Metro de Santiago on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
The Santiago Metro ( es, Metro de Santiago) is a
 The idea to build an underground railway network in Santiago dates back to 1944, when new ways to improve the chaotic transport system were sought after the rapid population growth the city was experiencing since the early 1930s. However, ideas would begin to take shape in the 1960s, when the government released an international tender for the development of an urban transport system. On 24 October 1968, the government of Eduardo Frei Montalva approved the draft submitted by the Franco-Chilean consortium BCEOM SOFRETU CADE, in which the construction of five lines with an extension of approximately 60 kilometres by 1990 was proposed. On 29 May 1969, works finally began for the construction of the first line, which would link the Civil District and the area of Barrancas (current-day Lo Prado).
On 15 September 1975, the first line of the metro was opened by
The idea to build an underground railway network in Santiago dates back to 1944, when new ways to improve the chaotic transport system were sought after the rapid population growth the city was experiencing since the early 1930s. However, ideas would begin to take shape in the 1960s, when the government released an international tender for the development of an urban transport system. On 24 October 1968, the government of Eduardo Frei Montalva approved the draft submitted by the Franco-Chilean consortium BCEOM SOFRETU CADE, in which the construction of five lines with an extension of approximately 60 kilometres by 1990 was proposed. On 29 May 1969, works finally began for the construction of the first line, which would link the Civil District and the area of Barrancas (current-day Lo Prado).
On 15 September 1975, the first line of the metro was opened by
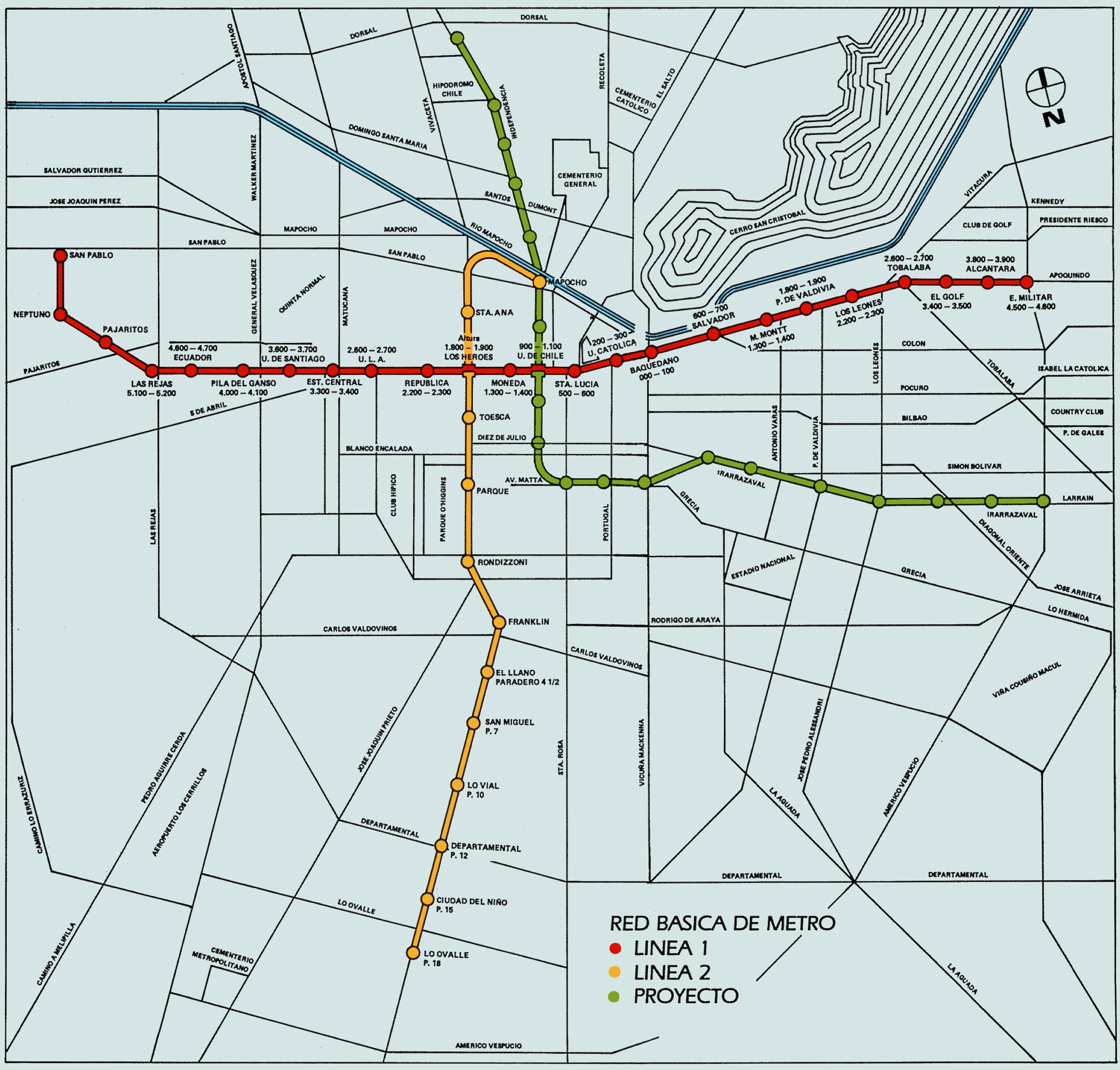 Despite the fast growth of the network, the severe economic crisis that affected the country in 1982 halted the original plans. Furthermore, studies showed that southeast Santiago was becoming more populated than the north end of the capital, area that was then covered by the planned extensions of the service.
In order to supply future demand, the layout for Line 2 was changed and the extension would start at Los Héroes and go around the Civic District, crossing Line 1 again at Baquedano to head south through Vicuña Mackenna. Meanwhile, Line 3 was projected through Independencia and Irarrázaval to supply the northern area that Line 2 was supposed to run.
However, these plans were affected once again when an earthquake struck the
Despite the fast growth of the network, the severe economic crisis that affected the country in 1982 halted the original plans. Furthermore, studies showed that southeast Santiago was becoming more populated than the north end of the capital, area that was then covered by the planned extensions of the service.
In order to supply future demand, the layout for Line 2 was changed and the extension would start at Los Héroes and go around the Civic District, crossing Line 1 again at Baquedano to head south through Vicuña Mackenna. Meanwhile, Line 3 was projected through Independencia and Irarrázaval to supply the northern area that Line 2 was supposed to run.
However, these plans were affected once again when an earthquake struck the  Line 5 was opened on 5 April 1997 by President
Line 5 was opened on 5 April 1997 by President
 The Santiago Metro currently operates 9 models of rolling stock: two models (the AS-2002 and the AS-2014) are steel-wheeled, while the others are all rubber-tyred. The NS 74 and NS 93 stock are based on the
The Santiago Metro currently operates 9 models of rolling stock: two models (the AS-2002 and the AS-2014) are steel-wheeled, while the others are all rubber-tyred. The NS 74 and NS 93 stock are based on the
File:NS 74, Metro de Santiago.jpg, NS-74
File:NS-88 en Estacion Santa Ana.jpg, NS-88
File:NS 93, Metro de Santiago.jpg,
Image:Estacionuchile.jpg, 
 Image:Estacionsantana.jpg, Santa Ana
Image:Estacionsantana.jpg, Santa Ana 
 Image:Metro de Santiago - Est. Vicuña Mackenna.jpg, Vicuña Mackenna
Image:Metro de Santiago - Est. Vicuña Mackenna.jpg, Vicuña Mackenna 
 Image:Estacionñuble.jpg, Ñuble
Image:Estacionñuble.jpg, Ñuble 

(warning: stations close earlier - se
timetable
Metro S.A.
Santiago Metro Map
Santiago Metro Track Map
Tarjeta Bip!
Plan and Authority of Transit of Santiago de Chile, Transantiago
* Santiago Metro in Wikipedia in Spanish {{Authority control Railway services introduced in 1975 1975 establishments in Chile 750 V DC railway electrification
rapid transit
Rapid transit or mass rapid transit (MRT), also known as heavy rail or metro, is a type of high-capacity public transport generally found in urban areas. A rapid transit system that primarily or traditionally runs below the surface may be ...
system serving the city of Santiago
Santiago (, ; ), also known as Santiago de Chile, is the capital and largest city of Chile as well as one of the largest cities in the Americas. It is the center of Chile's most densely populated region, the Santiago Metropolitan Region, whos ...
, the capital of Chile
Chile, officially the Republic of Chile, is a country in the western part of South America. It is the southernmost country in the world, and the closest to Antarctica, occupying a long and narrow strip of land between the Andes to the east a ...
. It currently consists of seven lines (numbered 1-6 and 4A), 136 stations, and of revenue route. The system is managed by the state-owned Metro S.A. and is the first and only rapid transit system in the country.
The Santiago Metro carries around 2.5 million passengers daily. This figure represents an increase of more than a million passengers per day compared to 2007, when the ambitious Transantiago project was launched, in which the metro plays an important role in the public transport system serving the city. Its highest passenger peak was reached on 2 May 2019, reaching 2,951,962 passengers.
In June 2017 the government announced plans for the construction of Line 7, connecting Renca
Renca is a commune of Chile located in Santiago Province, Santiago Metropolitan Region. It was founded on May 6, 1894.
Demographics
According to the 2002 census of the National Statistics Institute, Renca spans an area of and has 133,500 inha ...
in the northwest of Santiago with Vitacura
Vitacura is a commune of Chile located in Santiago Province, Santiago Metropolitan Region. It is one of the most expensive and fashionable areas of Santiago. Inhabitants are primarily high income families. It belongs to the Northeastern zone o ...
in the northeast. The new line will add 26 kilometers and 19 new stations to the Metro network, running along the municipalities of Renca, Cerro Navia, Quinta Normal, Santiago, Providencia, Las Condes and Vitacura. Its cost has been initially estimated at US$2.53 bn and it is projected to open in 2027.
In March 2012, the Santiago Metro was chosen as the best underground system in the Americas, after being honoured at the annual reception held by ''Metro Rail'' in London
London is the capital and List of urban areas in the United Kingdom, largest city of England and the United Kingdom, with a population of just under 9 million. It stands on the River Thames in south-east England at the head of a estuary dow ...
.
History and development
Early projections
 The idea to build an underground railway network in Santiago dates back to 1944, when new ways to improve the chaotic transport system were sought after the rapid population growth the city was experiencing since the early 1930s. However, ideas would begin to take shape in the 1960s, when the government released an international tender for the development of an urban transport system. On 24 October 1968, the government of Eduardo Frei Montalva approved the draft submitted by the Franco-Chilean consortium BCEOM SOFRETU CADE, in which the construction of five lines with an extension of approximately 60 kilometres by 1990 was proposed. On 29 May 1969, works finally began for the construction of the first line, which would link the Civil District and the area of Barrancas (current-day Lo Prado).
On 15 September 1975, the first line of the metro was opened by
The idea to build an underground railway network in Santiago dates back to 1944, when new ways to improve the chaotic transport system were sought after the rapid population growth the city was experiencing since the early 1930s. However, ideas would begin to take shape in the 1960s, when the government released an international tender for the development of an urban transport system. On 24 October 1968, the government of Eduardo Frei Montalva approved the draft submitted by the Franco-Chilean consortium BCEOM SOFRETU CADE, in which the construction of five lines with an extension of approximately 60 kilometres by 1990 was proposed. On 29 May 1969, works finally began for the construction of the first line, which would link the Civil District and the area of Barrancas (current-day Lo Prado).
On 15 September 1975, the first line of the metro was opened by Augusto Pinochet
Augusto José Ramón Pinochet Ugarte (, , , ; 25 November 1915 – 10 December 2006) was a Chilean general who ruled Chile from 1973 to 1990, first as the leader of the Military Junta of Chile from 1973 to 1981, being declared President of ...
during the military dictatorship. Line 1, during its opening stage, was mostly underground from San Pablo to La Moneda, running below the Alameda
An alameda is a Avenue (landscape), street or path lined with trees () and may refer to:
Places Canada
*Alameda, Saskatchewan, town in Saskatchewan
**Grant Devine Dam, formerly ''Alameda Dam'', a dam and reservoir in southern Saskatchewan
Chile
...
. In 1977, the line was extended towards Providencia and by 1980, the line reached as far as Escuela Militar.
In March 1978, Line 2 was opened. Its initial section ran at ground level from Los Héroes to Franklin. By December, the second segment of the line was opened, running underground towards the south along the Gran Avenida up to Lo Ovalle.
Project changes
 Despite the fast growth of the network, the severe economic crisis that affected the country in 1982 halted the original plans. Furthermore, studies showed that southeast Santiago was becoming more populated than the north end of the capital, area that was then covered by the planned extensions of the service.
In order to supply future demand, the layout for Line 2 was changed and the extension would start at Los Héroes and go around the Civic District, crossing Line 1 again at Baquedano to head south through Vicuña Mackenna. Meanwhile, Line 3 was projected through Independencia and Irarrázaval to supply the northern area that Line 2 was supposed to run.
However, these plans were affected once again when an earthquake struck the
Despite the fast growth of the network, the severe economic crisis that affected the country in 1982 halted the original plans. Furthermore, studies showed that southeast Santiago was becoming more populated than the north end of the capital, area that was then covered by the planned extensions of the service.
In order to supply future demand, the layout for Line 2 was changed and the extension would start at Los Héroes and go around the Civic District, crossing Line 1 again at Baquedano to head south through Vicuña Mackenna. Meanwhile, Line 3 was projected through Independencia and Irarrázaval to supply the northern area that Line 2 was supposed to run.
However, these plans were affected once again when an earthquake struck the Chilean Central Valley
The Central Valley ( es, Valle Central), Intermediate Depression, or Longitudinal Valley is the depression between the Chilean Coastal Range and the Andes Mountains. The Chilean Central Valley extends from the border with Peru to Puerto Montt in ...
on 3 March 1985. Most of the funds destined for the construction of the Line 2 extension and Line 3 were used to rebuild the city. The opening of two new stations towards the north in 1986 (Santa Ana) and 1987 (Puente Cal y Canto) were the only finalised works from these plans: Santa Ana and Mapocho stations on Line 2. The latter would change its name later, as remains of the old Calicanto Bridge –emblem of the city for over a century– were discovered during the excavation process. That same year, the Metrobús service was launched with services operating from Escuela Militar, Lo Ovalle and Las Rejas.
Institutionally, the management of Metro de Santiago was changed at the end of the decade. The former General Directorate of Metro, a branch of the Ministry of Public Works
This list indicates government departments in various countries dedicated to public works or infrastructure.
See also
* Public works
* Ministry or Board of Public Works, the imperial Chinese ministry overseeing public projects from the Tang ...
, became a state-funded public company, Metro S.A., with the provisions of Law 18,772 published on 28 January 1989.
Following the economic recovery after the second miracle, the metro's expansion plans resurged. Population growth in the southeastern area of the capital became unstoppable during the 1980s, and La Florida became the most populous commune in the country, thus the construction of a new line to supply that area was paramount. The first plans were drawn in 1989 and it was officially announced in 1991 by President Patricio Aylwin
Patricio Aylwin Azócar (; 26 November 1918 – 19 April 2016) was a Chilean politician from the Christian Democratic Party, lawyer, author, professor and former senator. He was the first president of Chile after dictator Augusto Pinochet, a ...
. This new line would start from Baquedano and head southwards to Américo Vespucio Avenue
Américo Vespucio Avenue is a
ring road in Santiago, Chile named after Renaissance cartographer Amerigo Vespucci. Two adjacent sections of the avenue are occupied by Vespucio Norte Express and Vespucio Sur free-flow tolling highways, which are ...
, crossing through Vicuña Mackenna.
 Line 5 was opened on 5 April 1997 by President
Line 5 was opened on 5 April 1997 by President Eduardo Frei Ruiz-Tagle
Eduardo Alfredo Juan Bernardo Frei Ruiz–Tagle (; born 24 June 1942) is a Chilean politician and civil engineer who served as president of Chile from 1994 to 2000. He was also a Senator, fulfilling the role of President of the Senate from 2006 ...
. This new line would have a length of 10.3 kilometres initially running underground from Baquedano to Irarrázaval, emerging as a viaduct on Vicuña Mackenna and going underground before reaching its southeastern terminus, Bellavista de la Florida.
In March 2000, a new section of Line 5 crossing the historic centre of the capital was opened to the public. The new connection between Baquedano and Santa Ana through Plaza de Armas
The ''Plaza de Armas'' (literally Weapons Square, but better translated as Parade Square or parade ground) is the name for Latin American main squares. In the central region of Mexico this space is known as El Zócalo and in Central America as ...
and Bellas Artes meant that all three at-the-time existing lines would be connected.
New lines and line extensions
With the election ofRicardo Lagos
Ricardo Froilán Lagos Escobar (; born 2 March 1938) is a Chilean lawyer, economist and social-democratic politician who served as president of Chile from 2000 to 2006. During the 1980s he was a well-known opponent of the Chilean military dic ...
as President of Chile
The president of Chile ( es, Presidente de Chile), officially known as the President of the Republic of Chile ( es, Presidente de la República de Chile), is the head of state and head of government of the Republic of Chile. The president is r ...
in 2000, one of his main objectives was an overhaul of the transport system serving the capital. To achieve this, a new extension for Line 5 was designed, heading westwards to Quinta Normal, following Catedral street, and an extension for Line 2 from both ends of the line to reach the northern and southern ends of the Américo Vespucio ring road.
Despite this, the biggest announcement was made in 2002 when Lagos disclosed the construction of a fourth line for the metro, serving the southeastern communes of Santiago to reach the heart of Puente Alto, which had taken over La Florida as the most populous commune of the country. With these new projects, the Metro network would double its extension by 2010, year in which the country would celebrate its bicentennial.
These new projects were designed to make Metro the key element of the new transport reform plan for the city, Transantiago. Along with the new extensions, exchange stations were designed to allow for a better interaction between the urban railways and other means of transport, mainly bus
A bus (contracted from omnibus, with variants multibus, motorbus, autobus, etc.) is a road vehicle that carries significantly more passengers than an average car or van. It is most commonly used in public transport, but is also in use for cha ...
es. The first exchange station would open in Quinta Normal after the Line 5 extension was finalised on 31 March 2004. However, the original plan to host a railway station would be discarded following the failure of the Melitrén construction.
On September 8, 2004, the Metro would make another breakthrough when the Mapocho river
The River Mapocho ( es, Río Mapocho) ( Mapudungun: ''Mapu chuco'', "water that penetrates the land") is a river in Chile. It flows from its source in the Andes mountains onto the west and divides Chile's capital Santiago in two.
Course
The Mapo ...
was crossed underground, with the opening of Patronato
Patronato may refer to:
*Club Atlético Patronato, an Argentine football club
*Patronato real, an arrangement between the Vatican and the Kingdom of Spain
*Barrio Patronato, a ''barrio'' (district) in Santiago, Chile
*Patronato metro station
Pat ...
and Cerro Blanco stations on Line 2. On 22 December 2004, the southern extension of the same line opened its new stations, El Parrón and La Cisterna. A second stretch of Line 2 towards the north would open on 25 November 2005, and the last in the series of extensions opened on 22 December 2005, with a total cost of US$170 million and a 27-million passenger increase annually.
On November 30, 2005, the first underground leg of Line 4 from Tobalaba to Grecia, and the viaduct between Vicente Valdés and Plaza de Puente Alto opened to the public. The unfinished track from Grecia and Vicente Valdés was covered by a rail replacement bus service operated by Transantiago until March 2, 2006, when the remaining stations and track were finished. Line 4 at this time was the longest of the network, with an extension of 24.7 kilometres and 22 stations serving Providencia, Las Condes, Ñuñoa
Ñuñoa (; from Mapudungun ''Ñuñohue'', "place of yellow flowers") is a commune of the Northeastern zone of Santiago, in the Santiago Metropolitan Region of Chile. According to the 2021 Urban Life Quality Index (ICVU), it is considered the fou ...
, La Reina
La Reina ( Spanish: "The Queen") is a commune of Chile located in Santiago Province, Santiago Metropolitan Region created in 1963 from an eastern portion of the Ñuñoa commune. It belongs to the Northeastern zone of Santiago de Chile.
La Re ...
, Peñalolén
Peñalolén (Mapudungun "fraternal meeting place") is a Chilean commune in Santiago Province, Santiago Metropolitan Region. It was founded on November 15, 1984.
History
The commune was founded on November 15, 1984.
Drug arrests
During 2019, Ch ...
, Macul
Macul ( Quechua: "to stretch out right hand") is a commune (smallest administrative subdivision in Chile) of Chile located in the central-eastern part of the Greater Santiago area, bordered by the communes of Ñuñoa to the north, San Joaquín ...
, La Florida and Puente Alto. This new line also saw the introduction of new rolling stock, the AS-2002, manufactured by Alstom in Brazil, featuring more interior space than those running other lines. Finally, Line 4 would be complemented with the opening of a branch service on August 16, 2006, Line 4A, which connected Line 2 from La Cisterna with Line 4 at Vicuña Mackenna, running through the Américo Vespucio ring road.
On May 26, 2016, Metro announced the extension of Lines 2 and 3, adding 8.9 kilometers and 7 new stations to the Metro network. Both extensions are expected to begin operations during the second half of 2021. The extension of Line 2 to the south will add 5.1 kilometers and 4 new stations connecting the current terminal station in La Cisterna with San Bernardo locality. The new terminal station will be located next to a hospital called ''Hospital El Pino'' in San Bernardo. Meanwhile, the extension of Line 3 to the west will add 3.8 kilometers and 3 new stations to the Metro network, connecting future station Los Libertadores with Quilicura.
On November 2, 2017, Line 6 was inaugurated from Cerrillos to Los Leones adding 10 new stations. This new line does not have staffed ticket offices; instead there are automatic machines for ticket sales and loading money onto bip! cards. It has platform-edge doors to protect passengers, and traction power is supplied by overhead line equipment, not by conductor rails as on the other lines. It has new entrance and exit turnstiles at stations. The trains on Line 6 only have steel wheels, and are driverless.
On January 22, 2019, Line 3 was inaugurated, after 9 years of prospecting and construction and being delayed since the 1980s after the 1985 Algarrobo earthquake
An earthquake measuring 8.0 struck Santiago Chile on 3 March 1985, and ended up killing 177 people and injuring about 2,575 others. This earthquake was being felt between the northern Antofagasta Region and the southern Los Lagos Region. It was ...
and the changing demographics of the city during the '80s and '90s. Its rolling stock material is identical to the Line 6 and were built simultaneously, so they're considered "twin lines".
2019 protests
During the month of October 2019, the Santiago metro network was affected by social protests due to the increase in the fare of the entire Metropolitan Mobility Network. Initially, secondary students staged massive acts of evasion between 6 and 11 October. The protests quickly escalated to several metro stations, resulting in train service being repeatedly interrupted. On Friday the 18th, the situation escalated and the entire network had to be closed due to attacks on stations and workers. At night, after the declaration of a state of emergency by PresidentSebastián Piñera
Miguel Juan Sebastián Piñera Echenique OMCh (; born 1 December 1949) is a Chilean billionaire businessman and politician who served as president of Chile from 2010 to 2014 and again from 2018 to 2022.
The son of a Christian Democratic polit ...
, several stations of the Metro were destroyed and burned, some of which were attacked again the next day, even though a curfew had been established. Meanwhile, the Instituto Nacional de Derechos Humanos investigated accusations that the Blaquedano station was used as a detention and torture center by police and military. On the morning of the same day, the site was reviewed by staff from the INDH, PDI and guarantee judges. The judges found no evidence of torture or illegal detentions at the site, but an investigation was launched to rule out any irregular situation.
The Metro network had been partially reactivated as of Monday, October 21; however, due to the damage of some stations, the network will only be available in its entirety within a period of up to 7 months. Damage costs are estimated at more than $300 million. Metro de Santiago indicated that it does not have insurance contracted for the infrastructure of the stations and trains. Lines 3 and 6, meanwhile, opened on 23 October, Lines 2 and 5 on the 25th, Line 4 on the 28th, and line 4A on November 25, in all cases partially and on a shortened schedule.
On October 23, it was reported that 79 stations had been damaged in all, with lines 4, 4A, and 5 having the highest number of stations destroyed or vandalized. There were also damage to 6 trains, 5 on line 4 and one on line 1 - the latter set on fire at the San Pablo station. Upon the reopening of the last two stations (Trinidad and Protectora de la Infancia) on September 25, 2020, the metro system was back to 100% operation.
Timeline
Rolling stock
 The Santiago Metro currently operates 9 models of rolling stock: two models (the AS-2002 and the AS-2014) are steel-wheeled, while the others are all rubber-tyred. The NS 74 and NS 93 stock are based on the
The Santiago Metro currently operates 9 models of rolling stock: two models (the AS-2002 and the AS-2014) are steel-wheeled, while the others are all rubber-tyred. The NS 74 and NS 93 stock are based on the MP 73
The MP 73 (Metro Pneu appel d'offres 1973) is rolling stock on tires for the Paris metro. It essentially equips line 6, a train being also operated on line 11 until 2022. Put into service in 1974, it is technically very close to the MP 59 wit ...
and MP 89
The MP 89 (French : Métro sur Pneus d'appel d'offres de 1989) is a rubber tired variant of electric multiple units used on the Paris Métro. Designed by Roger Tallon, two types are built by GEC-Alsthom for service on Lines 4 and 14, and so ...
stock of the Paris Metro
Paris () is the capital and most populous city of France, with an estimated population of 2,165,423 residents in 2019 in an area of more than 105 km² (41 sq mi), making it the 30th most densely populated city in the world in 2020. Si ...
respectively, while the NS-88 and NS-2007 stock are based on the FM-86 and NM-02 stock of the Mexico City Metro
The Mexico City Metro ( es, Metro de la Ciudad de México) is a rapid transit system that serves the metropolitan area of Mexico City, including some municipalities in Mexico State. Operated by the Sistema de Transporte Colectivo (STC), it is ...
respectively. All rubber-tyred stock is preceded with the acronym NS (for ''Neumático Santiago''); likewise, all steel-wheeled stock is preceded with the acronym AS (for ''Acero Santiago''). The number representing each type of rubber-tyred and steel-wheeled rolling stock is the year of design of a particular rolling stock, not year of first use, similar to the practice in the Mexico City Metro
The Mexico City Metro ( es, Metro de la Ciudad de México) is a rapid transit system that serves the metropolitan area of Mexico City, including some municipalities in Mexico State. Operated by the Sistema de Transporte Colectivo (STC), it is ...
and Paris Métro
The Paris Métro (french: Métro de Paris ; short for Métropolitain ) is a rapid transit system in the Paris metropolitan area, France. A symbol of the city, it is known for its density within the capital's territorial limits, uniform architec ...
.
Currently the NS-2007, NS-2012, AS-2014 stock and a number of the NS-93 stock are retrofitted with air conditioning.
In September 2012, the NS 2012 trains went into service on Line 1. These trains are the first to be built with air conditioning.
On November 2, 2017, the line 6 entered revenue service. This line utilizes the AS-2014 (Acero Santiago 2014) which are the most modern stock of the system , being the first model in the system that are driverless. However, in the first and last car there is a control panel meant to control the train when necessary. It is also the first with security cameras, energy obtainment via overhead rigid catenary, and evacuation doors at the front of the first and last car (with an evacuation ramp for people on wheelchairs) as well as on the sides of each convoy. They are also the second to be built with air conditioning, and the third with LED lights. The line that they operate in is also the first in revenue service with platform safety barriers, followed by Line 3 opened in January 2019.
NS 93
The NS 93 (Neumático Santiago 1993) is the third generation of rubber-tyred metro, rubber tired rolling stock used on the Santiago Metro system. The trains were manufactured by Alstom, GEC Alsthom in 1996 and went into operation in 1997. Original ...
File:AS 2002, Metro de Santiago.jpg, AS-2002
File:Neptuno L1.jpg, NS-2004
File:Ns2007.jpg, NS-2007
File:Ns12.jpg, NS-2012
File:Michelle_Bachelet_visita_instalaciones_del_Taller_Cerrillos_de_nueva_L%C3%ADnea_6_de_Metro_%2830657937662%29.jpg, AS-2014
File:Tren NS-2016.jpg, NS-2016
Stations
In bold are transfer stations. In grey are stations projected or currently under construction.Universidad de Chile
The University of Chile ( es, Universidad de Chile) is a public research university in Santiago, Chile. It was founded on November 19, 1842, and inaugurated on September 17, 1843.
Art in the Metro
The Santiago Metro incorporates a number of works of art in the design of its stations. The station ''Universidad de Chile'' has a giant mural created byMario Toral
Mario Toral Muñoz (born in Santiago, Chile, on 12 February 1934) is a Chilean painter and photographer.
Career
At the age of 16, Toral moved to Buenos Aires, where he saved money to enroll in the Escuela de Bellas Artes (School of Fine Arts) i ...
and represents the history of the country. Other pieces of art are in Baquedano (featuring modern art and a concert space), Bellas Artes (multimedia art), Santa Lucía (Portuguese
Portuguese may refer to:
* anything of, from, or related to the country and nation of Portugal
** Portuguese cuisine, traditional foods
** Portuguese language, a Romance language
*** Portuguese dialects, variants of the Portuguese language
** Portu ...
azulejo
''Azulejo'' (, ; from the Arabic ''al- zillīj'', ) is a form of Spanish and Portuguese painted tin-glazed ceramic tilework. ''Azulejos'' are found on the interior and exterior of churches, palaces, ordinary houses, schools, and nowadays, r ...
s, a gift made by the Lisbon Metro
The Lisbon Metro ( pt, Metropolitano de Lisboa) is the rapid transit system in Lisbon, Portugal. Opened in December 1959, it was the first metro system in Portugal.
, the system's four lines total of route and serve 56 stations.
History
In ...
), La Moneda (with realistic painting representing typical landscape), and various other stations.
Station amenities
A diverse array of services are provided within each Metro station. Ticket offices, public telephones and metro-network information panels exist in every station; ''Redbanc'', ''Cirrus'' and ''Plus''-enabled ATMs, typically provided by either the Banco de Chile company or the BancoEstado national bank, are common. Automatic recharge machines are also common, with all such machines charging a customer's ''Bip!'' card with either cash deposits or a ''Redbanc''-enabled card. In higher-traffic stations, there are screens that display MetroTV, featuring additional system information as well as music videos and short news segments. Some 21 of the busiest stations contain a branch of ''Bibliometro'', a system of lending libraries supported by the national Department of Libraries, Archives and Museums (Dibam). A Chilean ID or foreign passport allows any Metro customer to freely borrow from a reserve of books and other literature, but a registration is needed first. Customers may rent a parking space for their bicycles through the ''Bicimetro'' network, which opened in 2008 at six stations and is slowly expanding, for a starting cost of $300 (approximately US$0.50) a day. There are weekly and monthly rental services too, that guarantee a fixed space for the bike (contrary to the daily rent which relies on random free-space). Most underground Metro stations contain at least one shop or convenience store, with large line-transfer stations such as ''Baquedano'' featuring several food vendors and retailers, and even a small underground "shopping center" in ''Universidad de Chile''.Security and safety
Various private security agencies have day-to-day responsibility for maintaining order in the metro and deterring petty crime or attempts to board without paying. The largest transfer stations, such as Tobalaba, also feature depots of theCarabineros de Chile
( en, Carabiniers of Chile) are the Chilean national law enforcement police, who have jurisdiction over the entire national territory of the Republic of Chile. Created in 1927, their mission is to maintain order and enforce the laws of Chile. T ...
, the national military police force. Metro staff man the ticket counters in closed box offices and distribute tickets and money through small transaction windows.
Signage to advise customers of safety hazards is extensive, and each platform has a painted yellow line which customers are advised to not cross except to board a train. During rush hour, Metro staff line the platform edge to keep people from being crowded off the platform and to support disabled customers. There is no physical barrier between the edge and the tracks (with the exception of recently opened Lines 3 and 6), including the hazardous, electrified third rail
A third rail, also known as a live rail, electric rail or conductor rail, is a method of providing electric power to a railway locomotive or train, through a semi-continuous rigid conductor placed alongside or between the rails of a railway ...
. However, lines 3 and 6 use overhead line
An overhead line or overhead wire is an electrical cable that is used to transmit electrical energy to electric locomotives, trolleybuses or trams. It is known variously as:
* Overhead catenary
* Overhead contact system (OCS)
* Overhead equipm ...
s as the powersource of the trains.
Metro travelers are advised to keep a close guard on their belongings, as petty or opportunistic theft is somewhat of a problem in lines that connect some districts to the center of Santiago. This is most apparent with passengers who reverse their backpacks so that the bag is across the stomach, to ensure that no one can pilfer the pockets out of sight.
Pricing and working hours
Metro is part of Red Metropolitana de Movilidad, the integrated public transport system that serves the capital using also feeder and main bus routes. Red works with an integrated fare system, which allows passengers to make bus-bus or bus-metro transfers on a two-hour time limit from the first trip (maximum of two changes) using a contactless smart card called "Bip! card". Bus-to-bus, metro-to-bus and metro-to-train transfers do not cost extra. Bus-to-metro transfers costs $20 (approx. US$0.03) during ''Horario Valle'' ( low-use hours) and $80 (approx. US$0.12) during ''Horario Punta'' ( rush hour). Bip! cards are available in all the ticketing offices in every station at a cost of $1,550 (approx. US$2.23), with a minimum first charge of $1000 worth of credit (approx. US$1.41). Tickets are sold from 6:00 to 23:00 Monday to Friday, 6:30 to 23:00 on Saturdays, and 8:00 to 22:30 on Sundays and holidays. Cards can be topped up to $20000, and the credit only expires if the card it is not used in two years. Metro also used to sell single-trip, Metro-use only tickets, but they went out of circulation in early 2017. Fares depended on the time of the use of the system. The cost of a ticket in the ''Horario Punta'' ( rush hour, 7:00–8:59 and 18:00–19:59) was $700 (approx. US$1.01); in the ''Horario Valle'' (off-peak hours, 6:30–6:59, 9:00–18:00, 20:00–20:44, and all day on weekends and holidays) was $640 (approximately US$0.90); and in the ''Horario Bajo'' (low-use hours, 6:00–6:29 and 20:45–23:00) was $590 (approximately US0.85). Senior citizens (65 and older) and students holding concession cards pay $200 (US$0.28). Senior concession fare does not apply during rush hours. On weekdays, the metro operates from 5.35 am until 12.08 am, while on Saturdays it operates from 6.30 am until 12.08 am and on Sundays and public holidays the metro operates from 8 am (Line 1 from 9 am) until 11.48 pm. However, due to theCOVID-19 Pandemic
The COVID-19 pandemic, also known as the coronavirus pandemic, is an ongoing global pandemic of coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) caused by severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2). The novel virus was first identi ...
, operating hours have varied in accordance with national curfew.(warning: stations close earlier - se
timetable
Network Map
See also
*List of Latin American rail transit systems by ridership
The following is a list of all urban rail transit systems in Latin America, ranked by passenger ridership. These kinds of systems are most commonly known as ''metro'' (or ''subway'' in English), but may also be known as ''subte'', ''tren'', or ''tr ...
* List of metro systems
* Rail transport in Chile
References
External links
Metro S.A.
Santiago Metro Map
Santiago Metro Track Map
Tarjeta Bip!
Plan and Authority of Transit of Santiago de Chile, Transantiago
* Santiago Metro in Wikipedia in Spanish {{Authority control Railway services introduced in 1975 1975 establishments in Chile 750 V DC railway electrification