Metropolitan-Vickers on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Metropolitan-Vickers, Metrovick, or Metrovicks, was a British heavy
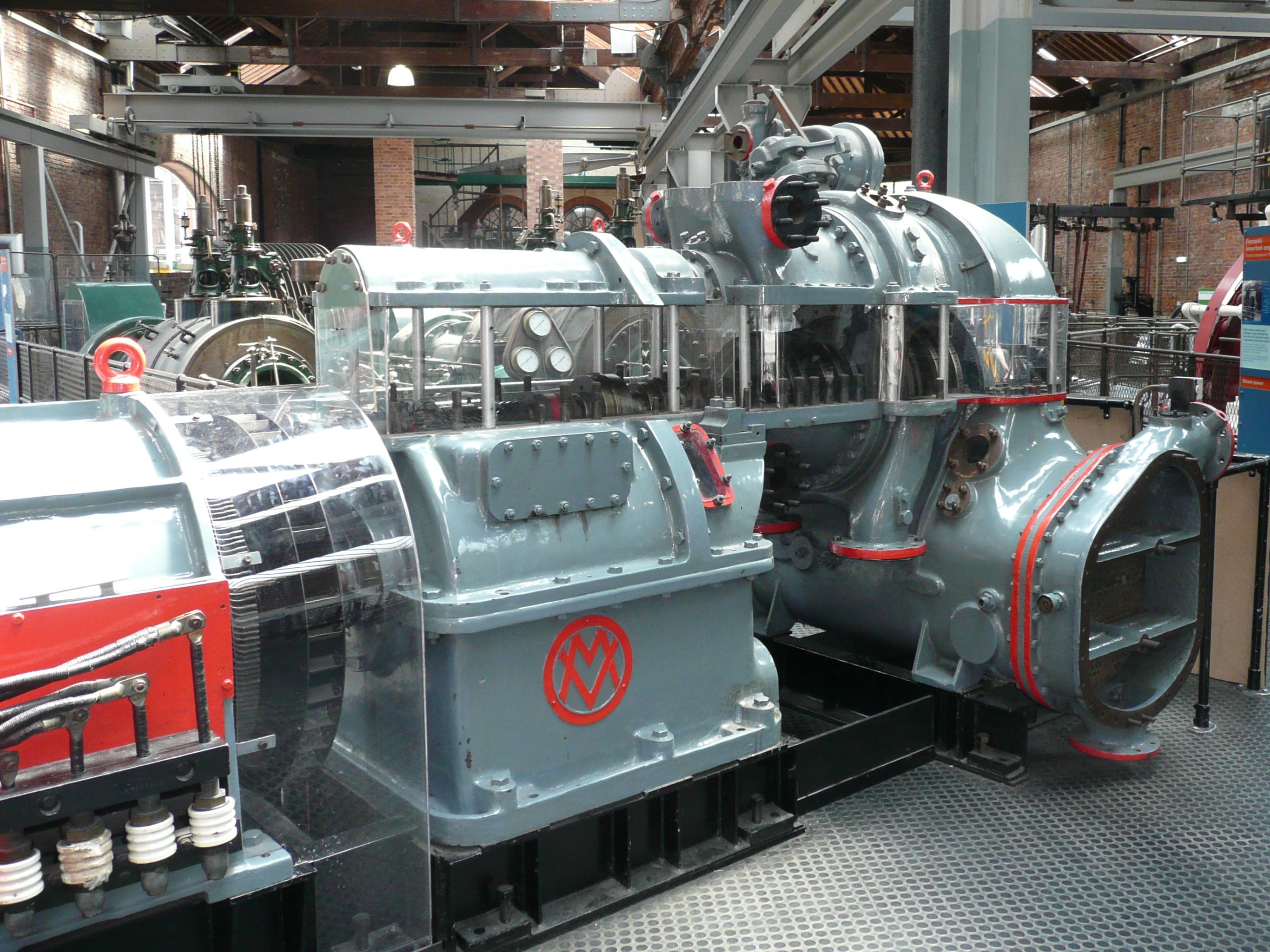
 Metrovick started as a way to separate the existing British Westinghouse Electrical and Manufacturing Company factories from United States control, which had proven to be a hindrance to gaining government contracts during the
Metrovick started as a way to separate the existing British Westinghouse Electrical and Manufacturing Company factories from United States control, which had proven to be a hindrance to gaining government contracts during the
 In mid-1938, MV was awarded a contract to build
In mid-1938, MV was awarded a contract to build
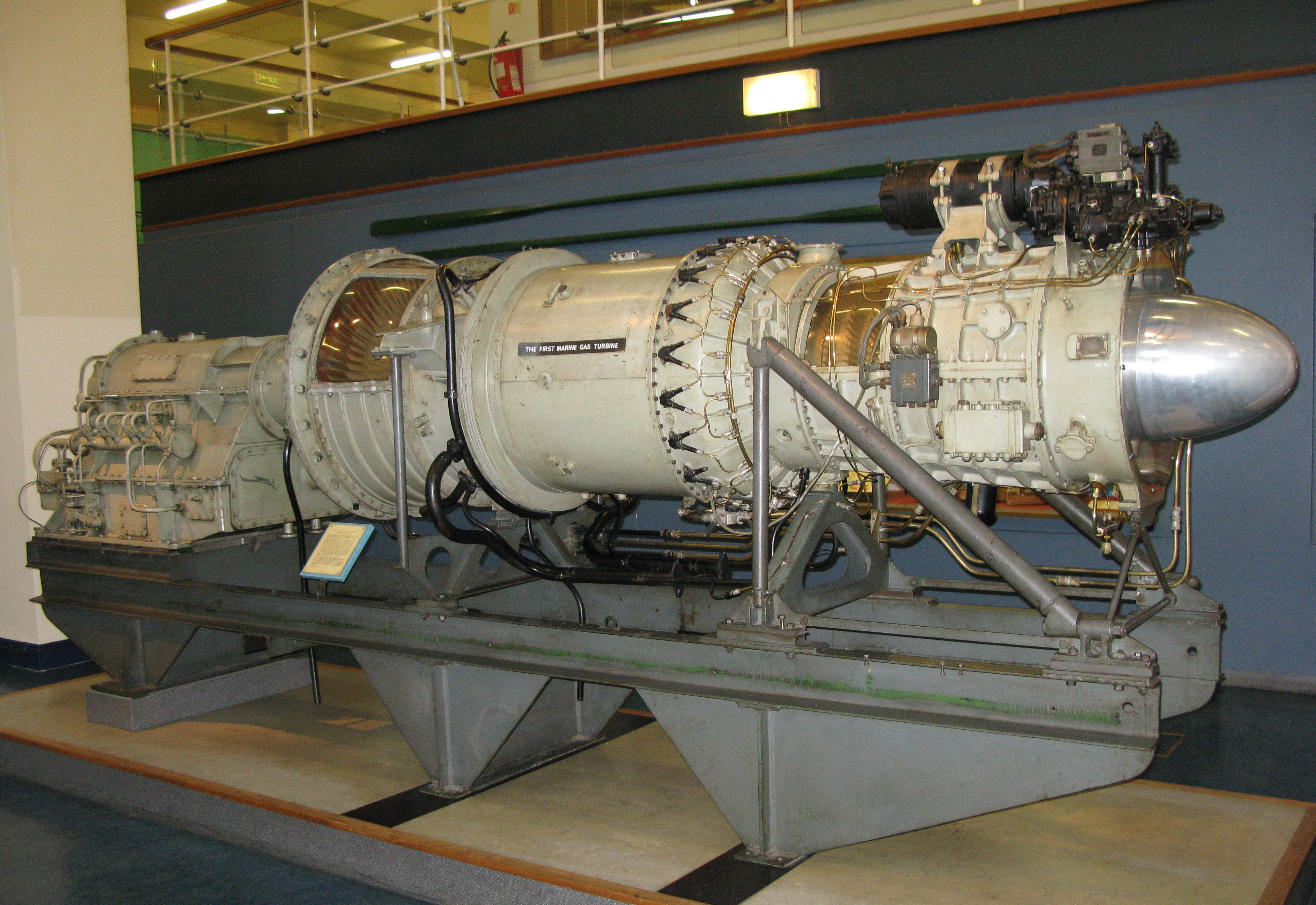
 The post-war era led to massive demand for electrical systems, leading to additional rivalries between Metrovick and BTH as each attempted to one-up the other in delivering ever-larger turbogenerator contracts. Metrovick also expanded its appliance division during this time, becoming a well known supplier of refrigerators and stoves.
The design and manufacture of sophisticated scientific instruments, such as
The post-war era led to massive demand for electrical systems, leading to additional rivalries between Metrovick and BTH as each attempted to one-up the other in delivering ever-larger turbogenerator contracts. Metrovick also expanded its appliance division during this time, becoming a well known supplier of refrigerators and stoves.
The design and manufacture of sophisticated scientific instruments, such as
"Metropolitan-Vickers Electrical Co. Ltd. 1899-1949" by John Dummelow
250 pages of text and pictures. (This is a mirror of the original, which was accessed from https://web.archive.org/web/20050308065049/http://www.mvbook.org.uk/ ) {{Authority control Turbines Locomotive manufacturers of the United Kingdom Engineering companies of the United Kingdom Electrical engineering companies of the United Kingdom Defunct manufacturing companies of the United Kingdom Associated Electrical Industries Radar manufacturers Defunct companies based in Manchester Manufacturing companies based in Manchester Manufacturing companies established in 1899 Manufacturing companies disestablished in 1960 Defunct aircraft engine manufacturers of the United Kingdom Former defence companies of the United Kingdom Science and technology in the United Kingdom British companies established in 1899 British companies disestablished in 1960
electrical engineering
Electrical engineering is an engineering discipline concerned with the study, design, and application of equipment, devices, and systems which use electricity, electronics, and electromagnetism. It emerged as an identifiable occupation in the l ...
company of the early-to-mid 20th century formerly known as British Westinghouse
British Westinghouse Electrical and Manufacturing Company was a subsidiary of the Pittsburgh, USA based Westinghouse Electric and Manufacturing Company. British Westinghouse would become a subsidiary of Metropolitan-Vickers in 1919; and after Me ...
. Highly diversified, it was particularly well known for its industrial electrical equipment such as generators, steam turbine
A steam turbine is a machine that extracts thermal energy from pressurized steam and uses it to do mechanical work on a rotating output shaft. Its modern manifestation was invented by Charles Parsons in 1884. Fabrication of a modern steam tu ...
s, switchgear, transformer
A transformer is a passive component that transfers electrical energy from one electrical circuit to another circuit, or multiple circuits. A varying current in any coil of the transformer produces a varying magnetic flux in the transformer' ...
s, electronics
The field of electronics is a branch of physics and electrical engineering that deals with the emission, behaviour and effects of electrons using electronic devices. Electronics uses active devices to control electron flow by amplification ...
and railway traction equipment. Metrovick holds a place in history as the builders of the first commercial transistor computer, the Metrovick 950, and the first British axial-flow jet engine
A jet engine is a type of reaction engine discharging a fast-moving jet (fluid), jet of heated gas (usually air) that generates thrust by jet propulsion. While this broad definition can include Rocket engine, rocket, Pump-jet, water jet, and ...
, the Metropolitan-Vickers F.2
The Metropolitan-Vickers F.2 is an early turbojet engine and the first British design to be based on an axial-flow compressor. It was an extremely advanced design for the era, using a nine-stage axial compressor, annular combustor, and a two ...
. Its factory in Trafford Park, Manchester
Manchester () is a city in Greater Manchester, England. It had a population of 552,000 in 2021. It is bordered by the Cheshire Plain to the south, the Pennines to the north and east, and the neighbouring city of Salford to the west. The ...
, was for most of the 20th century one of the biggest and most important heavy engineering facilities in Britain and the world.
History

 Metrovick started as a way to separate the existing British Westinghouse Electrical and Manufacturing Company factories from United States control, which had proven to be a hindrance to gaining government contracts during the
Metrovick started as a way to separate the existing British Westinghouse Electrical and Manufacturing Company factories from United States control, which had proven to be a hindrance to gaining government contracts during the First World War
World War I (28 July 1914 11 November 1918), often abbreviated as WWI, was List of wars and anthropogenic disasters by death toll, one of the deadliest global conflicts in history. Belligerents included much of Europe, the Russian Empire, ...
. In 1917 a holding company was formed to try to find financing to buy the company's properties.Scott (1963). pp. 140–142.
In May 1917, control of the holding company was obtained jointly by the Metropolitan Carriage, Wagon and Finance Company
Metro-Cammell, formally the Metropolitan Cammell Carriage and Wagon Company (MCCW), was an English manufacturer of railway carriages, locomotives and railway wagons, based in Saltley, and subsequently Washwood Heath, in Birmingham. Purchased ...
, of Birmingham
Birmingham ( ) is a city and metropolitan borough in the metropolitan county of West Midlands in England. It is the second-largest city in the United Kingdom with a population of 1.145 million in the city proper, 2.92 million in the We ...
, chaired by Dudley Docker, and Vickers Limited
Vickers Limited was a British engineering conglomerate. The business began in Sheffield in 1828 as a steel foundry and became known for its church bells, going on to make shafts and propellers for ships, armour plate and then artillery. Entir ...
, of Barrow-in-Furness
Barrow-in-Furness is a port town in Cumbria, England. Historically in Lancashire, it was incorporated as a municipal borough in 1867 and merged with Dalton-in-Furness Urban District in 1974 to form the Borough of Barrow-in-Furness. In 2023 t ...
.Gillham (1988), Chapter 2: ''The Manufacturers. On 15 March 1919, Docker agreed terms with Vickers, for Vickers to purchase all the shares
In financial markets, a share is a unit of equity ownership in the capital stock of a corporation, and can refer to units of mutual funds, limited partnerships, and real estate investment trusts. Share capital refers to all of the shares of ...
of the Metropolitan Carriage, Wagon and Finance Company for almost £13 million.Scott (1963). Appendix A. On 8 September 1919, Vickers changed the name of the British Westinghouse Electrical and Manufacturing Company to Metropolitan Vickers Electrical Company.
The immediate post-war era was marked by low investment and continued labour unrest. Fortunes changed in 1926 with the formation of the Central Electricity Board
The United Kingdom Central Electricity Board (CEB) was established by the Electricity (Supply) Act 1926. It had the duty to supply electricity to authorised electricity undertakers, to determine which power stations would be 'selected' stations ...
which standardized electrical supply and led to a massive expansion of electrical distribution, installations, and appliance purchases. Sales shot up, and 1927 marked the company's best year to date.
On 15 November 1922 the BBC was registered and the BBC's Manchester station, 2ZY
2ZY was the name of a radio station established by the British Broadcasting Company in Manchester, England, in 1922. Part of the newly nationalised British Broadcasting Corporation from 1 January 1927, the station continued broadcasting under the 2 ...
, was officially opened on 375 metres transmitting from the Metropolitan Vickers Electricity works in Old Trafford.
BTH merger and transition to AEI
In 1928 Metrovick merged with the rivalBritish Thomson-Houston
British Thomson-Houston (BTH) was a British engineering and heavy industrial company, based at Rugby, Warwickshire, England, and founded as a subsidiary of the General Electric Company (GE) of Schenectady, New York, United States. They were kno ...
(BTH), a company of similar size and basically the same product lineup. Combined, they would be one of the few companies able to compete with Marconi or English Electric
N.º UIC: 9094 110 1449-3 (Takargo Rail)
The English Electric Company Limited (EE) was a British industrial manufacturer formed after the Armistice of 11 November 1918, armistice of World War I by amalgamating five businesses which, during th ...
on an equal footing. In fact the merger was marked by poor communication and intense rivalry, and the two companies generally worked at cross purposes.
The next year the combined company was purchased by the Associated Electrical Industries
Associated Electrical Industries (AEI) was a British holding company formed in 1928 through the merger of the British Thomson-Houston Company (BTH) and Metropolitan-Vickers electrical engineering companies. In 1967 AEI was acquired by GEC, to c ...
(AEI) holding group, who also owned Edison Swan
The Edison and Swan Electric Light Company Limited was a manufacturer of incandescent lamp bulbs and other electrical goods. It was formed in 1883 with the name Edison & Swan United Electric Light Company with the merger of the Swan United Elect ...
(Ediswan); and Ferguson, Pailin & Co, manufacturers of electrical switchgear in Openshaw, Manchester. The rivalry between Metrovick and BTH continued, and AEI was never able to exert effective control over the two competing subsidiary companies.
Problems worsened in 1929 with the start of the great depression
The Great Depression (19291939) was an economic shock that impacted most countries across the world. It was a period of economic depression that became evident after a major fall in stock prices in the United States. The economic contagio ...
, but Metrovick's overseas sales were able to pick up some of the slack, notably a major railway electrification project in Brazil
Brazil ( pt, Brasil; ), officially the Federative Republic of Brazil (Portuguese: ), is the largest country in both South America and Latin America. At and with over 217 million people, Brazil is the world's fifth-largest country by area ...
. By 1933 world trade was growing again, but growth was nearly upset when six Metrovick engineers were arrested and found guilty of espionage
Espionage, spying, or intelligence gathering is the act of obtaining secret or confidential information ( intelligence) from non-disclosed sources or divulging of the same without the permission of the holder of the information for a tang ...
and " wrecking" in Moscow
Moscow ( , US chiefly ; rus, links=no, Москва, r=Moskva, p=mɐskˈva, a=Москва.ogg) is the capital and largest city of Russia. The city stands on the Moskva River in Central Russia, with a population estimated at 13.0 million ...
after a number of turbines built by the company in and for the Soviet Union
The Soviet Union,. officially the Union of Soviet Socialist Republics. (USSR),. was a transcontinental country that spanned much of Eurasia from 1922 to 1991. A flagship communist state, it was nominally a federal union of fifteen nationa ...
proved to be faulty. The British government intervened; the engineers were released and trade with Russia was resumed after a brief embargo.
During the 1930s Metropolitan Vickers produced two dozen very large diameter (3m/10 ft) three-phase AC traction motors for the Hungarian railway's V40 and V60 electric locomotives. The 1640 kW rated power machinery, designed by Kálmán Kandó, was paid for by British government economic aid.
In 1935 the company built a 105 MW steam turbogenerator
A turbo generator is an electric generator connected to the shaft of a steam turbine or gas turbine for the generation of electric power. Large steam-powered turbo generators provide the majority of the world's electricity and are also used b ...
, the largest in Europe at that time, for the Battersea Power Station.
In 1936 Metrovick started work with the Air Ministry
The Air Ministry was a department of the Government of the United Kingdom with the responsibility of managing the affairs of the Royal Air Force, that existed from 1918 to 1964. It was under the political authority of the Secretary of Stat ...
on automatic pilot systems, eventually branching out to gunlaying systems and building radar
Radar is a detection system that uses radio waves to determine the distance (''ranging''), angle, and radial velocity of objects relative to the site. It can be used to detect aircraft, Marine radar, ships, spacecraft, guided missiles, motor v ...
s the next year. In 1938 they reached an agreement with the Ministry to build a turboprop
A turboprop is a turbine engine that drives an aircraft propeller.
A turboprop consists of an intake, reduction gearbox, compressor, combustor, turbine, and a propelling nozzle. Air enters the intake and is compressed by the compressor. ...
design developed at the Royal Aircraft Establishment
The Royal Aircraft Establishment (RAE) was a British research establishment, known by several different names during its history, that eventually came under the aegis of the UK Ministry of Defence (MoD), before finally losing its identity in me ...
(RAE) under the direction of Hayne Constant
Hayne Constant, CB, CBE., MA., FRAeS., FRS, (26 September 1904 – 12 January 1968) was an English mechanical and aeronautical engineer who developed jet engines during World War II.
Education
Constant was born at Gravesend, the son of Frede ...
. It is somewhat ironic that BTH, its erstwhile partners, were at the same time working with Frank Whittle on his pioneering jet designs.
Wartime aircraft production
 In mid-1938, MV was awarded a contract to build
In mid-1938, MV was awarded a contract to build Avro Manchester
The Avro 679 Manchester was a British twin-engine heavy bomber developed and manufactured by the Avro aircraft company in the United Kingdom. While not being built in great numbers, it was the forerunner of the famed and vastly more successful ...
twin-engined heavy bombers under licence from A.V. Roe. As this type of work was very different from its traditional heavy engineering activities, a new factory was built on the western side of Mosley Road and this was completed in stages through 1940. There were significant problems producing this aircraft, not least being the unreliability of the Rolls-Royce Vulture
The Rolls-Royce Vulture was a British aero engine developed shortly before World War II that was designed and built by Rolls-Royce Limited. The Vulture used the unusual " X-24" configuration, whereby four cylinder blocks derived from the R ...
engine and that the first 13 Manchesters were destroyed in a ''Luftwaffe
The ''Luftwaffe'' () was the aerial-warfare branch of the German '' Wehrmacht'' before and during World War II. Germany's military air arms during World War I, the '' Luftstreitkräfte'' of the Imperial Army and the '' Marine-Fliegerabt ...
'' bombing raid on Trafford Park on 23 December. Despite this the firm went on to complete 43 examples. With the design of the much improved four-engined derivative, the Avro Lancaster
The Avro Lancaster is a British Second World War heavy bomber. It was designed and manufactured by Avro as a contemporary of the Handley Page Halifax, both bombers having been developed to the same specification, as well as the Short Stir ...
, MV switched production to that famous type, supplied with Rolls-Royce Merlin
The Rolls-Royce Merlin is a British liquid-cooled V-12 piston aero engine of 27-litres (1,650 cu in) capacity. Rolls-Royce designed the engine and first ran it in 1933 as a private venture. Initially known as the PV-12, it was late ...
engines from the Ford Trafford Park shadow factory. Three hangars were erected on the southside of Manchester's Ringway Airport for assembly and testing of its Lancasters, before a policy switch was made to assembling them in a hangar at Avro's Woodford airfield. By the end of the war, MV had built 1,080 Lancasters. These were followed by 79 Avro Lincoln
The Avro Type 694 Lincoln is a British four-engined heavy bomber, which first flew on 9 June 1944. Developed from the Avro Lancaster, the first Lincoln variants were initially known as the Lancaster IV and V; these were renamed Lincoln I and I ...
derivatives before remaining orders were cancelled and MV's aircraft production ceased in December 1945.
In 1940 the turboprop effort was re-engineered as a pure jet engine after the successful run of Whittle's designs. The new design became the Metrovick F.2 and eventually flew in 1943 on a Gloster Meteor. Considered to be too complex to bother with, Metrovick then re-engineered the design once again to produce roughly double the power, while at the same time starting work on a much larger design, the Metrovick F.9 ''Sapphire''. Although the F.9 proved to be a winner, the Ministry of Supply
The Ministry of Supply (MoS) was a department of the UK government formed in 1939 to co-ordinate the supply of equipment to all three British armed forces, headed by the Minister of Supply. A separate ministry, however, was responsible for airc ...
nevertheless forced the company to sell the jet division to Armstrong Siddeley in 1947 to reduce the number of companies in the business.
In addition to building aircraft, other wartime work included the manufacture of both Dowty and Messier undercarriages, automatic pilot units, searchlights and radar equipment. They also produced electric vans and lorries.
Metrovick postwar

 The post-war era led to massive demand for electrical systems, leading to additional rivalries between Metrovick and BTH as each attempted to one-up the other in delivering ever-larger turbogenerator contracts. Metrovick also expanded its appliance division during this time, becoming a well known supplier of refrigerators and stoves.
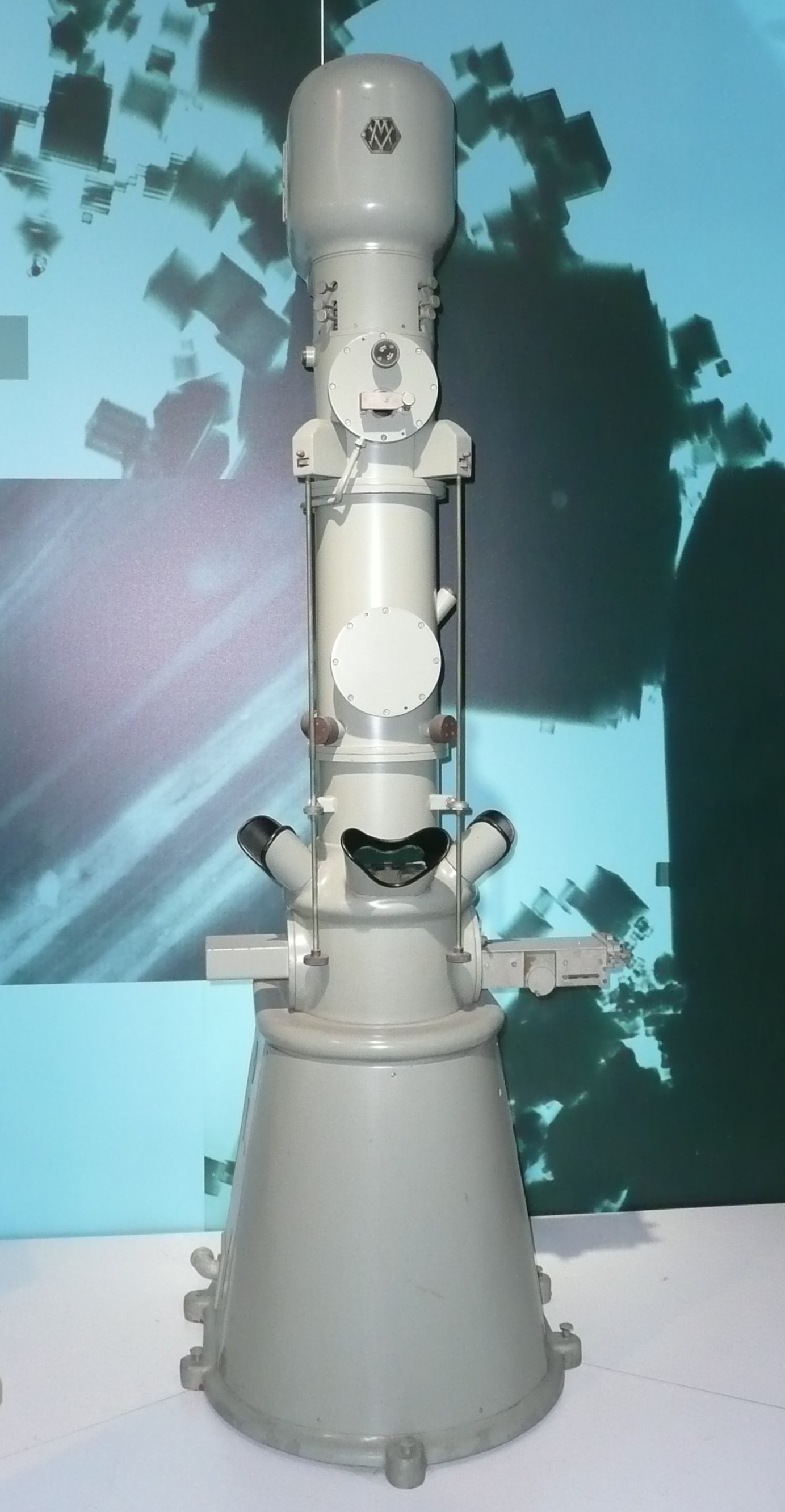
The design and manufacture of sophisticated scientific instruments, such as
The post-war era led to massive demand for electrical systems, leading to additional rivalries between Metrovick and BTH as each attempted to one-up the other in delivering ever-larger turbogenerator contracts. Metrovick also expanded its appliance division during this time, becoming a well known supplier of refrigerators and stoves.
The design and manufacture of sophisticated scientific instruments, such as electron microscope
An electron microscope is a microscope that uses a beam of accelerated electrons as a source of illumination. As the wavelength of an electron can be up to 100,000 times shorter than that of visible light photons, electron microscopes have a hi ...
s, and mass spectrometers, became an important area of scientific research for the company.
In 1947, a Metrovick G.1 Gatric gas turbine was fitted to the Motor Gun Boat
The motor gun boat (MGB) was a small, high-speed British military vessel of the Second World War, which was armed with a mix of guns, in contrast to the physically similar motor torpedo boat (MTB), whose main offensive weapon were torpedoes. ...
''MGB 2009'', making it the world's first gas turbine powered naval vessel. A subsequent marine gas turbine engine was the G.2 of 4,500 shp fitted to the Royal Navy Bold-class fast patrol boat
A patrol boat (also referred to as a patrol craft, patrol ship, or patrol vessel) is a relatively small naval vessel generally designed for coastal defence, border security, or law enforcement. There are many designs for patrol boats, and they ...
s '' Bold Pioneer'' and '' Bold Pathfinder'', which were built in 1953.
The Bluebird K7 jet-propelled 3-point hydroplane in which Donald Campbell broke the 200 mph water speed barrier was powered with a Metropolitan-Vickers Beryl jet engine producing 3,500 lbf (16 kN) of thrust. The K7 was unveiled in late 1954. Campbell succeeded on Ullswater on 23 July 1955, where he set a record of 202.15 mph (325.33 km/h), beating the previous record by some 24 mph (39 km/h) held by Stanley Sayres.
Another major area of expansion was in the diesel locomotive market, where they combined their own generators and traction motors with third-party diesel engines to develop in 1950 the Western Australian Government Railways X class 2-Do-2 locomotive and in 1958 the type 2 Co-Bo, later re-classified under the TOPS system as the British Rail Class 28. This diesel-electric locomotive was unusual on two counts; its Co-Bo wheel arrangement and its Crossley
Crossley, based in Manchester, United Kingdom, was a pioneering company in the production of internal combustion engines. Since 1988 it has been part of the Rolls-Royce Power Engineering group.
More than 100,000 Crossley oil and gas engines ...
2-Stroke diesel engine (evolved from a World War II marine engine). Intended as part the British Rail
British Railways (BR), which from 1965 traded as British Rail, was a state-owned company that operated most of the overground rail transport in Great Britain from 1948 to 1997. It was formed from the nationalisation of the Big Four (British ra ...
ways Modernisation Plan, the twenty-strong fleet saw service between Scotland and England before being deemed unsuccessful and withdrawn in the late 1960s. Metrovick also produced the CIE 001 Class (originally 'A' Class) from 1955, the first production mainline diesels in Ireland
Ireland ( ; ga, Éire ; Ulster-Scots: ) is an island in the North Atlantic Ocean, in north-western Europe. It is separated from Great Britain to its east by the North Channel, the Irish Sea, and St George's Channel. Ireland is the s ...
.
Metropolitan Vickers also produced electrical equipment for the British Rail Class 76 (EM1), and British Rail Class 77 (EM2), 1.5 kV DC locomotives, built at Gorton Works for the electrification
Electrification is the process of powering by electricity and, in many contexts, the introduction of such power by changing over from an earlier power source.
The broad meaning of the term, such as in the history of technology, economic histo ...
of the Woodhead Line in the early 1950s. Larger but broadly similar locomotives were also supplied to the New South Wales Government Railways as its 46 class. The company also designed the British Rail Class 82
The British Rail Class 82 (AL2 under the pre-TOPS classification scheme) electric locomotives were designed by the British manufacturing interest Metropolitan-Vickers and produced by Beyer, Peacock and Company on behalf of British Rail (BR).
T ...
, 25 kV AC locomotives built by Beyer, Peacock & Company
Beyer, Peacock and Company was an English railway locomotive manufacturer with a factory in Openshaw, Manchester. Founded by Charles Beyer, Richard Peacock and Henry Robertson, it traded from 1854 until 1966. The company exported locomotives, ...
in Manchester using Metrovick electrical equipment. The company also supplied electrical equipment for the British Rail Class 303 electric multiple units.
In the 1950s, the company built a large power transformer works at Wythenshawe
Wythenshawe () is a district of the city of Manchester, England. Historically in Cheshire, Wythenshawe was transferred in 1931 to the City of Manchester, which had begun building a massive housing estate there in the 1920s. With an area of approx ...
, Manchester. The factory opened in 1957, and was closed by GEC in 1971, after which it was sold to the American compressor manufacturer Ingersoll Rand.
In 1961, the Russian cosmonaut Yuri Gagarin was invited to the company's factory at Trafford Park as part of his tour of Manchester.
The rivalry between Metrovick and BTH was eventually ended in an unconvincing fashion when the AEI management eventually decided to rid themselves of both brands and be known as AEI universally, a change they made on 1 January 1960. This move was almost universally resented within both companies. Worse, the new brand name was utterly unknown to its customers, leading to a noticeable fall-off in sales and AEI's stock price.
General Electric Company (GEC) takeover
When AEI attempted to remove the doubled-up management structures, they found this task to be even more difficult. By the mid-1960s the company was struggling under the weight of two complete management hierarchies, and they appeared to be unable to control the company any more. This allowed AEI to be purchased byGeneral Electric Company
The General Electric Company (GEC) was a major British industrial conglomerate involved in consumer and defence electronics, communications, and engineering. The company was founded in 1886, was Britain's largest private employer with over 250 ...
in 1967, which was later restructured into many other companies, including Marconi plc in 1999, later Marconi Communications
Marconi Communications, the former telecommunications arm of Britain's General Electric Company plc (GEC), was founded in August 1998 through the amalgamation of GEC Plessey Telecommunications (GPT) with other GEC subsidiaries: Marconi SpA, GE ...
, and others.
See also
* :Metropolitan-Vickers locomotives *Bowesfield Works
Bowesfield Works was a railway locomotive manufacturing plant in Stockton-on-Tees. The works was operated by a joint venture company called Metropolitan Vickers-Beyer Peacock from 1949 until 1960.
Works history
Metropolitan-Vickers and Beyer, ...
* Metro-Vickers Affair
* Metrovick electric vehicles
References
Bibliography
* *External links
"Metropolitan-Vickers Electrical Co. Ltd. 1899-1949" by John Dummelow
250 pages of text and pictures. (This is a mirror of the original, which was accessed from https://web.archive.org/web/20050308065049/http://www.mvbook.org.uk/ ) {{Authority control Turbines Locomotive manufacturers of the United Kingdom Engineering companies of the United Kingdom Electrical engineering companies of the United Kingdom Defunct manufacturing companies of the United Kingdom Associated Electrical Industries Radar manufacturers Defunct companies based in Manchester Manufacturing companies based in Manchester Manufacturing companies established in 1899 Manufacturing companies disestablished in 1960 Defunct aircraft engine manufacturers of the United Kingdom Former defence companies of the United Kingdom Science and technology in the United Kingdom British companies established in 1899 British companies disestablished in 1960