Menstrual disorder on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 A menstrual disorder is characterized as any abnormal condition with regards to a person's menstrual cycle. There are many different types of menstrual disorders that vary with signs and symptoms, including pain during menstruation, heavy bleeding, or absence of menstruation. Normal variations can occur in menstrual patterns but generally menstrual disorders can also include periods that come sooner than 21 days apart, more than 3 months apart, or last more than 10 days in duration. Variations of the menstrual cycle are mainly caused by the immaturity of the hypothalamic-pituitary-ovarian (HPO) axis, and early detection and management is required in order to minimize the possibility of complications regarding future reproductive ability.
Though menstrual disorders were once considered more of a nuisance problem, they are now widely recognized as having a serious impact on society in the form of days lost from work brought about by the pain and suffering experienced by women. These disorders can arise from physiologic sources (pregnancy etc.), pathologic sources (stress, excessive exercise, weight loss, endocrine or structural abnormalities etc.), or iatrogenic sources (secondary to contraceptive use etc.).
A menstrual disorder is characterized as any abnormal condition with regards to a person's menstrual cycle. There are many different types of menstrual disorders that vary with signs and symptoms, including pain during menstruation, heavy bleeding, or absence of menstruation. Normal variations can occur in menstrual patterns but generally menstrual disorders can also include periods that come sooner than 21 days apart, more than 3 months apart, or last more than 10 days in duration. Variations of the menstrual cycle are mainly caused by the immaturity of the hypothalamic-pituitary-ovarian (HPO) axis, and early detection and management is required in order to minimize the possibility of complications regarding future reproductive ability.
Though menstrual disorders were once considered more of a nuisance problem, they are now widely recognized as having a serious impact on society in the form of days lost from work brought about by the pain and suffering experienced by women. These disorders can arise from physiologic sources (pregnancy etc.), pathologic sources (stress, excessive exercise, weight loss, endocrine or structural abnormalities etc.), or iatrogenic sources (secondary to contraceptive use etc.).
 The signs and symptoms of menstrual disorders can cause significant stress. Abnormal uterine bleeding (AUB) has the potential to be one of the most urgent gynecological problems during menstruation. Dysmenorrhea is the most common.
The signs and symptoms of menstrual disorders can cause significant stress. Abnormal uterine bleeding (AUB) has the potential to be one of the most urgent gynecological problems during menstruation. Dysmenorrhea is the most common.
 Diagnosis begins with an in-depth medical history and physical exam, including a
Diagnosis begins with an in-depth medical history and physical exam, including a
 A menstrual disorder is characterized as any abnormal condition with regards to a person's menstrual cycle. There are many different types of menstrual disorders that vary with signs and symptoms, including pain during menstruation, heavy bleeding, or absence of menstruation. Normal variations can occur in menstrual patterns but generally menstrual disorders can also include periods that come sooner than 21 days apart, more than 3 months apart, or last more than 10 days in duration. Variations of the menstrual cycle are mainly caused by the immaturity of the hypothalamic-pituitary-ovarian (HPO) axis, and early detection and management is required in order to minimize the possibility of complications regarding future reproductive ability.
Though menstrual disorders were once considered more of a nuisance problem, they are now widely recognized as having a serious impact on society in the form of days lost from work brought about by the pain and suffering experienced by women. These disorders can arise from physiologic sources (pregnancy etc.), pathologic sources (stress, excessive exercise, weight loss, endocrine or structural abnormalities etc.), or iatrogenic sources (secondary to contraceptive use etc.).
A menstrual disorder is characterized as any abnormal condition with regards to a person's menstrual cycle. There are many different types of menstrual disorders that vary with signs and symptoms, including pain during menstruation, heavy bleeding, or absence of menstruation. Normal variations can occur in menstrual patterns but generally menstrual disorders can also include periods that come sooner than 21 days apart, more than 3 months apart, or last more than 10 days in duration. Variations of the menstrual cycle are mainly caused by the immaturity of the hypothalamic-pituitary-ovarian (HPO) axis, and early detection and management is required in order to minimize the possibility of complications regarding future reproductive ability.
Though menstrual disorders were once considered more of a nuisance problem, they are now widely recognized as having a serious impact on society in the form of days lost from work brought about by the pain and suffering experienced by women. These disorders can arise from physiologic sources (pregnancy etc.), pathologic sources (stress, excessive exercise, weight loss, endocrine or structural abnormalities etc.), or iatrogenic sources (secondary to contraceptive use etc.).
Types of menstrual disorders
Premenstrual Disorders
* Premenstrual syndrome (PMS) or premenstrual tension refers to the emotional and physical symptoms that routinely occur in the two weeks leading up to menstruation. Symptoms are usually mild, but 5-8% of women experience moderate to severe symptoms that significantly affect daily activities. Symptoms may include anxiety, irritability, mood swings, depression, headache, food cravings, increased appetite, and bloating. * Premenstrual dysphoric disorder (PMDD) is a severe mood disorder that affects cognitive and physical functions in the week leading up to menstruation. Premenstrual dysphoric disorder is diagnosed with at least one affective, or mood, symptom and at least five physical, mood, and/or behavioral symptoms.Disorders of cycle length
Normal menstrual cycle length is 22–45 days. *Amenorrhea
Amenorrhea is the absence of a menstrual period in a woman of reproductive age. Physiological states of amenorrhoea are seen, most commonly, during pregnancy and lactation (breastfeeding). Outside the reproductive years, there is absence of menses ...
is the absence of a menstrual period in a woman of reproductive age. Physiologic states of amenorrhoea are seen during pregnancy
Pregnancy is the time during which one or more offspring develops (gestation, gestates) inside a woman, woman's uterus (womb). A multiple birth, multiple pregnancy involves more than one offspring, such as with twins.
Pregnancy usually occur ...
and lactation
Lactation describes the secretion of milk from the mammary glands and the period of time that a mother lactates to feed her young. The process naturally occurs with all sexually mature female mammals, although it may predate mammals. The proces ...
(breastfeeding). Outside of the reproductive years there is absence of menses during childhood and after menopause
Menopause, also known as the climacteric, is the time in women's lives when menstrual periods stop permanently, and they are no longer able to bear children. Menopause usually occurs between the age of 47 and 54. Medical professionals often ...
.
* Irregular menstruation
Irregular menstruation is a menstrual disorder whose manifestations include irregular cycle lengths as well as metrorrhagia (vaginal bleeding between expected periods). The possible causes of irregular menstruation may vary. The common factors of ...
is where there is variation in menstrual cycle length of more than approximately 8 days for a woman. The term metrorrhagia
Intermenstrual bleeding, previously known as metrorrhagia, is uterine bleeding at irregular intervals, particularly between the expected menstrual periods. It is a cause of vaginal bleeding.
In some women, menstrual spotting between periods occu ...
is often used for irregular menstruation that occurs between the expected menstrual periods.
* Oligomenorrhea
Oligomenorrhea is infrequent (or, in occasional usage, very light) menstruation. More strictly, it is menstrual periods occurring at intervals of greater than 35 days, with only four to nine periods in a year.thefreedictionary.com > oligomenorrhea ...
is the medical term for infrequent, often light menstrual periods (intervals exceeding 35 days).
* Polymenorrhea is the medical term for cycles with intervals of 21 days or fewer.
Disorders of flow
Normal menstrual flow length is 3–7 days. *Abnormal uterine bleeding
Abnormal uterine bleeding (AUB), also known as (AVB) or as atypical vaginal bleeding, is vaginal bleeding from the uterus that is abnormally frequent, lasts excessively long, is heavier than normal, or is irregular. The term dysfunctional uterin ...
(AUB) is a broad term used to describe any disruption in bleeding that involves the volume, duration, and/or regularity of flow. Bleeding may occur frequently or infrequently, and can occur between periods, after sexual intercourse, and after menopause. Bleeding during pregnancy is excluded.
* Hypomenorrhea is abnormally light menstrual bleeding.
* Menorrhagia (meno = prolonged, rrhagia = excessive flow/discharge) is an abnormally heavy and prolonged menstrual period.
* Metrorrhagia
Intermenstrual bleeding, previously known as metrorrhagia, is uterine bleeding at irregular intervals, particularly between the expected menstrual periods. It is a cause of vaginal bleeding.
In some women, menstrual spotting between periods occu ...
is bleeding at irregular times, especially outside the expected intervals of the menstrual cycle. If there is excessive menstrual and uterine bleeding other than that caused by menstruation, menometrorrhagia (meno = prolonged, metro = time, rrhagia = excessive flow/discharge) may be diagnosed. Causes may be due to abnormal blood clotting, disruption of normal hormonal regulation of periods or disorders of the endometrial
The endometrium is the inner epithelial layer, along with its mucous membrane, of the mammalian uterus. It has a basal layer and a functional layer: the basal layer contains stem cells which regenerate the functional layer. The functional layer ...
lining of the uterus
The uterus (from Latin ''uterus'', plural ''uteri'') or womb () is the organ in the reproductive system of most female mammals, including humans that accommodates the embryonic and fetal development of one or more embryos until birth. The ...
. Depending upon the cause, it may be associated with abnormally painful periods.
Disorders of ovulation
Disorders of ovulation include oligoovulation and anovulation: *Anovulation
Anovulation is when the ovaries do not release an oocyte during a menstrual cycle. Therefore, ovulation does not take place. However, a woman who does not ovulate at each menstrual cycle is not necessarily going through menopause. Chronic anovula ...
is absence of ovulation
Ovulation is the release of eggs from the ovaries. In women, this event occurs when the ovarian follicles rupture and release the secondary oocyte ovarian cells. After ovulation, during the luteal phase, the egg will be available to be fertilize ...
when it would be normally expected (in a post- menarchal, premenopausal woman). Anovulation usually manifests itself as irregularity of menstrual periods, that is, unpredictable variability of intervals, duration, or bleeding. Anovulation can also cause cessation of periods (secondary amenorrhea) or excessive bleeding (dysfunctional uterine bleeding
Abnormal uterine bleeding (AUB), also known as (AVB) or as atypical vaginal bleeding, is vaginal bleeding from the uterus that is abnormally frequent, lasts excessively long, is heavier than normal, or is irregular. The term dysfunctional uterin ...
).
*Oligoovulation is infrequent or irregular ovulation (usually defined as cycles of >35 days or <8 cycles a year).
Other menstrual disorders
* Dysmenorrhea (or dysmenorrhoea), cramps or painful menstruation, involves menstrual periods that are accompanied by either sharp, intermittent pain or dull, aching pain, usually in the pelvis or lowerabdomen
The abdomen (colloquially called the belly, tummy, midriff, tucky or stomach) is the part of the body between the thorax (chest) and pelvis, in humans and in other vertebrates. The abdomen is the front part of the abdominal segment of the to ...
.
Signs and symptoms of menstrual disorders
 The signs and symptoms of menstrual disorders can cause significant stress. Abnormal uterine bleeding (AUB) has the potential to be one of the most urgent gynecological problems during menstruation. Dysmenorrhea is the most common.
The signs and symptoms of menstrual disorders can cause significant stress. Abnormal uterine bleeding (AUB) has the potential to be one of the most urgent gynecological problems during menstruation. Dysmenorrhea is the most common.
Premenstrual Syndrome (PMS)
Symptoms may include irritability, bloating, depression, food cravings, aggressiveness, and mood swings. Fluid retention and fluctuating weight gain are also reported. Precipitating risk factors include: stress, alcohol consumption, exercise, smoking, and some medications.Amenorrhea
Lack of a menses by the age of 16 where secondary sexual characteristics have developed or by the age of 14 where no secondary sexual characteristics have developed (primary amenorrhea), or lack of a menses for more than 3–6 months after first menstruation cycle. Although missing a period is the main sign, other symptoms can include: excess facial, hair loss, headache, changes to vision, milky discharge from the breasts, or absence of breast development.Abnormal Uterine Bleeding
One-third of women will experience abnormal uterine bleeding in their life. Normal menstrual cycle has a frequency of 24 to 38 days, lasts 7 to 9 days, so bleeding that lasts longer could be considered abnormal. Very heavy bleeding (for example, needing to use 1 or more tampons or sanitary pads every hour) is another symptom.Dysmenorrhea
Especially painful or persistent menstrual cramping that occurs in the absence of any underlying pelvic disease. Pain radiating to the low back or upper thighs with onset of menstruation and lasting anywhere from 12 to 72 hours. Headache, nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, and fatigue may also accompany the pain. Pain may begin gradually, with the first several years of menses, and then intensified as menstruation becomes regular. Patients who also have secondary amenorrhea report symptoms beginning after age 20 and lasting 5–7 days with progressive worsening of pain over time. Pelvic pain is also reported.Causes of menstrual disorders
There are many causes of menstrual disorders, includinguterine fibroid
Uterine fibroids, also known as uterine leiomyomas or fibroids, are benign smooth muscle tumors of the uterus. Most women with fibroids have no symptoms while others may have painful or heavy periods. If large enough, they may push on the bl ...
s, hormonal imbalances, clotting disorders, cancer
Cancer is a group of diseases involving abnormal cell growth with the potential to invade or spread to other parts of the body. These contrast with benign tumors, which do not spread. Possible signs and symptoms include a lump, abnormal b ...
, sexually-transmitted infections, polycystic ovary syndrome
Polycystic ovary syndrome, or PCOS, is the most common endocrine disorder in women of reproductive age. The syndrome is named after the characteristic cysts which may form on the ovaries, though it is important to note that this is a sign and no ...
, and genetics. Uterine fibroid
Uterine fibroids, also known as uterine leiomyomas or fibroids, are benign smooth muscle tumors of the uterus. Most women with fibroids have no symptoms while others may have painful or heavy periods. If large enough, they may push on the bl ...
s are benign, non-cancerous growths in the uterus that affect most women at some point in their lives and usually does not require treatment unless they cause intolerable symptoms. Stress and lifestyle factors commonly impact menstruation, which includes weight changes, dieting, changes in exercise, travel, and illness.
Hyperprolactinaemia
Hyperprolactinaemia is the presence of abnormally high levels of prolactin in the blood. Reference ranges for common blood tests, Normal levels average to about 13 ng/mL in women, and 5 ng/mL in men, with an upper normal limit of serum ...
can also cause menstrual disorders.
Amenorrhea
There are different causes depending on the type of menstrual(period) disorder.Amenorrhea
Amenorrhea is the absence of a menstrual period in a woman of reproductive age. Physiological states of amenorrhoea are seen, most commonly, during pregnancy and lactation (breastfeeding). Outside the reproductive years, there is absence of menses ...
, or the absence of menstruation, is subdivided into primary and secondary amenorrhea. In primary amenorrhea, in which there is a failure to menstruate by the age of 16 with normal sexual development or by 14 without normal sexual development, causes can be from developmental abnormalities of the uterus, ovaries, or genital tract, or endocrine disorders. In secondary amenorrhea, or the absence of menstruation for greater than 6 months, can be caused by the same reasons as primary amenorrhea, as well as polycystic ovary syndrome
Polycystic ovary syndrome, or PCOS, is the most common endocrine disorder in women of reproductive age. The syndrome is named after the characteristic cysts which may form on the ovaries, though it is important to note that this is a sign and no ...
, pregnancy, chronic illness, and certain drugs like cocaine and opioids.
Hypomenorrhea
Causes of hypomenorrhea, or irregular light periods, include periods aroundmenopause
Menopause, also known as the climacteric, is the time in women's lives when menstrual periods stop permanently, and they are no longer able to bear children. Menopause usually occurs between the age of 47 and 54. Medical professionals often ...
, eating disorders, excessive exercise, thyroid dysfunction
Thyroid disease is a medical condition that affects the function of the thyroid gland. The thyroid gland is located at the front of the neck and produces thyroid hormones that travel through the blood to help regulate many other organs, meaning t ...
, uncontrolled diabetes
Diabetes, also known as diabetes mellitus, is a group of metabolic disorders characterized by a high blood sugar level ( hyperglycemia) over a prolonged period of time. Symptoms often include frequent urination, increased thirst and increased ...
, Cushing's syndrome
Cushing's syndrome is a collection of signs and symptoms due to prolonged exposure to glucocorticoids such as cortisol. Signs and symptoms may include high blood pressure, abdominal obesity but with thin arms and legs, reddish stretch marks, a ...
, hormonal birth control
Hormonal contraception refers to birth control methods that act on the endocrine system. Almost all methods are composed of steroid hormones, although in India one selective estrogen receptor modulator is marketed as a contraceptive. The origina ...
, and certain medications to treat epilepsy or mental health conditions.
Menorrhagia
Causes of menorrhagia, or heavy menstrual bleeding, includepolycystic ovary syndrome
Polycystic ovary syndrome, or PCOS, is the most common endocrine disorder in women of reproductive age. The syndrome is named after the characteristic cysts which may form on the ovaries, though it is important to note that this is a sign and no ...
, uterine fibroid
Uterine fibroids, also known as uterine leiomyomas or fibroids, are benign smooth muscle tumors of the uterus. Most women with fibroids have no symptoms while others may have painful or heavy periods. If large enough, they may push on the bl ...
s, endometrial polyp
An endometrial polyp or uterine polyp is a mass in the inner lining of the uterus.
They may have a large flat base ( sessile) or be attached to the uterus by an elongated pedicle ( pedunculated).
Pedunculated polyps are more common than sessile ...
s, bleeding disorders, and miscarriage.
Dysmenorrhea
Causes of dysmenorrhea, or menstrual pain, include endometriosis, pelvic scarring due tochlamydia
Chlamydia, or more specifically a chlamydia infection, is a sexually transmitted infection caused by the bacterium '' Chlamydia trachomatis''. Most people who are infected have no symptoms. When symptoms do appear they may occur only several we ...
or gonorrhea
Gonorrhea, colloquially known as the clap, is a sexually transmitted infection (STI) caused by the bacterium ''Neisseria gonorrhoeae''. Infection may involve the genitals, mouth, or rectum. Infected men may experience pain or burning with u ...
, and intrauterine devices or IUDs
An intrauterine device (IUD), also known as intrauterine contraceptive device (IUCD or ICD) or coil, is a small, often T-shaped birth control device that is inserted into the uterus to prevent pregnancy. IUDs are one form of long-acting reversi ...
. Primary dysmenorrhea is when there is no underlying cause that is identified, and secondary dysmenorrhea is when the menstrual pain is caused by other conditions such as endometriosis, fibroids, or infection.
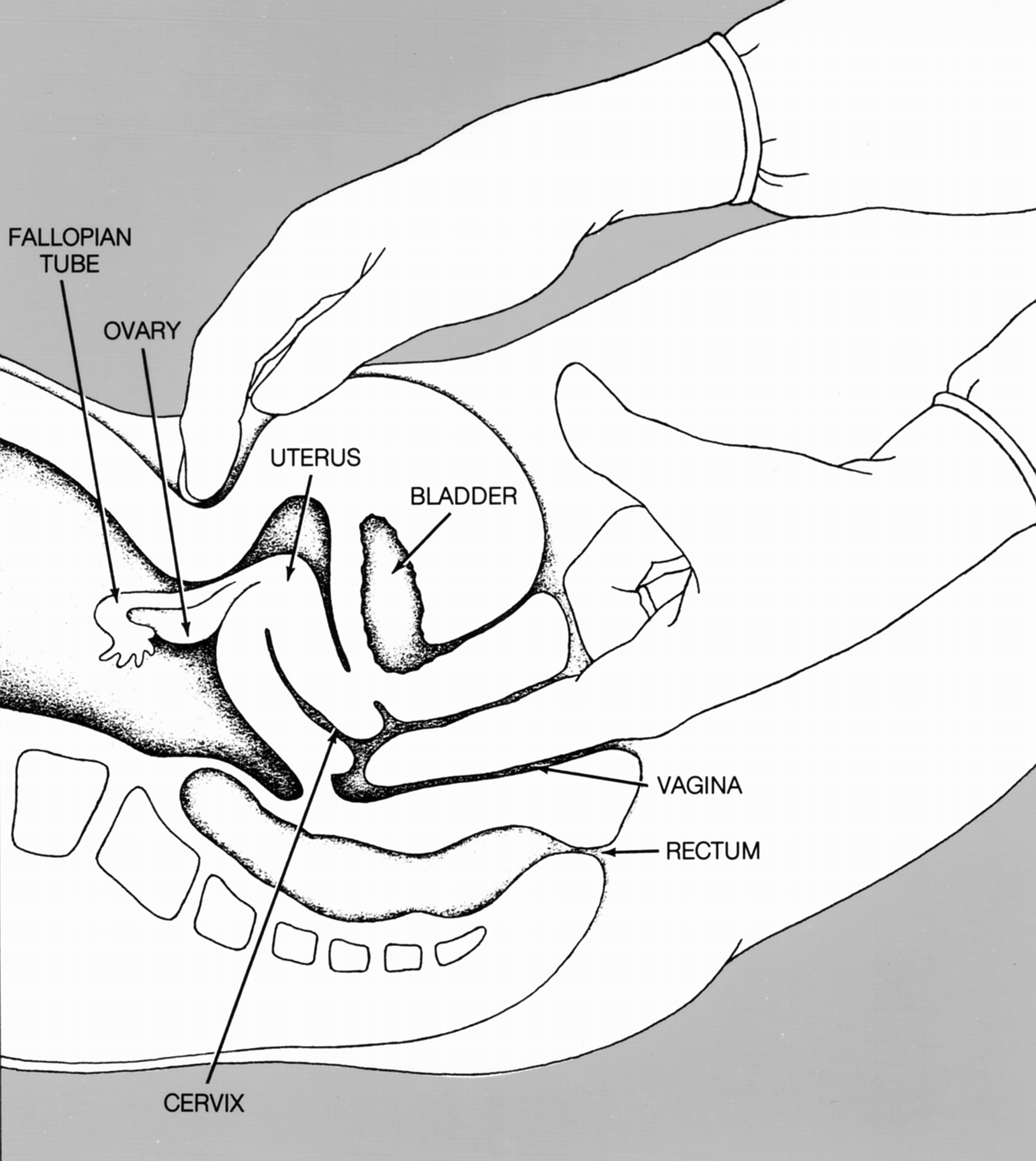
Diagnosis of menstrual disorders
 Diagnosis begins with an in-depth medical history and physical exam, including a
Diagnosis begins with an in-depth medical history and physical exam, including a pelvic exam
A pelvic examination is the physical examination of the external and internal female pelvic organs. It is frequently used in gynecology for the evaluation of symptoms affecting the female reproductive and urinary tract, such as pain, bleeding, d ...
and sometimes a Pap smear
The Papanicolaou test (abbreviated as Pap test, also known as Pap smear (AE), cervical smear (BE), cervical screening (BE), or smear test (BE)) is a method of cervical screening used to detect potentially precancerous and cancerous processes in t ...
.
Additional testing may include but are not limited to blood tests, hormonal tests, ultrasound
Ultrasound is sound waves with frequencies higher than the upper audible limit of human hearing. Ultrasound is not different from "normal" (audible) sound in its physical properties, except that humans cannot hear it. This limit varies ...
, gynecologic ultrasound, magnetic resonance imaging (MRI), hysteroscopy
Hysteroscopy is the inspection of the uterine cavity by endoscopy with access through the cervix. It allows for the diagnosis of intrauterine pathology and serves as a method for surgical intervention (operative hysteroscopy).
Hysteroscope
A hyst ...
, laparoscopy
Laparoscopy () is an operation performed in the abdomen or pelvis using small incisions (usually 0.5–1.5 cm) with the aid of a camera. The laparoscope aids diagnosis or therapeutic interventions with a few small cuts in the abdomen.Medlin ...
, endometrial biopsy
The endometrial biopsy is a medical procedure that involves taking a tissue sample of the lining of the uterus. The tissue subsequently undergoes a histologic evaluation which aids the physician in forming a diagnosis.
Medical uses
There are a ...
, and dilation and curettage
Dilation (or dilatation) and curettage (D&C) refers to the dilation (widening/opening) of the cervix and surgical removal of part of the lining of the uterus and/or contents of the uterus by scraping and scooping (curettage). It is a gynecolog ...
(D&C).
Treatment of menstrual disorders
Premenstrual syndrome and premenstrual dysphoric disorder
Due to the unclear etiology of premenstrual syndrome and premenstrual dysphoric disorder, symptom relief is the primary goal of treatment.Selective serotonin reuptake inhibitor
Selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs) are a class of drugs that are typically used as antidepressants in the treatment of major depressive disorder, anxiety disorders, and other psychological conditions.
SSRIs increase the extracellul ...
s and spironolactone
Spironolactone, sold under the brand name Aldactone among others, is a medication that is primarily used to treat fluid build-up due to heart failure, liver scarring, or kidney disease. It is also used in the treatment of high blood press ...
decrease physical and psychological symptoms associated with premenstrual syndrome. Oral contraceptives Oral contraceptives, abbreviated OCPs, also known as birth control pills, are medications taken by mouth for the purpose of birth control.
Female
Two types of female oral contraceptive pill, taken once per day, are widely available:
* The combin ...
may ameliorate physical symptoms of breast tenderness and bloating. Ovarian suppression treatment with gonadotropin-releasing hormone agonist
A gonadotropin-releasing hormone agonist (GnRH agonist) is a type of medication which affects gonadotropins and sex hormones. They are used for a variety of indications including in fertility medicine and to lower sex hormone levels in the treatm ...
as an off-label use may reduce symptoms but have adverse side effects including decreased bone density. Other less commonly use medications such as alprazolam
Alprazolam, sold under the brand name Xanax, among others, is a fast-acting, potent tranquilizer of medium duration in the triazolobenzodiazepine (TBZD) class, which are benzodiazepines (BZDs) fused with a triazole ring. It is most commonly u ...
may reduce anxiety symptoms but has potential for dependence, tolerance, and abuse. Pyridoxine, a form of vitamin B6, may be used as a dietary supplement to relieve overall symptoms.
Amenorrhea
Successful treatment varies depending on the diagnosis of amenorrhea. In patients with functional hypothalamic amenorrhea due to physical or psychological stress, non-pharmacological options include weight gain, resolution of emotional issues, or decreased intensity of exercise. Patients experiencing amenorrhea due to hypothyroidism may be started with thyroid replacement therapy. Dopamine agonists such asbromocriptine
Bromocriptine, originally marketed as Parlodel and subsequently under many brand names, is an ergoline derivative and dopamine agonist that is used in the treatment of pituitary tumors, Parkinson's disease, hyperprolactinaemia, neuroleptic ...
are used in patients with pituitary adenoma
Pituitary adenomas are tumors that occur in the pituitary gland. Most pituitary tumors are benign, approximately 35% are invasive and just 0.1% to 0.2% are carcinomas.
Amenorrhea associated with structural anomalies can be addressed with surgical treatment such as
NIHPutting tampon in painlessly
{{DEFAULTSORT:Menstrual Disorder Menstrual disorders
gonadectomy
Castration is any action, surgical, chemical, or otherwise, by which an individual loses use of the testicles: the male gonad. Surgical castration is bilateral orchiectomy (excision of both testicles), while chemical castration uses pharmaceu ...
.
Menorrhagia
Acute management of menstrual bleeding includeshormonal therapy
Hormone therapy or hormonal therapy is the use of hormones in medical treatment. Treatment with hormone antagonists may also be referred to as hormonal therapy or antihormone therapy. The most general classes of hormone therapy are oncologic horm ...
with estrogen
Estrogen or oestrogen is a category of sex hormone responsible for the development and regulation of the female reproductive system and secondary sex characteristics. There are three major endogenous estrogens that have estrogenic hormonal ac ...
or oral contraceptives until bleeding has stopped followed by an oral contraceptive tapering regimen. Adjunctive therapy may include iron supplements
Iron supplements, also known as iron salts and iron pills, are a number of iron formulations used to treat and prevent iron deficiency including iron deficiency anemia. For prevention they are only recommended in those with poor absorption, h ...
and nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs. Patients who do not respond to hormonal therapy may use antifibrinolytic Antifibrinolytics are a class of medication that are inhibitors of fibrinolysis. Examples include aminocaproic acid (ε-aminocaproic acid) and tranexamic acid
Tranexamic acid (TXA) is a medication used to treat or prevent excessive blood loss fr ...
s. Procedural therapy such as a suction curettage and intrauterine balloon tamponade are reserved for patients who do not respond to medication therapy and do not put fertility at risk. Life-threatening situations may consider more invasive procedures such as endometrial ablation
Endometrial ablation is a surgical procedure that is used to remove (ablation, ablate) or destroy the endometrial lining of the uterus in people who have heavy menstrual bleeding. Endometrial ablation is not recommended for people who wish to hav ...
, uterine artery embolization
Uterine artery embolization is a procedure in which an interventional radiologist uses a catheter to deliver small particles that block the blood supply to the uterine body. The procedure is done for the treatment of uterine fibroids and adenomyos ...
, and hysterectomy.
Long-term management include estrogen-containing therapy and progestin therapy.
Dysmenorrhea
Primary dysmenorrhea is commonly treated with nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs such as ibuprofen to reduce moderate to severe pain. Other simple analgesics such as aspirin or acetaminophen are less commonly used but may also reduce short-term pain. Supplements includingthiamine
Thiamine, also known as thiamin and vitamin B1, is a vitamin, an essential micronutrient, that cannot be made in the body. It is found in food and commercially synthesized to be a dietary supplement or medication. Phosphorylated forms of thi ...
and vitamin E
Vitamin E is a group of eight fat soluble compounds that include four tocopherols and four tocotrienols. Vitamin E deficiency, which is rare and usually due to an underlying problem with digesting dietary fat rather than from a diet low in vi ...
may reduce pain in younger women. Non-pharmacological interventions such as the use of external heat are also effective at reducing pain. Regular exercises can also reduce pain.
See also
* Premenstrual syndrome (PMS) * Pelvic inflammatory disease * Adenomyosis * Fibroids *Ovarian cyst
An ovarian cyst is a fluid-filled sac within the ovary. Often they cause no symptoms. Occasionally they may produce bloating, lower abdominal pain, or lower back pain. The majority of cysts are harmless. If the cyst either breaks open or causes ...
s
* Endometriosis
References
External links
NIH
{{DEFAULTSORT:Menstrual Disorder Menstrual disorders