Melodic pattern on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 In
In
 In
In music
Music is generally defined as the art of arranging sound to create some combination of form, harmony, melody, rhythm or otherwise expressive content. Exact definitions of music vary considerably around the world, though it is an aspe ...
and jazz improvisation
Jazz improvisation is the spontaneous invention of melodic solo lines or accompaniment parts in a performance of jazz music. It is one of the defining elements of jazz. Improvisation is composing on the spot, when a singer or instrumentalist inv ...
, a melodic pattern (or motive) is a cell or germ serving as the basis for repetitive pattern
A pattern is a regularity in the world, in human-made design, or in abstract ideas. As such, the elements of a pattern repeat in a predictable manner. A geometric pattern is a kind of pattern formed of geometric shapes and typically repeated li ...
. It is a figure that can be used with any scale. It is used primarily for solos because, when practiced enough, it can be extremely useful when improvising
Improvisation is the activity of making or doing something not planned beforehand, using whatever can be found. Improvisation in the performing arts is a very spontaneous performance without specific or scripted preparation. The skills of impr ...
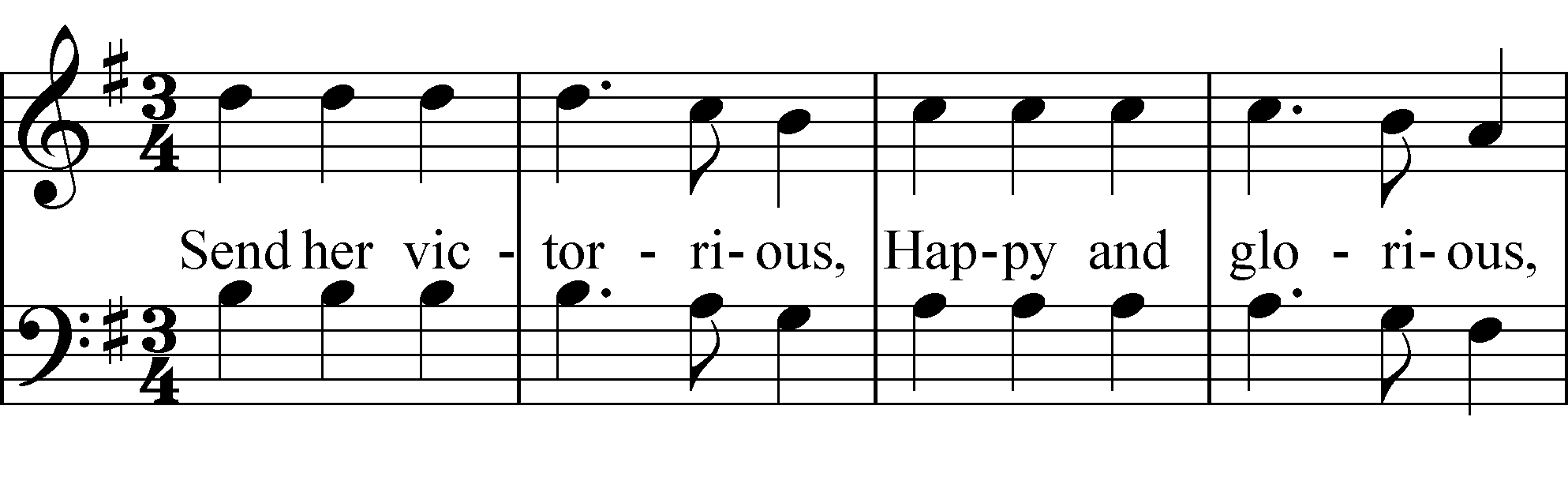
. "Sequence" refers to the repetition of a part at a higher or lower pitch, and melodic sequence is differentiated from harmonic sequence. One example of melodic motive and sequence are the pitches of the first line, "Send her victorious," repeated, a step lower, in the second line, "Happy and glorious," from "God Save the Queen
"God Save the King" is the national and/or royal anthem of the United Kingdom, most of the Commonwealth realms, their territories, and the British Crown Dependencies. The author of the tune is unknown and it may originate in plainchant, bu ...
".
"A melodic pattern is just what the name implies: a melody with some sort of fixed pattern to it." "The strong theme or motive
Motive(s) or The Motive(s) may refer to:
* Motive (law)
Film and television
* ''Motives'' (film), a 2004 thriller
* ''The Motive'' (film), 2017
* ''Motive'' (TV series), a 2013 Canadian TV series
* ''The Motive'' (TV series), a 2020 Israeli T ...
is stated. It is repeated more or less exactly, but at a different pitch level."Haerle, Dan (1993). ''Jazz Improvisation for Keyyboard Players'', p.2-7. Alfred. .
See also
* Color (isorhythm) *Imitation (music)
In music, imitation is the repetition of a melody in a polyphonic texture shortly after its first appearance in a different voice. The melody may vary through transposition, inversion, or otherwise, but retain its original character. The in ...
*Melody type
Melody type or type-melody is a set of melodic formulas, figures, and patterns.
Term and typical meanings
"Melody type" is a fundamental notion for understanding a nature of Western and non-Western musical modes, according to Harold Powers' ...
*Lick (music)
In popular music genres such as country, blues, jazz or rock music, a lick is "a stock pattern or phrase" consisting of a short series of notes used in solos and melodic lines and accompaniment. For musicians, learning a lick is usually a form o ...
*Phrase (music)
In music theory, a phrase ( gr, φράση) is a unit of musical meter that has a complete musical sense of its own, built from figures, motifs, and cells, and combining to form melodies, periods and larger sections.
Terms such as ''sen ...
References
Further reading
*Hanon, C.L. (2000) ''The Virtuoso Pianist''. . Cited in Baerman, Noah (2003). ''Big Book of Jazz Piano Improvisation'', p.33. . * Lateef, Yusef (1981). ''Repository of Scales and Melodic Patterns''. Fana Music. Cited in Baerman (2003), p.33. *Slonimsky, Nicolas
Nicolas Slonimsky ( – December 25, 1995), born Nikolai Leonidovich Slonimskiy (russian: Никола́й Леони́дович Сло́нимский), was a Russian-born American conductor, author, pianist, composer and lexicographer. B ...
(2000). ''Thesaurus of Scales and Melodic Patterns''. . Cited in Baerman (2003), p.33.
Melody
Repetition (music)
{{music-theory-stub