Melanchlaeni on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
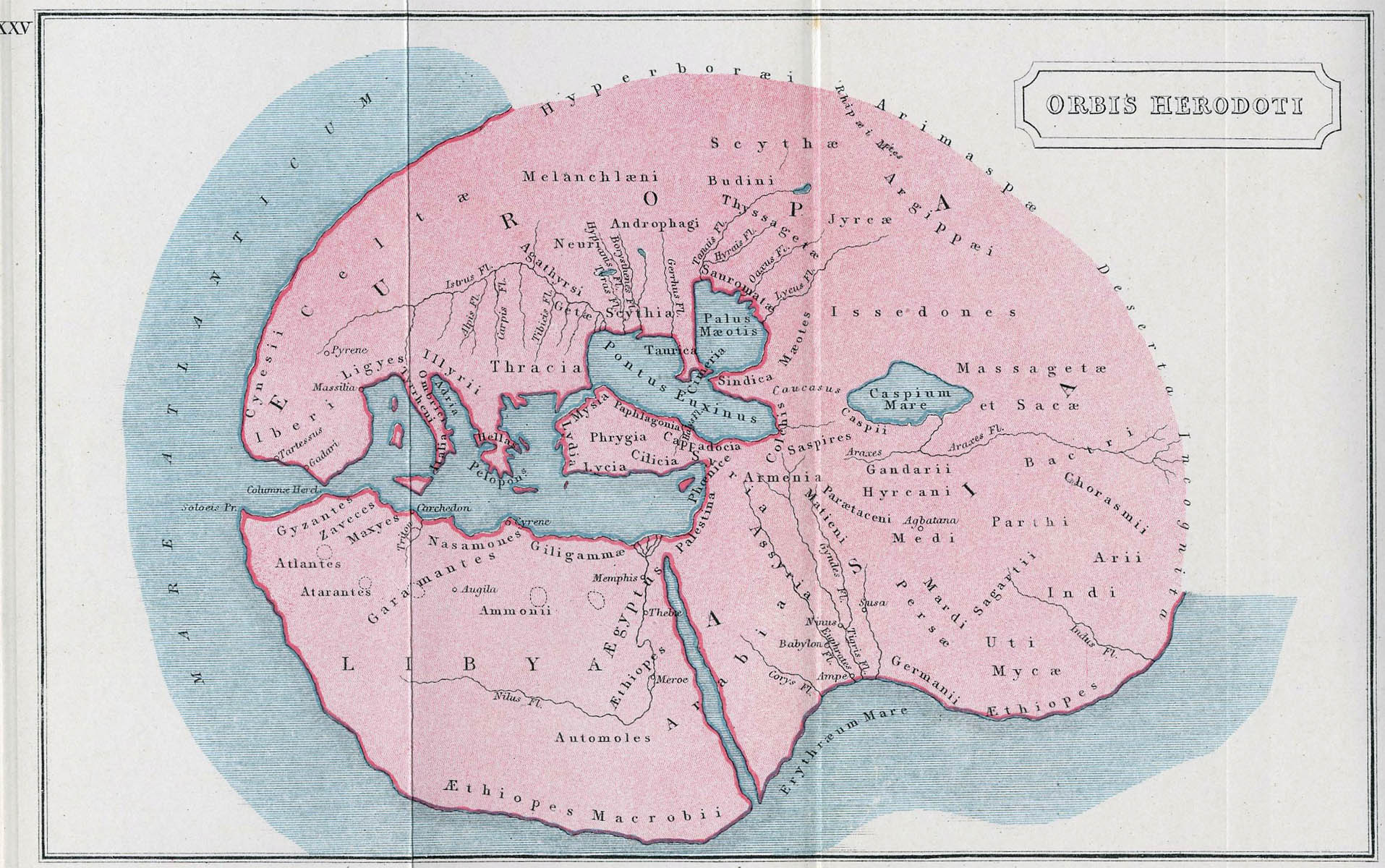 Melanchlaeni (, meaning "black-cloaks") may refer to three ancient tribes.
The first was a nomad tribe, the name of which first appears in Hecataeus (''ap.'' Steph. B., Fr. 154, ed. Klausen). In the geography of
Melanchlaeni (, meaning "black-cloaks") may refer to three ancient tribes.
The first was a nomad tribe, the name of which first appears in Hecataeus (''ap.'' Steph. B., Fr. 154, ed. Klausen). In the geography of

 Melanchlaeni (, meaning "black-cloaks") may refer to three ancient tribes.
The first was a nomad tribe, the name of which first appears in Hecataeus (''ap.'' Steph. B., Fr. 154, ed. Klausen). In the geography of
Melanchlaeni (, meaning "black-cloaks") may refer to three ancient tribes.
The first was a nomad tribe, the name of which first appears in Hecataeus (''ap.'' Steph. B., Fr. 154, ed. Klausen). In the geography of Herodotus
Herodotus ( ; grc, , }; BC) was an ancient Greek historian and geographer
A geographer is a physical scientist, social scientist or humanist whose area of study is geography, the study of Earth's natural environment and human society ...
(iv. 20,100--103,107) they are found occupying the districts east of the Androphagi
Androphagi ( grc, Ἀνδροφάγοι, cannibals, literally "man-eaters"), according to Herodotus, lived some distance north of Scythia in an area later hypothesised to be the forests between the upper waters of the Dnipro and Don. Also accord ...
, and north of the Royal Scythians
The Scythians or Scyths, and sometimes also referred to as the Classical Scythians and the Pontic Scythians, were an ancient Eastern
* : "In modern scholarship the name 'Sakas' is reserved for the ancient tribes of northern and eastern Centra ...
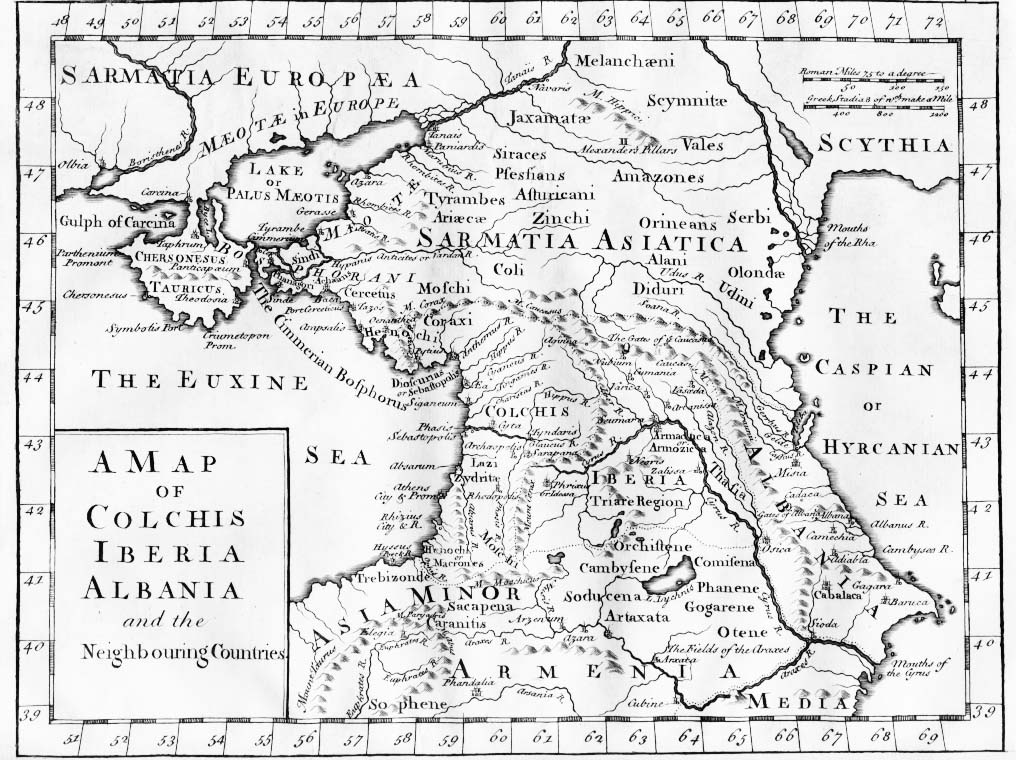
, 20 days' journey from the ''Palus Maeotis
The Maeotian Swamp or Maeotian Marshes ( grc, ἡ Μαιῶτις λίμνη, ''hē Maiōtis límnē'', literally ''Maeotian Lake''; la, Palus Maeotis) was a name applied in antiquity variously to the swamps at the mouth of the Tanais River in ...
''; over above them were lakes and lands unknown to man. It has been conjectured that Herodotus may refer, through some hearsay statement, to the lakes Ladoga and Onega. There has been considerable discussion among geographers as to the position which should be assigned to this tribe: it is of course impossible to fix this with any accuracy; but there would seem to be reason to place them as far north as the sources of the Volga
The Volga (; russian: Во́лга, a=Ru-Волга.ogg, p=ˈvoɫɡə) is the longest river in Europe. Situated in Russia, it flows through Central Russia to Southern Russia and into the Caspian Sea. The Volga has a length of , and a catchm ...
, or even further. (Schafarik, Slav. Alt. vol. i. p. 295.) Herodotus expressly says that they did not belong to the Scythian-Scolotic stock, although their customs were the same. The name, the Black-cloaks, like that of their cannibal neighbours, the ''Anthropophagi'', was applied to them by the Greeks, and was not a corrupted form of any indigenous appellation.
The second people bearing this name is mentioned by Scylax of Caryanda
Scylax of Caryanda ( el, Σκύλαξ ὁ Καρυανδεύς) was a Greek explorer and writer of the late 6th and early 5th centuries BCE. His own writings are lost, though occasionally cited or quoted by later Greek and Roman authors. The peri ...
(p. 32) as a tribe of Pontus
Pontus or Pontos may refer to:
* Short Latin name for the Pontus Euxinus, the Greek name for the Black Sea (aka the Euxine sea)
* Pontus (mythology), a sea god in Greek mythology
* Pontus (region), on the southern coast of the Black Sea, in modern ...
. Pomponius Mela
Pomponius Mela, who wrote around AD 43, was the earliest Roman geographer. He was born in Tingentera (now Algeciras) and died AD 45.
His short work (''De situ orbis libri III.'') remained in use nearly to the year 1500. It occupies less ...
(i. 19. § 4) and Pliny
Pliny may refer to:
People
* Pliny the Elder (23–79 CE), ancient Roman nobleman, scientist, historian, and author of ''Naturalis Historia'' (''Pliny's Natural History'')
* Pliny the Younger (died 113), ancient Roman statesman, orator, w ...
(vi. 5) coincide with Scylax, who speaks of two rivers flowing through their territory, the Metasoris (Μετάσωρις), probably the same as the Thessyris (Θέσσυρις, Ptol. v. 9. § § 10, 30: Kamisiliar), and the Aegipius (Αἰγίπιος: Kentichli). Dionysius Periegetes
Dionysius Periegetes ( grc-gre, Διονύσιος ὁ Περιηγητής, literally Dionysius the Voyager or Traveller, often Latinized to ''Dionysius Periegeta''), also known as Dionysius of Alexandria or Dionysius the African,''Encyclopædia ...
(v. 309) places this people (or perhaps confuses the prior) on the Borysthenes
Borysthenes (; grc, Βορυσθένης) is a geographical name from classical antiquity. The term usually refers to the Dnieper River and its eponymous river god, but also seems to have been an alternative name for Pontic Olbia, a town situate ...
, and Ptolemy
Claudius Ptolemy (; grc-gre, Πτολεμαῖος, ; la, Claudius Ptolemaeus; AD) was a mathematician, astronomer, astrologer, geographer, and music theorist, who wrote about a dozen scientific treatises, three of which were of importance ...
(v. 9. § 19) between the river Rha and the ''Hippici Montes'', in Asiatic Sarmatia
The Sarmatians (; grc, Σαρμαται, Sarmatai; Latin: ) were a large confederation of ancient Eastern Iranian equestrian nomadic peoples of classical antiquity who dominated the Pontic steppe from about the 3rd century BC to the 4th c ...
; but it would be a great error to found any observation concerning these ancient northern tribes upon either the Roman writers or Ptolemy, or to confuse the picture set before us by these geographers, and the more correct delineations of Herodotus.
The third people were the Melanchlaeni of Ammianus
Ammianus Marcellinus (occasionally anglicised as Ammian) (born , died 400) was a Roman soldier and historian who wrote the penultimate major historical account surviving from antiquity (preceding Procopius). His work, known as the ''Res Gest ...
(xxii. 8. § 31), which were the Alani.
See also
*European Scythian campaign of Darius I
The Scythian campaign of Darius I was a military expedition into parts of European Scythia by Darius I, the king of the Achaemenid Empire, in 513 BC. The Scythians were an East Iranian-speaking people who had invaded Media, revolted against Dariu ...
* Melanchlaeni and Cheremis (Mari)
References
Ancient peoples of Russia History of Pontus {{Ethno-stub