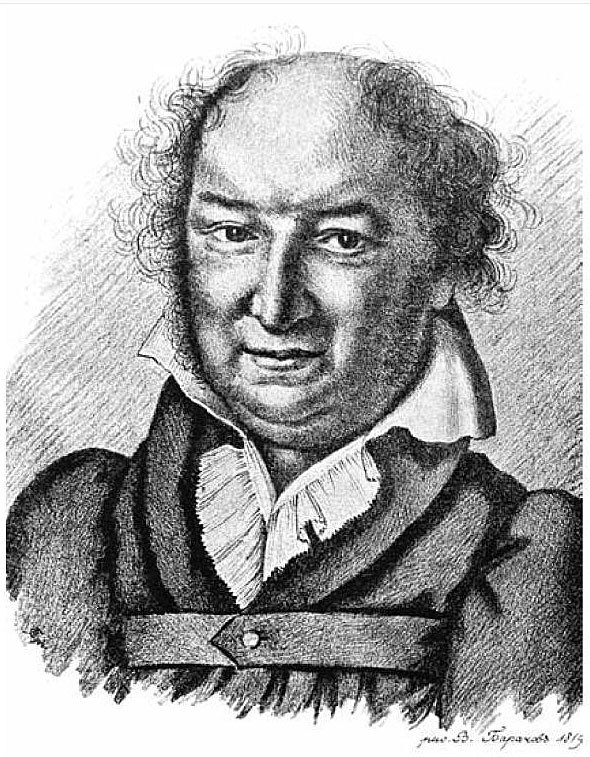
Mikhail Andreyevich Miloradovich on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Count Mikhail Andreyevich Miloradovich (russian: Граф Михаи́л Андре́евич Милора́дович, sh-Cyrl, Гроф Михаил Андрејевић Милорадовић ''Grof Mihail Andrejević Miloradović''; – ), spelled Miloradovitch in contemporary English sources, was a Russian general prominent during the
 Mikhail Miloradovich was the son of Major General
Mikhail Miloradovich was the son of Major General
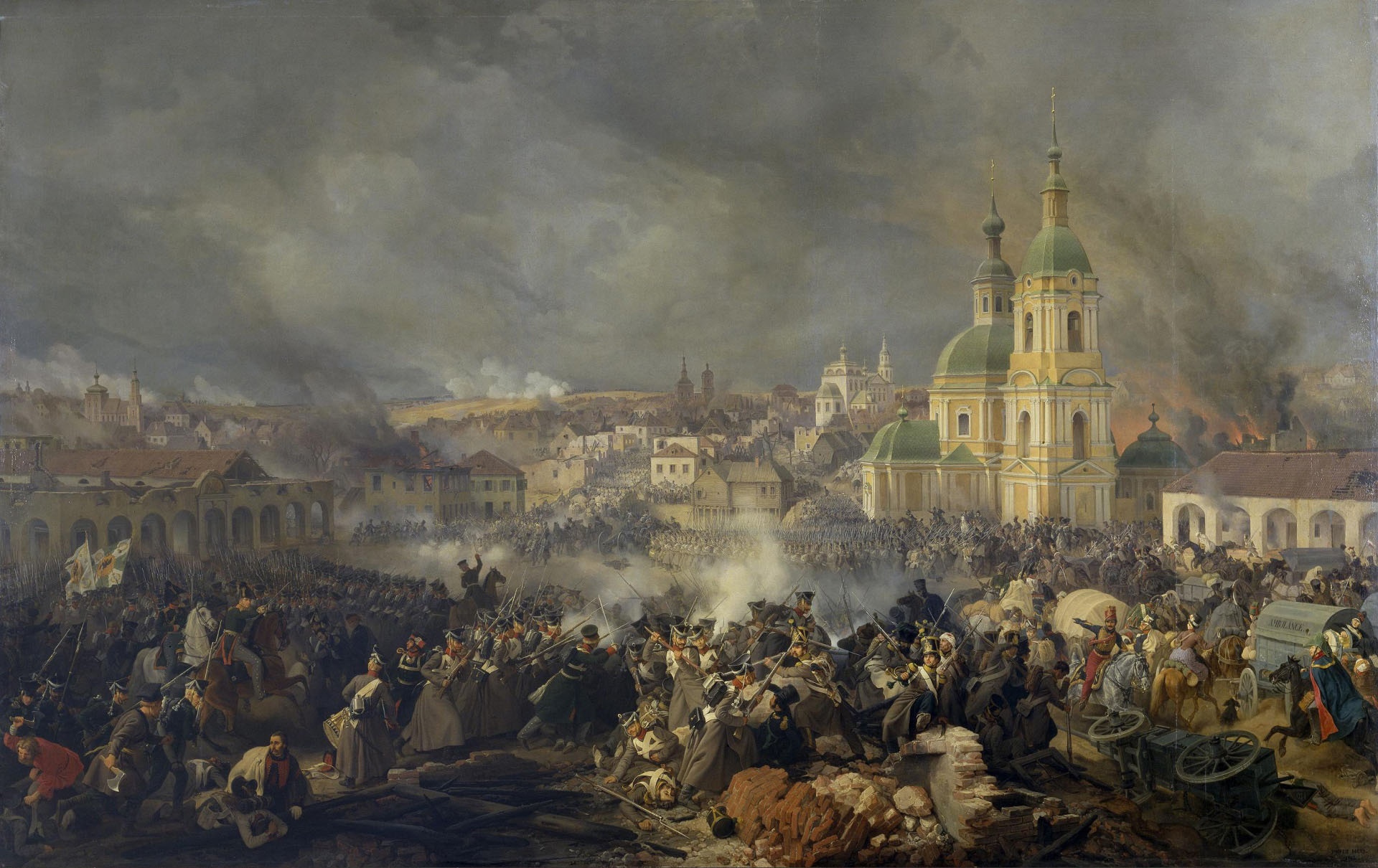 At the beginning of the 1812 campaign, Miloradovich was tasked with assembling and training volunteer
At the beginning of the 1812 campaign, Miloradovich was tasked with assembling and training volunteer
 In 1821, theatre managers Apollon Maikov and Prince Alexander Shakhovskoy allegedly tried to manipulate Miloradovich to overthrow the stern and frugal director of imperial theatres, Prince Tyufyakin. Miloradovich lent them support and then himself "grabbed both the power and the purse strings"; Miloradovich, Maikov and Shakhovskoy became a "committee of three formidable officials" that governed the everyday life of the imperial theatres. The change coincided with rumours of Shakhovskoy's trafficking in actresses; the death of Miloradovich and the ascension of Nicholas I ended Shakhovskoy's career.
The private life of Miloradovich, who never married and had no offspring, has been a controversial subject. Contemporaries condemned him for a desire "to create his own
In 1821, theatre managers Apollon Maikov and Prince Alexander Shakhovskoy allegedly tried to manipulate Miloradovich to overthrow the stern and frugal director of imperial theatres, Prince Tyufyakin. Miloradovich lent them support and then himself "grabbed both the power and the purse strings"; Miloradovich, Maikov and Shakhovskoy became a "committee of three formidable officials" that governed the everyday life of the imperial theatres. The change coincided with rumours of Shakhovskoy's trafficking in actresses; the death of Miloradovich and the ascension of Nicholas I ended Shakhovskoy's career.
The private life of Miloradovich, who never married and had no offspring, has been a controversial subject. Contemporaries condemned him for a desire "to create his own
 In the summer of 1823, Alexander I issued a secret manifest excluding Constantine from the order of succession and making Nicholas
In the summer of 1823, Alexander I issued a secret manifest excluding Constantine from the order of succession and making Nicholas
 At 8 p.m. on , Nicholas declared himself emperor; at 7 a.m. the next morning, along with all senior statesmen present in Saint Petersburg, Miloradovich pledged his loyalty to Nicholas (Korf suggested that Miloradovich recognised Nicholas as early as ). Once again Miloradovich assured Nicholas that the city was "perfectly tranquil"; Alexander von Benckendorff other witnesses wrote that he was in his usual boastful, optimistic mood. Three hours later when Miloradovich enjoyed breakfast with Teleshova, general Neidhardt reported to Nicholas that the troops were marching towards the palace "in absolute mutiny".
At about noon on Miloradovich, whom nobody had seen since the morning, reported to Nicholas on
At 8 p.m. on , Nicholas declared himself emperor; at 7 a.m. the next morning, along with all senior statesmen present in Saint Petersburg, Miloradovich pledged his loyalty to Nicholas (Korf suggested that Miloradovich recognised Nicholas as early as ). Once again Miloradovich assured Nicholas that the city was "perfectly tranquil"; Alexander von Benckendorff other witnesses wrote that he was in his usual boastful, optimistic mood. Three hours later when Miloradovich enjoyed breakfast with Teleshova, general Neidhardt reported to Nicholas that the troops were marching towards the palace "in absolute mutiny".
At about noon on Miloradovich, whom nobody had seen since the morning, reported to Nicholas on
Imperator Nikolai Pavlovich i graf M. A. Miloradovich (Император Николай Павлович и граф М. А. Милорадович)
'. СПБ: Философский век, выпуск 6 (The Philosophical Age. Almanac 6. Russia at the Time of Nicholas I: Science, Politics, Enlightenment. Ed. by T. Khartanovich, M. Mikeshin. St. Petersburg, 1998. 304 p.). * Bezotnosny, V. M. et al. (2004, in Russian). ''Otechestvennaya voina 1812 goda. Encyclopedia (Отечественная война 1812 года. Энциклопедия)''. Moscow: Rosspan. . * Bethea, David M. (2005).
The Pushkin Handbook
'. University of Wisconsin Press. , . * Browning, Oscar (2008 reprint).
A History of the Modern World 1815-1910
'. Read Books (reprint). , . * Castle, Ian; Hook, Christa (2002). ‘�
Austerlitz 1805: the fate of empires
��’. Osprey. , . * William Cathcart (1850).
Commentaries on the War in Russia and Germany in 1812 and 1813
'. London: J. Murray. Reissue: . * Cust, Edward (1863). ‘�
Annals of the wars of the nineteenth century, Volume 4
��’. London: John Murray. * Durova, Nadezhda; Zinn, Mary (translator) (1989 edition). ‘�
The Cavalry Maiden: Journals of a Russian Officer in the Napoleonic Wars
��’. Indiana University Press. , . * George, Hereford B. (2002 reissue).
Napoleon's Invasion of Russia
'. Janus Publishing Company Lim. , . Originally published in 1899. * Grech, Nikolai (2000 edition, in Russian).
Zapiski o moei zhizni (Записки о моей жизни)
'. Moscow: Zakharov. * Freer, Allan (1846).
Russian under Nicholas
'' North British Review, volume 5. Edinburgh: W. P. Kennedy. * Glinka, Fyodor (1870, in Russian).
Pisma russkogo ofitsera (Письма русского офицера)
'. Moscow. * Glinka, Fyodor (1814, in Russian).
Podvigi grafa Miloradovicha (Подвиги графа Милорадовича)
'. Moscow. * Herzen, Alexander; McDonald, Dwight (editor) (1982).
My past and thoughts: the memoirs of Alexander Herzen
'. University of California Press. , . * Kagan, Frederick (2007).
The End of the Old Order: Napoleon and Europe, 1801-1805
'' Da Capo Press. , . * Kelly, Laurence (2006).
Diplomacy and Murder in Tehran: Alexander Griboyedov and Imperial Russia's Mission to the Shah of Persia
'. Tauris Parke Paperbacks. , . * Korf, M. A. (1857).
The accession of Nicholas I
'. London: John Murray. * Leskov, Nikolay (2003 edition, in Russian). ''Graf Mikhail Andreevich Miloradovich (Граф Михаил Андреевич Милорадович)'', in: Desyatnikov, V. A. (editor) (2003, in Russian).
Blistatelny Sankt-Peterburg (Блистательный Санкт-Петербург)
'. Olma Media Group, , . pp. 448–453. Originally published in 1869. * Lotman, Jurij; Ouspensky, Boris (1990, in French).
Sémiotique de la culture russe: études sur l'histoire
'. L’Age du Homme. , 9782825100172. * Miloradovich, G. A. (1871, in Russian).
O rodine dvoryan i grafa Miloradovicha
'. First edition: Kiev. * Nabokov, Vladimir (1990 reprint).
Eugene Onegin: A Novel in Verse: Commentary
'. Princeton University Press. , . * Nicholas I (1848, Russian translation from French).
Memoirs of Nicholas I (in Russian)
'. * Schnitzler, Johann (1847).
Secret history of the court and government of Russia under the emperors Alexander and Nicholas
'. London: Richard Bentley. * Schuler, Catherine (2009).
Theatre and identity in imperial Russia
'. University of Iowa Press. , . * Safonov, M. M. (1994, in Russian).
K istorii mezhdutsarstviya (К истории междуцарстия)
'. Proceedings of the Mavrodinskie conference 10–12 December 1994, Saint Petersburg (Мавродинские чтения: материалы к докладам 10-12 октября 1994 г., Санкт-Петербург). Saint Petersburg University. * Safonov, M. M. (2001, in Russian).
'. Rodina magazine, no. 12, 2001. * Sapozhnikov, A. I. (2008, in Russian).
Neopublikovannaya Istoria kampanii 1812 goda A. I. Mihailovskogo-Danilevskogo (Неопубликованная «История кампании 1812 года» А.И. Михайловского-Данилевского)
'. *Schultz, C. C. (2004). . Taleon Club Magazine
Retrieved 2011-07-16. Archived fro
the original
on 2006-01-12. * Thiers, Adolphe (1865).
History of the consulate and the empire of France under Napoleon, Volume 2
'. London: Lippincott. * Thiers, Adolphe (1864).
History of the consulate and the empire of France under Napoleon, Volume 4
'. London: Lippincott. * Treasure, Geoffrey (1985).
The making of modern Europe, 1648-1780
'. Routledge. , . {{DEFAULTSORT:Miloradovich, Mikhail 1771 births 1825 deaths Military personnel from Saint Petersburg People from Saint Petersburg Governorate Imperial Russian Army generals Russian people of Serbian descent Knights Hospitaller Members of the State Council (Russian Empire) Recipients of the Order of St. George of the Second Degree Recipients of the Order of St. Anna, 1st class Recipients of the Order of St. Vladimir, 1st class Knights of the Order of St John Russian commanders of the Napoleonic Wars Russian nobility Governors-General of Kiev Burials at the Dukhovskaya Church Miloradović noble family
Napoleonic Wars
The Napoleonic Wars (1803–1815) were a series of major global conflicts pitting the French Empire and its allies, led by Napoleon I, against a fluctuating array of European states formed into various coalitions. It produced a period of Fre ...
, who, on his father side, descended from Serbian
Serbian may refer to:
* someone or something related to Serbia, a country in Southeastern Europe
* someone or something related to the Serbs, a South Slavic people
* Serbian language
* Serbian names
See also
*
*
* Old Serbian (disambiguation ...
noble family and the katun
Katun may refer to:
Places
* Katun (river), a tributary of the Ob in Siberia, Russia
* Katun Mountains or Katun Alps, a mountain range in Russia, part of the Altai Mountains
* Katun (Vranje), a village in Vranje Municipality, Serbia
* Katun ( ...
clan of Miloradović from Hum, in present-day Bosnia and Herzegovina
Bosnia and Herzegovina ( sh, / , ), abbreviated BiH () or B&H, sometimes called Bosnia–Herzegovina and often known informally as Bosnia, is a country at the crossroads of south and southeast Europe, located in the Balkans. Bosnia and ...
. He entered military service on the eve of the Russo-Swedish War of 1788–1790 and his career advanced rapidly during the reign (1796-1801) of Emperor Paul I. He served under Alexander Suvorov
Alexander Vasilyevich Suvorov (russian: Алекса́ндр Васи́льевич Суво́ров, Aleksándr Vasíl'yevich Suvórov; or 1730) was a Russian general in service of the Russian Empire. He was Count of Râmnicu Sărat, Rymnik, C ...
during Italian and Swiss campaigns of 1799.
Miloradovich served in wars against France and the Ottoman Empire
The Ottoman Empire, * ; is an archaic version. The definite article forms and were synonymous * and el, Оθωμανική Αυτοκρατορία, Othōmanikē Avtokratoria, label=none * info page on book at Martin Luther University ...
, earning distinction in the Battle of Amstetten
The Battle of Amstetten was a minor engagement during the War of the Third Coalition between the First French Empire and the alliance of Austria and Russia. It occurred on 5 November 1805, when the retreating Russo-Austrian troops, led by Mikhai ...
(1805), the capture of Bucharest (1806), the Battle of Borodino
The Battle of Borodino (). took place near the village of Borodino on during Napoleon's invasion of Russia. The ' won the battle against the Imperial Russian Army but failed to gain a decisive victory and suffered tremendous losses. Napole ...
(September 1812), the Battle of Tarutino
The Battle of Tarutino (russian: Тарутинo) was a part of Napoleon's invasion of Russia. In the battle Russian troops under the command of Bennigsen defeated French troops under the command of Joachim Murat.
The battle is sometimes ca ...
(October 1812) and the Battle of Vyazma
The Battle of Vyazma (November 3, 1812), occurred at the beginning of Napoleon's retreat from Moscow. In this encounter a Russian force commanded by General Miloradovich inflicted heavy losses on the rear guard of the Grande Armee. Although ...
(November 1812). He led the reserves into the Battle of Kulm
:''See Battle of Chlumec for the 1126 battle at Kulm
The Battle of Kulm was fought near the town Kulm () and the village Přestanov in northern Bohemia. It was fought on 29–30 August 1813, during the War of the Sixth Coalition. A French ...
(August 1813), the Battle of Leipzig
The Battle of Leipzig (french: Bataille de Leipsick; german: Völkerschlacht bei Leipzig, ); sv, Slaget vid Leipzig), also known as the Battle of the Nations (french: Bataille des Nations; russian: Битва народов, translit=Bitva ...
(October 1813) and the Battle of Paris (1814)
The Battle of Paris was fought on 30–31 March 1814 between the Sixth Coalition, consisting of Russia, Austria, and Prussia, against the French Empire. After a day of fighting in the suburbs of Paris, the French surrendered on March 31, ...
. Miloradovich attained the rank of General of the Infantry in 1809 and the title of count
Count (feminine: countess) is a historical title of nobility in certain European countries, varying in relative status, generally of middling rank in the hierarchy of nobility. Pine, L. G. ''Titles: How the King Became His Majesty''. New York ...
in 1813. His reputation as a daring battlefield commander (contemporaries called him "the Russian Murat Murat may refer to:
Places Australia
* Murat Bay, a bay in South Australia
* Murat Marine Park, a marine protected area
France
* Murat, Allier, a commune in the department of Allier
* Murat, Cantal, a commune in the department of Cantal
Elsewhe ...
" and "the Russian Bayard
Bayard may refer to:
People
*Bayard (given name)
* Bayard (surname)
*Pierre Terrail, seigneur de Bayard (1473–1524) French knight
Places
* Bayard, Delaware, an unincorporated community
* Bayard (Jacksonville), Florida, a neighborhood
* Bayard ...
") rivalled that of his bitter personal enemy Pyotr Bagration
Prince Pyotr Ivanovich Bagration (10 July 1765 – 24 September 1812) was a Georgian general and prince serving in the Russian Empire, prominent during the Napoleonic Wars.
Bagration, a member of the Bagrationi dynasty, was born in Tbilisi. Hi ...
, but Miloradovich also had a reputation for good luck. He boasted that he had fought fifty battles but had never been wounded nor even scratched by the enemy.
By 1818, when Miloradovich was appointed Governor General of Saint Petersburg, the retirement or death of other senior generals made him the most highly-decorated active officer of the Russian army, holding the Order of St. George
The Order of Saint George (russian: Орден Святого Георгия, Orden Svyatogo Georgiya) is the highest military decoration of the Russian Federation. Originally established on 26 November 1769 Julian (7 December 1769 Gregorian) a ...
2nd class, the Order of St. Andrew, the Order of St. Vladimir 1st class, the Order of St. Anna 1st class, the Order of St. John of Jerusalem and the Order of St. Alexander Nevsky with diamonds. A chivalrous man of boastful and flamboyant character, Miloradovich was a poor fit for the governorship. Vladimir Nabokov
Vladimir Vladimirovich Nabokov (russian: link=no, Владимир Владимирович Набоков ; 2 July 1977), also known by the pen name Vladimir Sirin (), was a Russian-American novelist, poet, translator, and entomologist. Bor ...
called him "a gallant soldier, ''bon vivant
''Bon'', also spelled Bön () and also known as Yungdrung Bon (, "eternal Bon"), is a Tibetan religious tradition with many similarities to Tibetan Buddhism and also many unique features.Samuel 2012, pp. 220-221. Bon initially developed in t ...
'' and a somewhat bizarre administrator"; Alexander Herzen
Alexander Ivanovich Herzen (russian: Алекса́ндр Ива́нович Ге́рцен, translit=Alexándr Ivánovich Gértsen; ) was a Russian writer and thinker known as the "father of Russian socialism" and one of the main fathers of agra ...
wrote that he was "one of those military men who occupied the most senior positions in civilian life with not the slightest idea about public affairs".
When news of the death of Alexander I Alexander I may refer to:
* Alexander I of Macedon, king of Macedon 495–454 BC
* Alexander I of Epirus (370–331 BC), king of Epirus
* Pope Alexander I (died 115), early bishop of Rome
* Pope Alexander I of Alexandria (died 320s), patriarch of A ...
reached Saint Petersburg, Miloradovich prevented the heir, the future Emperor Nicholas I, from acceding to the throne. From to , Miloradovich exercised ''de facto'' dictatorial authority, but he ultimately recognised Nicholas as his sovereign after the Romanovs had sorted out their confusion over the succession. Miloradovich had sufficient evidence of the mounting Decembrist revolt
The Decembrist Revolt ( ru , Восстание декабристов, translit = Vosstaniye dekabristov , translation = Uprising of the Decembrists) took place in Russia on , during the interregnum following the sudden death of Emperor Al ...
, but did not take any action until the rebels took over the Senate Square on . He rode into the rows of rebel troops and tried to talk them into obedience, but was fatally shot by Pyotr Kakhovsky
Pyotr Grigoryevich Kakhovsky (russian: Пётр Григо́рьевич Кахо́вский, 1799 – ) was a Russian Empire officer and active participant of Decembrist revolt, known for the murder of General Mikhail Miloradovich and Colonel ...
and stabbed by Yevgeny Obolensky
Prince Yevgeny Petrovich Obolensky (russian: Евге́ний Петро́вич Оболе́нский, – ) was a Russian officer from the Obolensky family, one of the most active participants in the Decembrist revolt.
Biography
Yevgeny Obole ...
.
Early years
 Mikhail Miloradovich was the son of Major General
Mikhail Miloradovich was the son of Major General Andrei Miloradovich
Andrei Stepanovich Miloradovich (Russian: Андре́й Степа́нович Милора́дович; 1727–2 May 1796) was a Russian military leader, statesman and lieutenant general. He is the father of general Mikhail Miloradovich.
B ...
(1726–1798). The Miloradovichs descended from an Eastern Orthodox Bosnian Vlach noble family and a ''katun
Katun may refer to:
Places
* Katun (river), a tributary of the Ob in Siberia, Russia
* Katun Mountains or Katun Alps, a mountain range in Russia, part of the Altai Mountains
* Katun (Vranje), a village in Vranje Municipality, Serbia
* Katun ( ...
'' clan from Hum, in present-day Bosnia and Herzegovina
Bosnia and Herzegovina ( sh, / , ), abbreviated BiH () or B&H, sometimes called Bosnia–Herzegovina and often known informally as Bosnia, is a country at the crossroads of south and southeast Europe, located in the Balkans. Bosnia and ...
who rose to a station of prominent Bosnian Ottoman nobility of Sanjak of Herzegovina
The Sanjak of Herzegovina ( tr, Hersek Sancağı; sh, Hercegovački sandžak) was an Ottoman administrative unit established in 1470. The seat was in Foča until 1572 when it was moved to Taşlıca (Pljevlja). The sanjak was initially part of ...
.. The Russian branch of the Miloradovich family was established in 1715, when Mikhail I Miloradovich (the first) ( sh-Cyrl, Михаило Милорадовић), one of three brothers recruited by Peter I Peter I may refer to:
Religious hierarchs
* Saint Peter (c. 1 AD – c. 64–88 AD), a.k.a. Simon Peter, Simeon, or Simon, apostle of Jesus
* Pope Peter I of Alexandria (died 311), revered as a saint
* Peter I of Armenia (died 1058), Catholicos ...
to incite rebellion against the Turks four years earlier, fled from Herzegovina
Herzegovina ( or ; sh-Latn-Cyrl, Hercegovina, separator=" / ", Херцеговина, ) is the southern and smaller of two main geographical region of Bosnia and Herzegovina, the other being Bosnia. It has never had strictly defined geogra ...
to Russia and joined Peter's service as a colonel. He was a commander of the Hadiach Regiment
The Hadiach Regiment ( uk, Гадяцький полк, translit=Hadiats’kyi polk) was one of then territorial-administrative subdivisions of the Cossack Hetmanate. The regiment's capital was the city of Hadiach, now in Poltava Oblast of central ...
. Towards the end of Peter's reign he was imprisoned in connection with Pavlo Polubotok
Pavlo Polubotok ( uk, Павло Леонтійович Полуботок, russian: Павел Леонтьевич Полуботок, pl, Paweł Połubotok; born around 1660, died on 29 December 1724), was a Ukrainian Cossack political and mil ...
's treason case, but was spared from further misfortune by Peter's death. His grandson Andrey served thirty years in the Russian Army and later moved into civil administration as the Governor of Little Russia
Little Russia (russian: Малороссия/Малая Россия, Malaya Rossiya/Malorossiya; uk, Малоросія/Мала Росія, Malorosiia/Mala Rosiia), also known in English as Malorussia, Little Rus' (russian: Малая Ру� ...
and the Chernigov governorate
The Chernigov Governorate (russian: Черниговская губерния; translit.: ''Chernigovskaya guberniya''; ), also known as the Government of Chernigov, was a guberniya in the historical Left-bank Ukraine region of the Russian ...
. The family owned lands in the Poltava Governorate
The Poltava Governorate (russian: Полтавская губерния, Poltavskaya guberniya; ua, Полтавська Губернія, translit=Poltavska huberniia) or Poltavshchyna was a gubernia (also called a province or government) in t ...
; Mikhail inherited up to fifteen hundred serf
Serfdom was the status of many peasants under feudalism, specifically relating to manorialism, and similar systems. It was a condition of debt bondage and indentured servitude with similarities to and differences from slavery, which developed ...
s.
Mikhail's father "enrolled" him in the military in his infancy, and later sent teenage Mikhail to study military sciences in the universities of Königsberg
Königsberg (, ) was the historic Prussian city that is now Kaliningrad, Russia. Königsberg was founded in 1255 on the site of the ancient Old Prussian settlement ''Twangste'' by the Teutonic Knights during the Northern Crusades, and was ...
and Göttingen
Göttingen (, , ; nds, Chöttingen) is a university city in Lower Saxony, central Germany, the capital of the eponymous district. The River Leine runs through it. At the end of 2019, the population was 118,911.
General information
The ori ...
, and in Strasbourg
Strasbourg (, , ; german: Straßburg ; gsw, label= Bas Rhin Alsatian, Strossburi , gsw, label= Haut Rhin Alsatian, Strossburig ) is the prefecture and largest city of the Grand Est region of eastern France and the official seat of the ...
and Metz
Metz ( , , lat, Divodurum Mediomatricorum, then ) is a city in northeast France located at the confluence of the Moselle and the Seille rivers. Metz is the prefecture of the Moselle department and the seat of the parliament of the Grand ...
. According to Nikolai Leskov
Nikolai Semyonovich Leskov (russian: Никола́й Семёнович Леско́в; – ) was a Russian novelist, short-story writer, playwright, and journalist, who also wrote under the pseudonym M. Stebnitsky. Praised for his unique w ...
, the education was superficial: Leskov described Mikhail as a boy of "charming ignorance" who did not even master the French language properly, and said that his French was littered with the "most grave and curious mistakes" (an anecdote credited him with blending ''pittoresque'' and ''synagogue'' into ''"pittagogue"''). Sixteen-year-old Mikhail returned to Russia in 1787, joined the army as a praporshchik
( rus, Пра́порщик, 3=ˈprapərɕːɪk, ) is a rank used by the Russian Armed Forces and a number of former communist states. The rank is a non-commissioned officer's and is equivalent to in navies. It is usually equivalent to Warrant ...
(a junior commissioned officer rank) in the Izmaylovsky Regiment and was soon sent into action in the Russo-Swedish War of 1788–1790.
Military career
Italian and Swiss campaigns
Miloradovich did not earn any distinction in the war of 1788–1790, but he advanced rapidly in peacetime. A captain of the Guards in 1796, Paul I regarded him favorably and he was promoted to the rank of colonel in 1797 and major general and chief of the Apsheron Artillery Regiment in 1798. In the same year, he departed to joinAlexander Suvorov
Alexander Vasilyevich Suvorov (russian: Алекса́ндр Васи́льевич Суво́ров, Aleksándr Vasíl'yevich Suvórov; or 1730) was a Russian general in service of the Russian Empire. He was Count of Râmnicu Sărat, Rymnik, C ...
's troops in Italy. He won Suvorov's unconditional trust for taking Lecco
Lecco (, , ; lmo, label= Lecchese, Lècch ) is a city of 48,131 inhabitants in Lombardy, northern Italy, north of Milan. It lies at the end of the south-eastern branch of Lake Como (the branch is named ''Branch of Lecco'' / ''Ramo di Lecco''). ...
on the eve of the Battle of Cassano and for commanding the rearguard in the crossing of the Gotthard Pass
german: Gotthardpass
, photo = File:Gotthardpass 2008.jpg
, photo_caption = The area of the Gotthard Pass from the west
, elevation_m = 2106
, elevation_ref =
, traversed = National Road 2 Old paved road ( Tremola) Gotthard Rail Tunnel Go ...
. At Bassignana
Bassignana (in Piedmontese dialect ''Bassgnan-na'') is a municipality in the Province of Alessandria, Piedmont, northern Italy. The village is situated near the confluence of the Po River and the Tanaro river.
Main sights include remains of the ...
he changed three horses killed by the enemy but was not even scratched; at Altdorf he led assault infantry over a burning bridge. These and similar episodes, true or anecdotal, forged public opinion of Miloradovich as a daring and lucky field commander, an opinion that he himself cultivated for the rest of his life. Miloradovich was adored at home, but the French held a different opinion: Adolphe Thiers
Marie Joseph Louis Adolphe Thiers ( , ; 15 April 17973 September 1877) was a French statesman and historian. He was the second elected President of France and first President of the French Third Republic.
Thiers was a key figure in the July Rev ...
described Miloradovich as "a Servian , of brilliant valour, but absolutely destitute of military knowledge, dissolute in manners, uniting all the vices of civilization with all the vices of barbarism".
Paul rewarded Miloradovich with the Order of St. Anne 1st class, the Order of St. John of Jerusalem and the Order of St. Alexander Nevsky. Suvorov, in violation of military codes, transferred Miloradovich from field troops to his staff as a "general in waiting"; Paul later cited this fact as a pretext to dismiss Suvorov. Friendship between Miloradovich and Paul's second son Constantine also dated back to the Swiss campaign. Constantine awarded Miloradovich a gilded sword with an inscription ''To my friend Miloradovich'', which Miloradovich had with him on the day of his death.
Amstetten and Austerlitz
Miloradovich played a key role in theBattle of Amstetten
The Battle of Amstetten was a minor engagement during the War of the Third Coalition between the First French Empire and the alliance of Austria and Russia. It occurred on 5 November 1805, when the retreating Russo-Austrian troops, led by Mikhai ...
, where Mikhail Kutuzov
Prince Mikhail Illarionovich Golenishchev-Kutuzov ( rus, Князь Михаи́л Илларио́нович Голени́щев-Куту́зов, Knyaz' Mikhaíl Illariónovich Goleníshchev-Kutúzov; german: Mikhail Illarion Golenishchev-Kut ...
ordered his three regiments to take a stand and provide relief for Pyotr Bagration
Prince Pyotr Ivanovich Bagration (10 July 1765 – 24 September 1812) was a Georgian general and prince serving in the Russian Empire, prominent during the Napoleonic Wars.
Bagration, a member of the Bagrationi dynasty, was born in Tbilisi. Hi ...
's troops. "Above all, skillful maneuvering of the Russian force, including timely arrival of Miloradovich and his intelligent application of the reserve forces at his disposal, prevented the collapse of the rear guard". The action at Amstetten allowed Kutuzov to break contact with the French and prevented an all-out battle that would have been disastrous for the Russians. Reports of the battle by Miloradovich himself contradict the French accounts and are not corroborated by Bagration's laconic report: each side presented their own perspective, and Miloradovich had a particular penchant for glorifying his own actions. His action at Amstetten was rewarded with the Order of St. George
The Order of Saint George (russian: Орден Святого Георгия, Orden Svyatogo Georgiya) is the highest military decoration of the Russian Federation. Originally established on 26 November 1769 Julian (7 December 1769 Gregorian) a ...
3rd class and promotion to lieutenant general. On November 11, 1805 Miloradovich attacked the French in the Battle of Dürenstein
A battle is an occurrence of combat in warfare between opposing military units of any number or size. A war usually consists of multiple battles. In general, a battle is a military engagement that is well defined in duration, area, and for ...
(referred to as the Battle of Krems in Russian sources), but the French withdrew before his corps could inflict significant damage.
The Battle of Austerlitz
The Battle of Austerlitz (2 December 1805/11 Frimaire An XIV FRC), also known as the Battle of the Three Emperors, was one of the most important and decisive engagements of the Napoleonic Wars. The battle occurred near the town of Austerlitz ...
saw Miloradovich in charge of the Russian part of a Russian-Austrian infantry column (2,875 out of 11,795 men), one of the four columns placed on Pratzen Heights, which had been abandoned by the French. Another, a larger part of the column was under Austrian command; the close presence of Kutuzov somewhat mitigated the perils of divided command. Tsar Alexander ordered this column to move before others were deployed; Kutuzov, unable to oppose the tsar, ordered Miloradovich to advance across the Goldbach Stream to Kobylnice, disregarding enemy action and difficult terrain. Hills and fog obstructed the view, and the column marched straight into the bulk of the French armies. Soult's troops mauled the mixed column and Miloradovich retreated. Alexander summoned his brother Constantine for help (although an alternative account by Bowden and Duffy Duffy may refer to:
People
*Duffy (surname), people with the surname Duffy or Duffey
* Duffy (nickname)
*Duffy (singer) (born 1984), Welsh singer, born Aimee Ann Duffy
Places
*Duffy, Australian Capital Territory, a suburb of Canberra
* Duffy, Ohi ...
asserts that Miloradovich contacted Constantine himself). Contrary to the popular view that "he was almost the only Russian general who obtained an advantage over the French" at Austerlitz, General Karl Wilhelm von Toll contested Miloradovich's actions, asserting that his column was the first to fall back and that it was Bagration, not Miloradovich, who saved the allied troops from annihilation.
Russian-Turkish War
The war of 1806–1812 began with Russian occupation ofMoldavia
Moldavia ( ro, Moldova, or , literally "The Country of Moldavia"; in Romanian Cyrillic: or ; chu, Землѧ Молдавскаѧ; el, Ἡγεμονία τῆς Μολδαβίας) is a historical region and former principality in Centr ...
and Wallachia
Wallachia or Walachia (; ro, Țara Românească, lit=The Romanian Land' or 'The Romanian Country, ; archaic: ', Romanian Cyrillic alphabet: ) is a historical and geographical region of Romania. It is situated north of the Lower Danube and s ...
. After the Turks responded by taking Bucharest
Bucharest ( , ; ro, București ) is the capital and largest city of Romania, as well as its cultural, industrial, and financial centre. It is located in the southeast of the country, on the banks of the Dâmbovița River, less than north o ...
, Russian commander-in-chief Ivan Ivanovich Michelson dispatched Miloradovich to intervene. Miloradovich captured Bucharest on December 13 without significant resistance from the Turks and was rewarded with a golden sword with diamonds ''"For the taking of Bucharest"''. The Turks, manipulated by the French envoy Sébastiani, did not declare war until five days later. No large-scale action followed. In May 1807 Miloradovich tried to capture Giurgiu
Giurgiu (; bg, Гюргево) is a city in southern Romania. The seat of Giurgiu County, it lies in the historical region of Muntenia. It is situated amongst mud-flats and marshes on the left bank of the Danube facing the Bulgarian city ...
, but failed and fell back to Bucharest. On 2 June 1807, he redeemed himself by checking the Turkish advance at Obilești.
The years 1808 and 1809 did not see any remarkable action either, but were marked by a dual intrigue among top Russian generals; at the top level, Mikhail Kutuzov was in conflict with Alexander Prozorovsky
Prince Alexander Alexandrovich Prozorovsky (russian: Алекса́ндр Алекса́ндрович Прозоро́вский, tr. ; 1733 – 21 August 1809) was the only Field Marshal from the Prozorovsky family.
Biography
Prozorovsky gain ...
, while below them burned a feud between Miloradovich and Pyotr Bagration. Bagration temporarily succeeded Prozorovsky as commander-in-chief, but later both Miloradovich and Bagration lost their commands. At the beginning of 1810 Alexander
Alexander is a male given name. The most prominent bearer of the name is Alexander the Great, the king of the Ancient Greek kingdom of Macedonia who created one of the largest empires in ancient history.
Variants listed here are Aleksandar, Al ...
recalled Miloradovich from front-line duty and tasked him with assembling a new army in Belarus
Belarus,, , ; alternatively and formerly known as Byelorussia (from Russian ). officially the Republic of Belarus,; rus, Республика Беларусь, Respublika Belarus. is a landlocked country in Eastern Europe. It is bordered by ...
. In April 1810 Miloradovich was appointed Governor of Kiev
Kyiv, also spelled Kiev, is the capital and most populous city of Ukraine. It is in north-central Ukraine along the Dnieper River. As of 1 January 2021, its population was 2,962,180, making Kyiv the seventh-most populous city in Europe.
Ky ...
but soon tended his resignation. He was officially discharged in September 1810 but was called up for service in November, again, as Governor of Kiev.
Napoleon's invasion of Russia
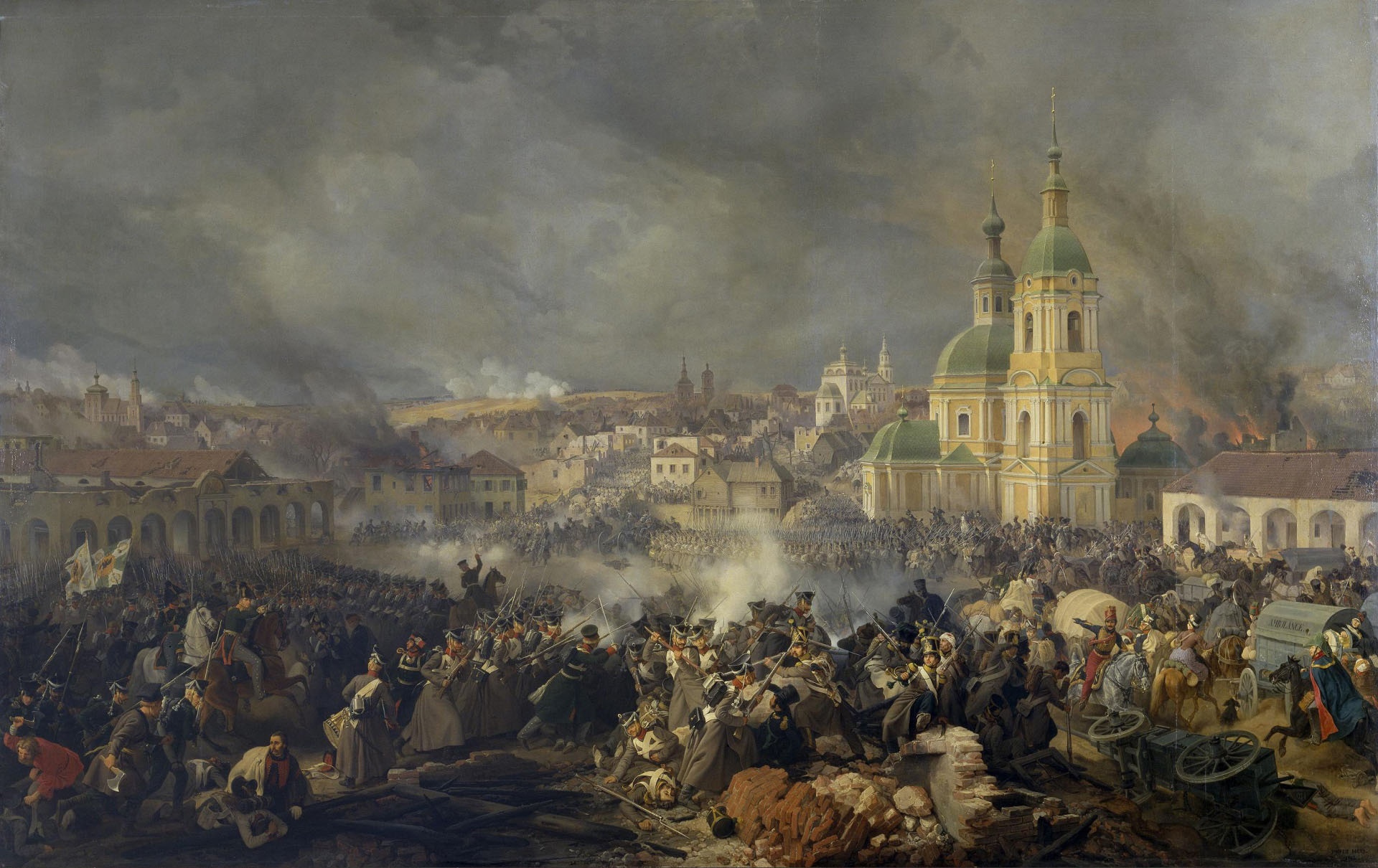 At the beginning of the 1812 campaign, Miloradovich was tasked with assembling and training volunteer
At the beginning of the 1812 campaign, Miloradovich was tasked with assembling and training volunteer militia
A militia () is generally an army or some other fighting organization of non-professional soldiers, citizens of a country, or subjects of a state, who may perform military service during a time of need, as opposed to a professional force of r ...
troops in the hinterland; he returned to action on the eve of the Battle of Borodino
The Battle of Borodino (). took place near the village of Borodino on during Napoleon's invasion of Russia. The ' won the battle against the Imperial Russian Army but failed to gain a decisive victory and suffered tremendous losses. Napole ...
with 14,600 militiamen. Kutuzov appointed Miloradovich commander of front-line forces of the right (northern) flank, comprising Baggovut's Second Infantry Corps and Ostermann-Tolstoy's Fourth Infantry Corps. The battle plan required Miloradovich to protect the old Smolensk
Smolensk ( rus, Смоленск, p=smɐˈlʲensk, a=smolensk_ru.ogg) is a city and the administrative center of Smolensk Oblast, Russia, located on the Dnieper River, west-southwest of Moscow. First mentioned in 863, it is one of the oldest ...
-Moscow road. On the day of the battle, , Kutuzov realised that enemy action was concentrated against his center and left flank and, at about 9 a.m., he ordered Miloradovich to march to the south and attack the French left flank. Riding in advance of his troops, Miloradovich was caught up in the heat of the battle for Semyonovskoe and, together with Barclay de Tolly
Barclay de Tolly () is the name of a Baltic German noble family of Scottish origin (Clan Barclay). During the time of the Revolution of 1688 in Britain, the family migrated to Swedish Livonia from Towy (Towie) in Aberdeenshire. Its subsequent ...
, Yermolov and Rayevsky, sought refuge in the defences of the Fourth Division. Between 10 a.m. and 12 noon his troops took a stand in the center of the Russian line and held off French attacks, with Baggovut's corps seeing critical action around noon, and Ostermann's corps around 4 p.m. By the end of the battle, the French succeeded in forcing the Russians from their defences, and Miloradovich's troops fell back to the same Smolensk road from where they had started. Baggovut took a stand there and held the road until nightfall against ferocious attacks by Polish cavalry.
After the battle, Miloradovich took command of the rearguard, sheltering Kutuzov's army from the advancing French. Enemy pressure prevented him from attending the Council in Fili that decided to surrender Moscow. Miloradovich, acting on behalf of Kutuzov, made a deal with Murat Murat may refer to:
Places Australia
* Murat Bay, a bay in South Australia
* Murat Marine Park, a marine protected area
France
* Murat, Allier, a commune in the department of Allier
* Murat, Cantal, a commune in the department of Cantal
Elsewhe ...
: if the French wanted Moscow intact, they had to allow Miloradovich free passage to the east, or face stubborn urban warfare
Urban warfare is combat conducted in urban areas such as towns and cities. Urban combat differs from combat in the open at both the operational and the tactical levels. Complicating factors in urban warfare include the presence of civilians a ...
. Hereford George wrote that "Murat apparently deemed it beneath his dignity to confer with a mere general" and that he left the talks to Sébastiani. According to Fyodor Glinka
Fyodor Nikolaevich Glinka ( rus, Фёдор Никола́евич Гли́нка, p=ˈfʲɵdər nʲɪkɐˈlajɪvʲɪdʑ ˈɡlʲinkə, a=Fyodor Nikolayevich Glinka.ru.vorb.oga; 1786–1880) was a Russian poet and author.
Biography
Glinka was bor ...
, however, Murat and Miloradovich negotiated directly with each other prior to the surrender of Moscow; Miloradovich contacted Sébastiani only after the French took Moscow and their cavalry engaged the Russian rear. Sébastiani honored the accord, called back the cavalry and allowed the safe retreat of two Russian regiments trapped between advancing French columns. Temporary loss of contact between Murat and the Russian rearguard allowed Kutuzov to make a westward turn: Murat kept on advancing south-east towards Bronnitsy while Kutuzov marched in the opposite direction.
On , Kutuzov took defensive positions at Podolsk
Podolsk ( rus, Подольск, p=pɐˈdolʲsk) is an industrial city, center of Podolsk Urban Okrug, Moscow Oblast, Russia, located on the Pakhra River (a tributary of the Moskva River).
History
The first mentions of the village of Podol, ...
and dispatched Miloradovich to take position in front of the advancing French, 12 kilometers to the east. Four days later, Murat engaged Miloradovich and forced him to fall back to Krasnaya Pakhra (deliberately setting a trap, according to Glinka). Miloradovich barely escaped death or captivity when his headquarters were raided by French cavalry scouts on . On , Miloradovich successfully counterattacked Murat's corps at Chirikovo, taking one general de brigade
Brigadier general or Brigade general is a military rank used in many countries. It is the lowest ranking general officer in some countries. The rank is usually above a colonel, and below a major general or divisional general. When appointed to ...
prisoner. At this point, Kutuzov preferred to retreat further south; the main army marched to Tarutino, while Miloradovich, now having Ostermann-Tolstoy's corps under his command, retreated to a fallback position on the Chernishnya River, 8 kilometers north of Tarutino. Glinka wrote that from to Miloradovich was continuously fighting the French, including four significant battles, and lamented that few of his deeds reached the public eye: "He is not a hero of the ''Vedomosti
''Vedomosti'' ( rus, Ведомости, p=ˈvʲedəməsʲtʲɪ, ) is a Russian-language business daily newspaper published in Moscow.
History
''Vedomosti'' was founded in 1999 as a joint venture between Dow Jones, who publishes ''The Wall ...
'', but a hero of history and of the future." During the standoff on the Chernishnya, Miloradovich had another person-to-person negotiation with Murat, while his own camp was filled with masses of French stragglers taken prisoner. Modern Russian historians criticized as indecisive his actions in the Battle of Tarutino
The Battle of Tarutino (russian: Тарутинo) was a part of Napoleon's invasion of Russia. In the battle Russian troops under the command of Bennigsen defeated French troops under the command of Joachim Murat.
The battle is sometimes ca ...
(), when poor coordination of Russian columns met its match in poor discipline of the French camp, but to contemporaries like Glinka and William Cathcart the battle was a clear success.
After the Battle of Maloyaroslavets
The Battle of Maloyaroslavets took place on 24 October 1812 as part of the French invasion of Russia. It was Kutuzov's decisive battle to force Napoleon to retreat northwest over Mozhaisk to Smolensk on the devastated route of his advance wi ...
, Russian troops split into three pursuit columns, led by Miloradovich, Matvey Platov and Kutuzov himself. Miloradovich marched directly on Vyazma
Vyazma (russian: Вя́зьма) is a town and the administrative center of Vyazemsky District in Smolensk Oblast, Russia, located on the Vyazma River, about halfway between Smolensk, the administrative center of the oblast, and Mozhaysk. Thr ...
, occupied by four French corps ( Beauharnais, Davout, Ney, Poniatowski), while Platov closed in on it from the north. On Miloradovich and Platov agreed to storm Vyazma. The Battle of Vyazma
The Battle of Vyazma (November 3, 1812), occurred at the beginning of Napoleon's retreat from Moscow. In this encounter a Russian force commanded by General Miloradovich inflicted heavy losses on the rear guard of the Grande Armee. Although ...
began at dawn of . Miloradovich quickly deployed front-line artillery that withstood Beauharnais's counterstrike and forced Davout's troops to take cover in the forest. Davout lost two hours taking a detour to reunite with Ney in Vyazma; at 2 p.m., when Miloradovich ordered a general assault, the French were already unable to resist. By 5 p.m. Miloradovich took control of the city, capturing French supply trains (but only three cannons).
On Miloradovich's three corps, marching ahead of the retreating French, took position to the French rear near Krasny. Miloradovich began the three-day Battle of Krasnoi
The Battle of Krasnoi (Krasny) was a series of skirmishes fought from 15 to 18 November 1812 during the final stage of Napoleon's retreat from Moscow.Lieven, p. 267. In this engagement the Russians under General Kutuzov inflicted heavy losses ...
by capturing a large supply train and cutting Ney and Beauharnais off from Napoleon's army. The next day, Beauharnais exhausted his troops in a breakthrough and refused Miloradovich's invitation to surrender; at night the decimated remains of his corps escaped through the woods. On Ney made his own unsuccessful attempt to break through Miloradovich's defences. Miloradovich again offered honorable surrender, but Ney arrested the messenger and expended his 10th and 11th divisions in a frontal assault. At night his forces of 3,000 men escaped over the frozen Dnieper
}
The Dnieper () or Dnipro (); , ; . is one of the major transboundary rivers of Europe, rising in the Valdai Hills near Smolensk, Russia, before flowing through Belarus and Ukraine to the Black Sea. It is the longest river of Ukraine an ...
, but only 800 made it to Orsha
Orsha ( be, О́рша, Во́рша, Orša, Vorša; russian: О́рша ; lt, Orša, pl, Orsza) is a city in Belarus in the Vitebsk Region, on the fork of the Dnieper and Arshytsa rivers.
History
Orsha was first mentioned in 1067 as R ...
. Miloradovich missed the opportunity to intercept the French crossing of Berezina by two days.
In December 1812, Alexander awarded Miloradovich the Order of St. George, 2nd class. In line with Kutuzov's ''December Plan'', Miloradovich led a Russian vanguard due west and took Warsaw
Warsaw ( pl, Warszawa, ), officially the Capital City of Warsaw,, abbreviation: ''m.st. Warszawa'' is the capital and largest city of Poland. The metropolis stands on the River Vistula in east-central Poland, and its population is officiall ...
on .
Campaign of 1813-1814
The appointment ofPeter Wittgenstein
, title = 1st Prince of Sayn-Wittgenstein-Ludwigsburg-Berleburg
, image = Pjotr-christianowitsch-wittgenstein.jpg
, image_size =
, caption = Portrait by George Dawe
, birth_date =
, birth_place = Pereias ...
as commander-in-chief of the united Russian and Prussian armies provoked open hostility from his new subordinates and, at the same time, from his seniors: Miloradovich, Barclay de Tolly, Langeron, Platov and Tormasov
Count Alexander Petrovich Tormasov (; 22 August 1752 – 25 November 1819) was a Russian cavalry general prominent during the Napoleonic Wars.
Early life
Alexander Tormasov was born on 22 August 1752 into an old Russian noble family. At t ...
. Tormasov refused to obey Wittgenstein altogether and left the army, while Miloradovich stayed and became the "official speaker" for the opposition. The conflict burned until the failures at Lutzen and Bautzen
Bautzen () or Budyšin () is a hill-top town in eastern Saxony, Germany, and the administrative centre of the district of Bautzen. It is located on the Spree river. In 2018 the town's population was 39,087. Until 1868, its German name was ''Budi ...
compelled Wittgenstein to resign his command.
Miloradovich's own record in May 1813 was mixed: at Lutzen his corps of 12,000 men arrived too late to influence the outcome. In the following week he covered the retreat to the Elbe
The Elbe (; cs, Labe ; nds, Ilv or ''Elv''; Upper and dsb, Łobjo) is one of the major rivers of Central Europe. It rises in the Giant Mountains of the northern Czech Republic before traversing much of Bohemia (western half of the Czech Re ...
. Thiers wrote that the French "made him pay dearly for his useless boast" (his resolve to defend a certain position). Cathcart praised his skillful rearguard action but noted that by May 12 his corps had shrunk to about 10,000. At Bautzen, Miloradovich managed to push Oudinot
Nicolas Charles Oudinot, 1st Count Oudinot, 1st Duke of Reggio (25 April 1767 in Bar-le-Duc – 13 September 1847 in Paris), was a Marshal of the Empire. He is known to have been wounded 34 times in battle, being hit by artillery shells, sabers ...
out of Tronberg, but the battle as a whole remained a French victory.
Miloradovich and Constantine spent the remainder of the war, almost a year, in close cooperation and proximity as chiefs of infantry and cavalry reserves. In August 1813, after expiry of the Truce of Pläswitz, Miloradovich led the reserve force of 24,000 Guards and Grenadiers into Bohemia
Bohemia ( ; cs, Čechy ; ; hsb, Čěska; szl, Czechy) is the westernmost and largest historical region of the Czech Republic. Bohemia can also refer to a wider area consisting of the historical Lands of the Bohemian Crown ruled by the Bohem ...
and Constantine followed him with 11,000 "splendid cavalry" and artillery. Together with Barclay's headquarters, they formed one of four allied columns that converged on Dresden
Dresden (, ; Upper Saxon: ''Dräsdn''; wen, label= Upper Sorbian, Drježdźany) is the capital city of the German state of Saxony and its second most populous city, after Leipzig. It is the 12th most populous city of Germany, the fourth ...
but had not been brought into the action of the Battle of Dresden
The Battle of Dresden (26–27 August 1813) was a major engagement of the Napoleonic Wars. The battle took place around the city of Dresden in modern-day Germany. With the recent addition of Austria, the Sixth Coalition felt emboldened in ...
. Three days later they were employed against Vandamme Vandamme is a surname. Notable people with the surname include:
* Alexandre Vandamme (born 1962), Belgian businessman
* Dominique Vandamme (1770–1830), French military officer
* George Vandamme, Belgian wheelchair racer
* Jamaïque Vandamme (born ...
in the Battle of Kulm
:''See Battle of Chlumec for the 1126 battle at Kulm
The Battle of Kulm was fought near the town Kulm () and the village Přestanov in northern Bohemia. It was fought on 29–30 August 1813, during the War of the Sixth Coalition. A French ...
, a "fortunate victory that conferred advantages beyond all calculations". On the eve of the Battle of Leipzig
The Battle of Leipzig (french: Bataille de Leipsick; german: Völkerschlacht bei Leipzig, ); sv, Slaget vid Leipzig), also known as the Battle of the Nations (french: Bataille des Nations; russian: Битва народов, translit=Bitva ...
the forces of Miloradovich and Constantine, stationed near Margeborn, formed the reserve of the coalition army. In December 1813 they crossed the Rhine
), Surselva, Graubünden, Switzerland
, source1_coordinates=
, source1_elevation =
, source2 = Rein Posteriur/Hinterrhein
, source2_location = Paradies Glacier, Graubünden, Switzerland
, source2_coordinates=
, source ...
and headed into France.
Miloradovich's actions in 1813 were rewarded with the Order of St. Andrew, the title of count and the right to wear Alexander's insignia on his shoulder, the first such honor ever granted in Russia. Miloradovich concluded the campaign of 1814, his last one, in Paris. After General Gorchakov's infantry overran the French defensive artillery, Miloradovich was the one to bring in twenty howitzer
A howitzer () is a long- ranged weapon, falling between a cannon (also known as an artillery gun in the United States), which fires shells at flat trajectories, and a mortar, which fires at high angles of ascent and descent. Howitzers, like ot ...
s and open fire at the city.
Governor of Saint Petersburg
After the Treaty of Fontainebleau Alexander appointed Miloradovich commander of the Russian Imperial Guard; in 1818 Miloradovich became Governor of Saint Petersburg, assuming command of all the troops, police and civil administration of the imperial capital. He had the unconditional trust of Alexander, who could hardly have found a worse candidate for the job. As chief of police, Miloradovich controlled political surveillance and investigation in Saint Petersburg, but the events of 1825 demonstrated that he ultimately failed to respond to the real threat: he dismissed the evidence against theDecembrists
The Decembrist Revolt ( ru , Восстание декабристов, translit = Vosstaniye dekabristov , translation = Uprising of the Decembrists) took place in Russia on , during the interregnum following the sudden death of Emperor Al ...
, saying "It's all stuff; leave these young blockheads alone to read to each other their trash of miserable verses."
His affection for the arts and his ex officio duty as a censor at the peak of the Golden Age of Russian Poetry Golden Age of Russian Poetry (or ''Age of Pushkin'') is the name traditionally applied by philologists to the first half of the 19th century. The most significant Russian poet Pushkin (in Nabokov's words, the greatest poet this world was blessed wit ...
resulted in frequent contacts with authors and actors, and, apart from his death and his actions during the disastrous flood of 1824, his administration was remembered largely through anecdotes and artists' memoirs of varying reliability. This was not uncommon for Russian commanders; Nikolay Raevsky said "They he writers of his timeturned me into a Roman, Miloradovich into a great man, Wittgenstein into the saviour of the fatherland, and Kutuzov into Fabius. I am not a Roman, and neither are these gentlemen."
Alexander Herzen
Alexander Ivanovich Herzen (russian: Алекса́ндр Ива́нович Ге́рцен, translit=Alexándr Ivánovich Gértsen; ) was a Russian writer and thinker known as the "father of Russian socialism" and one of the main fathers of agra ...
who met Miloradovich in early childhood and fondly remembered him as a storyteller "with the greatest vivacity, with lively mimicry, with roars of laughter" ridiculed Miloradovich as an administrator yet called him "a warrior poet who understood poetry ... grand things are done by great means." Herzen's memoirs provide a number of anecdotes about Miloradovich the administrator (none of which could have been witnessed by the narrator).
In 1820 Miloradovich interrogated Alexander Pushkin
Alexander Sergeyevich Pushkin (; rus, links=no, Александр Сергеевич ПушкинIn pre-Revolutionary script, his name was written ., r=Aleksandr Sergeyevich Pushkin, p=ɐlʲɪkˈsandr sʲɪrˈɡʲe(j)ɪvʲɪtɕ ˈpuʂkʲɪn, ...
on suspicion of political propaganda. Pushkin's name had already become a blanket cover for all kinds of incendiary pamphlets and he was desperate to clear himself of dangerous misattributions. Pushkin said that he burned his "contraband poems" and recited some from memory. Miloradovich said "Ah, c'est chevaleresque", dismissed the charges and sent Pushkin on a well-paid tour of the south. Vladimir Nabokov
Vladimir Vladimirovich Nabokov (russian: link=no, Владимир Владимирович Набоков ; 2 July 1977), also known by the pen name Vladimir Sirin (), was a Russian-American novelist, poet, translator, and entomologist. Bor ...
noted that all of Pushkin's influential friends could not have saved him had it not been for Miloradovich's "amiable conduct of the whole affair". There was a rumor that Pushkin was flogged on orders of Miloradovich, who fought a duel with at least one person who repeated it.
Author and publisher Nikolai Grech recounted another, less inspiring episode: in 1824 Miloradovich vigorously investigated an alleged breach of censorship rules at a printshop owned by Grech and Bezacque. Fifteen years earlier, when Miloradovich and Pyotr Bagration had a feud, Bezacque was Bagration's secretary and apparently became a lifelong enemy of Miloradovich. Grech easily refuted "factual evidence" and could have escaped unharmed, but Miloradovich brought his belated revenge down on Grech, inflicting on him a full police and court inquiry that dragged on until 1828. Miloradovich probably did not realise that the whole case was set up by Aleksey Arakcheyev and Mikhail Magnitsky to unseat .
The lifestyle of the "bizarre administrator" was just as bizarre. Miloradovich lived alone in a luxurious apartment "in complete disarray coupled with the most exquisite taste", without a single bedroom; "I spend the night where I feel like", he used to say. Family fortune and rewards from the tsar could not match his spending, and he sold off most of his lands and serfs. Posthumous sale of his remaining estate barely covered his debts.
Theatre and sexuality
 In 1821, theatre managers Apollon Maikov and Prince Alexander Shakhovskoy allegedly tried to manipulate Miloradovich to overthrow the stern and frugal director of imperial theatres, Prince Tyufyakin. Miloradovich lent them support and then himself "grabbed both the power and the purse strings"; Miloradovich, Maikov and Shakhovskoy became a "committee of three formidable officials" that governed the everyday life of the imperial theatres. The change coincided with rumours of Shakhovskoy's trafficking in actresses; the death of Miloradovich and the ascension of Nicholas I ended Shakhovskoy's career.
The private life of Miloradovich, who never married and had no offspring, has been a controversial subject. Contemporaries condemned him for a desire "to create his own
In 1821, theatre managers Apollon Maikov and Prince Alexander Shakhovskoy allegedly tried to manipulate Miloradovich to overthrow the stern and frugal director of imperial theatres, Prince Tyufyakin. Miloradovich lent them support and then himself "grabbed both the power and the purse strings"; Miloradovich, Maikov and Shakhovskoy became a "committee of three formidable officials" that governed the everyday life of the imperial theatres. The change coincided with rumours of Shakhovskoy's trafficking in actresses; the death of Miloradovich and the ascension of Nicholas I ended Shakhovskoy's career.
The private life of Miloradovich, who never married and had no offspring, has been a controversial subject. Contemporaries condemned him for a desire "to create his own harem
Harem ( Persian: حرمسرا ''haramsarā'', ar, حَرِيمٌ ''ḥarīm'', "a sacred inviolable place; harem; female members of the family") refers to domestic spaces that are reserved for the women of the house in a Muslim family. A har ...
in the theatre school" that allegedly became a reality with the aid of Shakhovskoy and Maikov. According to these sources, Miloradovich "had a weakness for women" and regularly spent evenings in the company of Shakhovskoy and female trainees of his theatre school; the chosen favorites then enjoyed the general's benevolence after graduation. Catherine Shuler noted that the appetites of Miloradovich and other dignitaries could be the cause of high "traffic in women" on stage and that "the resemblance between serf actresses and imperial actresses is surely not coincidental". Alexandra Kolosova
Alexandra Mikhailovna Kolosova (russian: Алекса́ндра Миха́йловна Колосова, 16 February 1802, Saint Petersburg, Russian Empire, - 19 March 1880, Saint Petersburg, Russian Empire) was a Russian stage actress, later tran ...
, in 1822, was the first actress to break the ring and flee to Paris; upon return to Saint Petersburg she sought protection from Alexander, but Miloradovich had her arrested for twenty-four hours for turning down "the most insignificant role" offered to her. Miloradovich had lead actor Vasily Karatygin
Vasily Andreevich Karatygin (russian: Василий Андреевич Каратыгин) (–-) was a leading actor of Russian Romanticism.
Karatygin joined the Bolshoi Theatre in St Petersburg in 1820 and moved to the Alexandrine Theatre in 1 ...
arrested for similar insubordination; when the prisoner's mother pleaded for mercy, Miloradovich responded: "I only like comedy onstage. I've seen blood, madam, tears don't move me".
Vladimir Bryukhanov suggested that Miloradovich was homosexual, disregarding or dismissing evidence to the contrary, such as the memoirs of Nadezhda Durova. (Durova, disguised as a young man, was aide to Miloradovich in 1810 and later wrote about his affairs with women and their influence on the general's demeanor and on his relationships with subordinate officers.) The standard version of events holds that his last passion was ballerina Yekaterina Teleshova, who earlier had an affair with Alexander Griboyedov
Alexander Sergeyevich Griboyedov (russian: Александр Сергеевич Грибоедов, ''Aleksandr Sergeevich Griboedov'' or ''Sergeevich Griboyedov''; 15 January 179511 February 1829), formerly romanized as Alexander Sergueevich Gr ...
, a diplomat "too short of money to be a long-term rival to the general" (In 1825, Griboyedov wrote "... Miloradovich, that boastful idiot whom Shakhovskoy grovels to and idolises. They are both cattle.").
Interregnum
 In the summer of 1823, Alexander I issued a secret manifest excluding Constantine from the order of succession and making Nicholas
In the summer of 1823, Alexander I issued a secret manifest excluding Constantine from the order of succession and making Nicholas heir presumptive
An heir presumptive is the person entitled to inherit a throne, peerage, or other hereditary honour, but whose position can be displaced by the birth of an heir apparent or a new heir presumptive with a better claim to the position in question. ...
to the throne. Historians argue as to whether or not Miloradovich had been formally made aware of Alexander's decision. Only three men – Aleksey Arakcheyev, Alexander Golitsyn, and Archbishop Filaret – definitely knew the contents and whereabouts of the manifest; neither Constantine nor Nicholas knew the whole story.
On , when news of Alexander's death in Taganrog
Taganrog ( rus, Таганрог, p=təɡɐnˈrok) is a port city in Rostov Oblast, Russia, on the north shore of the Taganrog Bay in the Sea of Azov, several kilometers west of the mouth of the Don River. Population:
History of Taganrog
Th ...
reached Saint Petersburg, Miloradovich bullied Nicholas into pledging allegiance to Constantine, who was then living in Warsaw
Warsaw ( pl, Warszawa, ), officially the Capital City of Warsaw,, abbreviation: ''m.st. Warszawa'' is the capital and largest city of Poland. The metropolis stands on the River Vistula in east-central Poland, and its population is officiall ...
as viceroy of Poland The Namiestnik (or Viceroy) of the Kingdom of Poland ( pl, namiestnik Królestwa Polskiego, russian: наместник Царства Польского) was the deputy of the Emperor of Russia who, under Congress Poland (1815–1874), styled himse ...
. Golitsyn arrived at the palace later and announced the terms of Alexander's manifest, but Miloradovich persuaded the State Council that Nicholas was aware of it and that his pledge of allegiance to Constantine was effectively an act of abdication
Abdication is the act of formally relinquishing monarchical authority. Abdications have played various roles in the succession procedures of monarchies. While some cultures have viewed abdication as an extreme abandonment of duty, in other societ ...
. Miloradovich then sent a messenger to Moscow with two instructions: to pledge allegiance to Constantin and to keep the original of Alexander's manifest secret and locked away. Faced with the question, "What if Constantine holds to his resignation?", Miloradovich allegedly responded, "When one has one hundred thousand bayonets in one's pocket, it is easy to speak with boldness".
Correspondence between Saint Petersburg and Warsaw took two weeks, during which Miloradovich acted as de facto interrex
The interrex (plural interreges) was literally a ruler "between kings" (Latin ''inter reges'') during the Roman Kingdom and the Roman Republic. He was in effect a short-term regent.
History
The office of ''interrex'' was supposedly created follow ...
and regularly assured Nicholas that "everything is quiet". Constantine firmly refused to reign and blessed his brother's accession to the throne, but for a while the hesitant Nicholas took no action. On the morning of , Nicholas received detailed reports of the brewing Decembrist revolt from Diebitsch and Chernyshov, and discussed the matter with Miloradovich and Golitsyn. According to Nicholas himself, the evidence was overwhelming. Miloradovich promised to mobilise all police resources but did nothing or, according to Korf, his "investigations remained completely fruitless. His researches had not discovered one person on whom suspicion could reasonably fall".
The actions of Miloradovich during the interregnum were highly controversial and provoked fringe conspiracy theories placing him at the top of the Decembrist rebel ring. Mainstream historians provide different explanations of his motives, none of which supports the theory of "Decembrist Miloradovich":
* Mikhail Safonov suggested that there were three contenders for the throne: Constantin, Nicholas and their mother Maria Fyodorovna. Miloradovich supported Maria but in public he aligned with Constantine and later with Nicholas. A similar version has been fictionalised by Igor Bunich.
* Yakov Gordin suggested that Miloradovich acted as an independent dictator, using Constantine merely as a front.
* Andreeva supports a toned-down variation of Gordin's suggestion: that, regardless of Alexander's manifest, Miloradovich acted in good faith, supporting what he thought was the legitimate solution to a crisis.
Revolt and death
 At 8 p.m. on , Nicholas declared himself emperor; at 7 a.m. the next morning, along with all senior statesmen present in Saint Petersburg, Miloradovich pledged his loyalty to Nicholas (Korf suggested that Miloradovich recognised Nicholas as early as ). Once again Miloradovich assured Nicholas that the city was "perfectly tranquil"; Alexander von Benckendorff other witnesses wrote that he was in his usual boastful, optimistic mood. Three hours later when Miloradovich enjoyed breakfast with Teleshova, general Neidhardt reported to Nicholas that the troops were marching towards the palace "in absolute mutiny".
At about noon on Miloradovich, whom nobody had seen since the morning, reported to Nicholas on
At 8 p.m. on , Nicholas declared himself emperor; at 7 a.m. the next morning, along with all senior statesmen present in Saint Petersburg, Miloradovich pledged his loyalty to Nicholas (Korf suggested that Miloradovich recognised Nicholas as early as ). Once again Miloradovich assured Nicholas that the city was "perfectly tranquil"; Alexander von Benckendorff other witnesses wrote that he was in his usual boastful, optimistic mood. Three hours later when Miloradovich enjoyed breakfast with Teleshova, general Neidhardt reported to Nicholas that the troops were marching towards the palace "in absolute mutiny".
At about noon on Miloradovich, whom nobody had seen since the morning, reported to Nicholas on Palace Square
Palace Square ( rus, Дворцо́вая пло́щадь, r=Dvortsovaya Ploshchad, p=dvɐˈrtsovəjə ˈploɕːɪtʲ), connecting Nevsky Prospekt with Palace Bridge leading to Vasilievsky Island, is the central city square of St Petersb ...
. Witnesses disagree on whether he was mounted or on foot, but all accounts point to his extraordinary excitement and loss of self-control. According to Nicholas, Miloradovich told him: "Сеlа va mаl; ils marchent au Sénat, mais je vais leur раrlеr" (French: "That is bad; they are marching toward the Senate, but I will talk to them"). Nicholas coldly responded that Miloradovich must do his duty as the military governor and calm his troops down. Miloradovich saluted, turned around, and headed to the barracks of the Mounted Guards. General Orlov of the Mounted Guards pleaded with Miloradovich to stay with the loyal troops but Miloradovich refused to take cover, mounted a horse and rode out to the rows of rebel troops, accompanied either by two aides or only by Bashutsky on foot. Miloradovich harangued the soldiers for obedience, showing Constantine's sword "to prove that he would have been incapable of betraying him". Safonov pointed out that, instead of executing the tsar's order to lead the Mounted Guards against the rebels, Miloradovich "disobeyed it in a most incredible way ... by going into the action alone."
Between 12:20 and 12:30 Pyotr Kakhovsky
Pyotr Grigoryevich Kakhovsky (russian: Пётр Григо́рьевич Кахо́вский, 1799 – ) was a Russian Empire officer and active participant of Decembrist revolt, known for the murder of General Mikhail Miloradovich and Colonel ...
shot Miloradovich point-blank in the back; "the bullet travelling up from below, from the back to the chest, tore the diaphragm, broke through all the parts and stopped beneath the right nipple". When Miloradovich slumped from his horse to the ground, Yevgeny Obolensky
Prince Yevgeny Petrovich Obolensky (russian: Евге́ний Петро́вич Оболе́нский, – ) was a Russian officer from the Obolensky family, one of the most active participants in the Decembrist revolt.
Biography
Yevgeny Obole ...
stabbed him with a bayonet
A bayonet (from French ) is a knife, dagger, sword, or spike-shaped weapon designed to fit on the end of the muzzle of a rifle, musket or similar firearm, allowing it to be used as a spear-like weapon.Brayley, Martin, ''Bayonets: An Illustr ...
. Miloradovich was taken to a nearby house, but by the time the surgeons arrived on the scene the marauders had stripped Miloradovich of his clothes, medals and jewelry. Medics removed the bullet (it was later delivered to Nicholas); Miloradovich remained conscious and dictated his last will in a letter to the tsar. There were three requests: to send His Majesty's regards to his relatives, to grant liberty to his serfs, and to "not forget the old Maikov". Miloradovich died around 3 a.m. on . After six days of lying in state, he was buried with honors at the Alexander Nevsky Lavra
Saint Alexander Nevsky Lavra or Saint Alexander Nevsky Monastery was founded by Peter I of Russia in 1710 at the eastern end of the Nevsky Prospekt in Saint Petersburg, in the belief that this was the site of the Neva Battle in 1240 when Alex ...
.
The investigation of the Decembrist revolt led to the hanging of Kakhovsky and four of his ringleaders; it did not reveal any illicit connection between the Decembrists and Miloradovich. The second killer, Obolensky, was stripped of his princely title and exiled to Siberia for thirty years.
Nobility
The Miloradović noble family is listed in the nobility of the Russian Empire.See also
*Andrei Miloradovich
Andrei Stepanovich Miloradovich (Russian: Андре́й Степа́нович Милора́дович; 1727–2 May 1796) was a Russian military leader, statesman and lieutenant general. He is the father of general Mikhail Miloradovich.
B ...
* Peter Mikhailovich Kaptzevich
Peter Mikhailovich Kaptzevich or Kapcević or Kapzewitch (1772 – 3 July 1840) was a General who led a Russian infantry corps during the 1814 Campaign in France. In 1812 he led the 7th Division at Smolensk, Borodino, Maloyaroslavets and Krasnoi. ...
* Nikolay Vuich
Nikolay Vasilyevich Vuich (also spelled Nikolaj Vasiljevič Vujič or Nikolaj Vasiljević Vujić; russian: Никола́й Васи́льевич Ву́ич; 1765–27 March 1836) was an Imperial Russian general who fought in the Russo-Swedis ...
* Peter Ivanovich Ivelich
* Ivan Shevich
* Avram Ratkov
Avram Petrovich Ratkov (21 October 1773 – 26 December 1829) was a Russian general of Serbian descent who participated in many battles, including the Battle of Borodino where he commanded the reserve military force with the rank of major general. ...
* Ivan Adamovich
* Nikolay Bogdanov
Nikolay Ivanovich Bogdanov (28 August 1751 - 16 March 1829) was a Russian General who participated in the wars against Napoleonic France. He received numerous awards and decorations for his work and with his experience also later fought the Ottoma ...
* Nikolay Depreradovich
* Ivan Lukačević (soldier)
Ivan Lukačević ( sr, Иван Лукачевић, russian: Иван Лукачевич; 1711–12), known as ''Podgoričanin'' (), was a Russian Imperial captain of Serb origin from Podgorica (now in Montenegro) that participated in planning of ...
* Jovan Šević
* Jovan Albanez
Jovan Albanez ( sr-Cyrl, Јован Албанез; –d. ) or Ivan Albanez (Serbian, russian: Иван Албанез, uk, Іван Албанез) ) was a military officer of Montenegrin Serb origin who led the first group of colonists from t ...
* Simeon Piščević
Simeon Piščević (Šid, 4 September 1731Imperial Russia, November 1798) was a Serbian memoirist and imperial Russian general.
Biography
Originally from the famed Serbian Paštrovići tribe, the Piščević family took their name from their ow ...
* Anto Gvozdenović
Anto Gvozdenović (Serbian Cyrillic: Анто Гвозденовић; 26 January 1853 – 2 September 1935) was a Montenegrin, Russian, and French general, a member of the Imperial Russian Privy Council, and a diplomat and statesman.
* Semyon Zorich
Count Semyon Zorich (1743–1799) was an Imperial Russian lieutenant-general and count of the Holy Roman Empire, born in Serbia, who served Imperial Russia against the Prussians and Turks. A member of the Russian court, he was presented to Empress ...
* Peter Tekeli
Peter Tekeli (russian: Петр Авраамович Текели, Serbian: Петар Поповић Текелија or ''Petar Popović Tekelija'',''Popović'' is often omitted. hu, Tököly-Popovics Péter) (1720–1792) was a Russian gener ...
* Georgi Emmanuel
* Dejan Subotić
Dejan Ivanovich Subotich (also spelled Dejan Subotić and Dean Subbotich; 7 May 1852 – 1920) was a Russo-Serbian military and state leader, military governor of Russian Dalian (''Primorye oblast''; 1897–1898);Transcaspian Oblast (''Zakaspiy ...
* Fedor Yakovlevich Mirkovich
* Marko Ivelich
* Rajko Depreradović
Notes
Further reading
* Andreeva, T. V. (1998, in Russian).Imperator Nikolai Pavlovich i graf M. A. Miloradovich (Император Николай Павлович и граф М. А. Милорадович)
'. СПБ: Философский век, выпуск 6 (The Philosophical Age. Almanac 6. Russia at the Time of Nicholas I: Science, Politics, Enlightenment. Ed. by T. Khartanovich, M. Mikeshin. St. Petersburg, 1998. 304 p.). * Bezotnosny, V. M. et al. (2004, in Russian). ''Otechestvennaya voina 1812 goda. Encyclopedia (Отечественная война 1812 года. Энциклопедия)''. Moscow: Rosspan. . * Bethea, David M. (2005).
The Pushkin Handbook
'. University of Wisconsin Press. , . * Browning, Oscar (2008 reprint).
A History of the Modern World 1815-1910
'. Read Books (reprint). , . * Castle, Ian; Hook, Christa (2002). ‘�
Austerlitz 1805: the fate of empires
��’. Osprey. , . * William Cathcart (1850).
Commentaries on the War in Russia and Germany in 1812 and 1813
'. London: J. Murray. Reissue: . * Cust, Edward (1863). ‘�
Annals of the wars of the nineteenth century, Volume 4
��’. London: John Murray. * Durova, Nadezhda; Zinn, Mary (translator) (1989 edition). ‘�
The Cavalry Maiden: Journals of a Russian Officer in the Napoleonic Wars
��’. Indiana University Press. , . * George, Hereford B. (2002 reissue).
Napoleon's Invasion of Russia
'. Janus Publishing Company Lim. , . Originally published in 1899. * Grech, Nikolai (2000 edition, in Russian).
Zapiski o moei zhizni (Записки о моей жизни)
'. Moscow: Zakharov. * Freer, Allan (1846).
Russian under Nicholas
'' North British Review, volume 5. Edinburgh: W. P. Kennedy. * Glinka, Fyodor (1870, in Russian).
Pisma russkogo ofitsera (Письма русского офицера)
'. Moscow. * Glinka, Fyodor (1814, in Russian).
Podvigi grafa Miloradovicha (Подвиги графа Милорадовича)
'. Moscow. * Herzen, Alexander; McDonald, Dwight (editor) (1982).
My past and thoughts: the memoirs of Alexander Herzen
'. University of California Press. , . * Kagan, Frederick (2007).
The End of the Old Order: Napoleon and Europe, 1801-1805
'' Da Capo Press. , . * Kelly, Laurence (2006).
Diplomacy and Murder in Tehran: Alexander Griboyedov and Imperial Russia's Mission to the Shah of Persia
'. Tauris Parke Paperbacks. , . * Korf, M. A. (1857).
The accession of Nicholas I
'. London: John Murray. * Leskov, Nikolay (2003 edition, in Russian). ''Graf Mikhail Andreevich Miloradovich (Граф Михаил Андреевич Милорадович)'', in: Desyatnikov, V. A. (editor) (2003, in Russian).
Blistatelny Sankt-Peterburg (Блистательный Санкт-Петербург)
'. Olma Media Group, , . pp. 448–453. Originally published in 1869. * Lotman, Jurij; Ouspensky, Boris (1990, in French).
Sémiotique de la culture russe: études sur l'histoire
'. L’Age du Homme. , 9782825100172. * Miloradovich, G. A. (1871, in Russian).
O rodine dvoryan i grafa Miloradovicha
'. First edition: Kiev. * Nabokov, Vladimir (1990 reprint).
Eugene Onegin: A Novel in Verse: Commentary
'. Princeton University Press. , . * Nicholas I (1848, Russian translation from French).
Memoirs of Nicholas I (in Russian)
'. * Schnitzler, Johann (1847).
Secret history of the court and government of Russia under the emperors Alexander and Nicholas
'. London: Richard Bentley. * Schuler, Catherine (2009).
Theatre and identity in imperial Russia
'. University of Iowa Press. , . * Safonov, M. M. (1994, in Russian).
K istorii mezhdutsarstviya (К истории междуцарстия)
'. Proceedings of the Mavrodinskie conference 10–12 December 1994, Saint Petersburg (Мавродинские чтения: материалы к докладам 10-12 октября 1994 г., Санкт-Петербург). Saint Petersburg University. * Safonov, M. M. (2001, in Russian).
'. Rodina magazine, no. 12, 2001. * Sapozhnikov, A. I. (2008, in Russian).
Neopublikovannaya Istoria kampanii 1812 goda A. I. Mihailovskogo-Danilevskogo (Неопубликованная «История кампании 1812 года» А.И. Михайловского-Данилевского)
'. *Schultz, C. C. (2004). . Taleon Club Magazine
Retrieved 2011-07-16. Archived fro
the original
on 2006-01-12. * Thiers, Adolphe (1865).
History of the consulate and the empire of France under Napoleon, Volume 2
'. London: Lippincott. * Thiers, Adolphe (1864).
History of the consulate and the empire of France under Napoleon, Volume 4
'. London: Lippincott. * Treasure, Geoffrey (1985).
The making of modern Europe, 1648-1780
'. Routledge. , . {{DEFAULTSORT:Miloradovich, Mikhail 1771 births 1825 deaths Military personnel from Saint Petersburg People from Saint Petersburg Governorate Imperial Russian Army generals Russian people of Serbian descent Knights Hospitaller Members of the State Council (Russian Empire) Recipients of the Order of St. George of the Second Degree Recipients of the Order of St. Anna, 1st class Recipients of the Order of St. Vladimir, 1st class Knights of the Order of St John Russian commanders of the Napoleonic Wars Russian nobility Governors-General of Kiev Burials at the Dukhovskaya Church Miloradović noble family