Milü on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
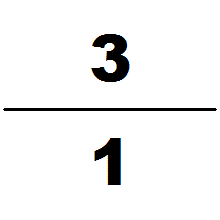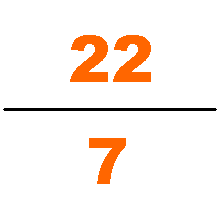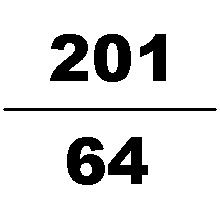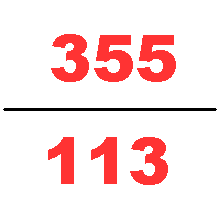 Milü (; "close ratio"), also known as Zulü ( Zu's ratio), is the name given to an approximation to (pi) found by Chinese mathematician and
Milü (; "close ratio"), also known as Zulü ( Zu's ratio), is the name given to an approximation to (pi) found by Chinese mathematician and
Fractional Approximations of Pi
{{DEFAULTSORT:Milu Pi History of mathematics History of science and technology in China Chinese mathematical discoveries Chinese words and phrases Approximations Rational numbers
astronomer
An astronomer is a scientist in the field of astronomy who focuses their studies on a specific question or field outside the scope of Earth. They observe astronomical objects such as stars, planets, natural satellite, moons, comets and galaxy, g ...
Zu Chongzhi in the 5th century. Using Liu Hui's algorithm (which is based on the areas of regular polygons approximating a circle), Zu famously computed to be between 3.1415926 and 3.1415927 and gave two rational approximations of , and , naming them respectively Yuelü (; "approximate ratio") and Milü.
is the best rational approximation of with a denominator of four digits or fewer, being accurate to six decimal places. It is within % of the value of , or in terms of common fractions overestimates by less than . The next rational number (ordered by size of denominator) that is a better rational approximation of is , still only correct to six decimal places and hardly closer to than . To be accurate to seven decimal places, one needs to go as far as . For eight, is needed.
The accuracy of Milü to the true value of can be explained using the continued fraction expansion of , the first few terms of which are . A property of continued fractions is that truncating the expansion of a given number at any point will give the "best rational approximation
In mathematics, a continued fraction is an expression obtained through an iterative process of representing a number as the sum of its integer part and the reciprocal of another number, then writing this other number as the sum of its integer pa ...
" to the number. To obtain Milü, truncate the continued fraction expansion of immediately before the term 292; that is, is approximated by the finite continued fraction , which is equivalent to Milü. Since 292 is an unusually large term in a continued fraction expansion (corresponding to the next truncation introducing only a very small term, , to the overall fraction), this convergent will be especially close to the true value of :
:
An easy mnemonic
A mnemonic ( ) device, or memory device, is any learning technique that aids information retention or retrieval (remembering) in the human memory for better understanding.
Mnemonics make use of elaborative encoding, retrieval cues, and imag ...
helps memorize this useful fraction by writing down each of the first three odd numbers twice: , then dividing the decimal number represented by the last 3 digits by the decimal number given by the first three digits. Alternatively,
Zu's contemporary calendarist and mathematician He Chengtian invented a fraction interpolation method called "harmonization of the divisor of the day" () to increase the accuracy of approximations of by iteratively adding the numerators and denominators of fractions. Zu Chongzhi's approximation ≈ can be obtained with He Chengtian's method.
See also
* Continued fraction expansion of and its convergents * History of approximations of * Pi Approximation DayReferences
External links
Fractional Approximations of Pi
{{DEFAULTSORT:Milu Pi History of mathematics History of science and technology in China Chinese mathematical discoveries Chinese words and phrases Approximations Rational numbers