on the south-western tip of India with its headquarters at the port city of Kollam/Quilon.Noburu Karashmia (ed.), A Concise History of South India: Is ...
in 1723 and built it into
Travancore
The Kingdom of Travancore ( /ˈtrævənkɔːr/), also known as the Kingdom of Thiruvithamkoor, was an Indian kingdom from c. 1729 until 1949. It was ruled by the Travancore Royal Family from Padmanabhapuram, and later Thiruvananthapuram. At ...
, one of the most powerful kingdoms in southern India. Marthanda Varma led the Travancore forces during the
Travancore-Dutch War of 1739–46, which culminated in the
Battle of Colachel. The defeat of the Dutch by Travancore is considered the earliest example of an organised power from
Asia
Asia (, ) is one of the world's most notable geographical regions, which is either considered a continent in its own right or a subcontinent of Eurasia, which shares the continental landmass of Afro-Eurasia with Africa. Asia covers an are ...
overcoming European military technology and tactics.
Marthanda Varma went on to conquer most of the petty principalities of the native rulers who had allied with the Dutch against him.
During
Dharma Raja
Dharma Raja Karthika Thirunal Rama Varma ( ml, ധർമ്മരാജാ കാർത്തിക തിരുനാൾ രാമവർമ്മ, 1724–17 February 1798) was the Maharajah of Travancore from 1758 until his death in 1798. He s ...
's reign,
Tipu Sultan
Tipu Sultan (born Sultan Fateh Ali Sahab Tipu, 1 December 1751 – 4 May 1799), also known as the Tiger of Mysore, was the ruler of the Kingdom of Mysore based in South India. He was a pioneer of rocket artillery.Dalrymple, p. 243 He i ...
invaded Travancore, but the commander-in-chief
Raja Kesavadas
Kunnathur Kesavan Raman Pillai, also known as Raja Kesavadas (1745-1799; Sanskrit ') was the Dewan of Travancore during the reign of Dharma Raja Karthika Thirunal Rama Varma. He is well known for his military tactics and administrative acumen ...
led Travancore to victory despite being outnumbered. This attack resulted in a Travancore-British alliance against Tipu in the
Third Anglo-Mysore War
The Third Anglo-Mysore War (1790–1792) was a conflict in South India between the Kingdom of Mysore and the British East India Company, the Kingdom of Travancore, the Maratha Empire, and the Nizam of Hyderabad. It was the third of four Angl ...
.
Velu Thampi Dalawa
Velayudhan Chempakaraman Thampi of Thalakulam (1765–1809) was the Dalawa or Prime Minister of the Indian kingdom of Travancore between 1802 and 1809 during the reign of Bala Rama Varma Kulasekhara Perumal. He is best known for being one ...
, the Dewan of Travancore,
fought against the British Empire but lost. Travancore became a British
vassal
A vassal or liege subject is a person regarded as having a mutual obligation to a lord or monarch, in the context of the feudal system in medieval Europe. While the subordinate party is called a vassal, the dominant party is called a suzerain ...
kingdom in 1805 following a treaty between Colonel Charles Macaulay and Dewan Velu Thampi.
Mysore Kingdom
The first iron-cased and metal-cylinder
rocket
A rocket (from it, rocchetto, , bobbin/spool) is a vehicle that uses jet propulsion to accelerate without using the surrounding air. A rocket engine produces thrust by reaction to exhaust expelled at high speed. Rocket engines work entirely fr ...
s were developed by the Mysorean army of the South Indian
Kingdom of Mysore in the 1780s.
[ The Mysoreans successfully used these iron-cased rockets against the larger forces of the ]British East India Company
The East India Company (EIC) was an English, and later British, joint-stock company founded in 1600 and dissolved in 1874. It was formed to trade in the Indian Ocean region, initially with the East Indies (the Indian subcontinent and South ...
during the Anglo-Mysore Wars
The Anglo-Mysore Wars were a series of four wars fought during the last three decades of the 18th century between the Sultanate of Mysore on the one hand, and the British East India Company (represented chiefly by the neighbouring Madras Pres ...
.["Hyder Ali, prince of Mysore, developed war rockets with an important change: the use of metal cylinders to contain the combustion powder. Although the hammered soft iron the Mysoreans used was crude, the bursting strength of the container of black powder was much higher than the earlier paper construction. Thus a greater internal pressure was possible, with a resultant greater thrust of the propulsive jet. The rocket body was lashed with leather thongs to a long bamboo stick. Range was perhaps up to three-quarters of a mile (more than a kilometre). Although individually these rockets were not accurate, dispersion error became less important when large numbers were fired rapidly in mass attacks. They were particularly effective against cavalry and were hurled into the air, after lighting, or skimmed along the hard dry ground. The Mysoreans continued to develop and expand the use of rocket weapons, reportedly increasing the number of rocket troops from 1,200 to a corps of 5,000. In battles at ]Seringapatam
Srirangapatna is a town and headquarters of one of the seven Taluks of Mandya district, in the Indian State of Karnataka. It gets its name from the Ranganthaswamy temple consecrated at around 984 CE. Later, under the British rule the city wa ...
in 1792 and 1799 these rockets were used with considerable effect against the British." – Encyclopædia Britannica (2008), ''rocket and missile''.
Rocket warfare.jpg, A painting showing the Mysorean army fighting the British forces with Mysorean rockets
Mysorean rockets were an Indian military weapon, the iron-cased rockets were successfully deployed for military use. The Mysorean army, under Hyder Ali and his son Tipu Sultan, used the rockets effectively against the British East India Compan ...
, which used metal cylinders to contain the combustion powder.
Indian soldier of Tipu Sultan's army.jpg, A Mysorean soldier from India, using his Mysorean rocket as a flagstaff (Robert Home
Robert Home (1752–1834) was a British oil portrait painter who travelled to the Indian subcontinent in 1791. During his travels he also painted historic scenes and landscapes.
Life and work
Born in Hull in the United Kingdom as the son of ...
, 1793/4).
Sikh Empire
Maharaja Ranjit Singh was a Sikh ruler of the sovereign country of Punjab
Punjab (; Punjabi: پنجاب ; ਪੰਜਾਬ ; ; also romanised as ''Panjāb'' or ''Panj-Āb'') is a geopolitical, cultural, and historical region in South Asia, specifically in the northern part of the Indian subcontinent, comprising a ...
and the Sikh Empire
The Sikh Empire was a state originating in the Indian subcontinent, formed under the leadership of Maharaja Ranjit Singh, who established an empire based in the Punjab. The empire existed from 1799, when Maharaja Ranjit Singh captured Lahor ...
. His father Maha Singh
Maha Singh ( pa, ਮਹਾਂ ਸਿੰਘ, Mahaṅ Singh; 1760 – 15 April 1790 or 1756 – April 1792), also spelt as Mahan or Mahn Singh, was the second chief of the Sukerchakia Misl. He was the eldest son of Sardar Charat Singh and Sardar ...
led Sukerchakia, a misl within the Sikh Confederacy
The Misls (derived from an Arabic word مِثْل meaning 'equal') were the twelve sovereign states of the Sikh Confederacy, which rose during the 18th century in the Punjab region in the northern part of the Indian subcontinent and is cit ...
. Born in 1780 in Gujranwala, Ranjit Singh succeeded his father at the age of 12. He united the Sikh factions into the Sikh Empire
The Sikh Empire was a state originating in the Indian subcontinent, formed under the leadership of Maharaja Ranjit Singh, who established an empire based in the Punjab. The empire existed from 1799, when Maharaja Ranjit Singh captured Lahor ...
and took the title "Maharaja" on 13 April 1801, to coincide with Baisakhi. Lahore
Lahore ( ; pnb, ; ur, ) is the second most populous city in Pakistan after Karachi and 26th most populous city in the world, with a population of over 13 million. It is the capital of the province of Punjab where it is the largest city ...
was his capital from 1799. In 1802 he conquered Amritsar, a holy city of the Sikh religion. In 1822 Ranjit Singh hired European mercenaries for the first time to train a part of his troops. He modernized his army, creating a military force whose power delayed the eventual British colonization of Punjab. The result was a powerful and heavily armed state. The Battle of Jamrud
The Battle of Jamrud was fought between the Emirate of Afghanistan and the Sikh Empire on 30 April 1837. It was the last effort made by Emir Dost Mohammad Khan to recapture the former Afghan winter capital of Peshawar. Afghan forces confronted the ...
in 1837 was a major setback for Ranjit Singh: his general Hari Singh Nalwa
Hari Singh Nalwa (1791–1837) was Commander-in-chief of the Sikh Khalsa Fauj, the army of the Sikh Empire. He is known for his role in the conquests of Kasur, Sialkot, Attock, Multan, Kashmir, Peshawar and Jamrud. Hari Singh Nalwa was respon ...
was killed, the Khyber Pass was established as the western limit of the Sikh Empire's influence.
Ranjit Singh died in 1839, and his empire crumbled under internal strife and poor governance by his heirs. On the east of his realm Gulab Singh
Gulab Singh Jamwal (1792–1857) was the founder of Dogra dynasty and the first Maharaja of the princely state of Jammu and Kashmir, the largest princely state under the British Raj, which was created after the defeat of the Sikh Empire in ...
extended Sikh authority in the Himalayas
The Himalayas, or Himalaya (; ; ), is a mountain range in Asia, separating the plains of the Indian subcontinent from the Tibetan Plateau. The range has some of the planet's highest peaks, including the very highest, Mount Everest. Over 10 ...
until stopped by the Qing Empire in the Sino-Sikh war (1841–1842). After the First Anglo-Sikh War
The First Anglo-Sikh War was fought between the Sikh Empire and the British East India Company in 1845 and 1846 in and around the Ferozepur district of Punjab. It resulted in defeat and partial subjugation of the Sikh empire and cession o ...
(1845–46), Punjab effectively ceased to be an independent state. The British Empire
The British Empire was composed of the dominions, colonies, protectorates, mandates, and other territories ruled or administered by the United Kingdom and its predecessor states. It began with the overseas possessions and trading posts e ...
annexed the Sikh Empire following the Second Anglo-Sikh War
The Second Anglo-Sikh War was a military conflict between the Sikh Empire and the British East India Company that took place in 1848 and 1849. It resulted in the fall of the Sikh Empire, and the annexation of the Punjab and what subsequently ...
(1848–49).
Colonial era
Company rule
The British Indian Army was raised to guard the factories of the British East India Company
The East India Company (EIC) was an English, and later British, joint-stock company founded in 1600 and dissolved in 1874. It was formed to trade in the Indian Ocean region, initially with the East Indies (the Indian subcontinent and South ...
. Following the fall of French Pondichéry in 1793, this was divided into Presidency armies of Bengal
Bengal ( ; bn, বাংলা/বঙ্গ, translit=Bānglā/Bôngô, ) is a geopolitical, cultural and historical region in South Asia, specifically in the eastern part of the Indian subcontinent at the apex of the Bay of Bengal, predom ...
, Madras and Bombay
Mumbai (, ; also known as Bombay — the official name until 1995) is the capital city of the Indian state of Maharashtra and the ''de facto'' financial centre of India. According to the United Nations, as of 2018, Mumbai is the second-m ...
in 1795. The Dutch trained the Nair
The Nair , also known as Nayar, are a group of Indian Hindu castes, described by anthropologist Kathleen Gough as "not a unitary group but a named category of castes". The Nair include several castes and many subdivisions, not all of whom histo ...
Brigade, the military of Travancore.
 During the
During the Indian Rebellion of 1857
The Indian Rebellion of 1857 was a major uprising in India in 1857–58 against the rule of the British East India Company, which functioned as a sovereign power on behalf of the British Crown. The rebellion began on 10 May 1857 in the fo ...
, some units of the Bengal Native Infantry and Cavalry mutinied against the British East India Company. However, the rebels received less support than they had expected from members of the Bombay and Madras Armies. A number of atrocities were perpetrated by the rebels, most infamously at the Siege of Cawnpore
The siege of Cawnpore was a key episode in the Indian rebellion of 1857. The besieged East India Company forces and civilians in Cawnpore (now Kanpur) were unprepared for an extended siege and surrendered to rebel forces under Nana Sahib in ret ...
. The rebellion ultimately failed because of lack of resources and coordination among the rebels. During their suppression of the rebellion, the British carried out numerous reprisals, and the revolt was largely quashed by 1858.
The British Raj
Following the Sepoy Mutiny, British rule in India was reorganised under the British Raj
The British Raj (; from Hindi ''rāj'': kingdom, realm, state, or empire) was the rule of the British Crown on the Indian subcontinent;
*
* it is also called Crown rule in India,
*
*
*
*
or Direct rule in India,
* Quote: "Mill, who was him ...
, made up of areas directly administered by the United Kingdom and princely states
A princely state (also called native state or Indian state) was a nominally sovereign entity of the British Indian Empire that was not directly governed by the British, but rather by an Indian ruler under a form of indirect rule, subject to ...
under the paramountcy
Suzerainty () is the rights and obligations of a person, state or other polity who controls the foreign policy and relations of a tributary state, while allowing the tributary state to have internal autonomy. While the subordinate party is calle ...
of the British Crown. Under terms of treaties with the Crown, these princely states were allowed some local autonomy in exchange for protection and representation in international affairs by the United Kingdom. The Raj included present-day India, Pakistan, and Bangladesh
Bangladesh (}, ), officially the People's Republic of Bangladesh, is a country in South Asia. It is the eighth-most populous country in the world, with a population exceeding 165 million people in an area of . Bangladesh is among the mos ...
.
After 1857, the Presidency armies were abolished in favour of a reconstituted British Indian Army under the control of the British Crown and the Viceroy
A viceroy () is an official who reigns over a polity in the name of and as the representative of the monarch of the territory. The term derives from the Latin prefix ''vice-'', meaning "in the place of" and the French word ''roy'', meaning " ...
. Many units were disbanded or reorganised, and new units of Sikhs, Gurkhas, and irregular horsemen were introduced. The majority of the Madras Native Infantry and Cavalry had their class compositions changed to North Indian tribes, considered more "martial" than the darker, shorter "thambis" who made up the majority of the Madras Presidency Army. Indian sepoys were banned from serving as officers or in the artillery corps. Recruiting focused more on Sikhs and Gurkhas, whom the British viewed as loyal. New caste-based and religion-based regiments were formed.
The British Indian Army consisted of members of all the major religious groups in India: Hindus
Hindus (; ) are people who religiously adhere to Hinduism. Jeffery D. Long (2007), A Vision for Hinduism, IB Tauris, , pages 35–37 Historically, the term has also been used as a geographical, cultural, and later religious identifier for ...
, Sikhs, Christians
Christians () are people who follow or adhere to Christianity, a monotheistic Abrahamic religion based on the life and teachings of Jesus Christ. The words '' Christ'' and ''Christian'' derive from the Koine Greek title ''Christós'' (Χρ ...
, and Muslims
Muslims ( ar, المسلمون, , ) are people who adhere to Islam, a monotheistic religion belonging to the Abrahamic tradition. They consider the Quran, the foundational religious text of Islam, to be the verbatim word of the God of Abrah ...
. The number of Sikhs in the army grew steadily with time as British commanders came to believe they were more loyal and martial, an impression reinforced by their conduct during the Sepoy Mutiny. The Sikhs, for their part, aligned with the British to prevent a resurgence of Mughal rule; Sikhs had been persecuted under the Mughal Empire.
The Indian Air Force was established in 1932.
World War I
 During
During World War I
World War I (28 July 1914 11 November 1918), often abbreviated as WWI, was one of the deadliest global conflicts in history. Belligerents included much of Europe, the Russian Empire, the United States, and the Ottoman Empire, with fightin ...
, over 800,000 volunteered for the army, and more than 400,000 volunteered for non-combat roles, compared with the pre-war annual recruitment of about 15,000 men. The Army saw action on the Western Front within a month of the start of the war, at the First Battle of Ypres
The First Battle of Ypres (french: Première Bataille des Flandres; german: Erste Flandernschlacht – was a battle of the First World War, fought on the Western Front around Ypres, in West Flanders, Belgium. The battle was part of the Firs ...
where Khudadad Khan
Subedar Khudadad Khan, VC (20 October 1888 – 8 March 1971) was a Pakistani and the recipient of the Victoria Cross (VC), the highest military award for gallantry in the face of the enemy given to British and Commonwealth forces. During t ...
became the first Indian to be awarded a Victoria Cross
The Victoria Cross (VC) is the highest and most prestigious award of the British honours system. It is awarded for valour "in the presence of the enemy" to members of the British Armed Forces and may be awarded posthumously. It was previously ...
. After a year of front-line duty, sickness and casualties had reduced the Indian Corps to the point where it had to be withdrawn. Nearly 700,000 Indians fought the Turks in the Mesopotamian campaign. Indian formations were also sent to East Africa, Egypt, and Gallipoli.
 Indian Army and
Indian Army and Imperial Service Troops
The Imperial Service Troops were forces raised by the princely states of the British Indian Empire. These troops were available for service alongside the Indian Army when such service was requested by the British government. At the beginning of ...
fought during the Sinai and Palestine Campaign's defence of the Suez Canal in 1915, at Romani
Romani may refer to:
Ethnicities
* Romani people, an ethnic group of Northern Indian origin, living dispersed in Europe, the Americas and Asia
** Romani genocide, under Nazi rule
* Romani language, any of several Indo-Aryan languages of the Roma ...
in 1916 and to Jerusalem
Jerusalem (; he, יְרוּשָׁלַיִם ; ar, القُدس ) (combining the Biblical and common usage Arabic names); grc, Ἱερουσαλήμ/Ἰεροσόλυμα, Hierousalḗm/Hierosóluma; hy, Երուսաղեմ, Erusałēm. i ...
in 1917. Indian units occupied the Jordan Valley and after the German spring offensive they became the major force in the Egyptian Expeditionary Force
The Egyptian Expeditionary Force (EEF) was a British Empire military formation, formed on 10 March 1916 under the command of General Archibald Murray from the Mediterranean Expeditionary Force and the Force in Egypt (1914–15), at the beginning ...
during the Battle of Megiddo and in the Desert Mounted Corps
The Desert Mounted Corps was an army corps of the British Army during the First World War, of three mounted divisions renamed in August 1917 by General Edmund Allenby, from Desert Column. These divisions which served in the Sinai and Pales ...
' advance to Damascus and on to Aleppo. Other divisions remained in India guarding the North-West Frontier and fulfilling internal security obligations.
One million Indian troops served abroad during the war. In total, 74,187 died,India Gate
The India Gate (formerly known as the All India War Memorial) is a war memorial located near the Rajpath on the eastern edge of the "ceremonial axis" of New Delhi, formerly called duty path. It stands as a memorial to 84,000 soldiers of the B ...
.
World War II
In 1939, the British Indian Army's strength was about 189,000, with about 3,000 British officers and 1,115 Indian officers. The army was expanded greatly to fight in World War II
World War II or the Second World War, often abbreviated as WWII or WW2, was a world war that lasted from 1939 to 1945. It involved the vast majority of the world's countries—including all of the great powers—forming two opposing ...
: by 1945, the strength of the Army had risen to about 2.5 million, with about 34,500 British officers and 15,740 Indian officers. The Army took part in campaigns in France, East Africa, North Africa, Syria, Tunisia
)
, image_map = Tunisia location (orthographic projection).svg
, map_caption = Location of Tunisia in northern Africa
, image_map2 =
, capital = Tunis
, largest_city = capital
, ...
, Malaya, Burma
Myanmar, ; UK pronunciations: US pronunciations incl. . Note: Wikipedia's IPA conventions require indicating /r/ even in British English although only some British English speakers pronounce r at the end of syllables. As John Wells explai ...
, Greece, Sicily
(man) it, Siciliana (woman)
, population_note =
, population_blank1_title =
, population_blank1 =
, demographics_type1 = Ethnicity
, demographics1_footnotes =
, demographi ...
and Italy. Particularly significant contributions came in the campaigns in Abyssinia and North Africa, against the Italians; at El Alamain and in Italy, against the Germans; and in the Burma Campaign against Japan. The army ultimately suffered 179,935 casualties: 24,338 killed, 64,354 wounded, 11,762 missing, and 79,481 taken risoner of war
During the war, Indian nationalist expatriates in Southeast Asia and the Japanese Army formed the Indian National Army (INA) to fight for Indian independence from Britain. For manpower, it relied on the approximately 45,000 Indian troops of the Indian Army whom the Japanese captured when Singapore fell in February 1942. Subhas Chandra Bose was parachuted in to lead the INA in 1943, and he greatly expanded the INA to include the mainly Tamil civilian Indian community in Malaya. He also negotiated a combat role for the INA from the reluctant Japanese, who were more inclined to use it intelligence and propaganda work. In 1944, INA units participated in the Japanese Army's offensives against British positions in the Arakan and the Imphal Plain. Not being a military man Bose – or "Netaji" (''respected leader'') naively believed that Indian soldiers of the Indian Army who deployed against the INA would flock to its standard. But these Indian troops stood fIrm, and actually defeated the INA. Despite this, Bose insisted that the INA be given an independent sector on the Irrawaddy in February 1945. Despite the desperate efforts of some INA troops, their sector was overrun, and desertions became commonplace. Militarily, the INA was finished. After the war, however, it made a political impact, due to the British decision to publicly court-martial three INA commanders. This was a miscalculation, because Indian nationalist politicians, who had previously come out against the INA, now whipped up popular sentiment for the release of the INA accused. Realizing their error, the British acquiesced. In this way, the INA was another sign that the Raj's days were numbered.
Post-war transition and the Dominion of India
At the end of the war in 1945, the Indian Army's officer corps included Indian Medical Service officer Hiraji Cursetji as its sole Indian major-general, one IMS brigadier, three Indian brigadiers in combatant arms and 220 other Indian officers in the temporary or acting ranks of colonel and lieutenant-colonel. From October 1945, the granting of regular commissions in the Indian Armed Forces was restricted to Indians, though provisions were made for the continued secondment of British officers for as long as was deemed necessary. In 1946, sailors of the Royal Indian Navy mutinied on board ships and in shore establishments, which had an impact across India. By early 1947, all three branches of the Indian Armed Forces had undergone large-scale demobilisation of over 1.25 million service personnel.
With Indian independence now a certainty and with a new Labour government recently elected in the UK, the Indianization of the armed forces continued to progress, though by June 1947, two months before independence, the Indian Army had only 14 Indian officers at the rank of brigadier serving in combatant arms, with no Indian flag, general or air officers in the combat arms of the armed services.
Republic of India
Major wars
The Republic of India has fought four wars with Pakistan and one border war with China.
First Indo-Pak war, 1947
 This is also called the First Kashmir War. The war started in October 1947 when Pakistan feared that the
This is also called the First Kashmir War. The war started in October 1947 when Pakistan feared that the Maharajah
Mahārāja (; also spelled Maharajah, Maharaj) is a Sanskrit title for a "great ruler", "great king" or " high king".
A few ruled states informally called empires, including ruler raja Sri Gupta, founder of the ancient Indian Gupta Empire, a ...
of the princely state of Kashmir and Jammu would accede to India. Following partition, states were left to choose whether to join India or Pakistan or to remain independent. Jammu and Kashmir, the largest of the princely states, had a predominantly Muslim population ruled by the Hindu Maharaja
Mahārāja (; also spelled Maharajah, Maharaj) is a Sanskrit title for a "great ruler", "great king" or " high king".
A few ruled states informally called empires, including ruler raja Sri Gupta, founder of the ancient Indian Gupta Empire, a ...
Hari Singh
Maharaja Sir Hari Singh (September 1895 – 26 April 1961) was the last ruling Maharaja of the princely state of Jammu and Kashmir.
Hari Singh was the son of Amar Singh and Bhotiali Chib. In 1923, following his uncle's death, Singh became ...
. Tribal forces with support from the army of Pakistan attacked and occupied parts of the princely state forcing the Maharajah to sign the Agreement to the accession of the princely state to the Dominion of India
The Dominion of India, officially the Union of India,* Quote: “The first collective use (of the word "dominion") occurred at the Colonial Conference (April to May 1907) when the title was conferred upon Canada and Australia. New Zealand and N ...
to get Indian military aid. The UN Security Council passed the Resolution 47 on 22 April 1948. The fronts solidified gradually along what came to be known as the Line of Control. A formal cease-fire was declared at 23:59 on the night of 1 January 1949.Jammu
Jammu is the winter capital of the Indian union territory of Jammu and Kashmir. It is the headquarters and the largest city in Jammu district of the union territory. Lying on the banks of the river Tawi, the city of Jammu, with an area of ...
and Ladakh
Ladakh () is a region administered by India as a union territory which constitutes a part of the larger Kashmir region and has been the subject of dispute between India, Pakistan, and China since 1947. (subscription required) Quote: "Jammu ...
) whereas Pakistan gained roughly a third of [
][
][
][
] Most neutral assessments, agree that India
India, officially the Republic of India (Hindi: ), is a country in South Asia. It is the seventh-largest country by area, the second-most populous country, and the most populous democracy in the world. Bounded by the Indian Ocean on the so ...
was the victor of the war
War is an intense armed conflict between states, governments, societies, or paramilitary groups such as mercenaries, insurgents, and militias. It is generally characterized by extreme violence, destruction, and mortality, using regular o ...
as it was able to conquer about two-thirds of the Kashmir including Kashmir valley, Jammu
Jammu is the winter capital of the Indian union territory of Jammu and Kashmir. It is the headquarters and the largest city in Jammu district of the union territory. Lying on the banks of the river Tawi, the city of Jammu, with an area of ...
and Ladakh
Ladakh () is a region administered by India as a union territory which constitutes a part of the larger Kashmir region and has been the subject of dispute between India, Pakistan, and China since 1947. (subscription required) Quote: "Jammu ...
.
Operation Polo, 1948
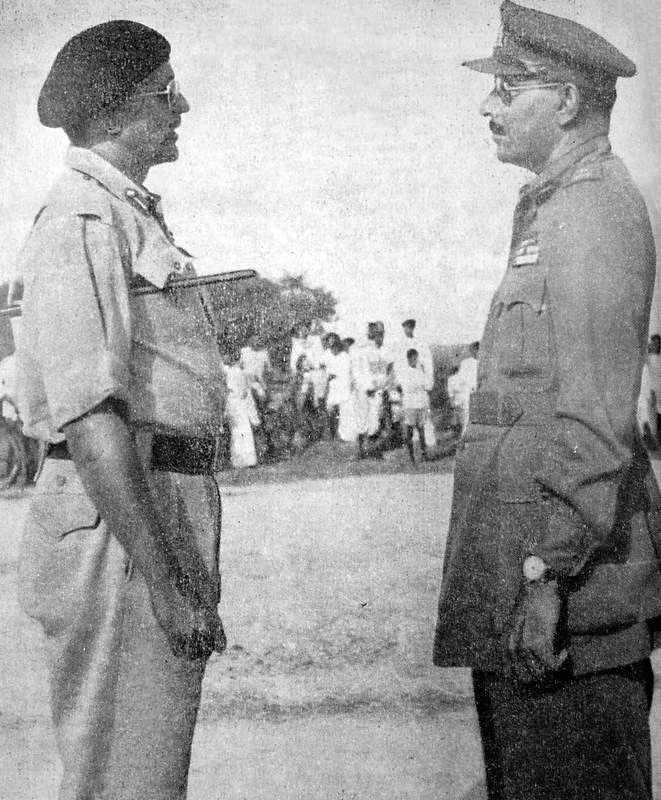 After the war with Pakistan, India turned its attention to the independent Hyderabad State. India perceived the nearby independent Muslim state and potential Pakistani ally as a threat. In a five-day operation, India reconquered and annexed Hyderabad.
After the war with Pakistan, India turned its attention to the independent Hyderabad State. India perceived the nearby independent Muslim state and potential Pakistani ally as a threat. In a five-day operation, India reconquered and annexed Hyderabad.
Liberation of Goa, 1961
In 1961 tension rose between India and Portugal over the Portuguese-occupied territory of Goa
Goa () is a state on the southwestern coast of India within the Konkan region, geographically separated from the Deccan highlands by the Western Ghats. It is located between the Indian states of Maharashtra to the north and Karnataka to the ...
, which India claimed for itself. After Portuguese police cracked down violently on a peaceful, unarmed demonstration for union with India, the Indian government decided to reconquer. A lopsided air, sea, and ground campaign resulted in the speedy surrender of Portuguese forces. Within 36 hours, 451 years of Portuguese colonial rule was ended, and Goa was annexed by India. Portuguese losses were 34 killed, 57 wounded, and 3,306 captured. Indian losses were 22 killed and 51 wounded.
Sino-Indian war, 1962
India fought a month-long border war against China in 1962. Neither nation deployed air or naval resources during a conflict heavy with mountain combat. China ended the war by declaring a unilateral ceasefire and withdrew their forces to the pre-war positions.
The defeat prompted India to make major changes in its military. The Department of Defence Production was established to create an indigenous defence production base, which would be self-reliant and self-sufficient. Since 1962, 16 new ordnance factories have been built under the program.
Second Indo-Pak war, 1965
 This war started following Pakistan's
This war started following Pakistan's Operation Gibraltar
Operation Gibraltar was the codename of a military operation planned and executed by the Pakistan Army in the disputed territory of Jammu and Kashmir in August 1965. The operation's strategy was to covertly cross the Line of Control (LoC) an ...
, which was designed to infiltrate forces into Jammu and Kashmir to precipitate an insurgency against rule by India. India retaliated by launching a full-scale military attack on West Pakistan
West Pakistan ( ur, , translit=Mag̱ẖribī Pākistān, ; bn, পশ্চিম পাকিস্তান, translit=Pôścim Pakistan) was one of the two Provincial exclaves created during the One Unit Scheme in 1955 in Pakistan. It was ...
. The seventeen-day war caused thousands of casualties on both sides and also witnessed the largest tank battle since World War II. The hostilities between the two countries ended after a ceasefire was declared following diplomatic intervention by the Soviet Union and USA and the subsequent issuance of the Tashkent Declaration
The Tashkent Declaration was signed between India and Pakistan on 10 January 1966 to resolve the Indo-Pakistani War of 1965. Peace was achieved on 23 September through interventions by the Soviet Union and the United States, both of which push ...
.[ Quote: Losses were relatively heavy—on the Pakistani side, twenty aircraft, 200 tanks, and 3,800 troops. Pakistan's army had been able to withstand Indian pressure, but a continuation of the fighting would only have led to further losses and ultimate defeat for Pakistan.][ Quote: The invading Indian forces outfought their Pakistani counterparts and halted their attack on the outskirts of Lahore, Pakistan's second-largest city. By the time the United Nations intervened on 22 September, Pakistan had suffered a clear defeat.] As Pakistan lost more territory than it gained during the war and failed to achieve its goal of capturing Kashmir, many impartial observers have viewed the result as a defeat for Pakistan and an Indian strategic victory.[Speech of Bill McCollum](_blank)
in United States House of Representatives
The United States House of Representatives, often referred to as the House of Representatives, the U.S. House, or simply the House, is the lower chamber of the United States Congress, with the Senate being the upper chamber. Together they ...
12 September 1994[South Asia in World Politics By Devin T. Hagerty, 2005 Rowman & Littlefield, , p. 26]
Indo-Sino Clash of 1967
The 1967 Sino-Indian clash also known as the Sino-Indian War of 1967
The Nathu La and Cho La clashes, sometimes referred to as the Sino-Indian War of 1967, consisted of a series of border clashes between India and China alongside the border of the Himalayan Kingdom of Sikkim, then an Indian protectorate.
T ...
(110 October 1967) was a military conflict
War is an intense armed conflict between State (polity), states, governments, Society, societies, or paramilitary groups such as Mercenary, mercenaries, Insurgency, insurgents, and militias. It is generally characterized by extreme violenc ...
between India
India, officially the Republic of India (Hindi: ), is a country in South Asia. It is the seventh-largest country by area, the second-most populous country, and the most populous democracy in the world. Bounded by the Indian Ocean on the so ...
and China in the Himalayan Kingdom of Sikkim
The Kingdom of Sikkim (Classical Tibetan and sip, འབྲས་ལྗོངས།, ''Drenjong''), officially Dremoshong (Classical Tibetan and sip, འབྲས་མོ་གཤོངས།) until the 1800s, was a hereditary monar ...
, then an Indian protectorate
A protectorate, in the context of international relations, is a state that is under protection by another state for defence against aggression and other violations of law. It is a dependent territory that enjoys autonomy over most of its int ...
. The Chinese People's Liberation Army infiltrated SikkimIndian Army
The Indian Army is the land-based branch and the largest component of the Indian Armed Forces. The President of India is the Supreme Commander of the Indian Army, and its professional head is the Chief of Army Staff (COAS), who is a four- ...
by 10 October. During the Cho La and Nathu La incidents, Indian losses were 88 killed in action and 163 wounded,[ while Chinese casualties were 340 killed in action and 450 wounded.]
Third Indo-Pak war, 1971
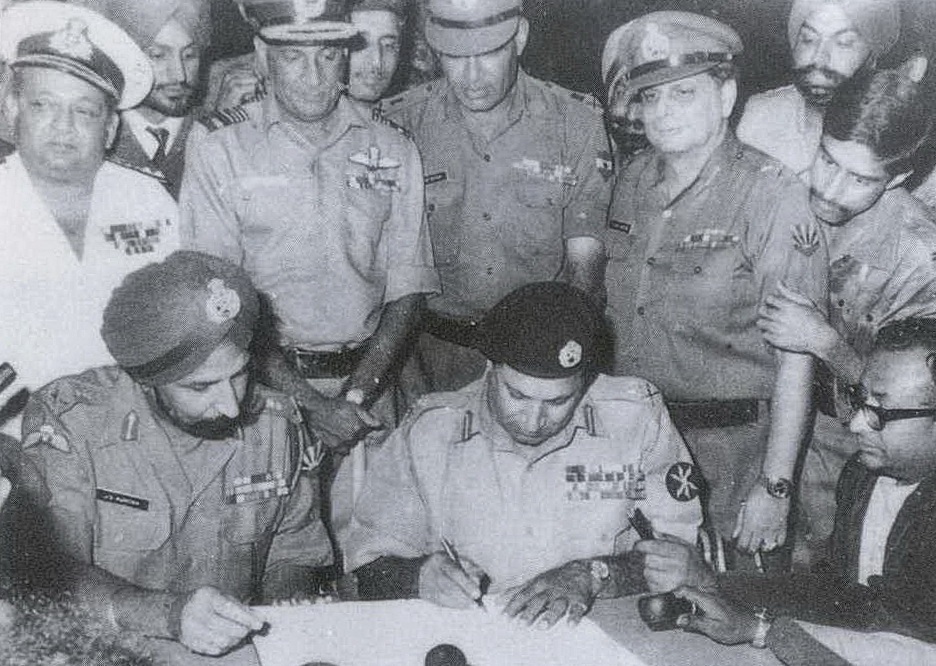 This war was unique in the way that it did not involve the issue of Kashmir, but was rather precipitated by the crisis created by the political battle between Sheikh Mujib, Leader of East Pakistan and Yahya-Bhutto, leaders of West Pakistan brewing in erstwhile
This war was unique in the way that it did not involve the issue of Kashmir, but was rather precipitated by the crisis created by the political battle between Sheikh Mujib, Leader of East Pakistan and Yahya-Bhutto, leaders of West Pakistan brewing in erstwhile East Pakistan
East Pakistan was a Pakistani province established in 1955 by the One Unit Policy, renaming the province as such from East Bengal, which, in modern times, is split between India and Bangladesh. Its land borders were with India and Myanmar, wi ...
culminating in the declaration of Independence of Bangladesh from the state system of Pakistan. Following Operation Searchlight
Operation Searchlight was the codename for a planned military operation carried out by the Pakistan Army in an effort to curb the Bengali nationalist movement in former East Pakistan in March 1971. Pakistan retrospectively justified the opera ...
and the 1971 Bangladesh genocide, about 10 million Bengalis in East Pakistan took refuge in neighbouring India.
India intervened in the ongoing Bangladesh liberation movement.Indian Army
The Indian Army is the land-based branch and the largest component of the Indian Armed Forces. The President of India is the Supreme Commander of the Indian Army, and its professional head is the Chief of Army Staff (COAS), who is a four- ...
successfully held their positions. The Indian Army quickly responded to the Pakistan Army's movements in the west and made some initial gains, including capturing around Pakistani Punjab
Punjab (; , ) is one of the four provinces of Pakistan. Located in central-eastern region of the country, Punjab is the second-largest province of Pakistan by land area and the largest province by population. It shares land borders with the ...
and Sindh sectors but gifted it back to Pakistan in the Simla Agreement
The Simla Agreement, also spelled Shimla Agreement, was a peace treaty signed between India and Pakistan on 2 July 1972 in Shimla, the capital city of the Indian state of Himachal Pradesh. It followed the Indo-Pakistani War of 1971, which ...
of 1972, as a gesture of goodwill). Within two weeks of intense fighting, Pakistani forces in East Pakistan
East Pakistan was a Pakistani province established in 1955 by the One Unit Policy, renaming the province as such from East Bengal, which, in modern times, is split between India and Bangladesh. Its land borders were with India and Myanmar, wi ...
surrendered to the joint command of Indian and Bangladeshi forces following which the People's Republic of Bangladesh
Bangladesh (}, ), officially the People's Republic of Bangladesh, is a country in South Asia. It is the eighth-most populous country in the world, with a population exceeding 165 million people in an area of . Bangladesh is among the mos ...
was created.
Siachen war, 1984
In the late 1970s and early 1980s, Pakistan began organising tourist expeditions on the Siachen Glacier
The Siachen Glacier is a glacier located in the eastern Karakoram range in the Himalayas at about , just northeast of the point NJ9842 where the Line of Control between India and Pakistan ends. At long, it is the longest glacier in the Kar ...
, disputed territory with India. Irked by this development, in April 1984 India initiated successful Operation Meghdoot
Operation Meghdoot ( "Operation Cloud Messenger" after a famous Sanskrit poem by Kalidasa) was the codename for the Indian Armed Forces' operation to seize control of the Siachen Glacier in Kashmir, precipitating the Siachen conflict. E ...
during which it gained control over all of the Siachen Glacier
The Siachen Glacier is a glacier located in the eastern Karakoram range in the Himalayas at about , just northeast of the point NJ9842 where the Line of Control between India and Pakistan ends. At long, it is the longest glacier in the Kar ...
. India has established control over all of the long Siachen Glacier and all of its tributary glaciers, as well as the three main passes of the Saltoro Ridge
The Saltoro Mountains are a subrange of the Karakoram Range. They are located in the southeast Karakoram on the southwest side of the Siachen Glacier, one of the two longest glaciers outside the polar regions. The name given to this range is sh ...
immediately west of the glacier—Sia La
Sia La is a mountain pass situated on Saltoro Ridge, in Ladakh, India, some north-northwest of map point NJ9842 which defined the end of the 1972 Line of Control between India and Pakistan as part of the Simla Agreement. Sia La sits near t ...
, Bilafond La, and Gyong La
Gyong La is a mountain pass situated on Saltoro Ridge southwest of the vast Siachen Glacier, some directly north of map point NJ9842 which defined the end of the 1972 Line of Control between India and Pakistan. With Pakistan controlling areas ...
.
Kargil War, 1999
 Commonly known as the Kargil War, or Operation Vijay in India, this conflict between the two countries was mostly limited. During early 1999, Pakistani troops infiltrated across the Line of Control (LoC) and occupied Indian territory mostly in the Kargil district. India responded by launching a major military and diplomatic offensive to drive out the Pakistani infiltrators.
Commonly known as the Kargil War, or Operation Vijay in India, this conflict between the two countries was mostly limited. During early 1999, Pakistani troops infiltrated across the Line of Control (LoC) and occupied Indian territory mostly in the Kargil district. India responded by launching a major military and diplomatic offensive to drive out the Pakistani infiltrators.[Kargil: where defence met diplomacy](_blank)
– India's then Chief of Army Staff VP Malik, expressing his views on Operation Vijay. Hosted on '' Daily Times''
The Fate of Kashmir By Vikas Kapur and Vipin Narang
Stanford Journal of International Relations
Book review of "The Indian Army: A Brief History by Maj Gen Ian Cardozo"
– Hosted on IPCS
Fearing large-scale escalation in military conflict, the international community, led by the United States
The United States of America (U.S.A. or USA), commonly known as the United States (U.S. or US) or America, is a country primarily located in North America. It consists of 50 states, a federal district, five major unincorporated territori ...
, increased diplomatic pressure on Pakistan to withdraw forces from remaining Indian territory.[Samina Ahmed. "Diplomatic Fiasco: Pakistan's Failure on the Diplomatic Front Nullifies its Gains on the Battlefield"](_blank)
(Belfer Center for International Affairs, Harvard Kennedy School
The Harvard Kennedy School (HKS), officially the John F. Kennedy School of Government, is the school of public policy and government of Harvard University in Cambridge, Massachusetts. The school offers master's degrees in public policy, public ...
) The morale of Pakistani forces after the withdrawal declined as many units of the Northern Light Infantry
The Northern Light Infantry Regiment (NLI) is a light infantry regiment in the Pakistan Army, based and currently headquartered in Gilgit, Pakistan. Along with other forces of the Pakistani military, the NLI has the primary responsibility of con ...
suffered heavy casualties.Nawaz Sharif
Mian Muhammad Nawaz Sharif (Urdu, Punjabi: ; born 25 December 1949) is a Pakistani businessman and politician who has served as the Prime Minister of Pakistan for three non-consecutive terms. He is the longest-serving prime minister of Pak ...
later said that over 4,000 Pakistani troops were killed in the operation and that Pakistan had lost the conflict. By the end of July 1999, organized hostilities in the Kargil district had ceased
By the end of July 1999, organized hostilities in the Kargil district had ceased[ and ]Kargil War
The Kargil War, also known as the Kargil conflict, was fought between India and Pakistan from May to July 1999 in the Kargil district of Jammu and Kashmir and elsewhere along the Line of Control (LoC). In India, the conflict is also referr ...
finally came to end with a decisive Indian military and diplomatic victory.
Other operations
The Mizo National Front, 1966
In March 1966, Mizo rebels in Assam
Assam (; ) is a state in northeastern India, south of the eastern Himalayas along the Brahmaputra and Barak River valleys. Assam covers an area of . The state is bordered by Bhutan and Arunachal Pradesh to the north; Nagaland and Manipur ...
declared independence and attacked government offices and military posts. The uprising was suppressed weeks later, and eventually Mizoram
Mizoram () is a state in Northeast India, with Aizawl as its seat of government and capital city. The name of the state is derived from "Mizo", the self-described name of the native inhabitants, and "Ram", which in the Mizo language means "lan ...
was made a separate state of India.
The Chola incident, 1967
A Sino-Indian skirmish known today as the Chola incident took place in October 1967. The People's Liberation Army made a brief incursion into Sikkim
Sikkim (; ) is a state in Northeastern India. It borders the Tibet Autonomous Region of China in the north and northeast, Bhutan in the east, Province No. 1 of Nepal in the west and West Bengal in the south. Sikkim is also close to the Silig ...
but retreated within 48 hours.
Operation Blue Star, 1984
In June 1984, then-Prime Minister Indira Gandhi ordered an attack on Sikh separatists belonging to the Khalistan movement
The Khalistan movement is a Sikh separatist movement seeking to create a homeland for Sikhs by establishing a sovereign state, called Khālistān (' Land of the Khalsa'), in the Punjab region. The proposed state would consist of land that cu ...
who had holed up in the Golden Temple in Amritsar. The operation resulted in 500–1,500 civilian deaths and heavy damage to the Akal Takht
The Akal Takht ("Throne of the Timeless One") is one of five takhts (seats of power) of the Sikhs. It is located in the Darbar Sahib (Golden Temple) complex in Amritsar, Punjab, India. The Akal Takht (originally called Akal Bunga) was built by ...
.
Sri Lanka mission, 1987–1990
The Indian Peace Keeping Force (IPKF) carried out a mission in northern and eastern Sri Lanka in 1987–1990 to disarm the Tamil Tigers
The Liberation Tigers of Tamil Eelam (LTTE; ta, தமிழீழ விடுதலைப் புலிகள், translit=Tamiḻīḻa viṭutalaip pulikaḷ, si, දෙමළ ඊළාම් විමුක්ති කොටි, t ...
per the Indo-Sri Lanka Accord
The Indo-Sri Lanka Peace Accord was an accord signed in Colombo on 29 July 1987, between Indian Prime Minister Rajiv Gandhi and Sri Lankan President J. R. Jayewardene. The accord was expected to resolve the Sri Lankan Civil War by enabling t ...
. It was a difficult battle for the Indian Army, which was not trained for an unconventional war. After losing approximately 1,200 in personnel and several T-72 tanks, India ultimately abandoned the mission in consultation with Sri Lankan government. In what was labeled as ''Operation Pawan'', the Indian Air Force flew about 70,000 sorties to and within Sri Lanka.
Operation Cactus, 1988
 In November 1988, the
In November 1988, the Maldives
Maldives (, ; dv, ދިވެހިރާއްޖެ, translit=Dhivehi Raajje, ), officially the Republic of Maldives ( dv, ދިވެހިރާއްޖޭގެ ޖުމްހޫރިއްޔާ, translit=Dhivehi Raajjeyge Jumhooriyyaa, label=none, ), is an archipelag ...
Government appealed India for military help against a mercenary
A mercenary, sometimes also known as a soldier of fortune or hired gun, is a private individual, particularly a soldier, that joins a military conflict for personal profit, is otherwise an outsider to the conflict, and is not a member of any ...
invasion. On the night of 3 November, the Indian Air Force airlifted the Para Special forces from Agra
Agra (, ) is a city on the banks of the Yamuna river in the Indian state of Uttar Pradesh, about south-east of the national capital New Delhi and 330 km west of the state capital Lucknow. With a population of roughly 1.6 million, Agra i ...
and flew them non-stop over 2,000 km to Maldives. The paracommandos landed at Hulule, secured the airfield, and restored government rule at Malé
Malé (, ; dv, މާލެ) is the capital and most populous city of the Maldives. With a population of 252,768 and an area of , it is also one of the most densely populated cities in the world. The city is geographically located at the southern ...
within hours and without bloodshed.
2001 Bangladesh–India border clashes
Also known as Bangladeshi-India border war, this brief war started on 15 April when Bangladeshis captured the disputed village of Pyrdiwah. The clashes lasted for about 5 days when the India and Bangladeshi forces took their original positions and the war ended in status quo ante bellum.
Missile program
 India has well developed missile capabilities with roots in the
India has well developed missile capabilities with roots in the Indian Space Program
The Department of Space is an Indian government department responsible for administration of the Indian space program. It manages several agencies and institutes related to space exploration and space technologies. The Indian space program und ...
. The Integrated Guided Missile Development Program (IGMDP
The Integrated Guided Missile Development Programme (IGMDP) was an Indian Ministry of Defence programme for the research and development of the comprehensive range of missiles. The programme was managed by the Defence Research and Development O ...
) was formed in 1983 with the aim of achieving self-sufficiency in missile development and production. Presently it comprises six core missile programs:
* Agni ballistic missile
* Prithvi ballistic missile
* Akash surface-to-air missile
* Trishul surface-to-air missile
* Nag anti-tank guided missile
The Nag missile (IAST: ''Nāga''; en: Cobra), also called "Prospina" for the land-attack version, is an Indian third-generation, all-weather, fire-and-forget, lock-on after launch, anti-tank guided missile (ATGM) with an operational range of 50 ...
* Nirbhay cruise missile
Currently the DRDO
The Defence Research and Development Organisation (DRDO) (IAST: ''Raksā Anūsandhān Evam Vikās Sangaṭhan'') is the premier agency under the Department of Defence Research and Development in Ministry of Defence of the Government of India, ...
is developing Surya (missile)
The Surya missile is a speculated intercontinental ballistic missile being developed by Defence research and development organization of India and its operational range is beyond 16,000 Km covering the entire earth
History
According to a 1995 ...
, an advanced series of ICBM that the government reports would have a range of more than 10,000 km. This would put its range on par with advanced missiles in the United States, Russia, and Israel.Indian Ballistic Missile Defense Program
The Indian Ballistic Missile Defence Program is an initiative to develop and deploy a multi-layered ballistic missile defence system to protect India from ballistic missile attacks. It was launched in 2000 after Kargil War by the Atal Bihari Vaj ...
.
Nuclear program
In 1974, India tested a nuclear weapon with a yield of up to 15 kiloton
TNT equivalent is a convention for expressing energy, typically used to describe the energy released in an explosion. The is a unit of energy defined by that convention to be , which is the approximate energy released in the detonation of a ...
s. The test was codenamed Smiling Buddha
Operation Smiling BuddhaThis test has many code names. Civilian scientists called it "Operation Smiling Buddha" and the Indian Army referred to it as ''Operation Happy Krishna''. According to United States Military Intelligence, ''Operation H ...
. On 11 and 13 May 1998, India conducted a total of five underground nuclear tests and declared itself a nuclear state
Eight sovereign states have publicly announced successful detonation of nuclear weapons. Five are considered to be nuclear-weapon states (NWS) under the terms of the Treaty on the Non-Proliferation of Nuclear Weapons (NPT). In order of acquisi ...
.
Recent developments
The Indian military ranks second in terms of number of troops after China. The paramilitary unit of the Republic of India is the world's largest paramilitary force at over one million strong. Eager to portray itself as a potential superpower, India began an intense phase of upgrading its armed forces in the late 1990s. India focuses on developing indigenous military equipment rather than relying on other countries for supplies. Most of the Indian naval ships and submarines, military armoured vehicles, missiles, and ammunition are indigenously designed and manufactured.
Military collaborations with other countries
 In 1997, India agreed to participate in the development of Russia's "Prospective Air Complex for Tactical Air Forces" program. One of the primary objectives of the program was to develop a 5th generation fighter aircraft; the Su-47 prototype flew its first successful test flight in 1997. The BrahMos, a supersonic cruise missile jointly developed with Russia, was successfully test fired in 2001. India is also collaborating with
In 1997, India agreed to participate in the development of Russia's "Prospective Air Complex for Tactical Air Forces" program. One of the primary objectives of the program was to develop a 5th generation fighter aircraft; the Su-47 prototype flew its first successful test flight in 1997. The BrahMos, a supersonic cruise missile jointly developed with Russia, was successfully test fired in 2001. India is also collaborating with Israel
Israel (; he, יִשְׂרָאֵל, ; ar, إِسْرَائِيل, ), officially the State of Israel ( he, מְדִינַת יִשְׂרָאֵל, label=none, translit=Medīnat Yīsrāʾēl; ), is a country in Western Asia. It is situated ...
to develop Unmanned Aerial Vehicle
An unmanned aerial vehicle (UAV), commonly known as a drone, is an aircraft without any human pilot, crew, or passengers on board. UAVs are a component of an unmanned aircraft system (UAS), which includes adding a ground-based controll ...
s.
India has focused recently on purchasing the technology behind military equipment rather than equipment itself. Recent examples include purchases of Sukhoi Su-30 MKI
The Sukhoi Su-30MKI (NATO reporting name: Flanker-H) is a twinjet multirole air superiority fighter developed by Russia's Sukhoi and built under licence by India's Hindustan Aeronautics Limited (HAL) for the Indian Air Force (IAF). A variant ...
multi-role fighter aircraft and T-90
The T-90 is a third-generation Russian main battle tank. It uses a 125mm 2A46 smoothbore main gun, the 1A45T fire-control system, an upgraded engine, and gunner's thermal sight. Standard protective measures include a blend of steel and comp ...
main battle tanks from Russia and diesel-powered Scorpene submarines from France. In 2004, India purchased US$5.7 billion worth of military equipment from other countries, making it the developing world's leading arms purchaser.
Disasters
On 28 April 2000, ammunition worth was destroyed in a fire at the Bharatpur ammunition depot. Another fire at the Pathankot
Pathankot is a city and the district headquarters of the Pathankot district in Punjab, India. Pathankot is the 6th most populous city of Punjab, after Ludhiana, Amritsar, Jalandhar, Patiala and Bathinda. Its local government is a municipal co ...
sub-depot resulted in loss of ammo worth . On 24 May 2001, another blaze at the Birdhwal sub-depot destroyed ammunition worth .
Awards
India's highest awards for military conduct in a time of war are, in descending order, the Param Vir Chakra
The Param Vir Chakra (PVC) is India's highest military decoration, awarded for displaying distinguished acts of valour during wartime. Param Vir Chakra translates as the "Wheel of the Ultimate Brave", and the award is granted for "most conspicu ...
, Maha Vir Chakra
The Maha Vir Chakra (MVC) () is the second highest military decoration in India, after the Param Vir Chakra, and is awarded for acts of conspicuous gallantry in the presence of the enemy, whether on land, at sea or in the air. It replaced the B ...
, and Vir Chakra
Vir Chakra (pronunciation: ʋ iː ɾ a tʃ a kɾa) is an Indian wartime military bravery award presented for acts of conspicuous gallantry in the presence of the enemy on the battlefield and is third in precedence in wartime gallantry awards a ...
. The peacetime equivalents are respectively the Ashoka Chakra
Ashoka (, ; also ''Asoka''; 304 – 232 BCE), popularly known as Ashoka the Great, was the third emperor of the Maurya Empire of Indian subcontinent during to 232 BCE. His empire covered a large part of the Indian subcontinent, s ...
, Kirti Chakra
The Kirti Chakra is an Indian military decoration awarded for valour, courageous action or self-sacrifice away from the field of battle. It may be awarded to civilians as well as military personnel, including posthumous awards. It is the ''pe ...
and Shaurya Chakra
The Shaurya Chakra is an Indian military decoration awarded for valour, courageous action or self-sacrifice while not engaged in direct action with the enemy. It may be awarded to civilians as well as military personnel, sometimes posthumously ...
. The latter two awards were formerly known as ''Ashoka Chakra, Class II'' and ''Ashoka Chakra, Class III'' respectively. The peacetime awards have occasionally been bestowed on civilians. For meritorious service, the awards are the Param Vishisht Seva Medal, the Athi Vishisht Seva Medal, and the Vishisht Seva Medal.
See also
* Indian Army Day
* History of India
* History of the Indian Navy
Maritime powers in the Indian subcontinent have possessed navies for many centuries. Indian dynasties such as the Cholas used naval power to extend their influence overseas, particularly to Southeast Asia. The Marakkar Navy under Zamorins duri ...
* Military history of India during World War II
A military, also known collectively as armed forces, is a heavily armed, highly organized force primarily intended for warfare. It is typically authorized and maintained by a sovereign state, with its members identifiable by their distinct ...
* Military of India
The Indian Armed Forces are the military forces of the Republic of India. It consists of three professional uniformed services: the Indian Army, Indian Navy, and Indian Air Force.—— Additionally, the Indian Armed Forces are supported by th ...
* Ancient Hindu wars
* Monsieur Raymond (1755–1798), French Adventurer, General and friend of the Nizam
The Nizams were the rulers of Hyderabad from the 18th through the 20th century. Nizam of Hyderabad (Niẓām ul-Mulk, also known as Asaf Jah) was the title of the monarch of the Hyderabad State ( divided between the state of Telangana, Mar ...
of India
Notes
Further reading
* Cohen, Stephen P. and Sunil Dasgupta, eds. ''Arming Without Aiming: India's Military Modernization'' (2010
excerpt and text search
* Davis, Zachary S. ''The India-Pakistan Military Standoff: Crisis and Escalation in South Asia'' (2011
excerpt and text search
focus on 2000–01 confrontation
* Deshpande, Anirudh. ''British Military Policy in India, 1900–1945: Colonial Constraints and Declining Power'' (2005)
* Holmes, James R. et al. ''Indian Naval Strategy in the Twenty-first Century'' (2009
excerpt and text search
* Khan, Iqtidar Alam. ''Gunpowder and Firearms: Warfare in Medieval India'' (2004)
* Marston, Daniel P. and Chandar S. Sundaram. ''A Military History of India and South Asia: From the East India Company to the Nuclear Era'' (2006)
* Roy, Kaushik. ''From Hydaspes to Kargil: A History of Warfare in India from 326 BC to AD 1999'' (2004)
* Roy, Kaushik. ''The Oxford Companion to Modern Warfare in India'' (2009)
* Sandhu, Gurcharn Singh. ''Military History of Medieval India'' (2003)
* Subramaniam, Arjun. ''India's Wars: A Military History, 1947–1971'' (2017), 576 pages.
* Sundaram, Chandar S., 'Warfare—South Asia', in W.H. McNeill and P. Stearns, eds., ''The Berkshire Encyclopaedia of World History'' 2005, vol. 5, pp. 1991–6, (2005)
* Sundaram, Chandar S., "A Paper Tiger: the Indian National Army in battle, 1944–1945", War & Society, 13(1), pp. 35–59 (1995)
*Jadunath Sarkar
Sir Jadunath Sarkar (10 December 1870 – 19 May 1958) was a prominent Indian historian and a specialist on the Mughal dynasty.
Academic career
Sarkar was born in Karachmaria village in Natore, Bengal to Rajkumar Sarkar, the local Zamindar ...
(1970). Military history of India. Bombay: Orient Longmans.
* Thapliyal, Uma Prasad. ''Warfare in Ancient India: Organizational and Operational Dimensions'' (2010)
Official war histories
Official war histories written by the History Division, Ministry of Defence, Government of India
The Government of India (ISO: ; often abbreviated as GoI), known as the Union Government or Central Government but often simply as the Centre, is the national government of the Republic of India, a federal democracy located in South Asia, ...
:
Sino-Indian war, 1962
External links
video of lecture by Stephen P. Cohen, Brookings Institution, hosted by the Program in Arms Control, Disarmament, and International Security (ACDIS), Un
iversity of Illinois, 15 October 2009
* ttps://web.archive.org/web/20090727005626/http://www.india-defence.com/ India Defence Defence And Military Portal
Indian Jawan
A Tribute to the Indian Soldier
Anne S. K. Brown Military Collection, Brown University Library
Military history and graphics, c. 1790 – 1918
{{DEFAULTSORT:Military History of India
History of Sindh
 The
The  War and conflict characterized the Shunga period. They are known to have warred with the Kalingas, Satavahanas, the Indo-Greeks, and possibly the Panchalas and Mathuras.
Extent of the Shunga Empire's wars with the Indo-Greek Kingdom figure greatly in the history of this period. From around 180 BCE the
War and conflict characterized the Shunga period. They are known to have warred with the Kalingas, Satavahanas, the Indo-Greeks, and possibly the Panchalas and Mathuras.
Extent of the Shunga Empire's wars with the Indo-Greek Kingdom figure greatly in the history of this period. From around 180 BCE the  According to some interpretations of the Puranas, the
According to some interpretations of the Puranas, the 
 In
In 
 Sultan Muzaffar Shah I, the governor of
Sultan Muzaffar Shah I, the governor of  The
The  During the
During the  During
During  Indian Army and
Indian Army and  This is also called the First Kashmir War. The war started in October 1947 when Pakistan feared that the
This is also called the First Kashmir War. The war started in October 1947 when Pakistan feared that the  After the war with Pakistan, India turned its attention to the independent Hyderabad State. India perceived the nearby independent Muslim state and potential Pakistani ally as a threat. In a five-day operation, India reconquered and annexed Hyderabad.
After the war with Pakistan, India turned its attention to the independent Hyderabad State. India perceived the nearby independent Muslim state and potential Pakistani ally as a threat. In a five-day operation, India reconquered and annexed Hyderabad.
 This war started following Pakistan's
This war started following Pakistan's  This war was unique in the way that it did not involve the issue of Kashmir, but was rather precipitated by the crisis created by the political battle between Sheikh Mujib, Leader of East Pakistan and Yahya-Bhutto, leaders of West Pakistan brewing in erstwhile
This war was unique in the way that it did not involve the issue of Kashmir, but was rather precipitated by the crisis created by the political battle between Sheikh Mujib, Leader of East Pakistan and Yahya-Bhutto, leaders of West Pakistan brewing in erstwhile  Commonly known as the Kargil War, or Operation Vijay in India, this conflict between the two countries was mostly limited. During early 1999, Pakistani troops infiltrated across the Line of Control (LoC) and occupied Indian territory mostly in the Kargil district. India responded by launching a major military and diplomatic offensive to drive out the Pakistani infiltrators. Two months into the conflict, Indian troops had slowly retaken most of the ridges that were encroached by the infiltrators. According to official count, an estimated 75%–80% of the intruded area and nearly all high ground was back under Indian control.Kargil: where defence met diplomacy
Commonly known as the Kargil War, or Operation Vijay in India, this conflict between the two countries was mostly limited. During early 1999, Pakistani troops infiltrated across the Line of Control (LoC) and occupied Indian territory mostly in the Kargil district. India responded by launching a major military and diplomatic offensive to drive out the Pakistani infiltrators. Two months into the conflict, Indian troops had slowly retaken most of the ridges that were encroached by the infiltrators. According to official count, an estimated 75%–80% of the intruded area and nearly all high ground was back under Indian control.Kargil: where defence met diplomacy By the end of July 1999, organized hostilities in the Kargil district had ceased and
By the end of July 1999, organized hostilities in the Kargil district had ceased and  India has well developed missile capabilities with roots in the
India has well developed missile capabilities with roots in the  In 1997, India agreed to participate in the development of Russia's "Prospective Air Complex for Tactical Air Forces" program. One of the primary objectives of the program was to develop a 5th generation fighter aircraft; the Su-47 prototype flew its first successful test flight in 1997. The BrahMos, a supersonic cruise missile jointly developed with Russia, was successfully test fired in 2001. India is also collaborating with
In 1997, India agreed to participate in the development of Russia's "Prospective Air Complex for Tactical Air Forces" program. One of the primary objectives of the program was to develop a 5th generation fighter aircraft; the Su-47 prototype flew its first successful test flight in 1997. The BrahMos, a supersonic cruise missile jointly developed with Russia, was successfully test fired in 2001. India is also collaborating with