Meo people on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 The Miao are a group of linguistically-related peoples living in
The Miao are a group of linguistically-related peoples living in
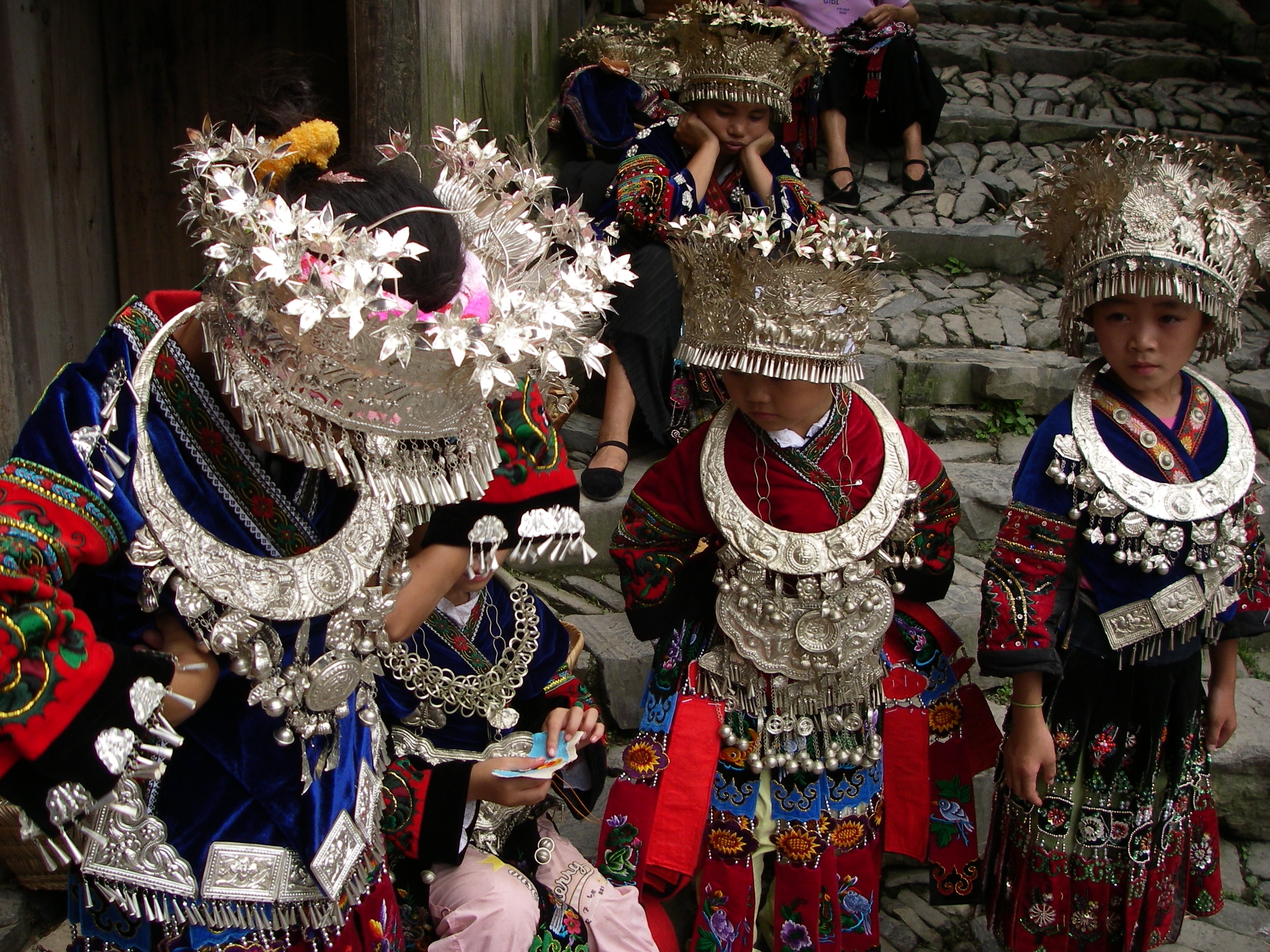


 The term "Miao" gained official status in 1949 as a ''minzu'' (ethnic group) encompassing a group of linguistically-related ethnic minorities in
The term "Miao" gained official status in 1949 as a ''minzu'' (ethnic group) encompassing a group of linguistically-related ethnic minorities in
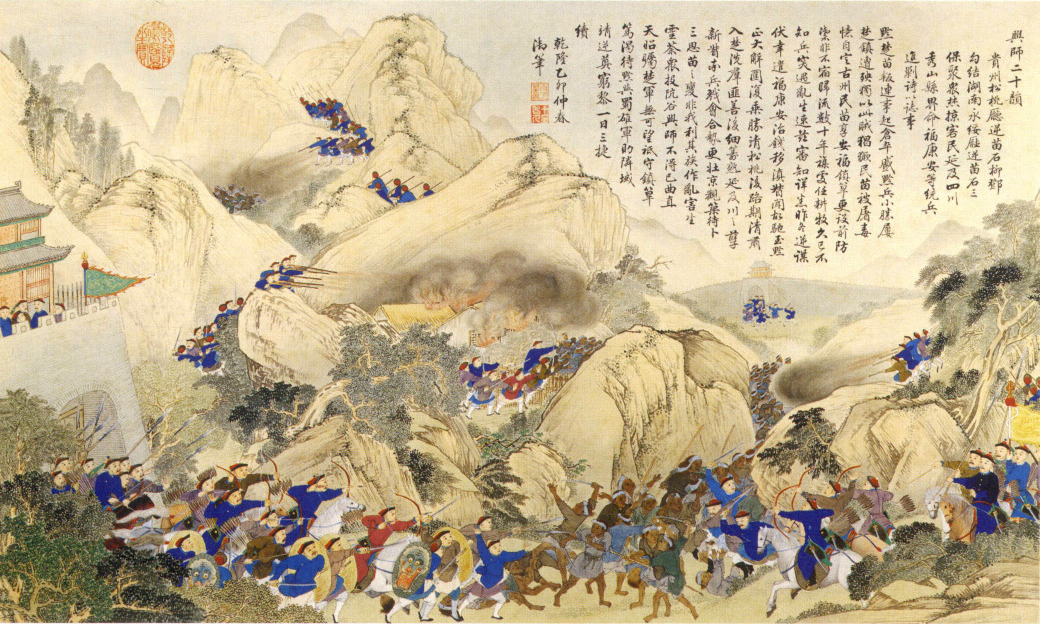
 During the Qing Dynasty the Miao fought three wars against the empire.Xiong, Yuepheng L
During the Qing Dynasty the Miao fought three wars against the empire.Xiong, Yuepheng L
"Chinese Odyssey: Summer Program offers Students rare opportunity to learn Hmong history in China"
HmongNet.org The issue was so serious that the Yongzheng emperor sent one of his most officials, Ortai, to be the Viceroy of the provinces with significant Miao populations in 1726, and through 1731, he spent his time putting down rebellions. In 1735 in the southeastern province of Guizhou, the Miao rose up against the government's forced assimilation. Eight counties involving 1,224 villages fought until 1738 when the revolt ended. According to

 According to the 2000 census, the number of Miao in China was estimated to be about 9.6 million. Outside of China, members of the Miao sub-group or nations of the Hmong live in
According to the 2000 census, the number of Miao in China was estimated to be about 9.6 million. Outside of China, members of the Miao sub-group or nations of the Hmong live in
File:Miao autonomous prefectures and counties in China.png, Miao autonomous prefectures and counties in China
File:Hmong_Mien_lang.png, Map of Hmong-Mien languages distribution
''Thai-Yunnan Project Newsletter''
No. 17, Department of Anthropology, Australian National University, June 1992. * * * * * * * * Feng, Xianghong. (2013)
Women's Work, Men's Work: Gender and Tourism among the Miao in Rural China
Hmong Studies Internet Resource CenterHmongNet.orgAn Album of the Miao Minority
from 1786
Map share of ethnic by county of China
{{DEFAULTSORT:Miao People Ethnic groups officially recognized by China Ethnic groups in Laos Ethnic groups in Thailand Ethnic groups in Vietnam Hmong
 The Miao are a group of linguistically-related peoples living in
The Miao are a group of linguistically-related peoples living in Southern China
South China () is a geographical and cultural region that covers the southernmost part of China. Its precise meaning varies with context. A notable feature of South China in comparison to the rest of China is that most of its citizens are not n ...
and Southeast Asia
Southeast Asia, also spelled South East Asia and South-East Asia, and also known as Southeastern Asia, South-eastern Asia or SEA, is the geographical south-eastern region of Asia, consisting of the regions that are situated south of mainlan ...
, who are recognized by the government of China as one of the 56 official ethnic groups. The Miao live primarily in southern China's mountains, in the provinces of Guizhou
Guizhou (; formerly Kweichow) is a landlocked province in the southwest region of the People's Republic of China. Its capital and largest city is Guiyang, in the center of the province. Guizhou borders the autonomous region of Guangxi to the ...
, Yunnan
Yunnan , () is a landlocked province in the southwest of the People's Republic of China. The province spans approximately and has a population of 48.3 million (as of 2018). The capital of the province is Kunming. The province borders the C ...
, Sichuan
Sichuan (; zh, c=, labels=no, ; zh, p=Sìchuān; alternatively romanized as Szechuan or Szechwan; formerly also referred to as "West China" or "Western China" by Protestant missions) is a province in Southwest China occupying most of the ...
, Hubei
Hubei (; ; alternately Hupeh) is a landlocked province of the People's Republic of China, and is part of the Central China region. The name of the province means "north of the lake", referring to its position north of Dongting Lake. The ...
, Hunan
Hunan (, ; ) is a landlocked province of the People's Republic of China, part of the South Central China region. Located in the middle reaches of the Yangtze watershed, it borders the province-level divisions of Hubei to the north, Jiangxi ...
, Guangxi, Guangdong
Guangdong (, ), alternatively romanized as Canton or Kwangtung, is a coastal province in South China on the north shore of the South China Sea. The capital of the province is Guangzhou. With a population of 126.01 million (as of 2020) ...
, and Hainan
Hainan (, ; ) is the smallest and southernmost province of the People's Republic of China (PRC), consisting of various islands in the South China Sea. , the largest and most populous island in China,The island of Taiwan, which is slightly l ...
. Some sub-groups of the Miao, most notably the Hmong people, have migrated out of China into Southeast Asia (Myanmar
Myanmar, ; UK pronunciations: US pronunciations incl. . Note: Wikipedia's IPA conventions require indicating /r/ even in British English although only some British English speakers pronounce r at the end of syllables. As John Wells explai ...
, Northern Vietnam
Vietnam or Viet Nam ( vi, Việt Nam, ), officially the Socialist Republic of Vietnam,., group="n" is a country in Southeast Asia, at the eastern edge of mainland Southeast Asia, with an area of and population of 96 million, making i ...
, Laos, and Thailand
Thailand ( ), historically known as Siam () and officially the Kingdom of Thailand, is a country in Southeast Asia, located at the centre of the Indochinese Peninsula, spanning , with a population of almost 70 million. The country is b ...
). Following the communist takeover of Laos in 1975, a large group of Hmong refugees resettled in several Western nations, mainly in the United States
The United States of America (U.S.A. or USA), commonly known as the United States (U.S. or US) or America, is a country primarily located in North America. It consists of 50 states, a federal district, five major unincorporated territori ...
, France
France (), officially the French Republic ( ), is a country primarily located in Western Europe. It also comprises of overseas regions and territories in the Americas and the Atlantic, Pacific and Indian Oceans. Its metropolitan area ...
, and Australia.
Miao is a Chinese
Chinese can refer to:
* Something related to China
* Chinese people, people of Chinese nationality, citizenship, and/or ethnicity
**''Zhonghua minzu'', the supra-ethnic concept of the Chinese nation
** List of ethnic groups in China, people of ...
term, while the component groups of people have their own autonyms, such as (with some variant spellings) Hmong
Hmong may refer to:
* Hmong people, an ethnic group living mainly in Southwest China, Vietnam, Laos, and Thailand
* Hmong cuisine
* Hmong customs and culture
** Hmong music
** Hmong textile art
* Hmong language, a continuum of closely related to ...
, Hmu, Xong (Qo-Xiong), and A-Hmao A-Hmao (''Big Flowery Miao'') are an Hmongic ethnic group in China. They are from Yunnan and Sichuan and also live in Guizhou. The number of persons within this group likely exceeds 400,000. They are speakers of the A-Hmao language
The A-Hmao la ...
. These people (except those in Hainan
Hainan (, ; ) is the smallest and southernmost province of the People's Republic of China (PRC), consisting of various islands in the South China Sea. , the largest and most populous island in China,The island of Taiwan, which is slightly l ...
) speak Hmongic languages, a subfamily of the Hmong–Mien languages
The Hmong–Mien languages (also known as Miao–Yao and rarely as Yangtzean) are a highly tonal language family of southern China and northern Southeast Asia. They are spoken in mountainous areas of southern China, including Guizhou, Hunan, Yunn ...
including many mutually unintelligible
In linguistics, mutual intelligibility is a relationship between languages or dialects in which speakers of different but related varieties can readily understand each other without prior familiarity or special effort. It is sometimes used as an ...
languages such as the Hmong
Hmong may refer to:
* Hmong people, an ethnic group living mainly in Southwest China, Vietnam, Laos, and Thailand
* Hmong cuisine
* Hmong customs and culture
** Hmong music
** Hmong textile art
* Hmong language, a continuum of closely related to ...
, Hmub, Xong and A-Hmao A-Hmao (''Big Flowery Miao'') are an Hmongic ethnic group in China. They are from Yunnan and Sichuan and also live in Guizhou. The number of persons within this group likely exceeds 400,000. They are speakers of the A-Hmao language
The A-Hmao la ...
.
Not all speakers of the Hmongic languages belong to the Miao. For example, the speakers of the Bunu and Bahengic languages
The Bahengic (Pahungic) languages are a divergent branch of the Miao (Hmongic) languages. Speakers are among the ethnic ''Bunu'': Miao-speaking Yao people of China.
Pa-Hng (Baheng) has long been recognized as a divergent language. Benedict (1 ...
are designated as the Yao, and the speakers of the Sheic languages
The Sheic or She–Jiongnai languages are a branch of the Miao (Hmongic) language family.
She (Ho-Ne) has long been recognized as a divergent language. It has been difficult to classify because of its numerous Chinese loanwords. Recently, it ha ...
are designated as the She
She most commonly refers to:
*She (pronoun), the third person singular, feminine, nominative case pronoun in modern English.
She or S.H.E. may also refer to:
Literature and films
*'' She: A History of Adventure'', an 1887 novel by H. Rider Hagga ...
and the Yao.
The Kem Di Mun people in Hainan
Hainan (, ; ) is the smallest and southernmost province of the People's Republic of China (PRC), consisting of various islands in the South China Sea. , the largest and most populous island in China,The island of Taiwan, which is slightly l ...
, despite being officially designated as Miao people, are linguistically and culturally identical to the Kim Mun people in continental China who are classified as a subgroup of the Yao.
Nomenclature: Miao or Hmong


 The term "Miao" gained official status in 1949 as a ''minzu'' (ethnic group) encompassing a group of linguistically-related ethnic minorities in
The term "Miao" gained official status in 1949 as a ''minzu'' (ethnic group) encompassing a group of linguistically-related ethnic minorities in Southwest China
Southwest China () is a region in the south of the People's Republic of China.
Geography
Southwest China is a rugged and mountainous region, transitioning between the Tibetan Plateau to the west and the Chinese coastal hills (东南丘陵) and ...
. This was part of a larger effort to identify and classify minority groups to clarify their role in the national government, including establishing autonomous administrative divisions
An autonomous administrative division (also referred to as an autonomous area, entity, unit, region, subdivision, or territory) is a subnational administrative division or internal territory of a sovereign state that has a degree of autonomy— ...
and allocating the seats for representatives in provincial and national government.
Historically, the term "Miao" had been applied inconsistently to a variety of non-Han
Han may refer to:
Ethnic groups
* Han Chinese, or Han People (): the name for the largest ethnic group in China, which also constitutes the world's largest ethnic group.
** Han Taiwanese (): the name for the ethnic group of the Taiwanese p ...
peoples. Early Chinese-based names use various transcriptions: Miao, Miao-tse, Miao-tsze, Meau, Meo, mo, Miao-tseu etc. In Southeast Asian contexts, words derived from the Chinese "Miao" took on a sense which was perceived as derogatory by the subgroups living in that region. The term re-appeared in the Ming dynasty
The Ming dynasty (), officially the Great Ming, was an imperial dynasty of China, ruling from 1368 to 1644 following the collapse of the Mongol-led Yuan dynasty. The Ming dynasty was the last orthodox dynasty of China ruled by the Han peo ...
(1368–1644), by which time it had taken on the connotation of "barbarian." Being a variation of Nanman, it was used to refer to the indigenous people in southern China who had not been assimilated into Han culture. During this time, references to “raw” (生 Sheng) and ”cooked” (熟 Shu) Miao appear, referring to the level of assimilation and political cooperation of the two groups, making them easier to classify. Not until the Qing dynasty (1644–1911) do more finely grained distinctions appear in writing. Even then, discerning which ethnic groups are included in various classifications can be complex. There has been a historical tendency by the Hmong, who resisted assimilation and political cooperation, to group all Miao peoples together under the term Hmong because of the potential derogatory use of the term Miao. In modern China, however, the term continues to be used regarding the Miao people there.
Though the Miao themselves use various self-designations, the Chinese traditionally classify them according to the most characteristic color of the women's clothes. The list below contains some of these self-designations, the color designations, and the main regions inhabited by the four major groups of Miao in China:
* Ghao Xong/Qo Xiong; Xong; Red Miao; Qo Xiong Miao: West Hunan
Hunan (, ; ) is a landlocked province of the People's Republic of China, part of the South Central China region. Located in the middle reaches of the Yangtze watershed, it borders the province-level divisions of Hubei to the north, Jiangxi ...
* Gha Ne/Ka Nao; Hmub; Black Miao; Mhub Miao: Southeast Guizhou
Guizhou (; formerly Kweichow) is a landlocked province in the southwest region of the People's Republic of China. Its capital and largest city is Guiyang, in the center of the province. Guizhou borders the autonomous region of Guangxi to the ...
* A-Hmao A-Hmao (''Big Flowery Miao'') are an Hmongic ethnic group in China. They are from Yunnan and Sichuan and also live in Guizhou. The number of persons within this group likely exceeds 400,000. They are speakers of the A-Hmao language
The A-Hmao la ...
; Big Flowery Miao: West Guizhou and Northeast Yunnan
Yunnan , () is a landlocked province in the southwest of the People's Republic of China. The province spans approximately and has a population of 48.3 million (as of 2018). The capital of the province is Kunming. The province borders the C ...
* Gha-Mu; Hmong, Mong; White Miao, Green/Blue Miao, Small Flowery Miao; South and East Yunnan
Yunnan , () is a landlocked province in the southwest of the People's Republic of China. The province spans approximately and has a population of 48.3 million (as of 2018). The capital of the province is Kunming. The province borders the C ...
, South Sichuan
Sichuan (; zh, c=, labels=no, ; zh, p=Sìchuān; alternatively romanized as Szechuan or Szechwan; formerly also referred to as "West China" or "Western China" by Protestant missions) is a province in Southwest China occupying most of the ...
and West Guizhou
Guizhou (; formerly Kweichow) is a landlocked province in the southwest region of the People's Republic of China. Its capital and largest city is Guiyang, in the center of the province. Guizhou borders the autonomous region of Guangxi to the ...
Gender roles
Women's status
Compared to the Confucian principles traditionally exercised over women in some regions of China, the Miao culture is generally less strict in categorization of women’s roles in society. Miao women exercise relatively more independence, mobility and social freedom. They are known to be strong willed and politically minded. They actively contribute to their communities in social welfare, education, arts and culture, and agricultural farming. Miao women demonstrate great skill and artistry when making traditional clothing and handicrafts. They excel at embroidering, weaving, paper-cutting, batik, and intricate jewelry casting. From vests, coats, hats, collars and cuffs, to full skirts, and baby carriers, the patterns on their clothes are extremely complicated and colorful with clean lines. Girls of around seven will learn embroidering from mothers and sisters, and by the time they are teenagers, they are quite deft. Additionally, Miao silver jewelry is distinctive for its design, style and craftsmanship. Miao silver jewelry is completely handmade, carved with fine decorative patterns. It’s not easy to make and there is not one final masterpiece exactly the same as another. The Miao embroidery and silver jewelry are highly valued, delicate and beautiful. Silver jewelry is a highly valuable craftwork of the Miao people. Apart from being a cultural tradition, it also symbolises the wealth of Miao women. As a Miao saying goes, “decorated with no silver or embroidery, a girl is not a girl”, Miao women are occasionally defined by the amount of silver jewelry she wears or owns. It is especially important to wear heavy and intricate silver headdresses and jewelry during significant occasions and festivals, notably during weddings, funerals and springtime celebration. Silver jewelry is an essential element of Miao marriages, particularly to the bride. Miao families would begin saving silver jewellery for the girls at an early age, wishing their daughters could marry well with the large amount of silver jewelry representing the wealth of the family. Although a growing Miao population is moving from rural Miao regions to cities, the new generation respects the families' silver heritage and is willing to pass on the practice as a cultural tradition more than a showcase of family wealth.Workforce and income
Although Miao women are not strictly-governed, their social status is often seen as lower than that of men, as in most patriarchal societies. Be it in the subsistence economy or otherwise, men are the main economic force and provide the stable source of income for the family. Women are primarily involved in social welfare, domestic responsibilities, and additionally earn supplementary income. As tourism became a major economic activity to this ethnic group, Miao women gained more opportunities to join the labor force and earn an income. Women mostly take up jobs that require modern day customer service skills; for example, working as tour guides, selling craftwork and souvenirs, teaching tourists how to make flower wreaths, and even renting ethnic costumes. These jobs require soft skills and hospitality and more visibility in public, but provide a low income. On the contrary, Miao men take up jobs that require more physical strengths and less visibility in public, such as engineering roads, building hotels, boats and pavilions. These jobs generally provide a more stable and profitable source of income. The above example of unequal division of labor demonstrates, in spite of socioeconomic changes in China, men are still considered the financial backbone of the family.Marriage and family
While the Miao people have had their own unique culture, the Confucian ideology exerted significant influences on this ethnic group. It is expected that men are the dominant figures and breadwinners of the family, while women occupy more domestic roles (like cooking and cleaning). There are strict social standards on women to be “virtuous wives and good mothers”, and to abide by “three obediences and four virtues”, which include cultural moral specifications of women’s behavior. A Miao woman has some cultural freedom in marrying a man of her choice. However, like many other cultures in Asia, there are strict cultural practices on marriage, one being clanexogamy
Exogamy is the social norm of marrying outside one's social group. The group defines the scope and extent of exogamy, and the rules and enforcement mechanisms that ensure its continuity. One form of exogamy is dual exogamy, in which two groups c ...
. It is a taboo to marry someone within the same family clan name, even when the couple are not blood related or from the same community.
In contrast to the common practice of the right of succession belonging to the firstborn son, the Miao’s inheritance descends to the youngest son. The older sons leave the family and build their own residences, usually in the same province and close to the family. The youngest son is responsible for living with and caring for the aging parents, even after marriage. He receives a larger share of the family’s inheritance and his mother’s silver jewelry collection, which is used as bridal wealth or dowry
A dowry is a payment, such as property or money, paid by the bride's family to the groom or his family at the time of marriage. Dowry contrasts with the related concepts of bride price and dower. While bride price or bride service is a payment ...
.
Some imperially commissioned Han Chinese chieftaincies assimilated with the Miao. Those became the ancestors of a part of the Miao population in Guizhou.
The Hmong Tian clan in Sizhou began in the seventh century as a migrant Han Chinese clan.
The origin of the Tunbao people traces back to the Ming dynasty when the Hongwu Emperor sent 300,000 Han Chinese male soldiers in 1381 to conquer Yunnan, with some of the men marrying Yao and Miao women.
The presence of women presiding over weddings was a feature noted in "Southeast Asian" marriages, such as in 1667 when a Miao woman in Yunnan married a Chinese official. Some Sinicization occurred, in Yunnan a Miao chief's daughter married a scholar in the 1600s who wrote that she could read, write, and listen in Chinese and read Chinese classics.
History

Legend of Chiyou and origins
According to a Tang dynasty Chinese legend, the Miao who descended from the Jiuli tribe led byChiyou
Chiyou (蚩尤, ) is a mythological being that appears in East Asian mythology.
Individual
According to the Song dynasty history book '' Lushi'', Chiyou's surname was Jiang (), and he was a descendant of flame.
According to legend, Chiyou had a ...
() were defeated at the Battle of Zhuolu
The Battle of Zhuolu () was the second battle in the history of China as recorded in the ''Records of the Grand Historian'', fought between the Yanhuang tribes led by the legendary Yellow Emperor and the Jiuli tribes led by Chiyou. The battle w ...
(, a defunct prefecture on the border of present provinces of Hebei
Hebei or , (; alternately Hopeh) is a northern province of China. Hebei is China's sixth most populous province, with over 75 million people. Shijiazhuang is the capital city. The province is 96% Han Chinese, 3% Manchu, 0.8% Hui, and 0 ...
and Liaoning) by the military coalition of Huang Di () and Yan Di, leaders of the Huaxia
''Huaxia'' (華夏, ) is a historical concept representing the Chinese nation, and came from the self-awareness of a common cultural ancestry by the various confederations of pre-Qin ethnic ancestors of Han people.
Etymology
The earliest ...
() tribe as the two tribes struggled for supremacy of the Yellow River
The Yellow River or Huang He (Chinese: , Mandarin: ''Huáng hé'' ) is the second-longest river in China, after the Yangtze River, and the sixth-longest river system in the world at the estimated length of . Originating in the Bayan Ha ...
valley.
The San Miao, according to legend, are the descendants of the Jiuli Tribe. Chinese records record a San Miao ( 三苗, Three Miao) kingdom around Dongting Lake
Dongting Lake () is a large, shallow lake in northeastern Hunan Province, China. It is a flood basin of the Yangtze River, so its volume depends on the season. The provinces of Hubei and Hunan are named after their location relative to the la ...
. It was defeated by Yu the Great
Yu the Great (大禹) was a legendary king in ancient China who was famed for his introduction of flood control, his establishment of the Xia dynasty which inaugurated dynastic rule in China, and his upright moral character. He figures promine ...
. Another Miao kingdom may have emerged in Yunnan
Yunnan , () is a landlocked province in the southwest of the People's Republic of China. The province spans approximately and has a population of 48.3 million (as of 2018). The capital of the province is Kunming. The province borders the C ...
around 704 BC that was subjugated by the Chinese in the 3rd century BC. In 2002, the Chu language
Chu, or Ch'u in Wade–Giles romanization, (, Hanyu Pinyin: Chǔ, Old Chinese: ''*s-r̥aʔ'') was a Zhou dynasty ancient Chinese states, vassal state. Their first ruler was King Wu of Chu in the early 8th century BCE. Chu was located in t ...
has been identified as perhaps having influence from Tai–Kam and Miao–Yao languages by researchers at University of Massachusetts Amherst
The University of Massachusetts Amherst (UMass Amherst, UMass) is a public research university in Amherst, Massachusetts and the sole public land-grant university in Commonwealth of Massachusetts. Founded in 1863 as an agricultural college, ...
.
Dispersal
The Miao were not mentioned again in Chinese records until theTang dynasty
The Tang dynasty (, ; zh, t= ), or Tang Empire, was an imperial dynasty of China that ruled from 618 to 907 AD, with an interregnum between 690 and 705. It was preceded by the Sui dynasty and followed by the Five Dynasties and Ten Kingdom ...
(618–907). In the following period, the Miao migrated throughout southern China and Southeast Asia
Southeast Asia, also spelled South East Asia and South-East Asia, and also known as Southeastern Asia, South-eastern Asia or SEA, is the geographical south-eastern region of Asia, consisting of the regions that are situated south of mainlan ...
. They generally inhabited mountainous or marginal lands and took up swidden or slash-and-burn cultivation techniques to farm these lands.
During the Miao Rebellions There have been several Miao rebellions in Chinese history:
*Miao rebellions in the Ming dynasty (14th–15th centuries)
*Bozhou rebellion (1589–1600)
*Miao Rebellion (1735–36)
*Miao Rebellion (1795–1806)
*Miao Rebellion (1854–73) There hav ...
of the Ming dynasty
The Ming dynasty (), officially the Great Ming, was an imperial dynasty of China, ruling from 1368 to 1644 following the collapse of the Mongol-led Yuan dynasty. The Ming dynasty was the last orthodox dynasty of China ruled by the Han peo ...
, thousands of Miao were killed by the imperial forces. Mass castrations of Miao boys also took place.
 During the Qing Dynasty the Miao fought three wars against the empire.Xiong, Yuepheng L
During the Qing Dynasty the Miao fought three wars against the empire.Xiong, Yuepheng L"Chinese Odyssey: Summer Program offers Students rare opportunity to learn Hmong history in China"
HmongNet.org The issue was so serious that the Yongzheng emperor sent one of his most officials, Ortai, to be the Viceroy of the provinces with significant Miao populations in 1726, and through 1731, he spent his time putting down rebellions. In 1735 in the southeastern province of Guizhou, the Miao rose up against the government's forced assimilation. Eight counties involving 1,224 villages fought until 1738 when the revolt ended. According to
Xiangtan University
Xiangtan University (XTU; ) is a national key university located in Xiangtan, Hunan, China. It was founded in 1958 and is currently organized into 23 schools and departments.
As of 2022, the Best Chinese Universities Ranking, also known as the " ...
Professor Wu half the Miao population were affected by the war.
The second war (1795–1806) involved the provinces of Guizhou and Hunan. Shi Sanbao and Shi Liudeng led this second revolt. Again, it ended in failure, but it took 11 years to quell the uprising.
The greatest of the three wars occurred from 1854 to 1873. Zhang Xiu-mei led this revolt in Guizhou until his capture and death in Changsha, Hunan. This revolt affected over one million people and all the neighbouring provinces. By the time the war ended Professor Wu said only 30 percent of the Miao were left in their home regions. This defeat led to the Hmong people migrating out of China into Laos and Vietnam.
During Qing times, more military garrisons were established in southwest China. Han Chinese soldiers moved into the Taijiang region of Guizhou
Guizhou (; formerly Kweichow) is a landlocked province in the southwest region of the People's Republic of China. Its capital and largest city is Guiyang, in the center of the province. Guizhou borders the autonomous region of Guangxi to the ...
, married Miao women, and the children were brought up as Miao. In spite of rebellion against the Han, Hmong leaders made allies with Han merchants.
The imperial government had to rely on political means to bring in Hmong people into the government: they created multiple competing positions of substantial prestige for Miao people to participate and assimilate into the Qing government system. During the Ming and Qing times, the official position of ''Kiatong'' was created in Indochina. The Miao would employ the use of the ''Kiatong'' government structure until the 1900s when they entered into French colonial politics in Indochina
Mainland Southeast Asia, also known as the Indochinese Peninsula or Indochina, is the continental portion of Southeast Asia. It lies east of the Indian subcontinent and south of Mainland China and is bordered by the Indian Ocean to the west an ...
.
20th century
During the founding of thePeople's Republic of China
China, officially the People's Republic of China (PRC), is a country in East Asia. It is the world's most populous country, with a population exceeding 1.4 billion, slightly ahead of India. China spans the equivalent of five time zones and ...
(PRC), the Miao played an important role in its birth when they helped Mao Zedong
Mao Zedong pronounced ; also romanised traditionally as Mao Tse-tung. (26 December 1893 – 9 September 1976), also known as Chairman Mao, was a Chinese communist revolutionary who was the founder of the People's Republic of China (PRC) ...
to escape the Kuomintang
The Kuomintang (KMT), also referred to as the Guomindang (GMD), the Nationalist Party of China (NPC) or the Chinese Nationalist Party (CNP), is a major political party in the Republic of China, initially on the Chinese mainland and in Tai ...
in the Long March with supplies and guides through their territory.
In Vietnam, a powerful Hmong named Vuong Chinh Duc, dubbed the king of the Hmong, aided Ho Chi Minh
(: ; born ; 19 May 1890 – 2 September 1969), commonly known as (' Uncle Hồ'), also known as ('President Hồ'), (' Old father of the people') and by other aliases, was a Vietnamese revolutionary and statesman. He served as P ...
's nationalist move against the French, and thus secured the Hmong's position in Vietnam. In Điện Biên Phủ
Điện Biên Phủ (, meaning: ''Established Frontier Prefecture''), is a city in the northwestern region of Vietnam. It is the capital of Điện Biên Province. The city is best known for the decisive Battle of Điện Biên Phủ, which occu ...
, Hmongs fought on the side of the communist Viet Minh against the pro-French Tai Dam
The Tai Dam ( Tai Dam: , lo, ໄຕດຳ, th, ไทดำ) are an ethnic minority predominantly from China, northwest Vietnam, Laos, Thailand. They are part of the Tai peoples and ethnically similar to the Thai from Thailand, the Lao from ...
aristocrats. During the Vietnam War
The Vietnam War (also known by other names) was a conflict in Vietnam, Laos, and Cambodia from 1 November 1955 to the fall of Saigon on 30 April 1975. It was the second of the Indochina Wars and was officially fought between North Vietnam a ...
, Miao fought on both sides, the Hmong in Laos primarily for the US, across the border in Vietnam for the North-Vietnam coalition, the Chinese-Miao for the Communists. However, after the war the Vietnamese were very aggressive towards the Hmong who suffered many years of reprisals. Most Hmong in Thailand also supported a brief Communist uprising during the war.
Miao clans with Han origins
Some of the origins of the Hmong and Miao clan names are a result of the marriage of Hmong women to Han Chinese men, with distinct Han Chinese-descended clans and lineages practicing Han Chinese burial customs. These clans were called "Han Chinese Hmong" ("Hmong Sua") inSichuan
Sichuan (; zh, c=, labels=no, ; zh, p=Sìchuān; alternatively romanized as Szechuan or Szechwan; formerly also referred to as "West China" or "Western China" by Protestant missions) is a province in Southwest China occupying most of the ...
, and were instructed in military tactics by fugitive Han Chinese rebels. Such Chinese "surname groups" are comparable to the patrilineal Hmong clans and also practice exogamy.
Han Chinese male soldiers who fought against the Miao rebellions during the Qing and Ming dynasties were known to have married with non-Han women such as the Miao because Han women were less desirable. The Wang clan, founded among the Hmong in Gongxian county of Sichuan's Yibin district, is one such clan and can trace its origins to several such marriages around the time of the Ming dynasty suppression of the Ah rebels. Nicholas Tapp wrote that, according to ''The Story of the Ha Kings'' in the village, one such Han ancestor was Wang Wu. It is also noted that the Wang typically sided with the Chinese, being what Tapp calls "cooked" as opposed to the "raw" peoples who rebelled against the Chinese.
Hmong women who married Han Chinese men founded a new Xem clan among Northern Thailand's Hmong. Fifty years later in Chiangmai two of their Hmong boy descendants were Catholics. A Hmong woman and Han Chinese man married and founded northern Thailand's Lau2, or Lauj, clan, , with another Han Chinese man of the family name Deng founding another Hmong clan. Some scholars believe this lends further credence to the idea that some or all of the present day Hmong clans were formed in this way.
Jiangxi
Jiangxi (; ; formerly romanized as Kiangsi or Chianghsi) is a landlocked province in the east of the People's Republic of China. Its major cities include Nanchang and Jiujiang. Spanning from the banks of the Yangtze river in the north int ...
Han Chinese are claimed by some as the forefathers of the southeast Guizhou
Guizhou (; formerly Kweichow) is a landlocked province in the southwest region of the People's Republic of China. Its capital and largest city is Guiyang, in the center of the province. Guizhou borders the autonomous region of Guangxi to the ...
Miao, and Miao children were born to the many Miao women married Han Chinese soldiers in Taijiang in Guizhou before the second half of the 19th century.

Archaeology
According toAndré-Georges Haudricourt
André-Georges Haudricourt (; 17 January 1911 – 20 August 1996) was a French botanist, anthropologist and linguist.
Biography
He grew up on his parents' farm, in a remote area of Picardy. From his early childhood, he was curious about technol ...
and David Strecker's claims based on limited secondary data, the Miao were among the first people to settle in present-day China. They claim that the Han borrowed a lot of words from the Miao in regard to rice farming. This indicated that the Miao were among the first rice farmers in China. In addition, some have connected the Miao to the Daxi Culture (5,300 – 6,000 years ago) in the middle Yangtze River region. The Daxi Culture has been credited with being amongst the first cultivators of rice in the Far East by Western scholars. However, in 2006 rice cultivation was found to have existed in the Shandong province even earlier than the Daxi Culture. Though the Yuezhuang culture has cultivated rice, it is more of collected wild rice and not actual cultivated and domesticated rice like that of the Daxi.
A western study mention that the Miao (especially the Miao-Hunan) has its origins in southern China but have some DNA from the Northeast people of China. Recent DNA samples of Miao males contradict this theory. The White Hmong have 25% C, 8% D, & 6% N(Tat) yet they have the least contact with the Han population.
Demographics
 According to the 2000 census, the number of Miao in China was estimated to be about 9.6 million. Outside of China, members of the Miao sub-group or nations of the Hmong live in
According to the 2000 census, the number of Miao in China was estimated to be about 9.6 million. Outside of China, members of the Miao sub-group or nations of the Hmong live in Thailand
Thailand ( ), historically known as Siam () and officially the Kingdom of Thailand, is a country in Southeast Asia, located at the centre of the Indochinese Peninsula, spanning , with a population of almost 70 million. The country is b ...
, Laos, Vietnam
Vietnam or Viet Nam ( vi, Việt Nam, ), officially the Socialist Republic of Vietnam,., group="n" is a country in Southeast Asia, at the eastern edge of mainland Southeast Asia, with an area of and population of 96 million, making i ...
and Burma
Myanmar, ; UK pronunciations: US pronunciations incl. . Note: Wikipedia's IPA conventions require indicating /r/ even in British English although only some British English speakers pronounce r at the end of syllables. As John Wells explai ...
due to outward migrations starting in the 18th century. As a result of recent migrations in the aftermath of the Indochina
Mainland Southeast Asia, also known as the Indochinese Peninsula or Indochina, is the continental portion of Southeast Asia. It lies east of the Indian subcontinent and south of Mainland China and is bordered by the Indian Ocean to the west an ...
and Vietnam War
The Vietnam War (also known by other names) was a conflict in Vietnam, Laos, and Cambodia from 1 November 1955 to the fall of Saigon on 30 April 1975. It was the second of the Indochina Wars and was officially fought between North Vietnam a ...
s from 1949–75, many Hmong people now live in the United States
The United States of America (U.S.A. or USA), commonly known as the United States (U.S. or US) or America, is a country primarily located in North America. It consists of 50 states, a federal district, five major unincorporated territori ...
, French Guiana
French Guiana ( or ; french: link=no, Guyane ; gcr, label=French Guianese Creole, Lagwiyann ) is an overseas department/region and single territorial collectivity of France on the northern Atlantic coast of South America in the Guianas. ...
, France
France (), officially the French Republic ( ), is a country primarily located in Western Europe. It also comprises of overseas regions and territories in the Americas and the Atlantic, Pacific and Indian Oceans. Its metropolitan area ...
and Australia. Altogether, there are approximately 10 million speakers in the Miao language family. This language family, which consists of 6 languages and around 35 dialects (some of which are mutually intelligible) belongs to the Hmong/Miao branch of the Hmong–Mien (Miao–Yao) language family.
A large population of the Hmong have emigrated to the northern mountainous reaches of Southeast Asia including Thailand, Laos, Vietnam, and Burma
Myanmar, ; UK pronunciations: US pronunciations incl. . Note: Wikipedia's IPA conventions require indicating /r/ even in British English although only some British English speakers pronounce r at the end of syllables. As John Wells explai ...
. However, many continue to live in far Southwest China mostly in the provinces of Yunnan
Yunnan , () is a landlocked province in the southwest of the People's Republic of China. The province spans approximately and has a population of 48.3 million (as of 2018). The capital of the province is Kunming. The province borders the C ...
, Guangxi and to a very limited extent in Guizhou
Guizhou (; formerly Kweichow) is a landlocked province in the southwest region of the People's Republic of China. Its capital and largest city is Guiyang, in the center of the province. Guizhou borders the autonomous region of Guangxi to the ...
.
:''Note: The Miao areas of Sichuan province became part of the newly created Chongqing Municipality in 1997.''
Most Miao currently live in China. Miao population growth in China:
* 1953: 2,510,000
* 1964: 2,780,000
* 1982: 5,030,000
* 1990: 7,390,000
3,600,000 Miao, about half of the entire Chinese Miao population, were in Guizhou
Guizhou (; formerly Kweichow) is a landlocked province in the southwest region of the People's Republic of China. Its capital and largest city is Guiyang, in the center of the province. Guizhou borders the autonomous region of Guangxi to the ...
in 1990. The Guizhou Miao and those in the following six provinces make up over 98% of all Chinese Miao:
* Hunan
Hunan (, ; ) is a landlocked province of the People's Republic of China, part of the South Central China region. Located in the middle reaches of the Yangtze watershed, it borders the province-level divisions of Hubei to the north, Jiangxi ...
: 1,550,000
* Yunnan
Yunnan , () is a landlocked province in the southwest of the People's Republic of China. The province spans approximately and has a population of 48.3 million (as of 2018). The capital of the province is Kunming. The province borders the C ...
: 890,000
* Sichuan
Sichuan (; zh, c=, labels=no, ; zh, p=Sìchuān; alternatively romanized as Szechuan or Szechwan; formerly also referred to as "West China" or "Western China" by Protestant missions) is a province in Southwest China occupying most of the ...
: 530,000
* Guangxi: 420,000
* Hubei
Hubei (; ; alternately Hupeh) is a landlocked province of the People's Republic of China, and is part of the Central China region. The name of the province means "north of the lake", referring to its position north of Dongting Lake. The ...
: 200,000
* Hainan
Hainan (, ; ) is the smallest and southernmost province of the People's Republic of China (PRC), consisting of various islands in the South China Sea. , the largest and most populous island in China,The island of Taiwan, which is slightly l ...
: 50,000 (known as Miao but ethnically Yao and Li)
In the above provinces, there are 6 Miao autonomous prefectures (shared officially with one other ethnic minority):
* Qiandongnan Miao and Dong Autonomous Prefecture
Qiandongnan Miao and Dong Autonomous Prefecture (; Hmu language: ''Qeef Dongb Naif Dol Hmub Dol Gud Zid Zid Zeb''; Kam language: ''Qeens Donc Nanc Nyenc Miiul Nyenc Gaeml Zil Zl Zous''), also known as Southeast Qian Autonomous Prefecture of Miao a ...
, Guizhou
* Qiannan Buyei and Miao Autonomous Prefecture
Qiannan Buyei and Miao Autonomous Prefecture (; Buyei: ''Qianfnanf Buxqyaix Buxyeeuz ziqziqzouy''; Hmu: ''Qeef Naif Dol Yat Dol Hmub Zid Zid Zeb'') is an autonomous prefecture of Guizhou province, People's Republic of China, bordering Guangxi ...
, Guizhou
* Qianxinan Buyei and Miao Autonomous Prefecture
Qianxinan Buyei and Miao Autonomous Prefecture (; Buyei: ''Qianfxiynanf Buxqyaix Buxyeeuz Ziqziqzouy''; Hmu: ''Qeef Xib Naif Dol Yat Dol Hmub Zid Zid Zeb''), is an autonomous prefecture of Guizhou province, People's Republic of China, bordering G ...
, Guizhou
* Xiangxi Tujia and Miao Autonomous Prefecture
Xiangxi Tujia and Miao Autonomous Prefecture (; Tujia: Xianxxix bifzivkar befkar zifzifzoux; Miao: Xangdxid tutjadcul maolcul zibzhibzhoud) is an autonomous prefecture of the People's Republic of China. It is located in northwestern Hunan provin ...
, Hunan
* Wenshan Zhuang and Miao Autonomous Prefecture
Wenshan Zhuang and Miao Autonomous Prefecture is an autonomous prefecture in southeastern Yunnan Province, People's Republic of China and the easternmost prefecture-level division of the province. It borders Baise, Guangxi to the east, Vietnam ...
, Yunnan
* Enshi Tujia and Miao Autonomous Prefecture
Enshi Tujia and Miao Autonomous Prefecture () is located in the mountainous southwestern corner of Hubei province, People's Republic of China. It forms Hubei's southwestern "panhandle", bordering on Hunan in the south and Chongqing Municipality ...
, Hubei
There are in addition 23 Miao autonomous counties
Autonomous counties () and autonomous banners () are county-level autonomous administrative divisions of China. The two are essentially identical except in name.
There are 117 autonomous counties and three autonomous banners. The latter are fo ...
:
* Hunan: Mayang
Mayang ( "''Mayang Miao Autonomous County''", ; usually referred to as "''Mayang County''", ) is an autonomous county of Miao people in Hunan Province, China, it is under the administration of the prefecture-level city of Huaihua.
Mayang is lo ...
, Jingzhou
Jingzhou () is a prefecture-level city in southern Hubei province, China, located on the banks of the Yangtze River. Its total residential population was 5,231,180 based on the 2020 census, 1,068,291 of whom resided in the built-up (''or metro' ...
, Chengbu
* Guizhou: Songtao, Yinjiang
Yinjiang Tujia and Miao Autonomous County () also known in Tujia language as "Yinv jiangr Bif Ziv Kar hev Bef Kar zouf xengv xianr" is a county in the northeast of Guizhou province, China. It is under the administration of the prefecture-level city ...
, Wuchuan, Daozhen
Daozhen Gelao and Miao Autonomous County (; usually referred to as "Daozhen County", commonly abbreviated as Daozhen ) is a county in northernmost Guizhou province, China. It is under the administration of the prefecture-level city of Zunyi. Daozhe ...
, Zhenning
Zhenning Buyei and Miao Autonomous County (; usually referred to as "Zhenning County", commonly abbreviated as Zhenning (); Buyei: Zenqninf Buxqyaix Buxyeeuz Ziqziqxianq) is an autonomous county under the administration of the prefecture-level ci ...
, Ziyun
Ziyun Miao and Buyei Autonomous County (; Bouyei: ) is a county in the southwest of Guizhou province, China. It is under the administration of the prefecture-level city
A prefecture-level city () or prefectural city is an administrative div ...
, Guanling
Guanling Buyei and Miao Autonomous County (; Bouyei: ) is an autonomous county in Anshun City, in the southwest of Guizhou Province, China.
Area:
Population: 334,900 in 2008.
Postal Code: 561300.
Telephone Area Code: 0853
The county govern ...
, Weining
* Yunnan: Pingbian, Jinping, Luquan
* Chongqing: Xiushan
Xiushan Tujia and Miao Autonomous County (), or Xiushan County for short, is located in the southeast of Chongqing Municipality, China. It is the municipality's southernmost county-level division.
* Area:
* Population
Population typically ...
, Youyang, Qianjiang, Pengshui
* Guangxi: Rongshui, Longsheng, Longlin
Longlin Various Nationalities (Gezu) Autonomous County () is an autonomous county, under the jurisdiction of the prefecture-level city of Baise, in the west of Guangxi, China, bordering Guizhou Province to the north. As of 2019, the county's pop ...
(including Hmong)
* Hainan
Hainan (, ; ) is the smallest and southernmost province of the People's Republic of China (PRC), consisting of various islands in the South China Sea. , the largest and most populous island in China,The island of Taiwan, which is slightly l ...
: Qiongzhong
Qiongzhong Li and Miao Autonomous County is an autonomous county in Hainan, China. It is one of 6 autonomous counties of the upper highlands of Hainan. Its postal code is 572900, and in 1999 its population was 196,581 people, largely made up of t ...
and Baoting
Bǎotíng Li and Miao Autonomous County () is an autonomous county in Hainan, China. One of the six autonomous counties on the island, its postal code is 572300. Baoting spans an area of , and has a population of about 168,000 as of 2020.
Histor ...
Most Miao reside in hills or on mountains, such as
* Wuling Mountain by the Qianxiang River ()
* Miao Mountain Miao may refer to:
* Miao people, linguistically and culturally related group of people, recognized as such by the government of the People's Republic of China
* Miao script or Pollard script, writing system used for Miao languages
* Miao (Unicode ...
(), Qiandongnan
* Yueliang Mountain (), Qiandongnan
* Greater and Lesser Ma Mountain (), Qiannan
* Greater Miao Mountain (), Guangxi
* Wumeng Mountain by the Tianqian River ()
Several thousands of Miao left their homeland to move to larger cities like Guangzhou
Guangzhou (, ; ; or ; ), also known as Canton () and alternatively romanized as Kwongchow or Kwangchow, is the capital and largest city of Guangdong province in southern China. Located on the Pearl River about north-northwest of Hong Kon ...
and Beijing
}
Beijing ( ; ; ), alternatively romanized as Peking ( ), is the capital of the People's Republic of China. It is the center of power and development of the country. Beijing is the world's most populous national capital city, with over 21 ...
. There are 789,000 Hmong spread throughout northern Vietnam
Vietnam or Viet Nam ( vi, Việt Nam, ), officially the Socialist Republic of Vietnam,., group="n" is a country in Southeast Asia, at the eastern edge of mainland Southeast Asia, with an area of and population of 96 million, making i ...
, Laos, Burma
Myanmar, ; UK pronunciations: US pronunciations incl. . Note: Wikipedia's IPA conventions require indicating /r/ even in British English although only some British English speakers pronounce r at the end of syllables. As John Wells explai ...
, and on other continents. 174,000 live in Thailand
Thailand ( ), historically known as Siam () and officially the Kingdom of Thailand, is a country in Southeast Asia, located at the centre of the Indochinese Peninsula, spanning , with a population of almost 70 million. The country is b ...
, where they are one of the six main hill tribes.
Distribution
By province
The2000 Chinese census
The 2000 Chinese census, officially the Fifth National Population Census of the People's Republic of China (), was conducted by the government of the People's Republic of China with 1 November 2000 as its zero hour. The total population was calcula ...
recorded 8,940,116 Miao in mainland China
"Mainland China" is a geopolitical term defined as the territory governed by the People's Republic of China (including islands like Hainan or Chongming), excluding dependent territories of the PRC, and other territories within Greater China. ...
.
;Provincial distribution of the Miao in mainland China
By county
;County-level distribution of the Miao in mainland China (Only includes counties or county-equivalents containing >0.25% of mainland China's Miao population.)Cuisine
Miao Fish (苗鱼 miáo yǘ)
Miao fish is a dish made by steaming fish with a mixture of fresh herbs, green peppers, ginger slices and garlic.See also
*Chiyou
Chiyou (蚩尤, ) is a mythological being that appears in East Asian mythology.
Individual
According to the Song dynasty history book '' Lushi'', Chiyou's surname was Jiang (), and he was a descendant of flame.
According to legend, Chiyou had a ...
* Ethnic groups in Chinese history
Ethnic groups in Chinese history refer to various or presumed ethnicities of significance to the history of China, gathered through the study of Classical Chinese literature, Chinese and non-Chinese literary sources and inscriptions, histori ...
* Ethnic minorities in China
* History of China
The earliest known written records of the history of China date from as early as 1250 BC, from the Shang dynasty (c. 1600–1046 BC), during the reign of king Wu Ding. Ancient historical texts such as the '' Book of Documents'' (early chapt ...
* Hmong people
* Hmong customs and culture
The Hmong people are an ethnic group currently native to several countries, believed to have come from the Yangtze river basin area in southern China. The Hmong are known in China as the ''Miao'', which encompasses not only Hmong, but also other ...
* Hmong–Mien languages
The Hmong–Mien languages (also known as Miao–Yao and rarely as Yangtzean) are a highly tonal language family of southern China and northern Southeast Asia. They are spoken in mountainous areas of southern China, including Guizhou, Hunan, Yunn ...
* Languages of China
* List of Hmong/Miao People
* Single bamboo drifting
Single-bamboo drifting or duzhu drifting ( zh, 独竹漂) is a sport traditionally practiced by various people inhabiting the Chishui River basin in Guizhou Province. Practitioners either perform dance movements or race one another using the bambo ...
* Pole worship
* Vang Pao
Vang Pao ( RPA: ''Vaj Pov'' , Lao: ວັງປາວ; 8 December 1929 – 6 January 2011) was a major general in the Royal Lao Army. He was a leader of the Hmong American community in the United States. He was also known as General Vang ...
References
Citations
Sources
* Enwall, Jaokim''Thai-Yunnan Project Newsletter''
No. 17, Department of Anthropology, Australian National University, June 1992. * * * * * * * * Feng, Xianghong. (2013)
Women's Work, Men's Work: Gender and Tourism among the Miao in Rural China
Anthropology of Work Review
The American Anthropological Association (AAA) is an organization of scholars and practitioners in the field of anthropology. With 10,000 members, the association, based in Arlington, Virginia, includes archaeologists, cultural anthropologists, ...
. 34. p. 4–10.
Further reading
*Tomoko Torimaru(September 1, 2008), One Needle, One Thread: Miao (Hmong) embroidery and fabric piecework from Guizhou, China, University of Hawaii Art Galle *External links
Hmong Studies Internet Resource Center
from 1786
Map share of ethnic by county of China
{{DEFAULTSORT:Miao People Ethnic groups officially recognized by China Ethnic groups in Laos Ethnic groups in Thailand Ethnic groups in Vietnam Hmong