Medical laboratory scientist on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
A medical laboratory scientist (MLS) or clinical laboratory scientist (CLS) or medical technologist (MT) performs diagnostic testing of blood and body fluids in clinical laboratories. The scope of a medical laboratory scientist's work begins with the receipt of patient or client specimens and terminates with the delivery of test results to physicians and other healthcare providers. The utility of clinical diagnostic testing relies squarely on the validity of test methodology. To this end, much of the work done by medical laboratory scientists involves ensuring specimen quality, interpreting test results, data-logging, testing control products, performing calibration, maintenance, validation, and troubleshooting of instrumentation as well as performing statistical analyses to verify the accuracy and repeatability of testing. Medical laboratory scientists may also assist healthcare providers with test selection and specimen collection and are responsible for prompt verbal delivery of critical lab results. Medical Laboratory Scientist in health settings also play an important role in the diagnosis of diseses conditions. An estimated 70% of medical decisions are based on laboratory test results and MLS contributions affect 95% of a health system's costs.
 The most common tests performed by medical laboratory scientists are
The most common tests performed by medical laboratory scientists are
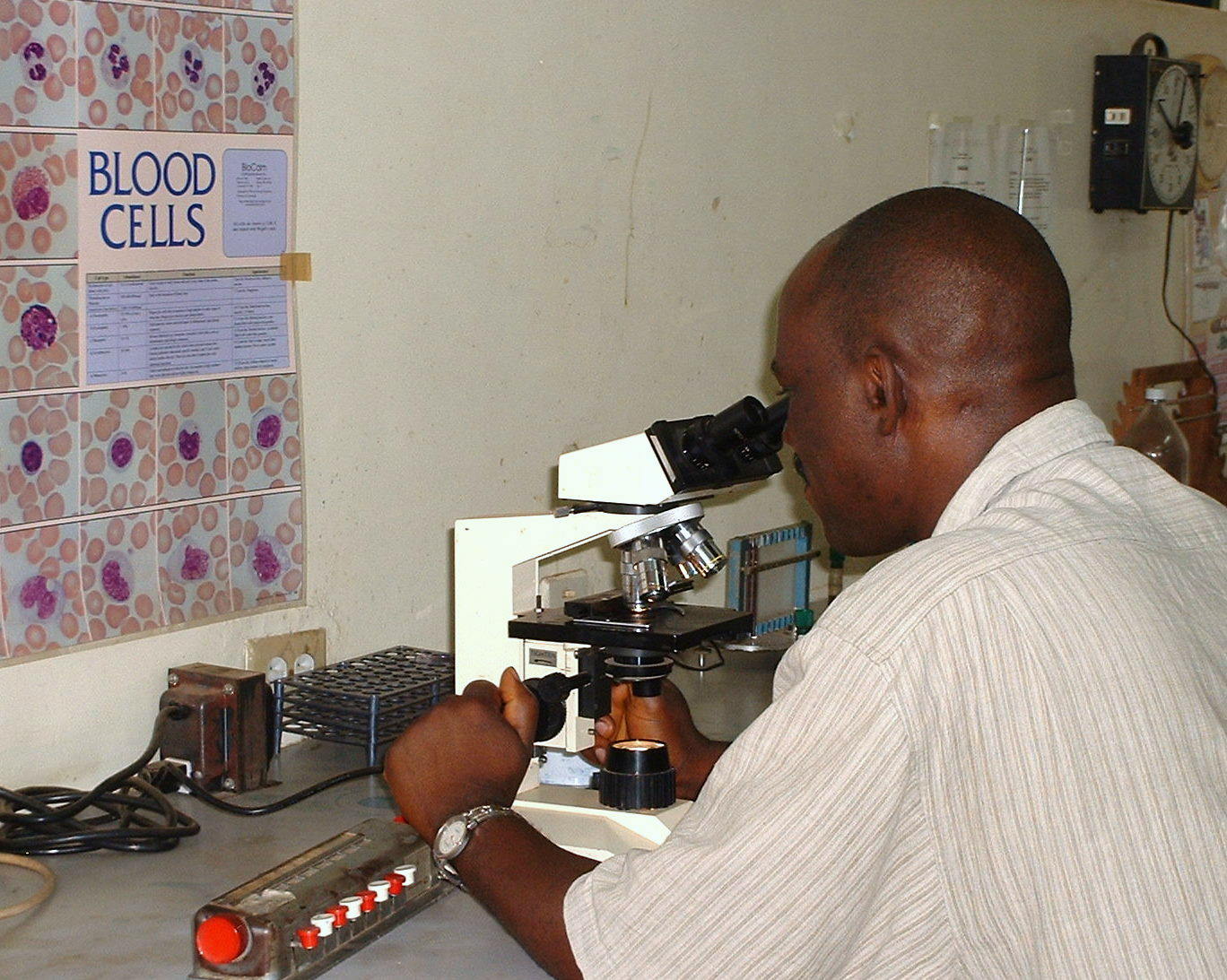
http://mlscn.gov.ng
 The informal abbreviations of job titles may be a source of confusion. In the United States Medical Laboratory Scientist (ASCP) and Medical Technologists (AMT) or (AAB) are often called "med techs" (based on the era in which they were known as "medical technologists"), but this shorthand term is shared by other healthcare employees, including pharmacy techs,
The informal abbreviations of job titles may be a source of confusion. In the United States Medical Laboratory Scientist (ASCP) and Medical Technologists (AMT) or (AAB) are often called "med techs" (based on the era in which they were known as "medical technologists"), but this shorthand term is shared by other healthcare employees, including pharmacy techs,
Canadian Society for medical Laboratory Science
* ttp://www.aacc.org/ American Association for Clinical Chemistrybr>American Society of Clinical PathologyAmerican Society of Clinical Laboratory ScienceNational Credentialing Agency for Laboratory PersonnelNational Accrediting Agency for Clinical Laboratory ScienceMedical Technologist Continuing EducationAIMS: Australian Institute of Medical ScientistsNew Zealand Institute of Medical Laboratory ScienceGreek Association of Medical Laboratory TechnologistsClinical Laboratory Scientists at Work
{{Authority control Health care occupations Science occupations
complete blood count
A complete blood count (CBC), also known as a full blood count (FBC), is a set of medical laboratory tests that provide information about the cells in a person's blood. The CBC indicates the counts of white blood cells, red blood cells and ...
(CBC), comprehensive metabolic panel
The comprehensive metabolic panel, or chemical screen (CMP; CPT code 80053), is a panel of 14 blood tests that serves as an initial broad medical screening tool. The CMP provides a rough check of kidney function, liver function, diabetic and par ...
(CMP), electrolyte panel, liver function tests
Liver function tests (LFTs or LFs), also referred to as a hepatic panel, are groups of blood tests that provide information about the state of a patient's liver. These tests include prothrombin time (PT/INR), activated partial thromboplastin ti ...
(LFT), renal function tests (RFT), thyroid function test (TFT), urinalysis
Urinalysis, a portmanteau of the words ''urine'' and ''analysis'', is a panel of medical tests that includes physical (macroscopic) examination of the urine, chemical evaluation using urine test strips, and microscopic examination. Macroscopic e ...
, coagulation profile, lipid profile, blood type
A blood type (also known as a blood group) is a classification of blood, based on the presence and absence of antibodies and inherited antigenic substances on the surface of red blood cells (RBCs). These antigens may be proteins, carbohydrates ...
, semen analysis (for fertility and post-vasectomy studies), serological studies and routine cultures
Culture () is an umbrella term which encompasses the social behavior, institutions, and norms found in human societies, as well as the knowledge, beliefs, arts, laws, customs, capabilities, and habits of the individuals in these groups.Tylo ...
. In some facilities that have few phlebotomist
Phlebotomy is the process of making a puncture in a vein, usually in the arm, with a cannula for the purpose of drawing blood. The procedure itself is known as a venipuncture, which is also used for intravenous therapy. A person who performs a ...
s, or none at all, (such as in rural areas) medical laboratory scientists may perform phlebotomy. Because medical laboratory scientists have many transferable technical skills, employment outside of the medical laboratory is common. Many medical laboratory scientists are employed in government positions such as the FDA, USDA, non-medical industrial laboratories, and manufacturing.
In the United Kingdom and the United States, senior laboratory scientists, who are typically post-doctoral scientists, take on significantly greater clinical responsibilities in the laboratory. In the United States these scientists may function in the role of clinical laboratory directors, while in the United Kingdom they are known as consultant clinical scientists.
Though clinical scientists have existed in the UK National Health Service for ~60 years, the introduction of formally-trained and accredited consultant-level clinical scientists is relatively new, and was introduced as part of the new Modernising Scientific Careers framework.
Consultant clinical scientists are expected to provide expert scientific and clinical leadership alongside and, at the same level as, medical consultant colleagues. While specialists in healthcare science will follow protocols, procedures and clinical guidelines, consultant clinical scientists will help shape future guidelines and the implementation of new and emerging technologies to help advance patient care.
In the United Kingdom, healthcare scientists including clinical scientists may intervene throughout entire care pathways from diagnostic tests to therapeutic treatments and rehabilitation. Although this workforce comprises approximately 5% of the healthcare workforce in the UK, their work underpins 80% of all diagnoses and clinical decisions made.
Specialty areas
Many Medical Laboratory Scientists are ''generalists'', skilled in most areas of the clinical laboratory. However, some are specialists, qualified by unique undergraduate education or additional training to perform more complex analyses than usual within a specific field. Specialties includeclinical biochemistry
Clinical chemistry (also known as chemical pathology, clinical biochemistry or medical biochemistry) is the area of chemistry that is generally concerned with analysis of bodily fluids for diagnostic and therapeutic purposes. It is an applied ...
, hematology
Hematology ( always spelled haematology in British English) is the branch of medicine concerned with the study of the cause, prognosis, treatment, and prevention of diseases related to blood. It involves treating diseases that affect the produc ...
, coagulation
Coagulation, also known as clotting, is the process by which blood changes from a liquid to a gel, forming a blood clot. It potentially results in hemostasis, the cessation of blood loss from a damaged vessel, followed by repair. The mechanism ...
, microbiology
Microbiology () is the scientific study of microorganisms, those being unicellular (single cell), multicellular (cell colony), or acellular (lacking cells). Microbiology encompasses numerous sub-disciplines including virology, bacteriology, ...
, bacteriology Bacteriology is the branch and specialty of biology that studies the morphology, ecology, genetics and biochemistry of bacteria as well as many other aspects related to them. This subdivision of microbiology involves the identification, classificat ...
, toxicology
Toxicology is a scientific discipline, overlapping with biology, chemistry, pharmacology, and medicine, that involves the study of the adverse effects of chemical substances on living organisms and the practice of diagnosing and treating e ...
, virology
Virology is the scientific study of biological viruses. It is a subfield of microbiology that focuses on their detection, structure, classification and evolution, their methods of infection and exploitation of host cells for reproduction, the ...
, parasitology
Parasitology is the study of parasites, their host (biology), hosts, and the relationship between them. As a List of biology disciplines, biological discipline, the scope of parasitology is not determined by the organism or environment in questio ...
, mycology
Mycology is the branch of biology concerned with the study of fungi, including their genetic and biochemical properties, their taxonomy and their use to humans, including as a source for tinder, traditional medicine, food, and entheogen ...
, immunology
Immunology is a branch of medicineImmunology for Medical Students, Roderick Nairn, Matthew Helbert, Mosby, 2007 and biology that covers the medical study of immune systems in humans, animals, plants and sapient species. In such we can see ther ...
, immunohematology (blood bank
A blood bank is a center where blood gathered as a result of blood donation is stored and preserved for later use in blood transfusion. The term "blood bank" typically refers to a department of a hospital usually within a Clinical Pathology laborat ...
), histopathology
Histopathology (compound of three Greek words: ''histos'' "tissue", πάθος ''pathos'' "suffering", and -λογία '' -logia'' "study of") refers to the microscopic examination of tissue in order to study the manifestations of disease. Sp ...
, histocompatibility, cytopathology
Cytopathology (from Greek , ''kytos'', "a hollow"; , ''pathos'', "fate, harm"; and , '' -logia'') is a branch of pathology that studies and diagnoses diseases on the cellular level. The discipline was founded by George Nicolas Papanicolaou in ...
, genetics
Genetics is the study of genes, genetic variation, and heredity in organisms.Hartl D, Jones E (2005) It is an important branch in biology because heredity is vital to organisms' evolution. Gregor Mendel, a Moravian Augustinian friar work ...
, cytogenetics
Cytogenetics is essentially a branch of genetics, but is also a part of cell biology/cytology (a subdivision of human anatomy), that is concerned with how the chromosomes relate to cell behaviour, particularly to their behaviour during mitosis an ...
, electron microscopy
An electron microscope is a microscope that uses a beam of accelerated electrons as a source of illumination. As the wavelength of an electron can be up to 100,000 times shorter than that of visible light photons, electron microscopes have a hi ...
, and IVF labs. Medical Technologists specialty may use additional credentials, such as "SBB" (Specialist in Blood Banking) from the American Association of Blood Banks, "SM" (Specialist in Microbiology) from the American Society for Microbiology, "SC" (Specialist in Chemistry) from the American Association for Clinical Chemistry, or "SH" (Specialist in Hematology) from the American Society for Clinical Pathology (ASCP). These additional notations may be appended to the base credential, for example, "MLS(ASCP)SBB". Additional information can be found in the ASCP Procedures for Examination & Certification.
Andrology Laboratory Scientist, Embryology Laboratory Scientist, and Molecular Diagnostics Technologist certifications are provided by the American Association of Bioanalysts; those with the certifications are classified as ALS(AAB), ELS(AAB), and MDxT(AAB) respectively. Certified Histocompatibility Associate, Certified Histocompatibility Technologist, Certified Histocompatibility Specialist, and Diplomate of the ABHI are titles granted by the American Board of Hisocompatibility and Immunogenetics after meeting education and experience requirements and passing the required examination; those individuals would hold the credentials CHA(ABHI), CHT(ABHI), CHS(AHBI), and D(ABHI) upon passing the corresponding examination.
In the United States, Medical Laboratory Scientists can be certified and employed in infection control
Infection prevention and control is the discipline concerned with preventing healthcare-associated infections; a practical rather than academic sub-discipline of epidemiology. In Northern Europe, infection prevention and control is expanded fro ...
. These professionals monitor and report infectious disease findings to help limit iatrogenic
Iatrogenesis is the causation of a disease, a harmful complication, or other ill effect by any medical activity, including diagnosis, intervention, error, or negligence. "Iatrogenic", ''Merriam-Webster.com'', Merriam-Webster, Inc., accessed 27 ...
and nosocomial infections
A hospital-acquired infection, also known as a nosocomial infection (from the Greek , meaning "hospital"), is an infection that is acquired in a hospital or other health care facility. To emphasize both hospital and nonhospital settings, it is ...
. They may also educate other healthcare workers about such problems and ways to minimize them.
In the United Kingdom the number of Clinical Scientists in a pathology discipline are typically greater, where less medically qualified pathologists train as consultants. Clinical Biochemistry, Clinical Immunology and Genomic Medicine are specialities with an abundance of UK Clinical Scientists, and where the role is well established. Infection services in the United Kingdom are generally undertaken by medically qualified Microbiologists, who may have overall responsibility for laboratory services in addition to Infection Prevention and Control responsibilities, and may be required to contribute to ward rounds and patient clinics. Therefore, the Royal College of Pathologists and Royal College of Physicians have developed Combined Infection Training 0 that medical trainees gain a much more patient focused experience, and undertake Physician examinations in addition to Pathology training. The result of this is that several regional medical deaneries no longer permit Medical Doctors to train in Microbiology or Virology as single disciplines, and instead advocate dual-specialisation as Infectious Disease/Microbiology or Infectious Disease/Virology 1 Simultaneously the expansion of higher specialist scientist trainees in microbiology mean that many of the laboratory and scientific responsibilities of medical doctors may be taken on by Clinical Scientists, and medical doctors will instead be expected to perform a much more patient facing role. The exception in Microbiology is the sub-discipline of Virology, which is well suited to the expertise of clinical scientists due to reliance on cutting-edge scientific methods, increasing use of specialised genetic technologies, and a technical understanding of virus biology, with a reduced emphasis on patient management compared with Microbiology as a whole 2
It is therefore likely that many patients in UK hospitals may come into contact with Clinical Scientists working in a patient facing speciality, who may be confused with medical doctors due to the complex nature of their role.
Educational requirements
Educational and licensing requirements vary by country due to differing scopes of practice and legislative differences.Australia
In Australia, medical laboratory scientists complete a four-year undergraduate degree program in medical science, medical laboratory science or laboratory medicine. These programs should be accredited by the Australian Institute of Medical and Clinical Scientists (AIMS).Canada
In Canada, three-year college or technical school programs are offered that include seven semesters, two of them comprising an unpaid internship. The student graduates before taking a standard examination (such as the Canadian Society for Medical Laboratory Science, or CSMLS, exam) to be qualified as a medical laboratory technologist. Many MLTs go on to receive a Bachelor of Science degree after they are certified, but a few university programs affiliated with a college MLT program to allow students to graduate with both MLT certification and a degree such as theUniversity of New Brunswick
The University of New Brunswick (UNB) is a public university with two primary campuses in Fredericton and Saint John, New Brunswick. It is the oldest English-language university in Canada, and among the oldest public universities in North Amer ...
's Bachelor of Medical Laboratory Sciences program.
Canada is currently experiencing an increasing problem with staffing shortages in medical laboratories.
New Zealand
In New Zealand, a medical laboratory scientist must complete a bachelor's degree in medical laboratory science or biological or chemical science recognized by the Medical Sciences Council of New Zealand. As part of this degree they must complete clinical placement. Once they graduate they must have worked at least six months under supervision, be registered with the Medical Sciences Counsel of New Zealand, and hold a current Annual Practicing Certificate.Ghana
In Ghana, a doctor of medical laboratory scientist (MLS.D) is a professional with a six years professionaldoctorate degree
A doctorate (from Latin ''docere'', "to teach"), doctor's degree (from Latin ''doctor'', "teacher"), or doctoral degree is an academic degree awarded by universities and some other educational institutions, derived from the ancient formalism ''li ...
in medical laboratory science, the medical laboratory scientist (MLS) has four years bachelor's degree
A bachelor's degree (from Middle Latin ''baccalaureus'') or baccalaureate (from Modern Latin ''baccalaureatus'') is an undergraduate academic degree awarded by colleges and universities upon completion of a course of study lasting three to si ...
in medical laboratory science and the medical laboratory technicians (MLT) has three years diploma
A diploma is a document awarded by an educational institution (such as a college or university) testifying the recipient has graduated by successfully completing their courses of studies. Historically, it has also referred to a charter or offici ...
in medical laboratory science.
The curriculum for the programme include internship rotations, where the students get hands-on experiences in each discipline of the laboratory and performs diagnostic testing in a functioning laboratory under supervision.
Pakistan
In Pakistan, the National Institute of Health (NIH) inIslamabad
Islamabad (; ur, , ) is the capital city of Pakistan. It is the country's ninth-most populous city, with a population of over 1.2 million people, and is federally administered by the Pakistani government as part of the Islamabad Capital ...
is the pioneer in Laboratory Sciences. The College of Medical Lab Technology (CMLT) of the NIH offers a two-year F.Sc degree in Medical Lab Technology (MLT). The previous two-year B.Sc. in MLT was discontinued and replaced by the four-year Bachelor Program in Medical Lab Sciences (MLS). The University of Health Sciences in Lahore
Lahore ( ; pnb, ; ur, ) is the second List of cities in Pakistan by population, most populous city in Pakistan after Karachi and 26th List of largest cities, most populous city in the world, with a population of over 13 million. It is th ...
also offers a four-year Bachelor program in MLS through approved colleges. The University of Lahore
The University of Lahore ( ur, ), abbreviated as UOL, is a private university located in Lahore, Punjab, Pakistan. It was founded at collegiate level in 1999 under the IBADAT Educational Trust and was granted full degree awarding status in 2002. ...
, University of Faisalabad, University of Sargodha, and Superior University in Lahore all offer a five-year Doctor of Medical Lab Sciences (DMLS) Program. Eligibility criteria for the four-year B.Sc. in MLS and the five-year Doctor of Medical Lab Sciences (DMLS) is the F.Sc. Pre-Medical.
United States
In the United States, a medical laboratory scientist (MLS), medical technologist (MT), or a clinical laboratory scientist (CLS) typically earns abachelor's degree
A bachelor's degree (from Middle Latin ''baccalaureus'') or baccalaureate (from Modern Latin ''baccalaureatus'') is an undergraduate academic degree awarded by colleges and universities upon completion of a course of study lasting three to si ...
in medical laboratory science, clinical laboratory science, or medical technology. Other routes include attaining a degree in biomedical science or in a life / biological science (biology, biochemistry, microbiology, etc.). Both routes typically requires the MLS/MT/CLS to obtain certification from a national certifying board (AAB, AMT, or ASCP) as most laboratories exceed the federal minimum requirements established by the Clinical Laboratory Improvement Amendments (CLIA).
Common comprehensive Medical laboratory scientist degree programs are set up in a few different ways.
* In 3+1 programs, the student attends classroom courses for three years and complete a clinical rotation their final year of study.
* In 2+2 programs, students have already completed their lower division coursework and return to complete their last two years of study in a CLS program.
* In 4+1 program, students who have already completed an undergraduate program return to complete a year of medical laboratory training. The training is typically completed at a clinical site rather than a college.
The core curriculum in medical technology generally comprises 20 credits in clinical chemistry, 20 credits in hematology, and 20 credits in clinical microbiology.
During clinical rotations, the student experiences hands-on learning in each discipline of the laboratory and performs diagnostic testing in a functioning laboratory under supervision. With limited or no compensation, a student in the clinical phase of training usually works 40 hours per week for 20 to 52 weeks. Some programs in the United States have halved the time students spend completing their clinical rotation reduced due to staffing shortages. For example, in 2015, the MLS program at the University of Minnesota reduced the clinical rotation portion of the program from 22 weeks to 12 weeks.
In the United States, a two-year academic program (associate's degree
An associate degree is an undergraduate degree awarded after a course of Tertiary education, post-secondary study lasting two to three years. It is a level of qualification above a high school diploma, GED, or matriculation, and below a bachelo ...
) qualifies the graduate to work as a medical laboratory technician (MLT). MLTs receive training more exclusively in laboratory sciences without the basic science coursework often required by MLS programs; however, there are many MLT training programs that require substantial basic didactic science course work prior to entry into a clinical practicum. Although the didactic coursework may be less for the MLT, the clinical practicum, in many cases, is similar to that of the MLS student's. This equates to MLTs who are well equipped to enter the work force with relevant and knowledge based practical application. The shorter training time may be attractive to many students, but there are disadvantages to this route. MTs, MLSs and CLSs usually earn higher salaries and have more responsibilities than MLTs. In 2018, medical laboratory technicians earned an average salary of $51,219, while medical laboratory scientists earned a salary of $67,888. An added disadvantage for MLTs is that some institutions will only employ MLSs, although that practice is starting to change due to recent efforts in cost reduction, and due to staffing shortages.
In practice, the term ''medical laboratory technician'' may apply to persons who are trained to operate equipment and perform tests, usually under the supervision of the certified medical technologist or laboratory scientist. Depending on the state where employment is granted, the job duties between MLSs and MLTs may or may not be similar. For example, in Florida, a MLT may only perform highly complex testing while under the direct supervision of a clinical laboratory technologist, a clinical laboratory supervisor, or a clinical laboratory director. This may make it impractical for a MLT to lawfully work in a Florida blood bank. California has similar restrictions on MLTs. To accommodate California's restrictions, the American Association of Bioanalysts (AAB) developed a separate certification examination for California licensure. However, this exam does not include material covering the areas of immunohematology or microscopy. Although the typical entry-level academic requirement for most MLTs is an associate degree, a 60 credit certificate program exists through military training programs; such as the U.S. Army's 68K military occupational specialty.
As in other countries, staffing shortages have become a major issue in many clinical laboratories in the United States. Due to several factors, including boomer retirement, and inadequate recruitment and retention efforts, the medical laboratory workforce is shrinking. For the decade 2010–2020, workforce needs are expected to grow by 13%. This translates into about 11,300 positions per year that will need to be filled, with only about 5000 new graduates per year coming out of various programs. By 2025, it is estimated that the shortage of medical laboratory professionals will reach 98,700 in the U.S.
United Kingdom
In the United Kingdom (UK) there are two varieties of registered healthcare scientist in hospitals - Clinical Scientists and Biomedical Scientists (BMS). There is a strict and formal post graduate training programme for both careers followed by statutory registration for each with the Health & Care Professions Council UK (HCPC): for the safety and assurance of the customers - the patients. They are two similar but distinct careers with parallel but different training paths and different entry requirements. The role of Clinical Scientists is to improve the health and well-being of patients and the public by practising alongside doctors, nurses, and other health and social care professionals in the delivery of healthcare. Their aim is to provide expert scientific and clinical advice to clinician colleagues, to aid in the diagnosis, treatment and management of patient care. Examples of the type of work they undertake include: * Advising, diagnosing, interpreting, and treating patients. * Advising health and social care professionals in the diagnosis and treatment of patients. * Researching the science, technology, and practise used in healthcare to innovate and improve services. * Designing, building, and operating technology for diagnosing and treating patients. * Ensuring the safety and reliability of tests and equipment used in healthcare. Trainee Clinical Scientist posts are advertised nationally, usually between November and February on the Clinical Scientists Recruitment webpages where application forms may be obtained and electronic submission of applications can be made. These posts are for the approved Pre-registration Training Programme, designed to prepare entrants for higher professional qualifications, further clinical training and eventual Consultant responsibility. Clinical Scientist training involves enrolment of graduates (first or second class honours degree or better is essential due to the high competition for limited training places) into an intensive three-year training scheme leading to certification and eventual registration before starting the higher career structure. The basic qualification for becoming a Clinical Biochemist, Clinical Immunologist or Clinical Microbiologist is a good Honours degree in an appropriate subject: for Clinical Biochemistry, that subject might be Biochemistry or Chemistry (or another life science subject which contains a substantial Biochemistry component); for Clinical Immunology, that subject might be any life science degree with an immunology component; for Clinical Microbiology that subject might be any life science degree with a microbiology component. Although not essential, some candidates will apply with higher degrees in an attempt to improve their chances of selection for training and several universities currently offer MSc courses in Clinical Biochemistry, Immunology and Microbiology which have been approved by the ACB or the AHCS. Full-time and 'sandwich' courses are available, and further information may be obtained from individual programmes, although the level of financial support provided varies, and should be clarified at interview. Some entrants to the profession will already have obtained a PhD, and the training and research experience that this provides is invaluable to the work of the Clinical Scientist. In larger Departments, there may be opportunities to study for a research degree after entering the profession and acquiring registration, but since this has to be fitted in with other responsibilities, it may take some years to complete. It should be clearly understood that the major role of the profession is patient care and that research, management and all the other aspects will come as side issues and not be the predominating factor in the career path. The work of Biomedical Scientists and Clinical Scientists have impact on the diagnosis and treatment of almost every patient admitted to hospitals in the United Kingdom. The United Kingdom is facing a shortage of qualified Clinical and Biomedical Scientists. The Royal College of Pathologists and the Royal College of Physicians have pointed out the need for increased government funding for medical training programs to prevent diagnostic facilities and medical infrastructure from being overwhelmed. MSF claims that these workers have lost out financially since the decision of the then health minister Kenneth Clarke to exclude them from the pay review body in 1984.Nigeria
In Nigeria, Medical Laboratory Science is a high skilled profession charged by Act 11 of 2003 Laws of the Federation of Nigeria. The initial qualification awarded graduates of the programme, like some other medical programmes, was Associate of the Institute of Medical Laboratory Technology/Science (AIMLT/AIMLS) The Medical Laboratory Science Council of Nigeria, which was established by Act. 2004 Cap 114 Laws of the Federation of Nigeria, regulates the practice of Medical Laboratory Science in Nigeria. In Nigeria, the Medical Laboratory Science programme is Bachelor of Medical Laboratory Science (BMLS), regulated by National Universities Commission (NUC) and by the Medical Laboratory Science Council of Nigeria (MLSCN). Students at their first year (100 level) are trained under the Faculty of Science in Basic Sciences and Faculty of Arts, Management and Social science in General studies and Entrepreneurship. At the 200 level, students are taught basic medical sciences and are introduced to Medical Laboratory Science. The third year of the programme marks the beginning of the professional training as students are engaged in the classroom for lectures as well as in the Hospital laboratory for the professional or practical training. At the fourth year students are taught the basics in all the special areas of Medical Laboratory Science. At the end of 400 level programme, successful students are presented for the First professional examination, to be moderated by the Medical Laboratory Science Council of Nigeria At the fifth year, students break into 4 core or specialized areas of Medical Laboratory Science, namely: medical microbiology/parasitology, chemical pathology/immunology, haematology/blood transfusion science and histopathology/cytopathology. At the end of the fifth year, suitable students are presented for final professional examination by the Medical Laboratory Science Council of Nigeria.Certification and licensing

United States
There are currently three major certification agencies in the United States of America for clinical laboratory scientists. They are the American Association of Bioanalysts (AAB), the American Medical Technologists (AMT), and the American Society for Clinical Pathology (ASCP). Clinical Laboratory Science programs have the option to be accredited by the National Accrediting Agency for Clinical Laboratory Science (NAACLS). All three national accrediting agencies will certify scientists in the clinical laboratory as generalist (chemistry, hematology, immunology, immunohematology/blood bank, and microbiology). The American Association of Bioanalysts and the American Medical Technologists certifications continue to use the traditional designation Medical Technologist (MT), while the American Society for Clinical Pathology has adopted the designation of Medical Laboratory Scientist (MLS). Regardless of terminology, these highly qualified individuals serve as scientists in the clinical laboratory. There are two other organizations that have previously provided proficiency examinations to clinical laboratory scientist. The first, is the US Department of Health and Human Services. The second, is the National Credentialing Agency for Laboratory Personnel (NCA). The NCA was absorbed by the American Society for Clinical Pathology in 2009 and promptly dissolved. In the United States, theClinical Laboratory Improvement Amendments
The Clinical Laboratory Improvement Amendments (CLIA) of 1988 are United States federal regulatory standards that apply to all clinical laboratory testing performed on humans in the United States, except clinical trials and basic research.
CLIA P ...
(CLIA '88) define the level of qualification required to perform tests of various complexity. Clinical Laboratory Scientists, Medical Technologists and Medical Laboratory Scientists are near the highest level of qualification among general testing personnel and are usually qualified to perform the most complex clinical testing including HLA testing (also known as tissue typing) and blood type reference testing. Provider Performed Microscopy, or PPM (doctorate or master's level health provider) and Cytology have additional requirements.
In addition to the national certification, 11 states (California, Florida, Georgia, Hawaii, Louisiana, Montana, Nevada, North Dakota, Rhode Island, West Virginia and New York) and Puerto Rico also require a state license. Puerto Rico, in order to provide the state license, requires either a local board certification with a state examination, or any of both the ASCP and the NCA. Minnesota, Texas, Illinois, Massachusetts, Michigan, Vermont, Washington, New Jersey, Iowa, Utah, Ohio, South Carolina, Wyoming, Pennsylvania, Virginia, South Dakota, Delaware, Missouri, and Alaska are currently attempting to obtain licensure. All states require documentation from a professional certification agency before issuing a state certification. A person applying for state certification may also be expected to submit fingerprints, education and training records, and competency certification. Some states also require completion of a specified number of continuing education contact hours prior to issuing or renewing a license. Licensing is somewhat controversial as it adds a bureaucratic layer in a field that is severely understaffed. Simply requiring testing personnel to obtain and maintain their national certification would help ensure competent testing personnel without increasing costs to testing personnel.
Some states recognize another state's license if it is equal or more stringent, but currently California does not recognize any other state license.
United Kingdom
In the United Kingdom all clinical scientists and biomedical scientists have had to be registered with the Health & Care Professions Council (HCPC) in order to work unsupervised, to develop through the careers grades of their profession and to use the protected titles of "Clinical Scientist" or "Biomedical Scientist". The HCPC registers nearly 200,000 healthcare professionals and while success in an approved degree course from an accredited University is sufficient for all other professions, both clinical scientists and biomedical scientists have post graduate training and no approved degree courses. Autonomous assessment of applicants in these two professions with subsequent certification for successful ones, is the only approved UK route to registration for them. "Clinical Scientist", just as "Biomedical Scientist", is a protected title under the law (there is a £5000 fine for transgressors who fraudulently use the title without being registered by the state). The HCPC can strike people off the register for malpractice in just the same way as for doctors with the General Medical Council (GMC). Those who are working in "Trainee" positions in the profession are permitted to use the title with an appropriate caveat, for example – "Pre-registration Clinical Scientist", Trainee Clinical Scientist, etc. Alternatively some may use titles specific to the discipline they train in, such as Trainee Clinical Biochemist", "Clinical Immunologist in Training" or “ Pre-Registrant Clinical Microbiologist” which is also perfectly acceptable since it is not implying the protected "Clinical Scientist" title of fully qualified and registered practitioners. It is against the law to formally work with the title of “Clinical Scientist” without professional registration Nigeria In Nigeria successful student at the end of the training in both academic and professional assessments with respect to the graduation requirements is certified by the respective University, inducted and licensed by the Medical Laboratory Science Council of Nigeria after a successful internship training.Further education
As in many healthcare professions, a Medical Laboratory Scientist may pursue higher education to advance or further specialize in their career. *Master of Science
A Master of Science ( la, Magisterii Scientiae; abbreviated MS, M.S., MSc, M.Sc., SM, S.M., ScM or Sc.M.) is a master's degree in the field of science awarded by universities in many countries or a person holding such a degree. In contrast t ...
, Master of Business Administration
A Master of Business Administration (MBA; also Master's in Business Administration) is a postgraduate degree focused on business administration. The core courses in an MBA program cover various areas of business administration such as accounti ...
, Master of Health Administration
The Master of Health Administration, Master of Healthcare Administration (MHA), or Master of Health Management (MHM), is a master's-level professional degree granted to students who complete a course of study in the knowledge and competencies neede ...
, Doctor of medical laboratory science for specialization, education and management roles.
*Doctor of Philosophy
A Doctor of Philosophy (PhD, Ph.D., or DPhil; Latin: or ') is the most common degree at the highest academic level awarded following a course of study. PhDs are awarded for programs across the whole breadth of academic fields. Because it is ...
for management and directorship roles in the clinical laboratory as well as for academic research and professorship. Doctors of Philosophy holding a degree in a biological science, and who are board certified by a CLIA-approved entity, are qualified as a medical laboratory director.
*Doctor of Medicine or Doctor of clinical laboratory Science - this is the position that qualifies an individual to oversee or direct almost all types of clinical laboratories. Under U.S. CLIA laws, a requirement of at least year of clinical laboratory experience (any MD) or pathology residency must be met.
In the United Kingdom The Modernising Scientific Careers (MSC) programme sets out for the first time a comprehensive training and career framework for the whole healthcare science workforce inclusive of the more than 50 different scientific professional specialisms. In its conception it aimed to provide a coherent framework that was accessible, affordable and designed specifically to both capture scientific and technological advances and to provide improved outcomes for patients, the service and professionals. A key aspect of the framework from the start was the formalisation of training to develop talented clinical scientists to undertake quality assured Higher Specialist Scientist Training (HSST) programmes to prepare them for roles as Consultant Clinical Scientists. It is envisaged that Consultant Clinical Scientists will work synergistically and in partnership with their medical colleagues and within multiprofessional clinical teams to support clinical scientific practice aimed at quality improvement, innovation and world-class outcomes for patients. This scientific expertise and leadership will provide important benefits and added value to patients and to the service as it moves forward through the 21st century. This will bring to fruition the vision of science and realise the potential of scientific and technological advances for both translational and personalised medicine.
Training through the Higher Specialist Scientist Training pathway is discipline specific. For life science disciplines (Immunology, Microbiology, Virology, Haematology, Biochemistry) the training curriculum and formal examinations are administered by the Royal College of Pathologists. The life science training pathway for Clinical Scientists follows a similar pathway to that undertaken by medically qualified specialist registrars in pathology. Clinical Scientists are therefore the only discipline of non-medical healthcare professionals examined by a Medical Royal College. Clinical Scientists who attain both part 1 examination certification and part 2 certification are awarded Fellowship of the Royal College of Pathologists (FRCPath) and are deemed to have the knowledge and expertise expected of a consultant level scientist. Consultant Clinical Scientist posts generally require candidates to have completed FRCPath qualification to be eligible.
All Clinical Scientists regardless of seniority or specialisation may have other responsibilities including academic appointments, responsibilities as clinical lead for a pathology service, or may have wider hospital responsibilities such as Directorship of Infection Prevention and Control, or responsibility for the hospital's Research and Development strategy. Junior clinical scientists may become involved in academic research, working towards award of a Ph.D. or DClinSci
Job title
 The informal abbreviations of job titles may be a source of confusion. In the United States Medical Laboratory Scientist (ASCP) and Medical Technologists (AMT) or (AAB) are often called "med techs" (based on the era in which they were known as "medical technologists"), but this shorthand term is shared by other healthcare employees, including pharmacy techs,
The informal abbreviations of job titles may be a source of confusion. In the United States Medical Laboratory Scientist (ASCP) and Medical Technologists (AMT) or (AAB) are often called "med techs" (based on the era in which they were known as "medical technologists"), but this shorthand term is shared by other healthcare employees, including pharmacy techs, radiographers
Radiographers, also known as radiologic technologists, diagnostic radiographers and medical radiation technologists are healthcare professionals who specialize in the imaging of human anatomy for the diagnosis and treatment of pathology. Radiog ...
(also known as radiologic technologists), and respiratory therapists.
In the United States there is a formal distinction between an MLT and a MT/MLS. Often, MT/MLS have at least a bachelor's degree, while MLT have an associate degree. However, due to grandfathering rules and certification requirements between the boards of registry, some MT/MLS may only have an associate degree. Scientists and technologists generally earn a higher income than technicians, have more responsibilities, and have more opportunities for advancement.
In the United Kingdom, there are defined training pathways leading to professional registration as either a Clinical Scientist, or as a Biomedical Scientist. The role descriptions for these healthcare scientists are very different, where clinical scientists generally undertake non-routine research and development, as well as improving and providing clinical service using scientific expertise. Biomedical Scientists in the United Kingdom are similar to the role of MLT and MT/CLS described above, and have similar regulatory requirements for professional regulation. Clinical Scientists in the United Kingdom may struggle with a lack of professional recognition. This is in part due to the myriad job titles used to describe them including Clinical Physiologists, Medical Physicists, and Clinical Biochemists, which generally mean the public and other healthcare workers assume Clinical Scientists to be medically qualified doctors, due to the sometimes complex nature of the role.
Labor shortage
Medical facilities throughout the United States have gradually been experiencing a shortage inmedical laboratory
A medical laboratory or clinical laboratory is a laboratory where tests are conducted out on clinical specimens to obtain information about the health of a patient to aid in diagnosis, treatment, and prevention of disease. Clinical Medical labor ...
science professionals. The current projectory of medical laboratory personnel through 2030 is not sufficient enough to serve medical services effectively. Reasons for the shortage include current professionals retiring, a modern increase in medical laboratory scientist and technician demand, changes in the practice caused by new technological advances (which need training to learn to use), and vacancy and retirement rates being greater than the number of graduates from medical laboratory programs. Lack of funding, low salaries, lack of a developed career ladder A career ladder or corporate ladder is a metaphor for job promotion. In business and human resources management, the career ladder typically describes the progression from entry level positions to higher levels of pay, skill, responsibility, or aut ...
, and a lack of clear job requirements has made recruitment and the hiring process difficult.
Newer recruiting attempts have increased the number of graduated professionals in the last five years, but not enough to meet the growing demand. Some clinical organizations suggest that professional-development programs for the allied health fields should be improved to cultivate interest in younger professionals and students. The Institute of Medicine is actively working on re-viewing policy reforms and new plans and recommendations to increase medical professional turnout among younger people. The COVID-19
Coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) is a contagious disease caused by a virus, the severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2). The first known case was identified in Wuhan, China, in December 2019. The disease quick ...
pandemic has highlighted the medical laboratory shortage in the medical field and organizations such as the American Society for Clinical Laboratory Science and The American Society for Clinical Pathology are pushing for new ways to reduce this shortage and meet the demands of the public.
See also
* Laboratory centrifuge *Laboratory information system
A laboratory information management system (LIMS), sometimes referred to as a laboratory information system (LIS) or laboratory management system (LMS), is a software-based solution with features that support a modern laboratory's operations. K ...
*Medical technology
Health technology is defined by the World Health Organization as the "application of organized knowledge and skills in the form of devices, medicines, vaccines, procedures, and systems developed to solve a health problem and improve quality of liv ...
*Medical laboratory
A medical laboratory or clinical laboratory is a laboratory where tests are conducted out on clinical specimens to obtain information about the health of a patient to aid in diagnosis, treatment, and prevention of disease. Clinical Medical labor ...
*Phlebotomist
Phlebotomy is the process of making a puncture in a vein, usually in the arm, with a cannula for the purpose of drawing blood. The procedure itself is known as a venipuncture, which is also used for intravenous therapy. A person who performs a ...
*Reference ranges for common blood tests
Reference ranges (reference intervals) for blood tests are sets of values used by a health professional to interpret a set of medical test results from blood samples. Reference ranges for blood tests are studied within the field of clinical chemis ...
*Urine test
A urine test is any medical test performed on a urine specimen. The analysis of urine is a valuable diagnostic tool because its composition reflects the functioning of many body systems, particularly the kidneys and urinary system, and specimens a ...
*Allied health professions
Allied health professions are health care professions distinct from optometry, dentistry, nursing, medicine, and pharmacy. They provide a range of diagnostic, technical, therapeutic, and support services in connection with health care.
Definit ...
*Automated analyser An automated analyser is a medical laboratory instrument designed to measure different chemicals and other characteristics in a number of biological samples quickly, with minimal human assistance. These measured properties of blood and other fluids ...
*Blood bank
A blood bank is a center where blood gathered as a result of blood donation is stored and preserved for later use in blood transfusion. The term "blood bank" typically refers to a department of a hospital usually within a Clinical Pathology laborat ...
*Blood test
A blood test is a laboratory analysis performed on a blood sample that is usually extracted from a vein in the arm using a hypodermic needle, or via fingerprick. Multiple tests for specific blood components, such as a glucose test or a choles ...
*Biomedical Scientist A biomedical scientist is a scientist trained in biology, particularly in the context of medical laboratory sciences or laboratory medicine. These scientists work to gain knowledge on the main principles of how the human body works and to find new w ...
similar career outside of the US
*Body fluids
Body fluids, bodily fluids, or biofluids, sometimes body liquids, are liquids within the human body. In lean healthy adult men, the total body water is about 60% (60–67%) of the total body weight; it is usually slightly lower in women (52-55%). ...
*Clinical pathology
Clinical pathology is a medical specialty that is concerned with the diagnosis of disease based on the laboratory analysis of bodily fluids, such as blood, urine, and tissue homogenates or extracts using the tools of chemistry, microbiology, h ...
* ISO 15189
References
External links
Canadian Society for medical Laboratory Science
* ttp://www.aacc.org/ American Association for Clinical Chemistrybr>American Society of Clinical Pathology
{{Authority control Health care occupations Science occupations